Electrochemical Oxidation of Primary Bile Acids: A Tool for Simulating Their Oxidative Metabolism?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
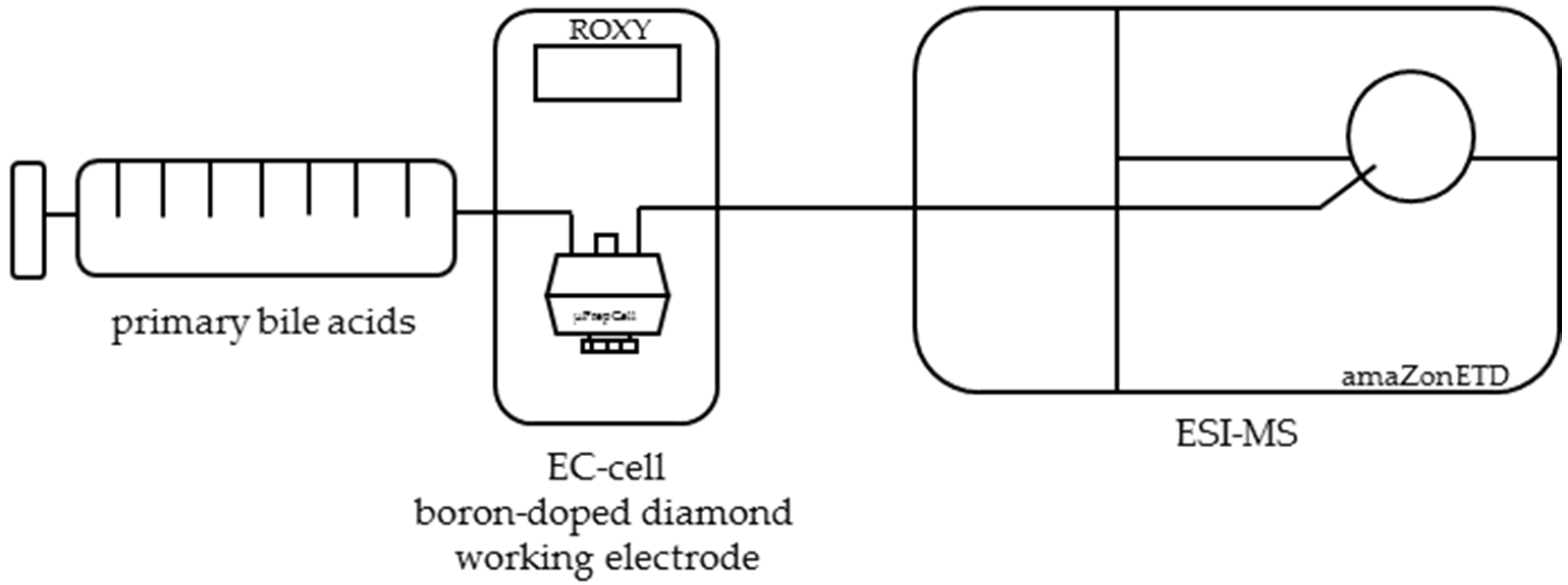
2.1. Electrochemical Oxidation of Primary Bile Acids by Means of EC-ESI-MS
2.2. Electrochemical Simulation of Endogenous Metabolism of Primary Bile Acids
2.3. Investigation of Adduct Formation of Primary Bile Acids and Glutathione Using EC-ESI-MS
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Electrochemical Oxidation of Primary Bile Acids by Means of EC-ESI-MS
4.3. Electrochemical Simulation of Endogenous Metabolism of Primary Bile Acids
4.4. Identification of Oxidized Metabolites via LC-ESI-MS
4.5. Investigation of Adduct Formation of Primary Bile Acids and Glutathione Using EC-ESI-MS
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jenkins, G.; Hardie, L.J. Bile Acids: Toxicology and Bioactivity; Royal Society of Chemistry: Cambridge, UK, 2008; Volume 48. [Google Scholar]
- Ferdinandusse, S.; Denis, S.; Faust, P.L.; Wanders, R.J. Bile acids: The role of peroxisomes. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, 2139–2147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, C.; Pellicciari, R.; Pruzanski, M.; Auwerx, J.; Schoonjans, K. Targeting bile-acid signalling for metabolic diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 678–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vance, D.E.; Vance, J.E. Biochemistry of Lipids, Lipoproteins and Membranes; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherland; Boston, MA, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Dawson, P.A.; Karpen, S.J. Intestinal transport and metabolism of bile acids. J. Lipid Res. 2015, 56, 1085–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridlon, J.M.; Kang, D.J.; Hylemon, P.B. Bile salt biotransformations by human intestinal bacteria. J. Lipid Res. 2006, 47, 241–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macdonald, I.A.; Bokkenheuser, V.D.; Winter, J.; McLernon, A.M.; Mosbach, E.H. Degradation of steroids in the human gut. J. Lipid Res. 1983, 24, 675–700. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gerard, P. Metabolism of cholesterol and bile acids by the gut microbiota. Pathogens 2013, 3, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, J.Y. Regulation of bile acid synthesis: Pathways, nuclear receptors, and mechanisms. J. Hepatol. 2004, 40, 539–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiang, J.Y. Bile acids: Regulation of synthesis. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, 1955–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, M.; Lund, E.G.; Setchell, K.D.; Kayden, H.J.; Zerwekh, J.E.; Bjorkhem, I.; Herz, J.; Russell, D.W. Disruption of cholesterol 7alpha-hydroxylase gene in mice. II. Bile acid deficiency is overcome by induction of oxysterol 7alpha-hydroxylase. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 18024–18031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofmann, A.F. The continuing importance of bile acids in liver and intestinal disease. Arch. Int. Med. 1999, 159, 2647–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worthmann, A.; John, C.; Ruhlemann, M.C.; Baguhl, M.; Heinsen, F.A.; Schaltenberg, N.; Heine, M.; Schlein, C.; Evangelakos, I.; Mineo, C.; et al. Cold-induced conversion of cholesterol to bile acids in mice shapes the gut microbiome and promotes adaptive thermogenesis. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 839–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faber, H.; Vogel, M.; Karst, U. Electrochemistry/mass spectrometry as a tool in metabolism studies-A. review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2014, 834, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oberacher, H.; Pitterl, F.; Erb, R.; Plattner, S. Mass spectrometric methods for monitoring redox processes in electrochemical cells. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2015, 34, 64–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lohmann, W.; Baumann, A.; Karst, U. Electrochemistry and LC-MS for Metabolite Generation and Identification: Tools, Technologies and Trends. Lc Gc Eur. 2010, 23, 8–16. [Google Scholar]
- Sayin, S.I.; Wahlstrom, A.; Felin, J.; Jantti, S.; Marschall, H.U.; Bamberg, K.; Angelin, B.; Hyotylainen, T.; Oresic, M.; Backhed, F. Gut microbiota regulates bile acid metabolism by reducing the levels of tauro-beta-muricholic acid, a naturally occurring FXR antagonist. Cell Metab. 2013, 17, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wegner, K.; Just, S.; Gau, L.; Mueller, H.; Gerard, P.; Lepage, P.; Clavel, T.; Rohn, S. Rapid analysis of bile acids in different biological matrices using LC-ESI-MS/MS for the investigation of bile acid transformation by mammalian gut bacteria. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2017, 409, 1231–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alnouti, Y.; Csanaky, I.L.; Klaassen, C.D. Quantitative-profiling of bile acids and their conjugates in mouse liver, bile, plasma, and urine using LC-MS/MS. J. Chromatogr. 2008, 873, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurva, U.; Wikstrom, H.V.; Bruins, A.P. In vitro mimicry of metabolic oxidation reactions by electrochemistry/mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2000, 14, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frensemeier, L.M.; Buter, L.; Vogel, M.; Karst, U. Investigation of the oxidative transformation of roxarsone by electrochemistry coupled to hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. J. Anal. Atom. Spectrom. 2017, 32, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Baumann, A.; Lohmann, W.; Schubert, B.; Oberacher, H.; Karst, U. Metabolic studies of tetrazepam based on electrochemical simulation in comparison to in vivo and in vitro methods. J. Chromatogr. A 2009, 1216, 3192–3198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jahn, S.; Baumann, A.; Roscher, J.; Hense, K.; Zazzeroni, R.; Karst, U. Investigation of the biotransformation pathway of verapamil using electrochemistry/liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry—A comparative study with liver cell microsomes. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 9210–9220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buter, L.; Vogel, M.; Karst, U. Adduct formation of electrochemically generated reactive intermediates wi th biomolecules. Trac-Trend Anal. Chem. 2015, 70, 74–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plattner, S.; Erb, R.; Pitterl, F.; Brouwer, H.J.; Oberacher, H. Formation and characterization of covalent guanosine adducts with electrochemistry-liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2012, 883–884, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pecková, K.; Nesmerák, K. Electrochemistry of Bile Acids, Cholesterol, and Related Compounds (An Overview). Sens. Electroanal. 2012, 7, 87–96. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, D.; Ni, Z.X.; Vetter, D.; Hoffmann, R.; Fedorova, M. Electrochemical oxidation of cholesterol: An easy way to generate numerous oxysterols in short reaction times. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2016, 118, 325–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bussy, U.; Boisseau, R.; Thobie-Gautier, C.; Boujtita, M. Electrochemistry-mass spectrometry to study reactive drug metabolites and CYP450 simulations. Trac-Trend Anal. Chem. 2015, 70, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotani, A.; Hakamata, H.; Nakayama, N.; Kusu, F. Picomole Level Determination of Cholesterol by HPLC with Electrochemical Detection Using Boron-doped Diamond Electrode after Performance Assessment Based on the FUMI Theory. Electroanal 2011, 23, 2709–2715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klouda, J.; Barek, J.; Nesmerak, K.; Schwarzova-Peckova, K. Non-Enzymatic Electrochemistry in Characterization and Analysis of Steroid Compounds. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2017, 47, 384–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klouda, J.; Barek, J.; Kočovský, P.; Herl, T.; Matysik, F.-M.; Nesměrák, K.; Schwarzová-Pecková, K. Bile acids: Electrochemical oxidation on bare electrodes after acid-induced dehydration. Electrochem. Commun. 2018, 86, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, X.; Ye, M.; Liu, C.F.; Yang, W.Z.; Miao, W.J.; Dong, J.; Guo, D.A. A tandem mass spectrometric study of bile acids: Interpretation of fragmentation pathways and differentiation of steroid isomers. Steroids 2012, 77, 204–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Njalsson, R.; Norgren, S. Physiological and pathological aspects of GSH metabolism. Acta Paediatr. 2005, 94, 132–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, P.P. The Bile Acids Chemistry, Physiology, and Metabolism; Plenum Press: New York, NY, USA, 1971; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Hylemon, P.B.; Harris, S.C.; Ridlon, J.M. Metabolism of hydrogen gases and bile acids in the gut microbiome. FEBS Lett. 2018, 592, 2070–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Macdonald, I.A.; Williams, C.N.; Mahony, D.E. A 3 alpha- and 7 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase assay for conjugated dihydroxy-bile acid mixtures. Anal. Biochem. 1974, 57, 127–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitamura, K.; Sogabe, M.; Sakanashi, H.; Watanabe, S.; Sakai, T.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Wakamiya, T.; Ikegawa, S. Analysis of bile acid glutathione thioesters by liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B 2007, 855, 88–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofmann, A.F.; Hagey, L.R. Bile acids: Chemistry, pathochemistry, biology, pathobiology, and therapeutics. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2008, 65, 2461–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, X.H.; Liu, Y.D.; Zhou, X.; Navaneethan, U.; Shen, B.; Guo, B.C. An LC-ESI-MS method for the quantitative analysis of bile acids composition in fecal materials. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2012, 26, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Navarro Suarez, L.; Brückner, L.; Rohn, S. Electrochemical Oxidation of Primary Bile Acids: A Tool for Simulating Their Oxidative Metabolism? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2491. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092491
Navarro Suarez L, Brückner L, Rohn S. Electrochemical Oxidation of Primary Bile Acids: A Tool for Simulating Their Oxidative Metabolism? International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(9):2491. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092491
Chicago/Turabian StyleNavarro Suarez, Laura, Lea Brückner, and Sascha Rohn. 2018. "Electrochemical Oxidation of Primary Bile Acids: A Tool for Simulating Their Oxidative Metabolism?" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 9: 2491. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092491
APA StyleNavarro Suarez, L., Brückner, L., & Rohn, S. (2018). Electrochemical Oxidation of Primary Bile Acids: A Tool for Simulating Their Oxidative Metabolism? International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(9), 2491. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092491




