Anti-inflammatory and Neuroprotective Effects of Fungal Immunomodulatory Protein Involving Microglial Inhibition
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
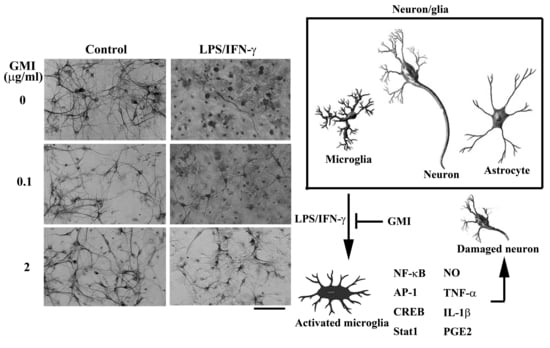
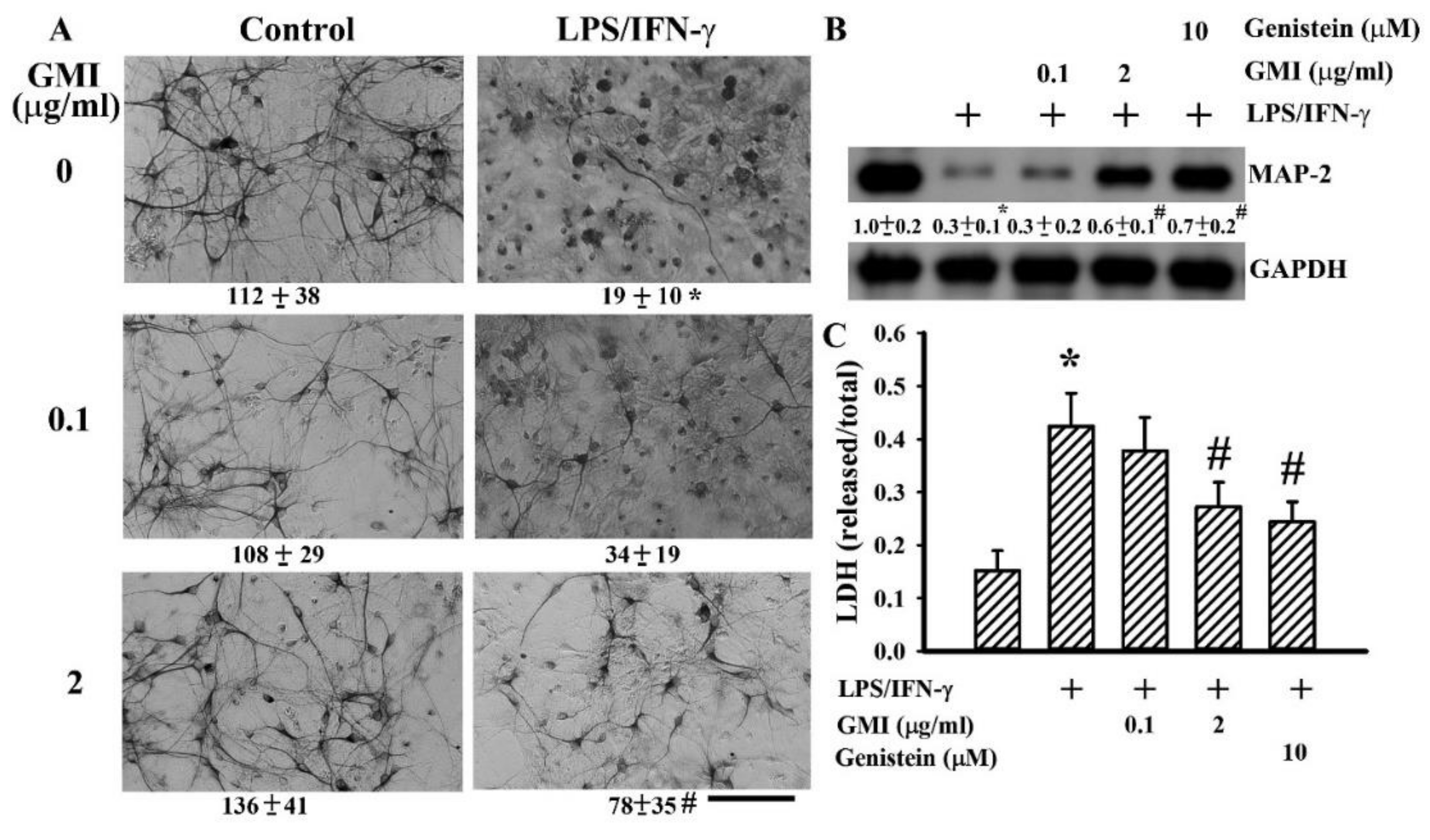
2.1. GMI Alleviated Neuronal Death
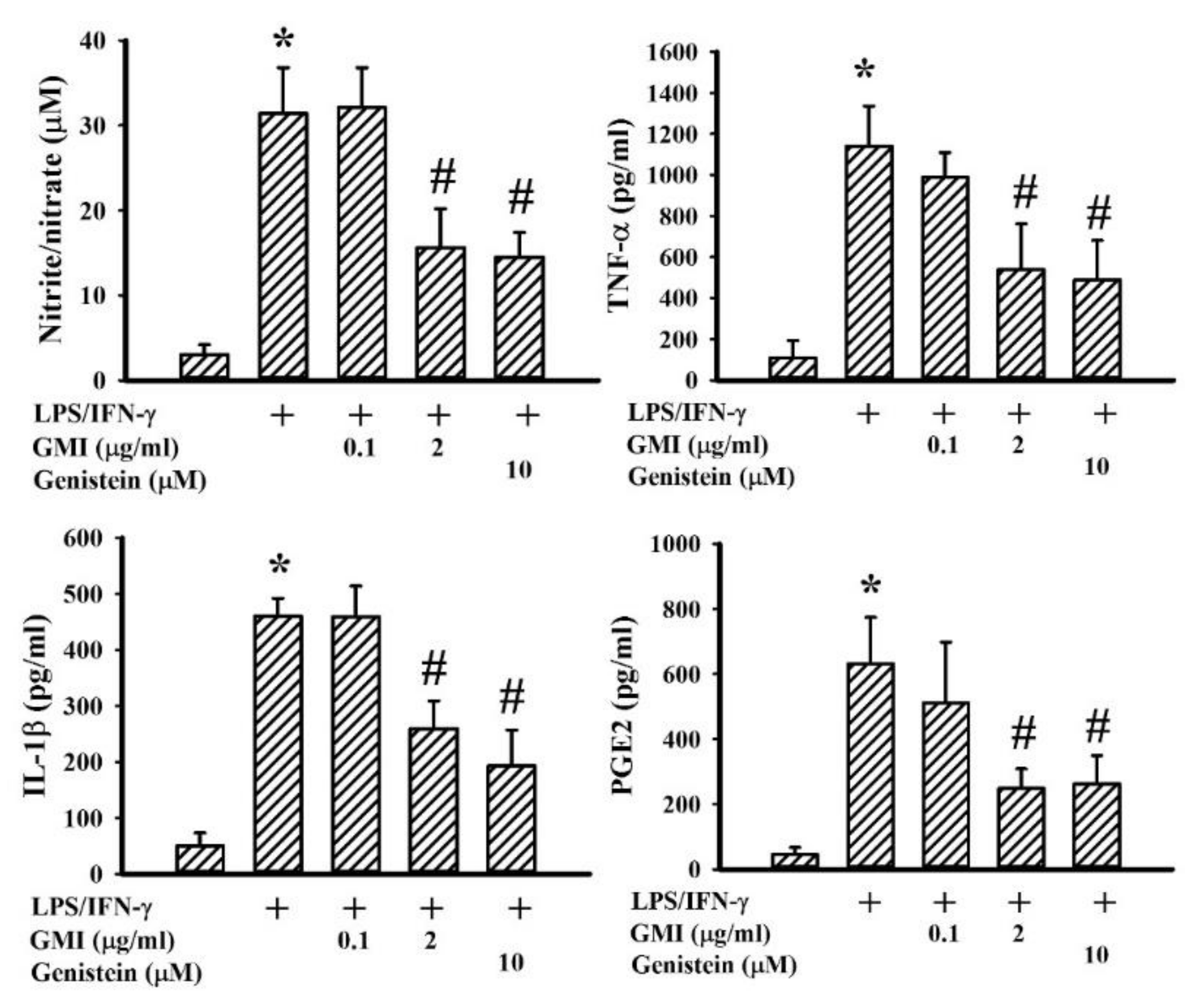
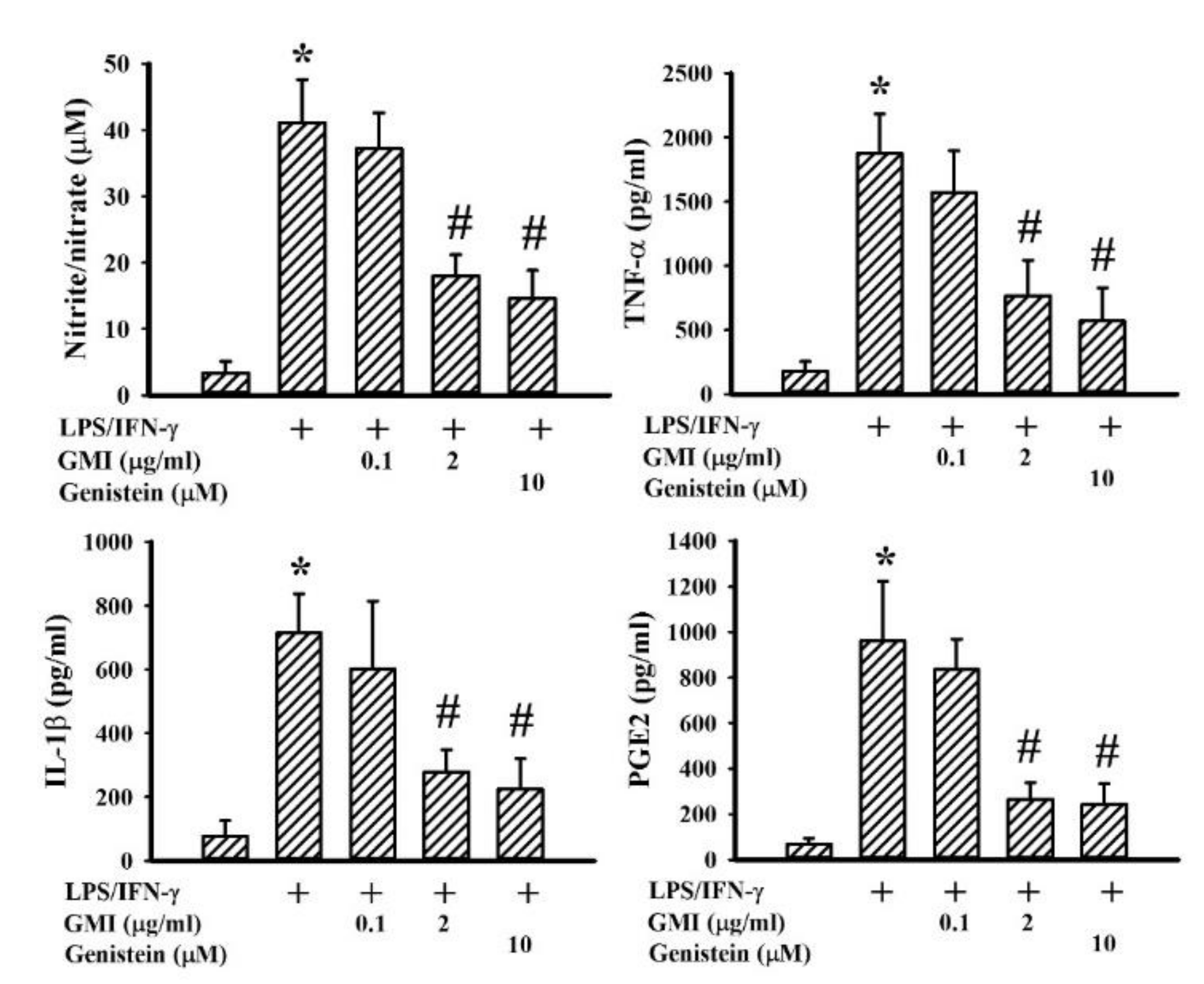
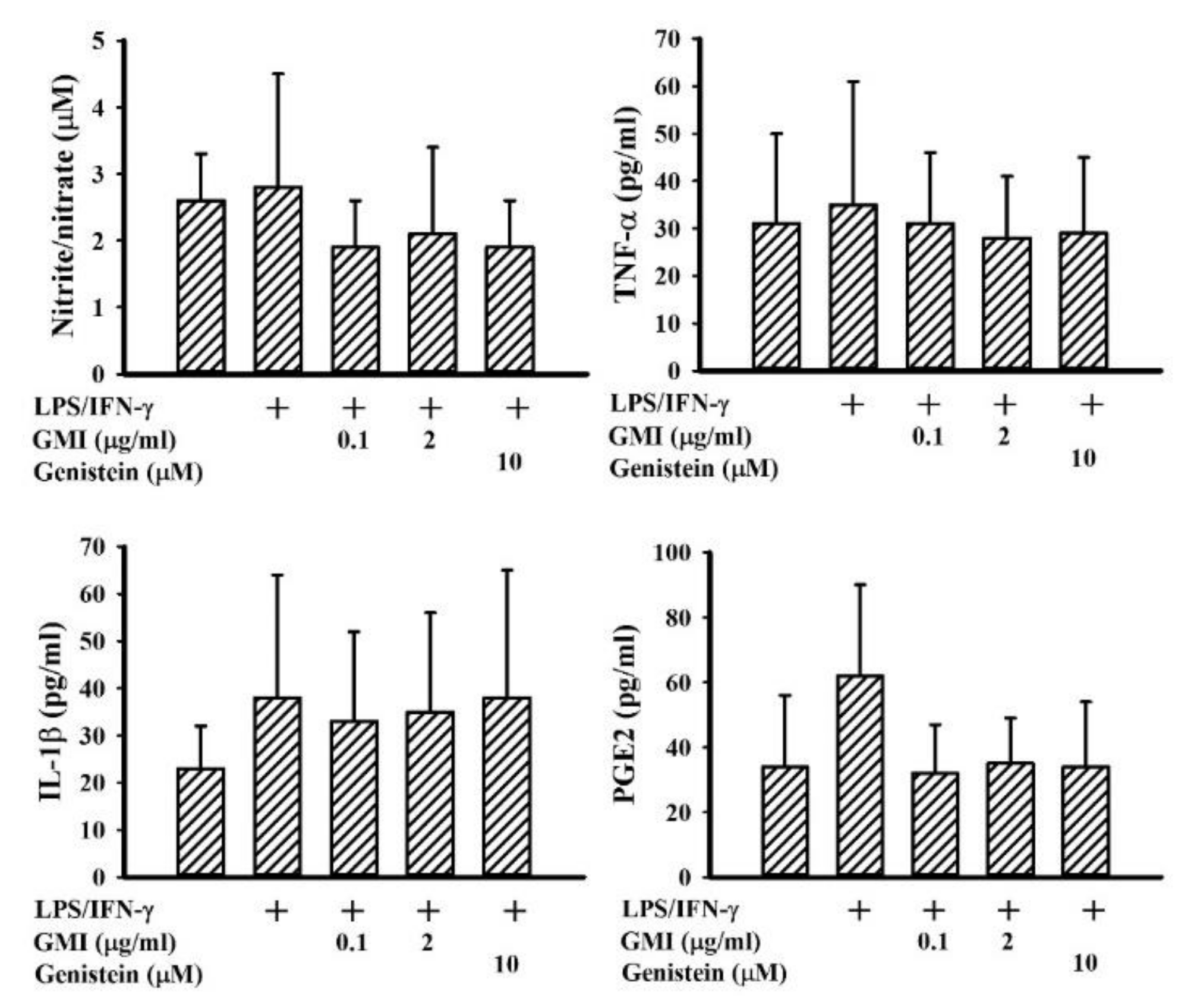
2.2. GMI Alleviated Inflammatory Cytokine and Neurotoxic Mediator Production
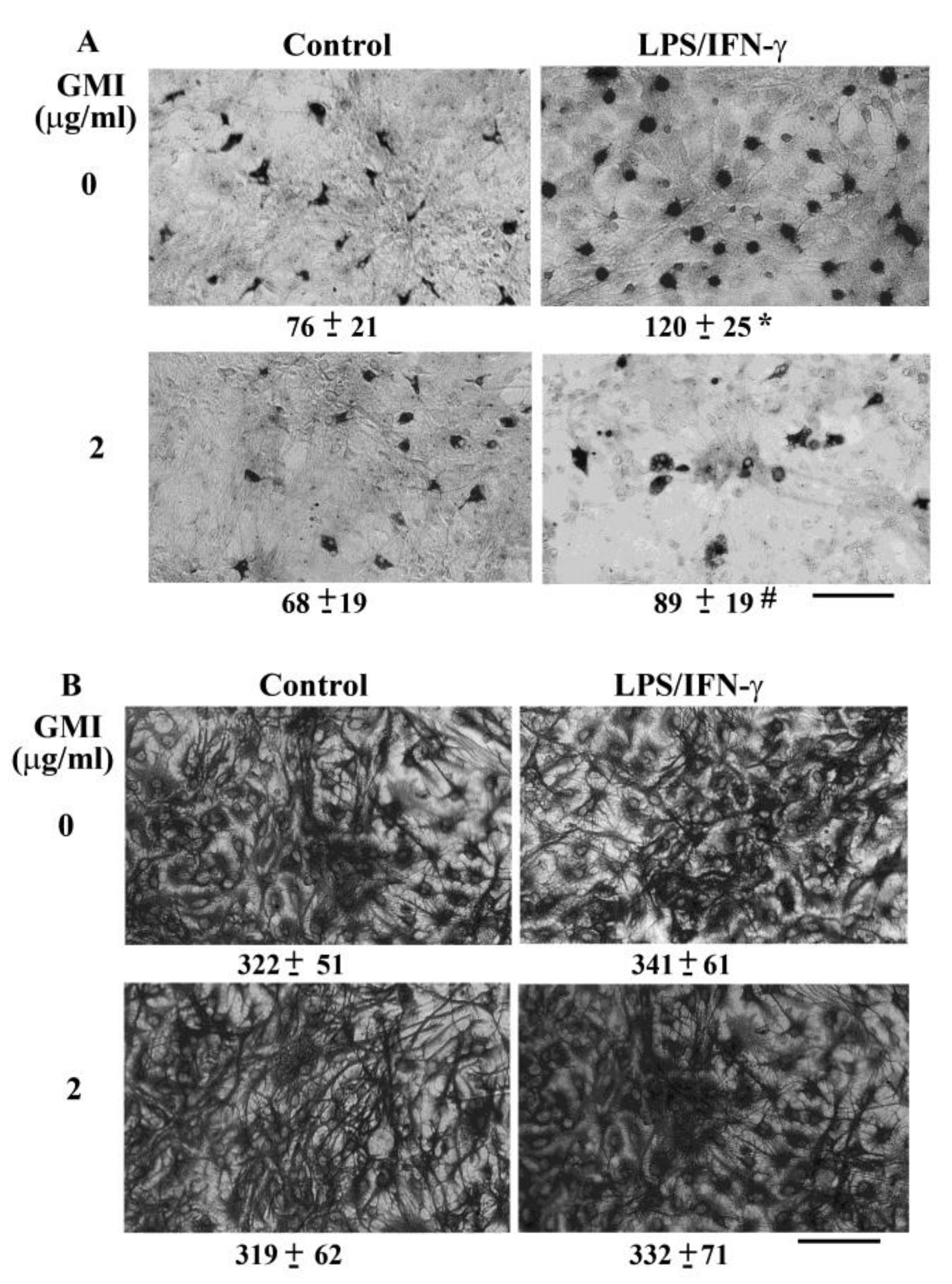
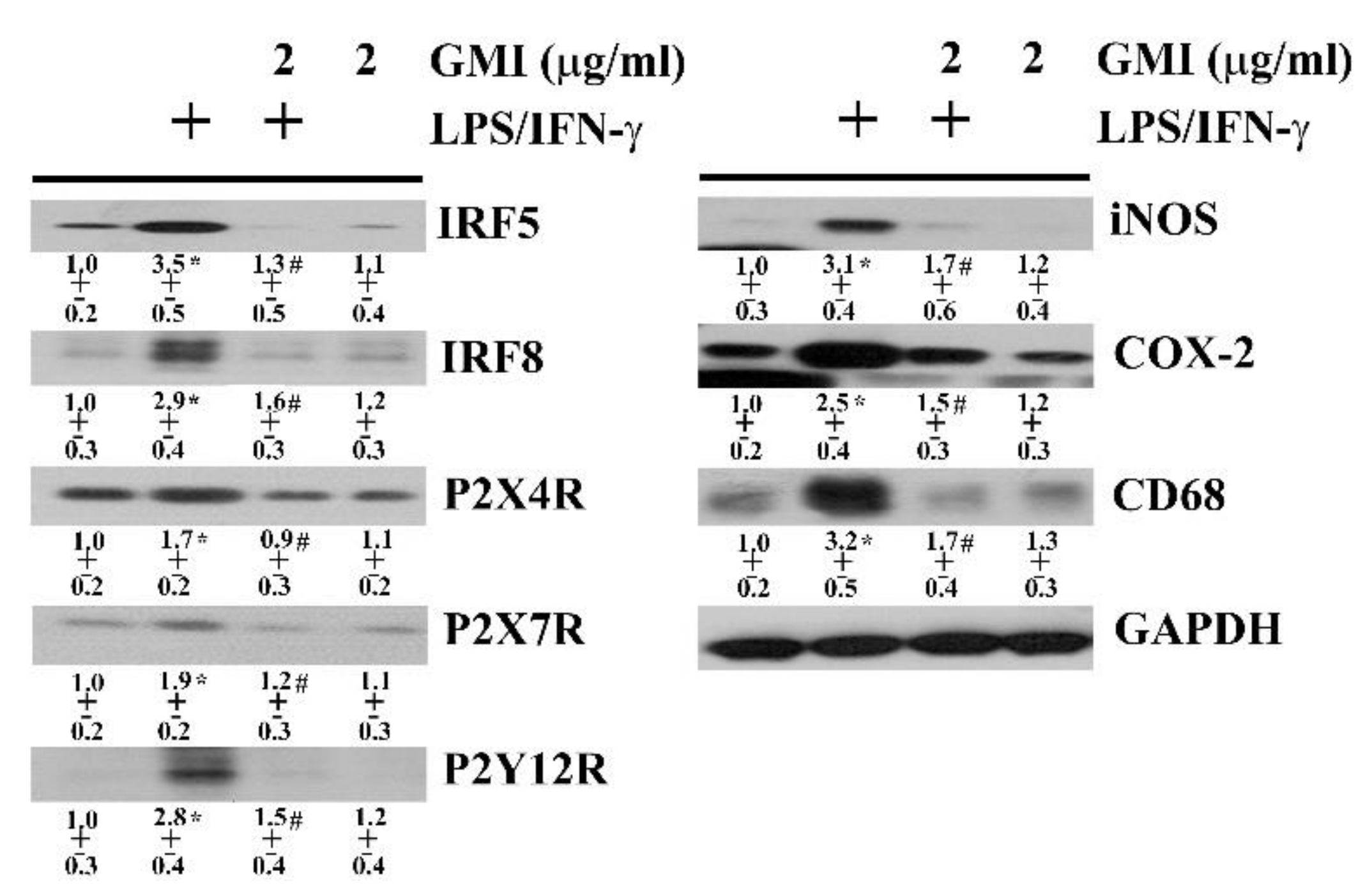
2.3. GMI Alleviated Microglial Activation
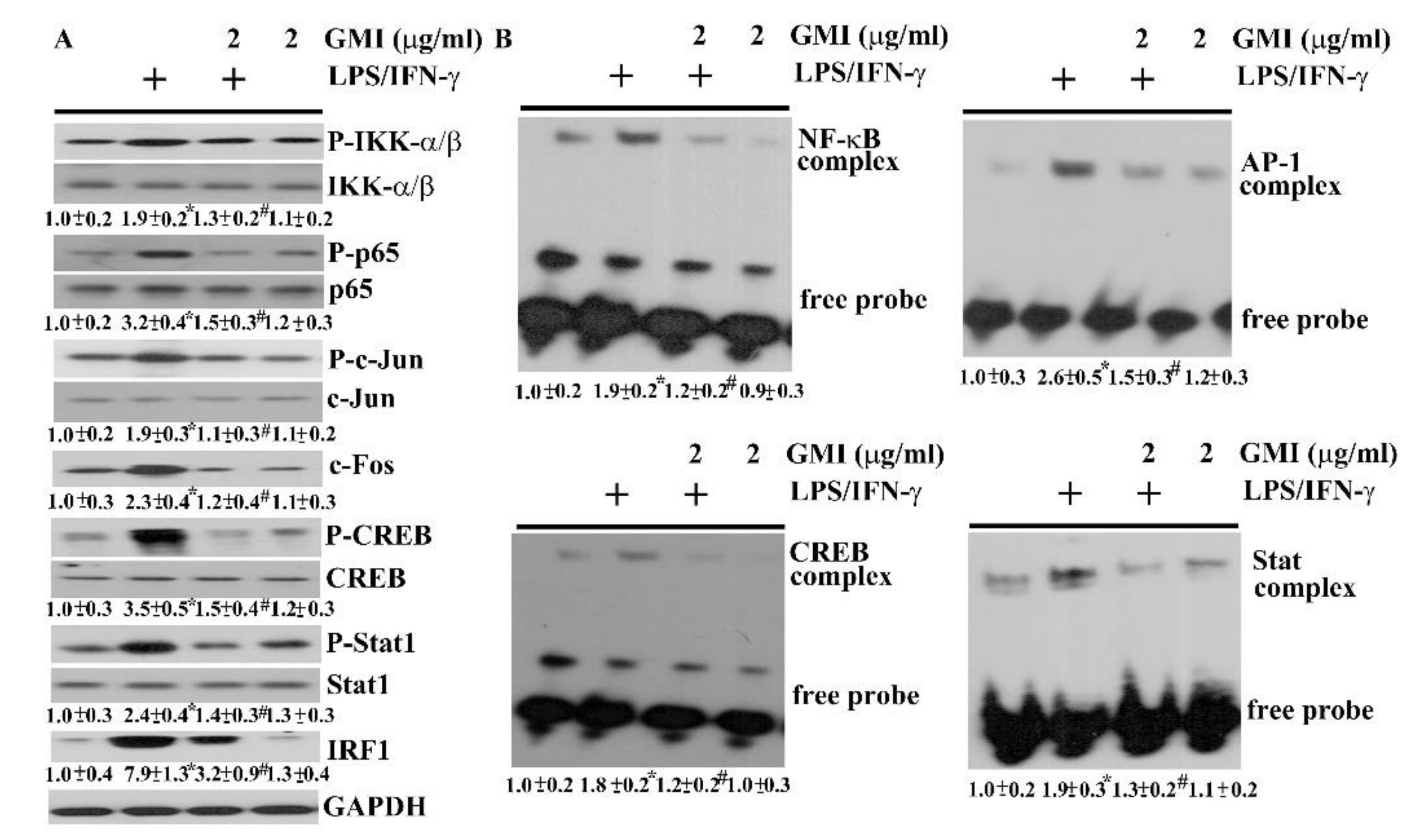
2.4. GMI Alleviated Inflammatory Transcription Factors
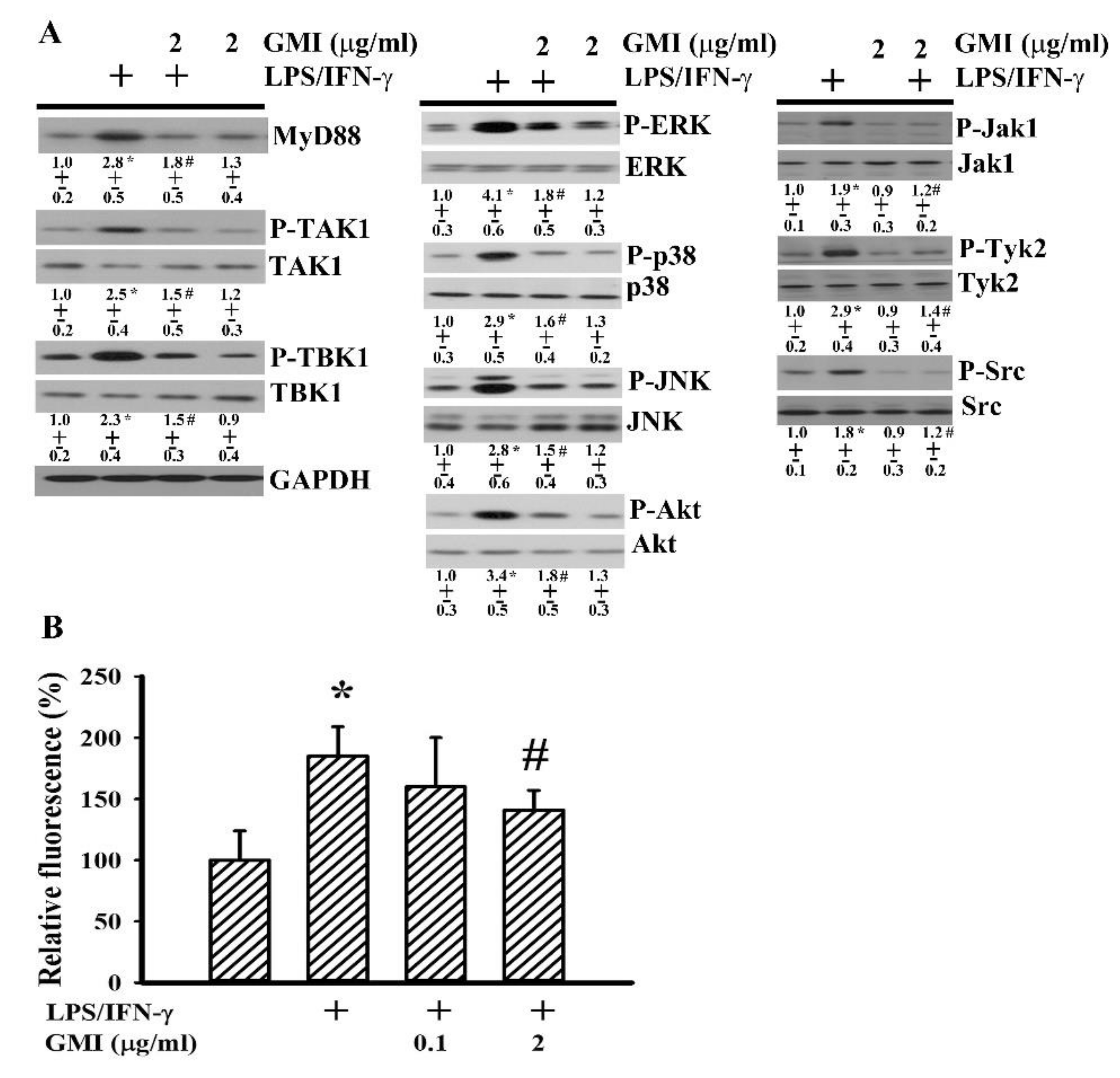
2.5. GMI Alleviated Inflammatory Intracellular Signaling
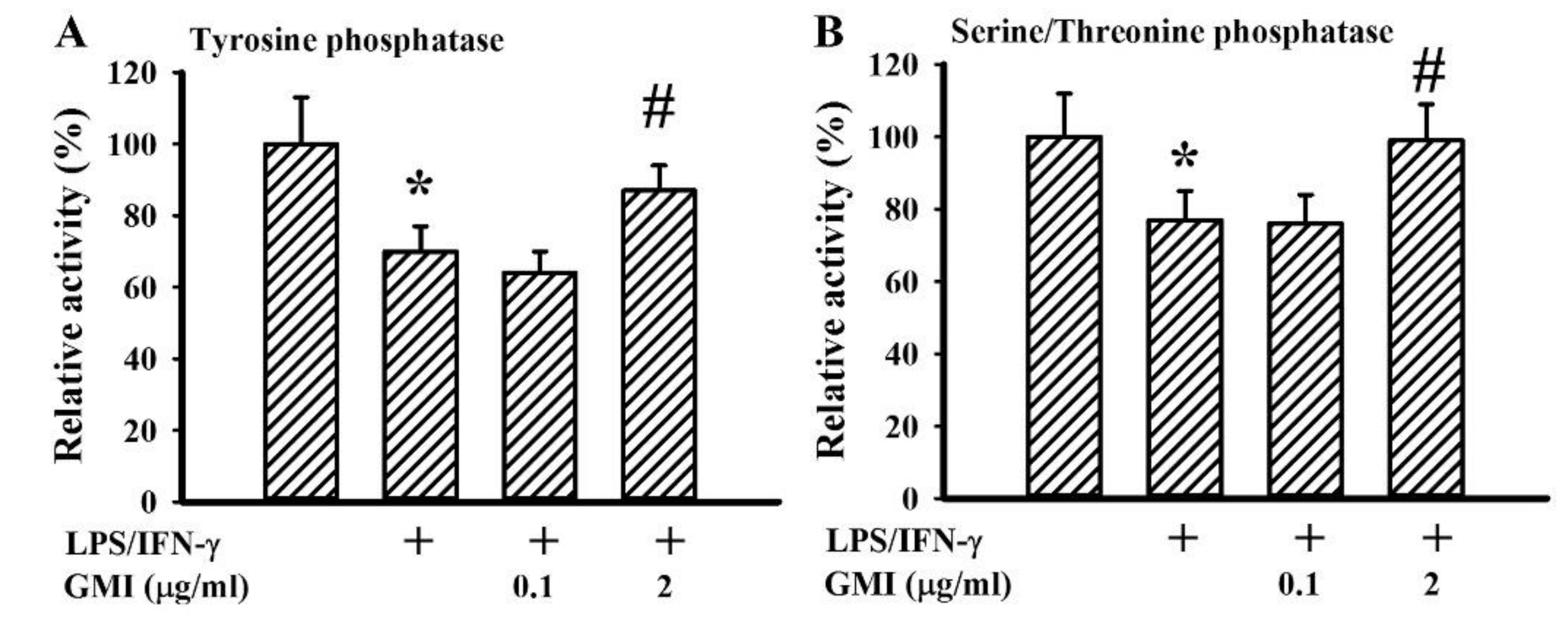
2.6. GMI Alleviated Protein Phosphatase Inactivation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Cultures
4.2. GMI Proteins
4.3. Cytotoxicity Assessment
4.4. Immunocytochemical Staining
4.5. Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.6. Nitric Oxide (NO) Determination
4.7. Free Radical Determination
4.8. Western Blot Analysis
4.9. Preparation of Nuclear Extracts and Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay (EMSA)
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CREB | Cyclic AMP Response Element-Binding Protein |
| COX-2 | Cyclooxygenase 2 |
| DCFDA | 2′, 7′-Dichlorodihydrofluorescein Diacetate |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium |
| EMSA | Electrophoretic Mobility Shift Assay |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay |
| ERK | Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase |
| FIP | Fungal Immunomodulatory Proteins |
| GAPDH | Glyceraldehyde 3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase |
| iNOS | Inducible Nitric Oxide Synthase |
| IFN-γ | Interferon-γ |
| IRF1 | Interferon Regulatory Factor 1 |
| JNK | Janus Kinase 1 |
| Jak1 | c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1β |
| LDH | Lactate Dehydrogenase |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| MAP-2 | Microtubule-Associated Protein 2 |
| NO | Nitric Oxide |
| PBS | Phosphate-Buffered Saline |
| PGE2 | Prostaglandin E2 |
| P2X4R | P2X Purinoceptor 4 |
| Stat1 | Signal Transducers and Activators of Transcription |
| TBK | TANK-Binding Kinase |
| TAK1 | Transforming Growth Factor β-Activated Kinase-1 |
| TNF-α | Tumor Necrosis Factor-α |
References
- Chang, C.Y.; Kuan, Y.H.; Li, J.R.; Chen, W.Y.; Ou, Y.C.; Pan, H.C.; Liao, S.L.; Raung, S.L.; Chang, C.J.; Chen, C.J. Docosahexaenoic acid reduces cellular inflammatory response following permanent focal cerebral ischemia in rats. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2013, 24, 2127–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, B.; Peplow, P.V. Neuroprotection by immunomodulatory agents in animal models of Parkinson’s disease. Neural Regen. Res. 2018, 13, 1493–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Lv, Y.G.; Du, Y.F.; Hu, M.; Reed, M.N.; Long, Y.; Suppiramaniam, V.; Hong, H.; Tang, S.S. Inhibitory effect of INT-777 on lipopolysaccharide-induced cognitive impairment, neuroinflammation, apoptosis, and synaptic dysfunction in mice. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2018, 88, 360–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, C.; Zhang, Q.; Jiang, Q.; Zhang, T.; Chen, M.; Fan, Y.; Ding, J.; Lu, M.; Hu, G. Inhibition of the hepatic Nlrp3 protects dopaminergic neurons via attenuating systemic inflammation in a MPTP/p mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. J. Neuroinflammation 2018, 15, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, Z.; Gan, Y.; Liu, Q.; Yin, J.X.; Liu, Q.; Shi, J.; Shi, F.D. CX3CR1 deficiency suppresses activation and neurotoxicity of microglia/macrophage in experimental ischemic stroke. J. Neuroinflammation 2014, 11, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kao, T.K.; Ou, Y.C.; Raung, S.L.; Lai, C.Y.; Liao, S.L.; Chen, C.J. Inhibition of nitric oxide production by quercetin in endotoxin/cytokine-stimulated microglia. Life Sci. 2010, 86, 315–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kao, T.K.; Ou, Y.C.; Lin, S.Y.; Pan, H.C.; Song, P.J.; Raung, S.L.; Lai, C.Y.; Liao, S.L.; Lu, H.C.; Chen, C.J. Luteolin inhibits cytokine expression in endotoxin/cytokine-stimulated microglia. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2011, 22, 612–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Q.; Li, Y.; Pei, G. Polysaccharides from Ganoderma lucidum attenuate microglia-mediated neuroinflammation and modulate microglial phagocytosis and behavioral response. J. Neuroinflammation 2017, 14, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, B.; Wang, S.; Bi, S.; Qin, W.; Wu, D.; Luo, Z.; Gui, S.; Wang, D.; Yin, X.; Wang, F. Effects of ganoderic acid A on lipopolysaccharide-induced proinflammatory cytokine release from primary mouse microglia cultures. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 15, 847–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, H.M.; Jang, K.J.; Han, M.S.; Jeong, J.W.; Kim, G.Y.; Lee, J.H.; Choi, Y.H. Ganoderma lucidum ethanol extract inhibits the inflammatory response by suppressing the NF-κB and toll-like receptor pathways in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated BV2 microglial cells. Exp. Ther. Med. 2013, 5, 957–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, R.; Xu, S.; Cai, Y.; Zhou, M.; Zuo, X.; Chan, P. Ganoderma lucidum protects dopaminergic neuron degeneration through inhibition of microglial activation. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2011, 2011, 156810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.Y.; Tang, Y.P.; Xiang, J.; Wua, P.; Jin, H.M.; Wang, Z.; Mori, M.; Cai, D.F. Neuroprotective effects of water-soluble Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides on cerebral ischemic injury in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 131, 154–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boh, B. Ganoderma lucidum: A potential for biotechnological production of anti-cancer and immunomodulatory drugs. Recent Pat. Anticancer Drug Discov. 2013, 8, 255–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeurink, P.V.; Noguera, C.L.; Savelkoul, H.F.; Wichers, H.J. Immunomodulatory capacity of fungal proteins on the cytokine production of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2008, 8, 1124–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.C.; Chow, Y.H.; Sun, H.L.; Liu, Y.F.; Lee, Y.T.; Lue, K.H.; Ko, J.L. Alleviation of respiratory syncytial virus replication and inflammation by fungal immunomodulatory protein FIP-fve from Flammulina velutipes. Antiviral Res. 2014, 110, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.C.; Hsiao, Y.M.; Hung, S.C.; Chen, Y.W.; Ou, C.C.; Chang, W.T.; Lue, K.H.; Ko, J.L. Alleviation of Dermatophagoides microceras-induced allergy by an immunomodulatory protein, FIP-fve, from Flammulina velutipes in mice. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2015, 79, 88–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, P.Y.; Sun, H.L.; Ko, J.L.; Ku, M.S.; Lin, L.J.; Lee, Y.T.; Liao, P.F.; Pan, H.H.; Lu, H.L.; Lue, K.H. Oral fungal immunomodulatory protein-Flammulina velutipes has influence on pulmonary inflammatory process and potential treatment for allergic airway disease: A mouse model. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2017, 50, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, K.Y.; Hsu, C.I.; Lin, J.Y.; Tsai, C.C.; Lin, R.H. Oral administration of an edible-mushroom-derived protein inhibits the development of food-allergic reactions in mice. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2003, 33, 1595–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.T.; Lee, S.S.; Sun, H.L.; Lu, K.H.; Ku, M.S.; Sheu, J.N.; Ko, J.L.; Lue, K.H. Effect of the fungal immunomodulatory protein FIP-fve on airway inflammation and cytokine production in mouse asthma model. Cytokine 2013, 61, 237–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.T.; Wu, C.T.; Sun, H.L.; Ko, J.L.; Lue, K.H. Fungal immunomodulatory protein-fve could modulate airway remodel through by affect IL17 cytokine. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2018, 51, 598–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.H.; Hsiao, Y.M.; Ou, C.C.; Lin, Y.W.; Chiu, Y.L.; Lue, K.H.; Chang, J.G.; Ko, J.L. GMI, a Ganoderma immunomodulatory protein, down-regulates tumor necrosis factor α-induced expression of matrix metalloproteinase 9 via NF-κB pathway in human alveolar epithelial A549 cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 12014–12021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.H.; Kao, M.C.; Lai, Y.L.; Tsai, J.J. Efficacy of local nasal immunotherapy for Dp2-induced airway inflammation in mice: Using Dp2 peptide and fungal immunomodulatory peptide. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 112, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsin, I.L.; Hsu, J.C.; Wu, W.J.; Lu, H.J.; Wu, M.F.; Ko, J.L. GMI, a fungal immunomodulatory protein from Ganoderma microsporum, induce apoptosis via β-catenin suppression in lung cancer cells. Environ. Toxicol. 2018, 33, 955–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raung, S.L.; Chen, S.Y.; Liao, S.L.; Chen, J.H.; Chen, C.J. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors attenuate Japanese encephalitis virus-induced neurotoxicity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 327, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.J.; Raung, S.L.; Liao, S.L.; Chen, S.Y. Inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase expression by baicalein in endotoxin/cytokine-stimulated microglia. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2004, 67, 957–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.J.; Ou, Y.C.; Lin, S.Y.; Raung, S.L.; Liao, S.L.; Lai, C.Y.; Chen, S.Y.; Chen, J.H. Glial activation involvement in neuronal death by Japanese encephalitis virus infection. J. Gen. Virol. 2010, 91, 1028–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.J.; Ou, Y.C.; Chang, C.Y.; Pan, H.C.; Lin, S.Y.; Liao, S.L.; Raung, S.L.; Chen, S.Y.; Chang, C.J. Src signaling involvement in Japanese encephalitis virus-induced cytokine production in microglia. Neurochem. Int. 2011, 58, 924–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Mamun, A.; Chauhan, A.; Yu, H.; Xu, Y.; Sharmeen, R.; Liu, F. Interferon regulatory factor 4/5 signaling impacts on microglial activation after ischemic stroke in mice. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2018, 47, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masuda, T.; Iwamoto, S.; Yoshinaga, R.; Tozaki-Saitoh, H.; Nishiyama, A.; Mak, T.W.; Tamura, T.; Tsuda, M.; Inoue, K. Transcription factor IRF5 drives P2X4R+-reactive microglia gating neuropathic pain. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Monif, M.; Reid, C.A.; Powell, K.L.; Drummond, K.J.; O’Brien, T.J.; Williams, D.A. Interleukin-1β has trophic effects in microglia and its release is mediated by P2X7R pore. J. Neuroinflammation 2016, 13, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.Y.; Li, J.R.; Ou, Y.C.; Lin, S.Y.; Wang, Y.Y.; Chen, W.Y.; Hu, Y.H.; Lai, C.Y.; Chang, C.J.; Chen, C.J. Interplay of inflammatory gene expression in pericytes following Japanese encephalitis virus infection. Brain Behav. Immun. 2017, 66, 230–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, C.Y.; Ou, Y.C.; Chang, C.Y.; Pan, H.C.; Chang, C.J.; Liao, S.L.; Su, H.L.; Chen, C.J. Endothelial Japanese encephalitis virus infection enhances migration and adhesion of leukocytes to brain microvascular endothelia via MEK-dependent expression of ICAM1 and the CINC and RANTES chemokines. J. Neurochem. 2012, 123, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.J.; Ou, Y.C.; Chang, C.Y.; Pan, H.C.; Liao, S.L.; Chen, S.Y.; Raung, S.L.; Lai, C.Y. Glutamate released by Japanese encephalitis virus-infected microglia involves TNF-α signaling and contributes to neuronal death. Glia 2012, 60, 487–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bok, E.; Chung, Y.C.; Kim, K.S.; Baik, H.H.; Shin, W.H.; Jin, B.K. Modulation of M1/M2 polarization by capsaicin contributes to the survival of dopaminergic neurons in the lipopolysaccharide-lesioned substantia nigra in vivo. Exp. Mol. Med. 2018, 50, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ślusarczyk, J.; Trojan, E.; Głombik, K.; Piotrowska, A.; Budziszewska, B.; Kubera, M.; Popiołek-Barczyk, K.; Lasoń, W.; Mika, J.; Basta-Kaim, A. Targeting the NLRP3 Inflammasome-related pathways via tianeptine treatment-suppressed microglia polarization to the M1 phenotype in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated cultures. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ou, C.C.; Hsiao, Y.M.; Wang, W.H.; Ko, J.L.; Lin, M.Y. Stability of fungal immunomodulatory protein, FIP-gts and FIP-fve, in IFN-γ production. Food Agric. Immunol. 2009, 20, 319–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, W.-Y.; Chang, C.-Y.; Li, J.-R.; Wang, J.-D.; Wu, C.-C.; Kuan, Y.-H.; Liao, S.-L.; Wang, W.-Y.; Chen, C.-J. Anti-inflammatory and Neuroprotective Effects of Fungal Immunomodulatory Protein Involving Microglial Inhibition. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3678. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113678
Chen W-Y, Chang C-Y, Li J-R, Wang J-D, Wu C-C, Kuan Y-H, Liao S-L, Wang W-Y, Chen C-J. Anti-inflammatory and Neuroprotective Effects of Fungal Immunomodulatory Protein Involving Microglial Inhibition. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(11):3678. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113678
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Wen-Ying, Cheng-Yi Chang, Jian-Ri Li, Jiaan-Der Wang, Chih-Cheng Wu, Yu-Hsiang Kuan, Su-Lan Liao, Wen-Yi Wang, and Chun-Jung Chen. 2018. "Anti-inflammatory and Neuroprotective Effects of Fungal Immunomodulatory Protein Involving Microglial Inhibition" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 11: 3678. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113678
APA StyleChen, W.-Y., Chang, C.-Y., Li, J.-R., Wang, J.-D., Wu, C.-C., Kuan, Y.-H., Liao, S.-L., Wang, W.-Y., & Chen, C.-J. (2018). Anti-inflammatory and Neuroprotective Effects of Fungal Immunomodulatory Protein Involving Microglial Inhibition. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(11), 3678. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113678