Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Thalidomide Derivatives as Potential Anti-Psoriasis Agents
Abstract
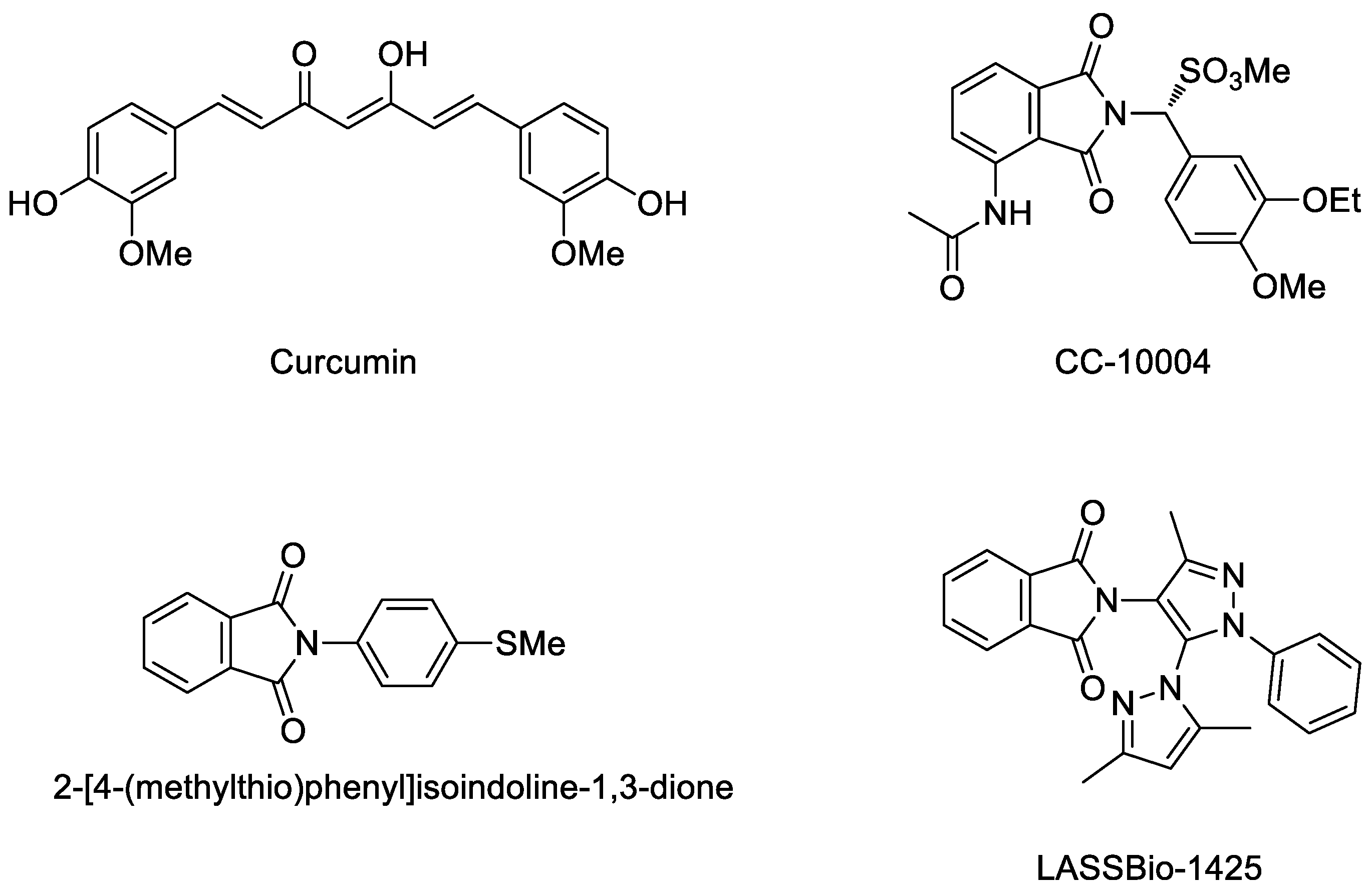
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
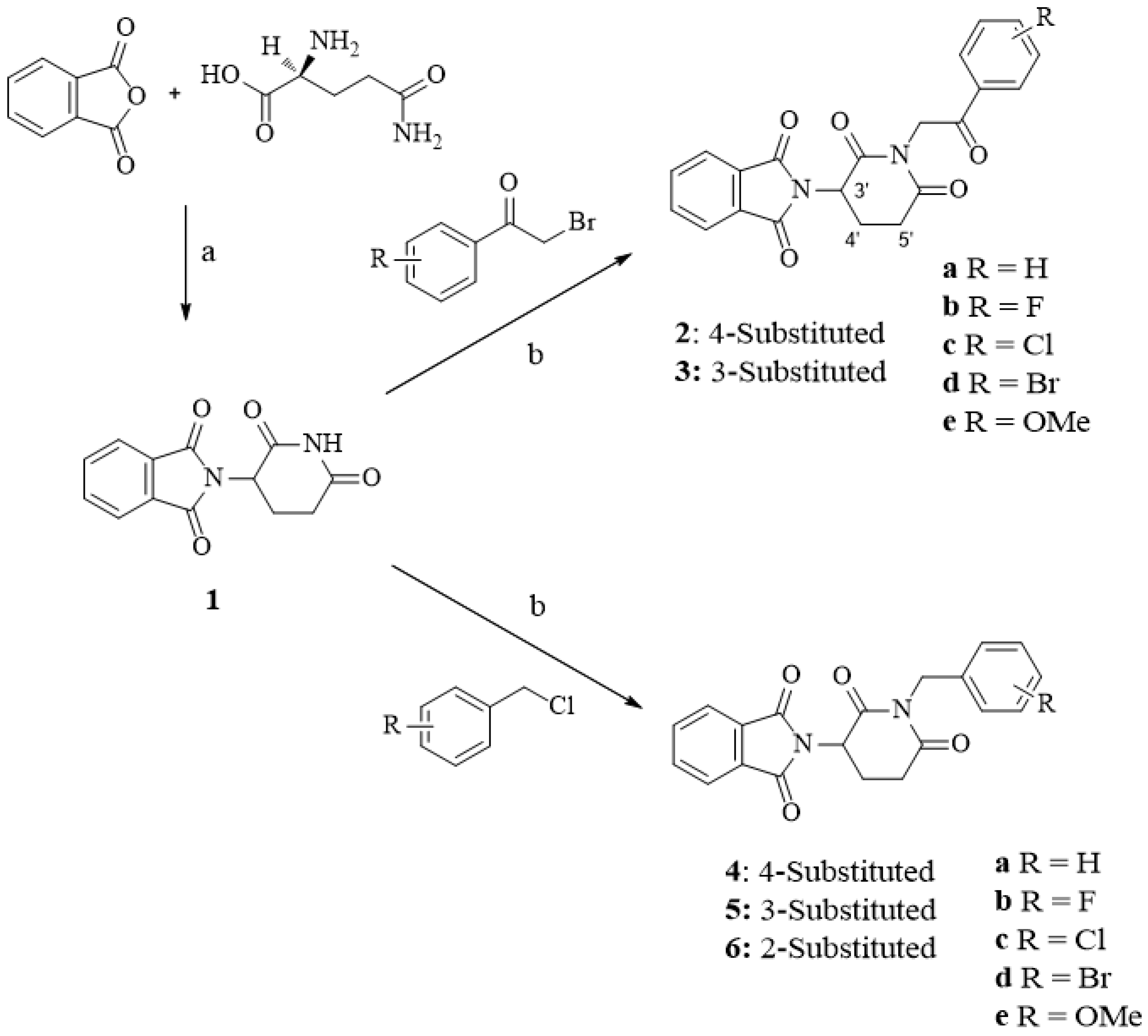
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Biology
2.2.1. In Vitro Anti-Psoriasis Activity
Thalidomide Derivatives Attenuated TNF-α and IL-6 Production
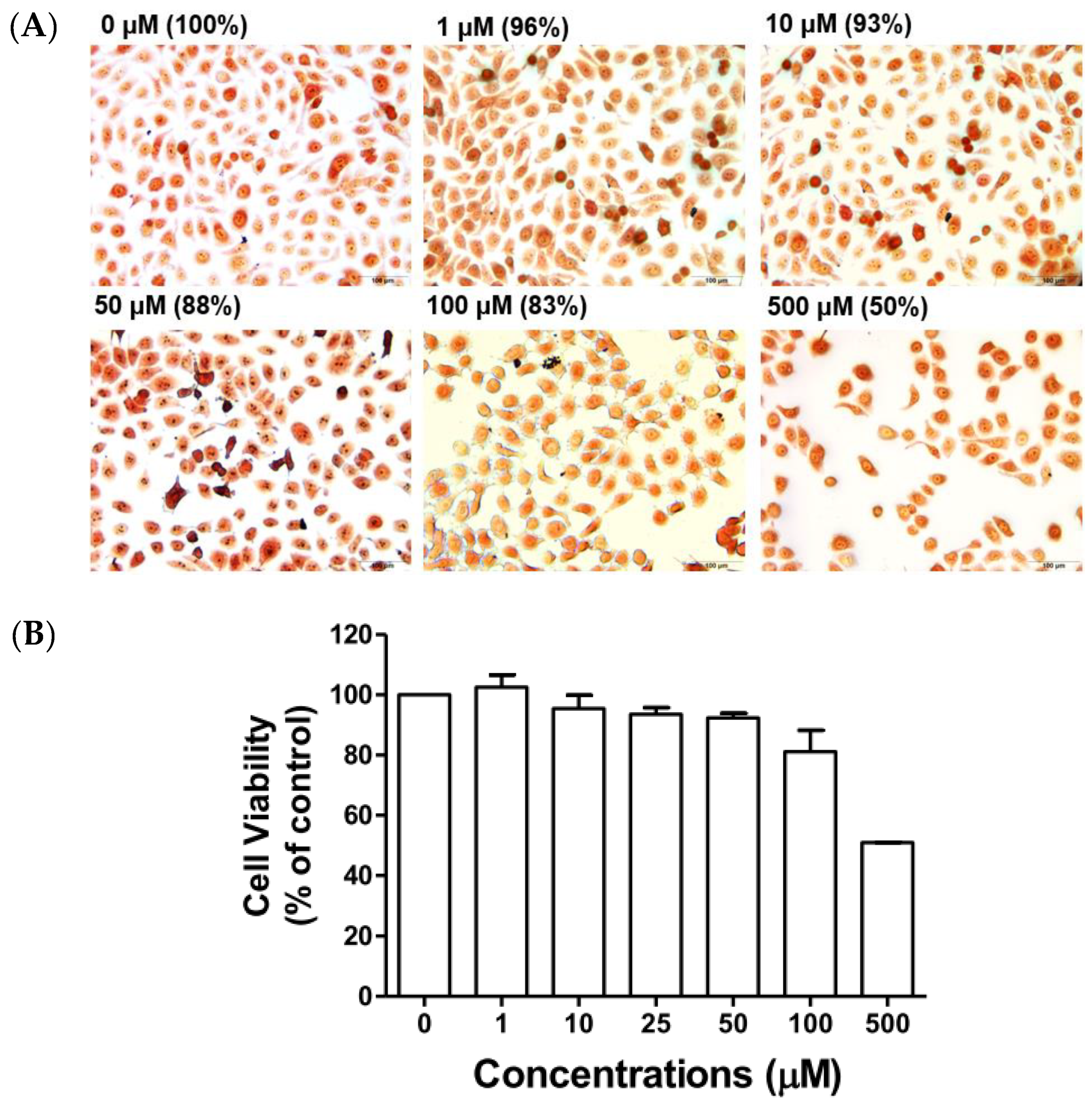
Effect of Compound 5c on Cell Viability
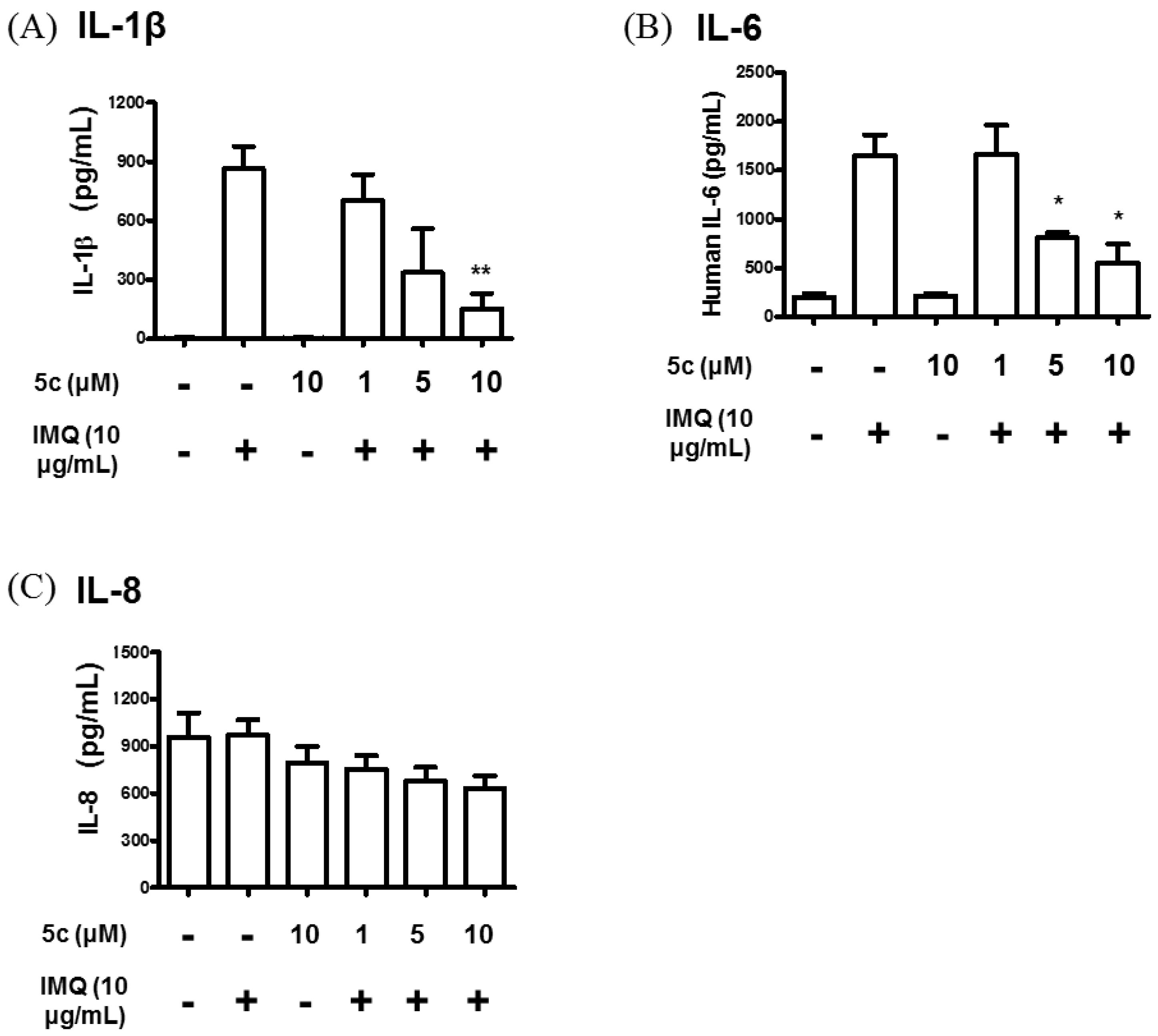
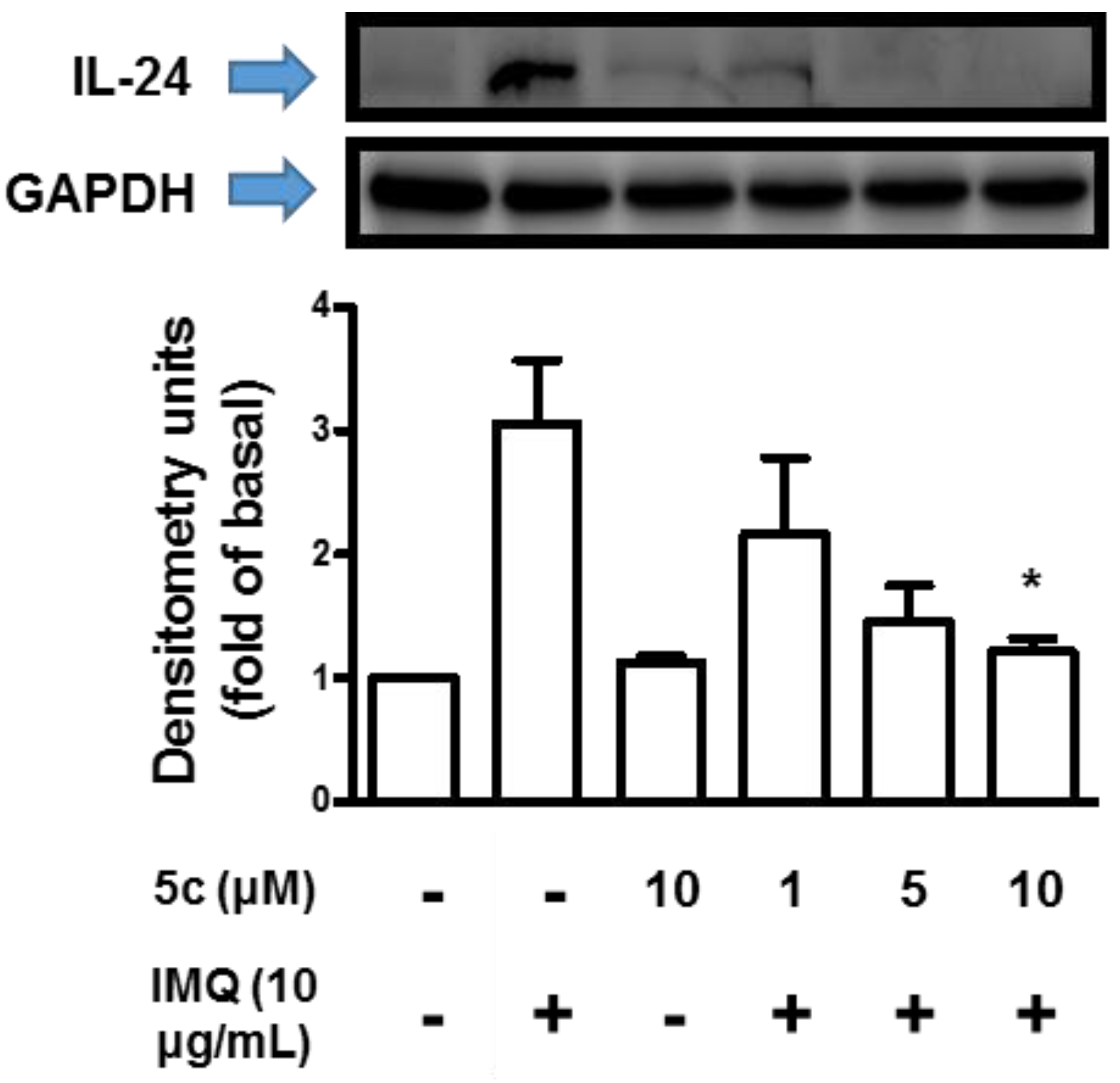
Compound 5c Attenuated IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8 and IL-24 Production
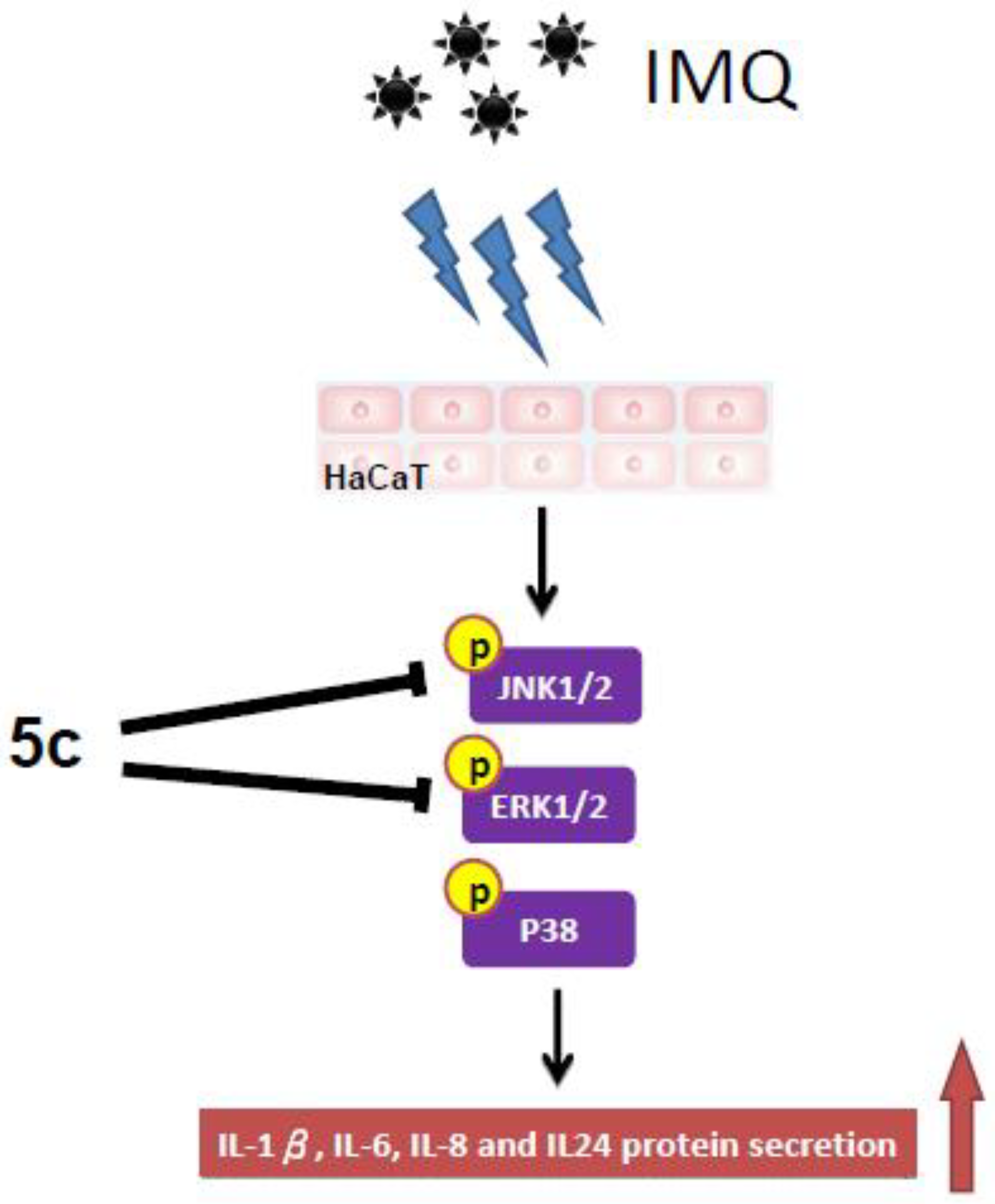
Compound 5c Inhibited MAPKs Signaling Transduction Pathway
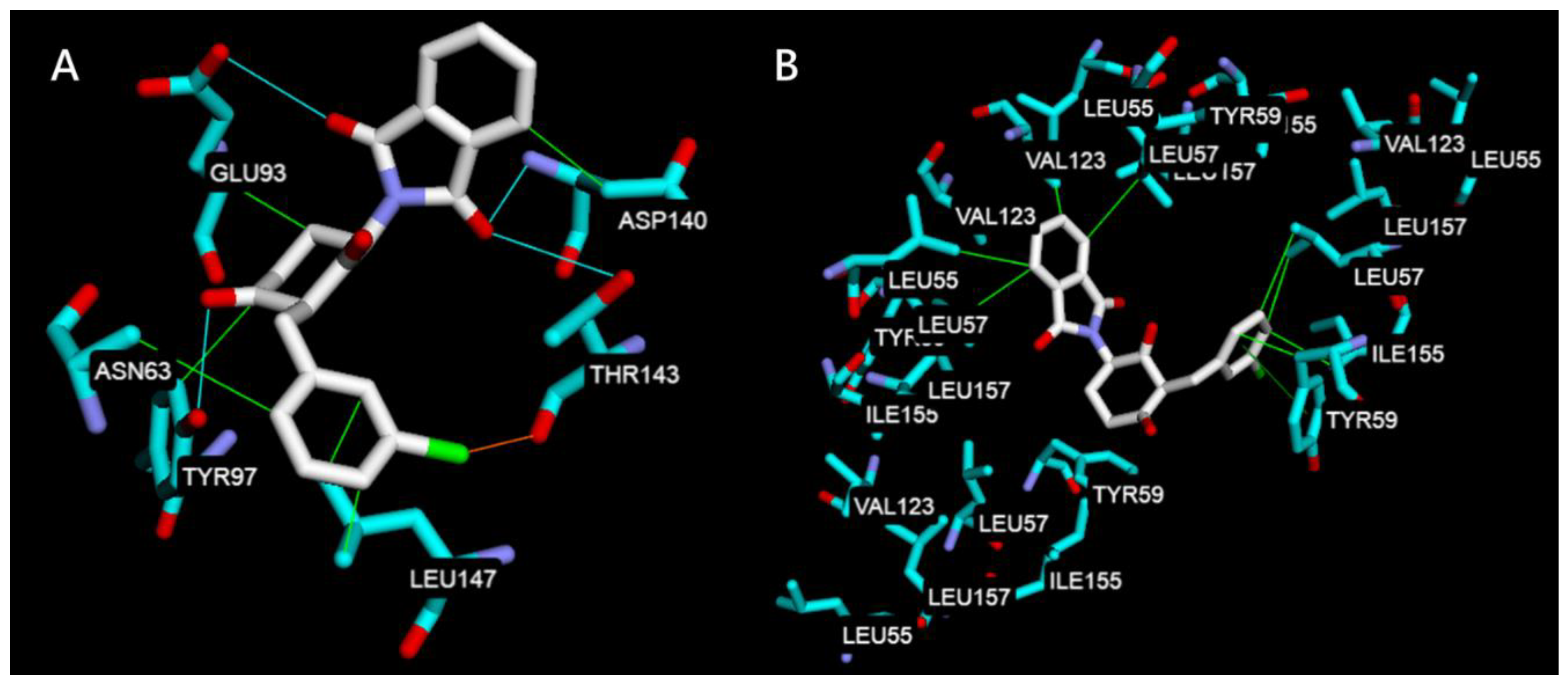
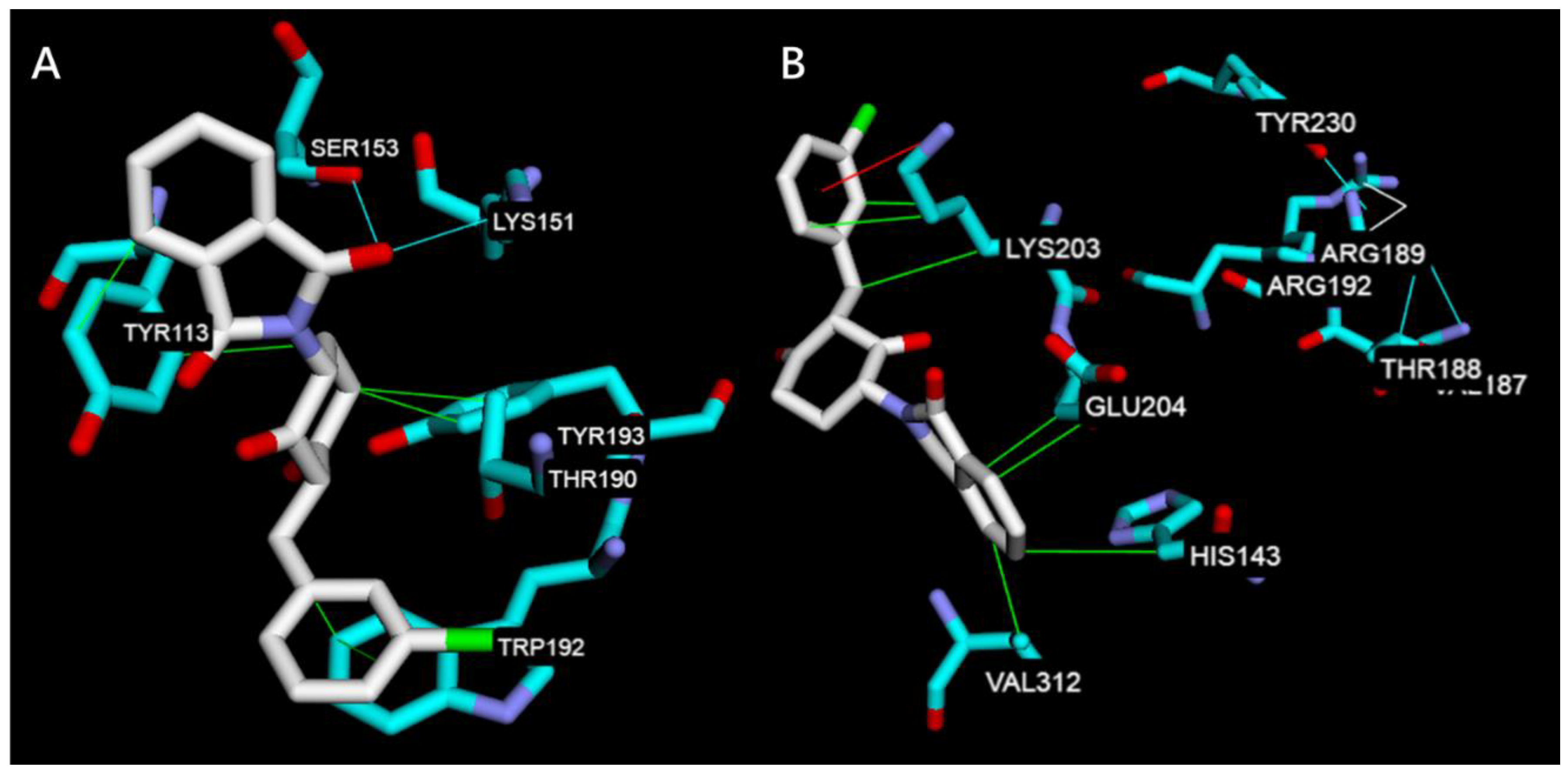
2.2.2. Molecular Docking Study on TNF-α, IL-6, JNK1, ERK2
3. Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemistry Section
4.1.1. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Compounds 2a–3c
4.1.2. General Procedure for the Synthesis of Compounds 4a–6e
4.2. Biological Activity
4.2.1. Cell Culture
4.2.2. Cell Viability Assays
4.2.3. ELISA
4.2.4. Western Blotting Analysis
4.2.5. Neutral Red Staining
4.3. Molecular Docking Study
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shear, N.H. Fulfilling an unmet need in psoriasis. Drug Saf. 2006, 29, 49–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowes, M.A.; Bowcock, A.M.; Krueger, J.G. Pathogenesis and therapy of psoriasis. Nature 2007, 445, 866–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, J.; Marangell, L.B.; Nakamur, M.; Armstrong, A.; Jeon, C.; Bhutani, T.; Wu, J.J. Depression and suicidality in psoriasis: Review of the literature including the cytokine theory of depression. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2017, 31, 1999–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strober, B.E.; Siu, K.; Menon, K. Conventional systemic agents for psoriasis: A systematic review. J. Rheumatol. 2006, 33, 1442–1446. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, C.E.; Clark, C.M.; Chalmers, R.J.; Li Wan Po, A.; Williams, H.C. A systematic review of treatments for severe psoriasis. Health Technol. Assess. 2000, 4, 1–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woolacott, N.; Hawkins, N.; Mason, A. Etanercept and efalizumab for the treatment of psoriasis: A systematic review. Health Technol. Assess. 2006, 10, 1–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bansback, N.; Sizto, S.; Sun, H. Efficacy of systemic treatments for moderate to severe plaque psoriasis: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Dermatology 2009, 219, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, V.W.; Ringold, S.; Devine, E.B. Comparison of ustekinumab with other biological agents for the treatment of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis: A Bayesian network meta-analysis. Arch. Dermatol. 2012, 148, 1403–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rustin, M.H. Long-term safety of biologics in the treatment of moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis: review of current data. Br. J. Dermatol. 2012, 167 (Suppl. 3), 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Randall, T. Thalidomide has 37-year history. JAMA 1990, 263, 1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koren, G.; Pastuszak, A.; Ito, S. Drugs in pregnancy. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998, 338, 1128–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheskin, J. Thalidomide in the treatment of lepra reactions. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1965, 6, 303–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sampaio, E.P.; Kaplan, G.; Miranda, A.; Nery, J.A.; Miguel, C.P.; Viana, S.M.; Sarno, E.N. The influence of thalidomide on the clinical and immunologic manifestation of erythema nodosum leprosum. J. Infect. Dis. 1993, 168, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Amato, R.J.; Loughnan, M.S.; Flynn, E.; Folkman, J. Thalidomide is an inhibitor of angiogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 4082–4085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, A.L.; Sampaio, E.P.; Zmuidzinas, A.; Frindt, P.; Smith, K.A.; Kaplan, G. Thalidomide exerts its inhibitory action on tumor necrosis factor alpha by enhancing mRNA degradation. J. Exp. Med. 1993, 177, 1675–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, G.; Sampaio, E.P. Method of Treating Abnormal Concentrations of TNFR. U.S. Patent 5,385,901, 1992. (to Rockefeller University). [Google Scholar]
- Richardson, P.; Hideshima, T.; Anderson, K. Thalidomide: Emerging role in cancer medicine. Annu. Rev. Med. 2002, 53, 629–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, S.C.; Wu, R.T. The G-rich promoter and G-rich coding sequence of basic fibroblast growth factor are the targets of thalidomide in glioma. Mol. Cancer. Ther. 2008, 7, 2405–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Keifer, J.A.; Guttridge, D.C.; Ashburner, B.P.; Baldwin, A.S. Inhibition of NF-kappa B activity by thalidomide through suppression of IkappaB kinase activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 22382–22387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.J.; Huang, D.B.; Pang, K.R.; Hsu, S.; Tyring, S.K. Thalidomide: Dermatological indications, mechanisms of action and side-effects. Br. J. Dermatol. 2005, 153, 254–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.H.; Wu, H.H.; Zhao, Y.K.; Wang, F.; Gao, Q.; Luo, D.Q. Thalidomide improves psoriasis-like lesions and inhibits cutaneous VEGF expression without alteration of microvessel density in imiquimod-induced psoriatic mouse model. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furue, M.; Tsuji, G.; Chiba, T.; Kadono, T. Cardiovascular and metabolic diseases comorbid with psoriasis: Beyond the skin. Intern. Med. 2017, 56, 1613–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eleutherakis-Papaiakovou, V.; Bamias, A.; Dimopoulos, M.A. Thalidomide in cancer medicine. Ann. Oncol. 2004, 15, 1151–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varma, S.R.; Sivaprakasam, T.O.; Mishra, A.; Prabhu, S.; Rafiq, M.; Rangesh, P. Imiquimod-induced psoriasis-like inflammation in differentiated Human keratinocytes: Its evaluation using curcumin. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 813, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dastidar, S.G.; Rajagopal, D.; Ray, A. Therapeutic benefit of PDE4 inhibitors in inflammatory diseases. Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs 2017, 8, 364. [Google Scholar]
- Assis, S.P.; Araújo, T.G.; Sena, V.L.; Catanho, M.T.J.; Ramos, M.N.; Srivastava, R.M.; Lima, V.L. Synthesis, hypolipidemic, and anti-inflammatory activities of arylphthalimides. Med. Chem. Res. 2014, 23, 708–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fumian, M.M.; da Motta, N.A.; Maia, R.; Fraga, C.A.; Barreiro, E.J.; Ferreira de Brito, F.C. LASSBio-1425, an analog of thalidomide, decreases triglyceride and increases HDL cholesterol levels by inhibition of TNF-alpha production. Int. J. Cardiol. 2016, 202, 497–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, C.H.; Lin, C.S.; Shih, P.K.; Tsao, L.T.; Wang, J.P.; Cheng, C.M.; Tzeng, C.C.; Chen, Y.L. Furo[3, 2 :3,4]naphtho[1,2-d]imidazole derivatives as potential inhibitors of inflammatory factors in sepsis. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2009, 17, 6773–6779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, C.H.; Tzeng, C.C.; Shih, P.K.; Yang, C.N.; Chuang, Y.C.; Peng, S.I.; Lin, C.S.; Wang, J.P.; Cheng, C.M.; Chen, Y.L. Identification of furo[3′,2′:3,4]naphtho[1,2-d] imidazole derivatives as orally active and selective inhibitors of microsomal prostaglandin E(2) synthase-1 (mPGES-1). Mol. Divers. 2012, 16, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, C.H.; Cheng, C.M.; Tzeng, C.C.; Peng, S.I.; Yang, C.L.; Chen, Y.L. Synthesis and anti-inflammatory evaluations of -lapachone derivatives. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.R.; Tseng, C.H.; Chen, Y.L.; Hwang, T.L.; Tzeng, C.C. Discovery of benzo[f]indole-4,9-dione derivatives as new type of anti-inflammatory agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 6532–6544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, C.H.; Tung, C.W.; Wu, C.H.; Tzeng, C.C.; Chen, Y.H.; Hwang, T.L.; Chen, Y.L. Discovery of indeno[1,2-c]quinoline derivatives as potent dual antituberculosis and anti-Inflammatory agents. Molecules 2017, 22, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, D.R.; Kankan, R.N.; Surve, M.; Birari, D. Processes for the Preparation of Thalidomide. WO 2009083724 A1, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Luzzio, F.A.; Mayorov, A.V.; Ng, S.S.; Kruger, E.A.; Figg, W.D. Thalidomide metabolites and analogues. 3. Synthesis and antiangiogenic activity of the teratogenic and TNF-α modulatory thalidomide analogue 2-(2,6-dioxopiperidine-3-yl) phthalimidine. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 46, 3793–3799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baliwag, J.; Barnes, D.H.; Johnston, A. Cytokines in psoriasis. Cytokine 2015, 73, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hawkes, J.E.; Gudjonsson, J.E.; Ward, N.L. The snowballing literature on imiquimod-induced skin inflammation in mice: A critical appraisal. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2017, 137, 546–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schön, M.P.; Schön, M.; Klotz, K.N. The small antitumoral immune response modifier imiquimod interacts with adenosine receptor signaling in a TLR7- and TLR8-independent fashion. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2006, 126, 1338–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansen, C.; Kragballe, K.; Westergaard, M.; Henningsen, J.; Kristiansen, K.; Iversen, L. The mitogen-activated protein kinases p38 and ERK1/2 are increased in lesional psoriatic skin. Br. J. Dermatol. 2005, 152, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Xiao, S.; Li, H.; Zheng, T.; Huang, J.; Hu, R.; Zhang, B.; Liu, X.; Huang, G. MAPK phosphatase-1 deficiency exacerbates the severity of imiquimod-induced psoriasiform skin disease. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dayakar, C.; Kumar, B.S.; Sneha, G.; Sagarika, G.; Meghana, K.; Ramakrishna, S.; Prakasham, R.S.; Raju, B.C. Synthesis, pharmacological activities and molecular docking studies of pyrazolyltriazoles as anti-bacterial and anti-inflammatory agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 5678–5691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Kaur, S.; Sharma, A.; Kaur, G.; Bhatti, R. TNF-α and IL-6 inhibitors: Conjugates of N-substituted indole and aminophenylmorpholin-3-one as anti-inflammatory agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 140, 92–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hisanaga, A.; Mukai, R.; Sakao, K.; Terao, J.; Hou, D.X. Anti-inflammatory effects and molecular mechanisms of 8-prenyl quercetin. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2016, 60, 1020–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Linares, I.; Pérez-Sánchez, H.; Cecilia, J.M.; García, J.M. High-Throughput parallel blind Virtual Screening using BINDSURF. BMC Bioinform. 2012, 13 (Suppl. 14), S13. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Rego, N.; Koes, D. 3Dmol.js: Molecular visualization with WebGL. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1322–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Compounds | % Inhibition at 5 µM | % Viability | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-6 | TNF-α | 5 µM | 10 µM | |
| Thalidomide (1) | 48.70 ± 1.10 | 22.97 ± 5.16 | 96.7 ± 3.4 | 86.7 ± 2.9 |
| 2a | 3.85 ± 1.66 | −2.45 ± 2.37 | 94.3 ± 2.5 | 86.0 ± 4.1 |
| 2b | 3.33 ± 0.44 | 5.67 ± 0.13 | 96.3 ± 2.1 | 91.7 ± 3.9 |
| 2c | 3.77 ± 0.56 | 12.93 ± 2.41 | 93.0 ± 4.3 | 94.7 ± 3.3 |
| 2d | 14.86 ± 3.20 | 30.38 ± 8.49 | 90.7 ± 2.1 | 89.7 ± 6.2 |
| 2e | 2.27 ± 1.66 | 39.77 ± 2.29 | 96.7 ± 2.1 | 84.0 ± 2.4 |
| 3b | 17.51 ± 6.41 | 12.69 ± 6.50 | 96.2 ± 3.5 | 89.8 ± 3.8 |
| 3c | 4.56 ± 2.91 | 8.28 ± 6.87 | 100.0 ± 0.3 | 98.1 ± 0.8 |
| 3e | 22.20 ± 0.27 | 11.39 ± 2.20 | 94.0 ± 3.6 | 89.3 ± 5.4 |
| 4a | 2.56 ± 0.52 | −5.21 ± 5.22 | 96.7 ± 2.1 | 93.0 ± 3.7 |
| 4b | 22.49 ± 1.90 | 0.28 ± 0.20 | 94.3 ± 2.9 | 93.3 ± 2.1 |
| 4c | 48.73 ± 2.25 | −1.32 ± 4.14 | 92.0 ± 4.5 | 93.7 ± 3.8 |
| 4d | 14.02 ± 8.97 | 12.59 ± 7.43 | 91.3 ± 3.3 | 91.3 ± 2.7 |
| 4e | 14.43 ± 0.68 | 5.01 ± 4.10 | 93.3 ± 0.5 | 88.0 ± 4.5 |
| 5b | 1.35 ± 0.18 | 2.89 ± 4.07 | 95.3 ± 3.3 | 95.0 ± 2.9 |
| 5c | 69.44 ± 4.39 | 75.01 ± 17.6 | 96.3 ± 2.5 | 90.3 ± 7.0 |
| 5e | 62.12 ± 3.22 | 3.17 ± 0.78 | 95.7 ± 4.0 | 66.3 ± 3.9 |
| 6b | 4.40 ± 1.61 | 34.46 ± 3.85 | 93.7 ± 3.1 | 90.3 ± 2.5 |
| 6c | 3.19 ± 0.80 | 7.35 ± 1.07 | 91.0 ± 2.4 | 58.7 ± 6.1 |
| 6e | 2.09 ± 1.86 | 2.19 ± 6.51 | 98.0 ± 1.6 | 97.0 ± 2.2 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tang, K.-W.; Lin, Z.-C.; Chen, Y.-L.; Tzeng, C.-C.; Fang, J.-Y.; Tseng, C.-H. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Thalidomide Derivatives as Potential Anti-Psoriasis Agents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3061. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103061
Tang K-W, Lin Z-C, Chen Y-L, Tzeng C-C, Fang J-Y, Tseng C-H. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Thalidomide Derivatives as Potential Anti-Psoriasis Agents. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(10):3061. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103061
Chicago/Turabian StyleTang, Kai-Wei, Zih-Chan Lin, Yeh-Long Chen, Cherng-Chyi Tzeng, Jia-You Fang, and Chih-Hua Tseng. 2018. "Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Thalidomide Derivatives as Potential Anti-Psoriasis Agents" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 10: 3061. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103061
APA StyleTang, K.-W., Lin, Z.-C., Chen, Y.-L., Tzeng, C.-C., Fang, J.-Y., & Tseng, C.-H. (2018). Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Thalidomide Derivatives as Potential Anti-Psoriasis Agents. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(10), 3061. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103061





