Endocrine Disruption at the Androgen Receptor: Employing Molecular Dynamics and Docking for Improved Virtual Screening and Toxicity Prediction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Docking of AR Agonists, Antagonists and Decoys towards Experimental AR Structures
2.2. Generation of AR Antagonist Structures Using Flexible Docking, Binding Pose Metadynamics and Classical MD Simulations
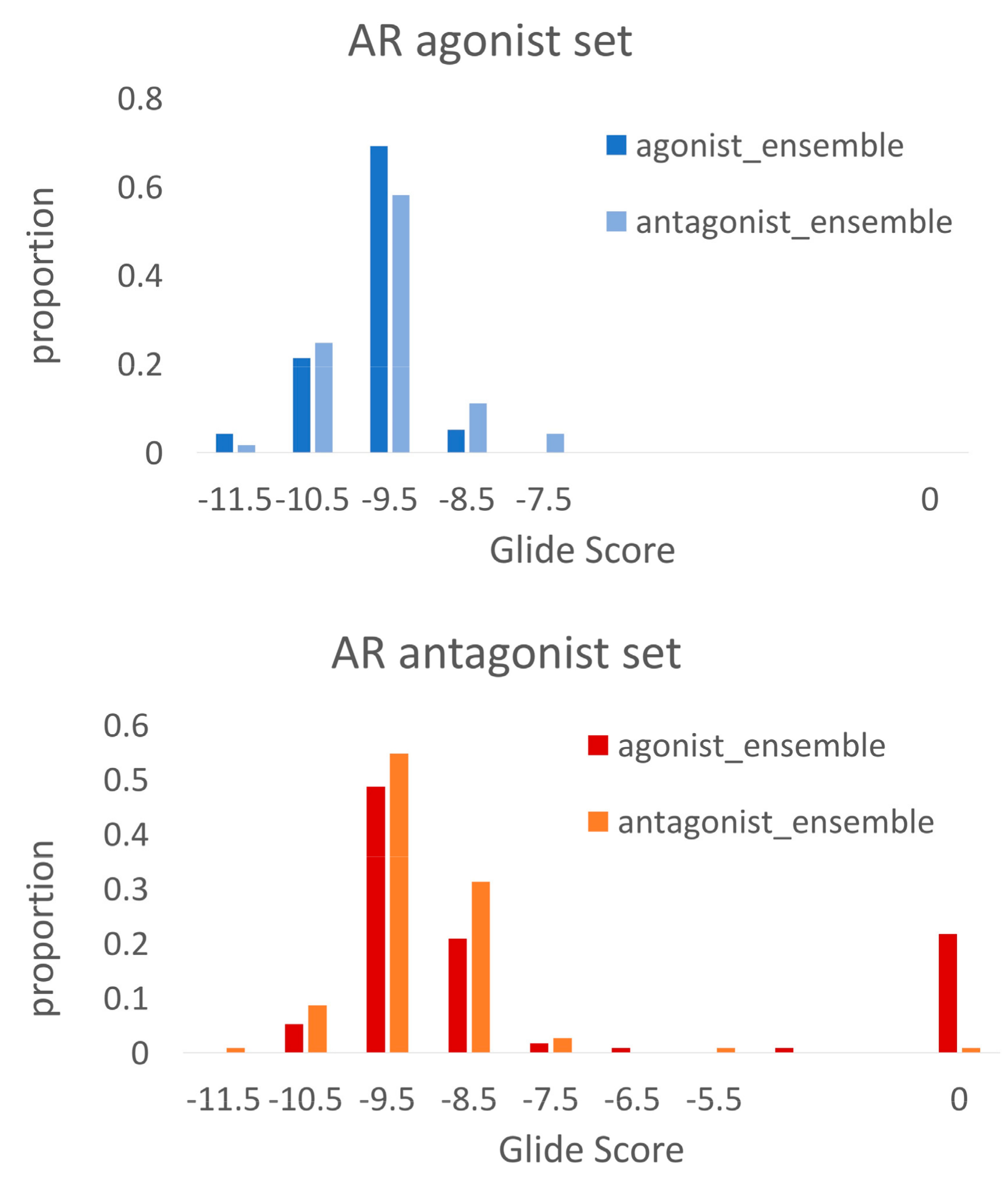
2.3. Docking Towards an Antagonist Ensemble Obtained from MD Simulations
2.4. Docking Towards an Agonist Ensemble Obtained from MD Simulations
2.5. Discriminating Agonists from Antagonists
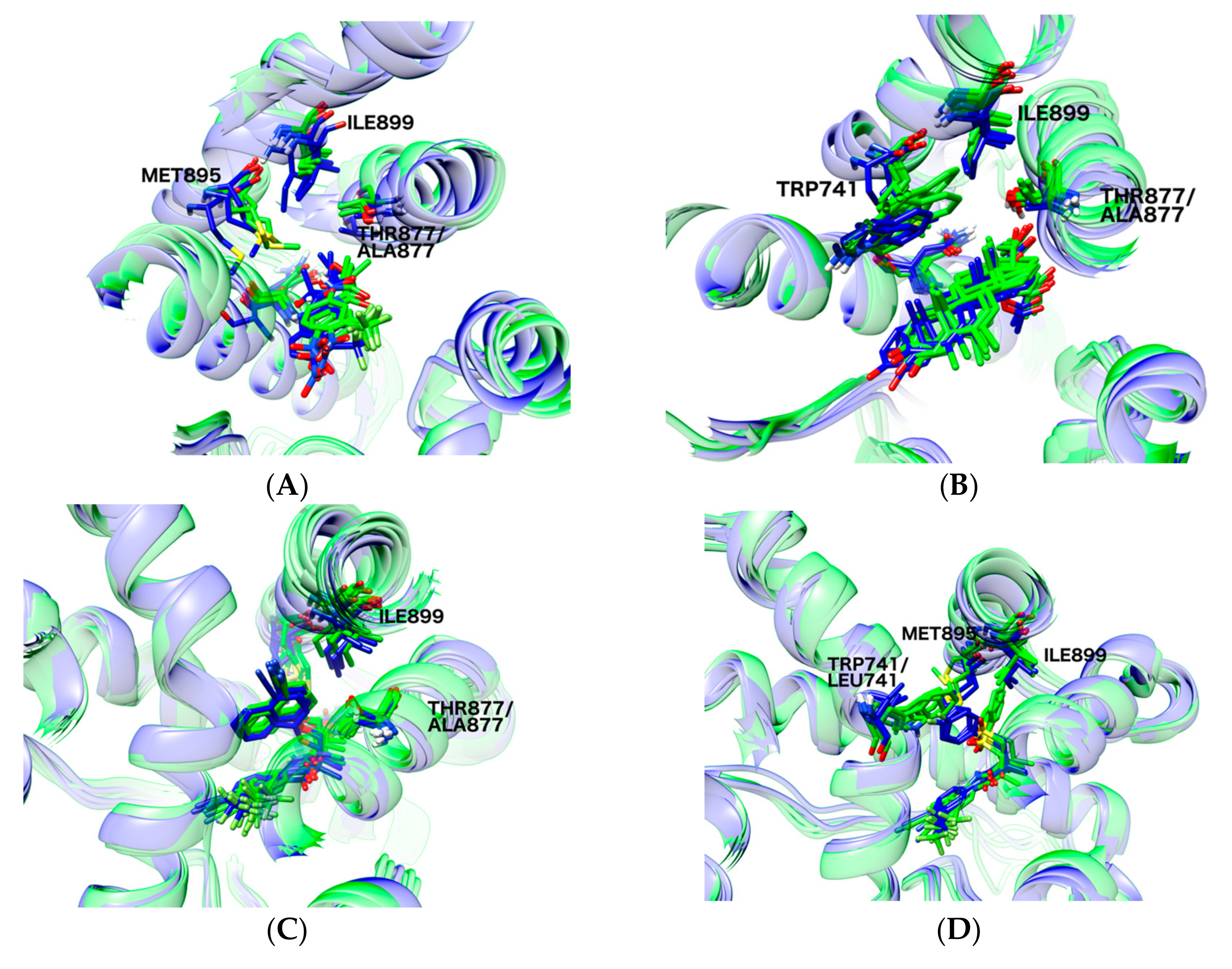
2.6. Structural Comparison between Antagonist and Agonist Ensembles
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. AR Agonists, Antagonists and Decoys
3.2. Preparation of Experimental AR Structures for Ensemble Docking
3.3. Molecular Dynamics Simulations
3.4. Binding Pose Metadynamics
3.5. Glide Docking
3.6. Induced-Fit Docking (IFD)
3.7. Ensemble Docking
3.8. Evaluation of the Docking Performance
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Heinlein, C.A.; Chang, C.S. Androgen Receptor in Prostate Cancer. Endocr. Rev. 2004, 25, 276–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luccio-Camelo, D.C.; Prins, G.S. Disruption of Androgen Receptor Signaling in Males by Environmental Chemicals. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2011, 127, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakkiah, S.; Wang, T.; Zou, W.; Wang, Y.; Pan, B.; Tong, W.; Hong, H. Endocrine Disrupting Chemicals Mediated through Binding Androgen Receptor Are Associated with Diabetes Mellitus. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2018, 15, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, M.H.E.; Li, J.; Xu, H.E.; Melcher, K.; Yong, E. Androgen Receptor: Structure, Role in Prostate Cancer and Drug Discovery. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2015, 36, 3–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Helsen, C.; Van den Broeck, T.; Voet, A.; Prekovic, S.; Poppel, H.V.; Joniau, S.; Claessens, F. Androgen Receptor Antagonists for Prostate Cancer Therapy. Endocr Relat Cancer 2014, 21, T105–T118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Dun, K.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; You, Q.; Li, Z. Recent Androgen Receptor Antagonists in Prostate Cancer. Mini. Rev. Med. Chem. 2014, 14, 655–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vedani, A.; Dobler, M.; Hu, Z.; Smieško, M. OpenVirtualToxLab—A Platform for Generating and Exchanging in Silico Toxicity Data. Toxicol. Lett. 2015, 232, 519–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, T.; Tsutsumi, O.; Ikezuki, Y.; Takai, Y.; Taketani, Y. Positive Relationship between Androgen and the Endocrine Disruptor, Bisphenol A, in Normal Women and Women with Ovarian Dysfunction. Endocr. J. 2004, 51, 165–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mnif, W.; Hassine, A.I.H.; Bouaziz, A.; Bartegi, A.; Thomas, O.; Roig, B. Effect of Endocrine Disruptor Pesticides: A Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2011, 8, 2265–2303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vedani, A.; Smiesko, M. In Silico Toxicology in Drug Discovery—Concepts Based on Three-Dimensional Models. Atla-Altern. Lab. Anim. 2009, 37, 477–496. [Google Scholar]
- Vedani, A.; Dobler, M.; Lill, M.A. The Challenge of Predicting Drug Toxicity in Silico. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2006, 99, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lill, M.A.; Winiger, F.; Vedani, A.; Ernst, B. Impact of Induced Fit on Ligand Binding to the Androgen Receptor: A Multidimensional QSAR Study to Predict Endocrine-Disrupting Effects of Environmental Chemicals. J. Med. Chem. 2005, 48, 5666–5674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osguthorpe, D.J.; Hagler, A.T. Mechanism of Androgen Receptor Antagonism by Bicalutamide in the Treatment of Prostate Cancer. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 4105–4113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, M.; Liu, N.; Zhou, W.; Li, D.; Yang, M.; Hou, T. Structural Diversity of Ligand-Binding Androgen Receptors Revealed by Microsecond Long Molecular Dynamics Simulations and Enhanced Sampling. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2016, 12, 4611–4619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Han, R.; Li, J.; Liu, H.; Zheng, L. Molecular Mechanism of R-Bicalutamide Switching from Androgen Receptor Antagonist to Agonist Induced by Amino Acid Mutations Using Molecular Dynamics Simulations and Free Energy Calculation. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2016, 30, 1189–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.-L.; Zhong, H.-Y.; Song, T.-Q.; Li, J.-Z. A Molecular Modeling Study of the Hydroxyflutamide Resistance Mechanism Induced by Androgen Receptor Mutations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Liu, B.; Geng, G.; Wu, J.H. Study of the Impact of the T877A Mutation on Ligand-Induced Helix-12 Positioning of the Androgen Receptor Resulted in Design and Synthesis of Novel Antiandrogens. Proteins Struct. Funct. Bioinform. 2010, 78, 623–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohl, C.E.; Miller, D.D.; Chen, J.; Bell, C.E.; Dalton, J.T. Structural Basis for Accommodation of Nonsteroidal Ligands in the Androgen Receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 37747–37754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duke, C.B.; Jones, A.; Bohl, C.E.; Dalton, J.T.; Miller, D.D. Unexpected Binding Orientation of Bulky-B-Ring Anti-Androgens and Implications for Future Drug Targets. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 3973–3976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGinley, P.L.; Koh, J.T. Circumventing Anti-Androgen Resistance by Molecular Design. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 3822–3823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, J.T.; Collins, J.L.; Pearce, K.H. The Nuclear Receptor Superfamily and Drug Discovery. ChemMedChem 2006, 1, 504–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lionta, E.; Spyrou, G.; Vassilatis, D.K.; Cournia, Z. Structure-Based Virtual Screening for Drug Discovery: Principles, Applications and Recent Advances. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2014, 14, 1923–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoichet, B.K. Virtual Screening of Chemical Libraries. Nature 2004, 432, 862–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, L.G.; Dos Santos, R.N.; Oliva, G.; Andricopulo, A.D. Molecular Docking and Structure-Based Drug Design Strategies. Mol. Basel Switz. 2015, 20, 13384–13421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villoutreix, B.O.; Miteva, R.E.; Miteva, M.A. Structure-Based Virtual Ligand Screening: Recent Success Stories. Available online: http://www.eurekaselect.com/70496/article (accessed on 9 April 2018).
- Smieško, M. DOLINA—Docking Based on a Local Induced-Fit Algorithm: Application toward Small-Molecule Binding to Nuclear Receptors. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2013, 53, 1415–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voet, A.; Helsen, C.; Zhang, K.Y.J.; Claessens, F. The Discovery of Novel Human Androgen Receptor Antagonist Chemotypes Using a Combined Pharmacophore Screening Procedure. ChemMedChem 2013, 8, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bassetto, M.; Ferla, S.; Pertusati, F.; Kandil, S.; Westwell, A.D.; Brancale, A.; McGuigan, C. Design and Synthesis of Novel Bicalutamide and Enzalutamide Derivatives as Antiproliferative Agents for the Treatment of Prostate Cancer. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 118, 230–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, H.C.; Shanmugasundaram, K.; Simon, N.I.; Cai, C.; Wang, H.; Chen, S.; Balk, S.P.; Rigby, A.C. In Silico Discovery of Androgen Receptor Antagonists with Activity in Castration Resistant Prostate Cancer. Mol. Endocrinol. 2012, 26, 1836–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisson, W.H.; Cheltsov, A.V.; Bruey-Sedano, N.; Lin, B.; Chen, J.; Goldberger, N.; May, L.T.; Christopoulos, A.; Dalton, J.T.; Sexton, P.M.; et al. Discovery of Antiandrogen Activity of Nonsteroidal Scaffolds of Marketed Drugs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 11927–11932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, A.J.; Lamb, M.L.; Joseph-McCarthy, D. Ensemble-Based Docking Using Biased Molecular Dynamics. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2014, 54, 2127–2138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, S.; Sun, H.; Pan, P.; Li, D.; Zhen, X.; Li, Y.; Hou, T. Assessing an Ensemble Docking-Based Virtual Screening Strategy for Kinase Targets by Considering Protein Flexibility. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2014, 54, 2664–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osguthorpe, D.J.; Sherman, W.; Hagler, A.T. Exploring Protein Flexibility: Incorporating Structural Ensembles From Crystal Structures and Simulation into Virtual Screening Protocols. J. Phys. Chem. B 2012, 116, 6952–6959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swift, R.V.; Jusoh, S.A.; Offutt, T.L.; Li, E.S.; Amaro, R.E. Knowledge-Based Methods to Train and Optimize Virtual Screening Ensembles. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2016, 56, 830–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagarde, N.; Ben Nasr, N.; Jérémie, A.; Guillemain, H.; Laville, V.; Labib, T.; Zagury, J.-F.; Montes, M. NRLiSt BDB, the Manually Curated Nuclear Receptors Ligands and Structures Benchmarking Database. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 3117–3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mysinger, M.M.; Carchia, M.; Irwin, J.J.; Shoichet, B.K. Directory of Useful Decoys, Enhanced (DUD-E): Better Ligands and Decoys for Better Benchmarking. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 6582–6594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagarde, N.; Zagury, J.-F.; Montes, M. Importance of the Pharmacological Profile of the Bound Ligand in Enrichment on Nuclear Receptors: Toward the Use of Experimentally Validated Decoy Ligands. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2014, 54, 2915–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.-L.; Liu, J.-S.; Wu, P.-L.; Guan, H.-H.; Chen, Y.-L.; Lin, A.-C.; Ting, H.-J.; Pang, S.-T.; Yeh, S.-D.; Ma, W.-L.; et al. Identification of a New Androgen Receptor (AR) Co-Regulator BUD31 and Related Peptides to Suppress Wild-Type and Mutated AR-Mediated Prostate Cancer Growth via Peptide Screening and X-ray Structure Analysis. Mol. Oncol. 2014, 8, 1575–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohl, C.E.; Wu, Z.; Miller, D.D.; Bell, C.E.; Dalton, J.T. Crystal Structure of the T877A Human Androgen Receptor Ligand-Binding Domain Complexed to Cyproterone Acetate Provides Insight for Ligand-Induced Conformational Changes and Structure-Based Drug Design. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 13648–13655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, A.J.; Tiwary, P.; Borrelli, K.; Feng, S.; Miller, E.B.; Abel, R.; Friesner, R.A.; Berne, B.J. Prediction of Protein—Ligand Binding Poses via a Combination of Induced Fit Docking and Metadynamics Simulations. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2016, 12, 2990–2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sander, T.; Freyss, J.; von Korff, M.; Rufener, C. DataWarrior: An Open-Source Program for Chemistry Aware Data Visualization and Analysis. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2015, 55, 460–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sastry, G.M.; Adzhigirey, M.; Day, T.; Annabhimoju, R.; Sherman, W. Protein and Ligand Preparation: Parameters, Protocols, and Influence on Virtual Screening Enrichments. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2013, 27, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epik, Schrödinger, LLC. Schrödinger Suite 2016-3 Protein Preparation Wizard; Epik, Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Osguthorpe, D.J.; Sherman, W.; Hagler, A.T. Generation of Receptor Structural Ensembles for Virtual Screening Using Binding Site Shape Analysis and Clustering. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2012, 80, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D.E. Shaw Research. Desmond Molecular Dynamics System; D.E. Shaw Research: New York, NY, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bowers, K.J.; Chow, E.; Xu, H.; Dror, R.O.; Eastwood, M.P.; Gregersen, B.A.; Klepeis, J.L.; Kolossvary, I.; Moraes, M.A.; Sacerdoti, F.D.; et al. Scalable Algorithms for Molecular Dynamics Simulations on Commodity Clusters. In Proceedings of the 2006 ACM/IEEE Conference on Supercomputing, Tampa, FL, USA, 11–17 November 2006; ACM: New York, NY, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Harder, E.; Damm, W.; Maple, J.; Wu, C.; Reboul, M.; Xiang, J.Y.; Wang, L.; Lupyan, D.; Dahlgren, M.K.; Knight, J.L.; et al. OPLS3: A Force Field Providing Broad Coverage of Drug-like Small Molecules and Proteins. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2016, 12, 281–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laio, A.; Parrinello, M. Escaping Free-Energy Minima. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 12562–12566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Friesner, R.A.; Banks, J.L.; Murphy, R.B.; Halgren, T.A.; Klicic, J.J.; Mainz, D.T.; Repasky, M.P.; Knoll, E.H.; Shelley, M.; Perry, J.K.; et al. Glide: A New Approach for Rapid, Accurate Docking and Scoring. 1. Method and Assessment of Docking Accuracy. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 47, 1739–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LigPrep, Schrödinger, LLC. Schrödinger Suite 2016-3; LigPrep, Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Glide, Schrödinger, LLC. Schrödinger Suite 2016-3 Induced Fit Docking Protocol; Glide, Schrödinger, LLC: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Park, S.-J.; Kufareva, I.; Abagyan, R. Improved Docking, Screening and Selectivity Prediction for Small Molecule Nuclear Receptor Modulators Using Conformational Ensembles. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2010, 24, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Korb, O.; Olsson, T.S.G.; Bowden, S.J.; Hall, R.J.; Verdonk, M.L.; Liebeschuetz, J.W.; Cole, J.C. Potential and Limitations of Ensemble Docking. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2012, 52, 1262–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truchon, J.-F.; Bayly, C.I. Evaluating Virtual Screening Methods: Good and Bad Metrics for the “Early Recognition” Problem. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2007, 47, 488–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicholls, A. What Do We Know and When Do We Know It? J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2008, 22, 239–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lagarde, N.; Delahaye, S.; Zagury, J.-F.; Montes, M. Discriminating Agonist and Antagonist Ligands of the Nuclear Receptors Using 3D-Pharmacophores. J. Cheminform. 2016, 8, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
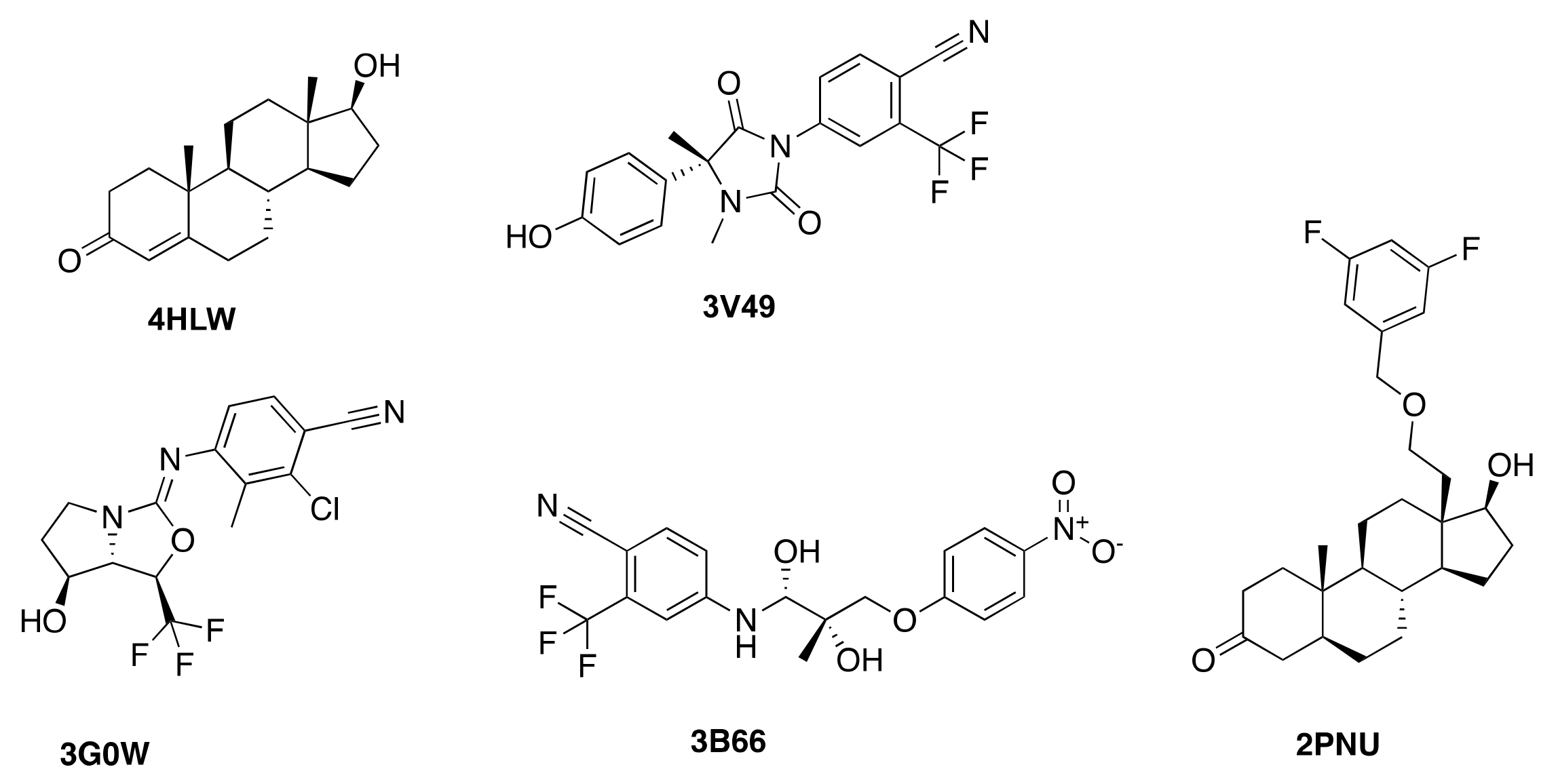



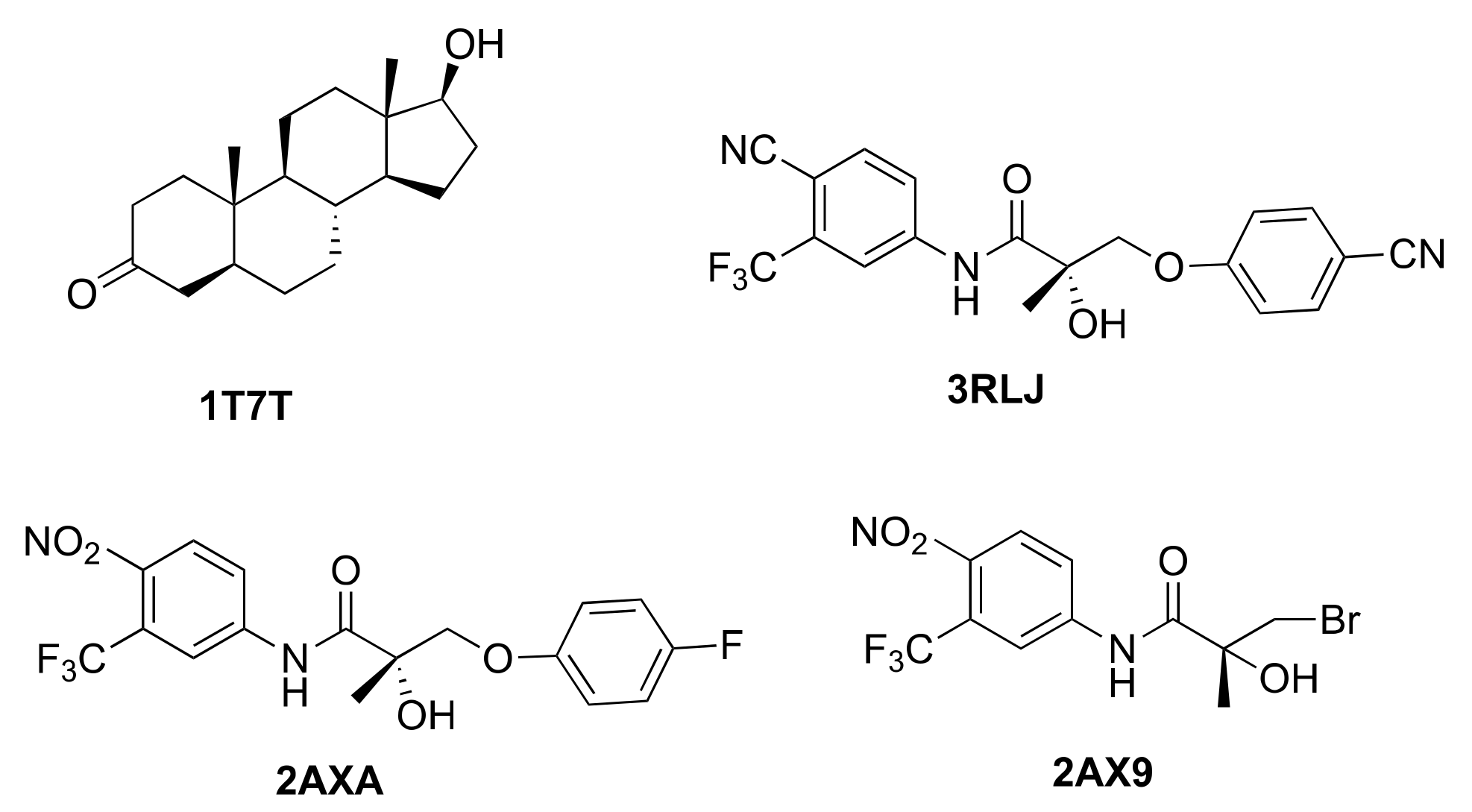
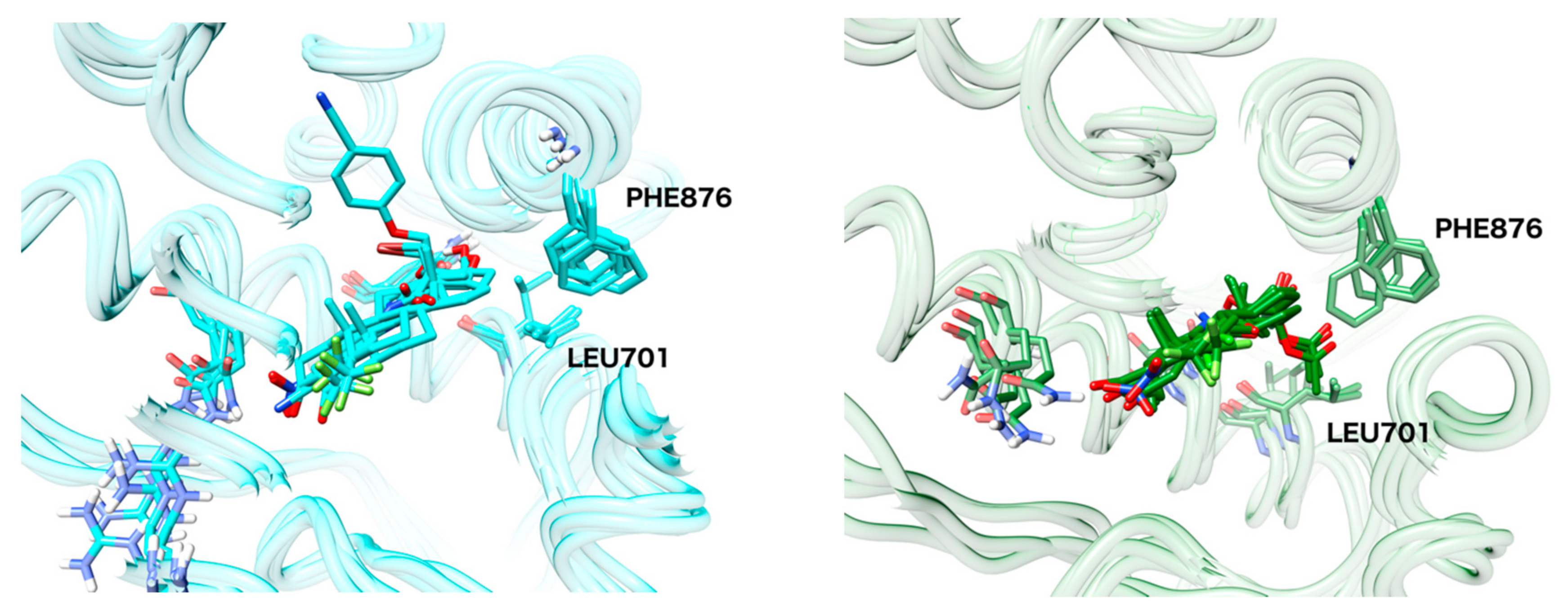
| Protein Structure | 3B66 | 3G0W | 3V49 | 4HLW | 2PNU |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ligand | |||||
| 3B66 | −12.2 | −8.5 | −8.9 | N/A | −10.9 |
| 3G0W | −10.8 | −11.2 | −10.6 | −8.4 | −10.0 |
| 3V49 | −10.5 | N/A | −12.2 | N/A | −9.7 |
| 4HLW | −8.8 | N/A | −9.4 | −11.3 | −10.0 |
| 2PNU | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | −14.2 |
| Ensemble | ROC AUC | Actives | Decoys |
|---|---|---|---|
| crystal structures | 0.92 | agonists | DUD-E |
| crystal structures | 0.80 | agonists | antagonists |
| crystal structures | 0.65 | antagonists | DUD-E |
| MD_antagonist_1 | 0.86 | antagonists | DUD-E |
| MD_antagonist_1 | 0.29 | antagonists | agonists |
| MD_antagonist_1 | 0.92 | agonists | DUD-E |
| MD_agonist_1 | 0.96 | agonists | DUD-E |
| MD_agonist_1 | 0.82 | agonists | antagonists |
| MD_agonist_1 | 0.69 | antagonists | decoys |
| MD_antagonist_2 | 0.96 | agonists | decoys |
| MD_agonist_2 | 0.74 | antagonists | decoys |
| MD_antagonist_3 | 0.79 | antagonists | decoys |
| MD_antagonist_3 | 0.56 | antagonists | agonists |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wahl, J.; Smieško, M. Endocrine Disruption at the Androgen Receptor: Employing Molecular Dynamics and Docking for Improved Virtual Screening and Toxicity Prediction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1784. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19061784
Wahl J, Smieško M. Endocrine Disruption at the Androgen Receptor: Employing Molecular Dynamics and Docking for Improved Virtual Screening and Toxicity Prediction. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(6):1784. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19061784
Chicago/Turabian StyleWahl, Joel, and Martin Smieško. 2018. "Endocrine Disruption at the Androgen Receptor: Employing Molecular Dynamics and Docking for Improved Virtual Screening and Toxicity Prediction" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 6: 1784. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19061784
APA StyleWahl, J., & Smieško, M. (2018). Endocrine Disruption at the Androgen Receptor: Employing Molecular Dynamics and Docking for Improved Virtual Screening and Toxicity Prediction. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(6), 1784. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19061784