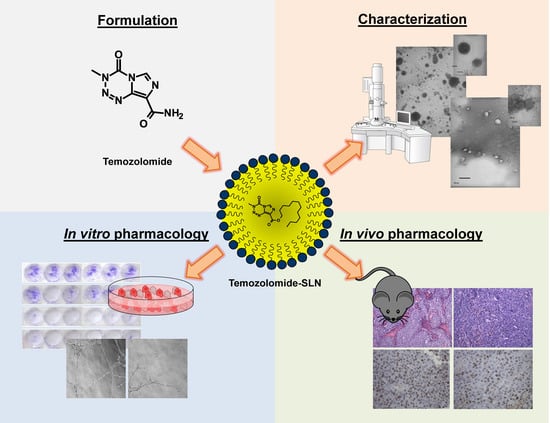
Solid Lipid Nanoparticles Carrying Temozolomide for Melanoma Treatment. Preliminary In Vitro and In Vivo Studies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Materials
4.1.1. Chemicals
4.1.2. TMZ-C12 Synthesis
4.1.3. SLN Preparation
4.1.4. SLN Characterization
4.1.5. Stability Studies in Plasma and Cell Medium
4.1.6. High Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
4.1.7. Cytotoxicity Assays
4.1.8. Clonogenic Assay
4.1.9. Tubule-Formation Assay on Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells (HUVEC)
4.2. Animal Studies
4.2.1. Histology and Immunohistochemistry on Animal Specimens
4.2.2. Real Time PCR on Tumors
4.2.3. Statistical Analysis
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stevens, M.F.; Hickman, J.A.; Stone, R.; Gibson, N.W.; Baig, G.U.; Lunt, E.; Newton, C.G. Antitumor imidazotetrazines. 1. Synthesis and chemistry of 8-carbamoyl-3-(2-chloroethyl)imidazo[5,1-d]-1,2,3,5-tetrazin-4(3H)-one, a novel broad-spectrum antitumor agent. J. Med. Chem. 1984, 27, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stupp, R.; Hegi, M.E.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.J.; Taphoorn, M.J.; Janzer, R.C.; Ludwin, S.K.; Allgeier, A.; Fisher, B.; Belanger, K.; et al. Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Clark, A.S.; Stevens, M.F.G.; Sansom, C.E.; Schwalbe, C.H. Anti-tumour imidazotetrazines. Part XXI. Mitozolomide and temozolomide: Probes for the major groove of DNA. Anticancer Drug Des. 1990, 5, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lowe, P.R.; Sansom, C.E.; Schwalbe, C.H.; Stevens, M.F.; Clark, A.S. Antitumor imidazotetrazines. 25. Crystal structure of 8-carbamoyl-3-methylimidazo[5,1-d]-1,2,3,5-tetrazin-4-(3H)-one (temozolomide) and structural comparisons with the related drugs mitozolomide and DTIC. J. Med. Chem. 1992, 35, 3377–3382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, A.S.; Deans, B.; Stevens, M.F.; Tisdale, M.J.; Wheelhouse, R.T.; Denny, B.J.; Hartley, J.A. Antitumor imidazotetrazines. 32. Synthesis of novel imidazotetrazinones and related bicyclic heterocycles to probe the mode of action of the antitumor drug temozolomide. J. Med. Chem. 1995, 38, 1493–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denny, B.J.; Wheelhouse, R.T.; Stevens, M.F.G.; Tsang, L.L.H.; Slack, J.A. NMR and molecular modeling investigation of the mechanism of activation of the antitumor drug temozolomide and its interaction with DNA. Biochemistry 1994, 33, 9045–9051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, M.; McCully, C.; Godwin, K.; Balis, F.M. Plasma and cerebrospinal fluid pharmacokinetics of temozolomide. Proc. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 1995, 14, 461a. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekeblad, S.; Sundin, A.; Janson, E.T.; Welin, S.; Granberg, D.; Kindmark, H.; Dunder, K.; Kozlovacki, G.; Orlefors, H.; Sigurd, M.; et al. Temozolomide as Monotherapy Is Effective in Treatment of Advanced Malignant Neuroendocrine Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 2986–2991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pegg, A.E.; Dolan, M.E.; Moschel, R.C. Structure, function, and inhibition of O6-alkylguanine-DNA alkyltransferase. Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol. 1995, 51, 167–223. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Reuland, S.N.; Goldstein, N.B.; Partyka, K.A.; Cooper, D.A.; Fujita, M.; Norris, D.A.; Shellman, Y.G. The combination of BH3-mimetic ABT-737 with the alkylating agent temozolomide induces strong synergistic killing of melanoma cells independent of p53. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, P.M.; Suciu, S.; Mortie, L.; Kruit, W.H.; Robert, C.; Schadendorf, D.; Trefzer, U.; Punt, C.J.; Dummer, R.; EORTC Melanoma Group. Extended schedule, escalated dose temozolomide versus dacarbazine in stage IV melanoma: Final results of a randomised phase III study (EORTC 18032). Eur. J. Cancer 2011, 47, 1476–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suppasansatorn, P.; Wang, G.; Conway, B.R.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y. Skin delivery potency and antitumor activities of temozolomide ester prodrugs. Cancer Lett. 2006, 244, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, S.S.; Kirkwood, J.M. Temozolomide, a Novel Alkylating Agent with Activity in the Central Nervous System, May Improve the Treatment of Advanced Metastatic Melanoma. Oncologist 2000, 5, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglia, L.; Gallarate, M. Lipid nanoparticles: State of the art, new preparation methods and challenges in drug delivery. Exp. Opin. Drug Deliv. 2012, 9, 497–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battaglia, L.; Gallarate, M.; Cavalli, R.; Trotta, M. Solid lipid nanoparticles produced through a coacervation method. J. Microencaps. 2010, 27, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annovazzi, L.; Schiffer, D.; Mellai, M.; Marina, G.; Luigi, B.; Daniela, C.; Elena, P.; Elisabetta, M.; Konstantin, C.; Alessandro, B.; et al. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles Loaded with Antitumor Lipophilic Prodrugs Aimed to Glioblastoma Treatment: Preliminary Studies on Cultured Cells. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2017, 17, 3606–3614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peira, E.; Chirio, D.; Battaglia, L.; Barge, A.; Chegaev, K.; Gigliotti, C.L.; Ferrara, B.; Dianzani, C.; Gallarate, M. Solid lipid nanoparticles carrying lipophilic derivatives of doxorubicin: Preparation, characterization, and in vitro cytotoxicity studies. J. Microencapsul. 2016, 33, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boggio, E.; Dianzani, C.; Gigliotti, C.L.; Soluri, M.F.; Clemente, N.; Cappellano, G.; Toth, E.; Raineri, D.; Ferrara, B.; Comi, C.; et al. Thrombin Cleavage of Osteopontin Modulates Its Activities in Human Cells In Vitro and Mouse Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis In Vivo. J Immunol Res. 2016, 2016, 9345495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurzen, H.; Schmitt, S.; Näher, H.; Möhler, T. Inhibition of angiogenesis by non-toxic doses of temozolomide. Anticancer Drugs 2003, 14, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabo, E.; Boltenko, A.; Sova, Y.; Stein, A.; Kleinhaus, S.; Resnick, M.B. Microscopic analysis and significance of vascular architectural complexity in renal cell carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 7, 533–537. [Google Scholar]
- Kumari, S.; Ahsan, S.M.; Kumar, J.M.; Kondapi, A.K.; Rao, N.M. Overcoming blood brain barrier with a dual purpose Temozolomide loaded Lactoferrin nanoparticles for combating glioma (SERP-17-12433). Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.S.; Rait, A.; Kim, E.; DeMarco, J.; Pirollo, K.F.; Chang, E.H. Encapsulation of temozolomide in a tumor-targeting nanocomplex enhances anti-cancer efficacy and reduces toxicity in a mouse model of glioblastoma. Cancer Lett. 2015, 369, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, C.; Wang, K.; Stephen, Z.R.; Mu, Q.; Kievit, F.M.; Chiu, D.T.; Press, O.W.; Zhang, M. Temozolomide nanoparticles for targeted glioblastoma therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2015, 7, 6674–6682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ananta, J.S.; Paulmurugan, R.; Massoud, T.F. Temozolomide-loaded PLGA nanoparticles to treat glioblastoma cells: A biophysical and cell culture evaluation. Neurol. Res. 2016, 38, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, G.; Sun, C.; Li, R.; Wei, Z.P.; Zheng, J.N.; Liu, Y.Q. Enhanced antitumor efficacy of a novel oncolytic adenovirus combined with temozolomide in the treatment of melanoma in vivo. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 141, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathieu, V.; le Mercier, M.; de Neve, N.; Sauvage, S.; Gras, T.; Roland, I.; Lefranc, F.; Kiss, R. Galectin-1 Knockdown Increases Sensitivity to Temozolomide in a B16F10 Mouse Metastatic Melanoma Model. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2007, 127, 2399–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Middleton, M.R.; Kelly, J.; Thatcher, N.; Donnelly, D.J.; McElhinney, R.S.; McMurry, T.B.H.; McCormick, J.E.; Margison, G.P. O6-(4-bromothenyl)guanine improves the therapeutic index of temozolomide against A375M melanoma xenografts. Int. J. Cancer 2000, 85, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmali, R.A.; Maxuitenko, Y.Y.; Gorman, G.S.; Qu, Z. Combinatorial treatment with carboxyamidotriazoleorotate and temozolomide in sc-implanted human LOX IMVI melanoma xenografts. J. Solid Tumors 2012, 2, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallarate, M.; Serpe, L.; Foglietta, F.; Zara, G.P.; Giordano, S.; Peira, E.; Chirio, D.; Battaglia, L. Solid lipid nanoparticles loaded with fluorescent-labelled Cyclosporine A: Anti-inflammatory activity in vitro. Protein Pept. Lett. 2014, 21, 1157–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert, C.; Thomas, L.; Bondarenko, I.; O′Day, S.; Weber, J.; Garbe, C.; Lebbe, C.; Baurain, J.F.; Testori, A.; Grob, J.J.; et al. Ipilimumab plus dacarbazine for previously untreated metastatic melanoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 2517–2526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrera, G.; Daga, M.; Ferrara, B.; Dianzani, C.; Pizzimenti, S.; Argenziano, M.; Cavalli, R.; Trotta, F. Drug delivery nanoparticles in treating chemoresistant tumor cells. Curr. Med. Chem. 2017, 24, 4800–4815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pizzimenti, S.; Dianzani, C.; Zara, G.P.; Barrera, G. Challenges and Opportunities of Nanoparticle-based Theranostics in Skin Cancer. In Nanoscience in Dermatology; Hamblin, M.R., Avci, P., Prow, T.W., Eds.; Elsevier: London, UK, 2016; pp. 177–188. [Google Scholar]
- Daga, M.; Dianzani, C.; Ferrara, B.; Nardozza, V.; Cavalli, R.; Barrera, G.; Pizzimenti, S. Latest News on Nanotechnology for Melanoma Therapy and Diagnosis. SM J. Neurol. Neurosci. 2016, 2, 1005. [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson, V. Recent advances in malignant melanoma. Intern. Med. J. 2017, 47, 1114–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, G.; Li, R.; Tang, J.; Ma, Y.; Hou, X.; Yang, C.; Guo, W.; Xin, Y.; Liu, Y. Formulation of temozolomide-loaded nanoparticles and their targeting potential to melanoma cells. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 995–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehrke, S.; Otsuka, A.; Huber, R.; Meier, B.; Kistowska, M.; Fenini, G.; Cheng, P.; Dummer, R.; Kerl, K.; Contassot, E.; et al. Metastatic melanoma cell lines do not secrete IL-1beta but promote IL-1beta production from macrophages. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2014, 74, 167–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malori, W.; Formisano, G.; Molinari, A. In vitro effects of 2,5 hexanedione on a melanoma cell line: A morphological study. Toxicology 1987, 43, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Method 1 | Method 2 | |
|---|---|---|
| 80% Hydrolyzed polyvinyl alcohol of 9000–10,000 MW (PVA9000) | 200 mg | 200 mg |
| Sodium behenate | 100 mg | 100 mg |
| NaOH 1 M | 120 μL | |
| Na2HPO4 1 M | 200 μL | |
| NH4Cl 5 M | 260 μL | |
| HCl 1 M | 400 μL | 400 μL |
| TMZ-C12 | 4 mg in 400 μL dimethylformammide (DMF) | |
| Deionized Water | 10 mL |
| Particle Size | Polydispersity | EE% Efficiency (Centrifugation) | EE% Efficiency (Gel Filtration) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank SLN method 1 | 400.1 ± 65 nm | 0.269 ± 0.83 | - | - |
| Blank SLN method 2 | 278.6 ± 4 nm | 0.066 ± 0.01 | - | - |
| Concentrated blank SLN | 278.8 ± 28 nm | 0.052 ± 0.02 | - | - |
| SLN-TMZ | 279.0 ± 50 nm | 0.038 ± 0.01 | 93.10 ± 3.29 | 57.91 ± 21.70 |
| Concentrated SLN-TMZ | 273.15 ± 5 nm | 0.084 ± 0.01 | 91.10 ± 0.22 | N.D. |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Clemente, N.; Ferrara, B.; Gigliotti, C.L.; Boggio, E.; Capucchio, M.T.; Biasibetti, E.; Schiffer, D.; Mellai, M.; Annovazzi, L.; Cangemi, L.; et al. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles Carrying Temozolomide for Melanoma Treatment. Preliminary In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020255
Clemente N, Ferrara B, Gigliotti CL, Boggio E, Capucchio MT, Biasibetti E, Schiffer D, Mellai M, Annovazzi L, Cangemi L, et al. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles Carrying Temozolomide for Melanoma Treatment. Preliminary In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(2):255. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020255
Chicago/Turabian StyleClemente, Nausicaa, Benedetta Ferrara, Casimiro Luca Gigliotti, Elena Boggio, Maria Teresa Capucchio, Elena Biasibetti, Davide Schiffer, Marta Mellai, Laura Annovazzi, Luigi Cangemi, and et al. 2018. "Solid Lipid Nanoparticles Carrying Temozolomide for Melanoma Treatment. Preliminary In Vitro and In Vivo Studies" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 2: 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020255
APA StyleClemente, N., Ferrara, B., Gigliotti, C. L., Boggio, E., Capucchio, M. T., Biasibetti, E., Schiffer, D., Mellai, M., Annovazzi, L., Cangemi, L., Muntoni, E., Miglio, G., Dianzani, U., Battaglia, L., & Dianzani, C. (2018). Solid Lipid Nanoparticles Carrying Temozolomide for Melanoma Treatment. Preliminary In Vitro and In Vivo Studies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(2), 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020255