The Biological Significance and Regulatory Mechanism of c-Myc Binding Protein 1 (MBP-1)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Basic Characteristics of MBP-1
3. MBP-1 in the Normal Tissues and Cancer Cells of Vertebrates
4. MBP-1 in Tumorigenesis
5. MBP-1 in Plant Growth and Development
6. MBP-1 in Abiotic Stress Responses
7. Regulatory Network of MBP-1
8. The Developing Potential of MBP-1 in Pharmaceuticals
9. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Piast, M.; Kustrzeba-Wójcicka, I.; Matusiewicz, M.; Banaś, T. Molecular evolution of enolase. Acta Biochim. Polonica 2005, 52, 507–513. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.; Guo, Y.; Ohta, M.; Xiong, L.M.; Stevenson, B.; Zhu, J.K. LOS2, a genetic locus required for cold-responsive gene transcription encodes a bi-functional ENOLASE. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 2692–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marangos, P.J.; Parma, A.M.; Goodwin, F.K. Functional properties of neuronal and glial isoenzymes of brain enolase. J. Neurochem. 1978, 31, 727–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibi, T.; Sahashi, K.; Kato, K.; Takahashi, A.; Sobue, I. Immunohistochemical demonstration of beta-enolase in human skeletal muscle. Muscle Nerve 1983, 6, 661–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, N.; Dai, Q.; Williams, J.; Goulding, E.H.; Willis, W.D.; Brown Paula, R.; Edward, M.E. Disruption of a Spermatogenic Cell-Specific Mouse Enolase 4 (Eno4) Gene Causes Sperm Structural Defects and Male Infertility. Biol. Reprod. 2013, 88, 808–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pancholi, V. Multifunctional alpha-enolase: Its role in diseases. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2001, 58, 902–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trojanowicz, B.; Hoang-Vu, C.; Sekulla, C. ENO1 (Enolase 1; (alpha)). Atlas Genet. Cytogenet. Oncol. Haematol. 2010, 14, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capello, M.; Ferriborgogno, S.; Cappello, P.; Novelli, F. α-Enolase: A promising therapeutic and diagnostic tumor target. FEBS J. 2011, 278, 1064–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merkulova, T.; Dehaupas, M.; Nevers, M.; Créminon, C.; Alameddine, H.; Keller, A. Differential modulation of α; β and γ enolase isoforms in regenerating mouse skeletal muscle. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000, 267, 3735–3743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avilán, L.; Gualdrón-López, M.; Quiñones, W.; González-González, L.; Hannaert, V.; Michels, P.A.M.; Concepción, J. Enolase: A key player in the metabolism and a probable virulence factor of trypanosomatid parasites-perspectives for its use as a therapeutic target. Enzyme Res. 2011, 1, 932549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinloch, A.; Tatzer, V.; Wait, R.; Peston, D.; Lundberg, K.; Donatien, P.; Moyes, D.; Taylor, P.C.; Venables, P.J. Identification of citrullinated α-enolase as a candidate autoantigen in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2005, 7, R1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rgwatzke, W. Clinical and electrophysiologic characterization of paraneoplastic and autoimmune reti-nopathies associated with antienolase antibodies. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2005, 139, 780–794. [Google Scholar]
- Miyoung, K.; Haggag, A.; Seonghee, L.; Reichert, A.; Mysore, K.S.; Allen, R.D. AtMBP-1; an alternative translation product of LOS2; affects abscisic acid responses and is modulated by the E3 ubiquitin ligase AtSAP5. Plant J. 2013, 76, 481–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marina, E.; Wilfried, R.; Saiqi, Y.; Poppenberger, B. ENO2 activity is required for the development and reproductive success of plants; and is feedback-repressed by AtMBP-1. Plant J. 2015, 81, 895–906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Ganeshan, S.; Fowler, D.B.; Chibbar, R.N. Characterisation of two wheat enolase cDNA showing distinct patterns of expression in leaf and crown tissues of plants exposed to low temperature. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2013, 162, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.H.; Chen, C.; Shi, Z.H.; Cheng, H.M.; Bing, J.; Ma, X.F.; Zheng, C.X.; Li, H.J.; Zhang, G.F. Identification of salinity-related genes in ENO2 mutant (ENO2−) of Arabidopsis thaliana. J. Integr. Agric. 2018, 17, 94–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feo, S.; Arcuri, D.; Piddini, E.; Passantino, R.; Giallongo, A. ENO1 gene product binds to the c-myc promoter and acts as a transcriptional repressor: Relationship with Myc promoter-binding protein 1 (MBP-1). FEBS Lett. 2000, 473, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, R.; Miller, D.M. Cloning and characterization of a human c-myc promoter-binding protein. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1991, 11, 2154–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, R.A.; Adkison, L.R.; Dowler, L.L.; Ray, R.B. Chromosomal localization of the human gene encoding c-myc promoter-binding protein (MPB-1) to chromosome 1p35-pter. Genomics 1997, 39, 406–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giallongo, A.; Feo, S.; Moore, R.; Croce, C.M.; Showe, L.C. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of a full-length cDNA for human alpha enolase. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 1986, 83, 6741–6745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, R.B.; Steele, R. Separate domains of MBP-1 involved in c-myc; promoter binding and growth suppressive activity. Gene 1997, 186, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lung, J.; Liu, K.J.; Chang, J.Y.; Leu, S.J.; Shih, N.Y. MBP-1 is efficiently encoded by an alternative transcript of the ENO1 gene but post-translationally regulated by proteasome-dependent protein turnover. FEBS J. 2010, 277, 4308–4321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subramanian, A.; Miller, D.M. Structural analysis of alpha-enolase. Mapping the functional domains involved in down-regulation of the c-myc protooncogene. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 5958–5965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, G.C.; Liu, K.J.; Hsieh, C.L.; Hu, T.S.; Charoenfuprasert, S.; Liu, H.K.; Luh, K.T.; Hsu, L.H.; Wu, C.W.; Ting, C.C.; et al. Identification of alpha-enolase as an autoantigen in lung cancer: Its overexpression is associated with clinical outcomes. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 5746–5754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Àngels, D.; Roig-Borrellas, A.; García-Melero, A.; Lopez-Alemany, R. α-Enolase; a Multifunctional Protein: Its Role on Pathophysiological Situations. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2012, 7, 156795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappello, P.; Principe, M.; Bulfamante, S.; Novelli, F. Alpha-Enolase (ENO1); a potential target in novel immunotherapies. Front. Biosci. 2017, 22, 944–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, K.W.; Hsieh, R.H.; Wu, C.W.; Chi, C.W.; Lee, Y.H.; Kuo, M.L.; Wu, K.J.; Yeh, T.S. MBP-1 Suppresses Growth and Metastasis of Gastric Cancer Cells through COX-2. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2009, 20, 5127–5137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, Z.; Yao, H.; Han, Y. Effects of RNAi of MBP-1 gene on proliferation of gastric cancer SGC-7901 cell line. Int. J. Lab. Med. 2014, 24, 3300–3304. [Google Scholar]
- Ray, R.B.; Steele, R.; Seftor, E.; Hendrix, M. Human Breast Carcinoma Cells Transfected with the Gene Encoding a c-myc Promoter-binding Protein (MBP-1) Inhibits Tumors in Nude Mice. Cancer Res. 1995, 55, 3747–3751. [Google Scholar]
- Lo, P.M.; Ferro, A.; Contino, F.; Mazzarella, C.; Sbacchi, S.; Roz, E.; Lupo, C.; Perconti, G.; Giallongo, A.; Migliorini, P.; Marrazzo, A.; Feo, S. Myc promoter-binding protein-1 (MBP-1) is a novel potential prognostic marker in invasive ductal breast carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e12961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, A.K.; Steele, R.; Ryerse, J.; Ray, R.B. Tumor-suppressive effects of MBP-1 in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 11907–11912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Cancer Society. Surveillance Research: Cancer Facts and Figures; American Cancer Society: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, A.K.; Steele, R.; Ray, R.B. c-Myc Promoter-binding protein 1 (MBP-1) regulates prostate cancer cell growth by inhibiting MAPK pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 14325–14330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steele, R.; Mott, J.L.; Ray, R.B. MBP-1 down-regulates miR-29b that represses Mcl-1; collagens; and matrix-metalloproteinase-2 in prostate cancer cells. Genes Cancer 2015, 1, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, A.K.; Steele, R.; Ray, R.B. Knockdown of MBP-1 in human prostate cancer cells delays cell cycle progression. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 23652–23657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Yuanming, L.I.; Wang, L.; Ye, L.B.; Yi, S.J.; Mu, S.F.; Ha, L.M.; Qi, H. Role of MBP-1 in proliferation;apoptosis and invasion of human esophageal cancer cells Ec109. Chongqing Med. 2018, 10, 1318–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Geng, Z.; Shi, X.; Ma, K.J.; Zhu, H.W.; Ren, W.; Zhou, Y.L. Effects of RNA Interfering of MBP-1 on Proliferation of Saos-2 Cell Line. J. China Med. Univ. 2016, 45, 604–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, R.B.; Srinivas, R.V. Inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 replication by a cellular transcriptional factor MBP-1. J. Cell. Biochem. 2015, 64, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaspert, N.; Weckermann, K.; Piotrowski, M. Enolase; a cross-link between glycolysis and stress response. In Proceedings of the 20th International Conference on Arabidopsis Research, Edinburgh, UK, 30 June–4 July 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Yi, T.F.; Dong, G.F.; Wang, Z.L.; Li, J.X. Identification and functional analysis of phosphoproteins regulated by auxin in Arabidopsis roots. J. Plant Biol. 2009, 52, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, H.; Maruyama, K.; Sakuma, Y.; Meshi, T.; Iwabuchi, M.; Shinozaki, K.; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K. Arabidopsis Cys2/His2-type zinc-finger proteins function as transcription repressors under drought cold and high-salinity stress conditions. Plant Physiol. 2004, 136, 2734–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgari, Y.; Zabihinpour, Z.; Salehzadeh-Yazdi, A.; Schreiber, F.; Masoudi-Nejad, A. Alterations in cancer cell metabolism: The Warburg effect and metabolic adaptation. Genomics 2015, 105, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takashima, M.; Kuramitsu, Y.; Yokoyama, Y.; Iizuka, N.; Fujimoto, M.; Nishisaka, T.; Okita, K.; Oka, M.; Nakamura, K. Overexpression of alpha enolase in hepatitis C virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma: Association with tumor progression as determined by proteomic analysis. Proteomics 2005, 5, 1686–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maranto, C.; Perconti, G.; Contino, F.; Rubino, P.; Feo, S.; Giallongo, A. Cellular stress induces cap-independent alpha-enolase/MBP-1 translation. FEBS Lett. 2016, 589, 2110–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, D.M.; Thomas, S.D.; Sedoris, K.C. Hypoxia induces differential translation of enolase/MBP-1. BMC Cancer 2010, 10, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedoris, K.C.; And, S.D.T.; Miller, D.M. c-myc Promoter Binding Protein Regulates the Cellular Response to an Altered Glucose Concentration. Biochemistry 2007, 46, 8659–8668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contino, F.; Mazzarella, C.; Ferro, A.; Lo Presti, M.; Roz, E.; Lupo, C.; Perconti, G.; Giallongo, A.; Feo, S. Negative transcriptional control of ERBB2 gene by MBP-1 and HDAC1: Diagnostic implications in breast cancer. BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, R.; Ghosh, A.; Steele, R.; Kanda, T. Inhibition of MBP-1 induces senescence in human foreskin fibroblasts. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 438. [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh, A.K.; Kanda, T.; Steele, R.; Ray, R. Knockdown of MBP-1 in Human Foreskin Fibroblasts Induces p53-p21 Dependent Senescence. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, 3649–3661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, T.; Raychoudhuri, A.; Steele, R.; Sagartz, J.E.; West, C.; Ray, R.B. MBP-1 inhibits breast cancer growth and metastasis in immunocompetent mice. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 9354–9359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, K.W.; Hsieh, R.H.; Lee, Y.H.; Chao, C.H.; Wu, K.J.; Tseng, M.J.; Yeh, T.S. The activated Notch1 receptor cooperates with alpha-enolase and MBP-1 in modulating c-myc activity. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008, 28, 4829–4842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perconti, G.; Ferro, A.; Amato, F.; Rubino, P.; Randazzo, D.; Wolff, T.; Feo, S.; Giallongo, A. The kelch protein NS1-BP interacts with alpha-enolase/MBP-1 and is involved in c-Myc gene transcriptional control. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1773, 1774–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Genomics; biogenesis; mechanism; and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, R.C.; Farh, K.H.; Burge, C.B.; Bartel, D.P. Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res. 2008, 19, 92–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, K.W.; Wang, A.M.; Ping, Y.H.; Huang, K.H.; Huang, T.T.; Lee, H.C.; Lo, S.S.; Chi, C.W.; Yeh, T.S. Down-regulation of tumor suppressor MBP-1 by microRNA-363 in gastric carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis 2014, 35, 208–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, A.T.; Ogino, S.; Fuchs, C.S. Aspirin use and survival after diagnosis of colorectal cancer. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2009, 302, 649–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Cheng, X.; Samma, M.K.; Sam, K.P.K.; Lee, C.M.; Chiu, S.K. Differential cellular responses by oncogenic levels of c-Myc expression in long-term confluent retinal pigment epithelial cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 443, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, C.V.; O’Donnell, K.A.; Zeller, K.I.; Nguyen, T.; Osthus, R.C.; Li, F. The c-Myc target gene network. Semin Cancer Biol. 2006, 16, 253–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vita, M.; Henriksson, M. The Myc oncoprotein as a therapeutic target for human canfor human cancer. Semin Cancer Biol. 2006, 16, 318–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKeown, M.R.; Bradner, J.E. Therapeutic strategies to inhibit MYC. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2014, 4, a014266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rothwell, P.M.; Price, J.F.; Fowkes, F.G.R.; Zanchetti, A.; Roncaglioni, M.C.; Tognoni, G.; Lee, R.; Belch, J.F.; Wilson, M.; Mehta, Z. Analysis of the time course of risks and benefits in 51 randomised controlled trials. Lancet 2012, 379, 1602–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahasrabuddhe, V.V.; Gunja, M.Z.; Graubard, B.I.; Trabert, B.; Schwartz, L.M.; Park, Y.; Hollenbeck, A.R.; Freedman, N.D.; McGlynn, K.A. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug use, chronic liver disease, and hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2012, 104, 1808–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamba, C.A.; Swetter, S.M.; Stefanick, M.L.; Kubo, J.; Desai, M.; Spaunhurst, K.M.; Sinha, A.A.; Asgari, M.M.; Sturgeon, S.; Tang, J.Y. Aspirin is associated with lower melanoma risk among postmenopausal Caucasian women: The Women’s Health Initiative. Cancer 2013, 119, 1562–1569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veitonmaki, T.; Tammela, T.L.; Auvinen, A.; Murtola, T.J. Use of aspirin, but not other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs is associated with decreased prostate cancer risk at the population level. Eur. J. Cancer 2013, 49, 938–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakesh, D.; Guoqiang, A.; Kumar, D.R.; Satya, S.; Sadhu, H.T.; Bhat, G.J. Cyclin a2 and cdk2 as novel targets of aspirin and salicylic acid: A potential role in cancer prevention. Mol. Cancer Res. 2016, 14, 241–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, G.; Dachineni, R.; Muley, P.; Tummala, H.; Bhat, G.J. Aspirin and salicylic acid decrease c-myc expression in cancer cells: A potential role in chemoprevention. Tumor Biol. 2016, 37, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopp, E.; Ghosh, S. Inhibition of NF-kappa B by sodium salicylate and aspirin. Science 1994, 265, 956–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vane, J.R.; Botting, R.M. The mechanism of action of aspirin. Thromb Res. 2003, 110, 255–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salouti, M.; Mirzaei, F.; Shapouri, R.; Ahangari, A. Synergistic Antibacterial Activity of Plant Peptide MBP-1 and Silver Nanoparticles Combination on Healing of Infected Wound Due toStaphylococcus aureus. Jundishapur. J. Microb. 2016, 9, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albihn, A.; Loven, J.J.; Osorio, L.M.; Henriksson, M. c-Myc-dependent etoposide-induced apoptosis involves activation of Bax and caspases, and PKCdelta signaling. J. Cell. Biochem. 2010, 98, 1597–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, S.; Prochownik, E.V. Small-molecule inhibitors of the Myc oncoprotein. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1849, 525–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

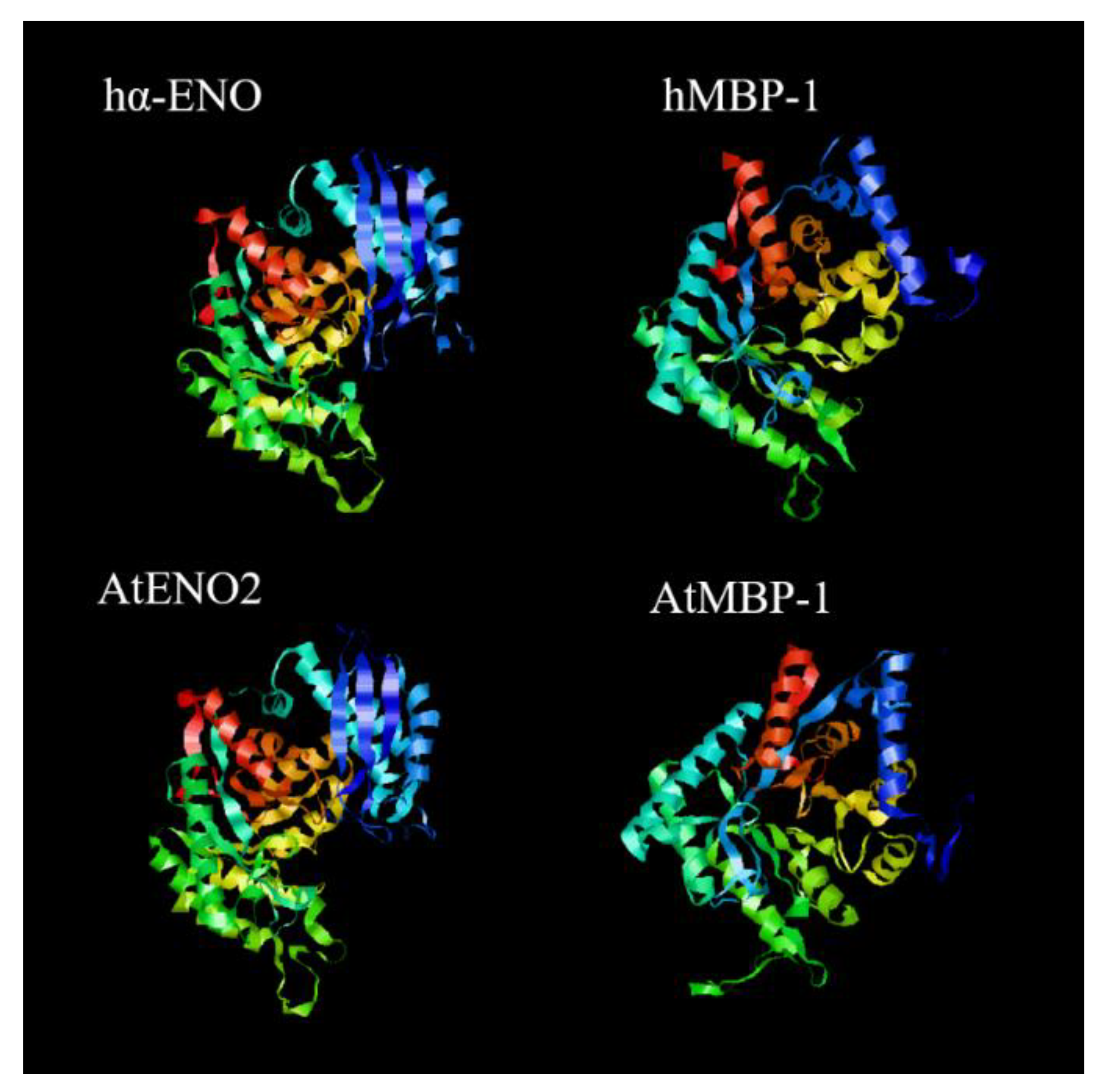

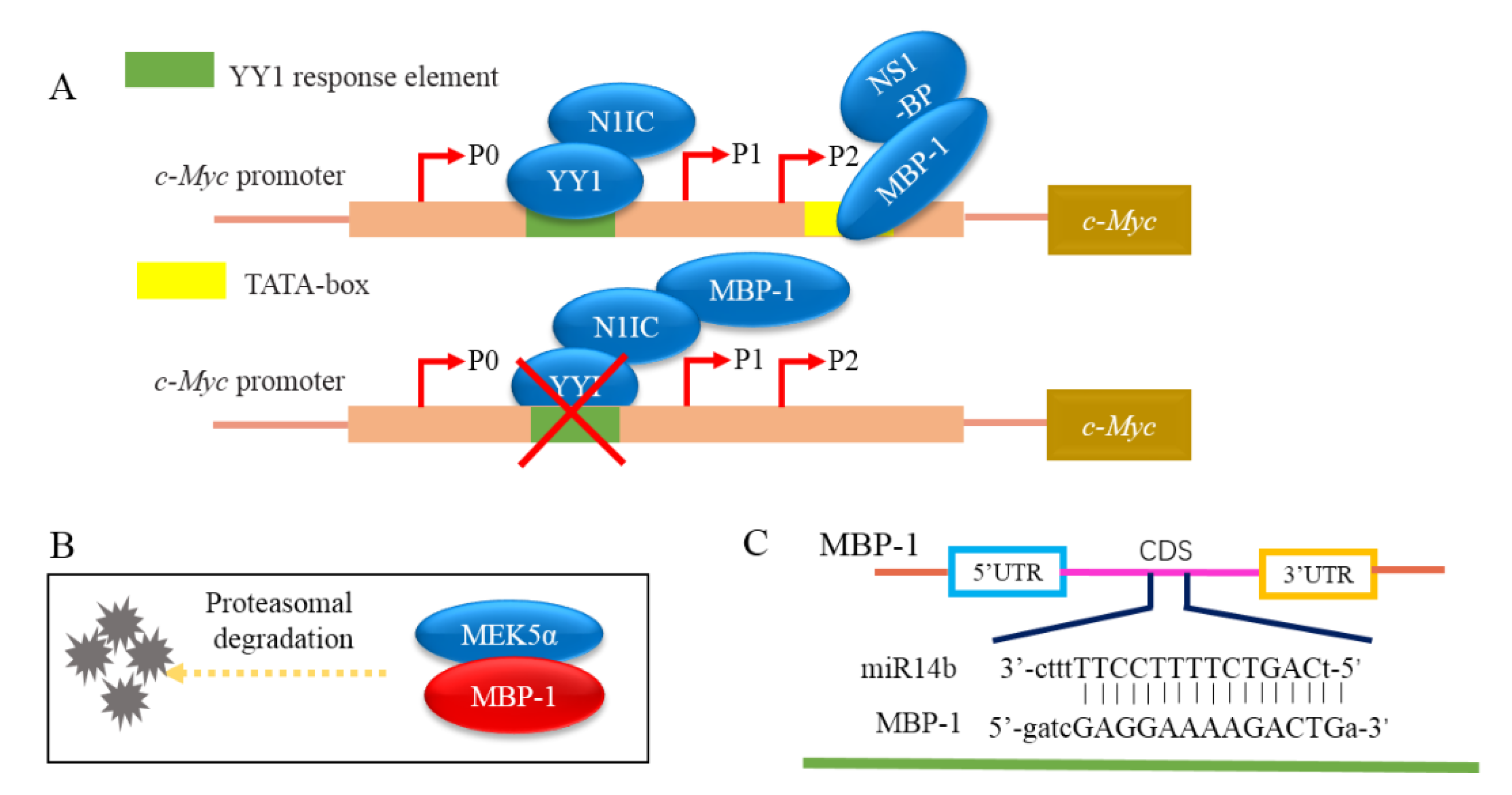
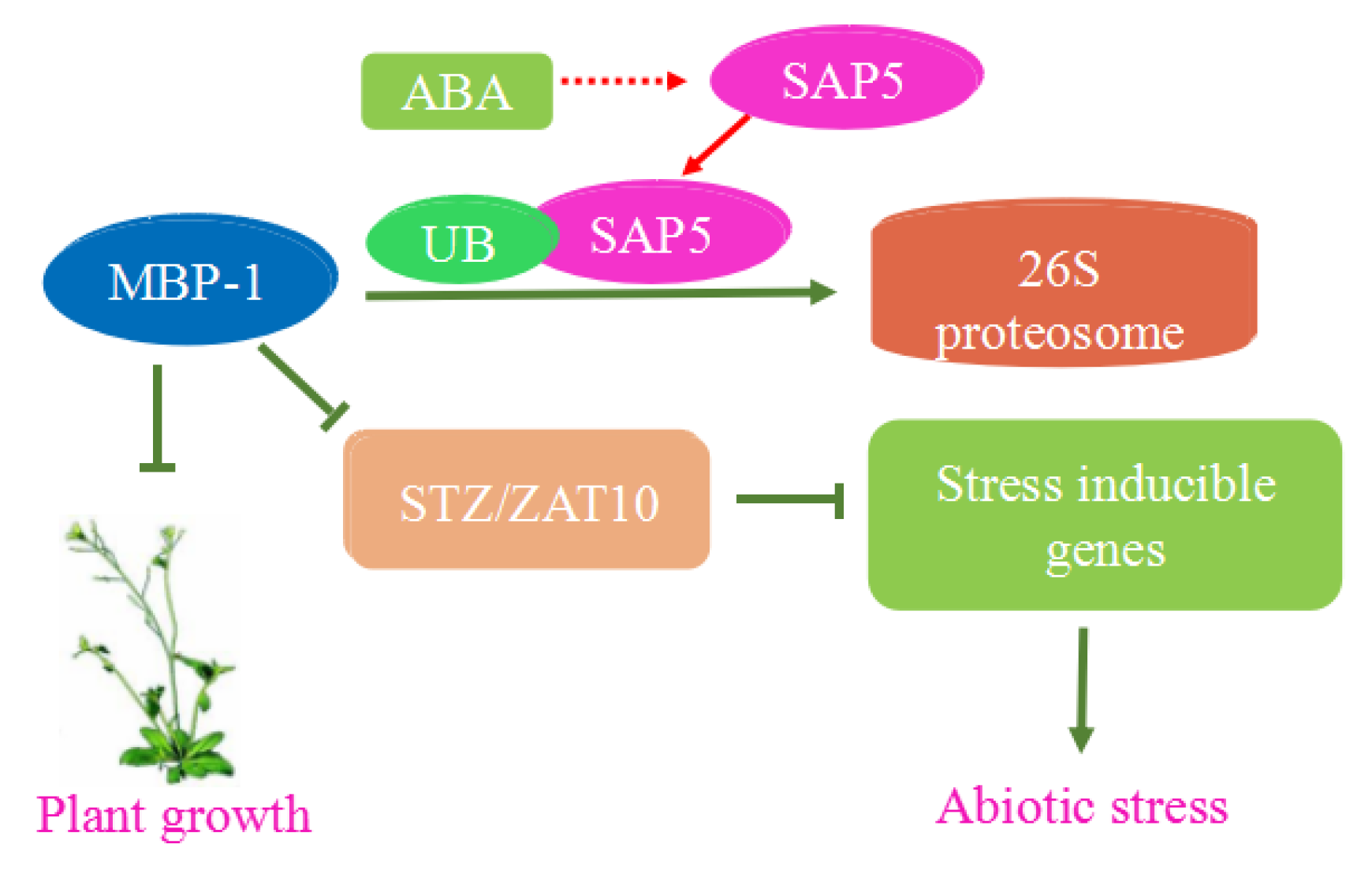
| Cancer | Cell Line | Influence |
|---|---|---|
| Breast cancer | MCF-7 | Inhibit anchorage-independent growth |
| EO771 | Inhibit growth and matrix metalloproteinase expression | |
| MDA-MB-231 | Suppress the tumorigenicity | |
| Esophageal cancer | EC109 | Inhibit proliferation, apoptosis and invasion |
| Gastric cancer | SC-M1 | Inhibit proliferation, colony formation, migration and invasion |
| SGC-7901 | Inhibit cell proliferation | |
| Lung cancer | H1299 | Inhibit proliferation and growth, induce necrosis-like cell death and mitochondrial dysfunction |
| Osteosarcoma | Saos-2 | Inhibit cell proliferation by decreasing the expression levels of cyclin D1 and cyclin E1 protein |
| Prostate cancer | PC13 | Inhibit cell growth |
| DU145 | Inhibit cell growth | |
| PC3-4.2 | Delay cell cycle progression |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Z.; Zhang, A.; Zheng, L.; Johnathan, A.-F.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, G. The Biological Significance and Regulatory Mechanism of c-Myc Binding Protein 1 (MBP-1). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3868. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123868
Liu Z, Zhang A, Zheng L, Johnathan A-F, Zhang J, Zhang G. The Biological Significance and Regulatory Mechanism of c-Myc Binding Protein 1 (MBP-1). International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(12):3868. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123868
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Zijin, Aileen Zhang, Lamei Zheng, Abou-Fadel Johnathan, Jun Zhang, and Genfa Zhang. 2018. "The Biological Significance and Regulatory Mechanism of c-Myc Binding Protein 1 (MBP-1)" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 12: 3868. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123868
APA StyleLiu, Z., Zhang, A., Zheng, L., Johnathan, A.-F., Zhang, J., & Zhang, G. (2018). The Biological Significance and Regulatory Mechanism of c-Myc Binding Protein 1 (MBP-1). International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(12), 3868. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123868








