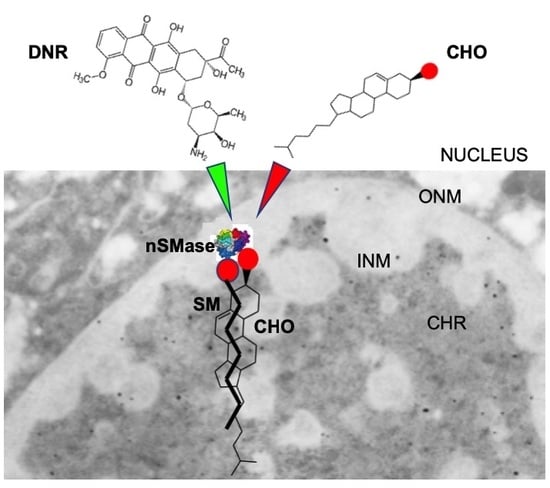
Nuclear Lipid Microdomains Regulate Daunorubicin Resistance in Hepatoma Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
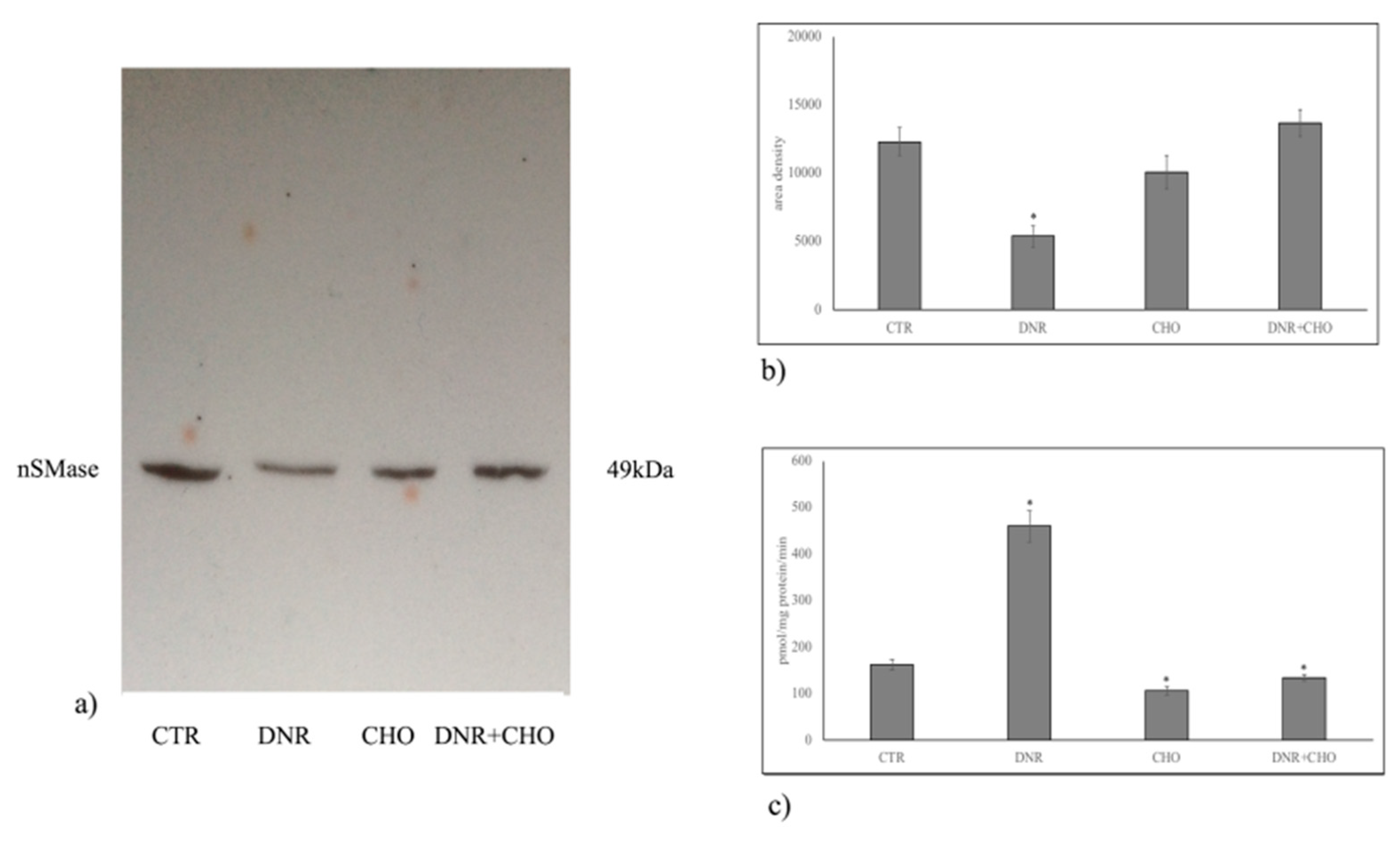
2.1. Specific Neutral Sphingomyelinase Down-Regulation with Daunorubicin Treatment
2.2. Sphingomyelin Metabolism of Nuclear Lipid Microdomains as an Emerging Target of Daunorubicin in Cancer: Role of Cholesterol in Drug-Resistance
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Nuclei-Free Lysates
4.4. Purification of Nuclear Lipid Microdomains
4.5. Reverse Transcription Quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR)
4.6. Protein Content
4.7. Electrophoresis and Western Blot Analysis
4.8. nSMase Activity Assay
4.9. Lipid Extraction and UFLC MS/MS Analysis
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Munger, C.; Ellis, A.; Woods, K.; Randolph, J.; Yanovich, S.; Gewirtz, D. Evidence for inhibition of growth related to compromised DNA synthesis in the interaction of daunorubicin with H-35 rat hepatoma. Cancer Res. 1988, 48, 2404–2411. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pugliese, L.; Bernardini, I.; Pacifico, N.; Peverini, M.; Damaskopoulou, E.; Cataldi, S.; Albi, E. Severe hypocholesterolaemia is often neglected in haematological malignancies. Eur. J. Cancer 2010, 46, 1735–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.J.; Koh, K.N.; Park, C.J.; Jang, S.; Im, H.J.; Kim, N. The Combination of Flavokawain B and Daunorubicin Induces Apoptosis in Human Myeloid Leukemic Cells by Modifying NF-κB. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 2771–2778. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Weston, V.J.; Wei, W.; Stankovic, T.; Kearns, P. Synergistic action of dual IGF1/R and MEK inhibition sensitizes childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) cells to cytotoxic agents and involves downregulation of STAT6 and PDAP1. Exp. Hematol. 2018, 63, 52–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamauchi, T. Incorporation of novel agents into the treatment for acute myeloid leukemia. Rinsho Ketsueki 2018, 59, 1988–1996. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vanegas, Y.A.M.; Azzouqa, A.M.; Menke, D.M.; Foran, J.M.; Vishnu, P. Myelodysplasia-related acute myeloid leukemia and acute promyelocytic leukemia: Concomitant occurrence of two molecularly distinct diseases. Hematol. Rep. 2018, 10, 7658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toniolo, G.; Efthimiadou, E.K.; Kordas, G.; Chatgilialoglu, C. Development of multi-layered and multi-sensitive polymeric nanocontainers for cancer therapy: In vitro evaluation. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samant, R.; Alomary, I.; Alsaeed, E.; Al-Jasir, B.; Bence-Bruckler, I.; Cross, P.; Genest, P.; Huebsch, L. Comparison of favorable early-stage hodgkin’s lymphoma treatments: A single-institution review. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2010, 76, 1166–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dombret, H.; Raffoux, E.; Gardin, C. New insights in the management of elderly patients with acute myeloid leukemia. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2009, 21, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uematsu, N.; Zhao, Y.; Kiyomi, A.; Yuan, B.O.; Onda, K.; Tanaka, S.; Sugiyama, K.; Sugiura, M.; Takagi, N.; Hayakawa, A.; et al. Chemo-sensitivity of Two-dimensional Monolayer and Three-dimensional Spheroid of Breast Cancer MCF-7 Cells to Daunorubicin, Docetaxel, and Arsenic Disulfide. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 2101–2108. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fergusson, J.R.; Ussher, J.E.; Kurioka, A.; Klenerman, P.; Walker, L.J. High MDR-1 expression by MAIT cells confers resistance to cytotoxic but not immunosuppressive MDR-1 substrates. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2018, 194, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, R.; Han, S.I. Extracellular acidity enhances tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL)-mediated apoptosis via DR5 in gastric cancer cells. Korean J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2018, 22, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Guo, J. Advance in research on regulatory mechanism and functions of neutral sphingomyelinse 2. Zhongguo Yi Xue Ke Xue Yuan Xue Bao 2013, 35, 581–585. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Laurent, G.; Jaffrézou, J.P. Signaling pathways activated by daunorubicin. Blood 2001, 98, 913–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carroll, B.L.; Bonica, J.; Shamseddine, A.A.; Hannun, Y.A.; Obeid, L.M. A role for caspase-2 in sphingosine kinase 1 proteolysis in response to doxorubicin in breast cancer cells—Implications for the CHK1-suppressed pathway. FEBS Open Bio 2017, 8, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cascianelli, G.; Villani, M.; Tosti, M.; Marini, F.; Bartoccini, E.; Magni, M.V.; Albi, E. Lipid microdomains in cell nucleus. Mol. Biol. Cell 2008, 19, 5289–5295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albi, E.; Lazzarini, A.; Lazzarini, R.; Floridi, A.; Damaskopoulou, E.; Curcio, F.; Cataldi, S. Nuclear lipid microdomain as place of interaction between sphingomyelin and DNA during liver regeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 6529–6541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazzarini, A.; Macchiarulo, A.; Floridi, A.; Coletti, A.; Cataldi, S.; Codini, M.; Lazzarini, R.; Bartoccini, E.; Cascianelli, G.; Ambesi-Impiombato, F.S.; et al. Very-long-chain fatty acid sphingomyelin in nuclear lipid microdomains of hepatocytes and hepatoma cells: Can the exchange from C24:0 to C16:0 affect signal proteins and vitamin D receptor? Mol. Biol. Cell 2015, 26, 2418–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartoccini, E.; Marini, F.; Damaskopoulou, E.; Lazzarini, R.; Cataldi, S.; Cascianelli, G.; Gil Garcia, M.; Albi, E. Nuclear lipid microdomains regulate nuclear vitamin D3 uptake and influence embryonic hippocampal cell differentiation. Mol. Biol. Cell 2011, 22, 3022–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kizek, R.; Adam, V.; Hrabeta, J.; Eckschlager, T.; Smutny, S.; Burda, J.V.; Frei, E.; Stiborova, M. Anthracyclinesand ellipticines asDNA-damaging anticancer drugs: Recent advances. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 133, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeidner, J.F.; Foster, M.C.; Blackford, A.L.; Litzow, M.R.; Morris, L.E.; Strickland, S.A.; Lancet, J.E.; Bose, P.; Levy, M.Y.; Tibes, R.; et al. Final results of a randomized multicenter phase II study of alvocidib, cytarabine, and mitoxantrone versus cytarabine anddaunorubicin (7 ± 3) in newly diagnosed high-risk acute myeloid leukemia (AML). Leuk. Res. 2018, 72, 92–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cataldi, S.; Codini, M.; Cascianelli, G.; Tringali, S.; Tringali, A.R.; Lazzarini, A.; Floridi, A.; Bartoccini, E.; Garcia-Gil, M.; Lazzarini, R.; et al. Nuclear lipid microdomain as resting place of dexamethasone to impair cell proliferation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 19832–19846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Codini, M.; Cataldi, S.; Lazzarini, A.; Tasegian, A.; Ceccarini, M.R.; Floridi, A.; Lazzarini, R.; Ambesi-Impiombato, F.S.; Curcio, F.; Beccari, T.; et al. Why high cholesterol levels help hematological malignancies: Role of nuclear lipid microdomains. Lipids Health Dis. 2016, 15, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamseddine, A.A.; Clarke, C.J.; Carroll, B.; Airola, M.V.; Mohammed, S.; Rella, A.; Obeid, L.M.; Hannun, Y.A. P53-dependent upregulation of neutralsphingomyelinase-2: Role in doxorubicin-induced growth arrest. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slotte, J.P. Molecular properties of various structurally defined sphingomyelins—Correlation of structure with function. Prog. Lipid Res. 2013, 52, 206–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobrzycka, M.; Spychalski, P.; Łachiński, A.J.; Kobiela, P.; Jędrusik, P.; Kobiela, J. Statins and Colorectal Cancer—A Systematic Review. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albi, E.; La Porta, C.A.; Cataldi, S.; Magni, M.V. Nuclear sphingomyelin-synthase and protein kinase C delta in melanoma cells. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2005, 438, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Codini, M.; Conte, C.; Cataldi, S.; Arcuri, C.; Lazzarini, A.; Ceccarini, M.R.; Patria, F.; Floridi, A.; Mecca, C.; Ambesi-Impiombato, F.S.; et al. Nuclear Lipid Microdomains Regulate Daunorubicin Resistance in Hepatoma Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3424. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113424
Codini M, Conte C, Cataldi S, Arcuri C, Lazzarini A, Ceccarini MR, Patria F, Floridi A, Mecca C, Ambesi-Impiombato FS, et al. Nuclear Lipid Microdomains Regulate Daunorubicin Resistance in Hepatoma Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(11):3424. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113424
Chicago/Turabian StyleCodini, Michela, Carmela Conte, Samuela Cataldi, Cataldo Arcuri, Andrea Lazzarini, Maria Rachele Ceccarini, Federica Patria, Alessandro Floridi, Carmen Mecca, Francesco Saverio Ambesi-Impiombato, and et al. 2018. "Nuclear Lipid Microdomains Regulate Daunorubicin Resistance in Hepatoma Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 11: 3424. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113424
APA StyleCodini, M., Conte, C., Cataldi, S., Arcuri, C., Lazzarini, A., Ceccarini, M. R., Patria, F., Floridi, A., Mecca, C., Ambesi-Impiombato, F. S., Beccari, T., Curcio, F., & Albi, E. (2018). Nuclear Lipid Microdomains Regulate Daunorubicin Resistance in Hepatoma Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(11), 3424. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113424