Effect of Acute Stress on the Expression of BDNF, trkB, and PSA-NCAM in the Hippocampus of the Roman Rats: A Genetic Model of Vulnerability/Resistance to Stress-Induced Depression
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
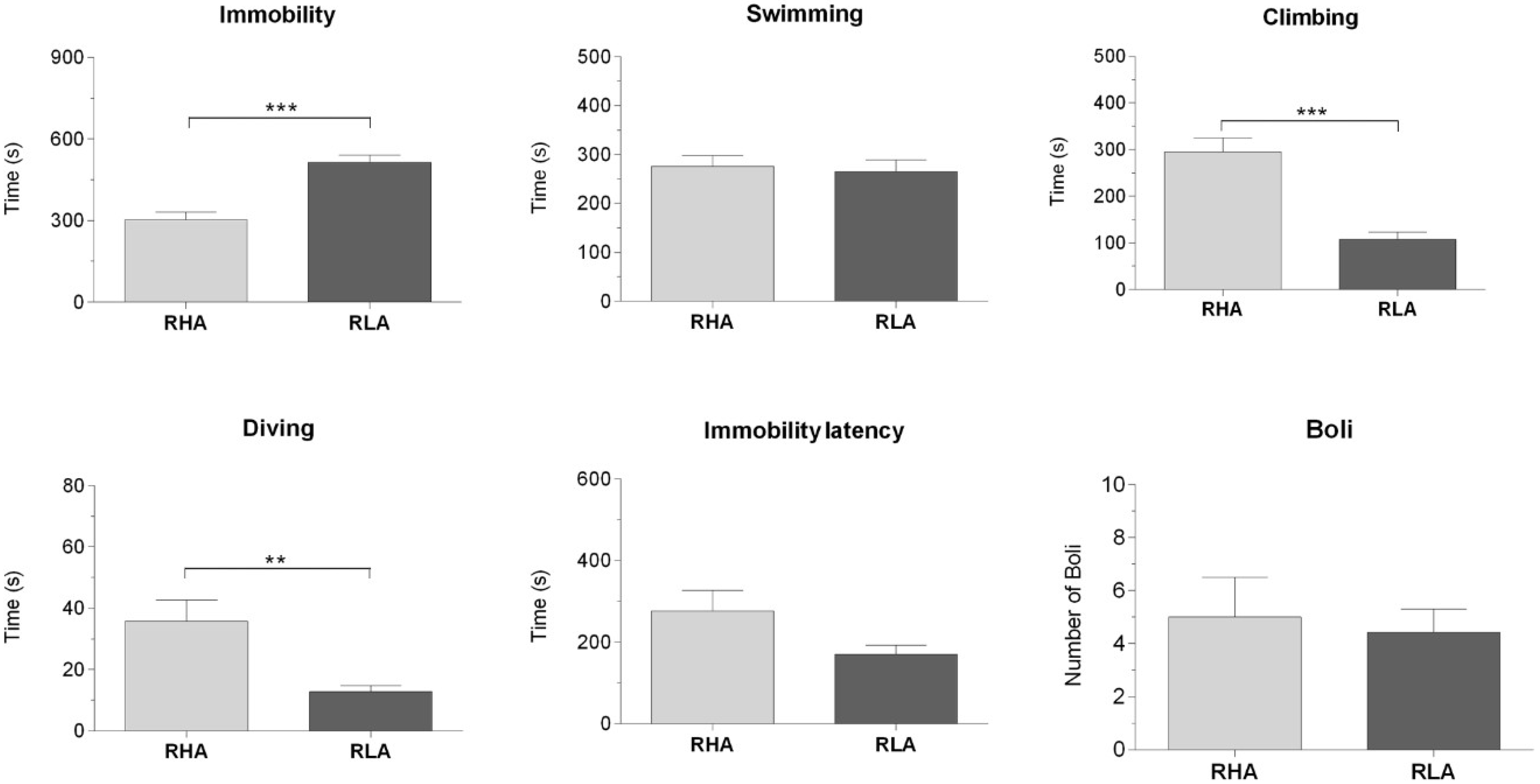
2.1. Behavioral Measurements During Forced Swimming
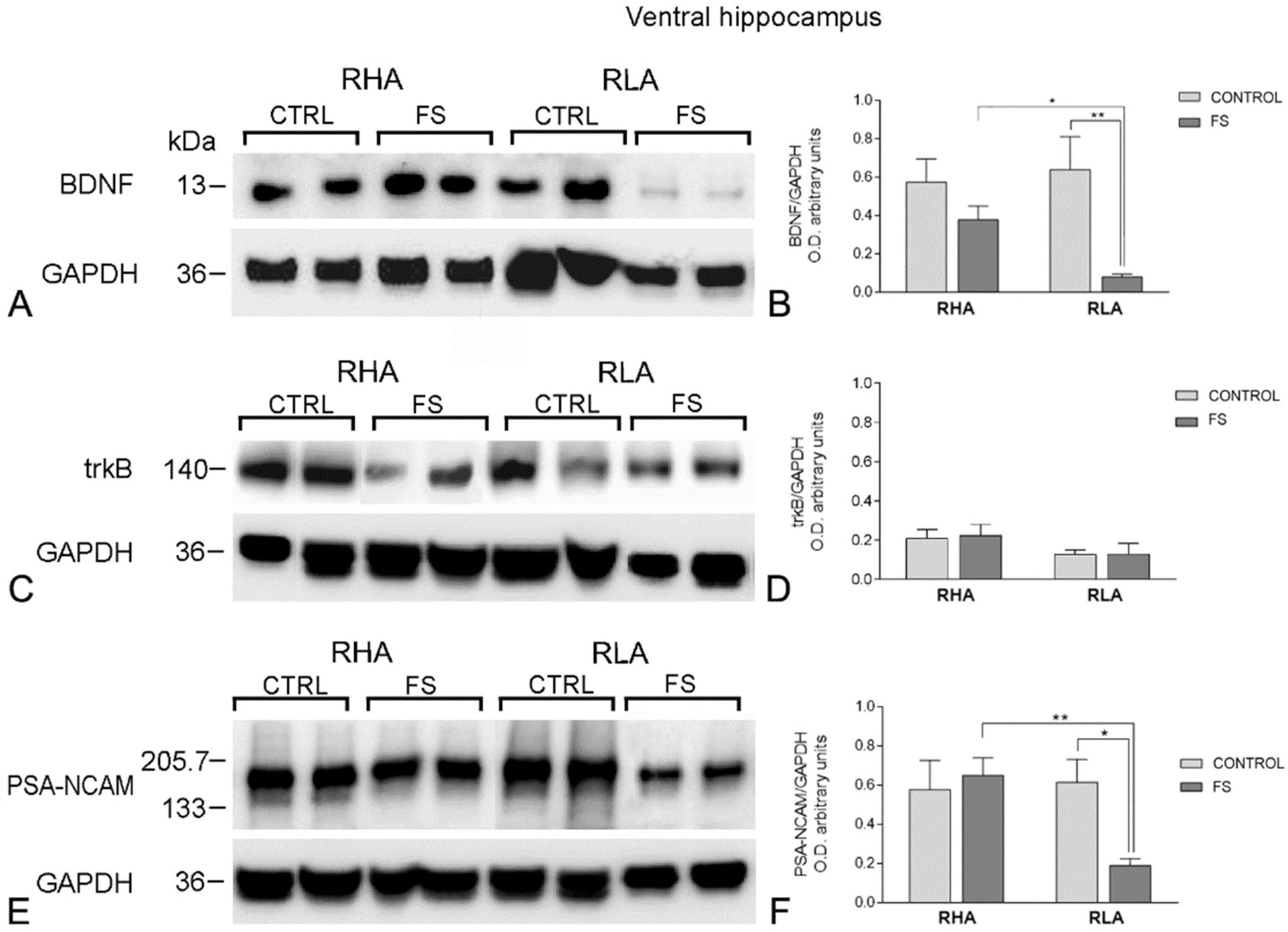
2.2. Western Blot Assays
2.2.1. The BDNF Protein Levels
2.2.2. The trkB Protein Levels
2.2.3. The PSA-NCAM Protein Levels
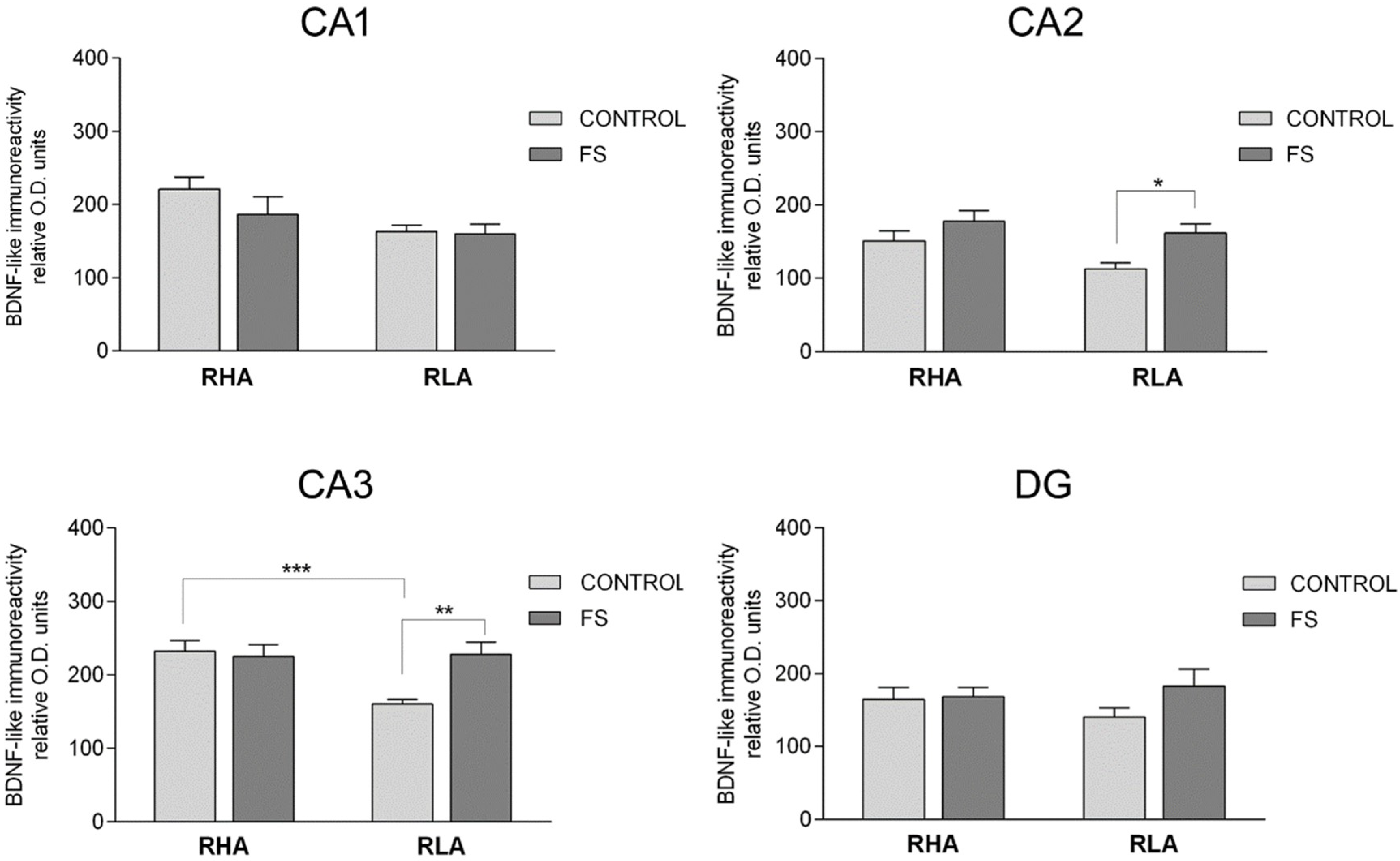
2.3. Immunohistochemistry
2.3.1. BDNF-Like Immunoreactivity
2.3.2. The trkB-Like Immunoreactivity
2.3.3. The PSA-NCAM-Like Immunoreactivity
3. Discussion
3.1. Effect of Acute Stress on the BDNF, trkB, and PSA-NCAM Protein Levels in the Dorsal and Ventral Hippocampus
3.2. Effect of Acute Stress on the Regional and Subregional Immunohistochemical Distribution of BDNF, trkB, and PSA-NCAM in the Dorsal and Ventral Hippocampus
3.3. Acute Stress-Induced Expression Changes of the BDNF, the trkB, and the PSA-NCAM in the Dentate Gyrus
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. FS and Behavioral Measurements
4.3. Sampling
4.4. Western Blot
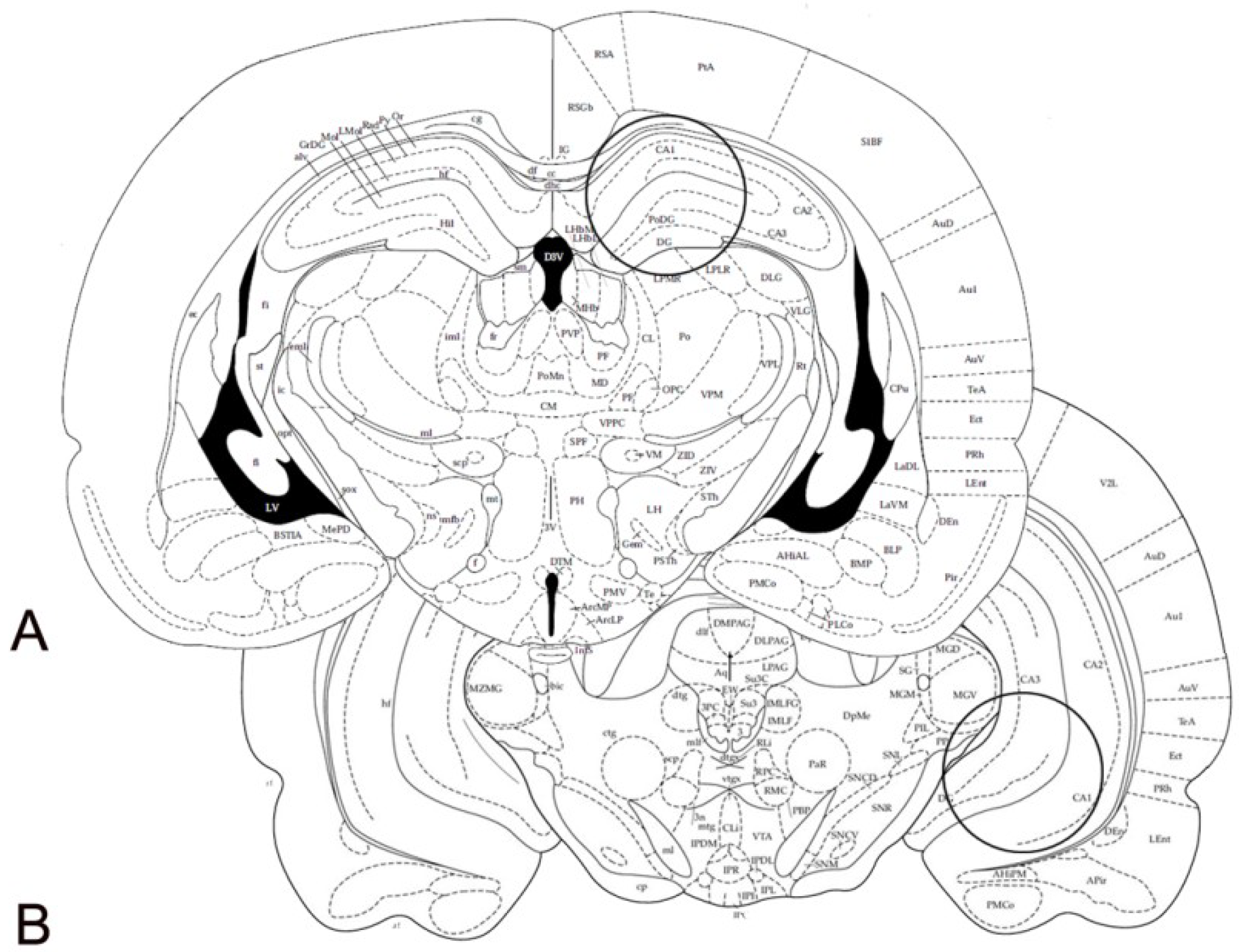
4.5. Immunohistochemistry
4.6. Image Densitometry
4.7. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ABC | Avidin–Biotin–peroxidase Complex |
| trkB | tyrosine receptor kinase B |
| GAPDH | Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase |
| O.D. | Relative optical density |
| BDNF | Brain Derived Neurotrophic Factor |
| HPA | Hypothalamus–Pituitary–Adrenal |
| DG | Dentate Gyrus |
| PBS | Phosphate Buffered Saline |
| RHA | Roman High-Avoidance |
| RLA | Roman Low Avoidance |
| SDS-PAGE | Sodium dodecyl sulphate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
| TBS-T | Tris base, Sodium chloride, Tween 2 |
| VTA | Ventral Tegmental Area |
| WB | Western Blot |
| FS | Forced Swimming |
| dHC | dorsal Hippocampus |
| vHC | ventral Hippocampus |
| PFA | Paraformaldehyde |
References
- Aan het Rot, M.; Mathew, S.J.; Charney, D.S. Neurobiological mechanisms in major depressive disorder. CMAJ 2009, 180, 305–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anisman, H.; Matheson, K. Stress, depression, and anhedonia: Caveats concerning animal models. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2005, 29, 525–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoge, C.W.; Clark, J.C.; Castro, C.A. Commentary: Women in combat and the risk of post-traumatic stress disorder and depression. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2007, 36, 327–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steimer, T.; Driscoll, P. Divergent stress responses and coping styles in psychogenetically selected Roman high-(RHA) and low-(RLA) avoidance rats: Behavioural, neuroendocrine and developmental aspects. Stress 2003, 6, 87–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Úbeda-Contreras, J.; Marín-Blasco, I.; Nadal, R.; Armario, A. Brain c-fos expression patterns induced by emotional stressors differing in nature and intensity. Brain Struct. Funct. 2018, 223, 2213–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caspi, A.; Moffitt, T.E. Gene-environment interactions in psychiatry: Joining forces with neuroscience. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2006, 7, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charney, D.S.; Manji, H.K. Life stress, genes, and depression: Multiple pathways lead to increased risk and new opportunities for intervention. Sci. STKE 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broadhurst, P.L.; Bignami, G. Correlative effects of psychogenetic selection: A study of the Roman high and low avoidance strains of rats. Behav. Res. Ther. 1965, 3, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driscoll, P.; Bättig, K. Behavioral, emotional and neurochemical profiles of rats selected for extreme differences in active, two-way avoidance performance. In Genetics of the Brain; Lieblich, I., Ed.; Elsevier Biomedical Press: Amsterdam, NL, USA, 1982; pp. 95–123. ISBN 10:0444804382. [Google Scholar]
- Giorgi, O.; Piras, G.; Corda, M.G. The psychogenetically selected Roman high-and low-avoidance rat lines: A model to study the individual vulnerability to drug addiction. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2007, 31, 148–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Escorihuela, R.M.; Tobeña, A.; Driscoll, P.; Fernández-Teruel, A. Effects of training, early handling, and perinatal flumazenil on shuttle box acquisition in Roman low-avoidance rats: Toward overcoming a genetic deficit. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 1995, 19, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escorihuela, R.M.; Fernández-Teruel, A.; Gil, L.; Aguilar, R.; Tobeña, A.; Driscoll, P. Inbred Roman high-and low-avoidance rats: Differences in anxiety, novelty-seeking, and shuttlebox behaviours. Physiol. Behav. 1999, 67, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Teruel, A.; Escorihuela, R.M.; Gray, J.A.; Aguilar, R.; Gil, L.; Giménez-Llort, L.; Tobeña, A.; Bhomra, A.; Nicod, A.; Mott, R.; et al. A quantitative trait locus influencing anxiety in the laboratory rat. Genome Res. 2002, 12, 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferré, P.; Fernández-Teruel, A.; Escorihuela, R.M.; Driscoll, P.; Corda, M.G.; Giorgi, O.; Tobeña, A. Behavior of the Roman/Verh high- and low-avoidance rat lines in anxiety tests: Relationship with defecation and self-grooming. Physiol Behav 1995, 58, 1209–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco, J.; Márquez, C.; Nadal, R.; Tobeña, A.; Fernández-Teruel, A.; Armario, A. Characterization of central and peripheral components of the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal axis in the inbred Roman rat strains. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2008, 33, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentsch, C.; Lichtsteiner, M.; Feer, H. Genetic and environmental influences on reactive and spontaneous locomotor activities in rats. Experientia 1991, 47, 998–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steimer, T.; Python, A.; Schulz, P.E.; Aubry, J.M. Plasma corticosterone, dexamethasone (DEX) suppression and DEX/CRH tests in a rat model of genetic vulnerability to depression. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2007, 32, 575–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holsboer, F. Stress, hypercortisolism and corticosteroid receptors in depression: Implications for therapy. J. Affect Disord. 2001, 62, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Teruel, A.; Driscoll, P.; Gil, L.; Aguilar, R.; Tobeña, A.; Escorihuela, R.M. Enduring effects of environmental enrichment on novelty seeking, saccharin and ethanol intake in two rat lines (RHA/Verh and RLA/Verh) differing in incentive seeking behavior. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2002, 73, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgi, O.; Lecca, D.; Piras, G.; Driscoll, P.; Corda, M.G. Dissociation between mesocortical dopamine release and fear related behaviors in two psychogenetically selected lines of rats that differ in coping strategies to aversive conditions. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2003, 17, 2716–2726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno, M.; Cardona, D.; Gómez, M.J.; Sánchez-Santed, F.; Tobeña, A.; Fernández-Teruel, A.; Campa, L.; Suñol, C.; Escarabajal, M.D.; Torres, C.; et al. Impulsivity characterization in the Roman high-and low-avoidance rat strains: Behavioral and neurochemical differences. Neuropsychopharmacology 2010, 35, 1198–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, J. Augmenting and reducing of visual evoked potentials in high- and low-sensation seeking humans, cats, and rats. Behav. Genet. 1997, 27, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piras, G.; Giorgi, O.; Corda, M.G. Effects of antidepressants on the performance in the forced swim test of two psychogenetically selected lines of rats that differ in coping strategies to aversive conditions. Psychopharmacology 2010, 211, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piras, G.; Piludu, M.A.; Giorgi, O.; Corda, M.G. Effects of chronic antidepressant treatments in a putative genetic model of vulnerability (Roman low-avoidance rats) and resistance (Roman high-avoidance rats) to stress-induced depression. Psychopharmacology 2014, 231, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porsolt, R.D.; Le Pichon, M.; Jalfre, M. Depression: A new animal model sensitive to antidepressant treatments. Nature 1977, 266, 730–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Detke, M.J.; Johnson, J.; Lucki, I. Acute and chronic antidepressant drug treatment in the rat forced swimming test model of depression. Exp. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 1997, 5, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prins, J.; Olivier, B.; Korte, S.M. Triple reuptake inhibitors for treating subtypes of major depressive disorder: The monoamine hypothesis revisited. Exp. Op. Investig. Drugs 2011, 20, 1107–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anacker, C.; Zunszain, P.A.; Carvalho, L.A.; Pariante, C.M. The glucocorticoid receptor: Pivot of depression and of antidepressant treatment? Psychoneuroendocrinology 2011, 36, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, A.H. Depression and immunity: A role for T cells? Brain Behav. Immun. 2010, 24, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castrén, E. Is mood chemistry? Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2005, 6, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duman, R.S.; Malberg, J.; Thome, J. Neural plasticity to stress and antidepressant treatment. Biol. Psychiatry 1999, 46, 1181–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stahl, S.M. Blue genes and the mechanism of action of antidepressants. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2000, 61, 164–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nestler, E.J.; Gould, E.; Manji, H.; Buncan, M.; Duman, R.S.; Greshenfeld, H.K.; Hen, R.; Koester, S.; Lederhendler, I.; Meaney, M.; et al. Preclinical models: Status of basic research in depression. Biol. Psychiatry 2002, 52, 503–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barde, Y.A.; Edgar, D.; Thoenen, H. Purification of a new neurotrophic factor from mammalian brain. EMBO J. 1982, 1, 549–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibáñez, C.F. Neurotrophic factors: From structure-function studies to designing effective therapeutics. Trends Biotechnol. 1995, 13, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binder, D.K.; Scharfman, H.E. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Growth Factors 2004, 22, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichardt, L.F. Neurotrophin-regulated signalling pathways. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2006, 361, 1545–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conner, J.M.; Lauterborn, J.C.; Yan, Q.; Gall, C.M.; Varon, S. Distribution of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) protein and mRNA in the normal adult rat CNS: Evidence for anterograde axonal transport. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 2295–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Q.; Radeke, M.J.; Matheson, C.R.; Talvenheimo, J.; Welcher, A.A.; Feinstein, S.C. Immunocytochemical localization of trkB in the central nervous system of the rat. J. Comp. Neurol. 1997, 378, 135–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Rosenfeld, R.D.; Matheson, C.R.; Hawkins, N.; Lopez, O.T.; Bennett, L.; Welcher, A.A. Expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor protein in the adult rat central nervous system. Neuroscience 1997, 78, 431–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, C.T.; Milner, T.A.; Patterson, S.L. Ultrastructural localization of full-length trkB immunoreactivity in rat hippocampus suggests multiple roles in modulating activity-dependent synaptic plasticity. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 8009–8026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, H.S.; Hains, J.M.; Armanini, M.; Laramee, G.R.; Johnson, S.A.; Winslow, J.W. BDNF mRNA is decreased in the hippocampus of individuals with Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron 1991, 7, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connor, B.; Young, D.; Yan, Q.; Faull, R.L.; Synek, B.; Dragunow, M. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor is reduced in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Brain Res. 1997, 49, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benisty, S.; Boissiere, F.; Faucheux, B.; Agid, Y.; Hirsch, E.C. trkB messenger RNA expression in normal human brain and in the substantia nigra of parkinsonian patients: An in situ hybridization study. Neuroscience 1997, 86, 813–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quartu, M.; Setzu, M.D.; Del Fiacco, M. trk-like immunoreactivity in the human trigeminal ganglion and subnucleus caudalis. Neuroreport 1996, 10, 1013–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quartu, M.; Lai, M.L.; Del Fiacco, M. Neurotrophin-like immunoreactivity in the human hippocampal formation. Brain Res. Bull. 1999, 48, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quartu, M.; Serra, M.P.; Manca, A.; Follesa, P.; Ambu, R.; Del Fiacco, M. High affinity neurotrophin receptors in the human pre-term newborn, infant, and adult cerebellum. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2003, 21, 309–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quartu, M.; Serra, M.P.; Manca, A.; Follesa, P.; Lai, M.L.; Del Fiacco, M. Neurotrophin-like immunoreactivity in the human pre-term newborn, infant, and adult cerebellum. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2003, 21, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quartu, M.; Serra, M.P.; Boi, M.; Melis, T.; Ambu, R.; Del Fiacco, M. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and polysialylated-neural cell adhesion molecule (PSA-NCAM): Codistribution in the human brainstem precerebellar nuclei from prenatal to adult age. Brain Res. 2010, 1363, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webster, M.J.; Herman, M.M.; Kleinman, J.E.; Weickert, C.S. BDNF and trkB mRNA expression in the hippocampus and temporal cortex during the human lifespan. Gene Expr. Patterns 2006, 6, 941–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quartu, M.; Serra, M.P.; Boi, M.; Demontis, R.; Melis, T.; Poddighe, L.; Del Fiacco, M. Polysialylated-neural cell adhesion molecule (PSA-NCAM) in the human nervous system at prenatal, postnatal and adult ages. In Recent Advances in Adhesion Research, Series Human Anatomy and Physiology-Materials Science and Technologies; McFarland, A., Akins, M., Eds.; Nova Science Publishers: Hauppauge, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 27–54. ISBN 978-1-62417-447-6. [Google Scholar]
- Vaidya, V.A.; Siuciak, J.A.; Du, F.; Duman, R.S. Hippocampal mossy fiber sprouting induced by chronic electroconvulsive seizures. Neuroscience 1999, 89, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malberg, J.E.; Eisch, A.J.; Nestler, E.J.; Duman, R.S. Chronic antidepressant treatment increases neurogenesis in adult rat hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 9104–9110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dias, B.G.; Banerjee, S.B.; Duman, R.S.; Vaidya, V.A. Differential regulation of brain derived neurotrophic factor transcripts by antidepressant treatments in the adult rat brain. Neuropharmacology 2003, 45, 553–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nibuya, M.; Morinobu, S.; Duman, R.S. Regulation of BDNF and trkB mRNA in rat brain by chronic electroconvulsive seizure and antidepressant drug treatments. J. Neurosci. 1995, 15, 7539–7547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duman, R.S.; Heninger, G.R.; Nestler, E.J. A molecular and cellular theory of depression. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1997, 54, 597–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaidya, V.A.; Duman, R.S. Depression-emerging insights from neurobiology. Br. Med. Bull. 2001, 57, 61–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duman, R.S. Role of neurotrophic factors in the etiology and treatment of mood disorders. Neuromol. Med. 2004, 5, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nestler, E.J.; Carlezon, W.A., Jr. The mesolimbic dopamine reward circuit in depression. Biol. Psychiatry 2006, 59, 1151–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burke, T.F.; Advani, T.; Adachi, M.; Monteggia, L.M.; Hensler, J.G. Sensitivity of hippocampal 5-HT1A receptors to mild stress in BDNF-deficient mice. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2013, 16, 631–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duman, R.S.; Voleti, B. Signaling pathways underlying the pathophysiology and treatment of depression: Novel mechanisms for rapid-acting agents. Trends Neurosci. 2012, 35, 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Autry, A.E.; Monteggia, L.M. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neuropsychiatric disorders. Pharmacol. Rev. 2012, 64, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castrén, E.; Rantamaki, T. The role of BDNF and its receptors in depression and antidepressant drug action: Reactivation of developmental plasticity. Dev. Neurobiol. 2010, 70, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shirayama, Y.; Chen, A.C.; Nakagawa, S.; Russell, D.S.; Duman, R.S. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor produces antidepressant effects in behavioral models of depression. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 223251–223261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisch, A.J.; Bolaños, C.A.; de Wit, J.; Simonak, R.D.; Pudiak, C.M.; Barrot, M.; Verhaagen, J.; Nestler, E.J. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the ventral midbrain-nucleus accumbens pathway: A role in depression. Biol. Psychiatry 2003, 54, 994–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McEwen, B.S.; Morrison, J.H. The brain on stress: Vulnerability and plasticity of the prefrontal cortex over the life course. Neuron 2013, 79, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonfanti, L. PSA-NCAM in mammalian structural plasticity and neurogenesis. Prog. Neurobiol. 2006, 80, 129–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merino, J.J.; Cordero, M.I.; Sandi, C. Regulation of hippocampal cell adhesion molecules NCAM and L1 by contextual fear conditioning is dependent upon time and stressor intensity. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2000, 12, 3283–3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bessa, J.M.; Ferreira, D.; Melo, I.; Marques, F.; Cerqueira, J.J.; Palha, J.A.; Almeida, O.F.; Sousa, N. The mood-improving actions of antidepressants do not depend on neurogenesis but are associated with neuronal remodeling. Mol. Psychiatry 2009, 14, 764–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wainwright, S.R.; Galea, L.A. The neural plasticity theory of depression: Assessing the roles of adult neurogenesis and PSA-NCAM within the hippocampus. Neural. Plast. 2013, 2013, 805497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanti, A.; Belzung, C. Neurogenesis along the septo-temporal axis of the hippocampus: Are depression and the action of antidepressants region-specific? Neuroscience 2013, 252, 234–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maras, P.M.; Molet, J.; Chen, Y.; Rice, C.; Ji, S.G.; Solodkin, A.; Baram, T.Z. Preferential loss of dorsal-hippocampus synapses underlies memory impairments provoked by short, multimodal stress. Mol. Psychiatry 2014, 19, 811–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Floriou-Servou, A.; von Ziegler, L.; Stalder, L.; Sturman, O.; Privitera, M.; Rassi, A.; Cremonesi, A.; Thöny, B.; Bohacek, J. Distinct Proteomic, Transcriptomic, and Epigenetic Stress Responses in Dorsal and Ventral Hippocampus. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 84, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serra, M.P.; Poddighe, L.; Boi, M.; Sanna, F.; Piludu, M.A.; Corda, M.G.; Giorgi, O.; Quartu, M. Expression of BDNF and trkB in the hippocampus of a rat genetic model of vulnerability (Roman low-avoidance) and resistance (Roman high-avoidance) to stress-induced depression. Brain Behav. 2017, 7, e00861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenthal, A.; Goeddel, D.V.; Nguyen, T.; Martin, E.; Burton, L.E.; Shih, A.; Laramee, G.R.; Wurm, F.; Mason, A.; Nikolics, K.; et al. Primary structure and biological activity of human brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Endocrinology 1991, 129, 1289–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, R.; Parada, L.F.; Coulier, F.; Barbacid, M. trkB, a novel tyrosine protein kinase receptor expressed during mouse neural development. EMBO J. 1989, 8, 3701–3709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubois, C.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Pastoret, C.; Rampini, C.; Karpati, G.; Rougon, G. Expression of NCAM and its polysialylated isoforms during mdx mouse muscle regeneration and in vitro myogenesis. Neuromuscul. Disord. 1994, 4, 171–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quartu, M.; Serra, M.P.; Boi, M.; Ibba, V.; Melis, T.; Del Fiacco, M. Polysialylated-neural cell adhesion molecule (PSA-NCAM) in the human trigeminal ganglion and brainstem at prenatal and adult ages. BMC Neurosci. 2008, 9, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seki, T.; Arai, Y. Distribution and possible roles of the highly polysialylated neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM-H) in the developing and adult central nervous system. Neurosci. Res. 1993, 17, 265–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, T.; Rutishauser, U. Removal of polysialic acid-neural cell adhesion molecule induces aberrant mossy fiber innervation and ectopic synaptogenesis in the hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 3757–3766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maggio, N.; Segal, M. Striking variations in corticosteroid modulation of long-term potentiation along the septotemporal axis of the hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 5757–5765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grigoryan, G.; Ardi, Z.; Albrecht, A.; Richter-Levin, G.; Segal, M. Juvenile stress alters LTP in ventral hippocampal slices: Involvement of noradrenergic mechanisms. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 278, 559–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, S.; Imbe, H.; Morikawa, Y.; Kubo, C.; Senba, E. Chronic stress, as well as acute stress, reduces BDNF mRNA expression in the rat hippocampus but less robustly. Neurosci. Res. 2005, 53, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, A.; Vadodaria, K.C.; Banerjee, S.B.; Benekareddy, M.; Dias, B.G.; Duman, R.S.; Vaidya, V.A. Stressor-specific regulation of distinct brain-derived neurotrophic factor transcripts and cyclic AMP response element-binding protein expression in the postnatal and adult rat hippocampus. Neuropsychopharmacology 2007, 32, 1504–1519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pittenger, C.; Duman, R.S. Stress, depression, and neuroplasticity: A convergence of mechanisms. Neuropsychopharmacology 2008, 33, 88–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozisek, M.E.; Middlemas, D.; Bylund, D.B. The differential regulation of BDNF and TrkB levels in juvenile rats after four days of escitalopram and desipramine treatment. Neuropharmacology 2008, 54, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molteni, R.; Calabrese, F.; Cattaneo, A.; Mancini, M.; Gennarelli, M.; Racagni, G.; Riva, M.A. Acute stress responsiveness of the neurotrophin BDNF in the rat hippocampus is modulated by chronic treatment with the antidepressant duloxetine. Neuropsychopharmacology 2009, 34, 1523–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, S.; Shao, S.; Yuan, B.; Pan, F.; Li, Z. Acute Stress and Chronic Stress Change Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) and Tyrosine Kinase-Coupled Receptor (TrkB) Expression in Both Young and Aged Rat Hippocampus. Yonsei Med. J. 2010, 51, 661–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uysal, N.; Sisman, A.R.; Dayi, A.; Ozbal, S.; Cetin, F.; Baykara, B.; Aksu, I.; Tas, A.; Cavus, S.A.; Gonenc-Arda, S.; Buyuk, E. Acute footshock-stress increases spatial learning-memory and correlates to increased hippocampal BDNF and VEGF and cell numbers in adolescent male and female rats. Neurosci. Lett. 2012, 514, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marmigère, F.; Givalois, L.; Rage, F.; Arancibia, S.; Tapia-Arancibia, L. Rapid induction of BDNF expression in the hippocampus during immobilization stress challenge in adult rats. Hippocampus 2003, 13, 646–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, D.; Djebbara-Hannas, Z.; Jourdain, P.; Vutskits, L.; Durbec, P.; Rougon, G.; Kiss, J.Z.; Durbec, P.; Rougon, G.; Kiss, J.Z. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor restores long-term potentiation in polysialic acid-neural cell adhesion molecule-deficient hippocampus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 4315–4320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durbec, P.; Cremer, H. Revisiting the function of PSA-NCAM in the nervous system. Mol. Neurobiol. 2001, 24, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isgor, C.; Pare, C.; McDole, B.; Coombs, P.; Guthrie, K. Expansion of the dentate mossy fiber-CA3 projection in the brain-derived neurotrophic factor-enriched mouse hippocampus. Neuroscience 2015, 288, 10–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakshminarasimhan, H.; Chattarji, S. Stress Leads to Contrasting Effects on the Levels of Brain Derived Neurotrophic Factor in the Hippocampus and Amygdala. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Righi, M.; Tongiorgi, E.; Cattaneo, A. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) Induces Dendritic Targeting of BDNF and Tyrosine KinaseB mRNAs in Hippocampal Neurons through a Phosphatidylinositol-3 Kinase-Dependent Pathway. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 3165–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baj, G.; D’Alessandro, V.; Musazzi, L.; Mallei, A.; Sartori, C.R.; Sciancalepore, M.; Tardito, D.; Langone, F.; Popoli, M.; Tongiorgi, E. Physical exercise and antidepressants enhance BDNF targeting in hippocampal CA3 dendrites: Further evidence of a spatial code for BDNF splice variants. Neuropsychopharmacology 2012, 37, 1600–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baj, G.; Pinhero, V.; Vaghi, V.; Tongiorgi, E. Signaling pathways controlling activity-dependent local translation of BDNF and their localization in dendritic arbors. J. Cell. Sci. 2016, 129, 2852–2864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altar, C.A.; Cai, N.; Bliven, T.; Juhasz, M.; Conner, J.M.; Acheson, A.L.; Lindsay, R.M.; Wiegand, S.J. Anterograde transport of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and its role in the brain. Nature 1997, 389, 856–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altar, C.A.; DiStefano, P.S. Neurotrophin trafficking by anterograde transport. Trends Neurosci. 1998, 21, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieni, S.; Matsumoto, T.; Dekkers, M.; Rauskolb, S.; Ionescu, M.S.; Deogracias, R.; Gundelfinger, E.D.; Kojima, M.; Nestel, S.; Frotscher, M.; et al. BDNF and its pro-peptide are stored in presynaptic dense core vesicles in brain neurons. J. Cell. Biol. 2012, 196, 775–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conboy, L.; Tanrikut, C.; Zoladz, P.R.; Campbell, A.M.; Park, C.R.; Gabriel, C.; Mocaer, E.; Sandi, C.; Diamond, D.M. The antidepressant agomelatine blocks the adverse effects of stress on memory and enables spatial learning to rapidly increase neural cell adhesion molecule (NCAM) expression in the hippocampus of rats. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2009, 12, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duman, R.S.; Monteggia, L.M. A neurotrophic model for stress-related mood disorders. Biol. Psychiatry 2006, 59, 1116–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaral, D.G.; Scharfman, H.E.; Lavenex, P. The dentate gyrus: Fundamental neuroanatomical organization (dentate gyrus for dummies). Prog. Brain Res. 2007, 163, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempermann, G.; Song, H.; Gage, F.H. Neurogenesis in the adult hippocampus. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2015, 7, a018812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scharfman, H.E. The enigmatic mossy cell of the dentate gyrus. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2016, 17, 562–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Römer, B.; Krebs, J.; Overall, R.W.; Fabel, K.; Babu, H.; Overstreet-Wadiche, L.; Brandt, M.D.; Williams, R.W.; Jessberger, S.; Kempermann, G. Adult hippocampal neurogenesis and plasticity in the infrapyramidal bundle of the mossy fiber projection: I. Co-regulation by activity. Front. Neurosci. 2011, 5, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krebs, J.; Römer, B.; Overall, R.W.; Fabel, K.; Babu, H.; Brandt, M.D.; Williams, R.W.; Jessberger, S.; Kempermann, G. Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis and Plasticity in the Infrapyramidal Bundle of the Mossy Fiber Projection: II. Genetic Covariation and Identification of Nos1 as Linking Candidate Gene. Front. Neurosci. 2011, 5, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adachi, M.; Barrot, M.; Autry, A.E.; Theobald, D.; Monteggia, L.M. Selective loss of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the dentate gyrus attenuates antidepressant efficacy. Biol. Psychiatry 2008, 63, 642–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, R.G.; McCarthy, K.J.; Milne, T.A.; Pfaff, D.W.; McEwen, B.S. Regulation of hippocampal H3 histone methylation by acute and chronic stress. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 20912–20917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, R.G.; Murakami, G.; Dewell, S.; Seligsohn, M.; Baker, M.E.R.; Datson, N.A.; Pfaff, D.W.; McEwen, B.S. Stress induced hippocampal transposon silencing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 17657–17662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ninan, P.T.; Shelton, R.C.; Bao, W.; Guico-Pabia, C.J. BDNF, interleukin-6, and salivary cortisol levels in depressed patients treated with desvenlafaxine. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 48, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hing, B.; Sathyaputri, L.; Potash, J.B. A comprehensive review of genetic and epigenetic mechanisms that regulate BDNF expression and function with relevance to major depressive disorder. Am. J. Med. Genet. B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2018, 177, 143–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morello, N.; Plicato, O.; Piludu, M.A.; Poddighe, L.; Serra, M.P.; Quartu, M.; Corda, M.G.; Giorgi, O.; Giustetto, M. Effects of forced swimming stress on ERK and histone H3 phosphorylation in limbic areas of Roman high- and low-avoidance rats. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0170093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandramohan, Y.; Droste, S.K.; Arthur, J.S.; Reul, J.M. The forced swimming-induced behavioural immobility response involves histone H3 phospho-acetylation and c-Fos induction in dentate gyrus granule neurons via activation of the N-methyl-D-aspartate/extracellular signal-regulated kinase/mitogen- and stress-activated kinase signalling pathway. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2008, 27, 2701–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bilang-Bleuel, A.; Ulbricht, S.; Chandramohan, Y.; De Carli, S.; Droste, S.K.; Reul, J.M. Psychological stress increases histone H3 phosphorylation in adult dentate gyrus granule neurons: Involvement in a glucocorticoid receptor-dependent behavioural response. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2005, 22, 1691–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saunderson, E.A.; Spiers, H.; Mifsud, K.R.; Gutierrez-Mecinas, M.; Trollope, A.F.; Shaikh, A.; Mill, J.; Reul, J.M.H.M. Stress-induced gene expression and behavior are controlled by DNA methylation and methyl donor availability in the dentate gyrus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 4830–4835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giorgi, O.; Piras, G.; Lecca, D.; Corda, M.G. Differential activation of dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens core and shell after acute or repeated amphetamine injections: A comparative study in the Roman high-and low-avoidance rat lines. Neuroscience 2005, 135, 987–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crabbe, J.C.; Wahlsten, D.; Dudek, B.C. Genetics of mouse behavior: Interactions with laboratory environment. Science 1999, 284, 1670–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driscoll, P.; Fernández-Teruel, A.; Corda, M.G.; Giorgi, O.; Steimer, T. Some guidelines for defining personality differences in rats. In Handbook of Behavior Genetic; Kim, Y.-K., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2009; pp. 281–300. [Google Scholar]
- Escorihuela, R.M.; Tobeña, A.; Fernández-Teruel, A. Environmental enrichment and postnatal handling prevent spatial learning deficits in aged hypoemotional (Roman high-avoidance) and hyperemotional (Roman low-avoidance) rats. Learn. Memory 1995, 2, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paxinos, G.; Watson, C. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 4th ed.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1998; p. 237. ISBN 10: 0125476191. [Google Scholar]
- Palkovits, M. Punch sampling biopsy technique. Methods Enzymol. 1983, 103, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lowry, O.H.; Rosebrough, N.J.; Farr, A.L.; Randall, R.J. Protein measurements with the Folin phenol reagent. J. Biol. Chem. 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sanna, F.; Poddighe, L.; Serra, M.P.; Boi, M.; Bratzu, J.; Sanna, F.; Corda, M.G.; Giorgi, O.; Melis, M.R.; Argiolas, A.; et al. c-Fos, ΔFosB, BDNF, trkB and Arc expression in the limbic system of male Roman High and Low Avoidance rats that show differences in sexual behaviour: Effect of sexual activity. Neuroscience 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kendler, K.S.; Karkowski, L.M.; Prescott, C.A. Causal relationship between stressful life events and the onset of major depression. Am. J. Psychiatry 1999, 156, 837–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitale, G.; Ruggieri, V.; Filaferro, M.; Frigeri, C.; Alboni, S.; Tascedda, F.; Brunello, N.; Guerrini, R.; Cifani, C.; Massi, M. Chronic treatment with the selective NOP receptor antagonist [Nphe 1, Arg 14, Lys 15]N/OFQ-NH 2 (UFP-101) reverses the behavioural and biochemical effects of unpredictable chronic mild stress in rats. Psychopharmacology 2009, 207, 173–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, G.Y.; Tam, W.W.; Lu, Y.; Ho, C.S.; Zhang, M.W.; Ho, R.C. Prevalence of Depression in the Community from 30 Countries between 1994 and 2014. Sci. Rep. 2018, 12, 2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Brain Area | Marker | Line | FS | Line × FS | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | p | F | p | F | p | d.f. | ||
| Dorsal Hippocampus | BDNF | 0.03923 | n.s. | 1.428 | n.s. | 8.524 | 0.0068 | 1.28 |
| trkB | 0.3064 | n.s. | 3.393 | n.s. | 6.086 | 0.002 | 1.28 | |
| PSA-NCAM | 24.55 | <0.0001 | 3.505 | n.s. | 10.23 | 0.003 | 1.28 | |
| Ventral Hippocampus | BDNF | 2.481 | n.s. | 14.41 | 0.0007 | 3.869 | n.s. | 1.28 |
| trkB | 3.514 | n.s. | 0.032 | n.s. | 0.018 | n.s. | 1.28 | |
| PSA-NCAM | 4.815 | 0.0367 | 3.010 | n.s. | 7.334 | 0.0114 | 1.28 | |
| Brain Area | Marker | Line | FS | Line × FS | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| F | p | F | p | F | p | d.f. | ||
| Dorsal Hippocampus | ||||||||
| CA1 | BDNF | 3.784 | n.s. | 2.088 | n.s. | 1.126 | n.s. | 1.44 |
| trkB | 1.703 | n.s. | 0.002 | n.s. | 2.289 | n.s. | 1.44 | |
| PSA-NCAM | 4.391 | 0.0419 | 2.9 | n.s. | 0.4548 | n.s. | 1.44 | |
| CA2 | BDNF | 4.643 | 0.0367 | 8.959 | 0.0045 | 0.738 | n.s. | 1.44 |
| trkB | 0.269 | n.s. | 1.759 | n.s. | 1.248 | n.s. | 1.44 | |
| PSA-NCAM | 2.214 | n.s. | 13.17 | 0.0007 | 0.01217 | n.s. | 1.44 | |
| CA3 | BDNF | 7.824 | 0.0076 | 5.807 | 0.0202 | 9.001 | 0.0044 | 1.44 |
| trkB | 0.067 | n.s. | 1.304 | n.s. | 1.025 | n.s. | 1.44 | |
| PSA-NCAM | 23.09 | 0.0001 | 6.969 | 0.0114 | 1.230 | n.s. | 1.44 | |
| DG | BDNF | 0.080 | n.s. | 1.837 | n.s. | 1.290 | n.s. | 1.44 |
| trkB | 34.75 | <0.0001 | 39.80 | <0.0001 | 15.99 | 0.0002 | 1.44 | |
| PSA-NCAM | 13.83 | 0.0006 | 1.471 | n.s. | 0.1820 | n.s. | 1.44 | |
| Ventral Hippocampus | ||||||||
| CA1 | BDNF | 0.089 | n.s. | 47.34 | <0.0001 | 0.562 | n.s. | 1.44 |
| trkB | 0.0048 | n.s. | 27.47 | <0.0001 | 0.0027 | n.s. | 1.44 | |
| PSA-NCAM | 2.473 | n.s. | 9.359 | 0.0038 | 0.7689 | n.s. | 1.44 | |
| CA3 | BDNF | 2.955 | n.s. | 39.99 | <0.0001 | 3.274 | n.s. | 1.44 |
| trkB | 0.3182 | n.s. | 4.087 | 0.0493 | 0.3437 | n.s. | 1.44 | |
| PSA-NCAM | 6.608 | 0.0136 | 17.32 | 0.0001 | 0.3567 | n.s. | 1.44 | |
| DG | BDNF | 1.984 | n.s. | 40.85 | <0.0001 | 4.728 | 0.0351 | 1.44 |
| trkB | 0.3049 | n.s. | 64.58 | <0.0001 | 0.04395 | n.s. | 1.44 | |
| PSA-NCAM | 1.198 | n.s. | 24.36 | <0.0001 | 1.753 | n.s. | 1.44 | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Serra, M.P.; Poddighe, L.; Boi, M.; Sanna, F.; Piludu, M.A.; Sanna, F.; Corda, M.G.; Giorgi, O.; Quartu, M. Effect of Acute Stress on the Expression of BDNF, trkB, and PSA-NCAM in the Hippocampus of the Roman Rats: A Genetic Model of Vulnerability/Resistance to Stress-Induced Depression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3745. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123745
Serra MP, Poddighe L, Boi M, Sanna F, Piludu MA, Sanna F, Corda MG, Giorgi O, Quartu M. Effect of Acute Stress on the Expression of BDNF, trkB, and PSA-NCAM in the Hippocampus of the Roman Rats: A Genetic Model of Vulnerability/Resistance to Stress-Induced Depression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(12):3745. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123745
Chicago/Turabian StyleSerra, Maria Pina, Laura Poddighe, Marianna Boi, Francesco Sanna, Maria Antonietta Piludu, Fabrizio Sanna, Maria G. Corda, Osvaldo Giorgi, and Marina Quartu. 2018. "Effect of Acute Stress on the Expression of BDNF, trkB, and PSA-NCAM in the Hippocampus of the Roman Rats: A Genetic Model of Vulnerability/Resistance to Stress-Induced Depression" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 12: 3745. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123745
APA StyleSerra, M. P., Poddighe, L., Boi, M., Sanna, F., Piludu, M. A., Sanna, F., Corda, M. G., Giorgi, O., & Quartu, M. (2018). Effect of Acute Stress on the Expression of BDNF, trkB, and PSA-NCAM in the Hippocampus of the Roman Rats: A Genetic Model of Vulnerability/Resistance to Stress-Induced Depression. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(12), 3745. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123745







