Identification, Classification, and Functional Analysis of AP2/ERF Family Genes in the Desert Moss Bryum argenteum
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification of the AP2/ERF Family Genes in B. argenteum
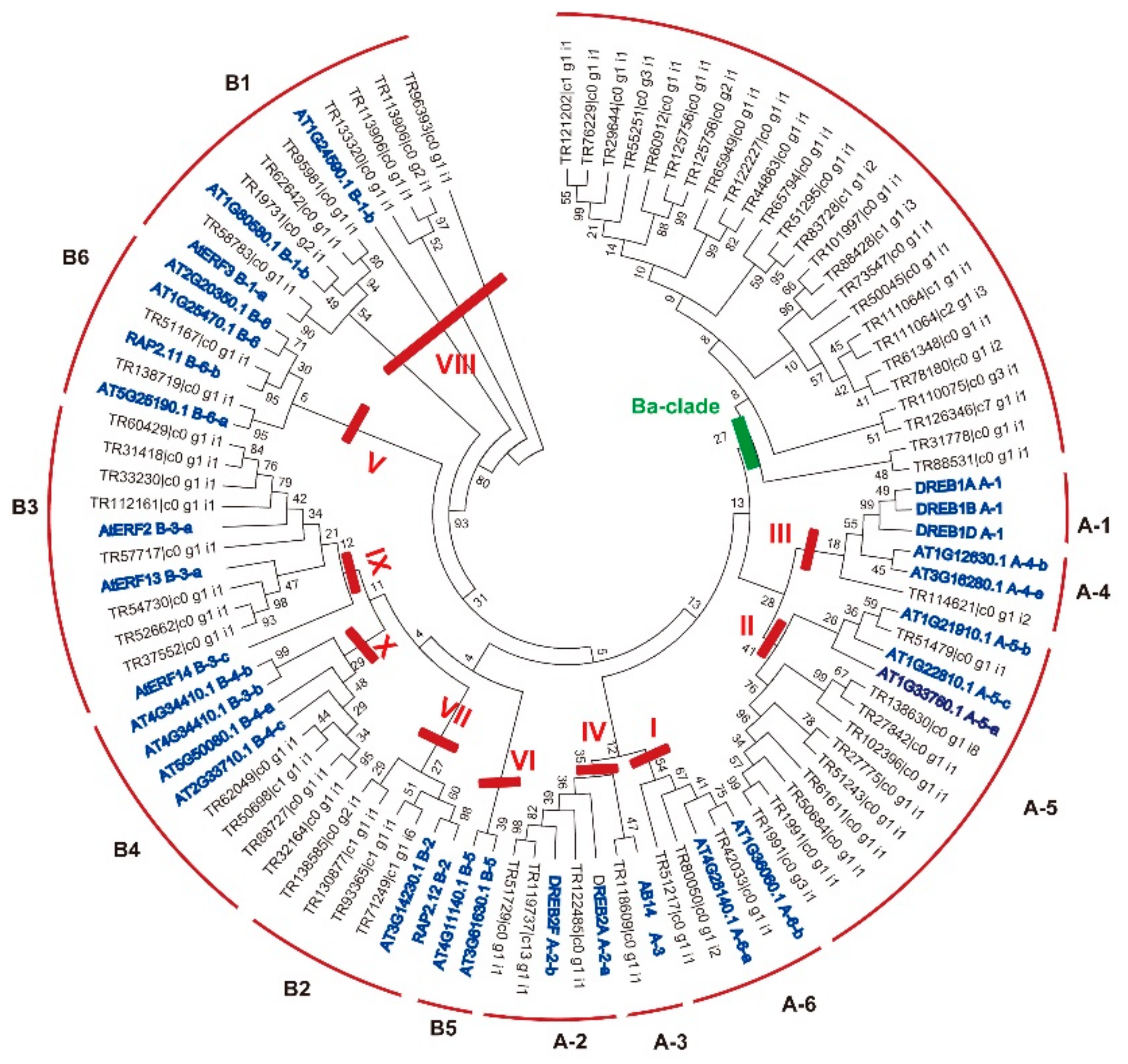
2.2. Classification of the AP2/ERF Genes in B. argenteum
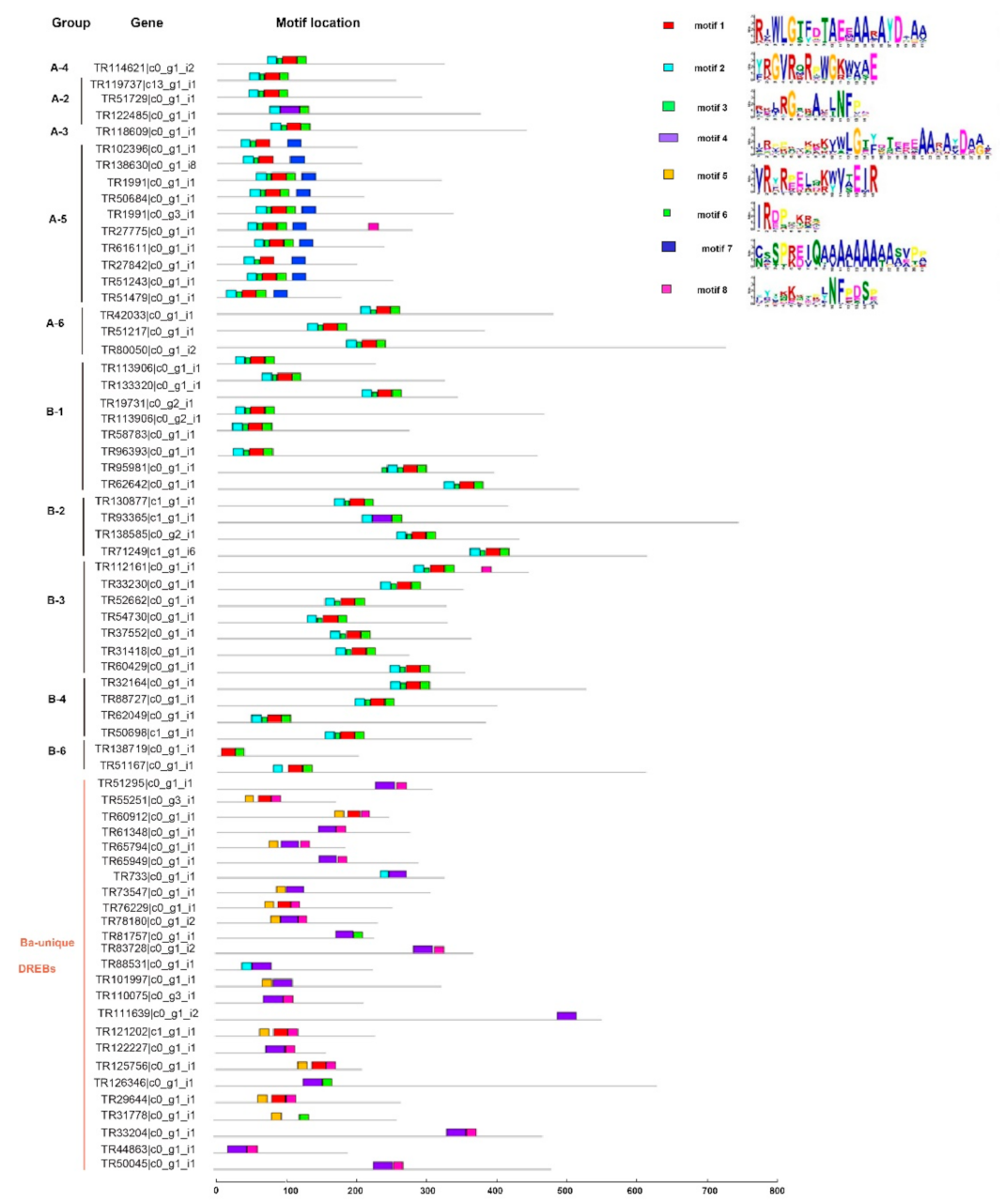
2.3. Conserved Amino Acids and Motifs Analysis of BaERF Genes
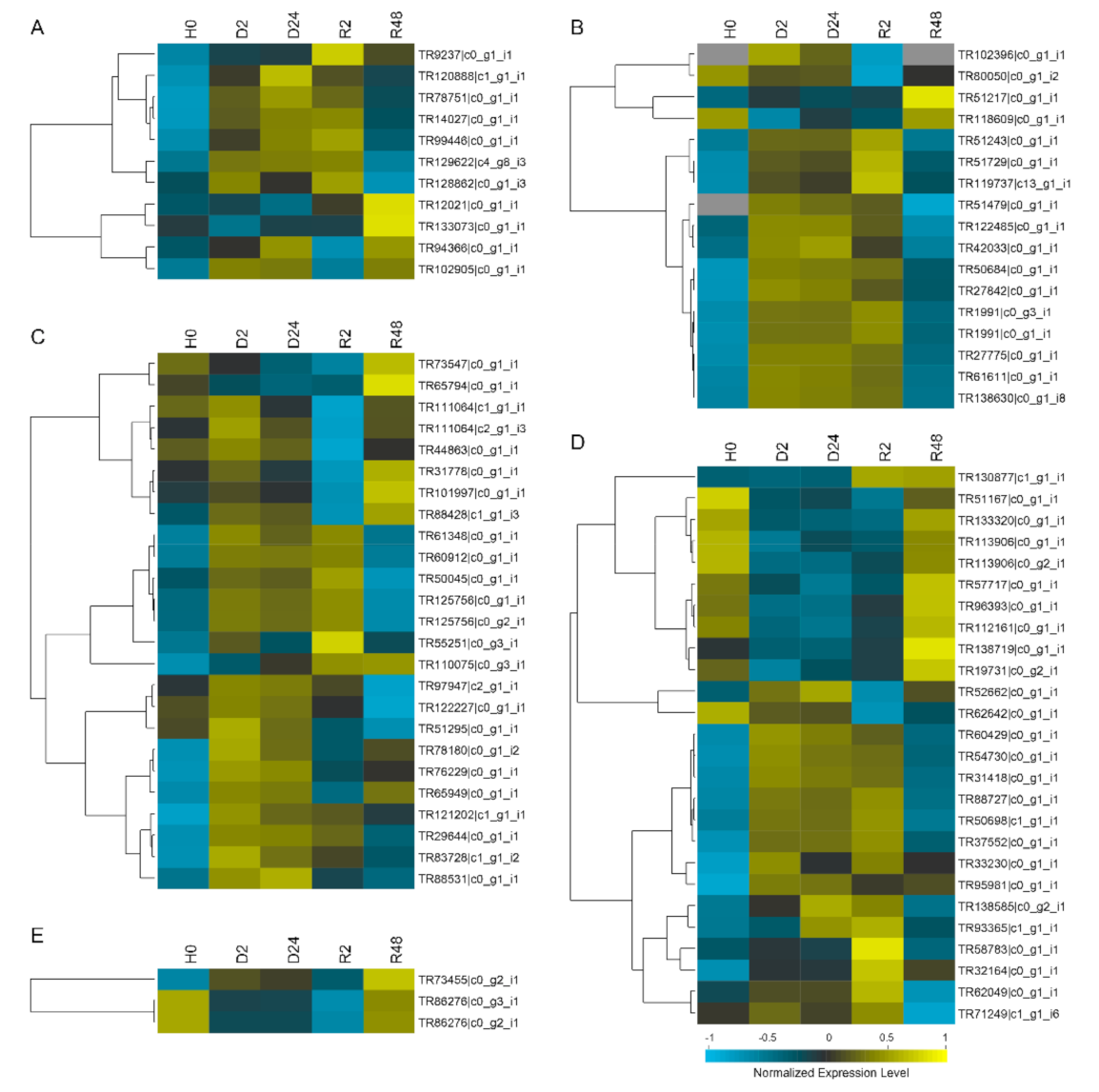
2.4. Gene Expression Analysis of all the BaAP2/ERFs during Moss Specific Dehydration–Rehydration Process Using RNA-seq Data
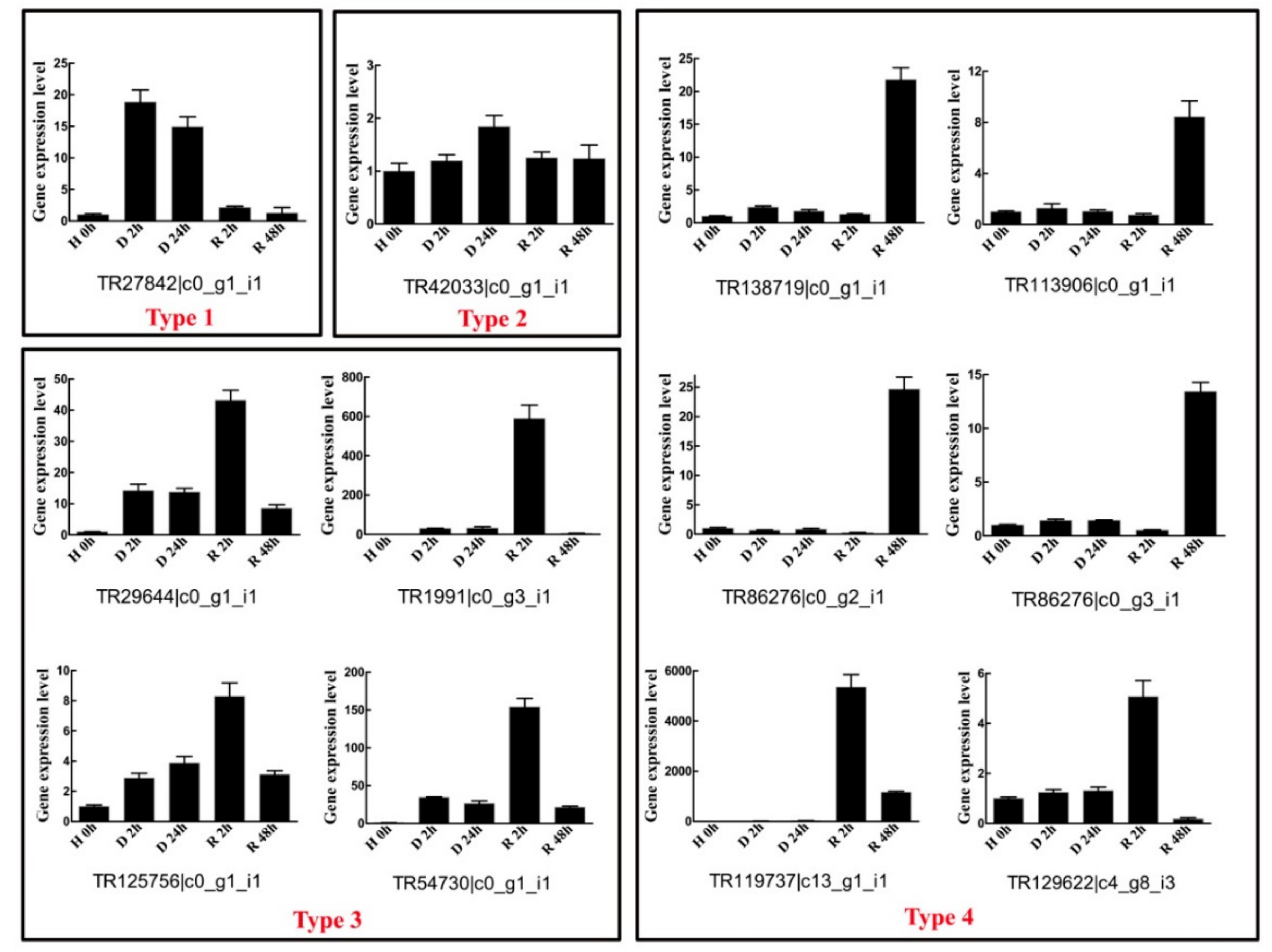
2.5. Diverse Gene Expression Patterns of Twelve BaAP2/ERFs during Dehydration–Rehydration Process Using RT-qPCR
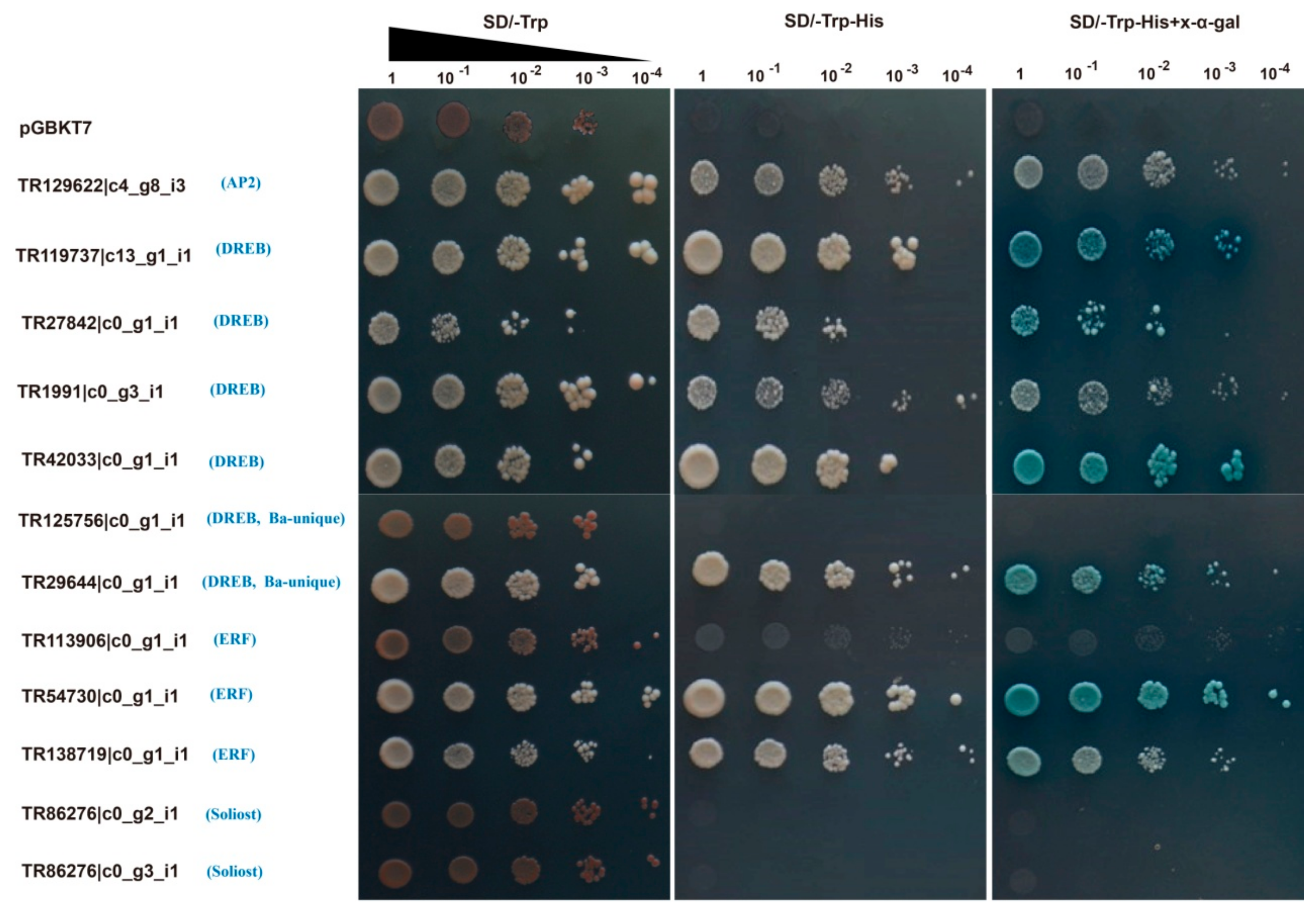
2.6. Transactivation Activity Analyses of Twelve BaAP2/ERFs
2.7. Stress Tolerance Ability Evaluation in Transgenic Yeast
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Identification of the AP2/ERF Protein Family in B. argenteum
4.2. Sequence Analysis and Classification of BaAP2/ERF Genes Using Phylogenetic Tree
4.3. Gene Expression Analysis of BaAP2/ERF Genes Using RNA-seq Data
4.4. Gene Expression Pattern Analysis of BaAP2/ERF Genes Using RT-qPCR Assay
4.5. Gene Cloning, Vector Construction and Transcriptional Activation Analysis in Yeast Cells
4.6. Stress Tolerance Studies in Yeast
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AP2/ERF | APETALA2/Ethylene responsive factor |
| DREB | dehydration-responsive element-binding protein |
| ERF | ethylene-responsive factor |
| RAV | related to ABI3/VP1 |
| RT-qPCR | reverse transcription quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction |
| TF | transcription factor |
| DT | desiccation tolerance |
References
- Zhang, Y.M.; Chen, J.; Wang, L.; Wang, X.Q.; Gu, Z.H. The spatial distribution patterns of biological soil crusts in the Gurbantunggut Desert, Northern Xinjiang, China. J. Arid Environ. 2007, 68, 599–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.R.; Zhou, H.Y.; Wang, X.P.; Zhu, Y.G.; O’Conner, P.J. The effects of sand stabilization and revegetation on cryptogam species diversity and soil fertility in the Tengger Desert, Northern China. Plant Soil 2003, 251, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, R.; Li, X.R.; Chen, C.Y.; Zhao, X.; Jia, R.L.; Liu, L.C.; Wei, Y.P. Responses of photosynthetic properties and chloroplast ultrastructure of Bryum argenteum from a desert biological soil crust to elevated ultraviolet-B radiation. Physiol. Plant. 2013, 147, 489–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.H.; Li, X.R.; Chen, C.Y. Degradation and reorganization of thylakoid protein complexes of Bryum argenteum in response to dehydration and rehydration. Bryologist 2014, 117, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, A.J. Invited essay: New frontiers in bryology and lichenology—The nature and distribution of vegetative desiccation-tolerance in hornworts, liverworts and mosses. Bryologist 2007, 110, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.H.; Li, X.R.; Zhang, P. Micro-morphology, ultrastructure and chemical composition changes of Bryum argenteum from a desert biological soil crust following one-year desiccation. Bryologist 2014, 117, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stark, L.R.; McLetchie, D.N.; Eppley, S.M. Sex ratios and the shy male hypothesis in the moss Bryum argenteum (Bryaceae). Bryologist 2010, 113, 788–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Zhang, D.Y.; Li, X.S.; Yang, H.L.; Zhang, Y.M.; Wood, A.J. De novo transcriptome characterization and gene expression profiling of the desiccation tolerant moss Bryum argenteum following rehydration. BMC Genom. 2015, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Licausi, F.; Ohme-Takagi, M.; Perata, P. APETALA2/Ethylene Responsive Factor (AP2/ERF) transcription factors: Mediators of stress responses and developmental programs. New Phytol. 2013, 199, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.S.; Chen, M.; Li, L.C.; Ma, Y.Z. Functions and Application of the AP2/ERF Transcription Factor Family in Crop Improvement. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2011, 53, 570–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizoi, J.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. AP2/ERF family transcription factors in plant abiotic stress responses. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gene Regul. Mech. 2012, 1819, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatta, M.; Morgounov, A.; Belamkar, V.; Baenziger, P. Genome-wide association study reveals novel genomic regions for grain yield and yield-related traits in drought-stressed Synthetic hexaploid Wheat. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.P.; Tian, F.; Yang, D.C.; Meng, Y.Q.; Kong, L.; Luo, J.C.; Gao, G. PlantTFDB 4.0: Toward a central hub for transcription factors and regulatory interactions in plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D1040–D1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.; Zhang, H.; Kong, L.; Gao, G.; Luo, J. PlantTFDB 3.0: A portal for the functional and evolutionary study of plant transcription factors. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D1182–D1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiss, M.; Laule, O.; Meskauskiene, R.M.; Arif, M.A.; Decker, E.L.; Erxleben, A.; Frank, W.; Hanke, S.T.; Lang, D.; Martin, A.; et al. Large-scale gene expression profiling data for the model moss Physcomitrella patens aid understanding of developmental progression, culture and stress conditions. Plant J. 2014, 79, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Zhong, N.Q.; Wang, G.L.; Li, L.J.; Liu, X.L.; He, Y.K.; Xia, G.X. Cloning and functional characterization of PpDBF1 gene encoding a DRE-binding transcription factor from Physcomitrella patens. Planta 2007, 226, 827–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, B.; Zhang, D.; Li, X.; Yang, H.; Wood, A.J. De novo assembly and characterization of the transcriptome in the desiccation-tolerant moss Syntrichia caninervis. BMC Res. Notes 2014, 7, 490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Zhang, D.; Li, X.; Guan, K.; Yang, H. Novel DREB A-5 subgroup transcription factors from desert moss (Syntrichia caninervis) confers multiple abiotic stress tolerance to yeast. J. Plant Physiol. 2016, 194, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhang, D.; Gao, B.; Liang, Y.; Yang, H.; Wang, Y.; Wood, A.J. Transcriptome-Wide Identification, Classification, and Characterization of AP2/ERF Family Genes in the Desert Moss Syntrichia caninervis. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, T.; Suzuki, K.; Fujimura, T.; Shinshi, H. Genome-wide analysis of the ERF gene family in Arabidopsis and rice. Plant Physiol. 2006, 140, 411–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.M.; Li, Y.; Hou, X.L. Genome-wide analysis of the AP2/ERF transcription factor superfamily in Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa ssp pekinensis). BMC Genom. 2013, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakuma, Y.; Liu, Q.; Dubouzet, J.G.; Abe, H.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. DNA-binding specificity of the ERF/AP2 domain of Arabidopsis DREBs, transcription factors involved in dehydration- and cold-inducible gene expression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 290, 998–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, C.; Argout, X.; Gebelin, V.; Summo, M.; Dufayard, J.F.; Leclercq, J.; Kuswanhadi; Piyatrakul, P.; Pirrello, J.; Rio, M.; et al. Identification of the Hevea brasiliensis AP2/ERF superfamily by RNA sequencing. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wu, Z.J.; Li, X.H.; Liu, Z.W.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.X.; Zhuang, J. Transcriptome-based discovery of AP2/ERF transcription factors related to temperature stress in tea plant (Camellia sinensis). Funct. Integr. Genom. 2015, 15, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, B.; Li, X.; Zhang, D.; Liang, Y.; Yang, H.; Chen, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wood, A.J. Desiccation tolerance in bryophytes: The dehydration and rehydration transcriptomes in the desiccation-tolerant bryophyte Bryum argenteum. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, P.K.; Gupta, K.; Lopato, S.; Agarwal, P. Dehydration responsive element binding transcription factors and their applications for the engineering of stress tolerance. J. Exp. Bot. 2017, 68, 2135–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lata, C.; Prasad, M. Role of DREBs in regulation of abiotic stress responses in plants. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 4731–4748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Licausi, F.; Giorgi, F.M.; Zenoni, S.; Osti, F.; Pezzotti, M.; Perata, P. Genomic and transcriptomic analysis of the AP2/ERF superfamily in Vitis vinifera. BMC Genom. 2010, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, J.; Cai, B.; Peng, R.H.; Zhu, B.; Jin, X.F.; Xue, Y.; Gao, F.; Fu, X.Y.; Tian, Y.S.; Zhao, W.; et al. Genome-wide analysis of the AP2/ERF gene family in Populus trichocarpa. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 371, 468–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.H.; Han, J.P.; Deng, X.M.; Tan, S.L.; Li, L.L.; Li, L.; Zhou, J.F.; Peng, H.; Yang, G.X.; He, G.Y.; et al. Expansion and stress responses of AP2/EREBP superfamily in Brachypodium Distachyon. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakhwani, D.; Pandey, A.; Dhar, Y.V.; Bag, S.K.; Trivedi, P.K.; Asif, M.H. Genome-wide analysis of the AP2/ERF family in Musa species reveals divergence and neofunctionalisation during evolution. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohta, M.; Matsui, K.; Hiratsu, K.; Shinshi, H.; Ohme-Takagi, M. Repression domains of class II ERF transcriptional repressors share an essential motif for active repression. Plant Cell 2001, 13, 1959–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, B.; Liu, J.Y. A cotton dehydration responsive element binding protein functions as a transcriptional repressor of DRE-mediated gene expression. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 343, 1023–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, C.J.; Liu, J.Y. The Arabidopsis EAR-motif-containing protein RAP2.1 functions as an active transcriptional repressor to keep stress responses under tight control. BMC Plant Biol. 2010, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Y.J.; Wei, W.; Song, Q.X.; Chen, H.W.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Wang, F.; Zou, H.F.; Lei, G.; Tian, A.G.; Zhang, W.K.; et al. Soybean NAC transcription factors promote abiotic stress tolerance and lateral root formation in transgenic plants. Plant J. 2011, 68, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Punta, M.; Coggill, P.C.; Eberhardt, R.Y.; Mistry, J.; Tate, J.; Boursnell, C.; Pang, N.; Forslund, K.; Ceric, G.; Clements, J.; et al. The Pfam protein families database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D290–D301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchler-Bauer, A.; Derbyshire, M.K.; Gonzales, N.R.; Lu, S.; Chitsaz, F.; Geer, L.Y.; Geer, R.C.; He, J.; Gwadz, M.; Hurwitz, D.I.; et al. CDD: NCBI’s conserved domain database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D222–D226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Letunic, I.; Doerks, T.; Bork, P. SMART: Recent updates, new developments and status in 2015. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, D257–D260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, T.L.; Boden, M.; Buske, F.A.; Frith, M.; Grant, C.E.; Clementi, L.; Ren, J.; Li, W.W.; Noble, W.S. MEME SUITE: Tools for motif discovery and searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, W202–W208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, K.; Peterson, D.; Peterson, N.; Stecher, G.; Nei, M.; Kumar, S. MEGA5: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 2731–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisen, M.B.; Spellman, P.T.; Brown, P.O.; Botstein, D. Cluster analysis and display of genome-wide expression patterns. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 14863–14868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brock, G.; Pihur, V.; Datta, S.; Datta, S. clValid, an R package for cluster validation. J. Stat. Softw. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saldanha, A.J. Java Treeview-extensible visualization of microarray data. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 3246–3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhang, D.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Wood, A.J. EsDREB2B, a novel truncated DREB2-type transcription factor in the desert legume Eremosparton songoricum, enhances tolerance to multiple abiotic stresses in yeast and transgenic tobacco. BMC Plant Biol. 2014, 14, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Gao, B.; Zhang, D.; Liang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, J.; Wood, A.J. Identification, Classification, and Functional Analysis of AP2/ERF Family Genes in the Desert Moss Bryum argenteum. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3637. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113637
Li X, Gao B, Zhang D, Liang Y, Liu X, Zhao J, Zhang J, Wood AJ. Identification, Classification, and Functional Analysis of AP2/ERF Family Genes in the Desert Moss Bryum argenteum. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(11):3637. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113637
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xiaoshuang, Bei Gao, Daoyuan Zhang, Yuqing Liang, Xiaojie Liu, Jinyi Zhao, Jianhua Zhang, and Andrew J. Wood. 2018. "Identification, Classification, and Functional Analysis of AP2/ERF Family Genes in the Desert Moss Bryum argenteum" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 11: 3637. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113637
APA StyleLi, X., Gao, B., Zhang, D., Liang, Y., Liu, X., Zhao, J., Zhang, J., & Wood, A. J. (2018). Identification, Classification, and Functional Analysis of AP2/ERF Family Genes in the Desert Moss Bryum argenteum. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(11), 3637. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113637








