Different Myosin Head Conformations in Bony Fish Muscles Put into Rigor at Different Sarcomere Lengths
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Results from Laboratory-Based Experiments
2.2. Results from Synchrotron Experiments
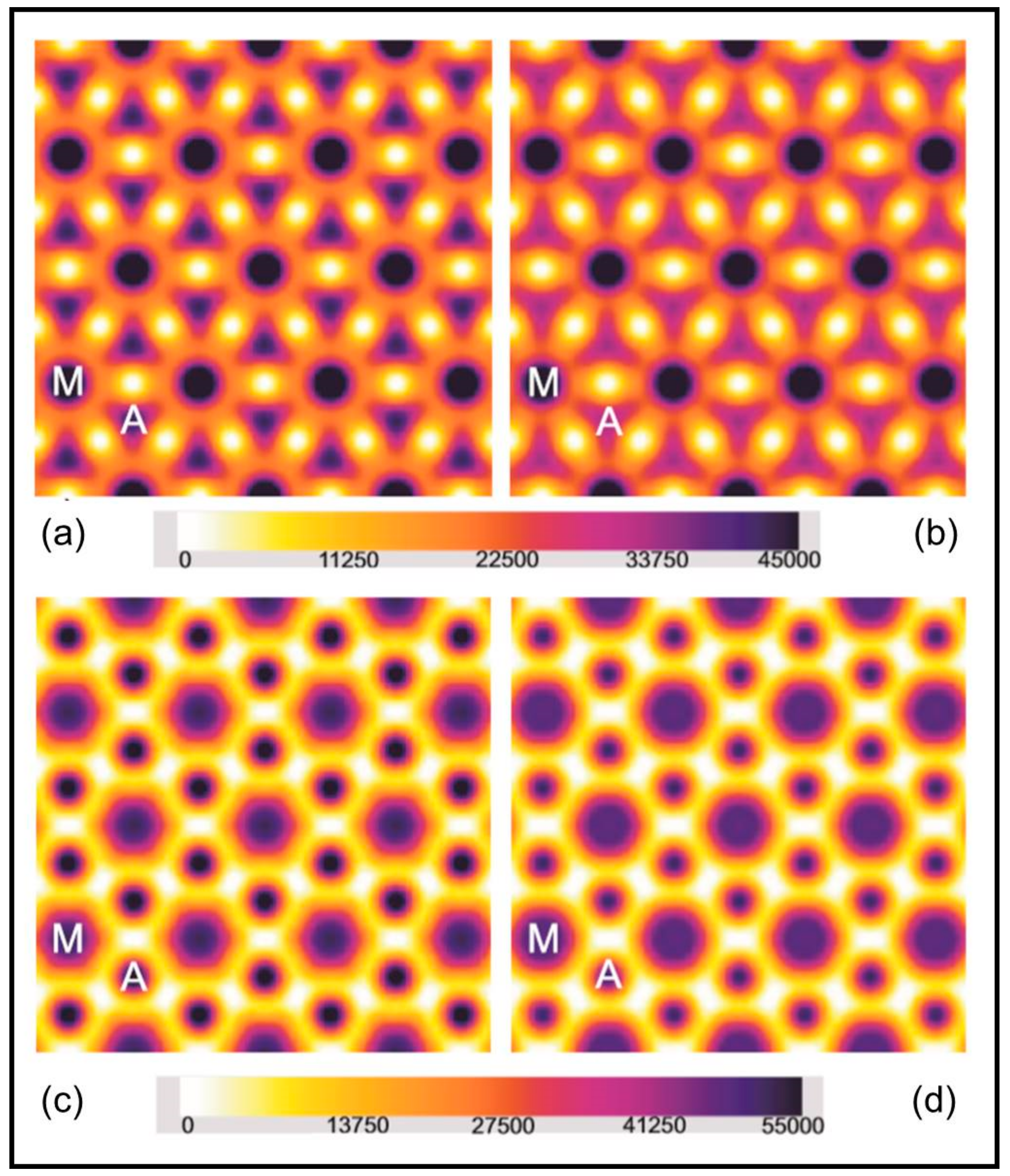
2.2.1. Differences on the Equator
2.2.2. Changes on the Meridian
3. Discussion
3.1. Head Mass Attached to Actin
3.2. Analysis of the Actin Layer-Lines
3.2.1. Steric Blocking by Tropomyosin
3.2.2. Analysis of the Higher Order Actin Layer Lines
3.2.3. Analysis of the Meridian
4. Materials and Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ATP | Adenosine triphosphate |
| BDM | 3,2-Butanedione monoxime |
| IFM | Insect flight muscle |
| SL | Sarcomere length |
| EGTA | Ethylene glycol-bis(β-aminoethyl ether)-N,N,N’,N’-tetraacetic acid |
Appendix A. Correcting the M3 and Other Meridional Intensities

References
- Lymn, R.W.; Taylor, E.W. Mechanism of adenosine triphosphate hydrolysis by actomyosin. Biochemistry 1971, 10, 4617–4624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rayment, I.; Rypniewski, W.R.; Schmidt-Base, K.; Smith, R.; Tomchick, D.R.; Benning, M.M.; Winkelmann, D.A.; Wesenberg, G.; Holden, H.M. Three-dimensional structure of myosin subfragment-1: A molecular motor. Science 1993, 261, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rayment, I.; Holden, H.M.; Whittaker, M.; Yohn, C.B.; Lorenz, M.; Holmes, K.C.; Milligan, R.A. Structure of the actin-myosin complex and its implications for muscle contraction. Science 1993, 261, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, K.C.; Angert, I.; Kull, F.J.; Jahn, W.; Schroder, R.R. Electron cryo-microscopy shows how strong binding of myosin to actin releases nucleotide. Nature 2003, 425, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von der Ecken, J.; Heissler, S.M.; Pathan-Chhatbar, S.; Manstein, D.J.; Raunser, S. Cryo-EM structure of a human cytoplasmic actomyosin complex at near-atomic resolution. Nature 2016, 534, 724–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.F.; Winkler, H.; Reedy, M.K.; Reedy, M.C.; Taylor, K.A. Molecular modeling of averaged rigor crossbridges from tomograms of insect flight muscle. J. Struct. Biol. 2002, 138, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reconditi, M.; Koubassova, N.; Linari, M.; Dobbie, I.; Narayanan, T.; Diat, O.; Piazzesi, G.; Lombardi, V.; Irving, M. The conformation of myosin head domains in rigor muscle determined by X-ray interference. Biophys. J. 2003, 85, 1098–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squire, J.M.; Harford, J.J. Actin filament organization and myosin head labelling patterns in vertebrate skeletal muscles in the rigor and weak binding states. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 1988, 9, 344–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reedy, M.K. Ultrastructure of insect flight muscle. I. screw sense and structural grouping in the rigor cross-bridge lattice. J. Mol. Biol. 1968, 31, 155–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Squire, J.M. General Model of myosin filament structure: II. Myosin filaments and cross-bridge interactions in vertebrate striated and insect flight muscles. J. Mol. Biol. 1972, 72, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagi, N. Labelling of thin filaments by myosin heads in contracting and rigor vertebrate skeletal muscles. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 1996, 52, 1169–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koubassova, N.A.; Tsaturyan, A.K. Direct modeling of X-ray diffraction pattern from skeletal muscle in rigor. Biophys. J. 2002, 83, 1082–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harford, J.J.; Squire, J.M. Static and time resolved X-ray diffraction studies of fish muscle. In Molecular Mechanisms in Muscular Contraction; Squire, J., Ed.; Macmillan Press: London, UK, 1990; pp. 287–320. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Reedy, M.C.; Goldman, Y.E.; Franzini-Armstrong, C.; Sasaki, H.; Tregear, R.T.; Lucaveche, C.; Winkler, H.; Baumann, B.A.; Squire, J.M.; et al. Electron tomography of fast frozen, stretched rigor fibers reveals elastic distortions in the myosin crossbridges. J. Struct. Biol. 2004, 147, 268–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Squire, J.M.; Knupp, C. X-ray diffraction studies of muscle and the crossbridge cycle. In Fibrous Proteins: Muscle and Molecular Motors; Advances in Protein Chemistry; Squire, J.M., Parry, D.A.D., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2005; Volume 71, pp. 195–255. [Google Scholar]
- Haselgrove, J.C. X-ray evidence for conformational changes in the myosin filaments of vertebrate striated muscle. J. Mol. Biol. 1975, 92, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harford, J.J.; Squire, J.M. Crystalline myosin cross-bridge array in relaxed bony fish muscle. Low-angle X-ray diffraction from plaice fin muscle and its interpretation. Biophys. J. 1986, 50, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajkumar, G.; Al-Khayat, H.A.; Eakins, F.; Knupp, C.; Squire, J.M. The ccp13 fibrefix program suite: Semi-automated analysis of diffraction patterns from non-crystalline materials. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2007, 40, 178–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huxley, H.E.; Faruqi, A.R.; Kress, M.; Bordas, J.; Koch, M.H. Time-resolved X-ray diffraction studies of the myosin layer-line reflections during muscle contraction. J. Mol. Biol. 1982, 158, 637–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harford, J.J.; Luther, P.; Squire, J.M. Equatorial a-band and I-band X-ray-diffraction from relaxed and active fish muscle—Further details of myosin crossbridge behavior. J. Mol. Biol. 1994, 239, 500–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, L.C.; Steven, A.C.; Naylor, G.R.; Gamble, R.C.; Podolsky, R.J. Distribution of mass in relaxed frog skeletal muscle and its redistribution upon activation. Biophys. J. 1985, 47, 311–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Irving, T.C.; Millman, B.M. Changes in thick filament structure during compression of the filament lattice in relaxed frog sartorius muscle. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 1989, 10, 385–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harford, J.J.; Squire, J.M. Time-resolved studies of muscle using synchrotron radiation. Rep. Prog. Phys. 1997, 60, 1723–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haselgrove, J.C.; Stewart, M.; Huxley, H.E. Cross-bridge movement during muscle contraction. Nature 1976, 261, 606–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harford, J.J.; Squire, J.M. Evidence for structurally different attached states of myosin cross-bridges on actin during contraction of fish muscle. Biophys. J. 1992, 63, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huxley, H.E. Structural changes in actin- and myosin-containing filaments during contraction. In Cold Spring Harbor Symposia on Quantitative Biology; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 1972; Volume 37, pp. 361–376. [Google Scholar]
- Haselgrove, J.C. X-ray evidence for a conformational change in actincontaining filaments of vertebrate striated muscle. In Cold Spring Harbor Symposia on Quantitative Biology; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Cold Spring Harbor, NY, USA, 1972; Volume 37, pp. 341–352. [Google Scholar]
- Parry, D.A.D.; Squire, J.M. Structural role of tropomyosin in muscle regulation: Analysis of the X-ray diffraction patterns from relaxed and contracting muscles. J. Mol. Biol. 1973, 75, 33–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, D.M.; Squire, J.M.; Morris, E.P. Relaxed and active thin filament structures; a new structural basis for the regulatory mechanism. J. Struct. Biol. 2017, 197, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Knupp, C.; Squire, J.M. HELIX: A helical diffraction simulation program. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2004, 37, 832–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakabayashi, K.; Tanaka, H.; Amemiya, Y.; Fujishima, A.; Kobayashi, T.; Hamanaka, T.; Sugi, H.; Mitsui, T. Time-resolved X-ray diffraction studies on the intensity changes of the 5.9 and 5.1 nm actin layer lines from frog skeletal muscle during an isometric tetanus using synchrotron radiation. Biophys. J. 1985, 47, 847–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harford, J.J. Diffraction Analysis of Vertebrate Muscle Crossbridge Arrangements. Ph.D. Thesis, Imperial College London, London, UK, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Eakins, F.; Pinali, C.; Gleeson, A.; Knupp, C.; Squire, J.M. X-ray Diffraction Evidence for Low Force Actin-Attached and Rigor-Like Cross-Bridges in the Contractile Cycle. Biology 2016, 5, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, R.A.; Fore, N.S.; Helsby, W.; Hall, C.; Jones, A.; Parker, B.; Sumner, I.; Worgan, J.S.; Budtzjorgensen, C. High counting rate gaseous X-ray detectors for synchrotron radiation applications. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1992, 63, 642–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferenczi, M.A.; Bershitsky, S.Y.; Koubassova, N.; Siththanandan, V.B.; Helsby, W.I.; Panine, P.; Roessle, M.; Narayanan, T.; Tsaturyan, A.K. The “roll and lock” mechanism of force generation in muscle. Structure 2005, 13, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]












| Reflection | Average Observed Intensity for Rigor at 2.2 µm | Average Observed Intensity for Rigor at 2.5 µm |
|---|---|---|
| A(10) | 100 | 100 |
| A(11) | 231.2 | 104.8 |
| A(20) | 18.4 | 12.4 |
| A(21) | 19.6 | 14.7 |
| A(30) | 6.6 | 0.86 |
| Measured Parameter | M1/C-Protein | Troponin | M2 | M3 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2.2 µm | 2.5 µm | 2.2 µm | 2.5 µm | 2.2 µm | 2.5 µm | 2.2 µm | 2.5 µm | |
| Intensity (×105 counts) | 4.581 | 0.917 | 2.187 | 3.588 | 5.519 | 5.226 | 5.018 | 6.999 |
| Spacing (×10−3 Å−1) | 2.248 | 2.254 | 2.579 | 2.572 | 4.469 | 4.514 | 6.865 | 6.865 |
| FWHM (×10−4 Å−1) | 3.08 | 4.80 | 4.18 | 5.42 | 5.42 | 8.04 | 9.36 | 13.48 |
| Corrected Intensity | 141.34 | 43.94 | 91.26 | 194.5 | 299.8 | 420.2 | 469.6 | 943.2 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Eakins, F.; Harford, J.J.; Knupp, C.; Roessle, M.; Squire, J.M. Different Myosin Head Conformations in Bony Fish Muscles Put into Rigor at Different Sarcomere Lengths. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2091. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19072091
Eakins F, Harford JJ, Knupp C, Roessle M, Squire JM. Different Myosin Head Conformations in Bony Fish Muscles Put into Rigor at Different Sarcomere Lengths. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(7):2091. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19072091
Chicago/Turabian StyleEakins, Felicity, Jeffrey J. Harford, Carlo Knupp, Manfred Roessle, and John M. Squire. 2018. "Different Myosin Head Conformations in Bony Fish Muscles Put into Rigor at Different Sarcomere Lengths" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 7: 2091. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19072091
APA StyleEakins, F., Harford, J. J., Knupp, C., Roessle, M., & Squire, J. M. (2018). Different Myosin Head Conformations in Bony Fish Muscles Put into Rigor at Different Sarcomere Lengths. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(7), 2091. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19072091





