Perineuronal Nets in Spinal Motoneurones: Chondroitin Sulphate Proteoglycan around Alpha Motoneurones
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. WFA-Positive PNNs Only Partially Overlap with Other CSPGs in the Ventral Motor Pools
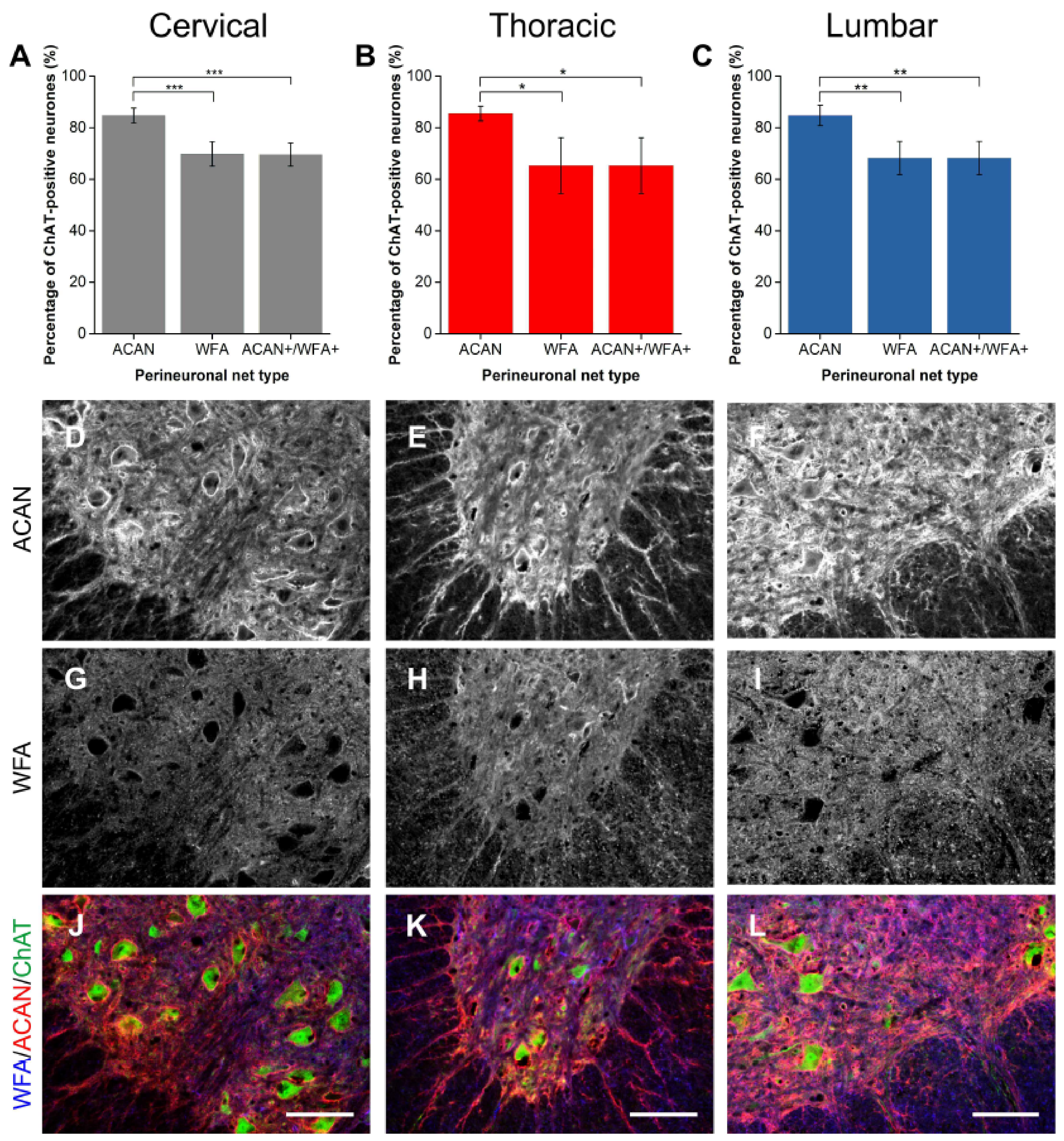
2.1.1. ACAN
2.1.2. BCAN
2.1.3. NCAN
2.1.4. VCAN
2.1.5. PTPRZ
2.2. Distinct Populations of CSPG-Positive yet WFA-Negative PNNs in the Motor Pools
2.3. Alpha Mns Are Preferentially Surrounded by PNNs
3. Discussion
3.1. PNNs in the Spinal Ventral Motor Pools
3.2. Differences in PNNs between the Brain and Spinal Cord
3.3. Composition of PNNs in the Spinal Motor Pools
3.4. Further Research and Conclusions
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Tissue Preparation
4.3. Staining Procedures
4.4. Image Acquisition and Quantification Methods
4.5. Experimental Design and Statistical Analysis
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACAN | Aggrecan core protein |
| BCAN | Brevican core protein |
| ChAT | Choline acetyltransferase |
| ChABC | Chondroitinase ABC |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| CS-GAG | Chondroitin sulphate glycosaminoglycan |
| CSPGs | Chondroitin sulphate proteoglycans |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| GalNAc | N-acetylgalactosamine |
| HA | Hyaluronic acid/hyaluronan |
| Mn | Motoneurone |
| NeuN | Neuron-specific nuclear protein |
| NCAN | Neurocan core protein |
| PTPRZ | Phosphacan/protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor zeta |
| PNN | Perineuronal net |
| Mn | Motoneurone |
| SCI | Spinal cord injury |
| VCAN | Versican core protein |
| WFA | Wisteria floribunda agglutinin |
References
- Celio, M.R.; Spreafico, R.; De Biasi, S.; Vitellaro-Zuccarello, L. Perineuronal nets: Past and present. Trends Neurosci. 1998, 21, 510–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suttkus, A.; Rohn, S.; Weigel, S.; Glöckner, P.; Arendt, T.; Morawski, M. Aggrecan, link protein and tenascin-R are essential components of the perineuronal net to protect neurons against iron-induced oxidative stress. Cell Death Dis. 2014, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cabungcal, J.-H.H.; Steullet, P.; Morishita, H.; Kraftsik, R.; Cuenod, M.; Hensch, T.K.; Do, K.Q. Perineuronal nets protect fast-spiking interneurons against oxidative stress. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 9130–9135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pantazopoulos, H.; Berretta, S. In Sickness and in Health: Perineuronal Nets and Synaptic Plasticity in Psychiatric Disorders. Neural Plast. 2016, 2016, 9847696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McRae, P.A.; Porter, B.E. The perineuronal net component of the extracellular matrix in plasticity and epilepsy. Neurochem. Int. 2012, 61, 963–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, L.D.F.; Asher, R.A.; Rhodes, K.E.; Fawcett, J.W. Regeneration of CNS axons back to their target following treatment of adult rat brain with chondroitinase ABC. Nat. Neurosci. 2001, 4, 465–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradbury, E.J.; Moon, L.D.; Popat, R.J.; King, V.R.; Bennett, G.S.; Patel, P.N.; Fawcett, J.W.; McMahon, S.B. Chondroitinase ABC promotes functional recovery after spinal cord injury. Nature 2002, 416, 636–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Alías, G.; Barkhuysen, S.; Buckle, M.; Fawcett, J.W. Chondroitinase ABC treatment opens a window of opportunity for task-specific rehabilitation. Nat. Neurosci. 2009, 12, 1145–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carulli, D.; Pizzorusso, T.; Kwok, J.C.; Putignano, E.; Poli, A.; Forostyak, S.; Andrews, M.R.; Deepa, S.S.; Glant, T.T.; Fawcett, J.W. Animals lacking link protein have attenuated perineuronal nets and persistent plasticity. Brain 2010, 133, 2331–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizzorusso, T.; Medini, P.; Berardi, N.; Chierzi, S.; Fawcett, J.W.; Maffei, L. Reactivation of ocular dominance plasticity in the adult visual cortex. Science 2002, 298, 1248–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsien, R.Y. Very long-term memories may be stored in the pattern of holes in the perineuronal net. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 12456–12461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giamanco, K.A.; Morawski, M.; Matthews, R.T. Perineuronal net formation and structure in aggrecan knockout mice. Neuroscience 2010, 170, 1314–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwok, J.C.; Carulli, D.; Fawcett, J.W. In vitro modeling of perineuronal nets: Hyaluronan synthase and link protein are necessary for their formation and integrity. J. Neurochem. 2010, 114, 1447–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kwok, J.C.; Dick, G.; Wang, D.; Fawcett, J.W. Extracellular matrix and perineuronal nets in CNS repair. Dev. Neurobiol. 2011, 71, 1073–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, Y. Lecticans: Organizers of the brain extracellular matrix. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2000, 57, 276–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitagawa, H. Using sugar remodeling to study chondroitin sulfate function. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2014, 37, 1705–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Gama, C.I.; Tully, S.E.; Sotogaku, N.; Clark, P.M.; Rawat, M.; Vaidehi, N.; Goddard, W.A.; Nishi, A.; Hsieh-Wilson, L.C. Sulfation patterns of glycosaminoglycans encode molecular recognition and activity. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2006, 2, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deepa, S.S.; Carulli, D.; Galtrey, C.; Rhodes, K.; Fukuda, J.; Mikami, T.; Sugahara, K.; Fawcett, J.W. Composition of perineuronal net extracellular matrix in rat brain: A different disaccharide composition for the net-associated proteoglycans. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 17789–17800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carulli, D.; Rhodes, K.E.; Brown, D.J.; Bonnert, T.P.; Pollack, S.J.; Oliver, K.; Strata, P.; Fawcett, J.W. Composition of perineuronal nets in the adult rat cerebellum and the cellular origin of their components. J. Comp. Neurol. 2006, 494, 559–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fader, S.M.; Imaizumi, K.; Yanagawa, Y.; Lee, C.C. Wisteria Floribunda Agglutinin-Labeled Perineuronal Nets in the Mouse Inferior Colliculus, Thalamic Reticular Nucleus and Auditory Cortex. Brain Sci. 2016, 6, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, J.; Jinno, S. Molecular heterogeneity of aggrecan-based perineuronal nets around five subclasses of parvalbumin-expressing neurons in the mouse hippocampus. J. Comp. Neurol. 2017, 525, 1234–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitellaro-Zuccarello, L.; Bosisio, P.; Mazzetti, S.; Monti, C.; De Biasi, S. Differential expression of several molecules of the extracellular matrix in functionally and developmentally distinct regions of rat spinal cord. Cell Tissue Res. 2007, 327, 433–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brauer, K.; Härtig, W.; Bigl, V.; Brückner, G. Distribution of parvalbumin-containing neurons and lectin-binding perineuronal nets in the rat basal forebrain. Brain Res. 1993, 631, 167–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, J.; Ohgomori, T.; Jinno, S. Perineuronal nets affect parvalbumin expression in GABAergic neurons of the mouse hippocampus. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2015, 41, 368–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galtrey, C.M.; Kwok, J.C.; Carulli, D.; Rhodes, K.E.; Fawcett, J.W. Distribution and synthesis of extracellular matrix proteoglycans, hyaluronan, link proteins and tenascin-R in the rat spinal cord. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2008, 27, 1373–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertolotto, A.; Manzardo, E.; Guglielmone, R. Immunohistochemical mapping of perineuronal nets containing chondroitin unsulfate proteoglycan in the rat central nervous system. Cell Tissue Res. 1996, 283, 283–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi-Iwanaga, H.; Murakami, T.; Abe, K. Three-dimensional microanatomy of perineuronal proteoglycan nets enveloping motor neurons in the rat spinal cord. J. Neurocytol. 1998, 27, 817–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manuel, M.; Zytnicki, D. Alpha, beta and gamma motoneurons: Functional diversity in the motor system’s final pathway. J. Integr. Neurosci. 2011, 10, 243–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, R.-R.R.; Andrews, M.R.; Wang, D.; Warren, P.; Gullo, M.; Schnell, L.; Schwab, M.E.; Fawcett, J.W. Combination treatment with anti-Nogo-A and chondroitinase ABC is more effective than single treatments at enhancing functional recovery after spinal cord injury. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2013, 38, 2946–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barritt, A.W.; Davies, M.; Marchand, F.; Hartley, R.; Grist, J.; Yip, P.; McMahon, S.B.; Bradbury, E.J. Chondroitinase ABC Promotes Sprouting of Intact and Injured Spinal Systems after Spinal Cord Injury. J. Neurosci. 2006, 26, 10856–10867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.C.; Mauricio, R.; Nobre, L.; Marsh, B.; Wüst, R.C.; Rossiter, H.B.; Ichiyama, R.M. Differential regulation of perineuronal nets in the brain and spinal cord with exercise training. Brain Res. Bull. 2015, 111, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Ichiyama, R.M.; Zhao, R.; Andrews, M.R.; Fawcett, J.W. Chondroitinase combined with rehabilitation promotes recovery of forelimb function in rats with chronic spinal cord injury. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 9332–9344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barber, R.P.; Phelps, P.E.; Houser, C.R.; Crawford, G.D.; Salvaterra, P.M.; Vaughn, J.E. The morphology and distribution of neurons containing choline acetyltransferase in the adult rat spinal cord: An immunocytochemical study. J. Comp. Neurol. 1984, 229, 329–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koppe, G.; Bruckner, G.; Hartig, W.; Delpech, B.; Bigl, V. Characterization of proteoglycan-containing perineuronal nets by enzymatic treatments of rat brain sections. Histochem. J. 1997, 29, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morawski, M.; Brückner, G.; Arendt, T.; Matthews, R.T. Aggrecan: Beyond cartilage and into the brain. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2012, 44, 690–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lendvai, D.; Morawski, M.; Négyessy, L.; Gáti, G.; Jäger, C.; Baksa, G.; Glasz, T.; Attems, J.; Tanila, H.; Arendt, T.; et al. Neurochemical mapping of the human hippocampus reveals perisynaptic matrix around functional synapses in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2013, 125, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Favuzzi, E.; Marques-Smith, A.; Deogracias, R.; Winterflood, C.M.; Sánchez-Aguilera, A.; Mantoan, L.; Maeso, P.; Fernandes, C.; Ewers, H.; Rico, B. Activity-Dependent Gating of Parvalbumin Interneuron Function by the Perineuronal Net Protein Brevican. Neuron 2017, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asher, R.A.; Morgenstern, D.A.; Fidler, P.S.; Adcock, K.H.; Oohira, A.; Braistead, J.E.; Levine, J.M.; Margolis, R.U.; Rogers, J.H.; Fawcett, J.W. Neurocan is upregulated in injured brain and in cytokine-treated astrocytes. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 2427–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dours-Zimmermann, M.T.; Maurer, K.; Rauch, U.; Stoffel, W.; Fässler, R.; Zimmermann, D.R. Versican V2 Assembles the Extracellular Matrix Surrounding the Nodes of Ranvier in the CNS. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 7731–7742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asher, R.A.; Morgenstern, D.A.; Shearer, M.C.; Adcock, K.H.; Pesheva, P.; Fawcett, J.W. Versican is upregulated in CNS injury and is a product of oligodendrocyte lineage cells. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 2225–2236. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maurel, P.; Rauch, U.; Flad, M.; Margolis, R.K.; Margolis, R.U. Phosphacan, a chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan of brain that interacts with neurons and neural cell-adhesion molecules, is an extracellular variant of a receptor-type protein tyrosine phosphatase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 2512–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwyer, C.A.; Katoh, T.; Tiemeyer, M.; Matthews, R.T. Neurons and Glia Modify Receptor Protein-tyrosine Phosphatase ζ (RPTPζ)/Phosphacan with Cell-specific O-Mannosyl Glycans in the Developing Brain. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 10256–10273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haunsø, A.; Celio, M.R.; Margolis, R.K.; Menoud, P.-A. Phosphacan immunoreactivity is associated with perineuronal nets around parvalbumin-expressing neurones. Brain Res. 1999, 834, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friese, A.; Kaltschmidt, J.A.; Ladle, D.R.; Sigrist, M.; Jessell, T.M.; Arber, S. Gamma and alpha motor neurons distinguished by expression of transcription factor Err3. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 13588–13593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, A.L.; Davis, A.; Sovich, S.; Carlson, S.S.; Robinson, F.R. Distribution of N-Acetylgalactosamine-Positive Perineuronal Nets in the Macaque Brain: Anatomy and Implications. Neural Plast. 2016, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jäger, C.; Lendvai, D.; Seeger, G.; Brückner, G.; Matthews, R.T.; Arendt, T.; Alpár, A.; Morawski, M. Perineuronal and perisynaptic extracellular matrix in the human spinal cord. Neuroscience 2013, 238, 168–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shneider, N.A.; Brown, M.N.; Smith, C.A.; Pickel, J.; Alvarez, F.J. Gamma motor neurons express distinct genetic markers at birth and require muscle spindle-derived GDNF for postnatal survival. Neural Dev. 2009, 4, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eccles, J.C.; Eccles, R.M.; Iggo, A.; Lundberg, A. Electrophysiological studies on gamma motoneurones. Acta Physiol. Scand. 1960, 50, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misawa, H.; Hara, M.; Tanabe, S.; Niikura, M.; Moriwaki, Y.; Okuda, T. Osteopontin is an alpha motor neuron marker in the mouse spinal cord. J. Neurosci. Res. 2012, 90, 732–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Härtig, W.; Brauer, K.; Brückner, G. Wisteria floribunda agglutinin-labelled nets surround parvalbumin-containing neurons. Neuroreport 1992, 3, 869–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalb, R.G.; Hockfield, S. Molecular evidence for early activity-dependent development of hamster motor neurons. J. Neurosci. 1988, 8, 2350–2360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, R.T.; Kelly, G.M.; Zerillo, C.A.; Gray, G.; Tiemeyer, M.; Hockfield, S. Aggrecan glycoforms contribute to the molecular heterogeneity of perineuronal nets. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 7536–7547. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bignami, A.; Perides, G.; Rahemtulla, F. Versican, a hyaluronate-binding proteoglycan of embryonal precartilaginous mesenchyma, is mainly expressed postnatally in rat brain. J. Neurosci. Res. 1993, 34, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueno, H.; Suemitsu, S.; Okamoto, M.; Matsumoto, Y.; Ishihara, T. Sensory experience-dependent formation of perineuronal nets and expression of Cat-315 immunoreactive components in the mouse somatosensory cortex. Neuroscience 2017, 355, 161–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dauth, S.; Grevesse, T.; Pantazopoulos, H.; Campbell, P.H.; Maoz, B.M.; Berretta, S.; Parker, K.K. Extracellular matrix protein expression is brain region dependent. J. Comp. Neurol. 2016, 524, 1309–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gage, G.J.; Kipke, D.R.; Shain, W. Whole animal perfusion fixation for rodents. J. Vis. Exp. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phelps, P.E.; Barber, R.P.; Houser, C.R.; Crawford, G.D.; Salvaterra, P.M.; Vaughn, J.E. Postnatal development of neurons containing choline acetyltransferase in rat spinal cord: An immunocytochemical study. J. Comp. Neurol. 1984, 229, 347–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Meth. 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullen, R.J.; Buck, C.R.; Smith, A.M. NeuN, a neuronal specific nuclear protein in vertebrates. Development 1992, 116, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]







| Detected Component | Marker | Host | Antibody Conc. | Source | Characterisation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CSPGs | |||||
| Aggrecan (mouse ACAN core protein) | Anti-ACAN | Rabbit polyclonal IgG | 500 µg/mL | Millipore #AB1031 | WB2 (Lendvai et al., 2013 & Sutkus et al., 2014) |
| Brevican (BCAN; mouse cell-line derived recombinant human Brevican) | Anti-BCAN | Sheep polyclonal IgG | 1 mg/mL | R&D Systems #AF4009 | WB2 (R&D Systems data sheet) |
| Neurocan (NCAN; N-terminal epitope) | Anti-NCAN | Mouse monoclonal IgG | 369 µg/mL | DSHB1 #1F6 | WB2 (Asher et al., 2000 & Deepa et al., 2006) |
| Versican (VCAN; hyaluronate-binding region) | Anti-VCAN | Mouse monoclonal IgG | 169 µg/mL | DSHB1 #12C5 | WB2 (Asher et al., 2002 & Deepa et al., 2006) |
| Phosphacan (PTPRZ) | Anti- PTPRZ | Mouse monoclonal IgG | 165 µg/mL | DSHB1 #3F8 | WB2 (Deepa et al., 2006 & Vitellaro-Zuccarello et al., 2006) |
| Lectins | |||||
| N-acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc) | Biotinylated Wisteria floribunda agglutinin (WFA) | N/A | 2 mg/mL | Sigma #L1766 | Koppe et al., 1996 |
| Neuronal markers | |||||
| Choline acetyltransferase (ChAT) | Anti-ChAT | Goat polyclonal IgG | - | Millipore #AB144P | - |
| Neuron-specific nuclear protein (NeuN) | Anti-NeuN | Mouse monoclonal IgG | 1 mg/mL | Millipore #MAB377 | WB2 (Jin et al., 2003) |
| Antibody | Host | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Alexa fluor 488 | chicken anti-goat IgG | Invitrogen #A21467 |
| Alexa fluor 568 | donkey anti-mouse IgG | Invitrogen #A31571 |
| Alexa fluor 568 | donkey anti-rabbit IgG | Invitrogen #A10042 |
| Alexa fluor 568 | donkey anti-sheep IgG | Invitrogen #A21099 |
| Alexa fluor 647 | Streptavidin-conjugated | Invitrogen #S32357 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Irvine, S.F.; Kwok, J.C.F. Perineuronal Nets in Spinal Motoneurones: Chondroitin Sulphate Proteoglycan around Alpha Motoneurones. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1172. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041172
Irvine SF, Kwok JCF. Perineuronal Nets in Spinal Motoneurones: Chondroitin Sulphate Proteoglycan around Alpha Motoneurones. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(4):1172. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041172
Chicago/Turabian StyleIrvine, Sian F., and Jessica C. F. Kwok. 2018. "Perineuronal Nets in Spinal Motoneurones: Chondroitin Sulphate Proteoglycan around Alpha Motoneurones" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 4: 1172. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041172
APA StyleIrvine, S. F., & Kwok, J. C. F. (2018). Perineuronal Nets in Spinal Motoneurones: Chondroitin Sulphate Proteoglycan around Alpha Motoneurones. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(4), 1172. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041172






