Abstract
Arterial hypertension is a disease with a complex pathogenesis. Despite considerable knowledge about this socially significant disease, the role of magnesium deficiency (MgD) as a risk factor is not fully understood. Magnesium is a natural calcium antagonist. It potentiates the production of local vasodilator mediators (prostacyclin and nitric oxide) and alters vascular responses to a variety of vasoactive substances (endothelin-1, angiotensin II, and catecholamines). MgD stimulates the production of aldosterone and potentiates vascular inflammatory response, while expression/activity of various antioxidant enzymes (glutathione peroxidase, superoxide dismutase, and catalase) and the levels of important antioxidants (vitamin C, vitamin E, and selenium) are decreased. Magnesium balances the effects of catecholamines in acute and chronic stress. MgD may be associated with the development of insulin resistance, hyperglycemia, and changes in lipid metabolism, which enhance atherosclerotic changes and arterial stiffness. Magnesium regulates collagen and elastin turnover in the vascular wall and matrix metalloproteinase activity. Magnesium helps to protect the elastic fibers from calcium deposition and maintains the elasticity of the vessels. Considering the numerous positive effects on a number of mechanisms related to arterial hypertension, consuming a healthy diet that provides the recommended amount of magnesium can be an appropriate strategy for helping control blood pressure.
1. Introduction
Magnesium (Mg2+) is the fourth most common mineral in the human body after calcium (Ca2+), potassium (K+), and sodium (Na+), and should be continuously replenished by food and water intake [1]. Mg2+ is the second richest intracellular cation after K+ and is a cofactor in more than 325 enzyme systems in cells [2]. Mg2+ is abundant in all green leafy vegetables, cereal, nuts, and legumes. Chocolate products, fruits, meat, and fish contain moderate amounts of Mg2+, and dairy products are low in Mg2+. Drinking water can be an important source of Mg2+ when it contains up to 30 mg/L of Mg2+ [3]. Chronic inadequate intake of Mg2+ over a long period of time can manifest as latent magnesium deficiency (MgD) [1]. Chronic MgD is associated with an increased risk of multiple preclinical and clinical manifestations including hypertension (HTN), atherosclerosis, cardiac arrhythmias, stroke, changes in lipid metabolism, insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome (MetS), type 2 diabetes (T2D), osteoporosis, depression, and other neuropsychiatric disorders [4] (Table 1). The assessment of Mg2+ status in the body is difficult because most is found in the cells or in the bones. Only 1% of the total Mg2+ in the body is present in extracellular fluids, and only 0.3% is found in the serum. The normal reference range for Mg2+ in the serum is 0.76–1.15 mmol/L [4]. In order to maintain these levels, the Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) for Mg2+ is 420 mg/day for men and 320 mg/day for women [5]. The hypomagnesaemia is defined as a condition where the serum concentration of Mg2+ in the body is <0.75 mmol/L [4]. When the Mg2+ intake is poor, the kidney can compensate by increasing reabsorption to >99% of the filtered amount, mainly in Henle’s loop and further in the distal tubules [1]. Signs and symptoms of hypomagnesemia usually occur when serum Mg2+ is decreased below 0.5 mmol/L. Many patients with hypomagnesemia remain asymptomatic [6,7].

Table 1.
Negative effects of MgD on the body and organs.
Over the last eight decades, nutritional and serum Mg2+ levels have received more attention and have been the subject of comprehensive cardiovascular health studies. MgD is considered an important risk factor for various types of cardiovascular diseases (CVD) [8] (Table 1). Dietary studies in Europe and the United States of America (USA) reveal that Mg2+ intake is lower than recommended [4]. The often recommended daily intake for adults is 320–400 mg/day (or 6 mg/kg/bodyweight for both sexes) [1]. Epidemiological studies in Europe and North America show that people who consume Western-style diets have low Mg2+ content, <30–50% of the RDA for Mg2+. It is assumed that the Mg2+ intake in the USA has decreased over the past 100 years from about 500 mg/day to 175–225 mg/day. This is probably the result of the increasing use of fertilizers and processed foods [4]. Refining or processing of food may deplete Mg2+ content by nearly 85%. Especially boiling of Mg2+-rich foods can result in a significant loss of Mg2+ [3]. Furthermore, the incidence rate of MgD can vary considerably in different regions due to the large differences of Mg2+ content in drinking water, which can provide up to 30% of daily needs [1].
Therefore, it seems reasonable to assume that MgD is mainly related to the low intake of Mg2+ in food and drinking water, including the use of purified salt to cook, which may lead to a negative balance over time [1]. The processing and cooking of food may therefore explain the apparently high prevalence of low Mg2+ intake in many populations [3]. In the USA, the prevalence of insufficient Mg2+ intake in adults is about 64% among men and 67% among women. Among people over 71 years of age, the figure increases to 81% for men and 82% for women respectively [8]. In the USA the RDA, set at 320 and 420 mg/day for females and males respectively, is higher than the Reference Nutrient Intake of the United Kingdom (UK). Reported data for Mg2+ intake in UK compared to the USA RDA are significantly lower than recommended for all population groups. The UK general population’s mean intake is 270 mg and 221.4 mg for males and females respectively, representing only 64% and 69% of the US RDA [9]. Dietary intake of Mg2+ has also been shown to be insufficient in middle aged French adults, as 77% of women and 72% of men consume less than the recommended levels [10]. Furthermore, MgD may be potentiated by malabsorption or medication intake, such as diuretics (loop and thiazide), proton pump inhibitors, some antibiotics, and chemotherapeutic agents. With age, the absorption of Mg2+ from the intestine is reduced and its loss from the body in the urine increases in both sexes [1].
A number of literature reviews and editorials have focused on the importance of Mg2+ for the occurrence of CVD. These examinations have shown that the prevalence of cardiovascular disease events caused by an inadequate intake of Mg2+ and low serum concentrations of Mg2+, have been underestimated and cardiovascular health may be associated with the intake of Mg2+. A significant association was found between dietary Mg2+ intake and total cardiovascular disease risk. The greatest risk reduction was observed when dietary Mg2+ intake increased from 150 mg/day to 400 mg/day. Higher serum Mg2+ concentrations with 0.1 mmol/L were associated with a 9% lower risk for total cardiovascular events [8].
A significant part of the experimental studies link MgD and CVD, such as HTN, and atherosclerosis [4]. Given the increasing incidence of HTN, the identification of effective and safe preventative measures that offer even modest lowering of blood pressure (BP), could have a significant public health impact. In this regard, Mg2+ may have beneficial health effects for the primary prevention of HTN [11]. HTN is the largest contributor to the global burden of cardiovascular disease. The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that the number of adults with high BP will increase from 1 billion to 1.5 billion worldwide by 2020 [12]. HTN is a major risk factor for heart disease and stroke [4]. According to WHO, 62% of all strokes and 49% of coronary heart disease events are attributable to high BP. Furthermore, experimental and epidemiological studies considered that HTN may serve as an effect modifier of the Mg2+ and CVD association [8].
2. Mechanisms Connecting MgD and Arterial Hypertension
Mg2+ is involved in BP regulation. Every modification of the endogenous Mg2+ status leads to changes in vascular tonus, and as a consequence, changes in arterial BP [4]. Mg2+ plays an important role in BP regulation by modulating vascular tone and reactivity [13]. Small changes in both extracellular and intracellular Mg2+ concentrations have significant effects on vascular tone, contractility, reactivity, and growth [14,15]. MgD can increase BP by affecting multiple molecular and cellular mechanisms [16] (Figure 1).
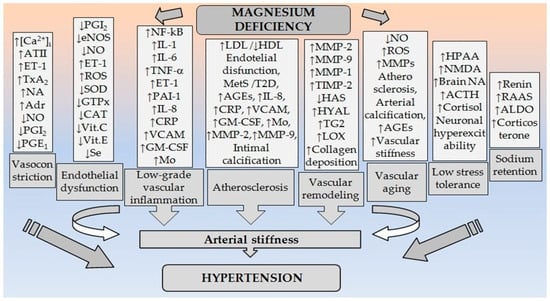
Figure 1.
Pathogenetic relationships between MgD and arterial hypertension. (Abbreviations: ↑: increased; ↓: decreased; [Ca2+]i: intracellular calcium in VSMCs; ATII: angiotensin II; ET-1: endothelin-1; TxA2: thromboxane A2; NO: nitric oxide; PGE1: prostaglandin E1; PGI2: prostaglandin I2; ROS: reactive oxygen species; NF-kB: nuclear factor kappa B; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor-α; IL-1: interleukin-1; IL-6: interleukin-1; IL-8: interleukin-8; PAI-1: plasminogen activator inhibitor-1; VCAM: vascular cell adhesion molecule-1; GM-CSF: granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor; Mo: monocytes; CRP: C-reactive protein; SOD: superoxide dismutase; GTPx: glutathione peroxidase; CAT: catalase; Vit.C: vitamin C; Vit.E: vitamin E; Se: selenium; LDL: low-density lipoproteins; HDL: high-density lipoproteins; MetS: metabolic syndrome; T2D: type 2 diabetes; AGEs: advanced glycation end products; MMPs: matrix metalloproteinases; MMP-1: matrix metalloproteinase-1; MMP-2: matrix metalloproteinase-2; MMP-9: matrix metalloproteinase-9; TIMP-2: tissue inhibitor of metalloprotease-2; HAS: hyaluronan synthases; HYAL: hyaluronidase; TG2: transglutaminase; LOX: lysyl oxidase; HPAA: hypothalamic pituitary adrenal axis; NMDA: N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor; NA: noradrenaline; Adr: adrenaline; ACTH: adrenocorticotropic hormone; RAAS: renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system; ALDO: aldosterone).
2.1. Disturbances of Mg2+ Transport and Its Endocrine Control
Mg2+ transport occurs through two main pathways—transcellular and paracellular [5]. Transcellular transport includes influx and efflux transport systems. Mg2+ influx is controlled by a number of transporters such as mitochondrial RNA splicing 2 protein (Mrs2p), human solute carrier family 41, members 1 and 2 (SLC41A1 and SLC41A2), ancient conserved domain protein 2 (ACDP2), and Mg2+ transporter 1 (MagT1), as well as specialized cationic channels—transient receptor potential melastatin-6 and -7 (TRPM6 and TRPM7) cation channels [17]. TRPM6 channels are predominantly expressed in the kidneys and caecum, where they regulate Mg2+ reabsorption. TRPM7 channels are ubiquitously expressed and their absence is lethal [18]. Mg2+ efflux is accomplished by Na+-dependent and Na+-independent pathways [17]. Na+-dependent transport involves Na+/Mg2+ pump. The following participate in Na+-independent transport. The Mg2+/Ca2+ pump and Mn2+/Mg2+ antiporter Cl−/Mg2+ co-transporter. Paracellular Mg2+ transport is a passive process and takes place through dense intercellular contacts of the epithelial cells in the intestinal tract and the kidneys and depends on the specific structural proteins—claudins. Intestinal Mg2+ absorption is connected with the relatively low expression of ‘tightening’ claudins 1, 3, 4, 5, and 8. In the kidney paracellular Mg2+ transport depends mainly of claudin 16 (paracellin-1) and claudin 19 [5]. Disturbances of Mg2+ transport may predispose to the development of HTN and subsequent CVD [17].
The data reported up to now indicates the potential regulatory role of cation TRPM7 channels in maintenance of vascular integrity [19]. In vascular cells Mg2+ influx is mainly determined by the TRPM7 channels and disturbances in vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) function in HTN can be partially linked to defective TRPM7 expression or activity [18]. TRPM7, implicated as a signaling kinase, is involved in a number of processes affecting VSMCs—growth, apoptosis, adhesion, cohesion, contraction, cytoskeletal organization, and migration. TRPM7 channels expressed in vasculature are regulated by vasoactive agents such as bradykinin, aldosterone (ALDO), endothelin-1 (ET-1), and angiotensin II (ATII) and different effects on the vascular wall such as pressure, tension, and osmotic changes. Thus these channels alter intracellular Mg2+ concentration by influencing the influx and efflux and may be associated with the onset and maintenance of HTN [17,18,20]. Experimental studies with Spontaneously Hypertensive (SHR) and Wistar-Kyoto (WKY) rats showed that TRPM6 and TRPM7 are differently regulated in their VSMCs. Inhibition of TRPM7, but not of TRPM6, may play a role in the altered Mg2+ homeostasis in VSMCs of SHR rats [21]. TRPM6 and TRPM7 are expressed in the endothelium, where they play an important role in intracellular Mg2+ homeostasis [22]. Because these channels have different effects on cell endothelial function it is suggested that they have potential importance, especially TRPM7, in the regulation of angiogenesis and vascular remodeling [23]. Mechanisms regulating vascular Mg2+ in health and disease remain unclear but TRPM7 could be important in HTN [20]. TRPM7 channels modulate endothelial behavior and any condition that leads to their increased expression, e.g., MgD or oxidative stress can damage endothelial function [19]. TRPM7 plays an important role in modulating VSMCs Mg2+ homeostasis, a major determinant of VSMCs function and vascular tone. Antunes et al. showed that in heterozygous TRPM7 kinase-deficient mice, ATII induces an exaggerated hypertensive response. These observations indicate that TRPM7 kinase differentially regulates vascular function in HTN. TRPM7 kinase is a modulator of BP regulation, which, when downregulated, promotes severe HTN and worsening of cardiovascular function. Moreover, ATII is a negative regulator of TRPM7. The study defines a novel TRPM7 kinase-sensitive mechanism involved in ATII-induced HTN. Based on these results, it can be concluded that aberrant TRPM7 expression/activity may contribute to impaired intracellular-free Mg2+ concentration and VSMCs contraction, proliferation, inflammation, and fibrosis, important determinants of vascular dysfunction and remodeling in HTN [20].
It has been proven that estrogens and epidermal growth factor (EGF) are magnesiotropic hormones [24,25,26,27]. Estrogens stimulate TRPM6 activity in short-term treatment and have long-term regulatory effects on TRPM6 transcription. The stimulation of a specific EGF receptor (EGFR) promotes TRPM6 trafficking to the plasma membrane. Long-term treatment with EGF regulates TRPM6 expression [28]. Considering the role of TRPM6 channels for changes of intracellular Mg2+ concentrations could be assumed that they are related to the modifications of the electrical and mechanical activity of cardiac myocytes or VSMCs and hence to CVD such as cardiac arrhythmias or HTN [29]. Thus, estrogen deficiency and the lack of their regulatory effects on Mg2+ exchange may be directly linked to increased loss of Mg2+ in postmenopausal women, which can lead to the development of HTN, cardiac arrhythmias, increased neuro-muscular excitability, and osteoporosis.
It is known that 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D [1,25(OH)2D] can stimulate intestinal Mg2+ absorption [30]. In addition, conversion of vitamin D by hepatic 25-hydroxylation and renal 1α-hydroxylation into the active form and the vitamin D-binding protein are Mg2+-dependent. MgD leads to reduced 1,25(OH)2D and impaired parathyroid hormone (PTH) response. Absorption of Mg2+ and Ca2+ is inter-related. MgD impairs hypocalcemic-induced PTH release, which can be corrected after infusion of Mg2+. Mg2+ is also an important factor for the sensitivity of the target tissues to PTH. On the other hand, PTH has significant effects on Mg2+ homeostasis. For example, PTH release enhances Mg2+ reabsorption in the kidneys and absorption in the gut. PTH influences Mg2+ absorption, however, hypercalcemia antagonizes this effect [4]. The findings indicate a possible link between the vasculature and mineral metabolism. Epidemiological studies have shown that both PTH and Ca2+ are associated with high BP [31], which may be due to Mg2+ homeostasis disturbances.
2.2. Mg2+ as a Regulator of Vascular Tone and Reactivity
Mg2+ is one of the important physiological regulators of blood vessel tone. It improves vascular relaxation responses and attenuates agonist-induced vasoconstriction, thus mitigating the increased peripheral vascular resistance. The effects of Mg2+ as a regulator of vascular tone are most often the result of a competitive relationship with Ca2+. MgD increases the contractile response to various agonists and changes vascular responses to a number of vasoactive substances (Figure 1).
2.2.1. Mg2+ as a Natural Calcium Antagonist
In the dissolved state, Mg2+ binds hydration water tighter than Ca2+. Thus, the hydrated Mg2+ is more difficult to dehydrate. The radius of hydrated Mg2+ is ~400 times larger than its dehydrated radius. This difference explains a lot of the biological properties of Mg2+, including its often antagonistic behavior to Ca2+, despite similar chemical reactivity and charge. For example, it is almost impossible for Mg2+ to pass through narrow channels in biological membranes, compared to Ca2+, because it cannot easily lose its hydration shell [32]. Because of its unique chemical properties, Mg2+ is linked to the modulation of intracellular Ca2+ homeostasis and decreased extracellular or intracellular Mg2+ can be combined with an increase in Ca2+ levels [16]. Ca2+ concentration in the cytosol is one of the principal factors determining the contractile properties of the VSMCs. Mg2+ counteracts Ca2+ and functions as physiological Ca2+ blocker, like synthetic Ca2+ antagonists [33,34,35]. Both extracellular and intracellular free Mg2+ can modulate VSMCs tone by voltage-dependent L-type Ca2+ channels. Extracellular Mg2+ inhibits Ca2+ current in VSMCs by two main mechanisms. First, extracellular Mg2+ effectively neutralizes the fixed negative charges on the external surface of the cell membrane. This stabilizes the excitable membranes and raises the excitation threshold which diminishes current via the voltage-gated Ca2+ channels. Second, some evidence suggests that extracellular Mg2+ can decrease Ca2+ current by directly binding to the Ca2+ channels. Binding of Mg2+ may either mechanically block the channel pore or may cause an allosteric modulation of the channel gating, resulting in its closure [36]. Elevated levels of extracellular Mg2+ inhibit Ca2+ influx, while decreased extracellular Mg2+ activates Ca2+ influx through Ca2+ channels [37]. Intracellular Mg2+ concentrations modulate VSMCs tone via its effects on ion channels and signal transduction pathways, especially those involving Ca2+. Changes in intracellular Mg2+ are known to influence these channels by affecting its amplitude, its activation/inactivation kinetics, and its modulation by factors such as phosphorylation, ultimately leading to decreased Ca2+ entry. Intracellular Mg2+ activates sarcoplasmic/endoplasmic reticular Ca2+ ATPase pump that sequesters intracellular Ca2+ into the sarcoplasmic reticulum. Elevated intracellular Mg2+ stimulates inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate (IP3) breakdown, inhibits IP3-induced Ca2+ release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum, and competes with intracellular Ca2+ for cytoplasmic and reticular binding sites [36]. Low intracellular Mg2+ stimulates IP3 mediated mobilization of Ca2+ from the sarcoplasmic reticulum and reduces Ca2+ ATPase activity, decreasing Ca2+ efflux and reuptake by the sarcoplasmic reticulum. This leads to accumulation of cytosolic Ca2+, increased intracellular Ca2+ concentration, which is a crucial factor for vasoconstriction [37]. Mg2+ can also block Ca2+ release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum via the ryanodine receptor [17]. An important property of Mg2+ is to compete with Ca2+ for binding sites on regulatory molecule troponin C. Thus, Mg2+ regulates the activity of contractile proteins and their dynamics [16]. Lastly, intracellular Mg2+ regulates activity of the G-protein-coupled receptors as AT1 (ATII), ETA (ET-1), V1a (vasopressin), and α1-adrenoceptors (norepinephrine and epinephrine) on VSMCs and intracellular Ca2+ signal transduction pathways as translocation of phospholipase C (PLC) and protein kinase C (PKC) activation [36].
Besides the direct effects of Mg2+ on VSMCs, Mg2+ also modulates endothelial function, which in turn contributes to its vasodilatory actions. Normal endothelium plays a fundamental role in regulating vasomotor tone by synthesizing vasodilatory prostacyclin (PGI2) and nitric oxide (NO). Mg2+ has been shown to increase endothelial release of PGI2 in cultured human endothelial cells and in healthy human volunteers [17,36].
2.2.2. MgD and Vascular Reactivity
Other Mg2+ effects could be due to altered binding of agonists to their specific cell membrane receptors and/or the production of vasoactive peptides, such as ATII and ET-1, which are powerful vasoconstrictors [38]. ATII, ET-1, vasopressin, and epinephrine/norepinephrine exert their vasoconstrictor effect via stimulation of AT1, ETA, V1a, and α1 receptors, respectively, on VSMCs. Activation of these Gq–protein-coupled receptors initiates the PLC, IP3, diacylglycerol, Ca2+, and PKC signal transduction pathway. Evidence suggests that following receptor–ligand interaction intracellular Mg2+ is also altered and that it too functions as a second messenger to modulate signal transduction [36]. For example, elevated levels of Mg2+ decrease ET-1 induced contraction, whereas decreased Mg2+ levels increase it [38]. Kharitonova et al. have explored the role of various Mg2+ compounds for the development of systemic inflammation and endothelial dysfunction in rats fed on a low Mg2+ diet for 74 days. Low Mg2+ diet reduces Mg2+ concentration in the plasma and red blood cells (RBCs), which is accompanied by a decreased concentration of endothelial NO synthase (eNOS), elevated levels of ET-1 in serum and impaired endothelial-dependent vasodilation. ET-1 produces multiple effects in the blood vessels: causes significant vasoconstriction, has proinflammatory effects, possesses mitogenic and proliferative properties, stimulates the formation of free radicals, and activates platelets. The analysis of the activity of the inorganic Mg2+ salts showed that supplementation with Mg-sulfate did not significantly reduce pathologically elevated levels of ET-1, but Mg-chloride completely restored the concentration of ET-1 to a normal value. Tested Mg-organic compounds Mg-oxybutyrate and Mg-L-aspartate reduce the concentration of ET-1 to a normal level, whereas treatment with Mg-N-acetyltaurate leads only to partial reduction of ET-1 in MgD groups [39]. Mg2+ is an essential cofactor of the enzyme δ-6-desaturase, which is the rate determining conversion of linoleic acid to gamma-linolenic, which in turn is converted to dihomo-γ-linoleic acid. The latter is a precursor of prostaglandin E1 (PGE1), which is both a vasodilator and inhibitor of platelet aggregation. MgD disrupts production of PGE1, which leads to vasoconstriction and increase in BP [17].
2.2.3. MgD and the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System (RAAS)
Few studies have investigated the effects of MgD on the hormonal systems which control BP. The RAAS plays an essential role in humoral and hemodynamic regulation [40]. It was established, that in hypertensive patients with high plasma renin activity, serum Mg2+ was much lower than in normotensive persons [16]. MgD increases the ATII-induced plasma concentration of ALDO, as well as the production of thromboxane A2 and vasoconstrictor prostaglandins [3]. Mg2+ has some direct effects on ALDO synthesis rather than indirect effects via the RAAS. ALDO secretion from the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal gland is Ca2+ dependent process. Mg2+ infusion in humans decreases the production of ALDO, by inhibiting the cellular Ca2+ influx. MgD facilitates cellular Ca2+ influx, which may stimulate the production and release of ALDO [40]. It was proved that MgD rats have increased plasma renin activity and circulating levels of ALDO and corticosterone. Additionally, other authors indicate that Mg2+ supplementation decreases ATII stimulated production and release of ALDO from the adrenal cortex of normotensive subjects [16]. Rats fed with an MgD diet showed a continuous increment of the juxtaglomerular granulation index and width of the zona glomerulosa of the adrenal cortex, whereas the thickness of the inner zones diminished slightly. In Mg2+-recovering rats juxtaglomerular granulation index the width of the zona glomerulosa returned to normal [41]. Thus, one could suggest that MgD, by facilitating cellular Ca2+ entry, may promote ALDO production and release. Experimental studies have reported that MgD-induced HTN in rats is associated with increased vascular total Ca2+ content, and increased vasoconstrictor activity to endogenous agonists such as ATII and noradrenaline (NA) [40]. Mg2+ supplementation can reduce the pressor effect of ATII and stimulate the production of the vasodilator PGI2 [3].
2.2.4. MgD and Catecholamines (CA)
Ca2+ exerts a major role in CA release from the adrenal gland and adrenergic nerve terminals in response to sympathetic stimulation. Because Mg2+ competes with Ca2+ for membrane channels, it can modify these types of Ca2+-mediated responses. The ability of Mg2+ to inhibit the release of CA from both the adrenal gland and peripheral adrenergic nerve terminals is well established in laboratory experiments. On the basis of these effects, Mg2+ can be used in patients where an excess of CA is prevalent, such as in phaeochromocytoma [42]. Acetylcholine (ACh) evoked CA release from adrenal glands. Ca2+ stimulates the secretion of ACh and there exists a direct relationship between Ca2+ concentration and the rate of CA release. Mg2+ antagonizes the stimulant effects of ACh on adrenal chromaffin cells; this effect can be overcome by the addition of Ca2+ [43]. Mg2+ is required for the catalytic action of adenylate cyclase (ADCY). For example, the decreased activity of the ADCY9 in the absence of Mg2+ results in increased secretion of ACh from preganglionic nerves, which in turn stimulates further release of CA from the adrenal glands [44]. On the other hand, Mg2+ together with ATP can greatly stimulate the release of CA from adrenal medullary granules. Neither ATP nor Mg2+ alone may have any effect on the release of CA. The effects of Ca2+, which cause the release of CA from the granules, are inhibited in the presence of ATP and Mg2+. The uptake of 14C-adrenaline (Adr) into the granules can also be stimulated by ATP and Mg2+ [45].
There are evidences that high concentrations of Mg2+ prevent the release of NA in some arteries by blocking N-type Ca2+ channels of nerve endings, which counteracts the rise in BP. Also rats fed with a MgD diet showed an increase in CA excretion [16]. The effects of Ca2+ and Mg2+ concentrations on responses to periarterial nervous sympathetic stimulation, NA, and tyramine have been investigated on the isolated rabbit central ear artery. An increase in Ca2+ concentrations potentiates responses to sympathetic stimulation until complete removal of Ca2+ inhibits these responses. The addition of the Mg2+ solution greatly reduced the responses to sympathetic stimulation, NA, and tyramine. These actions of Mg2+ on sympathetic transmission are important in determining the responsiveness of arterial smooth muscle to direct and indirectly acting sympathomimetic amines [46]. The effects of Adr infusion, sufficient to achieve its pathophysiological levels, and of therapeutic intravenous infusion of salbutamol, a β2-agonist, on plasma Mg2+ levels, were studied in a placebo-controlled design in healthy subjects. Plasma Mg2+ levels fell significantly during the Adr infusion and also during the salbutamol infusion, though more slowly. It is propose that intracellular shifts of Mg2+ occur as a result of β-adrenergic stimulation [47]. In another study, infusion of Adr in man significantly reduced the plasma Mg2+ levels in healthy males. This effect was abolished by simultaneous infusion of propranolol. NA had no such effect. These results suggest that the β-adrenergic system affect Mg2+ homeostasis [48]. On the other hand, dose-dependent increase in circulating Mg2+ was observed in rats infused with isoproterenol (ISO). Pretreatment with butoxamine or propranolol has prevented the ISO-induced increase in serum Mg2+ levels, whereas administration of atenolol has minimal effects. This evidence demonstrates the existence of a pool of Mg2+ that is mobilized into the circulation in response to selective β2-adrenergic stimulation [49].
2.3. MgD and Arterial Stiffness
Normally conduit arteries adapt pressure and blood flow during cardiac systole to facilitate perfusion to tissues during diastole. This is determined in large part by the elasticity, distensibility, and compliance of the arterial system. Loss of elasticity and increased stiffness demand greater force to accommodate blood flow, leading to increased systolic BP and consequent increased cardiac work load. Multiple interacting factors at the systemic (BP, hemodynamics), vascular (vascular contraction/dilatation, extracellular matrix remodeling), cellular (cytoskeletal organization and inflammatory responses), and molecular (oxidative stress, intracellular signaling, and mechanotransduction) levels contribute to arterial stiffness in HTN. Dysregulation of endothelial cells, VSMCs, and adaptive immune responses are also implicated in HTN [12]. Changes in Mg2+ concentrations play an important role in many of these processes.
2.3.1. MgD, Low-Grade Inflammation, and Oxidative Stress at the Vascular Wall
A number of immunopathological mechanisms may be at the basis of HTN. There are evidence in animal models and humans that link HTN with changes in both humoral and cellular immunity, and in particular with the key role of low-grade vascular inflammation [50]. One study showed that the total intracellular Mg2+ is considerably lower in lymphocytes of the hypertensive patients, compared with healthy subjects, whereas serum Mg2+, erythrocyte Mg2+ and ionized platelet Mg2+ were not significantly different [51]. MgD leads to inflammation and increased production of free radicals [52] in the vascular wall, and they in turn contribute to the development of endothelial dysfunction and vascular remodeling. Low Mg2+ intake is associated with a higher probability of increased serum C-reactive protein (CRP) levels in children [53]. There is also an association between the dietary intake of Mg2+ and elevated CRP levels in the adult population. Insufficient dietary intake of Mg2+ may be associated with an increased inflammatory response resulting in more frequent occurrence of cardiovascular accidents [54]. Intake of Mg2+ is also inversely related to the level of hs-CRP, interleukin 6 (IL-6), and fibrinogen [55]. MgD significantly increases production of various proinflammatory molecules such as, interleukin 1 (IL-1), IL-6, tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α), vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM), plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1), and decreases expression and activity of the antioxidant enzymes such as glutathione peroxidase, superoxide dismutase, and catalase. Cellular and tissue levels of important antioxidants such as glutathione, vitamin C, vitamin E and selenium are also reduced [16]. This shows that MgD can increase cytotoxicity of the free radicals to endothelial cells [56]. For example Mg2+ deficit, in rats leads to an increase in the inflammatory mediators, such as histamine, IL-1, IL-6, TNF-α, and ET-1, which is associated with leukocytosis and generation of free radicals [34] (Figure 1).
2.3.2. MgD, Vascular Structure and Remodeling
Vascular remodeling is a permanent process of structural changes in the vessel wall in response to a number of hemodynamic stimulus [57]. In HTN, resistance arteries undergo an inward remodeling, while larger arteries show outward hypertrophic remodeling [58,59,60]. The vascular extracellular matrix (ECM) comprises multiple structural proteins, including collagens, elastin, fibronectin, and proteoglycans. The absolute and relative quantities of collagen and elastin determine biomechanical properties of vessels. Excessive ECM protein deposition, in particular collagen and fibronectin, contributes to increased intima–media thickening, vascular fibrosis, and stiffening leading to the development of HTN [12]. Mg2+ regulates collagen and elastin turnover and the structure of the ECM. MgD leads to a delay in the synthesis of all structural molecules (collagen, elastin, proteoglycans and glycosaminoglycans) (Figure 1). Hyaluronan synthases (HAS)—HAS1, HAS2 and HAS3, contain Mg2+ ion in their active centers. On the other hand it is known that inhibitors of the hyaluronidase (HYAL) depend on the concentration of Mg2+ ions. Thus, low levels of Mg2+ could lead to decreased activity of HAS, and at the same time to an increased activity of HYAL. Tissue transglutaminase (TG2) is an enzyme of the transglutaminase superfamily that is ubiquitously expressed in the vasculature [61]. TG2 is associated with a wide range of CVD and processes, including the development of HTN, and the progression of atherosclerosis, regulating vascular permeability, and angiogenesis. TG2 activity is associated with arterial stiffening in humans and rats. TG2 forms glutamine-lysine cross-links between variety of extracellular proteins, including collagen and elastin [62]. TG2 is secreted through a Golgi-independent mechanism to the ECM, where it can be activated to a Ca2+-bound open conformation to catalyze the formation of isopeptide bonds [61]. Thus, Ca2+ may be limiting TG2 activity in the ECM [62]. TG2 is activated by Ca2+, and inhibited by Mg2+ [63]. A disturbance in lysyl oxidase (LOX) expression has also been reported in CVD, and an increase in vascular LOX activity has been described in experimental models of HTN. Mg2+ can inhibit LOX, which is also associated with crosslinking of chains of elastin and/or collagen [63,64]. Additionally, MgD could lead to the production of defective collagen, elastin, and fibronectin by fibroblasts [65].
Fundamental to many of the processes underlying ECM reorganization and fibrosis in HTN is activation of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMPs). ECM MMPs and TIMPs may contribute to the profibrotic phenotype in HTN. Activated MMPs degrade collagen, elastin, and other ECM proteins, resulting in a modified ECM, often associated with a proinflammatory microenvironment that triggers a shift of endothelial and VSMCs to a more secretory, migratory, and proliferative phenotype, which contributes to fibrosis, calcification, endothelial dysfunction, and increased intima–media thickness, further impacting on vascular remodeling and arterial stiffness [12]. In endothelial cells cultured in MgD medium, a significant increase in expression and activity of MMP-2 and MMP-9 has been reported. Also, MMP-2 and MMP-9 have been associated with alterations of the vascular wall in Mg2+-deficient rats [66]. In addition, there is evidence that the addition of Mg-sulfate effectively attenuated MMP-9 activity in а human umbilical cord vein endothelial cell line [67]. These data are confirmed by K. Kostov et al. who find that in patients with essential HTN there was a moderate negative correlation of serum Mg2+ with MMP-2 (r = −0.318, p = 0.013). There was a similar correlation of Mg2+ with MMP-9 in patients with HTN and T2D (r = −0.376, p = 0.003). The results show that lower and higher serum Mg2+ levels correlate inversely with MMP-2 and MMP-9 levels in HTN [68]. It is noteworthy that in Mg2+-deficient endothelial cells, MMP-2 and MMP-9 activity overrides the inhibitory effect of TIMP-2, which probably is induced as an attempt to counterbalance the effects of the proteases [66]. A nuclear factor (NF)-κB-binding site is present in the promoter of the MMP-9 gene. It is therefore possible that low Mg2+ availability might directly increase MMP-9 expression via NF-κB [66,69]. In cultured rat VSMCs, Mg2+ significantly reduced the production of MMP-2 under basal and platelet-derived growth factor-stimulated conditions in a dose-dependent manner, while neither verapamil nor nifedipine showed any effect under the same conditions. These data suggest that the beneficial effect of Mg2+ supplementation on vascular disease processes may be due, at least in part, to the inhibitory effect of Mg2+ on the production of MMP-2 in VSMCs [70]. Evidence supporting this data is that in cultured rat cardiac fibroblasts, Mg2+ significantly reduced the production of MMP-2 in a dose-dependent manner [71]. MgD may increase the activity of MMPs, including collagenases, which begin to degrade the extracellular vascular matrix and primarily collagen with an increased speed. The degradation of elastin fibers can significantly increase (up to 2–3 times) in the presence of Mg2+. MgD is associated with low elastase activity and an increased number of elastic fibers [63]. Altura et al. describe and other possible mechanisms by which MgD can affect vascular remodeling processes. They present new evidence for effects on platelet-activating factor, proto-oncogenes, and sphingolipids, e.g., ceramide and sphingosine with upstream regulation in both VSMCs and cardiac muscle cells. These findings will be helpful in explaining many of the known cardiovascular manifestations of MgD, especially vascular remodeling seen in atherosclerosis and HTN [72].
2.3.3. MgD, Endothelial Dysfunction and Atherosclerosis
MgD may potentiate the development of endothelial dysfunction via activation of NF-κB, which includes the transcriptional program leading to development of the proinflammatory phenotype [69]. Low extracellular Mg2+ slows endothelial cell proliferation, stimulates the adhesion of monocytes, and affect the synthesis of vasoactive molecules, such as NO and PGI2. Endothelial function is significantly impaired in a model of familial hypomagnesemia in mice. Compared to controls, in the aortas of these animals were found reduced amounts of eNOS and increased expression of proinflammatory molecules, such as VCAM, PAI-1, as well as of the TRPM7 channel [19]. Endothelial dysfunction is an early event in the process of atherogenesis and precedes the angiographic and ultrasound evidences of damage to the arterial wall [66]. The pathogenesis of atherosclerotic changes and disturbances in endothelial function are complex and multifactorial. In this context, Mg2+ deficit is too important [73]. This mineral is especially important because of its antiatherosclerotic effects [74]. Endothelial function correlates to the levels of Mg2+ and results of Mg2+ supplementation have showed significantly improved endothelial function in patients with ischemic heart disease and diabetes. These results in humans have also been observed in different experimental models in which Mg2+ deficit affects vascular structure and function. Low levels of extracellular Mg2+ favor and increase endothelial permeability. More specifically, MgD enhance the transport of low-density lipoproteins (LDL) through the endothelial layer [66]. Several studies have reported beneficial effects of Mg2+ supplementation on plasma LDL levels, as well as on high-density lipoproteins (HDL) levels, which are increased [75]. Another possibility by which Mg2+ contributes to the development of atherogenesis is through the effect on triglyceride levels which are increased in MgD. Accumulation of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins is accompanied by decreased concentration of HDL and increased plasma concentration of apolipoprotein B. Since the oxidation of lipoproteins play a key role in the development of atherosclerosis, it could be another mechanism by which Mg2+ influences. It is also possible proatherogenic lipoprotein changes found in MgD to be a consequence of the inflammatory response [76]. A central role for Mg2+ mediated effects on endothelial cells has IL-1α, which is regulated by NF-κB and may be inducer of the NF-κB. IL-1α increases significantly in the environment of low Mg2+ content. IL-1α also induces the production of various chemokines and adhesion molecules in vascular endothelial cells by activation of NF-κB, and thus favors aggregation, adhesion, and diapedesis of monocytes. In particular, low concentrations of Mg2+ stimulate the secretion of interleukin 8 (IL-8), and chemokines, which are overexpressed in human atherosclerotic lesions. IL-8 is essential for chemotaxis and adhesion of monocytes to endothelial cells, which is a fundamental event in the initiation of atherogenesis and also stimulates proliferation and migration of VSMCs. By induction of IL-1α, low serum Mg2+ may also stimulate overexpression of VCAM-1 on the surface of endothelial cells which assists in the migration of leukocytes. In addition, the secretion of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor is significantly higher in endothelial cells with Mg2+ deficit [66]. All these date indicate that the MgD is a potential factor for accumulation of monocytes/macrophages in the arterial wall during the early stages of atherosclerosis (Figure 1).
2.3.4. MgD, MetS, and T2D
The presence of MetS is also associated with altered Mg2+ metabolism [77]. Usually, the triad consisting of obesity, HTN, and impaired glucose tolerance/insulin resistance is denoted as MetS [78]. Furthermore, HTN is present in a high proportion of patients with T2D [79,80]. A common feature in patients with T2D, HTN, and low levels of HDL is MgD (Table 1).
Currently, there is little data on serum Mg2+ levels in people with MetS. The relationship between the intake of Mg2+ and MetS was investigated prospectively in 5115 young Americans (aged 18–30 years), initially without MetS and diabetes, which were enrolled in Coronary Artery Risk Development in Young Adults (CARDIA) study from 1985 to 1986. The total number of participants included in the analysis was 4637, and 74% were evaluated at the 15-year period in 2000–2001. During this interval 608 cases of MetS were diagnosed. The findings showed that young people with a high Mg2+ intake had a lower risk of developing MetS and that risk was dose-dependent [78]. Guerrero-Romero et al. found a link between Mg2+ levels, inflammation, and oxidative stress, as risk factors for the development of MetS. Mg2+ intake is inversely proportional to the components of MetS and fasting insulin levels, suggesting that higher Mg2+ intake may have a protective role against the risk of developing MetS [77]. The results of several clinical studies have shown that increased synthesis and release of proinflammatory cytokines trigger the process of chronic inflammation, which may be the link between obesity and MetS. On the other hand hypomagnesemia triggers low-grade chronic inflammation and Mg2+ deficit may be associated with the development of MetS. These findings support the hypothesis that MgD can play an important role in the pathophysiology of MetS, and the actuation of the inflammatory reaction caused by the shortage of Mg2+ could be the link between MgD and MetS [81]. Some studies linked decreased Mg2+ levels with chronic inflammatory stress in obese people. Obesity affects over 35% of the adult population of the USA and is a main risk factor for chronic diseases, associated with a lower Mg2+ status, such as atherosclerosis and T2D. MgD is often found in people with MetS and T2D, which are connected with higher plasma concentrations of CRP [82].
Mg2+ plays a very important role in the development of T2D [83]. Corica et al. have recently shown that patients with T2D having lipid profile with high risk, high BP, and abdominal obesity, have lower levels of Mg2+, compared with patients without metabolic risk factors. Furthermore, plasma triglycerides and waist circumference were independently associated with hypomagnesaemia [77]. T2D is often linked with hypomagnesaemia, as has been reported at an occurrence rate of 13.5–47.7% [78]. The relationship between insulin and Mg2+ is bipartite. Insulin regulates Mg2+ homeostasis, but on the other hand Mg2+ is a major factor determining insulin and glucose metabolism. Extracellular Mg2+ acts as Ca2+ antagonist and inhibits Ca2+ influx, required for insulin secretion. Thus a decreased concentration of extracellular free Mg2+ results in an increased Ca2+ influx and increased concentration of intracellular free Ca2+. The increased intracellular Ca2+ stimulates insulin secretion by beta-cells, as was demonstrated in experiments with an insulinoma cell line [84]. The effect of extracellular Mg2+ on insulin secretion was found in healthy human subjects. In subjects with 0.79 mmol/L plasma Mg2+, fasting plasma insulin was 23 μU/mL, while in those with plasma Mg2+ 0.87 or 1.00 mmol/L, fasting plasma insulin amounted to 11 μU/mL [85].
There are growing evidences that highlight the clinical significance of altered Mg2+ metabolism for the occurrence of peripheral insulin resistance. MgD can lead to disturbances of the tyrosine kinase activity of the insulin receptor (IR), associated with the development of post receptor insulin resistance and reduced cellular glucose utilization, as a lower Mg2+ concentration, requires a greater amount of insulin for glucose metabolism [77]. The effects of MgD on glucose-stimulated insulin secretion and insulin action on skeletal muscle were studied in experimental animals. The hypothesis that changes in Mg2+ metabolism induce insulin resistance is confirmed by data showing that lower dietary intake of Mg2+ is associated with insulin resistance. Rats fed on a low Mg2+ diet showed a significant increase of blood glucose and triglycerides. The insulin resistance, observed in the skeletal muscle of rats with MgD is partially associated with a defect of tyrosine kinase activity of the IR [86,87,88]. Insulin action begins with the binding of insulin to an IR on the cell membrane of the target cells. The IR is a transmembrane glycoprotein with tyrosine kinase activity [89]. Activation of the receptor is an important step in transmembrane signaling for insulin action. The activated kinase promotes autophosphorylation of receptor tyrosine residues. The insulin–receptor complex is internalized and phosphorylates IR substrates 1–6 (IRS 1–6) and other kinases in the insulin signaling cascade [90]. When the intrinsic tyrosine kinase activity of the receptor is triggered by insulin binding, two major signaling pathways have been activated: (1) Ras-mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway, which controls cell growth and differentiation; (2) Phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt (PI3K/Akt) pathway. Binding of IRS to the regulatory subunit of phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) results in activation of PI3K, which phosphorylates membrane phospholipids and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2). This complex activates the 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinases (PDK-1 and PDK-2) resulting in activation of Akt/protein kinase B and atypical protein kinase [91,92]. Activated Akt phosphorylates its 160 kDa substrate, which stimulates the translocation of insulin-mediated glucose transporter type 4 (GLUT4) from intracellular vesicles to the plasma membrane [93]. The PI3K/Akt pathway is a key component of the insulin signaling cascade, which is necessary for the metabolic effects of insulin and GLUT4 translocation [94]. Since Mg2+ is a necessary cofactor in all ATP transfer reactions, intracellular Mg2+ concentration is critical in the phosphorylation of the IR and other kinases [95]. In all these reactions Mg2+ operates together with ATP as a kinase substrate. Additionally Mg2+ is bound to a regulatory site of the IR tyrosine kinase (IRTK). The apparent affinity of the IRTK for Mg2+-ATP increased as the concentration of free Mg2+ increased, and the apparent affinity of the IRTK for free Mg2+ increased as the concentration of Mg2+-ATP increased [84]. There are evidences that show a link between decreased Mg2+ concentration and reduction of tyrosine-kinase activity at the IR level, which results in the impairment of insulin action and development of insulin resistance [96]. Studies in multiple insulin resistant cell models have demonstrated that an impaired response of the tyrosine kinase to insulin stimulation is one potential mechanism causing insulin-resistant state in T2D [97]. Nadler et al. have reported that insulin sensitivity decreases even in nondiabetic individuals after induction of MgD [98]. Finally, Mg2+ can also be a limiting factor in carbohydrate metabolism, since many of the enzymes in this process require Mg2+ as a cofactor during reactions that utilize the phosphorus bond [99].
Inadequate dietary intake of Mg2+ is an independent risk factor for the development of T2D. Lopez-Ridaura et al., evaluating 37,309 participants free of cardiovascular disease and T2D, found a significant inverse association between Mg2+ intake and diabetes risk [100]. Van Dam et al. reported a similar relationship. Their findings indicated that a diet high in Mg2+-rich foods, particularly whole grains, is associated with a substantially lower risk of T2D [101]. Benefits of Mg2+ supplementation in diabetic subjects have been found in some clinical studies. Rodriguez-Moran et al. reported that Mg2+ supplementation improves insulin sensitivity and secretion as well as metabolic control in patients with T2D [96]. Mooren et al. have shown beneficial effect of oral Mg2+ supplementation on insulin sensitivity in overweight, nondiabetic subjects [102].
2.3.5. MgD and Vascular Calcification
Vascular calcification is the extracellular deposition of Ca2+ in the arterial wall and is intimately linked with the HTN. On the other hand, HTN was considered a risk factor for atherosclerosis and associated calcification. Two types of extracellular vascular calcification are recognized, intimal and medial. Intimal calcification is exclusively associated with atherosclerosis. Medial calcification may contribute to increasing BP by decreasing the elasticity of the media. Decreased elasticity results in arterial stiffening which accelerates pulse wave velocity and widening the pulse pressure, leading ultimately to HTN. Intimal and, especially, medial vascular calcification are associated with arterial stiffening, the major cause of isolated systolic HTN in the elderly [103]. The first in vitro evidence in human aortic VSMCs for a protective role of Mg2+ on vascular calcification was based on the observation that living cells are necessary for Mg2+ ions to exert its protective effect. These studies suggested a potentially active intracellular role for Mg2+ ions in attenuating the vascular calcification process [33,35,104]. In confirmation of this, Hruby et al. reported on favorable associations between dietary and supplemental Mg2+ intake and lower calcification of the coronary arteries [105]. Furthermore, it was found that higher Mg2+ levels prevented calcification of bovine VSMCs, and further progression of the already established calcification. Inhibition of the Wnt/β -catenin signaling pathway was identified as one of the possible intracellular mechanisms by which Mg2+ achieved its anti-calcifying effect [104].
2.3.6. MgD and Vascular Aging
Aging represents a major risk factor for MgD. The total body Mg2+ content and intracellular Mg2+ tend to decrease with age. Aging is often associated with a Mg2+ deficiency due to reduced intake and/or absorption, increased renal wasting and/or reduced tubular reabsorption, as well as age-related illnesses and their treatment with certain drugs [106]. The aging process is associated with alterations in the properties of all the elements of the vascular wall, including endothelium, VSMCs, and ECM. This increases vascular stiffness and leads to the development of isolated systolic HTN. “Aging”-associated arterial changes and those associated with HTN (and early atherosclerosis and diabetes) are fundamentally intertwined at the cellular and molecular levels [107]. At the molecular and cellular levels, arterial aging and HTN-associated vascular changes are characterized by reduced NO production, increased generation of reactive oxygen species (oxidative stress), activation of transcription factors, induction of “aging” genes, stimulation of proinflammatory and profibrotic signaling pathways, reduced collagen turnover, calcification, VSMCs proliferation, and ECM remodeling. These processes contribute to increased fibrosis, which is further promoted by prohypertensive vasoactive agents, such as ATII, ET-1, and ALDO [12]. The cellular and molecular proinflammatory mechanisms that underlie arterial aging are novel putative candidates to be targeted by interventions aimed at attenuating arterial aging, and thus possibly attenuating the major risk factors for HTN and atherosclerosis [107]. Targeted interventions aimed at correcting MgD and maintaining an optimal Mg2+ balance may prove to be an appropriate strategy against arterial aging due to its positive effects on low-grade inflammation and oxidative stress associated with aging process (Figure 1).
2.4. MgD and Stress Response
Stress is among the potential psychological risk factors for HTN. Acute stressful events have no consistent association with the HTN. Chronic stress on the other hand, particularly the non-adaptive response to stress, may be a more likely cause of sustained elevation of BP. The mechanisms underlying the association between psychosocial stress and HTN can be divided into behavioral, psychological and pathophysiological. The latter involves neuro-endocrine activation mediated by the hypothalamic pituitary adrenal axis (HPAA) [108]. Mg2+ plays a key role in the activity of psychoneuroendocrine systems. For example, all elements of the limbic-HPAA are sensitive to the action of Mg2+. Mg2+ modulates activity of the HPAA which is a central substrate of the stress response system. Activation of the HPAA instigates adaptive autonomic, neuroendocrine, and behavioral responses to cope with the demands of the stressor [10]. MgD induced an increase in the transcription of the corticotropin releasing hormone in the paraventricular hypothalamic nucleus, and elevated adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) plasma levels, indicating an enhanced set-point of the HPAA [109]. MgD results in a stressor effect and increases susceptibility to the physiological damage produced by stress (Figure 1). Mg2+ supply has been shown to attenuate the development of adverse stress reactions. Stress activates the HPAA and the sympathetic nervous system. The innervation of the kidney may result in the overproduction of renin, which in turn activates the production of ATII, a powerful vasoconstrictor that elevates the BP [110]. Additionally, Mg2+ deficient mice are more sensitive to anxiety-provoking situations. Dysregulation of the HPAA evoked by MgD is normalizes by chronic desipramine or diazepam treatment. These data indicate that dysregulation in the HPAA may contribute to hyper-emotionality in response to dietary induced hypomagnesaemia [109].
Mg2+ ions also have a key role in the modulation of neurotransmission. Numerous studies have confirmed that the function of the native N-methyl-d-aspartate (NMDA) receptor is the result of equilibrium between extracellular and intracellular concentration of Mg2+. The blockade of the ion channel of the NMDA receptor is the most well-known and established way in which Mg2+ affects the functioning of the central nervous system (CNS) [109]. Mg2+ reduces neuronal hyperexcitability by inhibiting NMDA receptor activity and also is essential for the activity of metabotropic glutamate receptors (mGluRs) in the brain. The mGluRs play a key modulatory role in glutamatergic activity, secretion, and presynaptic release of glutamate, activity of the gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA)-ergic system, and regulation of the neuroendocrine system. Mg2+ may additionally modulate anxiety via increasing GABA availability by decreasing presynaptic glutamate release. GABA is a primary inhibitory transmitter in the CNS that counterbalances the excitatory action of glutamate [111]. The state of acute and chronic stress leads to depletion of intracellular Mg2+ and its loss in the urine, because in stressful situations secreted elevated amounts of Adr and NA help to remove Mg2+ from the cells. Intracellular RBCs Mg2+ depletion is found in patients with HTN. MgD affects the balance of monoamines, such as CA and serotonin in the brain. CA released into the blood is rapidly inactivated by the enzyme catechol-O-methyl transferase (COMT). The latter is activated by Mg2+ and is inhibited by Ca2+. MgD leads to decreased activity of COMT, which in turn increases the concentration of circulating CA [44]. Brain NA was determined in adult male mice with genetically low (MGL) or high (MGH) blood Mg2+ levels. NA levels were significantly higher in MGL than in MGH mice. These data together with the higher urinary NA excretion observed in the MGL line might account for the higher sensitivity and/or reactivity of MGL animals to stress [112]. Moreover, in stressful conditions, MGL mice displayed a more aggressive behavior than the control MGH strain. Altogether, MGL mice showed a more restless behavior, and much higher brain and urine NA levels than the MGH animals [113]. An analysis of the literature suggests the possible role of MgD in the susceptibility to CVD, observed among subjects displaying a type A behavior pattern. Type A subjects are more sensitive to stress and produce more CA than type B subjects. This, in turn, seems to induce an intracellular Mg2+ loss. In the long run, type A individuals would develop a state of MgD, which may promote a greater sensitivity to stress, and ultimately to the development of CVD [114], including HTN. Hypomagnesemia usually involves cellular Mg2+ depletion, but acute stress that increase serum concentrations of CA may lower serum Mg2+ concentration, which does not always imply depleted tissue Mg2+ stores [115].
The potential effect of Mg2+ in attenuating psychological response to stress merits further investigation since stress is a ubiquitous feature of modern life. The modulation of HPAA by Mg2+, which has been shown to reduce central (ACTH), peripheral (cortisol) endocrine responses [111], and reduces neuronal hyperexcitability by NMDA, mGluRs and GABA-effects suggests that behavioral responses to stress exposure may be attenuated by Mg2+ supplementation in patients with HTN.
3. MgD, Groups at Risk, Replacement Therapy and Prevention
3.1. Mg2+ Supplements in Hypertensive Subjects
HTN is a complex, heterogeneous disorder whose etiology, pathogenesis, and treatment still raises some unresolved questions. Maintenance of optimal Mg2+ status in the human body may help prevent or treat HTN. Although most epidemiological and experimental studies support a role of MgD in the pathophysiology of HTN, data from clinical studies have been less convincing [38]. In some studies the inverse association between Mg2+ and BP remained inconclusive, but not in others [116]. Ultimately, the view is that MgD in patients with HTN is linking with significant adverse effects on BP. In the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study, serum Mg2+ level in hypertensive patients was inversely proportional to the systolic BP. The study examined a cohort of 15248 participants aged 45–64 years [117]. In another meta-analysis of 34 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trials involving a total of 2028 subjects, it was found that oral administration of Mg2+ resulted in a significant reduction in both systolic and diastolic BP (2.00 mmHg and 1.78 mmHg respectively) [118]. An analytical review of 44 studies in humans have shown that low doses of Mg2+ supplementation, for example 243 mg/day can significantly lower BP in patients with uncomplicated HTN, treated six months or longer with antihypertensive drugs [119]. Moreover, the researchers reported that patients with MgD require higher doses of antihypertensive drugs compared to those with normal Mg2+ concentration [118]. The evidence supporting the cause–consequence antihypertensive effect of Mg2+ in adults suggest that oral Mg2+ supplements may be recommended for the prevention of arterial HTN or as adjuvant antihypertensive therapy [11]. It should be noted that MgD is not found in all patients with HTN. On the other hand, not all people with hypomagnesemia have high BP. These differences are probably due to the fact that patients with high BP do not constitute a homogenous group [78]. This may be one of the possible causes for the discrepancy between epidemiological and clinical data. Despite these discrepancies concerning Mg2+ status and high BP, some hypertensive patients constantly demonstrate hypomagnesemia. Among them are patients with obesity, insulin resistance, hypertriglyceridemia, severe forms of HTN, hyperaldosteronism (volume-dependent HTN), pregnancy induced HTN, and patients of African-American origin [120]. In view of the still ill-defined role of Mg2+ in clinical HTN, Mg2+ supplementation is advised in those hypertensive patients who are receiving diuretics, who have resistant or secondary HTN or who have frank MgD [121]. In the USA, the Estimated Average Requirement (EAR) and RDA of Mg2+ for adult women are set at 255–265 mg and 310–320 mg/day, respectively. The EAR and RDA of Mg2+ for adult men are set at 330–350 mg and 410–420 mg/day, respectively. These dietary reference intakes are based on data from 16 men and 18 women who have consumed self-selected diets and have had a decreased Mg2+ intake during the balance periods, which could have affected balance values [122,123]. The current RDA for Mg2+ ranges from 80 mg/day for children 1–3 years of age to 130 mg/day for children 4–8 years of age. For older males, the RDA for Mg2+ ranges from as low as 240 mg/day (range, 9–13 years of age) and increases to 420 mg/day for males 31–70 years of age and older. For females, the RDA ranges from 240 mg/day (9–13 years of age) to 360 mg/day for females 14–18 years of age. The RDA for females 31–70 years of age and older is 320 mg/day. Many nutritional experts feel the ideal intake for Mg2+ should be based on the body weight (e.g., 4–6 mg per kg/day) [4]. Intravenous Mg2+ supplementation may be more effective, but this treatment has the disadvantage that it requires regular hospital visits. The treatment regimen of intravenous Mg2+ supplementation normally consists of 8–12 g of Mg-sulfate in the first 24 h followed by 4–6 g/day for 3 or 4 days. When serum Mg2+ levels are extremely low or are accompanied by hypokalemia, Mg2+ supplementation may not be sufficient to restore normal Mg2+ levels. In that case, patients are often cosupplemented with K+ or receive amiloride to prevent K+ secretion [124]. Recent reports indicate that individuals with serum Mg2+ concentrations >0.75 mmol/L, or high as 0.85 mmol/L, could be Mg2+-deficient. Thus, to assess Mg2+ status of an individual with a serum Mg2+ concentration between 0.75 and 0.85 mmol/L is requires additional measures of status. A urinary excretion of <80 mg (3.29 mmol)/day and/or dietary intake history showing a Mg2+ intake of <250 mg/day would support the presence of MgD [122]. In the treatment of MgD are recommended organic bound Mg2+ salts, such as Mg2+ citrate, gluconate, orotate, or aspartate, because of their high bioavailability [4,125].
Hypermagnesemia is a rare condition and is seen most often in patients with renal impairment who take medicines containing Mg2+. Excessive intake of supplemental Mg2+ can result in adverse effects, especially in impaired renal function. Serum concentrations >8 mmol/L cause drowsiness, vasodilation, slowing of atrioventricular conduction, and hypotension [126,127,128].
3.2. Food and Water Sources of Mg2+
3.2.1. Mg2+ Intake from Food
In the Western World, dietary intake of Mg2+ is subnormal, with shortfalls of between 65 and 225 mg of Mg2+/day, depending upon geographic region. Several epidemiologic studies in North America and Europe have shown that children and adults, some which are pregnant women, consuming Western-type diets are low in Mg2+ content (i.e., 30–50% of the RDA for these populations) [129]. Epidemiological observations suggest a negative correlation between dietary Mg2+ intake and BP [11]. Overall, the current evidence supports the importance of adequate dietary Mg2+ intake for the reduction of BP and total CVD risk. These findings support the importance of increasing the consumption of Mg2+-rich foods, including fruits, vegetables, nuts, and whole grains in the treatment and prevention of high BP [125]. A Mg2+-rich diet should be encouraged in hypertensive subjects as well as in predisposed communities because of the advantages of such a diet in the prevention of HTN [121]. The Dietary Approaches to Stop HTN (DASH) diet (originally termed the “combination diet”4) contains larger amounts of Mg2+, K+, Ca2+, dietary fiber, and protein and smaller amounts of total and saturated fat and cholesterol than the typical diet [130]. The Mediterranean diet is also rich in Mg2+, dietary fiber, antioxidant capacity, and polyphenolic compounds [131]. In trials of vegetarian diets, replacing animal products with vegetable products reduced BP in normotensive and hypertensive people. Aspects of vegetarian diets believed to reduce BP include their high levels of fiber and minerals (such as Mg2+ and K+) and their reduced fat content. In observational studies, significant inverse associations of BP with intake of Mg2+, K+, Ca2+, and fiber have also been reported [132].
3.2.2. Mg2+ Intake from Water
Water is a variable source of Mg2+ intake. Typically, water with increased “hardness” has a higher concentration of Mg2+ salts. Since this varies depending on the area from which water comes, Mg2+ intake from water is usually not estimated to a sufficient extent. This omission may lead to impaired assessment and underestimation of total intake of Mg2+ in certain regions [123]. The modern processed food diet, which is low in Mg2+ and is spreading globally, makes this well-researched potential of drinking-water Mg2+ worth serious consideration, especially in areas where insufficient dietary intake of Mg2+ is prevalent. It would be wise and forward-thinking for public health officials to consider how high-Mg2+ drinking water might be made available to communities, i.e., water with Mg2+ levels of at least 10 mg/L and ideally 25–100 mg/L [133].
4. Conclusions
The enhancing effect of MgD on BP should be considered in the context of total intake and loss of Mg2+ in each individual patient with HTN. Special attention should be given to the risk groups in which serum Mg2+ levels should be monitored periodically. Considering the numerous positive effects of Mg2+ on a number of mechanisms related to HTN, consuming a healthy diet that provides the recommended amount of Mg2+ can be an appropriate strategy for helping control BP.
Author Contributions
K.K. designed the review, interpreted the data, and wrote the manuscript; K.K. and L.H. performed the literature research. The authors approved the final version of the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
This review was accomplished with the financial support from the Medical University-Pleven, Bulgaria.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| MgD | Magnesium deficiency |
| Mg2+ | Magnesium |
| Ca2+ | Calcium |
| K+ | Potassium |
| Na+ | Sodium |
| HTN | Hypertension |
| MetS | Metabolic syndrome |
| T2D | Type 2 diabetes |
| RDA | Recommended Dietary Allowance |
| EAR | Estimated Average Requirement |
| CVD | Cardiovascular diseases |
| BP | Blood pressure |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| TRPM6 | Transient receptor potential melastatin-6 channel |
| TRPM7 | Transient receptor potential melastatin-7 channel |
| VSMCs | Vascular smooth muscle cells |
| ET-1 | Endothelin-1 |
| ATII | Angiotensin II |
| ALDO | Aldosterone |
| SHR | Spontaneously hypertensive rats |
| WKY | Wistar-Kyoto rats |
| EGF | Epidermal growth factor |
| PTH | Parathyroid hormone |
| IP3 | Inositol-1,4,5-trisphosphate |
| PIP2 | Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate |
| AT1 | Angiotensin II receptor type 1 |
| ETA | Endothelin A receptor |
| V1a | Vasopressin receptor 1a |
| PLC | Phospholipase C |
| PKC | Protein kinase C |
| PGI2 | Prostacyclin |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| RBCs | Red blood cells |
| eNOS | Endothelial nitric oxide synthase |
| PGE1 | Prostaglandin E1 |
| RAAS | Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System |
| NA | Noradrenaline |
| Adr | Adrenaline |
| CA | Catecholamines |
| ACh | Acetylcholine |
| ADCY | Adenylate cyclase |
| ISO | Isoproterenol |
| CRP | C-reactive protein |
| IL | Interleukin |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-α |
| VCAM | Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 |
| PAI-1 | Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| HAS | Hyaluronan synthases |
| HYAL | Hyaluronidase |
| TG2 | Transglutaminase |
| LOX | Lysyl oxidase |
| MMPs | Matrix metalloproteinases |
| TIMPs | Tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor kappa B |
| LDL | Low-density lipoproteins |
| HDL | High-density lipoproteins |
| IR | Insulin receptor |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| PI3K | Phosphoinositide 3-kinase |
| PIP2 | Phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate |
| GLUT4 | Glucose transporter type 4 |
| IRTK | Insulin receptor tyrosine kinase |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| HPAA | Hypothalamic Pituitary Adrenal Axis |
| ACTH | Adrenocorticotropic hormone |
| NMDA | N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor |
| mGluRs | Metabotropic glutamate receptors |
| GABA | Gamma-aminobutyric acid |
| COMT | Catechol-O-methyl transferase |
| MGL | Magnesium low blood levels |
| MGH | Magnesium high blood levels |
References
- Ismail, A.A.; Ismail, N.A. Magnesium: A mineral essential for health yet generally underestimated or even ignored. J. Nutr. Food Sci. 2016, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, M.K.; Bae, Y.J. Association of magnesium intake with high blood pressure in Korean adults: Korea national health and nutrition examination survey 2007–2009. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swaminathan, R. Magnesium metabolism and its disorders. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2003, 24, 47. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gröber, U.; Schmidt, J.; Kisters, K. Magnesium in prevention and therapy. Nutrients 2015, 7, 8199–8226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Baaij, J.H.; Hoenderop, J.G.; Bindels, R.J. Regulation of magnesium balance: Lessons learned from human genetic disease. Clin. Kidney J. 2012, 5, i15–i24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, J.W.; Park, T.J. Magnesium metabolism. Electrolyte Blood Press. 2008, 6, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, G.; Konrad, M.; Heuss, L.T.; Schorn, R. A Case of Severe Hypomagnesaemia. Open J. Nephrol. 2013, 3, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, X.; Jin, F.; Hao, Y.; Li, H.; Tang, T.; Wang, H.; Yan, W.; Dai, K. Magnesium and the risk of cardiovascular events: A meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kass, L.; Sullivan, K.R. Low Dietary Magnesium Intake and Hypertension. World J. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2016, 6, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galan, P.; Preziosi, P.; Durlach, V.; Valeix, P.; Ribas, L.; Bouzid, D.; Favier, A.; Hercberg, S. Dietary magnesium intake in a French adult population. Magnes. Res. 1997, 10, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Del Gobbo, L.C.; Rosanoff, A.; Wang, J.; Zhang, W.; Song, Y. Effects of magnesium supplementation on blood pressure: A meta-analysis of randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trials. Hypertension 2016, 68, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, A.; Montezano, A.C.; Lopes, R.A.; Rios, F.; Touyz, R.M. Vascular fibrosis in aging and hypertension: Molecular mechanisms and clinical implications. Can. J. Cardiol. 2016, 32, 659–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landau, R.; Scott, J.A.; Smiley, R.M. Magnesium-induced vasodilation in the dorsal hand vein. BJOG 2004, 111, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, A.R.; Medeiros, F.; Umbelino, B.; Oigman, W.; Touyz, R.M.; Neves, M.F. Altered vascular structure and wave reflection in hypertensive women with low magnesium levels. J. Am. Soc. Hypertens. 2013, 7, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touyz, R.M.; Yao, G. Modulation of vascular smooth muscle cell growth by magnesium-role of mitogen-activated protein kinases. J. Cell. Physiol. 2003, 197, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belin, R.J.; He, K. Magnesium physiology and pathogenic mechanisms that contribute to the development of the metabolic syndrome. Magnes. Res. 2007, 20, 107–129. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Houston, M. The role of magnesium in hypertension and cardiovascular disease. J. Clin. Hypertens. (Greenwich) 2011, 13, 843–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paravicini, T.M.; Chubanov, V.; Gudermann, T. TRPM7: A unique channel involved in magnesium homeostasis. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2012, 44, 1381–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldoli, E.; Castiglioni, S.; Maier, J.A. Regulation and function of TRPM7 in human endothelial cells: TRPM7 as a potential novel regulator of endothelial function. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antunes, T.T.; Callera, G.E.; He, Y.; Yogi, A.; Ryazanov, A.G.; Ryazanova, L.V.; Zhai, A.; Stewart, D.J.; Shrier, A.; Touyz, R.M. Transient receptor potential melastatin 7 cation channel kinase: New player in angiotensin II-induced hypertension. Hypertension 2016, 67, 763–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touyz, R.M.; He, Y.; Montezano, A.C.; Yao, G.; Chubanov, V.; Gudermann, T.; Callera, G.E. Differential regulation of transient receptor potential melastatin 6 and 7 cation channels by ANG II in vascular smooth muscle cells from spontaneously hypertensive rats. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2006, 290, R73–R78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldoli, E.; Maier, J.A. Silencing TRPM7 mimics the effects of magnesium deficiency in human microvascular endothelial cells. Angiogenesis 2012, 15, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di, A.; Malik, A.B. TRP channels and the control of vascular function. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2010, 10, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groenestege, W.M.T.; Thébault, S.; van der Wijst, J.; van den Berg, D.; Janssen, R.; Tejpar, S.; van den Heuvel, L.P.; van Cutsem, E.; Hoenderop, J.G.; Knoers, N.V.; et al. Impaired basolateral sorting of pro-EGF causes isolated recessive renal hypomagnesemia. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 2260–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thebault, S.; Alexander, R.T.; Groenestege, W.M.T.; Hoenderop, J.G.; Bindels, R.J. EGF increases TRPM6 activity and surface expression. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 20, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groenestege, W.M.T.; Hoenderop, J.G.; van den Heuvel, L.; Knoers, N.; Bindels, R.J. The epithelial Mg2+ channel transient receptor potential melastatin 6 is regulated by dietary Mg2+ content and estrogens. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 1035–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, G.; van der Wijst, J.; van der Kemp, A.; van Zeeland, F.; Bindels, R.J.; Hoenderop, J.G. Regulation of the epithelial Mg2+ channel TRPM6 by estrogen and the associated repressor protein of estrogen receptor activity (REA). J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 14788–14795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Der Wijst, J.; Hoenderop, J.G.; Bindels, R.J. Epithelial Mg2+ channel TRPM6: Insight into the molecular regulation. Magnes. Res. 2009, 22, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mubagwa, K.; Gwanyanya, A.; Zakharov, S.; Macianskiene, R. Regulation of cation channels in cardiac and smooth muscle cells by intracellular magnesium. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2007, 458, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritchie, G.; Kerstan, D.; Dai, L.J.; Kang, H.S.; Canaff, L.; Hendy, G.N.; Quamme, G.A. 1,25(OH)2D3 stimulates Mg2+ uptake into MDCT cells: Modulation by extracellular Ca2+ and Mg2+. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2001, 280, F868–F878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagström, E.; Ahlström, T.; Ärnlöv, J.; Larsson, A.; Melhus, H.; Hellman, P.; Lind, L. Parathyroid hormone and calcium are independently associated with subclinical vascular disease in a community-based cohort. Atherosclerosis 2015, 238, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahnen-Dechent, W.; Ketteler, M. Magnesium basics. Clin. Kidney J. 2012, 5, i3–i14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louvet, L.; Bazin, D.; Büchel, J.; Steppan, S.; Passlick-Deetjen, J.; Massy, Z.A. Characterisation of calcium phosphate crystals on calcified human aortic vascular smooth muscle cells and potential role of magnesium. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0115342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborti, S.; Chakraborti, T.; Mandal, M.; Mandal, A.; Das, S.; Ghosh, S. Protective role of magnesium in cardiovascular diseases: A review. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2002, 238, 163–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villa-Bellosta, R. Impact of magnesium: Calcium ratio on calcification of the aortic wall. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolte, D.; Vijayaraghavan, K.; Khera, S.; Sica, D.A.; Frishman, W.H. Role of magnesium in cardiovascular diseases. Cardiol. Rev. 2014, 22, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, A.R.; Umbelino, B.; Correia, M.L.; Neves, M.F. Magnesium and vascular changes in hypertension. Int. J. Hypertens. 2012, 2012, 754250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sontia, B.; Touyz, R.M. Role of magnesium in hypertension. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2007, 458, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kharitonova, M.; Iezhitsa, I.; Zheltova, A.; Ozerov, A.; Spasov, A.; Skalny, A. Comparative angioprotective effects of magnesium compounds. J. Trace Elem. Med. Biol. 2015, 29, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laurant, P.; Dalle, M.; Berthelot, A.; Rayssiguier, Y. Time-course of the change in blood pressure level in magnesium-deficient Wistar rats. Br. J. Nutr. 1999, 82, 243–251. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cantin, M. Relationship of juxtaglomerular apparatus and adrenal cortex to biochemical and extracellular fluid volume changes in magnesium deficiency. Lab. Investig. 1970, 22, 558–568. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- James, M.F.; Beer, R.E.; Esser, J.D. Intravenous magnesium sulfate inhibits catecholamine release associated with tracheal intubation. Anesth. Analg. 1989, 68, 772–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Douglas, W.W.; Rubin, R.P. The mechanism of catecholamine release from the adrenal medulla and the role of calcium in stimulus-secretion coupling. J. Physiol. 1963, 167, 288–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torshin, I.Y.; Gromova, O.A.; Gusev, E.I. Mechanisms of antistress and antidepressant action of magnesium and pyridoxine. Korsakov’s J. Neurol. Psychiatry 2009, 109, 107–111. [Google Scholar]
- Oka, M.; Ohuchi, T.; Yoshida, H.; Imaizumi, R. Stimulatory effect of adenosine triphosphate and magnesium on the release of catecholamines from adrenal medullary granules. Jpn. J. Pharmacol. 1967, 17, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farmer, J.B.; Campbell, I.K. Calcium and magnesium ions: Influence on the response of an isolated artery to sympathetic nerve stimulation, noradrenaline and tyramine. Br. J. Pharmacol. 1967, 29, 319–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whyte, K.F.; Addis, G.J.; Whitesmith, R.; Reid, J.L. Adrenergic control of plasma magnesium in man. Clin. Sci. 1987, 72, 135–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joborn, H.; Akerström, G.; Ljunghall, S. Effects of exogenous catecholamines and exercise on plasma magnesium concentrations. Clin. Endocrinol. 1985, 23, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keenan, D.; Romani, A.; Scarpa, A. Differential regulation of circulating Mg2+ in the rat by β1-and β2-adrenergic receptor stimulation. Circ. Res. 1995, 77, 973–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boos, C.J.; Lip, G.Y. Is hypertension an inflammatory process? Curr. Pharm. Des. 2006, 12, 1623–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnaud, M.J. Update on the assessment of magnesium status. Br. J. Nutr. 2008, 99, S24–S36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbagallo, M.; Belvedere, M.; Dominguez, L.J. Magnesium homeostasis and aging. Magnes. Res. 2009, 22, 235–246. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- King, D.E.; Mainous, A.G., III; Geesey, M.E.; Ellis, T. Magnesium intake and serum C-reactive protein levels in children. Magnes. Res. 2007, 20, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- King, D.E.; Mainous, A.G., III; Geesey, M.E.; Woolson, R.F. Dietary magnesium and C-reactive protein levels. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2005, 24, 166–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, D.J.; Xun, P.; Liu, K.; Loria, C.; Yokota, K.; Jacobs, D.R.; He, K. Magnesium intake in relation to systemic inflammation, insulin resistance, and the incidence of diabetes. Diabetes Care 2010, 33, 2604–2610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier, J.A.; Malpuech-Brugère, C.; Zimowska, W.; Rayssiguier, Y.; Mazur, A. Low magnesium promotes endothelial cell dysfunction: Implications for atherosclerosis, inflammation and thrombosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2004, 1689, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friese, R.S.; Rao, F.; Khandrika, S.; Thomas, B.; Ziegler, M.G.; Schmid-Schönbein, G.W.; O’Connor, D.T. Matrix metalloproteinases: Discrete elevations in essential hypertension and hypertensive end-stage renal disease. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2009, 31, 521–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heagerty, A.M.; Aalkjaer, C.; Bund, S.J.; Korsgaard, N.; Mulvany, M.J. Small artery structure in hypertension. Dual processes of remodeling and growth. Hypertension 1993, 21, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulvany, M.J.; Baumbach, G.L.; Aalkjaer, C.; Heagerty, A.M.; Korsgaard, N.; Schiffrin, E.L.; Heistad, D.D. Vascular remodeling. Hypertension 1996, 28, 505–506. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mulvany, M.J. Small artery remodeling and significance in the development of hypertension. Physiology 2002, 17, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steppan, J.; Bergman, Y.; Viegas, K.; Armstrong, D.; Tan, S.; Wang, H.; Melucci, S.; Hori, D.; Park, S.Y.; Barreto, S.F.; et al. Tissue transglutaminase modulates vascular stiffness and function through crosslinking-dependent and crosslinking-independent functions. J. Am. Heart. Assoc. 2017, 6, e004161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bains, W. Transglutaminse 2 and EGGL, the protein cross-link formed by transglutaminse 2, as therapeutic targets for disabilities of old age. Rejuvenation Res. 2013, 16, 495–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torshin, I.Y.; Gromova, O.A. Connective tissue dysplasia, cell biology and molecular mechanisms of magnesium exposure. RMZh 2008, 16, 230–238. [Google Scholar]
- Martínez-Revelles, S.; García-Redondo, A.B.; Avendaño, M.S.; Varona, S.; Palao, T.; Orriols, M.; Roque, F.R.; Fortuño, A.; Touyz, R.M.; Martínez-González, J.; et al. Lysyl oxidase induces vascular oxidative stress and contributes to arterial stiffness and abnormal elastin structure in hypertension: Role of p38MAPK. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2017, 27, 379–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avtandilov, A.G.; Pukhaeva, A.A.; Manizer, E.D. Magnesium and mitral valve prolapse. Efficiency and application points. Ration. Pharmacother. Card. 2010, 6, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, J.A. Endothelial cells and magnesium: Implications in atherosclerosis. Clin. Sci. 2012, 122, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolinsky, B.M.; Ippolito, D.L.; Tinnemore, D.; Stallings, J.D.; Zelig, C.M.; Napolitano, P.G. The effect of magnesium sulfate on the activity of matrix metalloproteinase-9 in fetal cord plasma and human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2010, 203, 371e1–371e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostov, K. Pathophysiological Role of Endothelin-1, Matrix Metalloproteinases-2, -9 and Magnesium in the Development and Dynamics of Vascular Changes at Various Degrees of Arterial Hypertension. Doctoral Disertation, Medical University of Pleven, Pleven, Bulgaria, 2 December 2016. Available online: http://www.mu-pleven.bg/procedures/59/Avtoreferat.pdf (accessed on 1 December 2016).
- Ferrè, S.; Baldoli, E.; Leidi, M.; Maier, J.A. Magnesium deficiency promotes a pro-atherogenic phenotype in cultured human endothelial cells via activation of NFkB. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2010, 1802, 952–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, H.; Lee, J.D.; Shimizu, H.; Uzui, H.; Mitsuke, Y.; Ueda, T. Effects of magnesium on the production of extracellular matrix metalloproteinases in cultured rat vascular smooth muscle cells. Atherosclerosis 2003, 166, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, H.; Uzui, H.; Lee, J.D.; Shimizu, H.; Ueda, T. Effects of magnesium on matrix metalloproteinase-2 production in cultured rat cardiac fibroblasts. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2004, 99, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altura, B.M. Insights into the possible mechanisms by which platelet-activating factor and PAF-receptors function in vascular smooth muscle in magnesium deficiency and vascular remodeling: Possible links to atherogenesis, hypertension and cardiac failure. Int. J. Cardiol. Res. 2016, 3, 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Kisters, K.; Gröber, U. Magnesium in health and disease. Plant Soil 2013, 368, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaguchi, Y.; Fujii, N.; Shoji, T.; Hayashi, T.; Rakugi, H.; Isaka, Y. Hypomagnesemia is a significant predictor of cardiovascular and non-cardiovascular mortality in patients undergoing hemodialysis. Kidney Int. 2014, 85, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, S.; Padmanaban, P.; Deepti, G.N.; Sarkar, G.; Sumathi, S.; Toora, B.D. Serum magnesium and dyslipidemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Biomed. Res. 2012, 23, 295–300. [Google Scholar]
- King, D.E. Inflammation and elevation of C-reactive protein: Does magnesium play a key role? Magnes. Res. 2009, 22, 57–59. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barbagallo, M.; Dominguez, L.J. Magnesium metabolism in type 2 diabetes mellitus, metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2007, 458, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geiger, H.; Wanner, C. Magnesium in disease. Clin. Kidney J. 2012, 5, i25–i38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostov, K.; Blazhev, A.; Atanasova, M.; Dimitrova, A. Serum concentrations of endothelin-1 and matrix metalloproteinases-2,-9 in pre-hypertensive and hypertensive patients with type 2 diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Boer, I.H.; Bangalore, S.; Benetos, A.; Davis, A.M.; Michos, E.D.; Muntner, P.; Rossing, P.; Zoungas, S.; Bakris, G. Diabetes and hypertension: A position statement by the American Diabetes Association. Diabetes Care 2017, 40, 1273–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrero-Romero, F.; Bermudez-Peña, C.; Rodríguez-Morán, M. Severe hypomagnesemia and low-grade inflammation in metabolic syndrome. Magnes. Res. 2011, 24, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, F.H. Magnesium, inflammation, and obesity in chronic disease. Nutr. Rev. 2010, 68, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, D.P.; Sharma, R.; Bansal, D.D. Implications of magnesium deficiency in type 2 diabetes: A review. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2010, 134, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Günther, T. The biochemical function of Mg2+ in insulin secretion, insulin signal transduction and insulin resistance. Magnes. Res. 2010, 23, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rosolova, H.; Mayer, O., Jr.; Reaven, G.M. Insulin-mediated glucose disposal is decreased in normal subjects with relatively low plasma magnesium concentrations. Metabolism 2000, 49, 418–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venu, L.; Padmavathi, I.J.; Kishore, Y.D.; Bhanu, N.V.; Rao, K.R.; Sainath, P.B.; Ganeshan, M.; Raghunath, M. Long-term effects of maternal magnesium restriction on adiposity and insulin resistance in rat pups. Obesity 2008, 16, 1270–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suarez, A.; Pulido, N.; Casla, A.; Casanova, B.; Arrieta, F.J.; Rovira, A. Impaired tyrosine-kinase activity of muscle insulin receptors from hypomagnesaemic rats. Diabetologia 1995, 38, 1262–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbagallo, M.; Dominguez, L.J. Magnesium and the cardiometabolic syndrome. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2012, 1, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, C.W.; Lawrence, M.C. Ligand-induced activation of the insulin receptor: A multi-step process involving structural changes in both the ligand and the receptor. Bioessays 2009, 31, 422–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, M.; Hansen, B.; De Meyts, P.; Schäffer, L.; Ursø, B. Activation of the insulin receptor by insulin and a synthetic peptide leads to divergent metabolic and mitogenic signaling and responses. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 35179–35186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farese, R.V.; Sajan, M.P.; Standaert, M.L. Insulin-sensitive protein kinases (atypical protein kinase C and protein kinase B/Akt): Actions and defects in obesity and type II diabetes. Exp. Biol. Med. 2005, 230, 593–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sale, E.M.; Sale, G.J. Protein kinase B: Signalling roles and therapeutic targeting. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2008, 65, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sano, H.; Kane, S.; Sano, E.; Mı̂inea, C.P.; Asara, J.M.; Lane, W.S.; Garner, C.W.; Lienhard, G.E. Insulin-stimulated phosphorylation of a Rab GTPase-activating protein regulates GLUT4 translocation. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 14599–14602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddle, K. Signalling by insulin and IGF receptors: Supporting acts and new players. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2011, 47, R1–R10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbagallo, M.; Gupta, R.K.; Bardicef, O.; Bardicef, M.; Resnick, L.M. Altered ionic effects of insulin in hypertension: Role of basal ion levels in determining cellular responsiveness. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1997, 82, 1761–1765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Morán, M.; Guerrero-Romero, F. Oral magnesium supplementation improves insulin sensitivity and metabolic control in type 2 diabetic subjects: A randomized double-blind controlled trial. Diabetes Care 2003, 26, 1147–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Häring, H.U. The insulin receptor: Signalling mechanism and contribution to the pathogenesis of insulin resistance. Diabetologia 1991, 34, 848–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadler, J.L.; Rude, R.K. Disorders of magnesium metabolism. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 1995, 24, 623–641. [Google Scholar]
- Chaudhary, D.P.; Boparai, R.K.; Sharma, R.; Bansal, D.D. Studies on the development of an insulin resistant rat model by chronic feeding of low magnesium high sucrose diet. Magnes. Res. 2004, 17, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Ridaura, R.; Willett, W.C.; Rimm, E.B.; Liu, S.; Stampfer, M.J.; Manson, J.E.; Hu, F.B. Magnesium intake and risk of type 2 diabetes in men and women. Diabetes Care 2004, 27, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dam, R.M.; Hu, F.B.; Rosenberg, L.; Krishnan, S.; Palmer, J.R. Dietary calcium and magnesium, major food sources, and risk of type 2 diabetes in US black women. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 2238–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mooren, F.C.; Krüger, K.; Völker, K.; Golf, S.W.; Wadepuhl, M.; Kraus, A. Oral magnesium supplementation reduces insulin resistance in non-diabetic subjects—A double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized trial. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2011, 13, 281–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalra, S.S.; Shanahan, C.M. Vascular calcification and hypertension: Cause and effect. Ann. Med. 2012, 44, S85–S92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Floege, J. Magnesium in CKD: More than a calcification inhibitor? J. Neurol. 2015, 28, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hruby, A.; O’Donnell, C.J.; Jacques, P.F.; Meigs, J.B.; Hoffmann, U.; McKeown, N.M. Magnesium intake is inversely associated with coronary artery calcification: The Framingham Heart Study. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2014, 7, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbagallo, M.; Dominguez, L.J. Magnesium, oxidative stress, and aging muscle. Aging 2014, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakatta, E.G. The reality of aging viewed from the arterial wall. Artery Res. 2013, 7, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agyei, B.; Nicolaou, M.; Boateng, L.; Dijkshoorn, H.; Agyemang, C. Relationship between psychosocial stress and hypertension among Ghanaians in Amsterdam, the Netherlands–the GHAIA study. BMC Public Health 2014, 14, 692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pochwat, B.; Szewczyk, B.; Sowa-Kucma, M.; Siwek, A.; Doboszewska, U.; Piekoszewski, W.; Gruca, P.; Papp, M.; Nowak, G. Antidepressant-like activity of magnesium in the chronic mild stress model in rats: Alterations in the NMDA receptor subunits. Int. J. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014, 17, 393–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rayssiguier, Y.; Libako, P.; Nowacki, W.; Rock, E. Magnesium deficiency and metabolic syndrome: Stress and inflammation may reflect calcium activation. Magnes. Res. 2010, 23, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Boyle, N.B.; Lawton, C.; Dye, L. The effects of magnesium supplementation on subjective anxiety and stress–a systematic review. Nutrients 2017, 9, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amyard, N.; Leyris, A.; Monier, C.; Frances, H.; Boulu, R.G.; Henrotte, J.G. Brain catecholamines, serotonin and their metabolites in mice selected for low (MGL) and high (MGH) blood magnesium levels. Magnes. Res. 1995, 8, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Henrotte, J.G.; Franck, G.; Santarromana, M.; Francès, H.; Mouton, D.; Motta, R. Mice selected for low and high blood magnesium levels: A new model for stress studies. Physiol. Behav. 1997, 61, 653–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henrotte, J.G. Type A behavior and magnesium metabolism. Magnesium 1986, 5, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ryzen, E.; Servis, K.L.; Rude, R.K. Effect of intravenous epinephrine on serum magnesium and free intracellular red blood cell magnesium concentrations measured by nuclear magnetic resonance. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 1990, 9, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.; Fang, X.; Wei, X.; Liu, Y.; Jin, Z.; Chen, Q.; Fan, Z.; Aaseth, J.; Hiyoshi, A.; He, J.; et al. Dose-response relationship between dietary magnesium intake, serum magnesium concentration and risk of hypertension: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies. Nutr. J. 2017, 16, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Folsom, A.R.; Melnick, S.L.; Eckfeldt, J.H.; Sharrett, A.R.; Nabulsi, A.A.; Hutchinson, R.G.; Metcalf, P.A. Associations of serum and dietary magnesium with cardiovascular disease, hypertension, diabetes, insulin, and carotid arterial wall thickness: The ARIC study. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 1995, 48, 927–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whang, R.; Chrysant, S.; Dillard, B.; Smith, W.; Fryer, A. Hypomagnesemia and hypokalemia in 1,000 treated ambulatory hypertensive patients. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 1982, 1, 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosanoff, A. Magnesium supplements may enhance the effect of antihypertensive medications in stage 1 hypertensive subjects. Magnes. Res. 2010, 23, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Touyz, R.M. Magnesium in clinical medicine. Front. Biosci. 2004, 9, 1278–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touyz, R.M. Role of magnesium in the pathogenesis of hypertension. Mol. Aspects Med. 2003, 24, 107–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, F.H. Guidance for the determination of status indicators and dietary requirements for magnesium. Magnes. Res. 2016, 29, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Standing Committee on the Scientific Evaluation of Dietary Reference Intakes; Food and Nutrition Board; Institute of Medicine (IOM). Dietary Reference Intakes for Calcium, Phosphorus, Magnesium, Vitamin D, and Fluoride; National Academies Press: Washington, DC, USA, 1997.
- De Baaij, J.H.; Hoenderop, J.G.; Bindels, R.J. Magnesium in man: Implications for health and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2015, 95, 1–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosique-Esteban, N.; Guasch-Ferré, M.; Hernández-Alonso, P.; Salas-Salvadó, J. Dietary Magnesium and Cardiovascular Disease: A Review with Emphasis in Epidemiological Studies. Nutrients 2018, 10, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crosby, V.; Elin, R.J.; Twycross, R.; Mihalyo, M.; Wilcock, A. Magnesium. J. Pain Symptom Manag. 2013, 45, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikawa, M.; Shimada, N.; Kanzaki, M.; Ikegami, T.; Fukuoka, T.; Fukushima, M.; Asano, K. The characteristics of patients with hypermagnesemia who underwent emergency hemodialysis. Acute Med. Surg. 2018, 5, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celi, L.A.; Scott, D.J.; Lee, J.; Nelson, R.; Alper, S.L.; Mukamal, K.J.; Mark, R.G.; Danziger, J. Association of hypermagnesemia and blood pressure in the critically ill. J. Hypertens. 2013, 31, 2136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Altura, B.M.; Li, W.; Zhang, A.; Zheng, T.; Shah, N.C. Sudden cardiac death in infants, children and young adults: Possible roles of dietary magnesium intake and generation of platelet-activating factor in coronary arteries. J. Heart Health 2016, 2, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Sacks, F.M.; Svetkey, L.P.; Vollmer, W.M.; Appel, L.J.; Bray, G.A.; Harsha, D.; Obarzanek, E.; Conlin, P.R.; Miller, E.R., 3rd; Simons-Morton, D.G.; et al. Effects on blood pressure of reduced dietary sodium and the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet. N. Engl. J. Med. 2001, 344, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.M.; Steck, S.E.; Fung, T.T.; Zhang, J.; Hazlett, L.J.; Han, K.; Lee, S.H.; Kwon, H.S.; Merchant, A.T. Mediterranean diet, Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) style diet, and metabolic health in US adults. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 36, 1301–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appel, L.J.; Moore, T.J.; Obarzanek, E.; Vollmer, W.M.; Svetkey, L.P.; Sacks, F.M.; Bray, G.A.; Vogt, T.M.; Cutler, J.A.; Windhauser, M.M.; et al. A clinical trial of the effects of dietary patterns on blood pressure. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997, 336, 1117–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosanoff, A. The high heart health value of drinking-water magnesium. Med. Hypotheses 2013, 81, 1063–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).