The Timing of Melatonin Administration Is Crucial for Its Antidepressant-Like Effect in Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Nocturnal Circulating Melatonin in Swiss Webster Mice
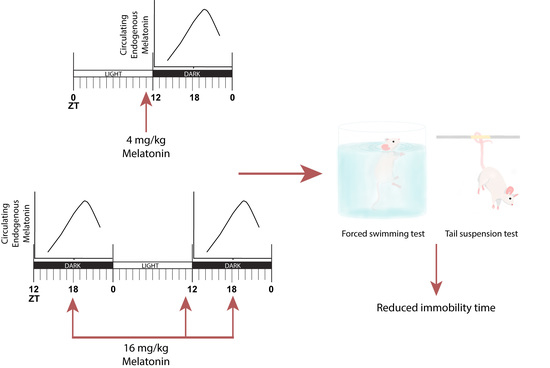
2.2. Melatonin-Mediated Antidepressant-Like Effect When Administered at ZT11
2.3. Acute Melatonin Administration at the Middle of the Dark Phase Reduced Immobility Only in the TST
2.4. Three Melatonin Doses over a 24 Hour-Period Induced a Significant Antidepressant-Like Effect in the FST
2.5. Melatonin Administration Does Not Alter General Locomotor Activity in Mice
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Serum Melatonin Detection by DIESI-MS
4.3. Pharmacological Treatments
4.4. Behavioral Tests
4.4.1. Forced Swimming Test (FST)
4.4.2. Tail Suspension Test (TST)
4.4.3. Open Field Test (OFT)
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CSF | Cerebrospinal fluid |
| DIESI/MS | Direct Infusion Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry |
| FST | Forced Swimming Test |
| OFT | Open Field Test |
| SSRIs | Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors |
| TST | Tail Suspension Test |
| ZT | Zeitgeber time |
References
- Reiter, R.J. The melatonin rhythm: Both a clock and a calendar. Experientia 1993, 49, 654–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaughan, G.M.; Pelham, R.W.; Pang, S.F.; Loughlin, L.L.; Wilson, K.M.; Sandock, K.L.; Vaughan, M.K.; Koslow, S.H.; Reiter, R.J. Nocturnal elevation of plasma melatonin and urinary 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid in young men: Attempts at modification by brief changes in environmental lighting and sleep and by autonomic drugs. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1976, 42, 752–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maronde, E.; Saade, A.; Ackermann, K.; Goubran-Botros, H.; Pagan, C.; Bux, R.; Bourgeron, T.; Dehghani, F.; Stehle, J.H. Dynamics in enzymatic protein complexes offer a novel principle for the regulation of melatonin synthesis in the human pineal gland. J. Pineal Res. 2011, 51, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tricoire, H.; Locatelli, A.; Chemineau, P.; Malpaux, B. Melatonin Enters the Cerebrospinal Fluid through the Pineal Recess. Endocrinology 2002, 143, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tan, D.-X.; Manchester, L.C.; Reiter, R.J. CSF generation by pineal gland results in a robust melatonin circadian rhythm in the third ventricle as an unique light/dark signal. Med. Hypotheses 2016, 86, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Legros, C.; Chesneau, D.; Boutin, J.A.; Barc, C.; Malpaux, B. Melatonin from Cerebrospinal Fluid but Not from Blood Reaches Sheep Cerebral Tissues under Physiological Conditions. J. Neuroendocrinol. 2014, 26, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinato, L.; da Silveira Cruz-Machado, S.; Franco, D.G.; Campos, L.M.G.; Cecon, E.; Fernandes, P.A.C.M.; Bittencourt, J.C.; Markus, R.P. Selective protection of the cerebellum against intracerebroventricular LPS is mediated by local melatonin synthesis. Brain Struct. Funct. 2015, 220, 827–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jimenez-Jorge, S.; Guerrero, J.M.; Jimenez-Caliani, A.J.; Naranjo, M.C.; Lardone, P.J.; Carrillo-Vico, A.; Osuna, C.; Molinero, P. Evidence for melatonin synthesis in the rat brain during development. J. Pineal Res. 2007, 42, 240–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acuña-Castroviejo, D.; Escames, G.; Venegas, C.; Díaz-Casado, M.E.; Lima-Cabello, E.; López, L.C.; Rosales-Corral, S.; Tan, D.-X.; Reiter, R.J. Extrapineal melatonin: Sources, regulation, and potential functions. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2014, 71, 2997–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayo, J.C.; Sainz, R.M.; González-Menéndez, P.; Hevia, D.; Cernuda-Cernuda, R. Melatonin transport into mitochondria. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2017, 74, 3927–3940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardeland, R.; Cardinali, D.P.; Srinivasan, V.; Spence, D.W.; Brown, G.M.; Pandi-Perumal, S.R. Melatonin—A pleiotropic, orchestrating regulator molecule. Prog. Neurobiol. 2011, 93, 350–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiter, R.J.; Manchester, L.C.; Tan, D.-X. Neurotoxins: Free radical mechanisms and melatonin protection. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2010, 8, 194–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galván-Arrieta, T.; Trueta, C.; Cercós, M.G.; Valdés-Tovar, M.; Alarcón, S.; Oikawa, J.; Zamudio-Meza, H.; Benítez-King, G. The role of melatonin in the neurodevelopmental etiology of schizophrenia: A study in human olfactory neuronal precursors. J. Pineal Res. 2017, 63, e12421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosales-Corral, S.; Tan, D.-X.; Reiter, R.J.; Valdivia-Velázquez, M.; Martínez-Barboza, G.; Acosta-Martínez, J.P.; Ortiz, G.G. Orally administered melatonin reduces oxidative stress and proinflammatory cytokines induced by amyloid-beta peptide in rat brain: A comparative, in vivo study versus vitamin C and E. J. Pineal Res. 2003, 35, 80–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.-J.; Wu, C.; Niu, H.-J.; Wang, K.; Mo, L.-J.; Shao, A.-W.; Dixon, B.J.; Zhang, J.-M.; Yang, S.-X.; Wang, Y.-R. Neuroprotective Mechanisms of Melatonin in Hemorrhagic Stroke. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 37, 1173–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yürüker, V.; Nazıroğlu, M.; Şenol, N. Reduction in traumatic brain injury-induced oxidative stress, apoptosis, and calcium entry in rat hippocampus by melatonin: Possible involvement of TRPM2 channels. Metab. Brain Dis. 2015, 30, 223–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, G.; Maes, M. Local melatonin regulates inflammation resolution: A common factor in neurodegenerative, psychiatric and systemic inflammatory disorders. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets 2014, 13, 817–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritchey, M.; Libby, L.A.; Ranganath, C. Cortico-hippocampal systems involved in memory and cognition: The PMAT framework. Prog. Brain Res. 2015, 219, 45–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, B.R.; Hen, R. The current state of the neurogenic theory of depression and anxiety. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2015, 30, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Drevets, W.C.; Price, J.L.; Furey, M.L. Brain structural and functional abnormalities in mood disorders: Implications for neurocircuitry models of depression. Brain Struct. Funct. 2008, 213, 93–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.A.; Lee, K.H.; Lee, B.H. Neuroprotective effect of melatonin against kainic acid-induced oxidative injury in hippocampal slice culture of rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 5940–5951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez-Rodríguez, G.; Klempin, F.; Babu, H.; Benítez-King, G.; Kempermann, G. Melatonin Modulates Cell Survival of New Neurons in the Hippocampus of Adult Mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 2009, 34, 2180–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Somera-Molina, K.C.; Hudson, R.L.; Dubocovich, M.L. Melatonin potentiates running wheel-induced neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of adult C3H/HeN mice hippocampus. J. Pineal Res. 2013, 54, 222–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, D.; Wei, N.; Man, H.-Y.; Lu, Y.; Zhu, L.-Q.; Wang, J.-Z. The MT2 receptor stimulates axonogenesis and enhances synaptic transmission by activating Akt signaling. Cell Death Differ. 2015, 22, 583–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domínguez-Alonso, A.; Ramírez-Rodríguez, G.; Benítez-King, G. Melatonin increases dendritogenesis in the hilus of hippocampal organotypic cultures. J. Pineal Res. 2012, 52, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeno, T.; Nelson, R.J. Acute melatonin treatment alters dendritic morphology and circadian clock gene expression in the hippocampus of Siberian hamsters. Hippocampus 2015, 25, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iggena, D.; Winter, Y.; Steiner, B. Melatonin restores hippocampal neural precursor cell proliferation and prevents cognitive deficits induced by jet lag simulation in adult mice. J. Pineal Res. 2017, 62, e12397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachurin, S.; Oxenkrug, G.; Lermontova, N.; Afanasiev, A.; Beznosko, B.; Vankin, G.; Shevtzova, E.; Mukhina, T.; Serkova, T. N-acetylserotonin, melatonin and their derivatives improve cognition and protect against beta-amyloid-induced neurotoxicity. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1999, 890, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Clough, S.J.; Dubocovich, M.L. Role of the MT1 and MT2 melatonin receptors in mediating depressive- and anxiety-like behaviors in C3H/HeN mice. Genes Brain Behav. 2017, 16, 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantovani, M.; Pértile, R.; Calixto, J.B.; Santos, A.R.S.; Rodrigues, A.L.S. Melatonin exerts an antidepressant-like effect in the tail suspension test in mice: Evidence for involvement of N-methyl-d-aspartate receptors and the L-arginine-nitric oxide pathway. Neurosci. Lett. 2003, 343, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Shen, S.; Ji, Y.-T.; Li, X.-Y.; Zhang, L.-S.; Wang, X.-D. Melatonin Augments the Effects of Fluoxetine on Depression-Like Behavior and Hippocampal BDNF-TrkB Signaling. Neurosci. Bull. 2018, 34, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez-Rodríguez, G.; Vega-Rivera, N.M.; Oikawa-Sala, J.; Gómez-Sánchez, A.; Ortiz-López, L.; Estrada-Camarena, E. Melatonin synergizes with citalopram to induce antidepressant-like behavior and to promote hippocampal neurogenesis in adult mice. J. Pineal Res. 2014, 56, 450–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Micale, V.; Arezzi, A.; Rampello, L.; Drago, F. Melatonin affects the immobility time of rats in the forced swim test: The role of serotonin neurotransmission. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2006, 16, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghavendra, V.; Kaur, G.; Kulkarni, S.K. Anti-depressant action of melatonin in chronic forced swimming-induced behavioral despair in mice, role of peripheral benzodiazepine receptor modulation. Eur. Neuropsychopharmacol. 2000, 10, 473–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosini, G.; Menaker, M. The clock in the mouse retina: Melatonin synthesis and photoreceptor degeneration. Brain Res. 1998, 789, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonken, L.K.; Workman, J.L.; Walton, J.C.; Weil, Z.M.; Morris, J.S.; Haim, A.; Nelson, R.J. Light at night increases body mass by shifting the time of food intake. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 18664–18669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maestroni, G.J.; Conti, A.; Pierpaoli, W. Role of the pineal gland in immunity: II. Melatonin enhances the antibody response via an opiatergic mechanism. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1987, 68, 384–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilad, E.; Zisapel, N. High-affinity binding of melatonin to hemoglobin. Biochem. Mol. Med. 1995, 56, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Vázquez, M.; Estrada-Reyes, R.; Araujo Escalona, A.G.; Ledesma Velázquez, I.; Martínez-Mota, L.; Moreno, J.; Heinze, G. Antidepressant-like effects of an alkaloid extract of the aerial parts of Annona cherimolia in mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2012, 139, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welp, A.; Manz, B.; Peschke, E. Development and validation of a high throughput direct radioimmunoassay for the quantitative determination of serum and plasma melatonin (N-acetyl-5-methoxytryptamine) in mice. J. Immunol. Methods 2010, 358, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naguib, M.; Gottumukkala, V.; Goldstein, P.A. Melatonin and anesthesia: A clinical perspective. J. Pineal Res. 2007, 42, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suresh Kumar, P.N.; Andrade, C.; Bhakta, S.G.; Singh, N.M. Melatonin in schizophrenic outpatients with insomnia: A double-blind, placebo-controlled study. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2007, 68, 237–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steru, L.; Chermat, R.; Thierry, B.; Simon, P. The tail suspension test: A new method for screening antidepressants in mice. Psychopharmacology 1985, 85, 367–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weil, Z.M.; Hotchkiss, A.K.; Gatien, M.L.; Pieke-Dahl, S.; Nelson, R.J. Melatonin receptor (MT1) knockout mice display depression-like behaviors and deficits in sensorimotor gating. Brain Res. Bull. 2006, 68, 425–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tenn, C.; Niles, L.P. Physiological regulation of melatonin receptors in rat suprachiasmatic nuclei: Diurnal rhythmicity and effects of stress. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 1993, 98, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laitinen, J.T.; Castren, E.; Vakkuri, O.; Saavedra, J.M. Diurnal rhythm of melatonin binding in the rat suprachiasmatic nucleus. Endocrinology 1989, 124, 1585–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masana, M.I.; Witt-Enderby, P.A.; Dubocovich, M.L. Melatonin differentially modulates the expression and function of the hMT1 and hMT2 melatonin receptors upon prolonged withdrawal. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2003, 65, 731–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdés-Tovar, M.; Estrada-Reyes, R.; Solís-Chagoyán, H.; Argueta, J.; Dorantes-Barrón, A.M.; Quero-Chávez, D.; Cruz-Garduño, R.; Cercós, M.G.; Trueta, C.; Oikawa-Sala, J.; et al. Circadian modulation of neuroplasticity by melatonin: A target in the treatment of depression. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evely, K.M.; Hudson, R.L.; Dubocovich, M.L.; Haj-Dahmane, S. Melatonin receptor activation increases glutamatergic synaptic transmission in the rat medial lateral habenula. Synapse 2016, 70, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cryan, J.F.; Mombereau, C.; Vassout, A. The tail suspension test as a model for assessing antidepressant activity: Review of pharmacological and genetic studies in mice. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2005, 29, 571–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holmes, M.C.; French, K.L.; Seckl, J.R. Dysregulation of diurnal rhythms of serotonin 5-HT2C and corticosteroid receptor gene expression in the hippocampus with food restriction and glucocorticoids. J. Neurosci. 1997, 17, 4056–4065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mateos, S.S.; Sánchez, C.L.; Paredes, S.D.; Barriga, C.; Rodríguez, A.B. Circadian Levels of Serotonin in Plasma and Brain after Oral Administration of Tryptophan in Rats. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2009, 104, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Matheson, G.J.; Schain, M.; Almeida, R.; Lundberg, J.; Cselényi, Z.; Borg, J.; Varrone, A.; Farde, L.; Cervenka, S. Diurnal and seasonal variation of the brain serotonin system in healthy male subjects. Neuroimage 2015, 112, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortega, J.E.; Gonzalez-Lira, V.; Horrillo, I.; Herrera-Marschitz, M.; Callado, L.F.; Meana, J.J. Additive effect of rimonabant and citalopram on extracellular serotonin levels monitored with in vivo microdialysis in rat brain. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 709, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anton-Tay, F.; Chou, C.; Anton, S.; Wurtman, R.J. Brain serotonin concentration: Elevation following intraperitoneal administration of melatonin. Science 1968, 162, 277–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porsolt, R.D.; Bertin, A.; Jalfre, M. Behavioral despair in mice: A primary screening test for antidepressants. Arch. Int. Pharmacodyn. Ther. 1977, 229, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Porsolt, R.D.; Le Pichon, M.; Jalfre, M. Depression: A new animal model sensitive to antidepressant treatments. Nature 1977, 266, 730–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McArthur, R.; Borsini, F. Animal models of depression in drug discovery: A historical perspective. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2006, 84, 436–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cassani, J.; Dorantes-Barrón, A.M.; Novales, L.M.; Real, G.A.; Estrada-Reyes, R. Anti-depressant-like effect of kaempferitrin isolated from Justicia spicigera Schltdl (Acanthaceae) in two behavior models in mice: Evidence for the involvement of the serotonergic system. Molecules 2014, 19, 21442–21461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estrada-Reyes, R.; López-Rubalcava, C.; Ferreyra-Cruz, O.A.; Dorantes-Barrón, A.M.; Heinze, G.; Moreno Aguilar, J.; Martínez-Vázquez, M. Central nervous system effects and chemical composition of two subspecies of Agastache mexicana; an ethnomedicine of Mexico. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 153, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Treatment (mg/kg) | Count Number/5 min | Rearing Number/5 min |
|---|---|---|
| VEH | 43.87 ± 4.42 | 34.50 ± 3.95 |
| MEL 4 | 41.12 ± 2.48 | 25.37 ± 2.18 |
| MEL 16 | 38.50 ± 3.74 | 25.12 ± 2.36 |
| F(2,23) = 0.54, p = 0.58 | F(2,23) = 3.29, p = 0.05 | |
| VEH | 43.87 ± 4.42 | 34.50 ± 3.95 |
| FLX 10 | 36.00 ± 3.576 | 25.62 ± 3.17 |
| FLX 15 | 47.75 ± 2.66 | 28.37 ± 0.75 |
| F(2,23) = 2.72, p= 0.08 | F(2,23) = 3.06, p = 0.10 | |
| VEH | 43.87 ± 4.42 | 34.50 ± 3.95 |
| IMI 12.5 | 36.12 ± 3.52 | 20.87 ± 3.45 |
| IMI 25 | 41.75 ± 5.89 | 34.50 ± 7.72 |
| F(2,23) = 1.48, p = 0.25 | F(2,23) = 2.69, p = 0.09 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Estrada-Reyes, R.; Valdés-Tovar, M.; Arrieta-Baez, D.; Dorantes-Barrón, A.M.; Quero-Chávez, D.; Solís-Chagoyán, H.; Argueta, J.; Dubocovich, M.L.; Benítez-King, G. The Timing of Melatonin Administration Is Crucial for Its Antidepressant-Like Effect in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2278. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19082278
Estrada-Reyes R, Valdés-Tovar M, Arrieta-Baez D, Dorantes-Barrón AM, Quero-Chávez D, Solís-Chagoyán H, Argueta J, Dubocovich ML, Benítez-King G. The Timing of Melatonin Administration Is Crucial for Its Antidepressant-Like Effect in Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(8):2278. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19082278
Chicago/Turabian StyleEstrada-Reyes, Rosa, Marcela Valdés-Tovar, Daniel Arrieta-Baez, Ana María Dorantes-Barrón, Daniel Quero-Chávez, Héctor Solís-Chagoyán, Jesús Argueta, Margarita L. Dubocovich, and Gloria Benítez-King. 2018. "The Timing of Melatonin Administration Is Crucial for Its Antidepressant-Like Effect in Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 8: 2278. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19082278
APA StyleEstrada-Reyes, R., Valdés-Tovar, M., Arrieta-Baez, D., Dorantes-Barrón, A. M., Quero-Chávez, D., Solís-Chagoyán, H., Argueta, J., Dubocovich, M. L., & Benítez-King, G. (2018). The Timing of Melatonin Administration Is Crucial for Its Antidepressant-Like Effect in Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(8), 2278. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19082278