Chronic Upregulation of Cleaved-Caspase-3 Associated with Chronic Myelin Pathology and Microvascular Reorganization in the Thalamus after Traumatic Brain Injury in Rats
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
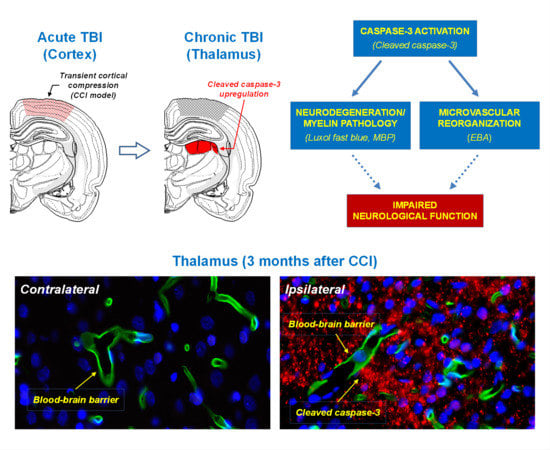
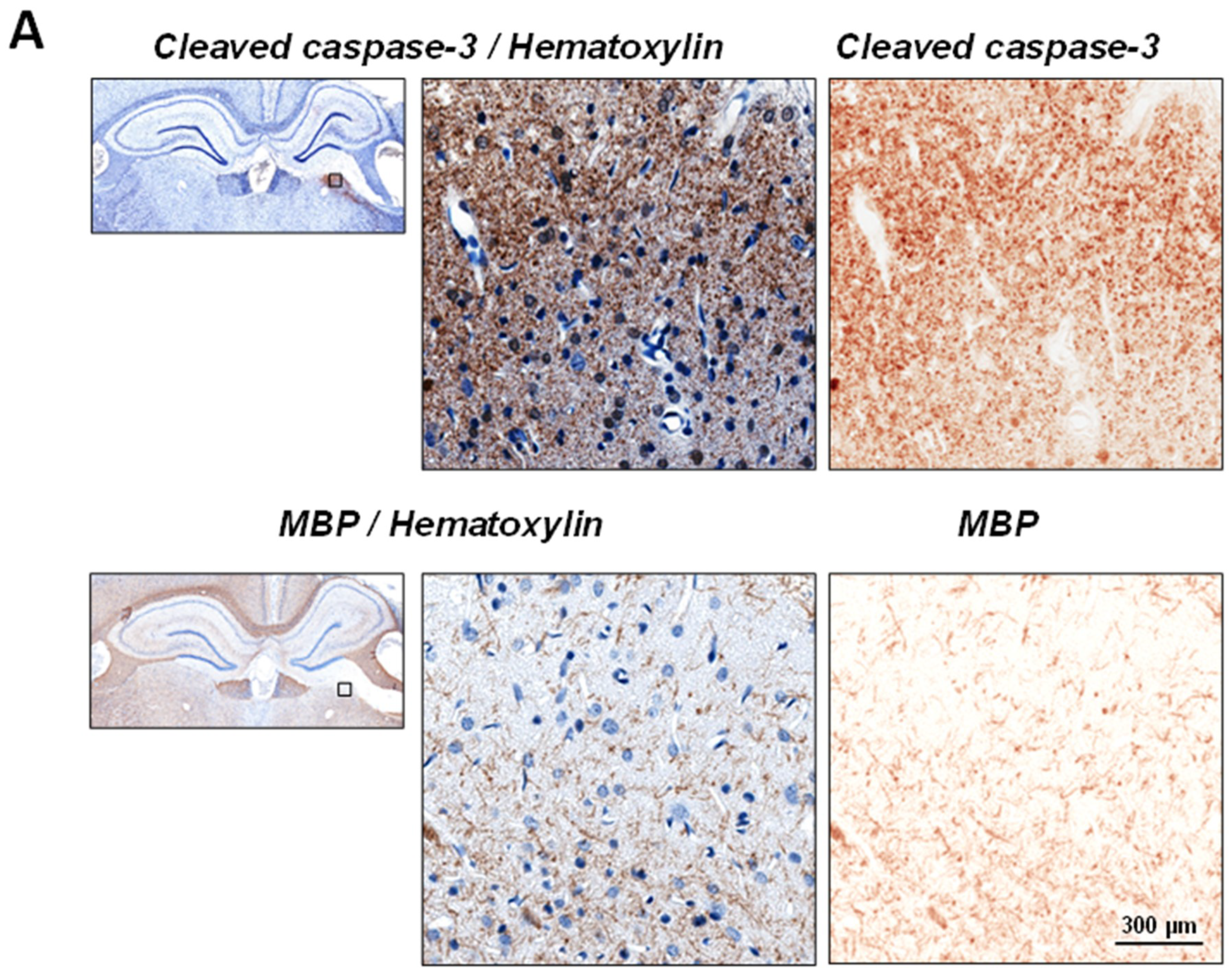
2.1. Upregulation of Cleaved-Caspase-3 Expression in the Thalamus Following CCI
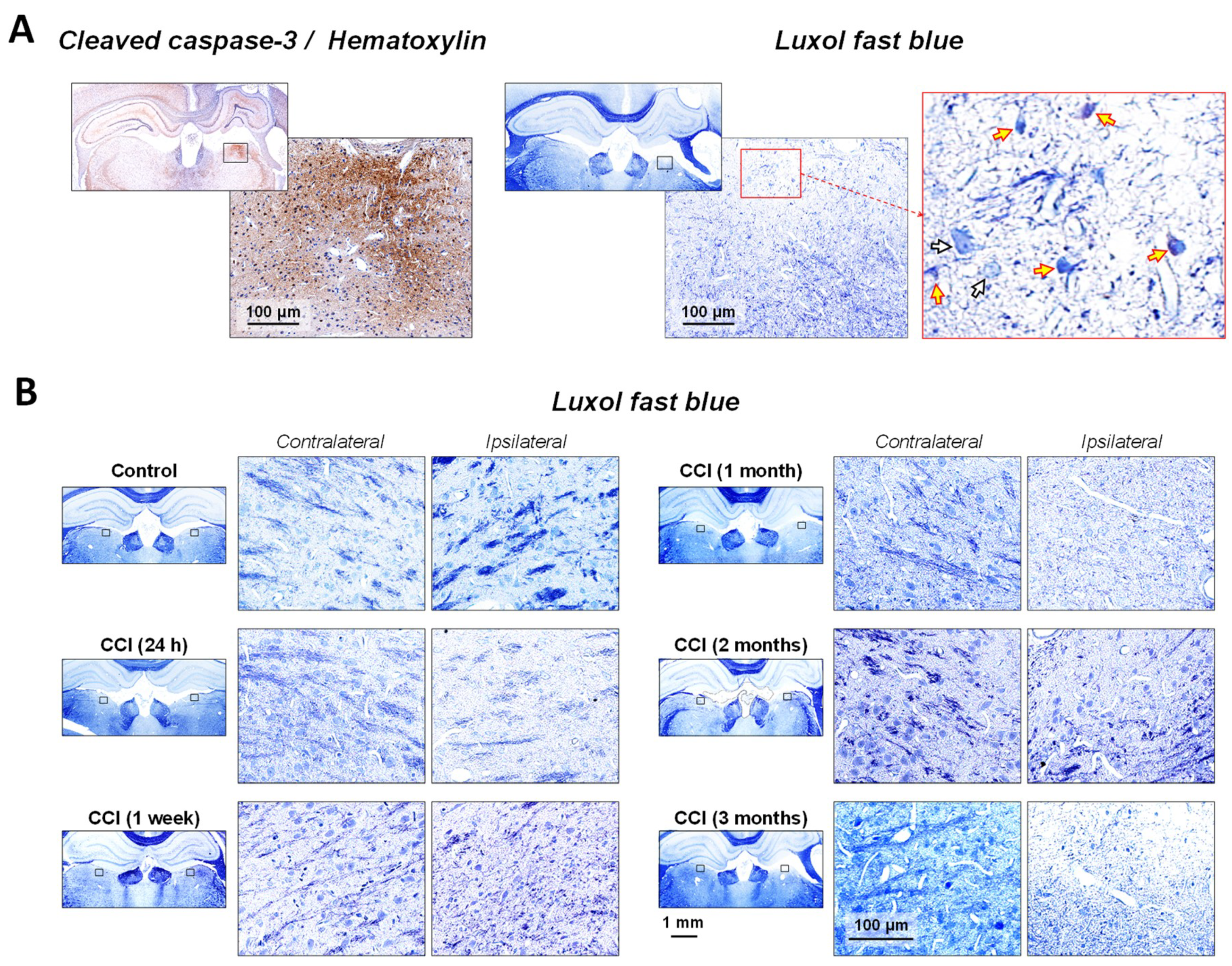
2.2. Neuronal Demyelination and Brain Tissue Degeneration in the Gray Matter of the Thalamus Are Associated with Cleaved-Caspase-3 Upregulation Following CCI
2.3. Association of Microvascular Reorganization and Loss of Blood-Brain Barrier Function in the Thalamus with Cleaved-Caspase-3 Upregulation after CCI
3. Discussion
3.1. Pathways and Mechanisms Involved in Chronic Pathologies in the Thalamus Following TBI
3.2. Neurological Functions Associated with Thalamic Regions and Their Clinical Implications in Chronic Sequelae of TBI
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Controlled Cortical Impact (CCI)
4.3. Immunohistochemical Analysis
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TBI | Traumatic brain injury |
| CCI | Controlled cortical impact |
| MBP | Myelin basic protein |
| EBA | Endothelial barrier antigen |
| PTH | Posttraumatic headaches |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| CSF | Cerebrospinal fluid |
| DAPI | 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole |
| DAB | 3,3′-diaminobenzidine |
| LP | Lateral posterior thalamic nucleus |
| LD | Laterodorsal thalamic nucleus |
| DLG | Dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus |
| VLG | Ventral lateral geniculate nucleus |
| RT | Reticular thalamic nucleus |
| IGL | Intergeniculate leaf |
| IMA | Intramedullary thalamic area |
| MD | Mediodorsal thalamic nucleus |
| Po | Posterior thalamic nuclear group |
| VPL | Ventral posterolateral thalamic nucleus |
| VPM | Ventral posteromedial thalamic nucleus |
| CL | Centrolateral thalamic nucleus |
| OPC | Oval paracentral thalamic nucleus |
| TUNEL | Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labeling |
| CCCK-18 | Caspase-3-cleaved cytokeratin-18 |
| SBDP120 | 120 and 150 kDa αII spectrin breakdown product |
| SBDP150 | 150 kDa αII spectrin breakdown product |
References
- Faul, M.; Coronado, V. Epidemiology of traumatic brain injury. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2015, 127, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pearson, W.S.; Sugerman, D.E.; McGuire, L.C.; Coronado, V.G. Emergency department visits for traumatic brain injury in older adults in the united states: 2006–08. West. J. Emerg. Med. 2012, 13, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, J.H.; Jennett, B.; Murray, L.S.; Teasdale, G.M.; Gennarelli, T.A.; Graham, D.I. Neuropathological findings in disabled survivors of a head injury. J. Neurotrauma 2011, 28, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laskowitz, D.; Grant, G. (Eds.) Translational Research in Traumatic Brain Injury; CRC Press/Taylor and Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2016. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK326725/ (accessed on 13 October 2018).
- Defrin, R. Chronic post-traumatic headache: Clinical findings and possible mechanisms. J. Man. Manip. Ther. 2014, 22, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castriotta, R.J.; Wilde, M.C.; Lai, J.M.; Atanasov, S.; Masel, B.E.; Kuna, S.T. Prevalence and consequences of sleep disorders in traumatic brain injury. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2007, 3, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Castriotta, R.J.; Atanasov, S.; Wilde, M.C.; Masel, B.E.; Lai, J.M.; Kuna, S.T. Treatment of sleep disorders after traumatic brain injury. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2009, 5, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.T.; Veenith, T.; Dewar, D.; Outtrim, J.G.; Mani, V.; Williams, C.; Pimlott, S.; Hutchinson, P.J.; Tavares, A.; Canales, R.; et al. Amyloid imaging with carbon 11-labeled pittsburgh compound B for traumatic brain injury. JAMA Neurol. 2014, 71, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucke-Wold, B.P.; Nguyen, L.; Turner, R.C.; Logsdon, A.F.; Chen, Y.W.; Smith, K.E.; Huber, J.D.; Matsumoto, R.; Rosen, C.L.; Tucker, E.S.; et al. Traumatic brain injury and epilepsy: Underlying mechanisms leading to seizure. Seizure 2015, 33, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendez, M.F.; Paholpak, P.; Lin, A.; Zhang, J.Y.; Teng, E. Prevalence of traumatic brain injury in early versus late-onset alzheimer’s disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2015, 47, 985–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, K.M.; Saint-Hilaire, M.H.; Sudarsky, L.; Simon, D.K.; Hersh, B.; Sparrow, D.; Hu, H.; Weisskopf, M.G. Head injury at early ages is associated with risk of parkinson’s disease. Park. Relat. Disord. 2016, 23, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dams-O’Connor, K.; Guetta, G.; Hahn-Ketter, A.E.; Fedor, A. Traumatic brain injury as a risk factor for alzheimer’s disease: Current knowledge and future directions. Neurodegener. Dis. Manag. 2016, 6, 417–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LoBue, C.; Wadsworth, H.; Wilmoth, K.; Clem, M.; Hart, J., Jr.; Womack, K.B.; Didehbani, N.; Lacritz, L.H.; Rossetti, H.C.; Cullum, C.M. Traumatic brain injury history is associated with earlier age of onset of alzheimer disease. Clin. Neuropsychol. 2017, 31, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daneshvar, D.H.; Goldstein, L.E.; Kiernan, P.T.; Stein, T.D.; McKee, A.C. Post-traumatic neurodegeneration and chronic traumatic encephalopathy. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2015, 66, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKee, A.C.; Stern, R.A.; Nowinski, C.J.; Stein, T.D.; Alvarez, V.E.; Daneshvar, D.H.; Lee, H.S.; Wojtowicz, S.M.; Hall, G.; Baugh, C.M.; et al. The spectrum of disease in chronic traumatic encephalopathy. Brain 2013, 136, 43–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glushakov, A.V.; Glushakova, O.Y.; Dore, S.; Carney, P.R.; Hayes, R.L. Animal models of posttraumatic seizures and epilepsy. Methods Mol. Boil. 2016, 1462, 481–519. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, D.H.; Chen, X.H.; Pierce, J.E.; Wolf, J.A.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Graham, D.I.; McIntosh, T.K. Progressive atrophy and neuron death for one year following brain trauma in the rat. J. Neurotrauma 1997, 14, 715–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bramlett, H.M.; Dietrich, W.D. Quantitative structural changes in white and gray matter 1 year following traumatic brain injury in rats. Acta Neuropathol. 2002, 103, 607–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, K.; Marquez de la Plata, C.; Wang, J.Y.; Mumphrey, M.; Moore, C.; Harper, C.; Madden, C.J.; McColl, R.; Whittemore, A.; Devous, M.D.; et al. Cerebral atrophy after traumatic white matter injury: Correlation with acute neuroimaging and outcome. J. Neurotrauma 2008, 25, 1433–1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bendlin, B.B.; Ries, M.L.; Lazar, M.; Alexander, A.L.; Dempsey, R.J.; Rowley, H.A.; Sherman, J.E.; Johnson, S.C. Longitudinal changes in patients with traumatic brain injury assessed with diffusion-tensor and volumetric imaging. Neuroimage 2008, 42, 503–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidaros, A.; Skimminge, A.; Liptrot, M.G.; Sidaros, K.; Engberg, A.W.; Herning, M.; Paulson, O.B.; Jernigan, T.L.; Rostrup, E. Long-term global and regional brain volume changes following severe traumatic brain injury: A longitudinal study with clinical correlates. Neuroimage 2009, 44, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, C.R.; Hagler, D.J., Jr.; Ahmadi, M.E.; Tecoma, E.; Iragui, V.; Dale, A.M.; Halgren, E. Subcortical and cerebellar atrophy in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy revealed by automatic segmentation. Epilepsy Res. 2008, 79, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laouchedi, M.; Galanaud, D.; Delmaire, C.; Fernandez-Vidal, S.; Messe, A.; Mesmoudi, S.; Oulebsir Boumghar, F.; Pelegrini-Issac, M.; Puybasset, L.; Benali, H.; et al. Deafferentation in thalamic and pontine areas in severe traumatic brain injury. J. Neuroradiol. 2015, 42, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, S.H.; Kwon, H.G. Injury of the ascending reticular activating system in patients with fatigue and hypersomnia following mild traumatic brain injury: Two case reports. Medicine 2016, 95, e2628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzzetta, F.; Battaglia, D.; Veredice, C.; Donvito, V.; Pane, M.; Lettori, D.; Chiricozzi, F.; Chieffo, D.; Tartaglione, T.; Dravet, C. Early thalamic injury associated with epilepsy and continuous spike-wave during slow sleep. Epilepsia 2005, 46, 889–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Losito, E.; Battaglia, D.; Chieffo, D.; Raponi, M.; Ranalli, D.; Contaldo, I.; Giansanti, C.; De Clemente, V.; Quintiliani, M.; Antichi, E.; et al. Sleep-potentiated epileptiform activity in early thalamic injuries: Study in a large series (60 cases). Epilepsy Res. 2015, 109, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Y.; Patel, M.B.; Chen, Q.; Grossman, E.J.; Zhang, K.; Miles, L.; Babb, J.S.; Reaume, J.; Grossman, R.I. Assessment of thalamic perfusion in patients with mild traumatic brain injury by true FISP arterial spin labelling MR imaging at 3T. Brain Inj. 2009, 23, 666–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llinas, R.R.; Ribary, U.; Jeanmonod, D.; Kronberg, E.; Mitra, P.P. Thalamocortical dysrhythmia: A neurological and neuropsychiatric syndrome characterized by magnetoencephalography. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 15222–15227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvey, P.M.; Hendey, B.; Monahan, A.J. The blood-brain barrier in neurodegenerative disease: A rhetorical perspective. J. Neurochem. 2009, 111, 291–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattson, M.P. Apoptosis in neurodegenerative disorders. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Boil. 2000, 1, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bramlett, H.M.; Dietrich, W.D. Long-term consequences of traumatic brain injury: Current status of potential mechanisms of injury and neurological outcomes. J. Neurotrauma 2015, 32, 1834–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholson, D.W. ICE/CED3-like proteases as therapeutic targets for the control of inappropriate apoptosis. Nat. Biotechnol. 1996, 14, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eldadah, B.A.; Faden, A.I. Caspase pathways, neuronal apoptosis, and CNS injury. J. Neurotrauma 2000, 17, 811–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Jenkins, L.W.; Kochanek, P.M.; Clark, R.S. Bench-to-bedside review: Apoptosis/programmed cell death triggered by traumatic brain injury. Crit. Care 2005, 9, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newcomb, J.K.; Zhao, X.; Pike, B.R.; Hayes, R.L. Temporal profile of apoptotic-like changes in neurons and astrocytes following controlled cortical impact injury in the rat. Exp. Neurol. 1999, 158, 76–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, E.A.; Svetlov, S.I.; Wang, K.K.; Hayes, R.L.; Pineda, J.A. Cell-specific DNA fragmentation may be attenuated by a survivin-dependent mechanism after traumatic brain injury in rats. Exp. Brain Res. 2005, 167, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glushakova, O.; Glushakov, A.; Wijesinghe, D.; Valadka, A.; Hayes, R.; Glushakov, A. Prospective clinical biomarkers of caspase-mediated apoptosis associated with neuronal and neurovascular damage following stroke and other severe brain injuries: Implications for chronic neurodegeneration. Brain Circ. 2017, 3, 87–108. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Glushakova, O.Y.; Johnson, D.; Hayes, R.L. Delayed increases in microvascular pathology after experimental traumatic brain injury are associated with prolonged inflammation, blood-brain barrier disruption, and progressive white matter damage. J. Neurotrauma 2014, 31, 1180–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glushakova, O.Y.; Glushakov, A.O.; Borlongan, C.V.; Valadka, A.B.; Hayes, R.L.; Glushakov, A.V. Role of caspase-3-mediated apoptosis in chronic caspase-3-cleaved tau accumulation and blood-brain barrier damage in the corpus callosum after traumatic brain injury in rats. J. Neurotrauma 2018, 35, 157–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Fontoura Costa, L.; Batista, J.L.; Ascoli, G.A. Communication structure of cortical networks. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2011, 5, 6. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Cabezas, M.A.; John, Y.J.; Barbas, H.; Zikopoulos, B. Distinction of neurons, glia and endothelial cells in the cerebral cortex: An algorithm based on cytological features. Front. Neuroanat. 2016, 10, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glushakov, A.V.; Robbins, S.W.; Bracy, C.L.; Narumiya, S.; Dore, S. Prostaglandin f2α fp receptor antagonist improves outcomes after experimental traumatic brain injury. J. Neuroinflamm. 2013, 10, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glushakov, A.V.; Arias, R.A.; Tolosano, E.; Dore, S. Age-dependent effects of haptoglobin deletion in neurobehavioral and anatomical outcomes following traumatic brain injury. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2016, 3, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiff, N.D.; Giacino, J.T.; Kalmar, K.; Victor, J.D.; Baker, K.; Gerber, M.; Fritz, B.; Eisenberg, B.; Biondi, T.; O’Connor, J.; et al. Behavioural improvements with thalamic stimulation after severe traumatic brain injury. Nature 2007, 448, 600–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, R.S.; Kochanek, P.M.; Watkins, S.C.; Chen, M.; Dixon, C.E.; Seidberg, N.A.; Melick, J.; Loeffert, J.E.; Nathaniel, P.D.; Jin, K.L.; et al. Caspase-3 mediated neuronal death after traumatic brain injury in rats. J. Neurochem. 2000, 74, 740–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghupathi, R.; Graham, D.I.; McIntosh, T.K. Apoptosis after traumatic brain injury. J. Neurotrauma 2000, 17, 927–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acosta, S.A.; Tajiri, N.; Shinozuka, K.; Ishikawa, H.; Grimmig, B.; Diamond, D.M.; Sanberg, P.R.; Bickford, P.C.; Kaneko, Y.; Borlongan, C.V. Long-term upregulation of inflammation and suppression of cell proliferation in the brain of adult rats exposed to traumatic brain injury using the controlled cortical impact model. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonaka, M.; Chen, X.H.; Pierce, J.E.; Leoni, M.J.; McIntosh, T.K.; Wolf, J.A.; Smith, D.H. Prolonged activation of nf-kappab following traumatic brain injury in rats. J. Neurotrauma 1999, 16, 1023–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siklos, M.; BenAissa, M.; Thatcher, G.R. Cysteine proteases as therapeutic targets: Does selectivity matter? A systematic review of calpain and cathepsin inhibitors. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2015, 5, 506–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beer, R.; Franz, G.; Krajewski, S.; Pike, B.R.; Hayes, R.L.; Reed, J.C.; Wang, K.K.; Klimmer, C.; Schmutzhard, E.; Poewe, W.; et al. Temporal and spatial profile of caspase 8 expression and proteolysis after experimental traumatic brain injury. J. Neurochem. 2001, 78, 862–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beer, R.; Franz, G.; Srinivasan, A.; Hayes, R.L.; Pike, B.R.; Newcomb, J.K.; Zhao, X.; Schmutzhard, E.; Poewe, W.; Kampfl, A. Temporal profile and cell subtype distribution of activated caspase-3 following experimental traumatic brain injury. J. Neurochem. 2000, 75, 1264–1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knoblach, S.M.; Nikolaeva, M.; Huang, X.; Fan, L.; Krajewski, S.; Reed, J.C.; Faden, A.I. Multiple caspases are activated after traumatic brain injury: Evidence for involvement in functional outcome. J. Neurotrauma 2002, 19, 1155–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, W.; Liu, H.; Liu, C.; Shao, L.; Liu, Y.; Fan, S.; Li, X.; Gong, L.L.; Zhu, S.; Gao, Y. Up-regulation of mcm3 relates to neuronal apoptosis after traumatic brain injury in adult rats. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 37, 683–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keane, R.W.; Kraydieh, S.; Lotocki, G.; Alonso, O.F.; Aldana, P.; Dietrich, W.D. Apoptotic and antiapoptotic mechanisms after traumatic brain injury. J. Cerebral Blood Flow Metab. 2001, 21, 1189–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolenec, P.; Pilipovic, K.; Rajic, J.; Zupan, G. Temporal pattern of neurodegeneration, programmed cell death, and neuroplastic responses in the thalamus after lateral fluid percussion brain injury in the rat. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2015, 74, 512–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conti, A.C.; Raghupathi, R.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; McIntosh, T.K. Experimental brain injury induces regionally distinct apoptosis during the acute and delayed post-traumatic period. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 5663–5672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamishina, H.; Conte, W.L.; Patel, S.S.; Tai, R.J.; Corwin, J.V.; Reep, R.L. Cortical connections of the rat lateral posterior thalamic nucleus. Brain Res. 2009, 1264, 39–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinkai, M.; Yokofujita, J.; Oda, S.; Murakami, K.; Igarashi, H.; Kuroda, M. Dual axonal terminations from the retrosplenial and visual association cortices in the laterodorsal thalamic nucleus of the rat. Anat. Embryol. 2005, 210, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shibata, H. Organization of retrosplenial cortical projections to the laterodorsal thalamic nucleus in the rat. Neurosci. Res. 2000, 38, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baratz-Goldstein, R.; Toussia-Cohen, S.; Elpaz, A.; Rubovitch, V.; Pick, C.G. Immediate and delayed hyperbaric oxygen therapy as a neuroprotective treatment for traumatic brain injury in mice. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2017, 83, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glushakov, A.V.; Fazal, J.A.; Narumiya, S.; Dore, S. Role of the prostaglandin e2 ep1 receptor in traumatic brain injury. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazra, A.; Macolino, C.; Elliott, M.B.; Chin, J. Delayed thalamic astrocytosis and disrupted sleep-wake patterns in a preclinical model of traumatic brain injury. J. Neurosci. Res. 2014, 92, 1434–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramlackhansingh, A.F.; Brooks, D.J.; Greenwood, R.J.; Bose, S.K.; Turkheimer, F.E.; Kinnunen, K.M.; Gentleman, S.; Heckemann, R.A.; Gunanayagam, K.; Gelosa, G.; et al. Inflammation after trauma: Microglial activation and traumatic brain injury. Ann. Neurol. 2011, 70, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, H.; Hioki, H.; Furuta, T.; Kaneko, T. Different cortical projections from three subdivisions of the rat lateral posterior thalamic nucleus: A single-neuron tracing study with viral vectors. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2015, 41, 1294–1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warton, S.S.; Dyson, S.E.; Harvey, A.R. Visual thalamocortical projections in normal and enucleated rats: Hrp and fluorescent dye studies. Exp. Neurol. 1988, 100, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Groen, T.; Kadish, I.; Wyss, J.M. The role of the laterodorsal nucleus of the thalamus in spatial learning and memory in the rat. Behav. Brain Res. 2002, 136, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamishina, H.; Yurcisin, G.H.; Corwin, J.V.; Reep, R.L. Striatal projections from the rat lateral posterior thalamic nucleus. Brain Res. 2008, 1204, 24–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reep, R.L.; Corwin, J.V. Posterior parietal cortex as part of a neural network for directed attention in rats. Neurobiol. Learn. Mem. 2009, 91, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Pardo, H.; Conejo, N.M.; Lana, G.; Arias, J.L. Different brain networks underlying the acquisition and expression of contextual fear conditioning: A metabolic mapping study. Neuroscience 2012, 202, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harrington, M.E. The ventral lateral geniculate nucleus and the intergeniculate leaflet: Interrelated structures in the visual and circadian systems. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 1997, 21, 705–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neil, M.; Gleitsmann, K.; Motu’apuaka, M.; Freeman, M.; Kondo, K.; Storzbach, D.; Kansagara, D.; Carlson, K. Visual Dysfunction in Patients with Traumatic Brain Injury: A Systematic Review; Department of Veterans Affairs: Washington, DC, USA, 2014.
- Schlageter, K.; Gray, B.; Hall, K.; Shaw, R.; Sammet, R. Incidence and treatment of visual dysfunction in traumatic brain injury. Brain Inj. 1993, 7, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, S.J.; Bushnell, M.C. Rodent functional and anatomical imaging of pain. Neurosci. Lett. 2012, 520, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, K.D.; Lifshitz, J. Diffuse traumatic brain injury initially attenuates and later expands activation of the rat somatosensory whisker circuit concomitant with neuroplastic responses. Brain Res. 2010, 1323, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macolino, C.M.; Daiutolo, B.V.; Albertson, B.K.; Elliott, M.B. Mechanical alloydnia induced by traumatic brain injury is independent of restraint stress. J. Neurosci. Methods 2014, 226, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elliott, M.B.; Oshinsky, M.L.; Amenta, P.S.; Awe, O.O.; Jallo, J.I. Nociceptive neuropeptide increases and periorbital allodynia in a model of traumatic brain injury. Headache 2012, 52, 966–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowe, R.K.; Striz, M.; Bachstetter, A.D.; Van Eldik, L.J.; Donohue, K.D.; O’Hara, B.F.; Lifshitz, J. Diffuse brain injury induces acute post-traumatic sleep. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e82507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustafa, G.; Hou, J.; Tsuda, S.; Nelson, R.; Sinharoy, A.; Wilkie, Z.; Pandey, R.; Caudle, R.M.; Neubert, J.K.; Thompson, F.J.; et al. Trigeminal neuroplasticity underlies allodynia in a preclinical model of mild closed head traumatic brain injury (CTBI). Neuropharmacology 2016, 107, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arida, R.M.; Fernandes, M.J.; Scorza, F.A.; Preti, S.C.; Cavalheiro, E.A. Physical training does not influence interictal lcmrglu in pilocarpine-treated rats with epilepsy. Physiol. Behav. 2003, 79, 789–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scorza, F.A.; Sanabria, E.R.; Calderazzo, L.; Cavalheiro, E.A. Glucose utilization during interictal intervals in an epilepsy model induced by pilocarpine: A qualitative study. Epilepsia 1998, 39, 1041–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafarian, M.; Karimzadeh, F.; Alipour, F.; Attari, F.; Lotfinia, A.A.; Speckmann, E.J.; Zarrindast, M.R.; Gorji, A. Cognitive impairments and neuronal injury in different brain regions of a genetic rat model of absence epilepsy. Neuroscience 2015, 298, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arai, T.; Jones, C.R.; Rapoport, S.I.; Weiss, S.R. Evidence for membrane remodeling in ipsilateral thalamus and amygdala following left amygdala-kindled seizures in awake rats. Brain Res. 1996, 743, 131–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ieraci, A.; Herrera, D.G. Nicotinamide protects against ethanol-induced apoptotic neurodegeneration in the developing mouse brain. PLoS Med. 2006, 3, e101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasquier, D.A.; Villar, M.J. Subcortical projections to the lateral geniculate body in the rat. Exp. Brain Res. 1982, 48, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, R.Y. The geniculohypothalamic tract in monkey and man. Brain Res. 1989, 486, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steriade, M.; McCormick, D.A.; Sejnowski, T.J. Thalamocortical oscillations in the sleeping and aroused brain. Science 1993, 262, 679–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llinas, R.R.; Steriade, M. Bursting of thalamic neurons and states of vigilance. J. Neurophysiol. 2006, 95, 3297–3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeitzer, J.M.; Friedman, L.; O’Hara, R. Insomnia in the context of traumatic brain injury. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2009, 46, 827–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouellet, M.C.; Morin, C.M. Subjective and objective measures of insomnia in the context of traumatic brain injury: A preliminary study. Sleep Med. 2006, 7, 486–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorente, L.; Martin, M.M.; Argueso, M.; Ramos, L.; Sole-Violan, J.; Riano-Ruiz, M.; Jimenez, A.; Borreguero-Leon, J.M. Serum caspase-3 levels and mortality are associated in patients with severe traumatic brain injury. BMC Neurol. 2015, 15, 228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dash, P.K.; Zhao, J.; Hergenroeder, G.; Moore, A.N. Biomarkers for the diagnosis, prognosis, and evaluation of treatment efficacy for traumatic brain injury. Neurotherapeutics 2010, 7, 100–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brophy, G.M.; Pineda, J.A.; Papa, L.; Lewis, S.B.; Valadka, A.B.; Hannay, H.J.; Heaton, S.C.; Demery, J.A.; Liu, M.C.; Tepas, J.J., 3rd; et al. Alphaii-spectrin breakdown product cerebrospinal fluid exposure metrics suggest differences in cellular injury mechanisms after severe traumatic brain injury. J. Neurotrauma 2009, 26, 471–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokobori, S.; Hosein, K.; Burks, S.; Sharma, I.; Gajavelli, S.; Bullock, R. Biomarkers for the clinical differential diagnosis in traumatic brain injury—A systematic review. CNS Neurosci. Therap. 2013, 19, 556–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, C.E.; Clifton, G.L.; Lighthall, J.W.; Yaghmai, A.A.; Hayes, R.L. A controlled cortical impact model of traumatic brain injury in the rat. J. Neurosci. Methods 1991, 39, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, J.; Hu, X.; Zhang, L.; Mao, L.; Jiang, X.; Liou, A.K.; Leak, R.K.; Gao, Y.; Chen, J. Microglia/macrophage polarization dynamics in white matter after traumatic brain injury. J. Cerebral Blood Flow Metab. 2013, 33, 1864–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glushakova, O.Y.; Jeromin, A.; Martinez, J.; Johnson, D.; Denslow, N.; Streeter, J.; Hayes, R.L.; Mondello, S. Cerebrospinal fluid protein biomarker panel for assessment of neurotoxicity induced by kainic acid in rats. Toxicol. Sci. 2012, 130, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Glushakov, A.O.; Glushakova, O.Y.; Korol, T.Y.; Acosta, S.A.; Borlongan, C.V.; Valadka, A.B.; Hayes, R.L.; Glushakov, A.V. Chronic Upregulation of Cleaved-Caspase-3 Associated with Chronic Myelin Pathology and Microvascular Reorganization in the Thalamus after Traumatic Brain Injury in Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3151. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103151
Glushakov AO, Glushakova OY, Korol TY, Acosta SA, Borlongan CV, Valadka AB, Hayes RL, Glushakov AV. Chronic Upregulation of Cleaved-Caspase-3 Associated with Chronic Myelin Pathology and Microvascular Reorganization in the Thalamus after Traumatic Brain Injury in Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(10):3151. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103151
Chicago/Turabian StyleGlushakov, Andriy O., Olena Y. Glushakova, Tetyana Y. Korol, Sandra A. Acosta, Cesar V. Borlongan, Alex B. Valadka, Ronald L. Hayes, and Alexander V. Glushakov. 2018. "Chronic Upregulation of Cleaved-Caspase-3 Associated with Chronic Myelin Pathology and Microvascular Reorganization in the Thalamus after Traumatic Brain Injury in Rats" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 10: 3151. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103151
APA StyleGlushakov, A. O., Glushakova, O. Y., Korol, T. Y., Acosta, S. A., Borlongan, C. V., Valadka, A. B., Hayes, R. L., & Glushakov, A. V. (2018). Chronic Upregulation of Cleaved-Caspase-3 Associated with Chronic Myelin Pathology and Microvascular Reorganization in the Thalamus after Traumatic Brain Injury in Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(10), 3151. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103151