Liposomes with an Ethanol Fraction as an Application for Drug Delivery
Abstract
:1. Introduction
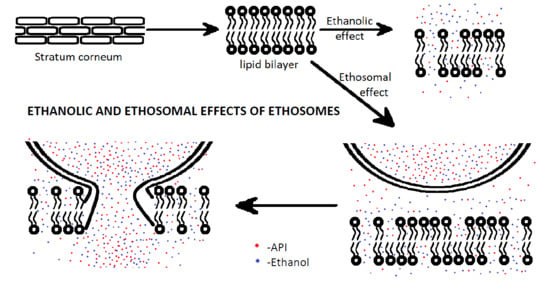
2. Mechanism of Action
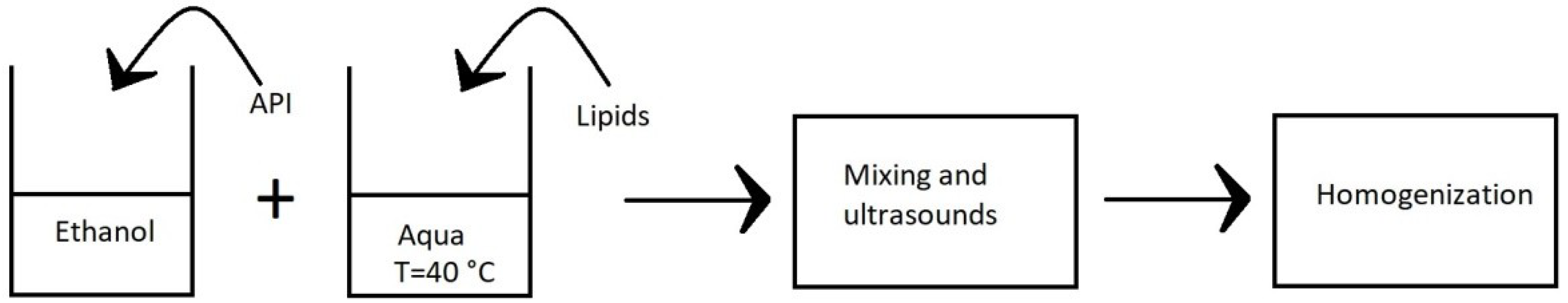
3. Methods of Preparation
4. Types of Drugs Encapsulated in Ethosomes
5. Anti-Viral Drugs
6. Antifungal Drugs
7. The Effects of Drugs on Cellular Metabolism
8. Antioxidants and Flavonoids
9. Antineoplastic Drugs and Immunomodulatory Drugs
10. Antibacterial Drugs
11. Methods of Testing
12. Stability
13. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Akbarzadeh, A.; Rezaei-Sadabady, R.; Davaran, S.; Woo Joo, S.; Zarghami, N.; Hanifehpour, Y.; Samiei, M.; Kouhi, M.; Nejati-Koshki, K. Liposome: Classification, preparation, and applications. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandel, A.; Patil, V.; Goyal, R.; Dhamija, H.; Parashar, B. Ethosomes: A Novel Approach towards Transdermal Drug Delivery. Int. J. Pharm. Chem. Sci. 2012, 1, 563–569. [Google Scholar]
- Touitou, E. Compositions for Applying Active Substances to or through the Skin. U.S. Patent US5540934A, 30 July 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Francisco, S.; Us, C.A. Therapeutic Liposome Composition and Method of Preparation. U.S. Patent US11479437, 17 October 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Kurek, K.; Piotrowska, D.M.; Wiesiołek, P.; Chabowski, A.; Zendzian-Piotrowska, M. Rola sfingolipidów w układzie pokarmowym. Postepy Hig. Med. Dosw. 2012, 66, 868–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finkelstein, J.; Heemels, M.T.; Shadan, S.; Weiss, U. Lipids in health and disease. Nature 2014, 510, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaefer, E.J.; Bongard, V.; Beiser, A.S.; Lamon-Fava, S.; Robins, S.J.; Au, R.; Tucker, K.L.; Kyle, D.J.; Wilson, P.W.F.; Wolf, P.A. Plasma phosphatidylcholine docosahexaenoic acid content and risk of dementia and alzheimer disease: The framingham heart study. Arch. Neurol. 2016, 63, 1545–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirjavainen, M.; Mönkkönen, J.; Saukkosaari, M.; Valjakka-Koskela, R.; Kiesvaara, J.; Urtti, A. Phospholipids affect stratum corneum lipid bilayer fluidity and drug partitioning into the bilayers. J. Control. Release 1999, 58, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, V.J.W.; Yardley, H.J. Phospholipids in Cultured Guinea Pig Skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1970, 54, 174–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozzuto, G.; Molinari, A. Liposomes as nanomedical devices. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 975–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, A.C.; Barry, B.W. Penetration enhancers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2004, 56, 603–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flynn, T.C.; Petros, J.; Clark, R.E.; Viehman, G.E. Dry skin and moisturizers. Clin. Dermatol. 2001, 19, 387–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandran, S.C. Ethosomes: A Novel Approach for Topical and Transdermal Delivery of Anti Fungal Drugs. Ph.D. Thesis, Kannur University, Kerala, India, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Harpin, V.; Rutter, N. Percutaneous alcohol absorption and skin necrosis in a preterm infant. Arch. Dis. Child. 1982, 1, 477–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachenmeier, D.W. Safety evaluation of topical applications of ethanol on the skin and inside the oral cavity. J. Occup. Med. Toxicol. 2008, 3, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirsch, T.; Koerber, A.; Jacobsen, F.; Dissemond, J.; Steinau, H.U.; Gatermann, S.; Al-Benna, S.; Kesting, M.; Seipp, H.M.; Steinstraesser, L. Evaluation of Toxic Side Effects of Clinically Used Skin Antiseptics In Vitro. J. Surg. Res. 2010, 164, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, H.; Patel, J.; Joshi, K.; Patel, P.; Upadhyay, U.M. Ethosomes: A Novel Drug Carrier. Int. J. Compr. Pharm. 2011, 2, 15–18. [Google Scholar]
- Barry, B.W. Reflections on transdermal drug delivery. Pharm. Sci. Technol. Today 1999, 2, 41–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkin, P.; Paula, J. Physical Chemistry; W. H. Freeman and Company: New York, NY, USA, 2006; pp. 28–37. [Google Scholar]
- Aoki, K. Simulation for memory effect of Fick’s first law. J. Chem. Sci. 2009, 121, 601–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touitou, E.; Dayan, N.; Bergelson, L.; Godin, B.; Eliaz, M. Ethosomes—Novel vesicular carriers for enhanced delivery: Characterization and skin penetration properties. J. Control. Release 2000, 65, 403–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mbah, C.; Uzor, P.; Omeje, E. Perspectives on Transdermal Drug Delivery. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2011, 3, 680–700. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, R.; Patil, S.; Patil, S.; Patil, S. Ethosome: A Versatile Tool for Novel Drug Delivery System. J. Curr. Pharm. Res. 2014, 4, 1172–1180. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J. Preparation of curcumin ethosomes. Afr. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2013, 7, 2246–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhalaria, M.K.; Naik, S.; Misra, A.N. Ethosomes: A novel delivery system for antifungal drugs in the treatment of topical fungal diseases. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2009, 47, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manosroi, A.; Jantrawut, P.; Khositsuntiwong, N.; Manosroi, W.; Manosroi, J. Novel elastic nanovesicles for cosmeceutical and pharmaceutical applications. Chiang Mai J. Sci. 2009, 36, 168–178. [Google Scholar]
- Kulkarni, R.D.H. In-vitro permeation of verapamil hydrochloride from polymeric membrane systems across rat and human cadaver skin. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2002, 6, 593–597. [Google Scholar]
- Satyam, G.; Shivani, S.; Garima, G. Ethosomes: A novel tool for drug delivery through the skin. J. Pharm. Res. 2010, 3, 688–691. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, D.K.; Balekar, N.; Dhote, V.; Mishra, P.K. Carrier-Mediated Dermal Delivery. Applications in the Prevention and Treatment of Skin Disorders; Pan Stanford Publishing Pte. Ltd.: Singapore, 2016; pp. 357–378. [Google Scholar]
- Bharat, P.; Paresh, M.; Sharma, R.K.; Tekade, B.W.; Thakre, V.M.; Patil, V.R. A review: Novel advances in semisolid dosage forms & patented technology in semisolid dosage forms. Int. J. PharmTech Res. 2011, 3, 420–430. [Google Scholar]
- Godin, B.; Touitou, E. Erythromycin ethosomal systems: Physicochemical characterization and enhanced antibacterial activity. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2005, 2, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paolino, D.; Lucania, G.; Mardente, D.; Alhaique, F.; Fresta, M. Ethosomes for skin delivery of ammonium glycyrrhizinate: In vitro percutaneous permeation through human skin and in vivo anti-inflammatory activity on human volunteers. J. Contr. Release 2005, 106, 99–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caddeo, C.; Sales, O.D.; Valenti, D.; Saurí, A.R.; Fadda, A.M.; Manconi, M. Pharmaceutical nanotechnology Inhibition of skin inflammation in mice by diclofenac in vesicular carriers: Liposomes, ethosomes and PEVs. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 443, 128–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Wei, Y.H.; Zhang, G.Q.; Wu, X.A. Synergistic penetration of ethosomes and lipophilic prodrug on the transdermal delivery of acyclovir. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2010, 33, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, S.; Umamaheshwari, R.; Bhadra, D.; Jain, N. Ethosomes: A novel vesicular carrier for enhanced transdermal delivery of an antihiv agent. Indian J. Pharm. Sci. 2004, 66, 72–81. [Google Scholar]
- Jain, S.; Tiwary, A.K.; Sapra, B.; Jain, N.K. Formulation and Evaluation of Ethosomes for Transdermal Delivery of Lamivudine. AAPS PharmSciTech 2007, 8, E1–E9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maheshwari, R.G.S.; Tekade, R.K.; Sharma, P.A.; Darwhekar, G.; Tyagi, A.; Patel, R.P.; Jain, D.K. Ethosomes and ultradeformable liposomes for transdermal delivery of clotrimazole: A comparative assessment. Saudi Pharm. J. 2012, 20, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, N.; Goindi, S. Dermatopharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic evaluation of ethosomes of griseofulvin designed for dermal delivery. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2013, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.P.; Wei, Y.H.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.Q.; Wu, X.A. Ethosomes, binary ethosomes and transfersomes of terbinafine hydrochloride: A comparative study. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2012, 35, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devi, M.; Kumar, M.S.; Mahadevan, N. Amphotericin-B Loaded Vesicular Systems for the Treatment of Topical Fungal Infection. Int. J. Rec. Adv. Pharm. Res. 2011, 4, 37–46. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmud, M.; Piwoni, A.; Filiczak, N.; Janicka, M.; Gubernator, J. Long-Circulating Curcumin-Loaded Liposome Formulations with High Incorporation Efficiency, Stability and Anticancer Activity towards Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma Cell Lines In Vitro. PLoS ONE 2016, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, K.S.; Preeti, K.S.; Manabendra, D.; Zaki, A.M. Tamoxifen Citrate Loaded Ethosomes for Transdermal Drug Delivery System: Preparation and Characterization. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2013, 10, 466–476. [Google Scholar]
- Chiu, C.W.; Chang, C.H.; Yang, Y.M. Ethanol effects on the gelation behavior of α-tocopherol acetate-encapsulated ethosomes with water-soluble polymers. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2013, 291, 1341–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.N.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, H.S.; Park, M.A.; Gu, H.A. Enhanced transdermal deposition and characterization of quercetin-loaded ethosomes. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2013, 30, 688–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.N.; Lee, H.J.; Gu, H.A. Enhanced skin delivery and characterization of rutin-loaded ethosomes. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2014, 31, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, D.; Mounika, A.; Bakshi, V.; Haque, M.A.; Sahoo, C.K. Ethosomes: A Novel Approach For Transdermal Drug Delivery. Int. J. ChemTech Res. 2018, 11, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, V.; Mishra, D.; Jain, N.K. Melatonin loaded ethanolic liposomes: Physicochemical characterization and enhanced transdermal delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2007, 67, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, Y.; Zheng, F.; Zhang, X.; Gao, J.; Liang, W. In vitro percutaneous permeation and skin accumulation of finasteride using vesicular ethosomal carriers. AAPS PharmSciTech 2008, 9, 860–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korade, S.; Deshmukh, M.T.; Shete, R.V. Formulation and Evaluation of Ethosomal Gel Containing Clobetasol. J. Eur. Pharm. Med. Res. 2016, 3, 664–672. [Google Scholar]
- Lakshmi, P. Statistically optimised ethosomes for transdermal delivery of tolterodine tartrate. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 26, 1117–1122. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, D.; Mishra, P.K.; Dubey, V.; Nahar, M.; Dabadghao, S.; Jain, N.K. Systemic and mucosal immune response induced by transcutaneous immunization using Hepatitis B surface antigen-loaded modified liposomes. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 33, 424–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godin, B.; Touitou, E. Ethosomes: New Prospects in Transdermal Delivery. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carrier Syst. 2003, 20, 63–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, H.-Y.; Wang, R.-H.; Pan, W.-S.; Liu, X.-F.; Yang, W.-X.; Liu, H.-M.; Zhao, H.-G.; Wu, L.-H. Content and entrapment efficiency determination of minoxidil ethosomes. J. Harbin Med. Univ. 2010, 3, 224–226. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.-G.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, Z.-B. Preparation of triptolide ethosomes. Afr. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2012, 6, 1341–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glujoy, M.; Salerno, C.; Bregni, C.; Carlucci, A.M. Percutaneous drug delivery systems for improving antifungal therapy effectiveness: A review. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 6, 8–16. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, L.-P.; Mao, W.; An, Y.-C. Study on in Vitro Percutaneous Permeabilities and Antibacterial Activities of Clotrimazole-Encapsulated Ethosomes and Liposomes. Chin. Pharm. J. 2009, 4, 278–282. [Google Scholar]
- Dynamic Light Scattering DLS. Available online: https://www.malvernpanalytical.com/en/products/technology/light-scattering/dynamic-light-scattering (accessed on 10 September 2018).
- Pandey, N. Proniosomes and ethosomes: New prospect in transdermal and dermal drug delivery system. Int. J. Pharm. Sci. Res. 2011, 2, 1988–1996. [Google Scholar]
- Yukselen-Aksoy, Y.; Kaya, A. A study of factors affecting on the zeta potential of kaolinite and quartz powder. Environ. Earth Sci. 2011, 62, 697–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erzin, Y.; Yukselen, Y. The use of neural networks for the prediction of zeta potential of kaolinite. Math. Geosci. 2009, 41, 779–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lage, O.M.; Bondoso, J.; Catita, J.A.M. Determination of zeta potential in Planctomycetes and its application in heavy metals toxicity assessment. Arch. Microbiol. 2012, 194, 847–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshiikan, S.R.; Papadopoulos, K.D. Modified Booth equation for the calculation of zeta potential. Colloid Polym. Sci. 1998, 276, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lis, L.J.; McAlister, M.; Fuller, N.; Rand, R.P.; Parsegian, V.A. Interactions between neutral phospholipid bilayer membranes. Biophys. J. 1982, 37, 657–665. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- McLaughlin, S.; Mulrine, N.; Gresalfi, T.; Vaio, G.; McLaughlin, A. Adsorption of divalent cations to bilayer membranes containing phosphatidylserine. J. Gen. Physiol. 1981, 77, 445–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Söderlund, T.; Alakoskela, J.-M.I.; Pakkanen, A.L.; Kinnunen, P.K.J. Comparison of the effects of surface tension and osmotic pressure on the interfacial hydration of a fluid phospholipid bilayer. Biophys. J. 2003, 85, 2333–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, I.; Oguz, E.C.; Bartlett, P.; Lowen, H.; Royall, C.P. Direct measurement of osmotic pressure via adaptive confinement of quasi hard disc colloids. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Hu, Y.; Vlassak, J.J.; Suo, Z. Experimental determination of equations of state for ideal elastomeric gels. Soft Matter 2012, 8, 8121–8128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dudowicz, J.; Freed, K.F.; Douglas, J.F. Flory-Huggins Model of Equilibrium Polymerization and Phase Separation in the Stockmayer Fluid. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2004, 92, 045502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, Z.; Ye, H.; Kröger, M.; Li, Y. Self-assembled core–polyethylene glycol–lipid shell nanoparticles demonstrate high stability in shear flow. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 13294–13306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, W.; Xu, G.; Feng, X. Self-assembly of lipids and nanoparticles in aqueous solution: Self-consistent field simulations. Theor. Appl. Mech. Lett. 2012, 2, 014004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, D.; Nautiyal, U. Ethosomes: A review. Int. J. Pharm. Med. Res. 2016, 4, 354–363. [Google Scholar]





| Therapeutic Group of Drugs | Type of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API) | Literature |
|---|---|---|
| Antibacterial | Erythromycin | [31] |
| Anti-inflammatory | Ammonium glycyrrhizinate | [32] |
| Diclofenac | [33] | |
| Anti-viral | Acyclovir | [34] |
| Zidovudine | [35] | |
| Lamivudine | [36] | |
| Indinavir | [28] | |
| Anti-fungal | Fluconazole | [25] |
| Clotrimazolum | [37] | |
| Griseofulvin | [38] | |
| Terbinafinum | [39] | |
| Amphotericin-B | [40] | |
| Antineoplastic | Curcumin | [41] |
| Tamoxifen | [42] | |
| Antioxidants and flavonoids | α-tocopherol acetate | [43] |
| Quercetin | [44] | |
| Rutin | [45] | |
| Hormones | Testosterone | [46] |
| Hypnotic | Melatonin | [47] |
| 5α-reductase inhibitor | Finasteridum | [48] |
| Steroids | Clobetazol | [49] |
| Tertiary amine | Tolterodine tartrate | [50] |
| Vaccines | Hepatitis B Antigen | [51] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pilch, E.; Musiał, W. Liposomes with an Ethanol Fraction as an Application for Drug Delivery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3806. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123806
Pilch E, Musiał W. Liposomes with an Ethanol Fraction as an Application for Drug Delivery. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(12):3806. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123806
Chicago/Turabian StylePilch, Ewa, and Witold Musiał. 2018. "Liposomes with an Ethanol Fraction as an Application for Drug Delivery" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 12: 3806. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123806
APA StylePilch, E., & Musiał, W. (2018). Liposomes with an Ethanol Fraction as an Application for Drug Delivery. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(12), 3806. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123806