Exploring microRNA Biomarker for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
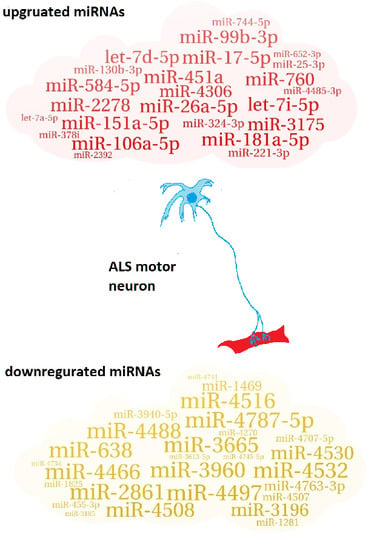
2.1. Identification of Up/Downregulated miRNAs
2.2. Identification of miRNAs Expressed Differentially between ALS Patients and Healthy Controls
3. Discussions
3.1. Uploading Down/Upregulated miRNAs to DIANA-Mirpath
3.2. KEGG Pathway Enrichment Analysis by DIANA-Mirpath
3.3. The Role of TDP-43
3.4. miRNAs Related to ALS
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. PCA Based Unsupervised FE
4.2. Procedure 1
- Step 1.
- Apply the R code “prcomp” on the expression profile matrix to obtain principal component (PC) loading.
- Step 2.
- Apply the R code “lm” to calculate p-values for the PC loading. p-values are adjusted by the R code “p.adjust”. We select the PC loading with an adjusted p-value less than 0.05. In this case, the adjusted p-value of the second PC loading is less than 0.05.
- Step 3.
- Based on the second PC score, apply the R code “pchisq” to calculate the p-values for miRNAs. p-values are adjusted by the R code “p.adjust”. In this case, 107 miRNAs with an adjusted p-value less than 0.01 are selected.
- Step 4.
- Apply the R code “prcomp” on the expression profile matrix of the 107 miRNAs to obtain PC loading.
- Step 5.
- Apply the R code “lm” to calculate p-values for the PC loading. p-values are adjusted by the R code “p.adjust”. We select the PC loading with a p-value less than 0.05. In this case, the p-values of the first, the third, the fourth and the eighth PC loadings are less than 0.05.
- Step 6.
- Based on the four PC loadings, apply the R code “lda” (Linear Discriminate Analysis) to classify the 53 samples to four categories.
4.3. Linear Discriminant Analysis with PC Scores Computed Using the Selected miRNAs
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tiryaki, E.; Horak, H.A. ALS and other motor neuron diseases. Continuum 2014, 20, 1185–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Sayana, P.; Zhang, X.; Le, W. Genetics of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: An update. Mol. Neurodegener. 2013, 8, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sau, D.; De Biasi, S.; Vitellaro-Zuccarello, L.; Riso, P.; Guarnieri, S.; Porrini, M.; Simeoni, S.; Crippa, V.; Onesto, E.; Palazzolo, I.; et al. Mutation of SOD1 in ALS: A gain of a loss of function. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2007, 16, 1604–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirano, M.; Quinzii, C.M.; Mitsumoto, H.; Hays, A.P.; Roberts, J.K.; Richard, P.; Rowland, L.P. Senataxin mutations and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. 2011, 12, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scotter, E.L.; Chen, H.J.; Shaw, C.E. TDP-43 Proteinopathy and ALS: Insights into Disease Mechanisms and Therapeutic Targets. Neurotherapeutics 2015, 12, 352–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotni, M.K.; Zhao, M.; Wei, D.Q. Gene expression profiles and protein-protein interaction networks in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis patients with C9orf72 mutation. Orphanet. J. Rare Dis. 2016, 11, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoye, M.L.; Koval, E.D.; Wegener, A.J.; Hyman, T.S.; Yang, C.; O’Brien, D.R.; Miller, R.L.; Cole, T.; Schoch, K.M.; Shen, T.; et al. MicroRNA Profiling Reveals Marker of Motor Neuron Disease in ALS Models. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 5574–5586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taguchi, Y.H. Identification of More Feasible MicroRNA-mRNA Interactions within Multiple Cancers Using Principal Component Analysis Based Unsupervised Feature Extraction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taguchi, Y.H. Identification of candidate drugs using tensor-decomposition-based unsupervised feature extraction in integrated analysis of gene expression between diseases and DrugMatrix datasets. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taguchi, Y.H.; Wang, H. Genetic Association between Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis and Cancer. Genes 2017, 8, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taguchi, Y.H. Principal Components Analysis Based Unsupervised Feature Extraction Applied to Gene Expression Analysis of Blood from Dengue Haemorrhagic Fever Patients. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freischmidt, A.; Muller, K.; Zondler, L.; Weydt, P.; Volk, A.E.; Bozic, A.L.; Walter, M.; Bonin, M.; Mayer, B.; von Arnim, C.A.; et al. Serum microRNAs in patients with genetic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and pre-manifest mutation carriers. Brain 2014, 137 Pt 11, 2938–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlachos, I.S.; Zagganas, K.; Paraskevopoulou, M.D.; Georgakilas, G.; Karagkouni, D.; Vergoulis, T.; Dalamagas, T.; Hatzigeorgiou, A.G. DIANA-miRPath v3.0: Deciphering microRNA function with experimental support. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W460–W466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phatnani, H.P.; Guarnieri, P.; Friedman, B.A.; Carrasco, M.A.; Muratet, M.; O’Keeffe, S.; Nwakeze, C.; Pauli-Behn, F.; Newberry, K.M.; Meadows, S.K.; et al. Intricate interplay between astrocytes and motor neurons in ALS. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E756–E765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Yi, J.; Zhang, Y.G.; Zhou, J.; Sun, J. Leaky intestine and impaired microbiome in an amyotrophic lateral sclerosis mouse model. Physiol. Rep. 2015, 3, e12356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.K.; Shin, J.H.; Hwang, S.G.; Gwag, B.J.; McKee, A.C.; Lee, J.; Kowall, N.W.; Ryu, H.; Lim, D.S.; Choi, E.J. MST1 functions as a key modulator of neurodegeneration in a mouse model of ALS. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 12066–12071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsuno, M.; Adachi, H.; Banno, H.; Suzuki, K.; Tanaka, F.; Sobue, G. Transforming growth factor-beta signaling in motor neuron diseases. Curr. Mol. Med. 2011, 11, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atkin, G.; Paulson, H. Ubiquitin pathways in neurodegenerative disease. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2014, 7, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegde, A.N.; Upadhya, S.C. Role of ubiquitin-proteasome-mediated proteolysis in nervous system disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1809, 128–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karademir, B.; Corek, C.; Ozer, N.K. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and proteasomal system in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 88 Pt A, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lautenschlaeger, J.; Prell, T.; Grosskreutz, J. Endoplasmic reticulum stress and the ER mitochondrial calcium cycle in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Amyotroph. Lateral Scler. 2012, 13, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaronen, M.; Goldsteins, G.; Koistinaho, J. ER stress and unfolded protein response in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-a controversial role of protein disulphide isomerase. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2014, 8, 402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matus, S.; Valenzuela, V.; Medinas, D.B.; Hetz, C. ER Dysfunction and Protein Folding Stress in ALS. Int. J. Cell Biol. 2013, 2013, 674751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perera, N.D.; Turner, B.J. AMPK Signalling and Defective Energy Metabolism in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Neurochem. Res. 2016, 41, 544–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perera, N.D.; Sheean, R.K.; Scott, J.W.; Kemp, B.E.; Horne, M.K.; Turner, B.J. Mutant TDP-43 deregulates AMPK activation by PP2A in ALS models. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e95549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.J.; Ju, T.C.; Chen, H.M.; Jang, Y.S.; Lee, L.M.; Lai, H.L.; Tai, H.C.; Fang, J.M.; Lin, Y.L.; Tu, P.H.; et al. Activation of AMP-activated protein kinase alpha1 mediates mislocalization of TDP-43 in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015, 24, 787–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freischmidt, A.; Muller, K.; Ludolph, A.C.; Weishaupt, J.H. Systemic dysregulation of TDP-43 binding microRNAs in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2013, 1, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawahara, Y.; Mieda-Sato, A. TDP-43 promotes microRNA biogenesis as a component of the Drosha and Dicer complexes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 3347–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, I.N.; Yartseva, V.; Salas, D.; Kumar, A.; Heidersbach, A.; Ando, D.M.; Stallings, N.R.; Elliott, J.L.; Srivastava, D.; Ivey, K.N. The RNA-binding protein TDP-43 selectively disrupts microRNA-1/206 incorporation into the RNA-induced silencing complex. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 14263–14271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buratti, E.; De Conti, L.; Stuani, C.; Romano, M.; Baralle, M.; Baralle, F. Nuclear factor TDP-43 can affect selected microRNA levels. FEBS J. 2010, 277, 2268–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pare, B.; Touzel-Deschenes, L.; Lamontagne, R.; Lamarre, M.S.; Scott, F.D.; Khuong, H.T.; Dion, P.A.; Bouchard, J.P.; Gould, P.; Rouleau, G.A.; et al. Early detection of structural abnormalities and cytoplasmic accumulation of TDP-43 in tissue-engineered skins derived from ALS patients. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2015, 3, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, S.; Sanelli, T.; Dib, S.; Sheps, D.; Findlater, J.; Bilbao, J.; Keith, J.; Zinman, L.; Rogaeva, E.; Robertson, J. RNA targets of TDP-43 identified by UV-CLIP are deregulated in ALS. Mol. Cell Neurosci. 2011, 47, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, M.; Kaneko, S.; Ito, H.; Jiang, S.; Fujita, K.; Wate, R.; Nakano, S.; Fujisawa, J.; Kusaka, H. Activation of transforming growth factor-beta/Smad signaling reduces aggregate formation of mislocalized TAR DNA-binding protein-43. Neurodegener. Dis. 2013, 11, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerreiro, R.J.; Schymick, J.C.; Crews, C.; Singleton, A.; Hardy, J.; Traynor, B.J. TDP-43 is not a common cause of sporadic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakabayashi, K.; Mori, F.; Kakita, A.; Takahashi, H.; Utsumi, J.; Sasaki, H. Analysis of microRNA from archived formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded specimens of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2014, 2, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benigni, M.; Ricci, C.; Jones, A.R.; Giannini, F.; Al-Chalabi, A.; Battistini, S. Identification of miRNAs as Potential Biomarkers in Cerebrospinal Fluid from Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis Patients. Neuromol. Med. 2016, 18, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Wei, Q.; Chen, X.; Li, C.; Cao, B.; Ou, R.; Hadano, S.; Shang, H.F. Aberration of miRNAs Expression in Leukocytes from Sporadic Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2016, 9, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, L.; Jorgensen, L.H.; Bech, R.D.; Frandsen, U.; Schroder, H.D. Skeletal Muscle Remodelling as a Function of Disease Progression in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 5930621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Russell, A.P.; Wada, S.; Vergani, L.; Hock, M.B.; Lamon, S.; Leger, B.; Ushida, T.; Cartoni, R.; Wadley, G.D.; Hespel, P.; et al. Disruption of skeletal muscle mitochondrial network genes and miRNAs in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Neurobiol. Dis. 2013, 49, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos-Melo, D.; Droppelmann, C.A.; He, Z.; Volkening, K.; Strong, M.J. Altered microRNA expression profile in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: A role in the regulation of NFL mRNA levels. Mol. Brain 2013, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parisi, C.; Arisi, I.; D’Ambrosi, N.; Storti, A.E.; Brandi, R.; D’Onofrio, M.; Volonte, C. Dysregulated microRNAs in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis microglia modulate genes linked to neuroinflammation. Cell Death Dis. 2013, 4, e959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, I.; Hama, Y.; Matsushima, M.; Hirotani, M.; Kano, T.; Hohzen, H.; Yabe, I.; Utsumi, J.; Sasaki, H. Identification of plasma microRNAs as a biomarker of sporadic Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Mol. Brain 2015, 8, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinde, S.; Arora, N.; Bhadra, U. A Complex Network of MicroRNAs Expressed in Brain and Genes Associated with Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Int. J. Genom. 2013, 2013, 383024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| 27 downregulated miRNAs |
| miR-3960; miR-3665; miR-4497; miR-4787-5p; miR-4466; miR-2861; miR-638; miR-4516; miR-4532; miR-4488; miR-4508; miR-4530; miR-3196; miR-4763-3p; miR-1469; miR-3940-5p; miR-4507; miR-4707-5p; miR-1281; miR-455-3p; miR-4270; miR-1825; miR-4745-5p; miR-4734; miR-3613-5p; miR-4741; miR-3185 |
| 24 upregulated miRNAs |
| miR-26a-5p; miR-451a; miR-181a-5p; miR-151a-5p; miR-17-5p; let-7i-5p; miR-106a-5p; miR-2278; miR-99b-3p; miR-760; miR-584-5p; let-7d-5p; miR-3175; miR-4306; miR-130b-3p; miR-324-3p; miR-221-3p; miR-744-5p; miR-25-3p; miR-4485-3p; miR-378i; miR-652-3p; miR-2392; let-7a-5p |
| True | Healthy Control | sALS Patient | ALS Mutation Carrier | fALS Patient | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prediction | |||||
| healthy Control | 14 (16) | 6 (-) | 0 (1) | 0 (0) | |
| sALS Patient | 3 (-) | 8 (-) | 2 (-) | 0 (-) | |
| ALS Mutation Carrier | 0 (1) | 2 (-) | 8 (7) | 1 (2) | |
| fALS Patient | 0 (0) | 2 (-) | 2 (4) | 5 (4) | |
| KEGG Pathway | p-Value | #Genes | #miRNAs |
|---|---|---|---|
| ECM-receptor interaction | 1.45 × 10−10 | 10 | 3 |
| Adherens junction * | 1.21 × 10−9 | 16 | 6 |
| Transcriptional misregulation in cancer * | 4.39 × 10−6 | 23 | 6 |
| Cell cycle * | 4.39 × 10−6 | 25 | 8 |
| Hippo signaling pathway * | 6.77 × 10−6 | 24 | 9 |
| Oocyte meiosis * | 3.39 × 10−5 | 18 | 5 |
| TGF-beta signaling pathway * | 0.000314 | 13 | 2 |
| Protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum * | 0.000971 | 25 | 8 |
| Pantothenate and CoA biosynthesis | 0.001459 | 3 | 5 |
| RNA transport * | 0.002423 | 23 | 7 |
| Focal adhesion * | 0.005153 | 29 | 8 |
| Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis * | 0.008498 | 21 | 8 |
| Colorectal cancer * | 0.010697 | 10 | 7 |
| 2-Oxocarboxylic acid metabolism | 0.017091 | 3 | 3 |
| mRNA surveillance pathway * | 0.023398 | 15 | 4 |
| AMPK signaling pathway * | 0.023398 | 19 | 6 |
| Proteoglycans in cancer * | 0.023929 | 23 | 6 |
| Regulation of actin cytoskeleton * | 0.03352 | 23 | 6 |
| Spliceosome | 0.03352 | 18 | 7 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Taguchi, Y.-h.; Wang, H. Exploring microRNA Biomarker for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1318. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19051318
Taguchi Y-h, Wang H. Exploring microRNA Biomarker for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(5):1318. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19051318
Chicago/Turabian StyleTaguchi, Y.-h., and Hsiuying Wang. 2018. "Exploring microRNA Biomarker for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 5: 1318. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19051318
APA StyleTaguchi, Y.-h., & Wang, H. (2018). Exploring microRNA Biomarker for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(5), 1318. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19051318