The Effect of Ca2+, Lobe-Specificity, and CaMKII on CaM Binding to NaV1.1
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Binding of CaM to NaV1.1 IQ/EQ Domain
2.2. Binding of CaM Mutants to NaV1.1 IQ Domain
2.3. Binding of Individual N-Lobe or C-Lobe of CaM to NaV1.1 IQ Domain
2.4. The Effect of CaMKII on CaM Binding to NaV1.1 IQ Domain
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. cDNA Construction and Site-Directed Mutagenesis
3.2. Expression and Purification of Recombinant GST Fusion Peptides
3.3. GST Pull-Down Assay
3.4. Computational Docking
3.5. Statistical Analysis
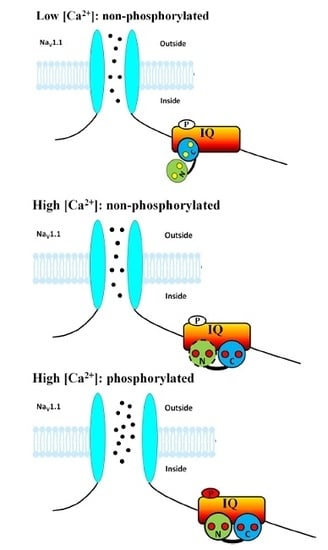
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Adams, P.J.; Ben-Johny, M.; Dick, I.E.; Inoue, T.; Yue, D.T. Apocalmodulin itself promotes ion channel opening and Ca(2+) regulation. Cell 2014, 159, 608–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asmara, H.; Minobe, E.; Saud, Z.A.; Kameyama, M. Interactions of calmodulin with the multiple binding sites of CaV1.2 Ca2+ channels. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2010, 112, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, J.H.; Cerda, O.; Trimmer, J.S. Mass spectrometry-based phosphoproteomics reveals multisite phosphorylation on mammalian brain voltage-gated sodium and potassium channels. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2011, 22, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, J.H.; Rubinstein, M.; Scheuer, T.; Trimmer, J.S. Reciprocal changes in phosphorylation and methylation of mammalian brain sodium channels in response to seizures. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 15363–15373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahler, M.; Rhoads, A. Calmodulin signaling via the IQ motif. FEBS Lett. 2002, 513, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendt, F.J.; Park, K.S.; Trimmer, J.S. Multisite phosphorylation of voltage-gated sodium channel alpha subunits from rat brain. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 1976–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chagot, B.; Chazin, W.J. Solution NMR structure of Apo-calmodulin in complex with the IQ motif of human cardiac sodium channel NaV1.5. J. Mol. Biol. 2011, 406, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Zhao, R.; Zhao, M.; Liang, X.; Bhattarai, D.; Dhiman, R.; Shetty, S.; Idell, S.; Ji, H.L. Regulation of epithelial sodium channels in urokinase plasminogen activator deficiency. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2014, 307, L609–L617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dick, I.E.; Tadross, M.R.; Liang, H.; Tay, L.H.; Yang, W.; Yue, D.T. A modular switch for spatial Ca2+ selectivity in the calmodulin regulation of CaV channels. Nature 2008, 451, 830–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldkamp, M.D.; Yu, L.; Shea, M.A. Structural and energetic determinants of apo calmodulin binding to the IQ motif of the Na(V)1.2 voltage-dependent sodium channel. Structure 2011, 19, 733–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaudioso, C.; Carlier, E.; Youssouf, F.; Clare, J.J.; Debanne, D.; Alcaraz, G. Calmodulin and calcium differentially regulate the neuronal Nav1.1 voltage-dependent sodium channel. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 411, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, F.; Minobe, E.; Yazawa, K.; Asmara, H.; Bai, X.Y.; Han, D.Y.; Hao, L.Y.; Kameyama, M. Both N- and C-lobes of calmodulin are required for Ca2+-dependent regulations of CaV1.2 Ca2+ channels. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 391, 1170–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, F.; Zhou, P.D.; Gao, Q.H.; Gong, J.; Feng, R.; Xu, X.X.; Liu, S.Y.; Hu, H.Y.; Zhao, M.M.; Adam, H.C.; et al. Low-Mg(2+) treatment increases sensitivity of voltage-gated Na(+) channels to Ca(2+)/calmodulin-mediated modulation in cultured hippocampal neurons. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2015, 308, C594–C605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, D.Y.; Minobe, E.; Wang, W.Y.; Guo, F.; Xu, J.J.; Hao, L.Y.; Kameyama, M. Calmodulin- and Ca2+-dependent facilitation and inactivation of the CaV1.2 Ca2+ channels in guinea-pig ventricular myocytes. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2010, 112, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Tai, C.; Westenbroek, R.E.; Yu, F.H.; Cheah, C.S.; Potter, G.B.; Rubenstein, J.L.; Scheuer, T.; de la Iglesia, H.O.; Catterall, W.A. Autistic-like behaviour in Scn1a+/− mice and rescue by enhanced GABA-mediated neurotransmission. Nature 2012, 489, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, L.Y.; Wang, W.Y.; Minobe, E.; Han, D.Y.; Xu, J.J.; Kameyama, A.; Kameyama, M. The distinct roles of calmodulin and calmodulin kinase II in the reversal of run-down of L-type Ca(2+) channels in guinea-pig ventricular myocytes. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2009, 111, 416–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, G.; Guo, F.; Zhu, T.; Shao, D.; Feng, R.; Yin, D.; Sun, X.; Hu, H.; Hwang, A.; Minobe, E.; et al. Lobe-related concentration- and Ca(2+)-dependent interactions of calmodulin with C- and N-terminal tails of the CaV1.2 channel. J. Physiol. Sci. 2013, 63, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herren, A.W.; Weber, D.M.; Rigo, R.R.R.; Margulies, K.B.; Phinney, B.S.; Bers, D.M. CaMKII Phosphorylation of Na(V)1.5: Novel in Vitro Sites Identified by Mass Spectrometry and Reduced S516 Phosphorylation in Human Heart Failure. J. Proteome Res. 2015, 14, 2298–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hund, T.J.; Koval, O.M.; Li, J.; Wright, P.J.; Qian, L.; Snyder, J.S.; Gudmundsson, H.; Kline, C.F.; Davidson, N.P.; Cardona, N.; et al. A beta(IV)-spectrin/CaMKII signaling complex is essential for membrane excitability in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2010, 120, 3508–3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.Y.; Rumpf, C.H.; Fujiwara, Y.; Cooley, E.S.; van Petegem, F.; Minor, D.L., Jr. Structures of CaV2 Ca2+/CaM-IQ domain complexes reveal binding modes that underlie calcium-dependent inactivation and facilitation. Structure 2008, 16, 1455–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazrak, A.; Nita, I.; Subramaniyam, D.; Wei, S.; Song, W.; Ji, H.L.; Janciauskiene, S.; Matalon, S. Alpha(1)-antitrypsin inhibits epithelial Na+ transport in vitro and in vivo. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2009, 41, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Lin, Y.; Lu, X.; Qiu, Y. Neuroprotective effects of ischemic preconditioning on global brain ischemia through up-regulation of acid-sensing ion channel 2a. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 140–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minobe, E.; Asmara, H.; Saud, Z.A.; Kameyama, M. Calpastatin domain L is a partial agonist of the calmodulin-binding site for channel activation in CaV1.2 Ca2+ channels. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 39013–39022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitt, G.S.; Lee, S.Y. Current view on regulation of voltage-gated sodium channels by calcium and auxiliary proteins. Protein Sci. 2016, 25, 1573–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potet, F.; Chagot, B.; Anghelescu, M.; Viswanathan, P.C.; Stepanovic, S.Z.; Kupershmidt, S.; Chazin, W.J.; Balser, J.R. Functional Interactions between Distinct Sodium Channel Cytoplasmic Domains through the Action of Calmodulin. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 8846–8854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarhan, M.F.; Tung, C.C.; van Petegem, F.; Ahern, C.A. Crystallographic basis for calcium regulation of sodium channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 3558–3563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saud, Z.A.; Minobe, E.; Wang, W.Y.; Han, D.Y.; Horiuchi, M.; Hao, L.Y.; Kameyama, M. Calpastatin binds to a calmodulin-binding site of cardiac CaV1.2 Ca2+ channels. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 364, 372–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheuer, T. Regulation of sodium channel activity by phosphorylation. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2011, 22, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, V.N.; Wingo, T.L.; Weiss, K.L.; Williams, C.K.; Balser, J.R.; Chazin, W.J. Calcium-dependent regulation of the voltage-gated sodium channel hH1: Intrinsic and extrinsic sensors use a common molecular switch. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 3592–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, D.; Zhao, M.; Xu, J.; Feng, R.; Guo, F.; Hu, H.; Sun, X.; Gao, Q.; He, G.; Sun, W.; et al. The individual N- and C-lobes of calmodulin tether to the CaV1.2 channel and rescue the channel activity from run-down in ventricular myocytes of guinea-pig heart. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 3855–3861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shifman, J.M.; Choi, M.H.; Mihalas, S.; Mayo, S.L.; Kennedy, M.B. Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) is activated by calmodulin with two bound calciums. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 13968–13973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefan, M.I.; Marshall, D.P.; le Novere, N. Structural analysis and stochastic modelling suggest a mechanism for calmodulin trapping by CaMKII. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turabekova, M.A.; Rasulev, B.F.; Levkovich, M.G.; Abdullaev, N.D.; Leszczynski, J. Aconitum and Delphinium sp. alkaloids as antagonist modulators of voltage-gated Na+ channels. AM1/DFT electronic structure investigations and QSAR studies. Comput. Biol. Chem. 2008, 32, 88–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stigler, J.; Rief, M. Calcium-dependent folding of single calmodulin molecules. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 17814–17819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Feng, R.; Hu, H.; Guo, F.; Gao, Q.; Shao, D.; Yin, D.; Wang, H.; Sun, X.; Zhao, M.; et al. The Ca(2+)-dependent interaction of calpastatin domain L with the C-terminal tail of the CaV1.2 channel. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tadross, M.R.; Dick, I.E.; Yue, D.T. Mechanism of local and global Ca2+ sensing by calmodulin in complex with a Ca2+ channel. Cell 2008, 133, 1228–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, W.; Halling, D.B.; Black, D.J.; Pate, P.; Zhang, J.Z.; Pedersen, S.; Altschuld, R.A.; Hamilton, S.L. Apocalmodulin and Ca2+ calmodulin-binding sites on the CaV1.2 channel. Biophys. J. 2003, 85, 1538–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theoharis, N.T.; Sorensen, B.R.; Theisen-Toupal, J.; Shea, M.A. The neuronal voltage-dependent sodium channel type II IQ motif lowers the calcium affinity of the C-domain of calmodulin. Biochemistry 2008, 47, 112–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, C.H.; Hawkins, N.A.; Kearney, J.A.; George, A.L., Jr. CaMKII modulates sodium current in neurons from epileptic Scn2a mutant mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 1696–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Petegem, F.; Lobo, P.A.; Ahern, C.A. Seeing the forest through the trees: Towards a unified view on physiological calcium regulation of voltage-gated sodium channels. Biophys. J. 2012, 103, 2243–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vetter, S.W.; Leclerc, E. Novel aspects of calmodulin target recognition and activation. Eur. J. Biochem. 2003, 270, 404–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Pelton, R. A new route to poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) microgels supporting a polyvinylamine corona. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 276, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Li, Q.; Liu, X.; Liu, S. Roles of Voltage-Gated Tetrodotoxin-Sensitive Sodium Channels NaV1.3 and NaV1.7 in Diabetes and Painful Diabetic Neuropathy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Liu, N.; He, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ge, L.; Zou, L.; Song, S.; Xiong, W.; Liu, X. Improved calcium sensor GCaMP-X overcomes the calcium channel perturbations induced by the calmodulin in GCaMP. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, L.; Fan, P.; Jiang, Z.; Viatchenko-Karpinski, S.; Wu, Y.; Kornyeyev, D.; Hirakawa, R.; Budas, G.R.; Rajamani, S.; Shryock, J.C.; et al. Nav1.5-dependent persistent Na+ influx activates CaMKII in rat ventricular myocytes and N1325S mice. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2011, 301, C577–C586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Yu, Y.; Wu, X.; Liu, S.; Liu, B.; Du, J.; Li, B.; Jiang, L.; Feng, X. A Role of BK Channel in Regulation of Ca(2+) Channel in Ventricular Myocytes by Substrate Stiffness. Biophys. J. 2017, 112, 1406–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, J.; Salarian, M.; Chen, Y.; Veenstra, R.; Louis, C.F.; Yang, J.J. Gap junction regulation by calmodulin. FEBS Lett. 2014, 588, 1430–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Parameters | CaM | CaM12 | CaM34 | CaM1234 | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [Ca2+] ≈ Free | 100 (nM) | 500 (nM) | 2 (mM) | [Ca2+] ≈ Free | 100 (nM) | 500 (nM) | 2 (mM) | [Ca2+] ≈ Free | 100 (nM) | 500 (nM) | 2 (mM) | [Ca2+] ≈ Free | 100 (nM) | 500 (nM) | 2 (mM) | |
| Bmax1 (mol/mol) | 1.2296 | 0.2796 | 0.2505 | 0.1258 | 1.272 | 0.6985 | 0.822 | 0.9093 | 0.7911 | 0.5719 | 1.3305 | 0.7875 | 0.6932 | 0.061 | 0.1927 | 0.2423 |
| Kd1 (μM) | 0.1036 | 0.063 | 0.0433 | 0.0682 | 0.0453 | 0.1533 | 0.1481 | 0.1347 | 0.0665 | 0.0978 | 0.4231 | 0.3865 | 0.1023 | 0.1684 | 0.0132 | 0.0297 |
| Bmax2 (mol/mol) | 0.8282 | 0.3838 | 0.8312 | 1.2559 | 0.3712 | 0.9562 | 0.8682 | 0.792 | ||||||||
| Kd2 (μM) | 4.5817 | 2.9054 | 1.5099 | 0.5589 | 1.632 | 0.3822 | 0.6179 | 0.952 | ||||||||
| R2 | 0.9824 | 0.9861 | 0.9745 | 0.9955 | 0.9978 | 0.9725 | 0.9762 | 0.9858 | 0.9935 | 0.9841 | 0.9908 | 0.9879 | 0.9902 | 0.9984 | 0.9857 | 0.9783 |
| p | 0.004 | 0.002 | 0.002 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.296 | 0.017 | 0.104 | 0.105 | 0.031 | ||||
| Parameters | N-Lobe | C-Lobe | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [Ca2+] ≈ Free | 100 (nM) | 500 (nM) | 2 (mM) | [Ca2+] ≈ Free | 100 (nM) | 500 (nM) | 2 (mM) | |
| Bmax1 (mol/mol) | 0.0893 | 0.0973 | 0.1532 | 0.085 | 0.1483 | 0.0928 | 0.0675 | 0.0784 |
| Kd1 (μM) | 0.0214 | 0.0144 | 0.0137 | 0.016 | 0.0124 | 0.0167 | 0.0231 | 0.0225 |
| Bmax2 (mol/mol) | 0.0859 | 0.0645 | 0.1531 | 0.0836 | 0.1691 | 0.0369 | 0.0652 | 0.0755 |
| Kd2 (μM) | 0.0214 | 6.3762 | 0.0137 | 0.016 | 0.0124 | 3.3088 | 0.0231 | 0.0225 |
| R2 | 0.9788 | 0.9937 | 0.9879 | 0.9891 | 0.9873 | 0.9954 | 0.9832 | 0.9817 |
| p | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.198 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | ||
| Parameters | ‘Phosphorylation ([Ca2+] ≈ Free) | Phosphorylation ([Ca2+] = 100nM) | Phosphorylation ([Ca2+] = 500nM) | Phosphorylation ([Ca2+] = 2mM) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CIP | Control | CaMKII | CIP | Control | CaMKII | CIP | Control | CaMKII | CIP | Control | CaMKII | |
| Bmax1 (mol/mol) | 0.3662 | 0.3753 | 0.3623 | 0.1141 | 0.2063 | 0.2925 | 0.1624 | 0.2952 | 0.4425 | 0.1308 | 0.2304 | 0.4709 |
| Kd1 (μM) | 0.0371 | 0.0376 | 0.0361 | 0.0365 | 0.029 | 0.0251 | 0.0163 | 0.0163 | 0.013 | 0.0383 | 0.0283 | 0.0473 |
| Bmax2 (mol/mol) | 0.3713 | 0.3862 | 0.3572 | 0.1967 | 0.2572 | 0.2667 | 0.3969 | 0.4848 | 0.5894 | 0.2564 | 0.3163 | 0.24 |
| Kd2 (μM) | 2.0347 | 2.4926 | 1.4381 | 1.4219 | 3.0904 | 3.026 | 3.9451 | 5.0388 | 8.1743 | 2.006 | 1.1043 | 1.9515 |
| R2 | 0.9955 | 0.9891 | 0.9951 | 0.9944 | 0.9962 | 0.9987 | 0.991 | 0.9939 | 0.9789 | 0.9861 | 0.9937 | 0.9954 |
| p | 0.91 | 0.175 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.001 | 0.002 | 0.001 | ||||
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, J.; Yu, Z.; Xu, J.; Feng, R.; Gao, Q.; Boczek, T.; Liu, J.; Li, Z.; Wang, Q.; Lei, M.; et al. The Effect of Ca2+, Lobe-Specificity, and CaMKII on CaM Binding to NaV1.1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2495. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092495
Li J, Yu Z, Xu J, Feng R, Gao Q, Boczek T, Liu J, Li Z, Wang Q, Lei M, et al. The Effect of Ca2+, Lobe-Specificity, and CaMKII on CaM Binding to NaV1.1. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(9):2495. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092495
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Jianing, Zhiyi Yu, Jianjun Xu, Rui Feng, Qinghua Gao, Tomasz Boczek, Junyan Liu, Zhi Li, Qianhui Wang, Ming Lei, and et al. 2018. "The Effect of Ca2+, Lobe-Specificity, and CaMKII on CaM Binding to NaV1.1" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 9: 2495. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092495
APA StyleLi, J., Yu, Z., Xu, J., Feng, R., Gao, Q., Boczek, T., Liu, J., Li, Z., Wang, Q., Lei, M., Gong, J., Hu, H., Minobe, E., Ji, H.-L., Kameyama, M., & Guo, F. (2018). The Effect of Ca2+, Lobe-Specificity, and CaMKII on CaM Binding to NaV1.1. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(9), 2495. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092495