The Genomics and Molecular Biology of Natural Killer/T-Cell Lymphoma: Opportunities for Translation
Abstract
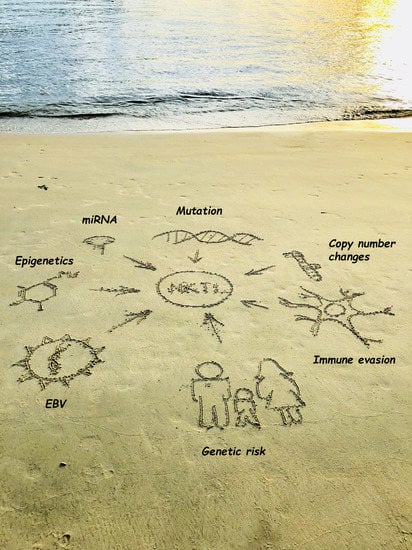
:1. Introduction
2. Insights from Gene Expression Profiling
2.1. Classification
2.2. Deregulated Single Genes
2.2.1. Survivin
2.2.2. AURKA
2.2.3. C-MYC
2.2.4. EZH2
2.2.5. RUNX3
2.3. Deregulated Signaling Pathways
2.3.1. JAK/STAT
2.3.2. PDGF pathway
2.3.3. NOTCH-1
2.3.4. NF-κB
2.3.5. Other Signaling Pathways
3. Insights from Copy Number Analysis
3.1. Copy Number Loss (Potential Tumor Suppressor Genes)
3.1.1. PRDM1
3.1.2. HACE1
3.1.3. PTPRK
3.1.4. Other Candidate Genes in the Commonly Deleted 6q21 Region
3.2. Other Chromosomal Gains and Losses
4. Insights from Genome Wide Association Studies
5. Insights from Mutational Profiling
5.1. JAK/STAT Pathway Associated Genes
5.2. Epigenetic Regulators
5.3. DDX3X
5.4. TP53 and Pro-Apoptotic Genes
5.5. ECSIT
5.6. Pro-Survival Signaling Pathways
6. Epigenetic Dysregulation in ENKTL
6.1. Dysregulated Promoter Methylation
6.2. MicroRNA deregulation in ENKTL
6.3. Mechanisms of microRNA Dysregulation in ENKTL
7. Potential Immunotherapeutic Targets in ENKTL
8. Opportunities for Translation
8.1. Refining Diagnosis
8.2. Risk Stratification
8.3. Conclusions, Promising Therapeutic Targets and Future Directions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chan, J.K.C.; Quintanilla-Martinez, L.; Ferry, J.A. Extranodal nk/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. In Who classification of tumours of haematopoietic and lymphoid tissues; Swerdlow, S.H., Campo, E., Harris, N.L., Jaffe, E.S., Pileri, S.A., Stein, H., Thiele, J., Arber, D.A., Hasserjian, R.P., Le Beau, M.M., et al., Eds.; International Agency for Research on Cancer: Lyon, France, 2017; pp. 368–371. [Google Scholar]
- Ko, Y.H.; Chan, J.K.C.; Quintanilla-Martinez, L. Virally associated T-cell and NK-cell neoplasms. In Hematopathology, 2nd ed.; Jaffe, E.S., Arber, D.A., Campo, E., Harris, N.L., Quintanilla-Martinez, L., Eds.; Elsevier: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2017; pp. 565–598. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, S.B.; Khoury, J.D. Epstein-barr virus in lymphoproliferative processes: An update for the diagnostic pathologist. Adv. Anat. Pathol. 2009, 16, 40–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzumiya, J.; Ohshima, K.; Takeshita, M.; Kanda, M.; Kawasaki, C.; Kimura, N.; Tamura, K.; Kikuchi, M. Nasal lymphomas in japan: A high prevalence of epstein-barr virus type a and deletion within the latent membrane protein gene. Leuk. Lymphoma. 1999, 35, 567–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elenitoba-Johnson, K.S.; Zarate-Osorno, A.; Meneses, A.; Krenacs, L.; Kingma, D.W.; Raffeld, M.; Jaffe, E.S. Cytotoxic granular protein expression, epstein-barr virus strain type, and latent membrane protein-1 oncogene deletions in nasal T-lymphocyte/natural killer cell lymphomas from Mexico. Mod. Pathol 1998, 11, 754–761. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; de Leval, L.; Gaulard, P. Molecular underpinning of extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Haematol. 2013, 26, 57–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attygalle, A.D.; Cabecadas, J.; Gaulard, P.; Jaffe, E.S.; de Jong, D.; Ko, Y.H.; Said, J.; Klapper, W. Peripheral T-cell and NK-cell lymphomas and their mimics; taking a step forward—Report on the lymphoma workshop of the XVIth meeting of the european association for haematopathology and the society for hematopathology. Histopathology 2014, 64, 171–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Campo, E.; Pileri, S.A.; Harris, N.L.; Stein, H.; Siebert, R.; Advani, R.; Ghielmini, M.; Salles, G.A.; Zelenetz, A.D.; et al. The 2016 revision of the world health organization classification of lymphoid neoplasms. Blood 2016, 127, 2375–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, M.; Kwong, Y.L.; Kim, W.S.; Maeda, Y.; Hashimoto, C.; Suh, C.; Izutsu, K.; Ishida, F.; Isobe, Y.; Sueoka, E.; et al. Phase ii study of smile chemotherapy for newly diagnosed stage iv, relapsed, or refractory extranodal natural killer (NK)/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type: The NK-cell tumor study group study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 4410–4416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tse, E.; Kwong, Y.L. The diagnosis and management of NK/T -cell lymphomas. J. hematol. Oncol. 2017, 10, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alizadeh, A.A.; Eisen, M.B.; Davis, R.E.; Ma, C.; Lossos, I.S.; Rosenwald, A.; Boldrick, J.C.; Sabet, H.; Tran, T.; Yu, X.; et al. Distinct types of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identified by gene expression profiling. Nature 2000, 403, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strati, P.; Keating, M.J.; O’Brien, S.M.; Ferrajoli, A.; Burger, J.; Faderl, S.; Tambaro, F.P.; Jain, N.; Wierda, W.G. Outcomes of first-line treatment for chronic lymphocytic leukemia with 17p deletion. Haematologica 2014, 99, 1350–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lemonnier, F.; Couronne, L.; Parrens, M.; Jais, J.P.; Travert, M.; Lamant, L.; Tournillac, O.; Rousset, T.; Fabiani, B.; Cairns, R.A.; et al. Recurrent TET2 mutations in peripheral T-cell lymphomas correlate with TFH-like features and adverse clinical parameters. Blood 2012, 120, 1466–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, S.; Chuang, S.S.; Ashton-Key, M.; Ochoa, E.; Bolli, N.; Vassiliou, G.; Gao, Z.; Du, M.Q. Angioimmunoblastic T cell lymphoma: Novel molecular insights by mutation profiling. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 17763–17770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Couronne, L.; Bastard, C.; Bernard, O.A. Tet2 and dnmt3a mutations in human T-cell lymphoma. New Eng. J. Med. 2012, 366, 95–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, J.; Wilcox, R.; Naushad, H.; Rohr, J.; Heavican, T.B.; Wang, C.; Bouska, A.; Fu, K.; Chan, W.C.; Vose, J.M. Genomic signatures in T-cell lymphoma: How can these improve precision in diagnosis and inform prognosis? Blood Rev. 2016, 30, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; de Reynies, A.; de Leval, L.; Ghazi, B.; Martin-Garcia, N.; Travert, M.; Bosq, J.; Briere, J.; Petit, B.; Thomas, E.; et al. Gene expression profiling identifies emerging oncogenic pathways operating in extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. Blood 2010, 115, 1226–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, J.; Kucuk, C.; Deleeuw, R.J.; Srivastava, G.; Tam, W.; Geng, H.; Klinkebiel, D.; Christman, J.K.; Patel, K.; Cao, K.; et al. Genomic analyses reveal global functional alterations that promote tumor growth and novel tumor suppressor genes in natural killer-cell malignancies. Leukemia 2009, 23, 1139–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Iqbal, J.; Weisenburger, D.D.; Chowdhury, A.; Tsai, M.Y.; Srivastava, G.; Greiner, T.C.; Kucuk, C.; Deffenbacher, K.; Vose, J.; Smith, L.; et al. Natural killer cell lymphoma shares strikingly similar molecular features with a group of non-hepatosplenic gammadelta T-cell lymphoma and is highly sensitive to a novel aurora kinase a inhibitor in vitro. Leukemia 2011, 25, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, S.B.; Selvarajan, V.; Huang, G.; Zhou, J.; Feldman, A.L.; Law, M.; Kwong, Y.L.; Shimizu, N.; Kagami, Y.; Aozasa, K.; et al. Activated oncogenic pathways and therapeutic targets in extranodal nasal-type NK/T cell lymphoma revealed by gene expression profiling. J. Pathol. 2011, 223, 496–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, J.; Wright, G.; Wang, C.; Rosenwald, A.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Weisenburger, D.D.; Greiner, T.C.; Smith, L.; Guo, S.; Wilcox, R.A.; et al. Gene expression signatures delineate biological and prognostic subgroups in peripheral T-cell lymphoma. Blood 2014, 123, 2915–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ng, S.B.; Chung, T.H.; Kato, S.; Nakamura, S.; Takahashi, E.; Ko, Y.H.; Khoury, J.D.; Yin, C.C.; Soong, R.; Jeyasekharan, A.D.; et al. Epstein-barr virus-associated primary nodal t/NK-cell lymphoma shows a distinct molecular signature and copy number changes. Haematologica 2018, 103, 278–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- d’Amore, F.; Gaulard, P.; Trumper, L.; Corradini, P.; Kim, W.S.; Specht, L.; Bjerregaard Pedersen, M.; Ladetto, M.; Committee, E.G. Peripheral T-cell lymphomas: Esmo clinical practice guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann. Oncol. 2015, 26 Suppl. 5, v108–v115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Campo, E.; Harris, N.L.; Jaffe, E.S.; Pileri, S.A.; Stein, H.; Thiele, J.; Vardiman, J.W. Who Classification of Tumours of Haematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues, 4th ed.; IARC: Lyon, France, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Ng, S.B.; Ohshima, K.; Selvarajan, V.; Huang, G.; Choo, S.N.; Miyoshi, H.; Wang, S.; Chua, H.C.; Yeoh, A.E.; Quah, T.C.; et al. Prognostic implication of morphology, cycline2 and proliferation in EBV-associated t/nk lymphoproliferative disease in non-immunocompromised hosts. Orphanet. J. Rare Dis. 2014, 9, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, S.B.; Ohshima, K.; Selvarajan, V.; Huang, G.; Choo, S.N.; Miyoshi, H.; Shimizu, N.; Reghunathan, R.; Chua, H.C.; Yeoh, A.E.; et al. Epstein-barr virus-associated T/natural killer-cell lymphoproliferative disorder in children and young adults has similar molecular signature to extranodal nasal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma but shows distinctive stem cell-like phenotype. Leuk. Lymphoma. 2015, 56, 2408–2415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, M.H.; Svane, I.M.; Becker, J.C.; Straten, P.T. The universal character of the tumor-associated antigen survivin. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 5991–5994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, S.; Penrhyn-Lowe, S.; Venkitaraman, A.R. Aurora-a amplification overrides the mitotic spindle assembly checkpoint, inducing resistance to taxol. Cancer Cell 2003, 3, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta-Simmons, J.; Zhang, Y.; Gorgun, G.; Gatt, M.; Mani, M.; Hideshima, T.; Takada, K.; Carlson, N.E.; Carrasco, D.E.; Tai, Y.T.; et al. Aurora kinase a is a target of wnt/beta-catenin involved in multiple myeloma disease progression. Blood 2009, 114, 2699–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Kaneko, S.; Yang, L.; Feldman, R.I.; Nicosia, S.V.; Chen, J.; Cheng, J.Q. Aurora-a abrogation of p53 DNA binding and transactivation activity by phosphorylation of serine 215. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 52175–52182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Ou, C.C.; Feldman, R.I.; Nicosia, S.V.; Kruk, P.A.; Cheng, J.Q. Aurora-a kinase regulates telomerase activity through c-MYC in human ovarian and breast epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 463–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng, S.B.; Yan, J.; Huang, G.; Selvarajan, V.; Tay, J.L.; Lin, B.; Bi, C.; Tan, J.; Kwong, Y.L.; Shimizu, N.; et al. Dysregulated microRNAs affect pathways and targets of biologic relevance in nasal-type natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. Blood 2011, 118, 4919–4929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jung, L.A.; Gebhardt, A.; Koelmel, W.; Ade, C.P.; Walz, S.; Kuper, J.; von Eyss, B.; Letschert, S.; Redel, C.; d’Artista, L.; et al. Omomyc blunts promoter invasion by oncogenic MYC to inhibit gene expression characteristic of MYC-dependent tumors. Oncogene 2017, 36, 1911–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Ng, S.B.; Tay, J.L.; Lin, B.; Koh, T.L.; Tan, J.; Selvarajan, V.; Liu, S.C.; Bi, C.; Wang, S.; et al. Ezh2 overexpression in natural killer/T-cell lymphoma confers growth advantage independently of histone methyltransferase activity. Blood 2013, 121, 4512–4520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bracken, A.P.; Dietrich, N.; Pasini, D.; Hansen, K.H.; Helin, K. Genome-wide mapping of polycomb target genes unravels their roles in cell fate transitions. Genes Dev. 2006, 20, 1123–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Li, B.; Lin, B.; Lee, P.T.; Chung, T.H.; Tan, J.; Bi, C.; Lee, X.T.; Selvarajan, V.; Ng, S.B.; et al. Ezh2 phosphorylation by JAK3 mediates a switch to noncanonical function in natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. Blood 2016, 128, 948–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCabe, M.T.; Ott, H.M.; Ganji, G.; Korenchuk, S.; Thompson, C.; Van Aller, G.S.; Liu, Y.; Graves, A.P.; Della Pietra, A., 3rd; Diaz, E.; et al. Ezh2 inhibition as a therapeutic strategy for lymphoma with EZH2-activating mutations. Nature 2012, 492, 108–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selvarajan, V.; Osato, M.; Nah, G.S.S.; Yan, J.; Chung, T.H.; Voon, D.C.; Ito, Y.; Ham, M.F.; Salto-Tellez, M.; Shimizu, N.; et al. RUNX3 is oncogenic in natural killer/T-cell lymphoma and is transcriptionally regulated by MYC. Leukemia 2017, 31, 2219–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ito, Y.; Bae, S.C.; Chuang, L.S. The RUNX family: Developmental regulators in cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 81–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Guilloty, F.; Pipkin, M.E.; Djuretic, I.M.; Levanon, D.; Lotem, J.; Lichtenheld, M.G.; Groner, Y.; Rao, A. RUNX3 and T-box proteins cooperate to establish the transcriptional program of effector CTLs. J. Exp. Med. 2009, 206, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Coppo, P.; Gouilleux-Gruart, V.; Huang, Y.; Bouhlal, H.; Bouamar, H.; Bouchet, S.; Perrot, C.; Vieillard, V.; Dartigues, P.; Gaulard, P.; et al. STAT3 transcription factor is constitutively activated and is oncogenic in nasal-type NK/T-cell lymphoma. Leukemia 2009, 23, 1667–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, S.; Park, H.Y.; Kang, S.Y.; Kim, S.J.; Hwang, J.; Lee, S.; Kwak, S.H.; Park, K.S.; Yoo, H.Y.; Kim, W.S.; et al. Genetic alterations of JAK/STAT cascade and histone modification in extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma nasal type. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 17764–17776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kimura, H.; Karube, K.; Ito, Y.; Hirano, K.; Suzuki, M.; Iwata, S.; Seto, M. Rare occurrence of jak3 mutations in natural killer cell neoplasms in japan. Leuk. Lymphoma. 2014, 55, 962–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, G.C.; Tan, S.Y.; Tang, T.; Poon, S.L.; Allen, G.E.; Tan, L.; Chong, S.C.; Ong, W.S.; Tay, K.; Tao, M.; et al. Janus kinase 3-activating mutations identified in natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 591–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Arakawa, F.; Miyoshi, H.; Niino, D.; Kawano, R.; Ohshima, K. Activated janus kinase 3 expression not by activating mutations identified in natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. Pathol. Int. 2014, 64, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouchekioua, A.; Scourzic, L.; de Wever, O.; Zhang, Y.; Cervera, P.; Aline-Fardin, A.; Mercher, T.; Gaulard, P.; Nyga, R.; Jeziorowska, D.; et al. JAK3 deregulation by activating mutations confers invasive growth advantage in extranodal nasal-type natural killer cell lymphoma. Leukemia 2014, 28, 338–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrae, J.; Gallini, R.; Betsholtz, C. Role of platelet-derived growth factors in physiology and medicine. Genes Dev. 2008, 22, 1276–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, C.; He, H. Treatment of relapsed extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma with bortezomib plus fludarabine. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 7, 525–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, T.; Tay, K.; Tao, M.; Quek, R.H.H.; Farid, M.; Lim, S.T. A phase ii study of bortezomib-gifox (gemcitabine, ifosfamide, oxaliplatin) in patients with newly diagnosed natural-killer/T-cell lymphoma. Blood 2016, 128, 5353. [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt, C.; Sako, N.; Bagot, M.; Huang, Y.; Gaulard, P.; Bensussan, A. Extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma: Toward the identification of clinical molecular targets. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2011, 2011, 790871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganjoo, K.; Hong, F.; Horning, S.J.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Natkunam, Y.; Swinnen, L.J.; Habermann, T.M.; Kahl, B.S.; Advani, R.H. Bevacizumab and cyclosphosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine and prednisone in combination for patients with peripheral T-cell or natural killer cell neoplasms: An eastern cooperative oncology group study (e2404). Leuk. Lymphoma. 2014, 55, 768–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westin, J.R. Status of PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway inhibitors in lymphoma. Clin Lymph. Myeloma Leuk. 2014, 14, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, Y.H.; Choi, K.E.; Han, J.H.; Kim, J.M.; Ree, H.J. Comparative genomic hybridization study of nasal-type NK/T-cell lymphoma. Cytometry 2001, 46, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nakashima, Y.; Tagawa, H.; Suzuki, R.; Karnan, S.; Karube, K.; Ohshima, K.; Muta, K.; Nawata, H.; Morishima, Y.; Nakamura, S.; et al. Genome-wide array-based comparative genomic hybridization of natural killer cell lymphoma/leukemia: Different genomic alteration patterns of aggressive NK-cell leukemia and extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2005, 44, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siu, L.L.; Chan, V.; Chan, J.K.; Wong, K.F.; Liang, R.; Kwong, Y.L. Consistent patterns of allelic loss in natural killer cell lymphoma. Am. J. Pathol. 2000, 157, 1803–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siu, L.L.; Wong, K.F.; Chan, J.K.; Kwong, Y.L. Comparative genomic hybridization analysis of natural killer cell lymphoma/leukemia. Recognition of consistent patterns of genetic alterations. Am. J. Pathol. 1999, 155, 1419–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Li, M.; Huang, X.; Xu, J.; Gao, Z.; Liu, C. High-resolution genome-wide analysis identified recurrent genetic alterations in NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type, which are associated with disease progression. Med. Oncol. 2014, 31, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.S.; Su, I.J.; Lin, Y.C.; Chen, J.S.; Fang, S.Y. A 2.6 mb interval on chromosome 6q25.2-q25.3 is commonly deleted in human nasal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. Br. J. Haematol. 2003, 122, 590–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minnich, M.; Tagoh, H.; Bonelt, P.; Axelsson, E.; Fischer, M.; Cebolla, B.; Tarakhovsky, A.; Nutt, S.L.; Jaritz, M.; Busslinger, M. Multifunctional role of the transcription factor Blimp-1 in coordinating plasma cell differentiation. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 17, 331–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Liang, L.; Li, D.; Nong, L.; Liu, J.; Qu, L.; Zheng, Y.; Zhang, B.; Li, T. Hypermethylation of PRDM1/Blimp-1 promoter in extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type: An evidence of predominant role in its downregulation. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 35, 645–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, L.; Nong, L.; Zhang, S.; Zhao, J.; Ti, H.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, B.; Li, T. The downregulation of PRDM1/Blimp-1 is associated with aberrant expression of mir-223 in extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 33, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Anglesio, M.S.; O’Sullivan, M.; Zhang, F.; Yang, G.; Sarao, R.; Mai, P.N.; Cronin, S.; Hara, H.; Melnyk, N.; et al. The e3 ligase hace1 is a critical chromosome 6q21 tumor suppressor involved in multiple cancers. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 1060–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucuk, C.; Hu, X.; Iqbal, J.; Gaulard, P.; Klinkebiel, D.; Cornish, A.; Dave, B.J.; Chan, W.C. Hace1 is a tumor suppressor gene candidate in natural killer cell neoplasms. Am. J. Pathol. 2013, 182, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sako, N.; Dessirier, V.; Bagot, M.; Bensussan, A.; Schmitt, C. Hace1, a potential tumor suppressor gene on 6q21, is not involved in extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma pathophysiology. Am. J. Pathol. 2014, 184, 2899–2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, C.; Sako, N.; Bagot, M.; Bensussan, A. Lack of evidence that hace1 is not a tumor suppressor gene in NKTCL: To the editor-in-chief. Authors’ reply. Am. J. Pathol. 2015, 185, 1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.W.; Guo, T.; Shen, L.; Wong, K.Y.; Tao, Q.; Choi, W.W.; Au-Yeung, R.K.; Chan, Y.P.; Wong, M.L.; Tang, J.C.; et al. Receptor-type tyrosine-protein phosphatase kappa directly targets stat3 activation for tumor suppression in nasal NK/T-cell lymphoma. Blood 2015, 125, 1589–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousefi, S.; Perozzo, R.; Schmid, I.; Ziemiecki, A.; Schaffner, T.; Scapozza, L.; Brunner, T.; Simon, H.U. Calpain-mediated cleavage of ATG5 switches autophagy to apoptosis. Nat. Cell Biol. 2006, 8, 1124–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haffner, M.C.; Esopi, D.M.; Chaux, A.; Gurel, M.; Ghosh, S.; Vaghasia, A.M.; Tsai, H.; Kim, K.; Castagna, N.; Lam, H.; et al. Aim1 is an actin-binding protein that suppresses cell migration and micrometastatic dissemination. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karube, K.; Nakagawa, M.; Tsuzuki, S.; Takeuchi, I.; Honma, K.; Nakashima, Y.; Shimizu, N.; Ko, Y.H.; Morishima, Y.; Ohshima, K.; et al. Identification of FOXO3 and PRDM1 as tumor-suppressor gene candidates in NK-cell neoplasms by genomic and functional analyses. Blood 2011, 118, 3195–3204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adams, S.V.; Newcomb, P.A.; Shustov, A.R. Racial patterns of peripheral T-cell lymphoma incidence and survival in the united states. J. Clin. Oncol. 2016, 34, 963–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanno, H.; Kojya, S.; Li, T.; Ohsawa, M.; Nakatsuka, S.; Miyaguchi, M.; Harabuchi, Y.; Aozasa, K. Low frequency of HLA-A*0201 allele in patients with Epstein-Barr virus-positive nasal lymphomas with polymorphic reticulosis morphology. Int. J Cancer 2000, 87, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Xia, Y.; Feng, L.N.; Chen, J.R.; Li, H.M.; Cui, J.; Cai, Q.Q.; Sim, K.S.; Nairismagi, M.L.; Laurensia, Y.; et al. Genetic risk of extranodal natural killer T-cell lymphoma: A genome-wide association study. Lancet. Oncol. 2016, 17, 1240–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, J.; Sato, A. The hla system. First of two parts. New Eng. J. Med. 2000, 343, 702–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamatani, Y.; Wattanapokayakit, S.; Ochi, H.; Kawaguchi, T.; Takahashi, A.; Hosono, N.; Kubo, M.; Tsunoda, T.; Kamatani, N.; Kumada, H.; et al. A genome-wide association study identifies variants in the hla-dp locus associated with chronic hepatitis b in Asians. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 591–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Yang, H.; He, W.; Xia, Y.; Xia, Z.; Li, S.; Huang, H.; Li, Z.; Liu, P.; Jiang, W. Association between extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma and hepatitis b viral infection: A case-control study. J. Cancer 2017, 8, 2676–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Gu, Z.H.; Yan, Z.X.; Zhao, X.; Xie, Y.Y.; Zhang, Z.G.; Pan, C.M.; Hu, Y.; Cai, C.P.; Dong, Y.; et al. Exome sequencing identifies somatic mutations of DDX3X in natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1061–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sim, S.H.; Kim, S.; Kim, T.M.; Jeon, Y.K.; Nam, S.J.; Ahn, Y.O.; Keam, B.; Park, H.H.; Kim, D.W.; Kim, C.W.; et al. Novel JAK3-activating mutations in extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. Am. J. Pathol. 2017, 187, 980–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kucuk, C.; Jiang, B.; Hu, X.; Zhang, W.; Chan, J.K.; Xiao, W.; Lack, N.; Alkan, C.; Williams, J.C.; Avery, K.N.; et al. Activating mutations of STAT5B and STAT3 in lymphomas derived from gammadelta-T or NK cells. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 6025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nairismagi, M.; Gerritsen, M.E.; Li, Z.M.; Wijaya, G.C.; Chia, B.K.H.; Laurensia, Y.; Lim, J.Q.; Yeoh, K.W.; Yao, X.S.; Pang, W.L.; et al. Oncogenic activation of JAK3-STAT signaling confers clinical sensitivity to PRN371, a novel selective and potent JAK3 inhibitor, in natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. Leukemia 2018, 32, 1147–1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, W.; Liu, H.; Li, J. Therapeutic options in peripheral T cell lymphoma. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2016, 9, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huynh, K.D.; Fischle, W.; Verdin, E.; Bardwell, V.J. Bcor, a novel corepressor involved in BCL-6 repression. Genes Dev. 2000, 14, 1810–1823. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Milne, T.A.; Briggs, S.D.; Brock, H.W.; Martin, M.E.; Gibbs, D.; Allis, C.D.; Hess, J.L. Mll targets SET domain methyltransferase activity to Hox gene promoters. Mol. Cell 2002, 10, 1107–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobashi, A.; Tsuyama, N.; Asaka, R.; Togashi, Y.; Ueda, K.; Sakata, S.; Baba, S.; Sakamoto, K.; Hatake, K.; Takeuchi, K. Frequent bcor aberrations in extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. Genes Chromosom. Cancer 2016, 55, 460–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vousden, K.H.; Lane, D.P. P53 in health and disease. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell. Biology 2007, 8, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Hongyo, T.; Syaifudin, M.; Nomura, T.; Dong, Z.; Shingu, N.; Kojya, S.; Nakatsuka, S.; Aozasa, K. Mutations of the p53 gene in nasal NK/T-cell lymphoma. Lab. Invest. 2000, 80, 493–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahara, M.; Kishibe, K.; Bandoh, N.; Nonaka, S.; Harabuchi, Y. P53, N- and K-Ras, and beta-catenin gene mutations and prognostic factors in nasal NK/T-cell lymphoma from Hokkaido, Japan. Hum. Pathol. 2004, 35, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurniawan, A.N.; Hongyo, T.; Hardjolukito, E.S.; Ham, M.F.; Takakuwa, T.; Kodariah, R.; Hoshida, Y.; Nomura, T.; Aozasa, K. Gene mutation analysis of sinonasal lymphomas in indonesia. Oncol. Rep. 2006, 15, 1257–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hongyo, T.; Hoshida, Y.; Nakatsuka, S.; Syaifudin, M.; Kojya, S.; Yang, W.I.; Min, Y.H.; Chan, H.; Kim, C.H.; Harabuchi, Y.; et al. P53, K-ras, c-kit and beta-catenin gene mutations in sinonasal NK/T-cell lymphoma in korea and japan. Oncol. Rep. 2005, 13, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Quintanilla-Martinez, L.; Kremer, M.; Keller, G.; Nathrath, M.; Gamboa-Dominguez, A.; Meneses, A.; Luna-Contreras, L.; Cabras, A.; Hoefler, H.; Mohar, A.; et al. P53 mutations in nasal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma from mexico: Association with large cell morphology and advanced disease. Am. J. Pathol. 2001, 159, 2095–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takakuwa, T.; Dong, Z.; Nakatsuka, S.; Kojya, S.; Harabuchi, Y.; Yang, W.I.; Nagata, S.; Aozasa, K. Frequent mutations of fas gene in nasal NK/T cell lymphoma. Oncogene 2002, 21, 4702–4705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wi, S.M.; Moon, G.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.T.; Shim, J.H.; Chun, E.; Lee, K.Y. TAK1-ECSIT-TRAF6 complex plays a key role in the TLR4 signal to activate NF-kappab. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 35205–35214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, H.; Ma, H.; Cai, Q.; Lin, S.; Lei, X.; He, B.; Wu, S.; Wang, Z.; Gao, Y.; Liu, W.; et al. Recurrent ecsit mutation encoding v140a triggers hyperinflammation and promotes hemophagocytic syndrome in extranodal NK/T cell lymphoma. Nat. Med. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbaspour Babaei, M.; Kamalidehghan, B.; Saleem, M.; Huri, H.Z.; Ahmadipour, F. Receptor tyrosine kinase (c-kit) inhibitors: A potential therapeutic target in cancer cells. Drug Des. Devel. Ther. 2016, 10, 2443–2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hongyo, T.; Li, T.; Syaifudin, M.; Baskar, R.; Ikeda, H.; Kanakura, Y.; Aozasa, K.; Nomura, T. Specific c-kit mutations in sinonasal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma in China and Japan. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 2345–2347. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hoshida, Y.; Hongyo, T.; Jia, X.; He, Y.; Hasui, K.; Dong, Z.; Luo, W.J.; Ham, M.F.; Nomura, T.; Aozasa, K. Analysis of p53, K-ras, c-kit, and beta-catenin gene mutations in sinonasal NK/T cell lymphoma in northeast district of China. Cancer Sci. 2003, 94, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kucuk, C.; Hu, X.; Jiang, B.; Klinkebiel, D.; Geng, H.; Gong, Q.; Bouska, A.; Iqbal, J.; Gaulard, P.; McKeithan, T.W.; et al. Global promoter methylation analysis reveals novel candidate tumor suppressor genes in natural killer cell lymphoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 1699–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paik, J.H.; Jang, J.Y.; Jeon, Y.K.; Kim, W.Y.; Kim, T.M.; Heo, D.S.; Kim, C.W. MicroRNA-146a downregulates nfkappab activity via targeting TRAF6 and functions as a tumor suppressor having strong prognostic implications in NK/T cell lymphoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 4761–4771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. MicroRNAs: Target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaulieu, A.M.; Bezman, N.A.; Lee, J.E.; Matloubian, M.; Sun, J.C.; Lanier, L.L. MicroRNA function in NK-cell biology. Immunol. Rev. 2013, 253, 40–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sullivan, R.P.; Leong, J.W.; Fehniger, T.A. MicroRNA regulation of natural killer cells. Front. Immunol. 2013, 4, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saki, N.; Abroun, S.; Soleimani, M.; Hajizamani, S.; Shahjahani, M.; Kast, R.E.; Mortazavi, Y. Involvement of microRNA in T-cell differentiation and malignancy. Int. J. Hematol. Stem Cell Res. 2015, 9, 33–49. [Google Scholar]
- Motsch, N.; Alles, J.; Imig, J.; Zhu, J.; Barth, S.; Reineke, T.; Tinguely, M.; Cogliatti, S.; Dueck, A.; Meister, G.; et al. MicroRNA profiling of epstein-barr virus-associated NK/T-cell lymphomas by deep sequencing. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e42193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamanaka, Y.; Tagawa, H.; Takahashi, N.; Watanabe, A.; Guo, Y.M.; Iwamoto, K.; Yamashita, J.; Saitoh, H.; Kameoka, Y.; Shimizu, N.; et al. Aberrant overexpression of microRNAs activate AKT signaling via down-regulation of tumor suppressors in natural killer-cell lymphoma/leukemia. Blood 2009, 114, 3265–3275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, H.Q.; Huang, G.L.; Guo, C.C.; Pu, X.X.; Lin, T.Y. Diagnostic and prognostic value of circulating mir-221 for extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. Dis. Markers 2010, 29, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watanabe, A.; Tagawa, H.; Yamashita, J.; Teshima, K.; Nara, M.; Iwamoto, K.; Kume, M.; Kameoka, Y.; Takahashi, N.; Nakagawa, T.; et al. The role of microRNA-150 as a tumor suppressor in malignant lymphoma. Leukemia 2011, 25, 1324–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, H.; Fan, L.; Zhan, R.; Wu, S.; Niu, W. Expression of microRNA-10a, microRNA-342-3p and their predicted target gene tiam1 in extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 11, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramakrishnan, R.; Donahue, H.; Garcia, D.; Tan, J.; Shimizu, N.; Rice, A.P.; Ling, P.D. Epstein-Barr virus BART9 mirna modulates LMP1 levels and affects growth rate of nasal NK T cell lymphomas. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, T.C.; Yu, D.; Lee, Y.S.; Wentzel, E.A.; Arking, D.E.; West, K.M.; Dang, C.V.; Thomas-Tikhonenko, A.; Mendell, J.T. Widespread microRNA repression by MYC contributes to tumorigenesis. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 43–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godshalk, S.E.; Bhaduri-McIntosh, S.; Slack, F.J. Epstein-barr virus-mediated dysregulation of human microRNA expression. Cell Cycle 2008, 7, 3595–3600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatto, G.; Rossi, A.; Rossi, D.; Kroening, S.; Bonatti, S.; Mallardo, M. Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 trans-activates miR-155 transcription through the NF-kappab pathway. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, 6608–6619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, K.Y.; So, C.C.; Loong, F.; Chung, L.P.; Lam, W.W.; Liang, R.; Li, G.K.; Jin, D.Y.; Chim, C.S. Epigenetic inactivation of the miR-124-1 in haematological malignancies. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boussiotis, V.A. Molecular and biochemical aspects of the PD-1 checkpoint pathway. New Eng. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1767–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, B.J.; Chapuy, B.; Ouyang, J.; Sun, H.H.; Roemer, M.G.; Xu, M.L.; Yu, H.; Fletcher, C.D.; Freeman, G.J.; Shipp, M.A.; et al. PD-L1 expression is characteristic of a subset of aggressive B-cell lymphomas and virus-associated malignancies. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 3462–3473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, X.W.; Wang, H.; Zhang, W.W.; Wang, J.H.; Liu, W.J.; Xia, Z.J.; Huang, H.Q.; Jiang, W.Q.; Zhang, Y.J.; Wang, L. Pd-l1 is upregulated by EBV-driven LMP1 through NF-kappab pathway and correlates with poor prognosis in natural killer/T-cell lymphoma. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2016, 9, 109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, S.T.; Song, T.; Lim, J.Q.; Laurensia, Y.; Pang, J.W.L.; Nagarajan, S.; Claresta, G.; Jing, T.; Tang, T.P.L.; Nairismagi, M.-L.; et al. Oncogenic activation of STAT3 pathway drives PD-L1 expression in natural killer/T cell lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 7549. [Google Scholar]
- Kwong, Y.L.; Chan, T.S.Y.; Tan, D.; Kim, S.J.; Poon, L.M.; Mow, B.; Khong, P.L.; Loong, F.; Au-Yeung, R.; Iqbal, J.; et al. Pd1 blockade with pembrolizumab is highly effective in relapsed or refractory NK/T-cell lymphoma failing l-asparaginase. Blood 2017, 129, 2437–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ok, C.Y.; Young, K.H. Checkpoint inhibitors in hematological malignancies. J Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 10, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizzardi, A.E.; Johnson, A.T.; Vogel, R.I.; Pambuccian, S.E.; Henriksen, J.; Skubitz, A.P.; Metzger, G.J.; Schmechel, S.C. Quantitative comparison of immunohistochemical staining measured by digital image analysis versus pathologist visual scoring. Diagn. Pathol. 2012, 7, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Parra, E.R.; Villalobos, P.; Mino, B.; Rodriguez-Canales, J. Comparison of different antibody clones for immunohistochemistry detection of programmed cell death ligand 1 (pd-l1) on non-small cell lung carcinoma. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2018, 26, 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bollard, C.M.; Gottschalk, S.; Torrano, V.; Diouf, O.; Ku, S.; Hazrat, Y.; Carrum, G.; Ramos, C.; Fayad, L.; Shpall, E.J.; et al. Sustained complete responses in patients with lymphoma receiving autologous cytotoxic t lymphocytes targeting Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane proteins. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 32, 798–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malavasi, F.; Funaro, A.; Roggero, S.; Horenstein, A.; Calosso, L.; Mehta, K. Human CD38: A glycoprotein in search of a function. Immunol. Today 1994, 15, 95–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wang, H.; Li, P.F.; Lu, Y.; Xia, Z.J.; Huang, H.Q.; Zhang, Y.J. CD38 expression predicts poor prognosis and might be a potential therapy target in extranodal NK/T cell lymphoma, nasal type. Ann. Hematol. 2015, 94, 1381–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lokhorst, H.M.; Plesner, T.; Laubach, J.P.; Nahi, H.; Gimsing, P.; Hansson, M.; Minnema, M.C.; Lassen, U.; Krejcik, J.; Palumbo, A.; et al. Targeting CD38 with daratumumab monotherapy in multiple myeloma. New Eng. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1207–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustafa, N.; Nee, H.F.A.; Lee, X.T.J.; Jin, W.; Yu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yang, J.; Chng, W.J. Daratumumab efficiently targets NK/T cell lymphoma with high CD38 expression. Blood 2017, 130, 2814. [Google Scholar]
- Hari, P.; Raj, R.V.; Olteanu, H. Targeting CD38 in refractory extranodal natural killer cell-T-cell lymphoma. New Eng. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1501–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.J.; Choi, J.Y.; Hyun, S.H.; Ki, C.S.; Oh, D.; Ahn, Y.C.; Ko, Y.H.; Choi, S.; Jung, S.H.; Khong, P.L.; et al. Risk stratification on the basis of deauville score on pet-ct and the presence of epstein-barr virus DNA after completion of primary treatment for extranodal natural killer/T-cell lymphoma, nasal type: A multicentre, retrospective analysis. Lancet. Haematol. 2015, 2, e66–e74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaccard, A.; Hermine, O. A major turning point in NK/T-cell lymphoma? Blood 2017, 129, 2342–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Burr, M.L.; Sparbier, C.E.; Chan, Y.C.; Williamson, J.C.; Woods, K.; Beavis, P.A.; Lam, E.Y.N.; Henderson, M.A.; Bell, C.C.; Stolzenburg, S.; et al. CMTM6 maintains the expression of pd-l1 and regulates anti-tumour immunity. Nature 2017, 549, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Gene | Reported Frequency | No. of Positive Cases (Total No. of Cases Tested) | Overall Frequency (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| ARID1A | 6 | 6 (105) | 5.7 |
| ASXL3 | 4 | 4 (105) | 3.8 |
| BCOR | 6–32 | 20 (147) | 13.6 |
| b-catenin | 16–30 | 41 (179) | 22.9 |
| BIRC3 | 3 | 3 (88) | 3.4 |
| BAK | 25.9 | 7 (27) | 25.9 |
| CHPF2 | 4 | 4 (105) | 3.8 |
| C-KIT | 5–52 | 30 (170) | 18.8 |
| CMPK1 | 2 | 2 (88) | 2.3 |
| DDX3X | 8–50 | 33 (283) | 11.7 |
| ECSIT | 19 | 17 (88) | 19.3 |
| EP300 | 4–6 | 7 (156) | 4.5 |
| FAT4 | 2–8 | 4 (113) | 3.5 |
| FAS | 4 | 3 (76) | 3.9 |
| IKBKB | 2 | 2 (88) | 2.3 |
| IL6R | 6 | 2(34) | 5.9 |
| JAK1 | 2-8 | 3 (90) | 3.3 |
| JAK3 | 5-35 | 36 (227) | 13 |
| KRAS | 3–25 | 11 (251) | 4.4 |
| MLL2 | 2–18 | 14(190) | 7.4 |
| MLL3 | 12 | 3 (25) | 12 |
| MSH3 | 2 | 2 (88) | 2.3 |
| M6PR | 2 | 2 (88) | 2.3 |
| MIR17HG | 8 | 2 (25) | 8 |
| MSN | 9 | 9 (105) | 8.6 |
| MGAM | 4 | 4 (105) | 3.8 |
| MGA | 9 | 9 (105) | 8.6 |
| NRAS | 2–25 | 6 (227) | 2.6 |
| NOTCH2 | 2–25 | 3 (153) | 2 |
| STAT1 | 4 | 1 (25) | 4 |
| STAT3 | 1–26 | 30 (387) | 8.3 |
| STAT5B | 2–6 | 8 (244) | 3.3 |
| STAT6 | 4 | 1 (25) | 4 |
| TP53 | 4–63 | 139 (611) | 22.7 |
| TET2 | 8 | 2 (25) | 8 |
| WDR66 | 2 | 2 (88) | 2.3 |
| MicroRNA | Evidence Supporting Their Biological Significance | References |
|---|---|---|
| MicroRNAs underexpressed in ENKTL | ||
| miR-146a | Overexpression of mir-146a suppressed cell proliferation, induced apoptosis, and enhanced chemosensitivity by inhibiting the NF-kB pathway via targeted downregulation of TRAF6. ENKTL patients with low miRNA-146a expression had higher frequency of non-response to chemotherapy. | Paik et al. 2011 [97] |
| miR-150 | MiR-150 is expressed at lower levels in both ENKTL cell lines and tumor tissue compared to normal NK cells. Its aberrant downregulation induced continuous activation of the PI3K–AKT pathway, leading to telomerase activation and immortalization of cancer cells. | Watanabe et al. 2011 [105] |
| miR-26 and miR-101 | Downregulation of miR-26a and miR-101 resulted in upregulation of their target Enhancer of Zeste Homolog 2 (EZH2) in ENKTL tumor tissue and cell lines. | Yan et al. 2013 [34] |
| miR-223 | MiR-223 targets PRDM1, a potential tumor suppressor gene in ENKTL: (i) miR-223 and PRDM1 exhibited inverse patterns of expression in ENKTL tissues and cell lines; (ii) PRDM1 was identified as a direct target gene of miR-223 by luciferase assays; (iii) ectopic expression of miR-223 led to downregulation of the PRDM1 protein in vitro whereas a decrease in miR-223 restored the level of PRDM1 protein. | Liang et al. 2014 [61] |
| miR-142-3p and miR-205 | miR-142-3p and miR-205 are downregulated in ENKTL compared with normal thymic tissue. Mir-142-3p targets the proinflammatory cytokine interleukin 1 alpha (IL1A) and mir-205 targets the oncogene BCL6 in vitro. | Motsch et al. 2012 [102] |
| miR-10, miR-342-3p | Expression of miR-10a and miR-342-3p, which are downregulated in ENTKL tissues, is inversely correlated with protein expression of their predicted target gene, T-lymphoma invasion and metastasis inducing factor 1 (TIAM1). | Huang et al. 2016 [106] |
| MicroRNAs overexpressed in ENKTL | ||
| miR-155 and miR-21 | MiR-21 and miR-155 are over-expressed in ENKTL samples and cell lines. Mir-21 downregulates phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) and programmed cell death 4 (PDCD4), whilst mir-155 directly targets SHIP1 in ENTKL cell lines. Both PTEN and SHIP1 are involved in the AKT signaling pathway. | Yamanaka et al. 2009 [103] |
| EBV-encoded microRNAs | ||
| BART9 | BART9 shows a pro-proliferative effect in two ENKTL cell lines (SNK6 and SNT16) that is mediated, at least in part by upregulation of LMP-1 levels. | Ramakrishnan etal. 2011 [107] |
| Therapeutic Targets or Signaling Pathway | Clinical Significance for Therapeutics | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| JAK-3 | JAK-3 inhibition is shown to have potent anti-tumor activity in pre-clinical models. Clinical trials evaluating JAK inhibitors in ENKTL are in progress. | Sim et al. 2017 [77] Narisimagi et al. 2017 [79] |
| STAT-3 | STAT-3 mutant ENKTL are sensitive to STAT-3 inhibition in vitro. | Sim et al. 2017 [77] |
| NF-kB | NF-kB upregulation is an important event in ENKTL pathogenesis. Bortezomib is being evaluated in early phase clinical trials. | Tang et al. 2016 [49] |
| CD38 | CD38 is upregulated in ENKTL. Daratumumab has good in vitro efficacy and one case report documenting complete response. | Mustafa et al. 2017 [124] Hari et al. 2016 [125] |
| PD-1 | PD-L1 is upregulated in ENKTL. Early clinical trials show potent single agent activity of anti PD-1 therapy in relapsed, refractory ENKTL. | Kwong et al. 2017 [116] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
De Mel, S.; Soon, G.S.-T.; Mok, Y.; Chung, T.-H.; Jeyasekharan, A.D.; Chng, W.-J.; Ng, S.-B. The Genomics and Molecular Biology of Natural Killer/T-Cell Lymphoma: Opportunities for Translation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1931. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19071931
De Mel S, Soon GS-T, Mok Y, Chung T-H, Jeyasekharan AD, Chng W-J, Ng S-B. The Genomics and Molecular Biology of Natural Killer/T-Cell Lymphoma: Opportunities for Translation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(7):1931. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19071931
Chicago/Turabian StyleDe Mel, Sanjay, Gwyneth Shook-Ting Soon, Yingting Mok, Tae-Hoon Chung, Anand D. Jeyasekharan, Wee-Joo Chng, and Siok-Bian Ng. 2018. "The Genomics and Molecular Biology of Natural Killer/T-Cell Lymphoma: Opportunities for Translation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 7: 1931. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19071931
APA StyleDe Mel, S., Soon, G. S.-T., Mok, Y., Chung, T.-H., Jeyasekharan, A. D., Chng, W.-J., & Ng, S.-B. (2018). The Genomics and Molecular Biology of Natural Killer/T-Cell Lymphoma: Opportunities for Translation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(7), 1931. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19071931