Functions of Rhotekin, an Effector of Rho GTPase, and Its Binding Partners in Mammals
Abstract
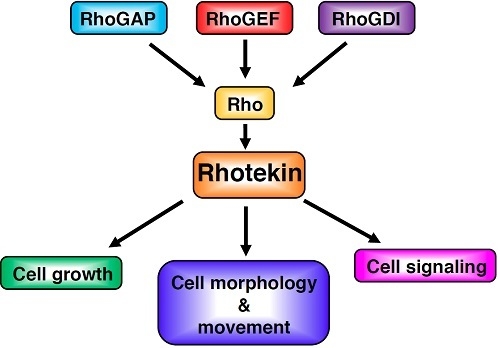
1. Introduction
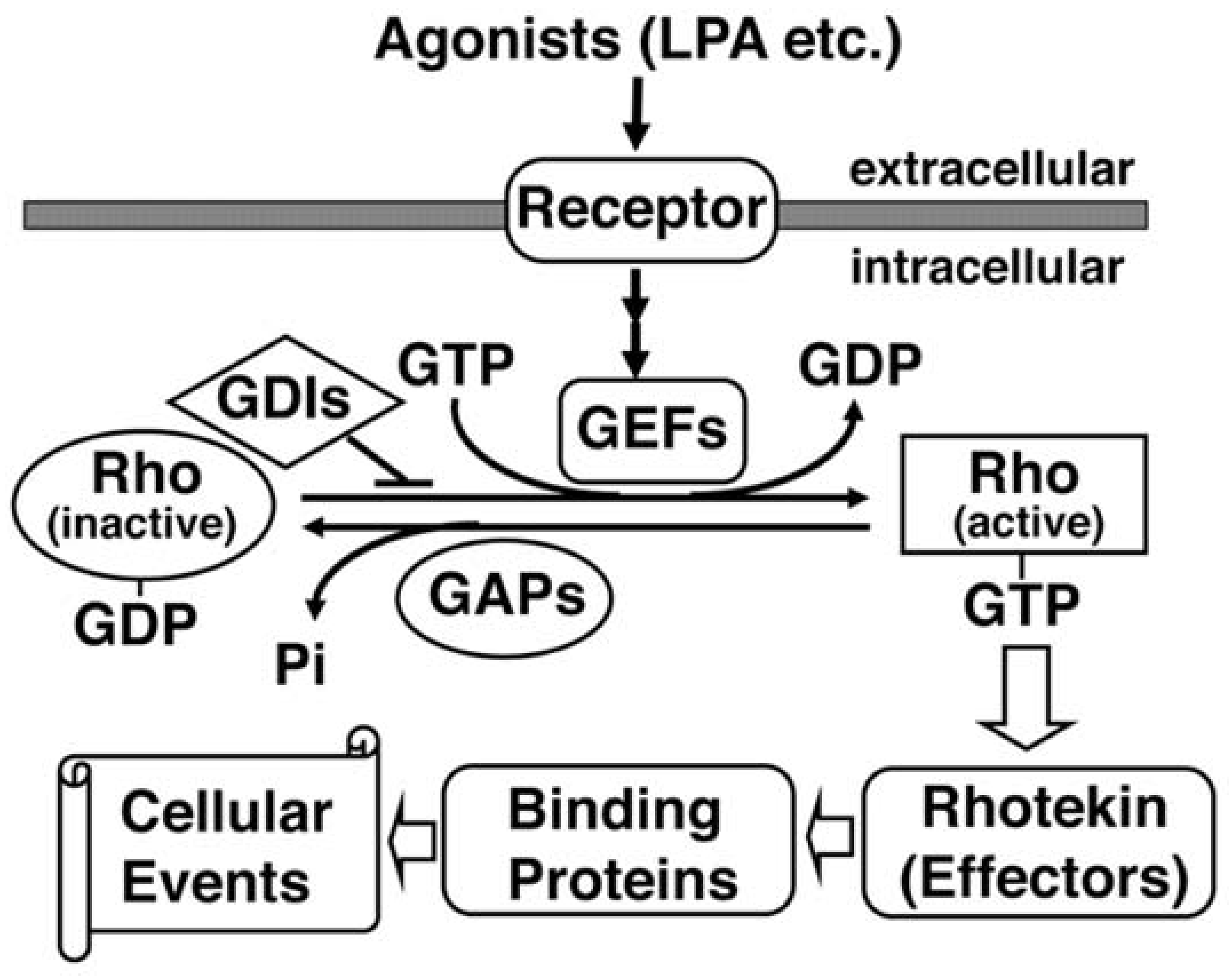
2. Rho Family of Small GTPases
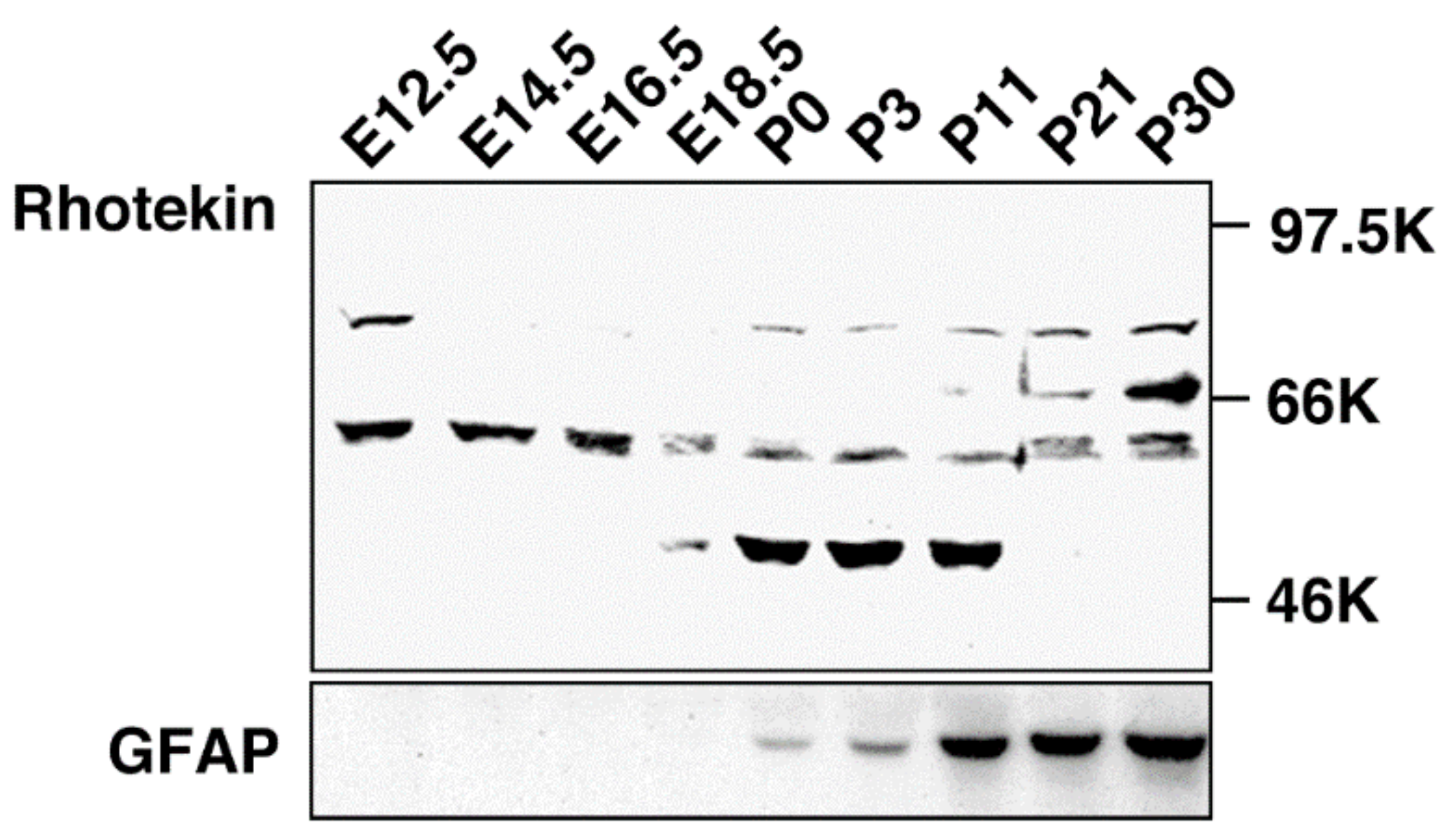
3. Rhotekin in Neuronal Tissues
4. Rhotekin and Cancer Cells
5. Regulation of the Septin Cytoskeletal Organization by Rhotekin
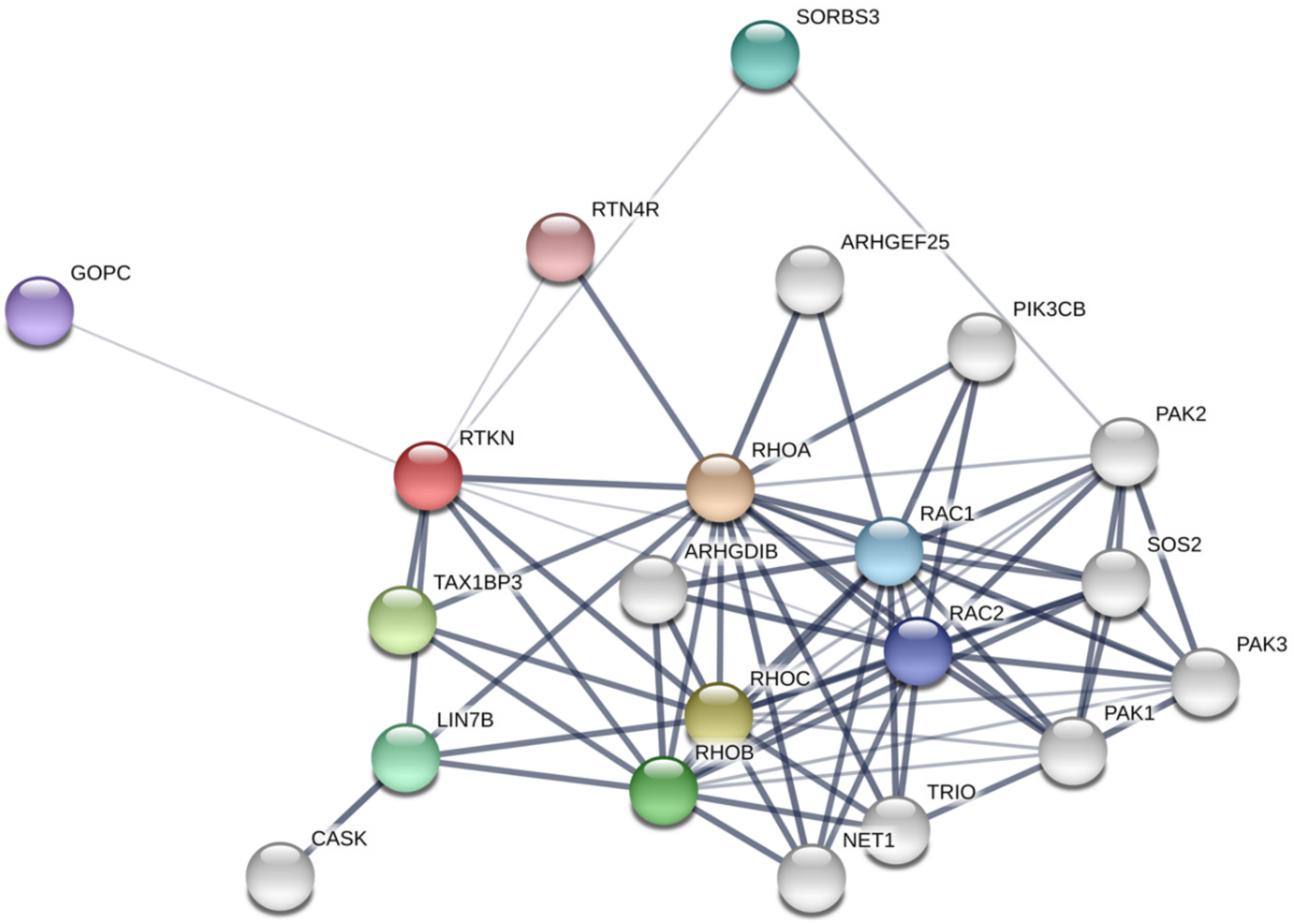
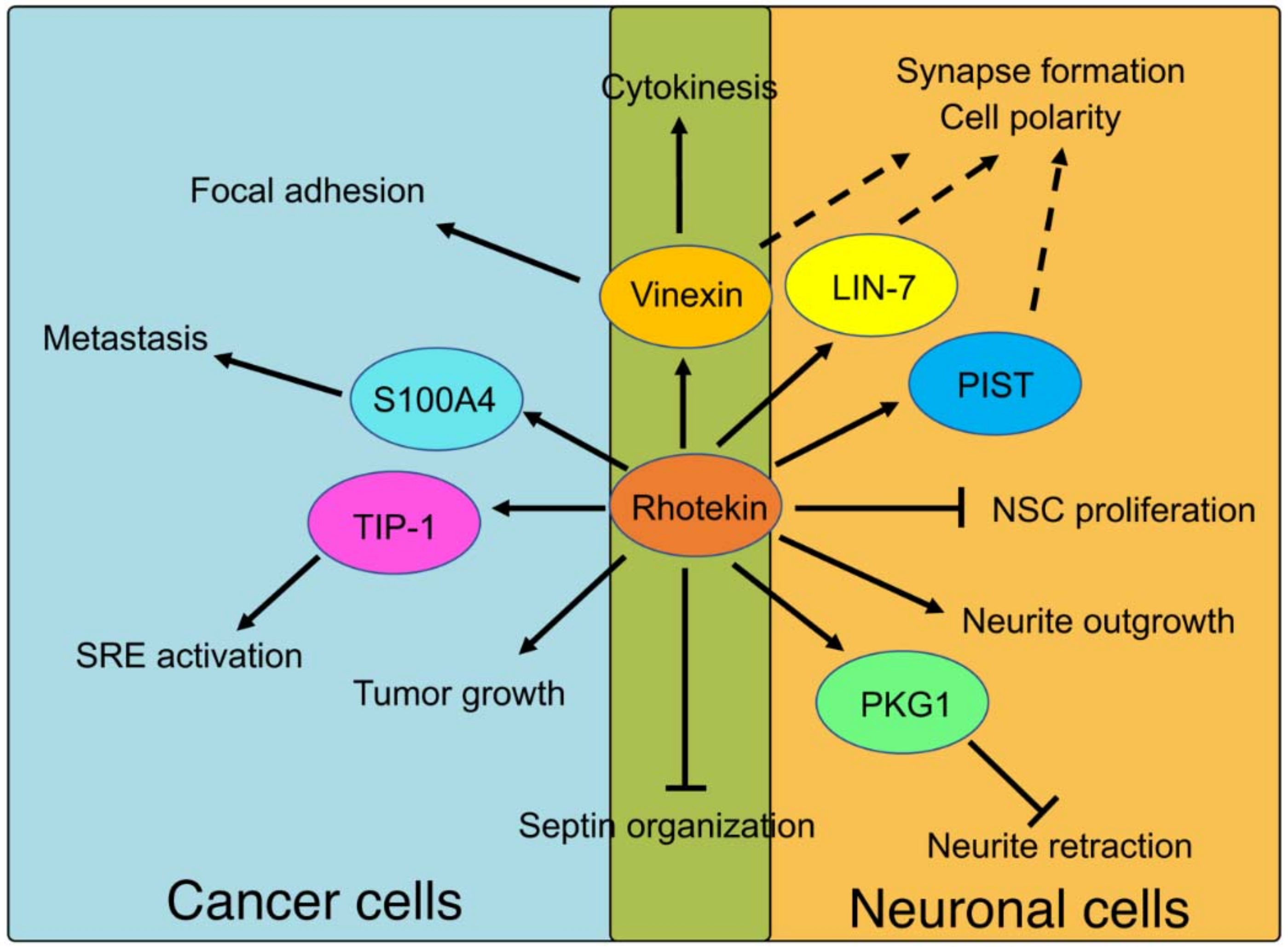
6. Identification and Characterization of Binding Partners for Rhotekin
6.1. TIP-1 (TAX1BP3)
6.2. PIST (GOPC, FIG, CAL)
6.3. LIN-7 (Veli, MALS)
6.4. Vinexin (SORBS3)
6.5. S100 Calcium-Binding Protein A4 (S100A4)
6.6. Cyclic GMP-Dependent Kinase (PKG or cGK)
7. Concluding Remarks
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| RBD | Rho binding domain |
| PH | pleckstrin homology |
| GAP | GTPase activating protein |
| GEF | guanine nucleotide exchange factor |
| GDI | GDP-dissociation inhibitor |
| NF-κB | nuclear kappa B |
| HCC | hepatocellular carcinoma |
| MDCK | Madin-Darby canine kidney |
| AJ | adherence junctions |
| PKG | cyclic GMP dependent kinase |
| SH3 | Src homology 3 |
| NSC | neural stem cells |
| SRE | serum response element |
References
- Etienne-Manneville, S.; Hall, A. Rho GTPases in cell biology. Nature 2002, 420, 629–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaffe, A.B.; Hall, A. Rho GTPases in transformation and metastasis. Adv. Cancer Res. 2002, 84, 57–80. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Govek, E.E.; Newey, S.E.; Van Aelst, L. The role of the Rho GTPases in neuronal development. Genes Dev. 2005, 19, 1–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Negishi, M.; Katoh, H. Rho family GTPases as key regulators for neuronal network formation. J. Biochem. (Tokyo) 2002, 132, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bito, H. Dynamic control of neuronal morphogenesis by rho signaling. J. Biochem. (Tokyo) 2003, 134, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, T.; Furuyashiki, T.; Ishizaki, T.; Watanabe, G.; Watanabe, N.; Fujisawa, K.; Morii, N.; Madaule, P.; Narumiya, S. Rhotekin, a new putative target for Rho bearing homology to a serine/threonine kinase, PKN, and rhophilin in the rho-binding domain. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 13556–13560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, H.; Iwamoto, I.; Mizutani, K.; Morishita, R.; Deguchi, T.; Nozawa, Y.; Asano, T.; Nagata, K. Possible interaction of a Rho effector, Rhotekin, with a PDZ-protein, PIST, at synapses of hippocampal neurons. Neurosci. Res. 2006, 56, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudo, K.; Ito, H.; Iwamoto, I.; Morishita, R.; Asano, T.; Nagata, K. Identification of a cell polarity-related protein, Lin-7B, as a binding partner for a Rho effector, Rhotekin, and their possible interaction in neurons. Neurosci. Res. 2006, 56, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collier, F.M.; Gregorio-King, C.C.; Gough, T.J.; Talbot, C.D.; Walder, K.; Kirkland, M.A. Identification and characterization of a lymphocytic Rho-GTPase effector: Rhotekin-2. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 324, 1360–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, M.; Sala, C. PDZ domains and the organization of supramolecular complexes. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2001, 24, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemmon, M.A.; Ferguson, K.M. Signal-dependent membrane targeting by pleckstrin homology (PH) domains. Biochem. J. 2000, 350, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.S. Specificity and versatility of SH3 and other proline-recognition domains: Structural basis and implications for cellular signal transduction. Biochem. J. 2005, 390, 641–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.D.; Kiosses, W.B.; Schwartz, M.A. Regulation of the small GTP-binding protein Rho by cell adhesion and the cytoskeleton. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 578–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, A.L.; Hall, A. Rho GTPases and their effector proteins. Biochem. J. 2000, 348, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, H.; Iwamoto, I.; Morishita, R.; Nozawa, Y.; Narumiya, S.; Asano, T.; Nagata, K. Possible role of Rho/Rhotekin signaling in mammalian septin organization. Oncogene 2005, 24, 7064–7072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwai, T.; Saitoh, A.; Yamada, M.; Takahashi, K.; Hashimoto, E.; Ukai, W.; Saito, T. Rhotekin modulates differentiation of cultured neural stem cells to neurons. J. Neurosci. Res. 2012, 90, 1359–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.A.; Wang, M.J.; Chi, C.W.; Wu, C.W.; Chen, J.Y. Overexpression of rho effector rhotekin confers increased survival in gastric adenocarcinoma. J. Biomed. Sci. 2004, 11, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.A.; Wang, M.J.; Chi, C.W.; Wu, C.W.; Chen, J.Y. Rho/Rhotekin-mediated NF-kappaB activation confers resistance to apoptosis. Oncogene 2004, 23, 8731–8742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying-Tao, Z.; Yi-Ping, G.; Lu-Sheng, S.; Yi-Li, W. Proteomic analysis of differentially expressed proteins between metastatic and non-metastatic human colorectal carcinoma cell lines. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2005, 17, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, X.; Li, R.; Shi, D.; Pan, X.; Ma, C.; Zhang, G.; Mu, C.; Chen, W. Knockdown of Rhotekin 2 expression suppresses proliferation and induces apoptosis in colon cancer cells. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 8028–8034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Ma, L.J.; Xia, S.J.; Yu, L.; Fu, Q.; Wu, C.Q.; Huang, X.H.; Jiang, J.M.; Tang, X.D. Association between clinical characteristics and expression abundance of RTKN gene in human bladder carcinoma tissues from Chinese patients. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 131, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Liang, Z.; Li, J. Inhibition of rhotekin exhibits antitumor effects in lung cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 35, 2529–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, Y.; Yu, D.; Shao, Q.; Liang, J. MicroRNA-152 inhibits tumor cell growth by directly targeting RTKN in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 1227–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Chen, P.; Chang, Y.; Qi, J.; Fu, H.; Guo, H. Let-7a inhibits tumor cell growth and metastasis by directly targeting RTKN in human colon cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 478, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Field, C.M.; Kellogg, D. Septins: Cytoskeletal polymers or signalling GTPases? Trends Cell Biol. 1999, 9, 387–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trimble, W.S. Septins: A highly conserved family of membrane-associated GTPases with functions in cell division and beyond. J. Membr. Biol. 1999, 169, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolat, L.; Hu, Q.; Spiliotis, E.T. Septin functions in organ system physiology and pathology. Biol. Chem. 2014, 395, 123–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinoshita, M. Assembly of mammalian septins. J. Biochem. (Tokyo) 2003, 134, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joberty, G.; Perlungher, R.R.; Sheffield, P.J.; Kinoshita, M.; Noda, M.; Haystead, T.; Macara, I.G. Borg proteins control septin organization and are negatively regulated by Cdc42. Nat. Cell Biol. 2001, 3, 861–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelis, D.; Spiliotis, E.T. Septin Mutations in Human Cancers. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 4, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Morris, J.H.; Cook, H.; Kuhn, M.; Wyder, S.; Simonovic, M.; Santos, A.; Doncheva, N.T.; Roth, A.; Bork, P.; et al. The STRING database in 2017: Quality-controlled protein-protein association networks, made broadly accessible. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017, 45, D362–D368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, H.; Iwamoto, I.; Morishita, R.; Nozawa, Y.; Asano, T.; Nagata, K. Identification of a PDZ protein, PIST, as a binding partner for Rho effector Rhotekin: Biochemical and cell-biological characterization of Rhotekin-PIST interaction. Biochem. J. 2006, 397, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagata, K.; Ito, H.; Iwamoto, I.; Morishita, R.; Asano, T. Interaction of a multi-domain adaptor protein, vinexin, with a Rho-effector, Rhotekin. Med. Mol. Morphol. 2009, 42, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rousset, R.; Fabre, S.; Desbois, C.; Bantignies, F.; Jalinot, P. The C-terminus of the HTLV-1 Tax oncoprotein mediates interaction with the PDZ domain of cellular proteins. Oncogene 1998, 16, 643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynaud, C.; Fabre, S.; Jalinot, P. The PDZ protein TIP-1 interacts with the Rho effector rhotekin and is involved in Rho signaling to the serum response element. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 33962–33968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charest, A.; Lane, K.; McMahon, K.; Housman, D.E. Association of a novel PDZ domain-containing peripheral Golgi protein with the Q-SNARE (Q-soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive fusion protein (NSF) attachment protein receptor) protein syntaxin 6. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 29456–29465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neudauer, C.L.; Joberty, G.; Macara, I.G. PIST: A novel PDZ/coiled-coil domain binding partner for the rho-family GTPase TC10. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 280, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, R.; Maeda, T.; Takada, S.; Noda, T. Identification of a PDZ domain containing Golgi protein, GOPC, as an interaction partner of frizzled. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 286, 771–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.; Moyer, B.D.; Milewski, M.; Loffing, J.; Ikeda, M.; Mickle, J.E.; Cutting, G.R.; Li, M.; Stanton, B.A.; Guggino, W.B. A Golgi-associated PDZ domain protein modulates cystic fibrosis transmembrane regulator plasma membrane expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 3520–3529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gentzsch, M.; Cui, L.; Mengos, A.; Chang, X.B.; Chen, J.H.; Riordan, J.R. The PDZ-binding chloride channel ClC-3B localizes to the Golgi and associates with cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator-interacting PDZ proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 6440–6449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassel, B.; Schreff, M.; Stube, E.M.; Blaich, U.; Schumacher, S. CALEB/NGC interacts with the Golgi-associated protein PIST. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 40136–40143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koliwer, J.; Park, M.; Bauch, C.; von Zastrow, M.; Kreienkamp, H.J. The golgi-associated PDZ domain protein PIST/GOPC stabilizes the beta1-adrenergic receptor in intracellular compartments after internalization. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuadra, A.E.; Kuo, S.H.; Kawasaki, Y.; Bredt, D.S.; Chetkovich, D.M. AMPA receptor synaptic targeting regulated by stargazin interactions with the Golgi-resident PDZ protein nPIST. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 7491–7502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, Z.; Horton, A.; Bravin, M.; DeJager, P.L.; Selimi, F.; Heintz, N. A novel protein complex linking the delta 2 glutamate receptor and autophagy: Implications for neurodegeneration in lurcher mice. Neuron 2002, 35, 921–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irie, M.; Hata, Y.; Deguchi, M.; Ide, N.; Hirao, K.; Yao, I.; Nishioka, H.; Takai, Y. Isolation and characterization of mammalian homologues of Caenorhabditis elegans lin-7: Localization at cell-cell junctions. Oncogene 1999, 18, 2811–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butz, S.; Okamoto, M.; Südhof, T.C. A Tripartite Protein Complex with the Potential to Couple Synaptic Vesicle Exocytosis to Cell Adhesion in Brain. Cell 1998, 94, 773–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, K.; Derin, R.; Li, M.; Bredt, D.S. Characterization of MALS/Velis-1, -2, and -3: A Family of Mammalian LIN-7 Homologs Enriched at Brain Synapses in Association with the Postsynaptic Density-95/NMDA Receptor Postsynaptic Complex. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 4189–4199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoskins, R.; Hajnal, A.F.; Harp, S.A.; Kim, S.K. The C. elegans vulval induction gene lin-2 encodes a member of the MAGUK family of cell junction proteins. Development 1996, 122, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kaech, S.M.; Whitfield, C.W.; Kim, S.K. The LIN-2/LIN-7/LIN-10 Complex Mediates Basolateral Membrane Localization of the C. elegans EGF Receptor LET-23 in Vulval Epithelial Cells. Cell 1998, 94, 761–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simske, J.S.; Kaech, S.M.; Harp, S.A.; Kim, S.K. LET-23 Receptor Localization by the Cell Junction Protein LIN-7 during C. elegans Vulval Induction. Cell 1996, 85, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borg, J.-P.; Straight, S.W.; Kaech, S.M.; de Taddéo-Borg, M.; Kroon, D.E.; Karnak, D.; Turner, R.S.; Kim, S.K.; Margolis, B. Identification of an Evolutionarily Conserved Heterotrimeric Protein Complex Involved in Protein Targeting. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 31633–31636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, A.R.; Wood, D.F.; Marfatia, S.M.; Walther, Z.; Chishti, A.H.; Anderson, J.M. Human CASK/LIN-2 Binds Syndecan-2 and Protein 4.1 and Localizes to the Basolateral Membrane of Epithelial Cells. J. Cell Biol. 1998, 142, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hata, Y.; Butz, S.; Sudhof, T.C. CASK: A novel dlg/PSD95 homolog with an N-terminal calmodulin-dependent protein kinase domain identified by interaction with neurexins. J. Neurosci. 1996, 16, 2488–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, M.; Südhof, T.C. Mints, Munc18-interacting Proteins in Synaptic Vesicle Exocytosis. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 31459–31464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsueh, Y.-P.; Yang, F.-C.; Kharazia, V.; Naisbitt, S.; Cohen, A.R.; Weinberg, R.J.; Sheng, M. Direct Interaction of CASK/LIN-2 and Syndecan Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycan and Their Overlapping Distribution in Neuronal Synapses. J. Cell Biol. 1998, 142, 139–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perego, C.; Vanoni, C.; Massari, S.; Longhi, R.; Pietrini, G. Mammalian LIN-7 PDZ proteins associate with β-catenin at the cell–cell junctions of epithelia and neurons. EMBO J. 2000, 19, 3978–3989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lanktree, M.; Squassina, A.; Krinsky, M.; Strauss, J.; Jain, U.; Macciardi, F.; Kennedy, J.L.; Muglia, P. Association study of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and LIN-7 homolog (LIN-7) genes with adult attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Am. J. Med. Genet. B 2008, 147B, 945–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinawi, M.; Sahoo, T.; Maranda, B.; Skinner, S.A.; Skinner, C.; Chinault, C.; Zascavage, R.; Peters, S.U.; Patel, A.; Stevenson, R.E.; et al. 11p14.1 microdeletions associated with ADHD, autism, developmental delay, and obesity. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2011, 155, 1272–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuno, M.; Matsumoto, A.; Hamada, N.; Ito, H.; Miyauchi, A.; Jimbo, E.F.; Momoi, M.Y.; Tabata, H.; Yamagata, T.; Nagata, K. Role of an adaptor protein Lin-7B in brain development: Possible involvement in autism spectrum disorders. J. Neurochem. 2015, 132, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kioka, N.; Sakata, S.; Kawauchi, T.; Amachi, T.; Akiyama, S.K.; Okazaki, K.; Yaen, C.; Yamada, K.M.; Aota, S. Vinexin: A novel vinculin-binding protein with multiple SH3 domains enhances actin cytoskeletal organization. J. Cell Biol. 1999, 144, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kioka, N.; Ueda, K.; Amachi, T. Vinexin, CAP/ponsin, ArgBP2: A novel adaptor protein family regulating cytoskeletal organization and signal transduction. Cell Struct. Funct. 2002, 27, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, H.; Usuda, N.; Atsuzawa, K.; Iwamoto, I.; Sudo, K.; Katoh-Semba, R.; Mizutani, K.; Morishita, R.; Deguchi, T.; Nozawa, Y.; et al. Phosphorylation by extracellular signal-regulated kinase of a multidomain adaptor protein, vinexin, at synapses. J. Neurochem. 2007, 100, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.W.; Huang, Y.S. Midbody localization of vinexin recruits rhotekin to facilitate cytokinetic abscission. Cell Cycle 2017, 16, 2046–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, H.; Cheng, W.L.; Guo, J.; Chao, M.L.; Zhang, Y.; Gong, J.; Zhu, X.Y.; She, Z.G.; Huang, Z.; Li, H. Vinexin β Ablation Inhibits Atherosclerosis in Apolipoprotein E–Deficient Mice by Inactivating the Akt–Nuclear Factor κB Inflammatory Axis. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Wan, N.; Zhang, X.-J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, G.; Wan, F.; Zhang, R.; Zhu, X.; Xia, H.; et al. Vinexin-β exacerbates cardiac dysfunction post-myocardial infarction via mediating apoptotic and inflammatory responses. Clin. Sci. 2015, 128, 923–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, M.; Guo, S.; Zhang, P.; Gong, J.; Zheng, A.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H. Vinexin-beta deficiency protects against cerebral ischaemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting neuronal apoptosis. J. Neurochem. 2015, 134, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marenholz, I.; Lovering, R.C.; Heizmann, C.W. An update of the S100 nomenclature. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1763, 1282–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santamaria-Kisiel, L.; Rintala-Dempsey, A.C.; Shaw, G.S. Calcium-dependent and -independent interactions of the S100 protein family. Biochem. J. 2006, 396, 201–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.; Hussain, T.; MacLennan, G.T.; Fu, P.; Patel, J.; Mukhtar, H. Differential expression of S100A2 and S100A4 during progression of human prostate adenocarcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2003, 21, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, K.; Endo, Y.; Yonemura, Y.; Heizmann, C.W.; Schafer, B.W.; Watanabe, Y.; Sasaki, T. Clinical significance of S100A4 and E-cadherin-related adhesion molecules in non-small cell lung cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2000, 16, 1125–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maelandsmo, G.M.; Florenes, V.A.; Mellingsaeter, T.; Hovig, E.; Kerbel, R.S.; Fodstad, O. Differential expression patterns of S100A2, S100A4 and S100A6 during progression of human malignant melanoma. Int. J. Cancer 1997, 74, 464–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudland, P.S.; Platt-Higgins, A.; Renshaw, C.; West, C.R.; Winstanley, J.H.; Robertson, L.; Barraclough, R. Prognostic significance of the metastasis-inducing protein S100A4 (p9Ka) in human breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2000, 60, 1595–1603. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Takenaga, K.; Nakanishi, H.; Wada, K.; Suzuki, M.; Matsuzaki, O.; Matsuura, A.; Endo, H. Increased expression of S100A4, a metastasis-associated gene, in human colorectal adenocarcinomas. Clin. Cancer Res. 1997, 3, 2309–2316. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yonemura, Y.; Endou, Y.; Kimura, K.; Fushida, S.; Bandou, E.; Taniguchi, K.; Kinoshita, K.; Ninomiya, I.; Sugiyama, K.; Heizmann, C.W.; et al. Inverse expression of S100A4 and E-cadherin is associated with metastatic potential in gastric cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2000, 6, 4234–4242. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Bresnick, A.R.; O’Connor, K.L. Coupling S100A4 to Rhotekin alters Rho signaling output in breast cancer cells. Oncogene 2013, 32, 3754–3764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamazaki, M.; Chiba, K.; Mohri, T. Fundamental role of nitric oxide in neuritogenesis of PC12h cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2005, 146, 662–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, A.J.; Peace, A.G.; Shewan, D.A. cGMP promotes neurite outgrowth and growth cone turning and improves axon regeneration on spinal cord tissue in combination with cAMP. Brain Res. 2009, 1294, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Wang, Z.; Gu, Y.; Feil, R.; Hofmann, F.; Ma, L. Regulate axon branching by the cyclic GMP pathway via inhibition of glycogen synthase kinase 3 in dorsal root ganglion sensory neurons. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 1350–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuasa, K.; Nagame, T.; Dohi, M.; Yanagita, Y.; Yamagami, S.; Nagahama, M.; Tsuji, A. cGMP-dependent protein kinase I is involved in neurite outgrowth via a Rho effector, rhotekin, in Neuro2A neuroblastoma cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 421, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirose, M.; Ishizaki, T.; Watanabe, N.; Uehata, M.; Kranenburg, O.; Moolenaar, W.H.; Matsumura, F.; Maekawa, M.; Bito, H.; Narumiya, S. Molecular Dissection of the Rho-associated Protein Kinase (p160ROCK)-regulated Neurite Remodeling in Neuroblastoma N1E-115 Cells. J. Cell Biol. 1998, 141, 1625–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalink, K.; van Corven, E.J.; Hengeveld, T.; Morii, N.; Narumiya, S.; Moolenaar, W.H. Inhibition of lysophosphatidate- and thrombin-induced neurite retraction and neuronal cell rounding by ADP ribosylation of the small GTP-binding protein Rho. J. Cell Biol. 1994, 126, 801–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.I.; Kass, D.A. Phosphodiesterases and cyclic GMP regulation in heart muscle. Physiology (Bethesda) 2012, 27, 248–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ito, H.; Morishita, R.; Nagata, K.-i. Functions of Rhotekin, an Effector of Rho GTPase, and Its Binding Partners in Mammals. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2121. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19072121
Ito H, Morishita R, Nagata K-i. Functions of Rhotekin, an Effector of Rho GTPase, and Its Binding Partners in Mammals. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(7):2121. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19072121
Chicago/Turabian StyleIto, Hidenori, Rika Morishita, and Koh-ichi Nagata. 2018. "Functions of Rhotekin, an Effector of Rho GTPase, and Its Binding Partners in Mammals" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 7: 2121. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19072121
APA StyleIto, H., Morishita, R., & Nagata, K.-i. (2018). Functions of Rhotekin, an Effector of Rho GTPase, and Its Binding Partners in Mammals. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(7), 2121. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19072121