Differential Metabolic Responses to Adipose Atrophy Associated with Cancer Cachexia and Caloric Restriction in Rats and the Effect of Rikkunshito in Cancer Cachexia
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Fat and Muscle Mass
2.2. Adipocyte Size
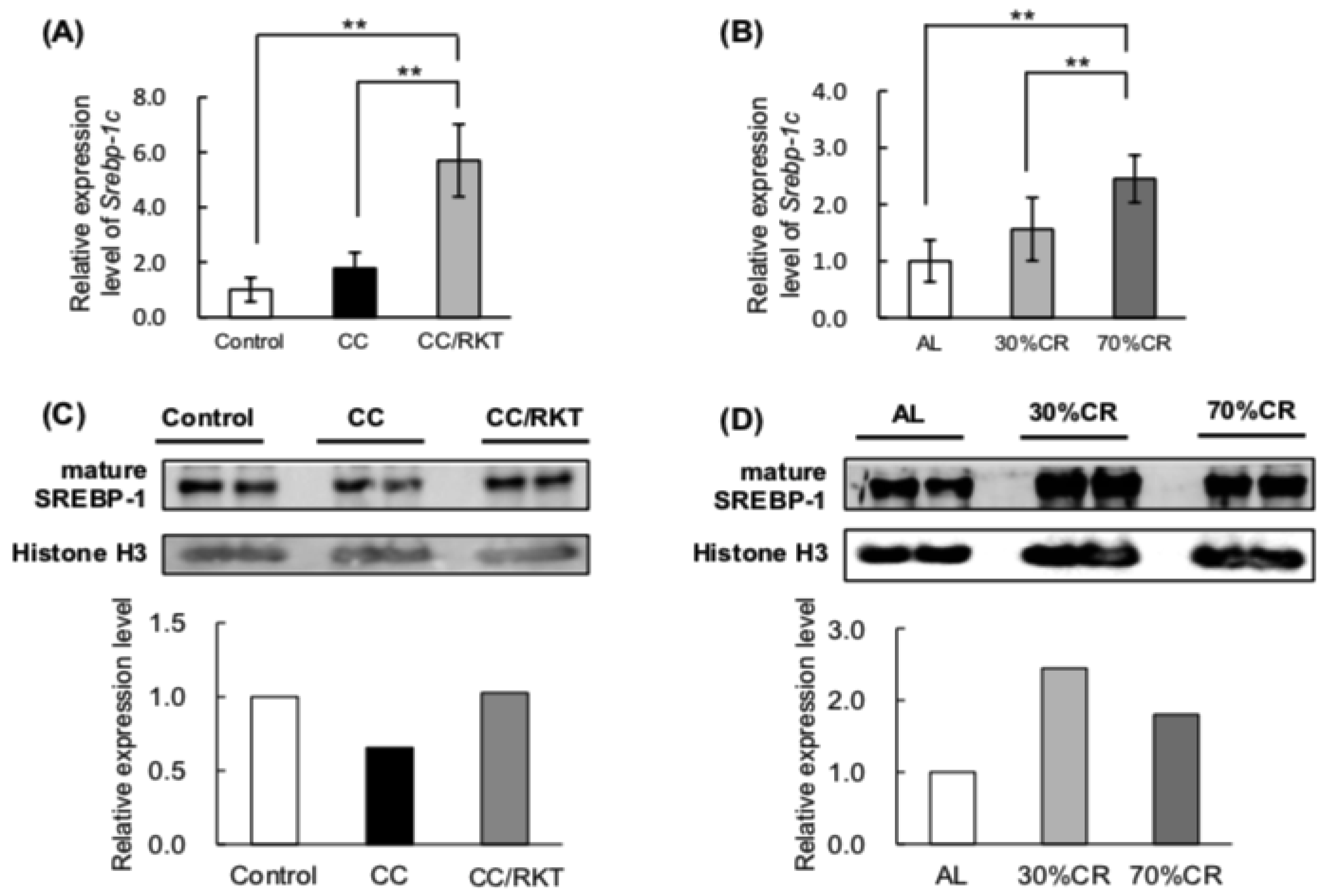
2.3. Expression Levels of Proteins Involved in Lipid Metabolism
2.4. Expression and Activity of Mitochondrial Factors
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animal Experiments
4.2. Histologic Examination
4.3. Protein Extraction and Western Blot Analysis of Target Protein Levels
4.4. RNA Extraction and Real-Time Reverse-Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction
4.5. Analysis of Citrate Synthase Activity
4.6. Analysis of mtDNA Content
4.7. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Evans, W.J.; Morley, J.E.; Argilés, J.; Bales, C.; Baracos, V.; Guttridge, D.; Jatoi, A.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Lochs, H.; Mantovani, G.; et al. Cachexia: A new definition. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 27, 793–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurdana, M. Cancer cachexia-anorexia syndrome and skeletal muscle wasting. Radiol. Oncol. 2009, 43, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.R.; Yaffee, P.M.; Jamil, L.H.; Lo, S.K.; Nissen, N.; Pandol, S.J.; Tuli, R.; Hendifar, A.E. Pancreatic cancer cachexia: A review of mechanisms and therapeutics. Front. Physiol. 2014, 5, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theologides, A. Cancer cachexia. Cancer 1979, 43, 2004–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisdale, M.J. Cachexia in cancer patients. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 862–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topkan, E.; Yavuz, A.A.; Ozyilkan, O. Cancer cachexia: Pathophysiologic aspects and treatment options. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2015, 8, 445–451. [Google Scholar]
- Bosaeus, I.; Daneryd, P.; Svanberg, E.; Lundholm, K. Dietary intake and resting energy expenditure in relation to weight loss in unselected cancer patients. Int. J. Cancer 2001, 93, 380–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laviano, A.; Meguid, M.M.; Inui, A.; Muscaritoli, M.; Rossi-Fanelli, F. Therapy insight: Cancer anorexia-cachexia syndrome—When all you can eat is yourself. Nat. Clin. Pract. Oncol. 2005, 2, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruera, E. ABC of palliative care. Anorexia, cachexia, and nutrition. BMJ 1997, 315, 1219–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tisdale, M.J. Mechanisms of Cancer Cachexia. Physiol. Rev. 2009, 89, 381–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.W.-C.; Yeh, K.-Y.; Shen, Y.-C.; Hsieh, J.-J.; Chuang, C.-K.; Liao, S.-K.; Tsai, L.-H.; Wang, C.-H. Production of multiple cytokines and induction of cachexia in athymic nude mice by a new anaplastic thyroid carcinoma cell line. J. Endocrinol. 2003, 179, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahimi, B.; Tucker, S.L.; Li, D.; Abbruzzese, J.L.; Kurzrock, R. Cytokines in pancreatic carcinoma: Correlation with phenotypic characteristics and prognosis. Cancer 2004, 101, 2727–2736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, M.; Yamaguchi, K.; Honda, S.; Factor, P.L. Cancer Cachexia Syndrome Developed in Nude Mice Bearing Melanoma Cells Producing Leukemia-inhibitory Factor. Cancer Res. 1991, 51, 6656–6659. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Glickman, M.H.; Ciechanover, A. The Ubiquitin-Proteasome Proteolytic Pathway: Destruction for the Sake of Construction. Physiol. Rev. 2002, 82, 373–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagoe, R.T.; Redfern, C.P.F.; Roberts, R.G.; Gibson, G.J.; Goodship, T.H.J. Skeletal muscle mRNA levels for cathepsin B, but not components of the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway, are increased in patients with lung cancer referred for thoracotomy. Clin. Sci. (Lond.) 2002, 102, 353–361. [Google Scholar]
- Shaw, J.H.; Wolfe, R.R. Fatty acid and glycerol kinetics in septic patients and in patients with gastrointestinal cancer. The response to glucose infusion and parenteral feeding. Ann. Surg. 1987, 205, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, M.P.; Cooper, S.T.; Parry, B.R.; Tuckey, J.A. Increased expression of the mRNA for hormone-sensitive lipase in adipose tissue of cancer patients. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1993, 1180, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam-Ali, B.; Khan, S.; Price, S.A.; Tisdale, M.J. Modulation of adipocyte G-protein expression in cancer cachexia by a lipid-mobilizing factor (LMF). Br. J. Cancer 2001, 85, 758–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agustsson, T.; Ryden, M.; Hoffstedt, J.; van Harmelen, V.; Dicker, A.; Laurenickiene, J.; Isaksson, B.; Permert, J.; Arner, P. Mechanism of increased lipolysis in cancer cachexia. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 5531–5537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.K.; Eder, S.; Schauer, S.; Diwoky, C.; Temmel, H.; Guertl, B.; Gorkiewicz, G.; Tamilarasan, K.P.; Kumari, P.; Trauner, M.; et al. Adipose triglyceride lipase contributes to cancer-associated cachexia. Science 2011, 333, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouchi, N.; Parker, J.L.; Lugus, J.J.; Walsh, K. Adipokines in inflammation and metabolic disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, R.M.; Weindruch, R. Metabolic reprogramming in dietary restriction. Interdiscip. Top. Gerontol. 2007, 35, 18–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, B.K.; Steffen, K.K.; Kaeberlein, M. Ruminations on dietary restriction and aging. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2007, 64, 1323–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piper, M.D.W.; Bartke, A. Diet and Aging. Cell Metab. 2008, 8, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okita, N.; Hayashida, Y.; Kojima, Y.; Fukushima, M.; Yuguchi, K.; Mikami, K.; Yamauchi, A.; Watanabe, K.; Noguchi, M.; Nakamura, M.; et al. Differential responses of white adipose tissue and brown adipose tissue to caloric restriction in rats. Mech. Aging Dev. 2012, 133, 255–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chujo, Y.; Fujii, N.; Okita, N.; Konishi, T.; Narita, T.; Yamada, A.; Haruyama, Y.; Tashiro, K.; Chiba, T.; Shimokawa, I.; et al. Caloric restriction-Associated remodeling of rat white adipose tissue: Effects on the growth hormone/insulin-like growth factor-1 axis, sterol regulatory element binding protein-1, and macrophage infiltration. Age (Omaha) 2013, 35, 1143–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okita, N.; Tsuchiya, T.; Fukushima, M.; Itakura, K.; Yuguchi, K.; Narita, T.; Hashizume, Y.; Sudo, Y.; Chiba, T.; Shimokawa, I.; et al. Chronological analysis of caloric restriction-induced alteration of fatty acid biosynthesis in white adipose tissue of rats. Exp. Gerontol. 2015, 63, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, N.; Narita, T.; Okita, N.; Kobayashi, M.; Furuta, Y.; Chujo, Y.; Sakai, M.; Yamada, A.; Takeda, K.; Konishi, T.; et al. Sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1c orchestrates metabolic remodeling of white adipose tissue by caloric restriction. Aging Cell 2017, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terawaki, K.; Sawada, Y.; Kashiwase, Y.; Hashimoto, H.; Yoshimura, M.; Suzuki, M.; Miyano, K.; Sudo, Y.; Shiraishi, S.; Higami, Y.; et al. New cancer cachexia rat model generated by implantation of a peritoneal dissemination-derived human stomach cancer cell line. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 306, E373–E387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terawaki, K.; Kashiwase, Y.; Sawada, Y.; Hashimoto, H.; Yoshimura, M.; Ohbuchi, K.; Sudo, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Miyano, K.; Shiraishi, S.; et al. Development of ghrelin resistance in a cancer cachexia rat model using human gastric cancer-derived 85As2 cells and the palliative effects of the Kampo medicine rikkunshito on the model. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, H.; Sadakane, C.; Hattori, T.; Katsurada, T.; Ohkawara, T.; Nagai, K.; Asaka, M. Rikkunshito, an Herbal Medicine, Suppresses Cisplatin-Induced Anorexia in Rats Via 5-HT2 Receptor Antagonism. Gastroenterology 2008, 134, 2004–2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujitsuka, N.; Asakawa, A.; Hayashi, M.; Sameshima, M.; Amitani, H.; Kojima, S.; Fujimiya, M.; Inui, A. Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors Modify Physiological Gastrointestinal Motor Activities via 5-HT2c Receptor and Acyl Ghrelin. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 65, 748–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujitsuka, N.; Asakawa, A.; Uezono, Y.; Minami, K.; Yamaguchi, T.; Niijima, A.; Yada, T.; Maejima, Y.; Sedbazar, U.; Sakai, T.; et al. Potentiation of ghrelin signaling attenuates cancer anorexia-cachexia and prolongs survival. Transl. Psychiatry 2011, 1, e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujitsuka, N.; Uezono, Y. Rikkunshito, a ghrelin potentiator, ameliorates anorexia-cachexia syndrome. Front. Pharmacol. 2014, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taroni, F.; Di Donato, S. Purification and properties of cytosolic malic enzyme from human skeletal muscle. Int. J. Biochem. 1988, 20, 857–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimano, H.; Yahagi, N.; Amemiya-Kudo, M.; Hasty, A.H.; Osuga, J.I.; Tamura, Y.; Shionoiri, F.; Iizuka, Y.; Ohashi, K.; Harada, K.; et al. Sterol regulatory element-binding protein-1 as a key transcription factor for nutritional induction of lipogenic enzyme genes. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 35832–35839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, T.F.; Espenshade, P.J. Evolutionary conservation and adaptation in the mechanism that regulates SREBP action: What a long, strange tRIP it’s been. Genes Dev. 2009, 23, 2578–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, R.A.; Wilke, M.S.; Perrine, M.; Pawlowicz, M.; Mourtzakis, M.; Lieffers, J.R.; Maneshgar, M.; Bruera, E.; Clandinin, M.T.; Baracos, V.E.; et al. Loss of adipose tissue and plasma phospholipids: Relationship to survival in advanced cancer patients. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 29, 482–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Sebastiano, K.M.; Yang, L.; Zbuk, K.; Wong, R.K.; Chow, T.; Koff, D.; Moran, G.R.; Mourtzakis, M. Accelerated muscle and adipose tissue loss may predict survival in pancreatic cancer patients: The relationship with diabetes and anaemia. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 109, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouladiun, M.; Körner, U.; Bosaeus, I.; Daneryd, P.; Hyltander, A.; Lundholm, K.G. Body composition and time course changes in regional distribution of fat and lean tissue in unselected cancer patients on palliative care—Correlations with food intake, metabolism, exercise capacity, and hormones. Cancer 2005, 103, 2189–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuijdgeest-van Leeuwen, S.D.; van den Berg, J.W.; Wattimena, J.L.; van der Gaast, A.; Swart, G.R.; Wilson, J.H.; Dagnelie, P.C. Lipolysis and lipid oxidation in weight-losing cancer patients and healthy subjects. Metabolism 2000, 49, 931–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyltander, A.; Daneryd, P.; Sandstrom, R.; Korner, U.; Lundholm, K. β-Adrenoceptor activity and resting energy metabolism in weight-losing cancer patients. Eur. J. Cancer 2000, 36, 330–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, S.; Wolfe, R.R. Whole-body lipolysis and triglyceride-fatty acid cycling in cachectic patients with esophageal cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 1990, 86, 1403–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kliewer, K.L.; Ke, J.Y.; Tian, M.; Cole, R.M.; Andridge, R.R.; Belury, M.A. Adipose tissue lipolysis and energy metabolism in early cancer cachexia in mice. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2015, 16, 886–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bing, C.; Russell, S.; Becket, E.; Pope, M.; Tisdale, M.J.; Trayhurn, P.; Jenkins, J.R. Adipose atrophy in cancer cachexia: Morphologic and molecular analysis of adipose tissue in tumour-bearing mice. Br. J. Cancer 2006, 95, 1028–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feingold, K.R.; Marshall, M.; Gulli, R.; Moser, A.H.; Grunfeld, C. Effect of endotoxin and cytokines on lipoprotein lipase activity in mice. Arterioscler. Thromb. 1994, 14, 1866–1872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, M.K.; Doerrler, W.; Feingold, K.R.; Grunfeld, C. Leukemia inhibitory factor induces changes in lipid metabolism in cultured adipocytes. Endocrinology 1994, 135, 141–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hogan, J.C.; Kliewer, K.L.; Ke, J.Y.; Tian, M.; Cole, R.M.; Andridge, R.R.; Belury, M.A.; Varela, L.; Vázquez, M.J.; Cordido, F.; et al. Effects of leukemia inhibitory factor on 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J. Endocrinol. 2005, 185, 485–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, M.; Hosoda, H.; Date, Y.; Nakazato, M.; Matsuo, H.; Kangawa, K. Ghrelin is a growth-hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach. Nature 1999, 402, 656–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumura, T.; Arai, M.; Yonemitsu, Y.; Maruoka, D.; Tanaka, T.; Suzuki, T.; Yoshikawa, M.; Imazeki, F.; Yokosuka, O. The traditional Japanese medicine Rikkunshito increases the plasma level of ghrelin in humans and mice. J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 45, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, H.; Muto, S.; Hattori, T.; Sadakane, C.; Tsuchiya, K.; Katsurada, T.; Ohkawara, T.; Oridate, N.; Asaka, M. Rikkunshito ameliorates the aging-associated decrease in ghrelin receptor reactivity via phosphodiesterase III inhibition. Endocrinology 2010, 151, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varela, L.; Vázquez, M.J.; Cordido, F.; Nogueiras, R.; Vidal-Puig, A.; Diéguez, C.; López, M. Ghrelin and lipid metabolism: Key partners in energy balance. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2011, 46, 43–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogueiras, R.; López, M.; Diéguez, C. Regulation of lipid metabolism by energy availability: A role for the central nervous system. Obes. Rev. 2010, 11, 185–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porteiro, B.; Díaz-Ruíz, A.; Martínez, G.; Senra, A.; Vidal, A.; Serrano, M.; Gualillo, O.; López, M.; Malagón, M.M.; Diéguez, C.; Nogueiras, R. Ghrelin requires p53 to stimulate lipid storage in fat and liver. Endocrinology 2013, 154, 3671–3679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alp, P.R.; Newsholme, E.A.; Zammit, V.A. Activities of citrate synthase and NAD+-linked and NADP+-linked isocitrate dehydrogenase in muscle from vertebrates and invertebrates. Biochem. J. 1976, 154, 689–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koekemoer, T.C.; Downing, T.G.; Oelofsen, W. An alternative PCR assay for quantifying mitochondrial DNA in crude preparations. Nucleic Acids Res. 1998, 26, 2829–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahnke, V.E.; Sabido, O.; Defour, A.; Castells, J.; Lefai, E.; Roussel, D.; Freyssenet, D. Evidence for mitochondrial respiratory deficiency in rat rhabdomyosarcoma cells. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e8637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sudo, Y.; Otsuka, H.; Miyakawa, R.; Goto, A.; Kashiwase, Y.; Terawaki, K.; Miyano, K.; Hirao, Y.; Taki, K.; Tagawa, R.; et al. Differential Metabolic Responses to Adipose Atrophy Associated with Cancer Cachexia and Caloric Restriction in Rats and the Effect of Rikkunshito in Cancer Cachexia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3852. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123852
Sudo Y, Otsuka H, Miyakawa R, Goto A, Kashiwase Y, Terawaki K, Miyano K, Hirao Y, Taki K, Tagawa R, et al. Differential Metabolic Responses to Adipose Atrophy Associated with Cancer Cachexia and Caloric Restriction in Rats and the Effect of Rikkunshito in Cancer Cachexia. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(12):3852. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123852
Chicago/Turabian StyleSudo, Yuka, Hiroki Otsuka, Ryota Miyakawa, Akifumi Goto, Yohei Kashiwase, Kiyoshi Terawaki, Kanako Miyano, Yuto Hirao, Kanari Taki, Ryoma Tagawa, and et al. 2018. "Differential Metabolic Responses to Adipose Atrophy Associated with Cancer Cachexia and Caloric Restriction in Rats and the Effect of Rikkunshito in Cancer Cachexia" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 12: 3852. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123852
APA StyleSudo, Y., Otsuka, H., Miyakawa, R., Goto, A., Kashiwase, Y., Terawaki, K., Miyano, K., Hirao, Y., Taki, K., Tagawa, R., Kobayashi, M., Okita, N., Uezono, Y., & Higami, Y. (2018). Differential Metabolic Responses to Adipose Atrophy Associated with Cancer Cachexia and Caloric Restriction in Rats and the Effect of Rikkunshito in Cancer Cachexia. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(12), 3852. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123852




