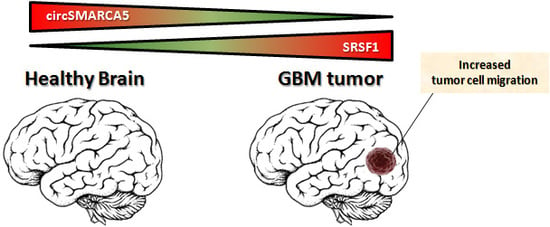
CircSMARCA5 Inhibits Migration of Glioblastoma Multiforme Cells by Regulating a Molecular Axis Involving Splicing Factors SRSF1/SRSF3/PTB
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. CircRNA Expression Profile
2.3. CircSMARCA5 Cloning and Expression in GBM Cells
2.4. CircSMARCA5 Inhibits GBM Cells Migration without Altering Cell Viability
2.5. CircSMARCA5 Is Predicted to Function as Modulator of Several RBPs
2.6. Splicing of Serine and Arginine Rich Splicing Factor 3 (SRSF3) Is Regulated by CircSMARCA5
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. GBM Specimens and Cell Lines
4.2. Immunohistochemistry
4.3. Constructs and Transfections
4.4. RNA Extraction
4.5. CircRNA Candidates Selection and Primer Design
4.6. Northern Blotting
4.7. qRT-PCR
4.8. Cell Migration Assay
4.9. Cell Viability Assay
4.10. In Silico Analysis
4.11. eCLIP Analysis
4.12 TCGA Data
4.13 Nomenclature of Genes and Proteins
4.14. Statistical Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Memczak, S.; Jens, M.; Elefsinioti, A.; Torti, F.; Krueger, J.; Rybak, A.; Maier, L.; Mackowiak, S.D.; Gregersen, L.H.; Munschauer, M.; et al. Circular RNAs are a large class of animal RNAs with regulatory potency. Nature 2013, 495, 333–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, I.; Chen, C.Y.; Chuang, T.J. Biogenesis, identification, and function of exonic circular RNAs. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2015, 6, 563–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.O.; Chen, T.; Xiang, J.F.; Yin, Q.F.; Xing, Y.H.; Zhu, S.; Yang, L.; Chen, L.L. Circular intronic long noncoding RNAs. Mol. Cell 2013, 51, 792–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Huang, C.; Bao, C.; Chen, L.; Lin, M.; Wang, X.; Zhong, G.; Yu, B.; Hu, W.; Dai, L.; et al. Exon-intron circular RNAs regulate transcription in the nucleus. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2015, 22, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicens, Q.; Westhof, E. Biogenesis of Circular RNAs. Cell 2014, 159, 13–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conn, S.J.; Pillman, K.A.; Toubia, J.; Conn, V.M.; Salmanidis, M.; Phillips, C.A.; Roslan, S.; Schreiber, A.W.; Gregory, P.A.; Goodall, G.J. The RNA binding protein quaking regulates formation of circRNAs. Cell 2015, 160, 1125–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, H.; Tsukahara, T. A view of pre-mRNA splicing from RNase R resistant RNAs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 9331–9342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salzman, J.; Chen, R.E.; Olsen, M.N.; Wang, P.L.; Brown, P.O. Cell-type specific features of circular RNA expression. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeck, W.R.; Sorrentino, J.A.; Wang, K.; Slevin, M.K.; Burd, C.E.; Liu, J.; Marzluff, W.F.; Sharpless, N.E. Circular RNAs are abundant, conserved, and associated with ALU repeats. RNA 2013, 19, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lasda, E.; Parker, R. Circular RNAs: Diversity of form and function. RNA 2014, 20, 1829–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rybak-Wolf, A.; Stottmeister, C.; Glazar, P.; Jens, M.; Pino, N.; Giusti, S.; Hanan, M.; Behm, M.; Bartok, O.; Ashwal-Fluss, R.; et al. Circular RNAs in the Mammalian Brain Are Highly Abundant, Conserved, and Dynamically Expressed. Mol. Cell 2015, 58, 870–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruner, H.; Cortes-Lopez, M.; Cooper, D.A.; Bauer, M.; Miura, P. CircRNA accumulation in the aging mouse brain. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 38907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahn, J.H.; Zhang, Q.; Li, F.; Chan, T.M.; Lin, X.; Kim, Y.; Wong, D.T.; Xiao, X. The landscape of microRNA, Piwi-interacting RNA, and circular RNA in human saliva. Clin. Chem. 2015, 61, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Bao, C.; Li, S.; Guo, W.; Zhao, J.; Chen, D.; Gu, J.; He, X.; Huang, S. Circular RNA is enriched and stable in exosomes: A promising biomarker for cancer diagnosis. Cell Res. 2015, 25, 981–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Memczak, S.; Papavasileiou, P.; Peters, O.; Rajewsky, N. Identification and Characterization of Circular RNAs as a New Class of Putative Biomarkers in Human Blood. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Pietro, V.; Ragusa, M.; Davies, D.; Su, Z.; Hazeldine, J.; Lazzarino, G.; Hill, L.J.; Crombie, N.; Foster, M.; Purrello, M.; et al. MicroRNAs as Novel Biomarkers for the Diagnosis and Prognosis of Mild and Severe Traumatic Brain Injury. J. Neurotrauma 2017, 34, 1948–1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romano, G.L.; Platania, C.B.M.; Drago, F.; Salomone, S.; Ragusa, M.; Barbagallo, C.; Di Pietro, C.; Purrello, M.; Reibaldi, M.; Avitabile, T.; et al. Retinal and Circulating miRNAs in Age-Related Macular Degeneration: An In vivo Animal and Human Study. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristensen, L.S.; Hansen, T.B.; Veno, M.T.; Kjems, J. Circular RNAs in cancer: Opportunities and challenges in the field. Oncogene 2018, 37, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbagallo, D.; Condorelli, A.; Ragusa, M.; Salito, L.; Sammito, M.; Banelli, B.; Caltabiano, R.; Barbagallo, G.; Zappala, A.; Battaglia, R.; et al. Dysregulated miR-671-5p/CDR1-AS/CDR1/VSNL1 axis is involved in glioblastoma multiforme. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 4746–4759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragusa, M.; Barbagallo, C.; Statello, L.; Condorelli, A.G.; Battaglia, R.; Tamburello, L.; Barbagallo, D.; Di Pietro, C.; Purrello, M. Non-coding landscapes of colorectal cancer. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 11709–11739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, T.B.; Jensen, T.I.; Clausen, B.H.; Bramsen, J.B.; Finsen, B.; Damgaard, C.K.; Kjems, J. Natural RNA circles function as efficient microRNA sponges. Nature 2013, 495, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Q.; Bao, C.; Guo, W.; Li, S.; Chen, J.; Chen, B.; Luo, Y.; Lyu, D.; Li, Y.; Shi, G.; et al. Circular RNA profiling reveals an abundant circHIPK3 that regulates cell growth by sponging multiple miRNAs. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashwal-Fluss, R.; Meyer, M.; Pamudurti, N.R.; Ivanov, A.; Bartok, O.; Hanan, M.; Evantal, N.; Memczak, S.; Rajewsky, N.; Kadener, S. circRNA biogenesis competes with pre-mRNA splicing. Mol. Cell 2014, 56, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelmohsen, K.; Panda, A.C.; Munk, R.; Grammatikakis, I.; Dudekula, D.B.; De, S.; Kim, J.; Noh, J.H.; Kim, K.M.; Martindale, J.L.; et al. Identification of HuR target circular RNAs uncovers suppression of PABPN1 translation by CircPABPN1. RNA Biol. 2017, 14, 361–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, W.W.; Yang, W.; Chen, Y.; Wu, Z.K.; Foster, F.S.; Yang, Z.; Li, X.; Yang, B.B. Foxo3 circular RNA promotes cardiac senescence by modulating multiple factors associated with stress and senescence responses. Eur. Heart J. 2017, 38, 1402–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, W.W.; Yang, W.; Liu, E.; Yang, Z.; Dhaliwal, P.; Yang, B.B. Foxo3 circular RNA retards cell cycle progression via forming ternary complexes with p21 and CDK2. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, 2846–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holdt, L.M.; Stahringer, A.; Sass, K.; Pichler, G.; Kulak, N.A.; Wilfert, W.; Kohlmaier, A.; Herbst, A.; Northoff, B.H.; Nicolaou, A.; et al. Circular non-coding RNA ANRIL modulates ribosomal RNA maturation and atherosclerosis in humans. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.G.; Awan, F.M.; Du, W.W.; Zeng, Y.; Lyu, J.; Gupta, S.; Yang, W.; Yang, B.B. The Circular RNA Interacts with STAT3, Increasing Its Nuclear Translocation and Wound Repair by Modulating Dnmt3a and miR-17 Function. Mol. Ther. 2017, 25, 2062–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghigna, C.; Giordano, S.; Shen, H.; Benvenuto, F.; Castiglioni, F.; Comoglio, P.M.; Green, M.R.; Riva, S.; Biamonti, G. Cell motility is controlled by SF2/ASF through alternative splicing of the Ron protooncogene. Mol. Cell 2005, 20, 881–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.; Zhang, N.; Han, P.; Moon, B.S.; Lai, R.K.; Wang, K.; Lu, W. Circular RNA profile in gliomas revealed by identification tool UROBORUS. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, e87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jumaa, H.; Nielsen, P.J. The splicing factor SRp20 modifies splicing of its own mRNA and ASF/SF2 antagonizes this regulation. EMBO J. 1997, 16, 5077–5085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siede, D.; Rapti, K.; Gorska, A.A.; Katus, H.A.; Altmuller, J.; Boeckel, J.N.; Meder, B.; Maack, C.; Volkers, M.; Muller, O.J.; et al. Identification of circular RNAs with host gene-independent expression in human model systems for cardiac differentiation and disease. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2017, 109, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Jia, J.; Jia, R. PTBP1 and PTBP2 impaired autoregulation of SRSF3 in cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lareau, L.F.; Inada, M.; Green, R.E.; Wengrod, J.C.; Brenner, S.E. Unproductive splicing of SR genes associated with highly conserved and ultraconserved DNA elements. Nature 2007, 446, 926–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, J.Z.; Grate, L.; Donohue, J.P.; Preston, C.; Nobida, N.; O’Brien, G.; Shiue, L.; Clark, T.A.; Blume, J.E.; Ares, M., Jr. Ultraconserved elements are associated with homeostatic control of splicing regulators by alternative splicing and nonsense-mediated decay. Genes Dev. 2007, 21, 708–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Krainer, A.R. Emerging functions of SRSF1, splicing factor and oncoprotein, in RNA metabolism and cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2014, 12, 1195–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dvinge, H.; Kim, E.; Abdel-Wahab, O.; Bradley, R.K. RNA splicing factors as oncoproteins and tumour suppressors. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 413–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, H.C.; Hai, T.; Zhu, W.; Baggerly, K.A.; Tsavachidis, S.; Krahe, R.; Cote, G.J. Splicing factors PTBP1 and PTBP2 promote proliferation and migration of glioma cell lines. Brain 2009, 132 Pt 8, 2277–2288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, D.N.; Ohgaki, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Cavenee, W.K.; Burger, P.C.; Jouvet, A.; Scheithauer, B.W.; Kleihues, P. The 2007 WHO classification of tumours of the central nervous system. Acta Neuropathol. 2007, 114, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Caltabiano, R.; Puzzo, L.; Barresi, V.; Ieni, A.; Loreto, C.; Musumeci, G.; Castrogiovanni, P.; Ragusa, M.; Foti, P.; Russo, A.; et al. ADAM 10 expression in primary uveal melanoma as prognostic factor for risk of metastasis. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2016, 212, 980–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragusa, M.; Statello, L.; Maugeri, M.; Majorana, A.; Barbagallo, D.; Salito, L.; Sammito, M.; Santonocito, M.; Angelica, R.; Cavallaro, A.; et al. Specific alterations of the microRNA transcriptome and global network structure in colorectal cancer after treatment with MAPK/ERK inhibitors. J. Mol. Med. (Berl.) 2012, 90, 1421–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbagallo, D.; Piro, S.; Condorelli, A.G.; Mascali, L.G.; Urbano, F.; Parrinello, N.; Monello, A.; Statello, L.; Ragusa, M.; Rabuazzo, A.M.; et al. miR-296-3p, miR-298-5p and their downstream networks are causally involved in the higher resistance of mammalian pancreatic alpha cells to cytokine-induced apoptosis as compared to beta cells. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paz, I.; Kosti, I.; Ares, M., Jr.; Cline, M.; Mandel-Gutfreund, Y. RBPmap: A web server for mapping binding sites of RNA-binding proteins. Nucl. Acids Res. 2014, 42, W361–W367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wain, H.M.; Bruford, E.A.; Lovering, R.C.; Lush, M.J.; Wright, M.W.; Povey, S. Guidelines for human gene nomenclature. Genomics 2002, 79, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Type of Samples | N° of Samples | Mean Age (Years ± StdDev) | Sex | Mean Overall Survival (Months) | Preoperative Tumor Volume (mm3) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M | F | |||||
| Training set (Fresh-frozen biopsies) | 10 | 60.5 ± 12.1 | 5 | 5 | 19.1 ± 7.2 | 39.9 ± 11.8 |
| Test set (FFPE biopsies) | 56 | 62 ± 12.7 | 33 | 23 | 17 ± 14.2 | 28.2 ± 9.2 |
| Normal Brain Parenchyma | 7 | 60.4 ± 11.1 | 2 | 5 | ||
| FirstChoice® Human Brain Reference Total RNA | 1 (commercially available) | 68.3 ± 15 | 13 | 10 | ||
| # | Candidate circRNA (circBase ID) | Parental Gene Symbol | Known Modulation or Function of circRNA Expression in Specific Cell Context | Source (PMID) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | hsa_circ_0028270 | ATXN2 | Upregulated during EMT. This circRNA is also highly expressed in several SNC districts (see PMID: 25921068) | 25768908 |
| 2 | hsa_circ_0008702 | GNB1 | Downregulated during EMT. This circRNA is also highly expressed in several SNC districts (see PMID: 25921068) | 25768908 |
| 3 | hsa_circ_0000284 | HIPK3 | Involved in cell growth. Highly expressed in normal Brain | 27050392 |
| 4 | hsa_circ_0008002 | POLE2 | Upregulated during EMT. This circRNA is also highly expressed in several SNC districts (see PMID: 25921068) | 25768908 |
| 5 | hsa_circ_0132250 | RIMS1 | Downregulated in GBM vs. Normal Brain (another dataset) | 26873924 |
| 6 | hsa_circ_0099634 | Rmst | LncRNA Rmst (host gene of the same name circ_Rmst) regulates neuronal differentiation in mouse | 25921068 |
| 7 | hsa_circ_0054598 | RTN4 | Upregulated during neuronal differentiation both in humans and mice | 25921068 |
| 8 | hsa_circ_0001649 | SHPRH | Upregulated during EMT. This circRNA is also highly expressed in several SNC districts (see PMID: 25921068) | 25768908 |
| 9 | hsa_circ_0003694 | SMAD2 | Upregulated during EMT. This circRNA is also highly expressed in several SNC districts (see PMID: 25921068) | 25768908 |
| 10 | hsa_circ_0001445 | SMARCA5 | Upregulated during EMT. This circRNA is also highly expressed in several SNC districts (see PMID: 25921068) | 25768908 |
| 11 | hsa_circ_0073237 | VCAN | Upregulated in GBM vs. Normal Brain (another dataset) | 26873924 |
| 12 | hsa_circ_0004383 | ZNF292 | Upregulated in HUVEC under hypoxia. Its silencing reduces endothelial cell proliferation and suppresses tube formation by inhibiting glioma cell proliferation and cell cycle progression in human glioma U87MG and U251 cells | 26377962; 27613831 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Barbagallo, D.; Caponnetto, A.; Cirnigliaro, M.; Brex, D.; Barbagallo, C.; D’Angeli, F.; Morrone, A.; Caltabiano, R.; Barbagallo, G.M.; Ragusa, M.; et al. CircSMARCA5 Inhibits Migration of Glioblastoma Multiforme Cells by Regulating a Molecular Axis Involving Splicing Factors SRSF1/SRSF3/PTB. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 480. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020480
Barbagallo D, Caponnetto A, Cirnigliaro M, Brex D, Barbagallo C, D’Angeli F, Morrone A, Caltabiano R, Barbagallo GM, Ragusa M, et al. CircSMARCA5 Inhibits Migration of Glioblastoma Multiforme Cells by Regulating a Molecular Axis Involving Splicing Factors SRSF1/SRSF3/PTB. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(2):480. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020480
Chicago/Turabian StyleBarbagallo, Davide, Angela Caponnetto, Matilde Cirnigliaro, Duilia Brex, Cristina Barbagallo, Floriana D’Angeli, Antonio Morrone, Rosario Caltabiano, Giuseppe Maria Barbagallo, Marco Ragusa, and et al. 2018. "CircSMARCA5 Inhibits Migration of Glioblastoma Multiforme Cells by Regulating a Molecular Axis Involving Splicing Factors SRSF1/SRSF3/PTB" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 2: 480. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020480
APA StyleBarbagallo, D., Caponnetto, A., Cirnigliaro, M., Brex, D., Barbagallo, C., D’Angeli, F., Morrone, A., Caltabiano, R., Barbagallo, G. M., Ragusa, M., Di Pietro, C., Hansen, T. B., & Purrello, M. (2018). CircSMARCA5 Inhibits Migration of Glioblastoma Multiforme Cells by Regulating a Molecular Axis Involving Splicing Factors SRSF1/SRSF3/PTB. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(2), 480. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020480