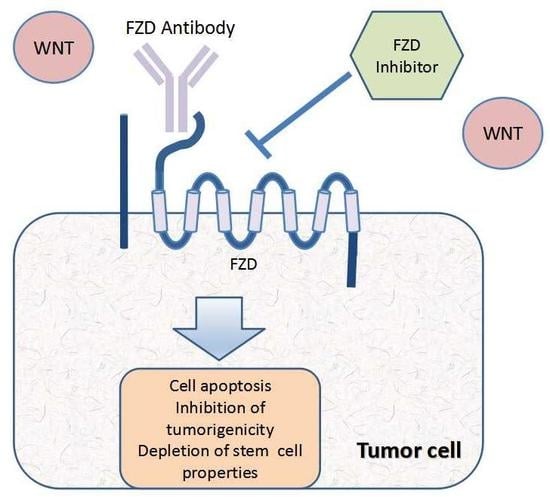
Frizzled Receptors as Potential Therapeutic Targets in Human Cancers
Abstract
Share and Cite
Zeng, C.-M.; Chen, Z.; Fu, L. Frizzled Receptors as Potential Therapeutic Targets in Human Cancers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1543. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19051543
Zeng C-M, Chen Z, Fu L. Frizzled Receptors as Potential Therapeutic Targets in Human Cancers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(5):1543. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19051543
Chicago/Turabian StyleZeng, Chui-Mian, Zhe Chen, and Li Fu. 2018. "Frizzled Receptors as Potential Therapeutic Targets in Human Cancers" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 5: 1543. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19051543
APA StyleZeng, C.-M., Chen, Z., & Fu, L. (2018). Frizzled Receptors as Potential Therapeutic Targets in Human Cancers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(5), 1543. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19051543