SUMOs Mediate the Nuclear Transfer of p38 and p-p38 during Helicobacter Pylori Infection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
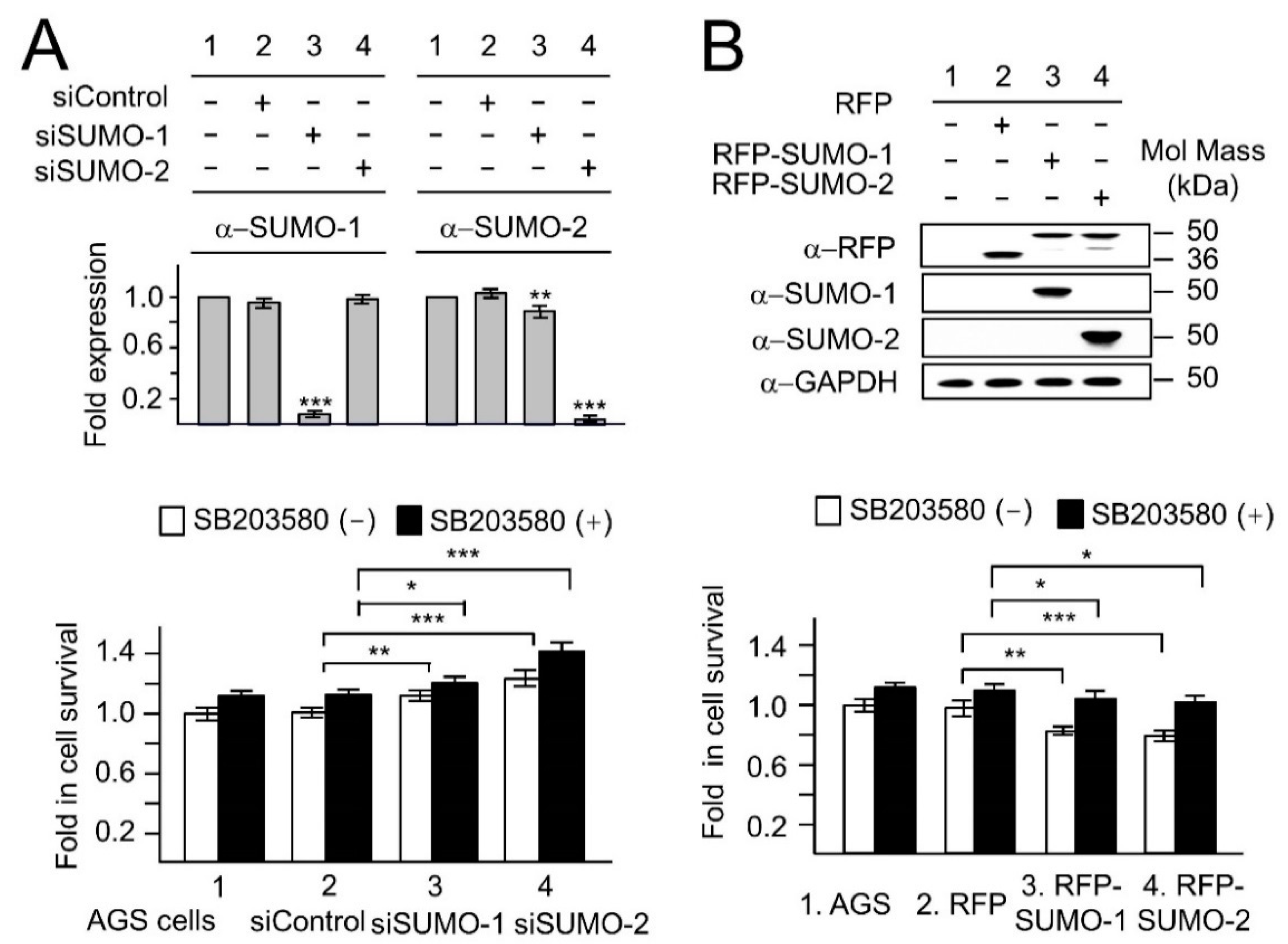
2.1. The Association between Up-Regulation of SUMOs and Activation of the p38 Pathway, in Response to H. pylori Infection
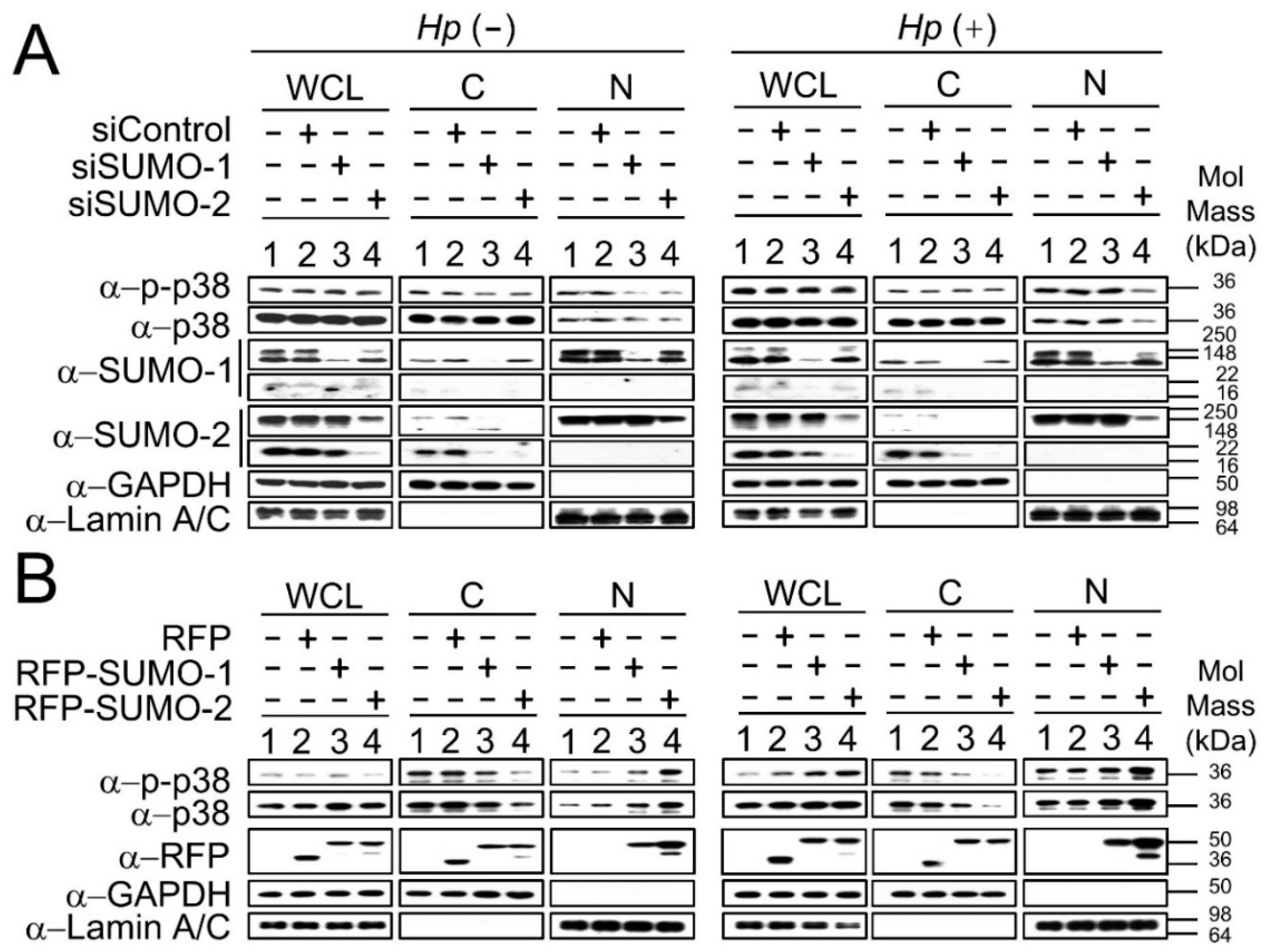
2.2. The Nuclear Localization of p38 and p-p38 Is Dependent on the Levels of SUMOs
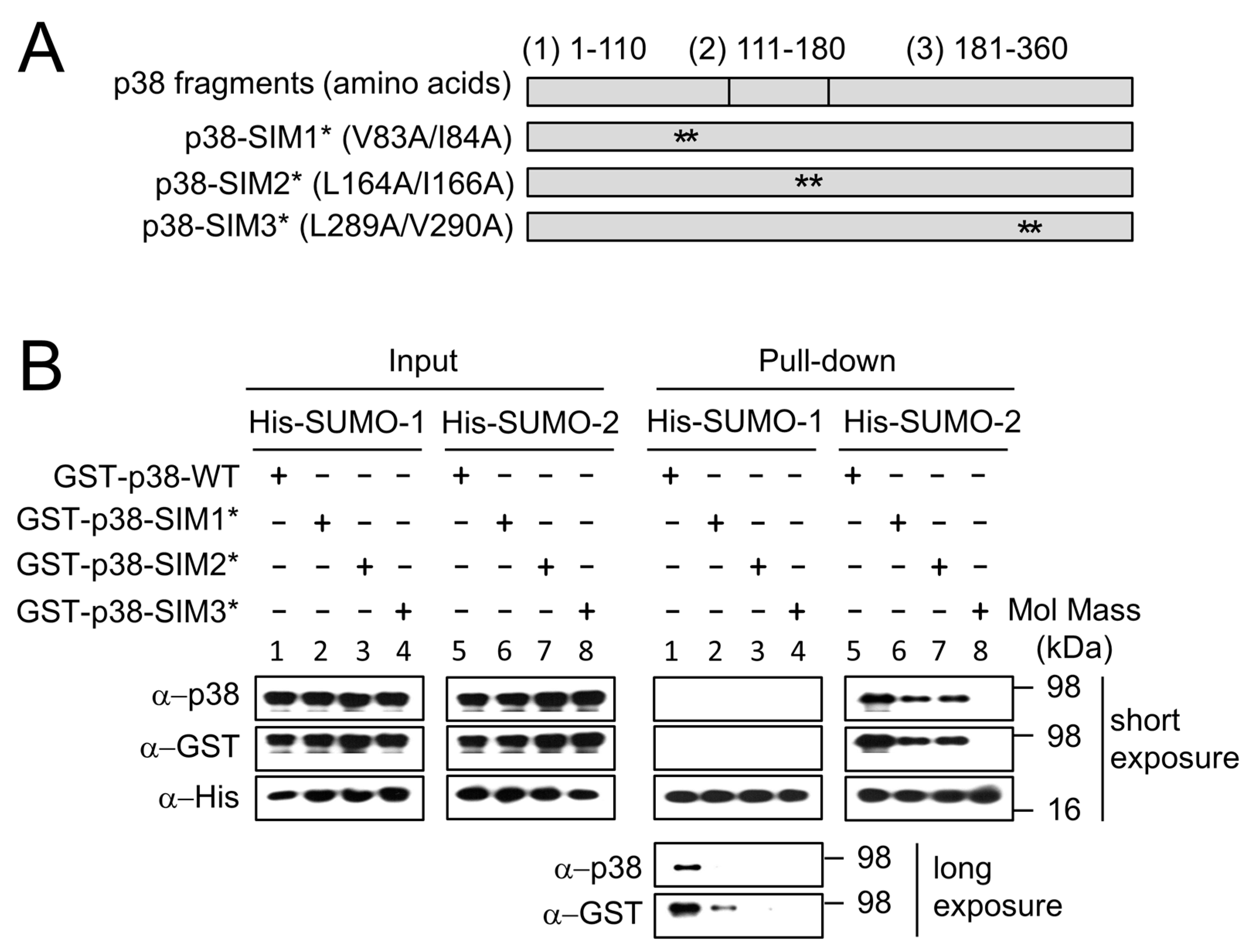
2.3. SUMO Mediated Nuclear Transfer of p38 and p-p38 Is SUMO Interacting Motif (SIM) Dependent
2.4. SUMO Interacts with p38 Non-Covalently
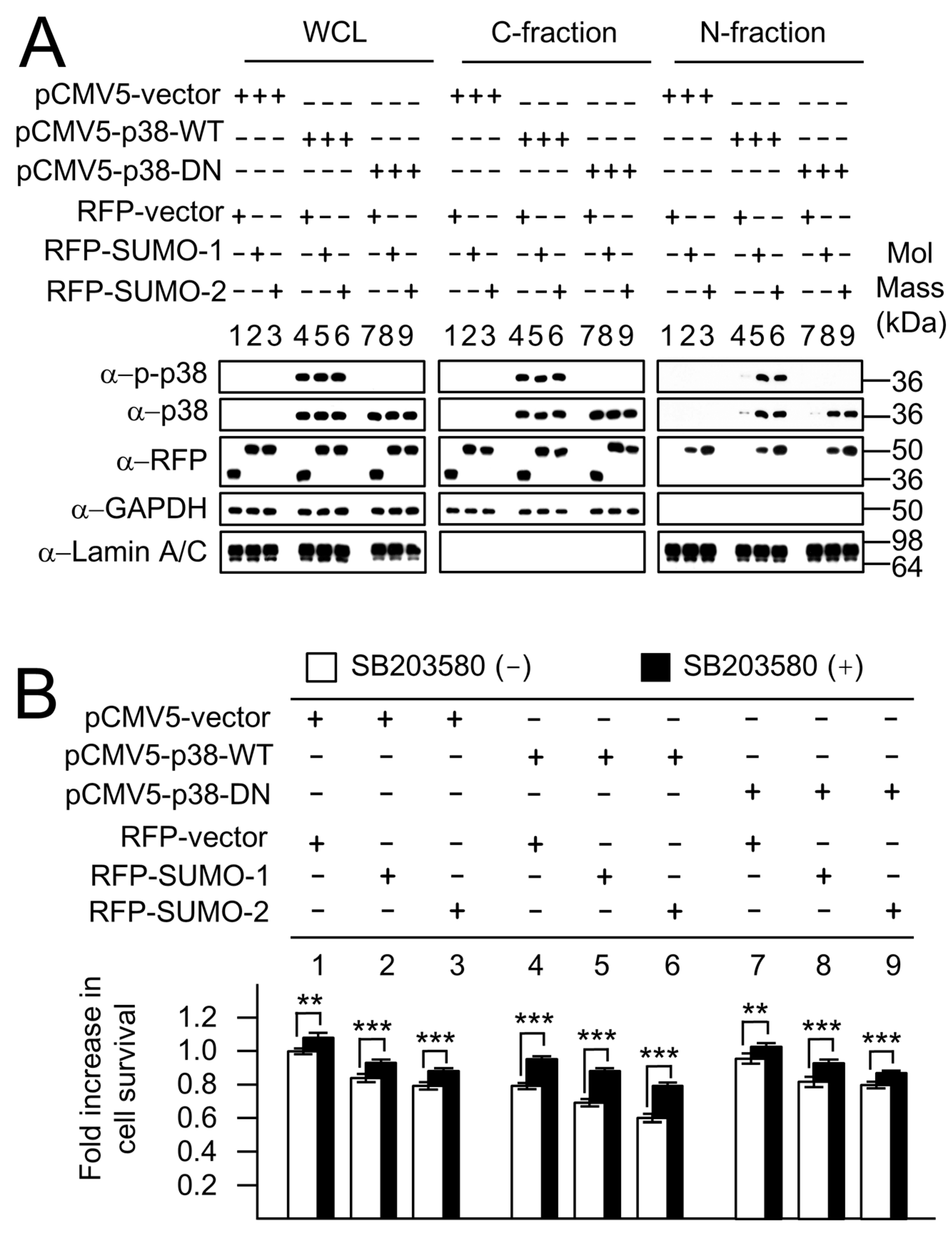
2.5. SUMO-Mediated Nuclear Localization of p38 Is Independent of p38 Phosphorylation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture and H. pylori Infection
4.2. p38 SUMO-Interacting Motif (SIM) Prediction and Production of Full Length p38-SIM Mutant Constructs
4.3. Plasmids
4.4. Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (RT-PCR)
4.5. Transfections
4.6. Western Blots
4.7. Antibodies
4.8. MTT Assay
4.9. In Vitro p38 Phosphorylation
4.10. In Vitro Pull-Down Assay
4.11. In Vitro SUMOylation Assay
4.12. Nuclear and Cytosolic Isolation
4.13. Statistical Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| H. pylori | Helicobacter pylori |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| MOI | Multiplicity of infection |
| SIM | SUMO interacting motif |
| SUMO-1 | Small ubiquitin-like modifier-1 |
| SUMOs | Small ubiquitin-like modifier-1 or 2 |
References
- Han, J.; Jiang, Y.; Li, Z.; Kravchenko, V.V.; Ulevitch, R.J. Activation of the transcription factor MEF2C by the MAP kinase p38 in inflammation. Nature 1997, 386, 296–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyriakis, J.M.; Avruch, J. Mammalian mitogen-activated protein kinase signal transduction pathways activated by stress and inflammation. Physiol. Rev. 2001, 81, 807–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derijard, B.; Raingeaud, J.; Barrett, T.; Wu, I.H.; Han, J.; Ulevitch, R.J.; Davis, R.J. Independent human MAP-kinase signal transduction pathways defined by MEK and MKK isoforms. Science 1995, 267, 682–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raingeaud, J.; Gupta, S.; Rogers, J.S.; Dickens, M.; Han, J.; Ulevitch, R.J.; Davis, R.J. Pro-inflammatory cytokines and environmental stress cause p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation by dual phosphorylation on tyrosine and threonine. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 7420–7426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, X.; Ming, X.; Deng, P.; Jiang, Y. Mechanisms regulating the nuclear translocation of p38 MAP kinase. J. Cell. Biochem. 2010, 110, 1420–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuder, L.E.; Keener, J.M.; Eckert, R.E.; Trujillo, J.C.; Jones, S.L. Role of p38 MAPK in LPS induced pro-inflammatory cytokine and chemokine gene expression in equine leukocytes. Vet. Immunol. Immunopathol. 2009, 129, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulavin, D.V.; Higashimoto, Y.; Popoff, I.J.; Gaarde, W.A.; Basrur, V.; Potapova, O.; Appella, E.; Fornace, A.J., Jr. Initiation of a G2/M checkpoint after ultraviolet radiation requires p38 kinase. Nature 2001, 411, 102–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brand, P.; Plochmann, S.; Valk, E.; Zahn, S.; Saloga, J.; Knop, J.; Becker, D. Activation and translocation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase after stimulation of monocytes with contact sensitizers. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2002, 119, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adachi, M.; Fukuda, M.; Nishida, E. Two co-existing mechanisms for nuclear import of MAP kinase: Passive diffusion of a monomer and active transport of a dimer. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 5347–5358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, N.L.; Shannon, P.T.; Cutz, E.; Yeger, H.; Sherman, P.M. Increase in proliferation and apoptosis of gastric epithelial cells early in the natural history of Helicobacter pylori infection. Am. J. Pathol. 1997, 151, 1695–1703. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ding, S.Z.; Minohara, Y.; Fan, X.J.; Wang, J.; Reyes, V.E.; Patel, J.; Dirden-Kramer, B.; Boldogh, I.; Ernst, P.B.; Crowe, S.E. Helicobacter pylori infection induces oxidative stress and programmed cell death in human gastric epithelial cells. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 4030–4039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomorski, T.; Meyer, T.F.; Naumann, M. Helicobacter pylori-induced prostaglandin E(2) synthesis involves activation of cytosolic phospholipase A(2) in epithelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 804–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keates, S.; Keates, A.C.; Warny, M.; Peek, R.M.; Murray, P.G.; Kelly, C.P. Differential activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases in AGS gastric epithelial cells by cag+ and cag− Helicobacter pylori. J. Immunol. 1999, 163, 5552–5559. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ki, M.R.; Lee, H.R.; Goo, M.J.; Hong, I.H.; Do, S.H.; Jeong, D.H.; Yang, H.J.; Yuan, D.W.; Park, J.K.; Jeong, K.S. Differential regulation of ERK1/2 and p38 MAP kinases in VacA-induced apoptosis of gastric epithelial cells. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2008, 294, G635–G647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Um, J.W.; Chung, K.C. Functional modulation of parkin through physical interaction with SUMO-1. J. Neurosci. Res. 2006, 84, 1543–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saitoh, H.; Hinchey, J. Functional heterogeneity of small ubiquitin-related protein modifiers SUMO-1 versus SUMO-2/3. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 6252–6258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dohmen, R.J. SUMO protein modification. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2004, 1695, 113–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, A.; Wang, P.Y.; Yang, Y.C.; Huang, Y.H.; Yeh, J.J.; Chou, Y.H.; Cheng, J.T.; Hong, Y.R.; Li, S.S. SUMO regulates the cytoplasmonuclear transport of its target protein Daxx. J. Cell. Biochem. 2006, 98, 895–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powell, L.M.; Chen, A.; Huang, Y.C.; Wang, P.Y.; Kemp, S.E.; Jarman, A.P. The SUMO pathway promotes basic helix-loop-helix proneural factor activity via a direct effect on the Zn finger protein senseless. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2012, 32, 2849–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Everett, R.D.; Freemont, P.; Saitoh, H.; Dasso, M.; Orr, A.; Kathoria, M.; Parkinson, J. The disruption of ND10 during herpes simplex virus infection correlates with the Vmw110- and proteasome-dependent loss of several PML isoforms. J. Virol. 1998, 72, 6581–6591. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Manza, L.L.; Codreanu, S.G.; Stamer, S.L.; Smith, D.L.; Wells, K.S.; Roberts, R.L.; Liebler, D.C. Global shifts in protein sumoylation in response to electrophile and oxidative stress. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2004, 17, 1706–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truong, K.; Lee, T.D.; Baozong, L.I.; Chen, Y. Sumoylation of SAE2 C terminus regulates SAE nuclear localization. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 42611–42619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hecker, C.M.; Rabiller, M.; Haglund, K.; Bayer, P.; Dikic, I. Specification of SUMO1- and SUMO2-interacting motifs. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 16117–16127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, J.; Zhu, S.; Guzzo, C.M.; Ellis, N.A.; Sung, K.S.; Choi, C.Y.; Matunis, M.J. Small ubiquitin-related modifier (SUMO) binding determines substrate recognition and paralog-selective SUMO modification. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 29405–29415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, D.Y.; Huang, Y.S.; Jeng, J.C.; Kuo, H.Y.; Chang, C.C.; Chao, T.T.; Ho, C.C.; Chen, Y.C.; Lin, T.P.; Fang, H.I.; et al. Role of SUMO-interacting motif in Daxx SUMO modification, subnuclear localization, and repression of sumoylated transcription factors. Mol. Cell 2006, 24, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tempe, D.; Piechaczyk, M.; Bossis, G. SUMO under stress. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2008, 36, 874–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrivastava, V.; Pekar, M.; Grosser, E.; Im, J.; Vigodner, M. SUMO proteins are involved in the stress response during spermatogenesis and are localized to DNA double-strand breaks in germ cells. Reproduction 2010, 139, 999–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaebisch, R.; Mejías-Luque, R.; Prinz, C.; Gerhard, M. Helicobacter pylori cytotoxin-associated gene A impairs the filtration barrier function of podocytes via p38 MAPK signaling pathway. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2017, 64, 471–475. [Google Scholar]
- Song, J.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, W.; Chen, Y. Small ubiquitin-like modifier (SUMO) recognition of a SUMO binding motif: A reversal of the bound orientation. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 40122–40129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerscher, O. SUMO junction-what’s your function? New insights through SUMO-interacting motifs. EMBO Rep. 2007, 8, 550–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.Y. SUMOs Mediate the Nuclear Transfer of p38 and p-p38 during Helicobacter Pylori Infection. Ph.D. Thesis, National Sun Yat-sen University, Kaohsiung, Taiwan, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Charruyer, A.; Gradize, S.; Bezombes, C.; Muller, S.; Laurent, G.; Jaffrézou, J.P. UV-C light induces raft-associated acid sphingomyelinase and JNK activation and translocation independently on a nuclear signal. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 19196–19204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuderland, D.; Konson, A.; Seger, R. Identification and characterization of a general nuclear translocation signal in signaling proteins. Mol. Cell 2008, 31, 850–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khokhlatchev, A.V.; Canagarajah, B.; Wilsbacher, J.; Robinson, M.; Atkinson, M.; Goldsmith, E.; Cobb, M.H. Phosphorylation of the MAP kinase ERK2 promotes its homodimerization and nuclear translocation. Cell 1998, 93, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Vega, L.; Fröbius, K.; Moreno, R.; Calzado, M.A.; Geng, H.; Schmitz, M.L. Control of nuclear HIPK2 localization and function by a SUMO interaction motif. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1813, 283–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armstrong, A.A.; Mohideen, F.; Lima, C.D. Recognition of SUMO-modified PCNA requires tandem receptor motifs in Srs2. Nature 2012, 483, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, J.J.; Tsai, S.; Wu, D.C.; Wu, J.Y.; Liu, T.C.; Chen, A. P-selectin-dependent platelet aggregation and apoptosis may explain the decrease in platelet count during Helicobacter pylori infection. Blood 2010, 115, 4247–4253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatham, M.H.; Jaffray, E.; Vaughan, O.A.; Desterro, J.M.; Botting, C.; Naismith, J.H.; Hay, R.T. Polymeric chains of SUMO-2 and SUMO-3 are conjugated to protein substrates by SAE1/SAE2 and Ubc9. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 35368–35374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.H.; Sharrocks, A.D. The SUMO E3 ligase activity of Pc2 is coordinated through a SUMO interaction motif. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2010, 30, 2193–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, P.Y.; Hsu, P.I.; Wu, D.C.; Chen, T.C.; Jarman, A.P.; Powell, L.M.; Chen, A. SUMOs Mediate the Nuclear Transfer of p38 and p-p38 during Helicobacter Pylori Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2482. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092482
Wang PY, Hsu PI, Wu DC, Chen TC, Jarman AP, Powell LM, Chen A. SUMOs Mediate the Nuclear Transfer of p38 and p-p38 during Helicobacter Pylori Infection. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(9):2482. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092482
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Pin Yao, Ping I. Hsu, Deng Chyang Wu, Te Chung Chen, Andrew Paul Jarman, Lynn Marie Powell, and Angela Chen. 2018. "SUMOs Mediate the Nuclear Transfer of p38 and p-p38 during Helicobacter Pylori Infection" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 9: 2482. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092482
APA StyleWang, P. Y., Hsu, P. I., Wu, D. C., Chen, T. C., Jarman, A. P., Powell, L. M., & Chen, A. (2018). SUMOs Mediate the Nuclear Transfer of p38 and p-p38 during Helicobacter Pylori Infection. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(9), 2482. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092482




