The Role of IL-33/ST2 Pathway in Tumorigenesis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The IL-33/ST2 Signaling Pathway
2.1. Interleukin 33
2.2. The ST2 Receptor
2.3. Signaling by the IL-33/ST2 Pathway
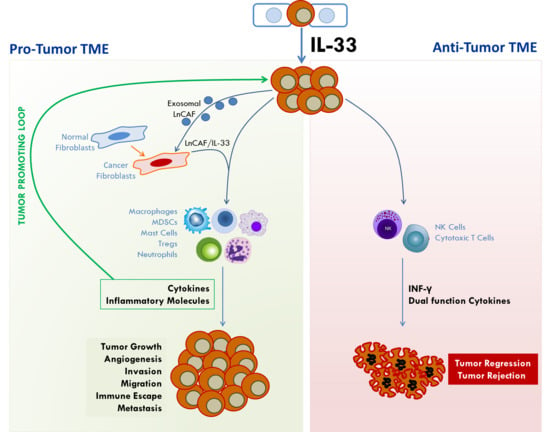
3. The Role of IL33/ST2 in Tumorigenesis
3.1. Breast Cancer
3.2. Colorectal Cancer
3.3. Gastric Cancer
3.4. Hepatocellular Carcinoma
3.5. Hepatobiliary Cancers
3.6. Pancreatic Cancer
3.7. Lung Cancer
3.8. Prostate and Kidney Cancer
3.9. Ovarian Cancer
3.10. Uterine Cancer
3.11. Endometrial Cancer
3.12. Cervical Cancer
3.13. Head and Neck Cancer
3.14. Brain Tumors and Gliomas
3.15. Gingivitis and Salivary Tumors
3.16. Skin Cancer and Inflammatory Diseases
3.17. Squamous Cell Carcinoma:
3.18. Blood Cancers
3.19. Lymphoma
3.20. Bone Cancer Pain Management
4. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IL-33 | Interleukin 33 |
| ST2 | Suppressor of tumorigenesis |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor κB |
| NK | Natural killer cells |
| MDSC | Myeloid derived suppressor cells |
| TME | Tumor microenvironment |
| HDAC | Histone deacetylase |
| IL1-RacP | IL1-like receptor accessory protein |
| MVD | Microvessel density |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
| CRC | Colorectal cancer |
| NSCLC | Non-small cell lung carcinoma |
| ELISA | Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay |
| MPN | Myeloproliferative neoplasms |
| CAF | Cancer associated fibroblasts |
References
- National Center for Health Statistics. United States 2016: With Chartbook on Long-Term Trands in Health; Health and Human Services, Ed.; US Government Printing Office: Hyattsville, MD, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quail, D.F.; Joyce, J.A. Microenvironmental regulation of tumor progression and metastasis. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1423–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hanahan, D.; Coussens, L.M. Accessories to the crime: Functions of cells recruited to the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Cell 2012, 21, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz, J.; Owyang, A.; Oldham, E.; Song, Y.; Murphy, E.; McClanahan, T.K.; Zurawski, G.; Moshrefi, M.; Qin, J.; Li, X.; et al. IL-33, an interleukin-1-like cytokine that signals via the IL-1 receptor-related protein ST2 and induces T helper type 2-associated cytokines. Immunity 2005, 23, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liew, F.Y.; Girard, J.P.; Turnquist, H.R. Interleukin-33 in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 676–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liew, F.Y.; Pitman, N.I.; McInnes, I.B. Disease-associated functions of IL-33: The new kid in the IL-1 family. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verri, W.A., Jr.; Souto, F.O.; Vieira, S.M.; Almeida, S.C.; Fukada, S.Y.; Xu, D.; Alves-Filho, J.C.; Cunha, T.M.; Guerrero, A.T.; Mattos-Guimaraes, R.B.; et al. IL-33 induces neutrophil migration in rheumatoid arthritis and is a target of anti-TNF therapy. Ann. Rheum Dis. 2010, 69, 1697–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, M.; Matsuda, A.; Yanagisawa, K.; Hirota, T.; Akahoshi, M.; Inomata, N.; Ebe, K.; Tanaka, K.; Sugiura, H.; Nakashima, K.; et al. Functional SNPs in the distal promoter of the ST2 gene are associated with atopic dermatitis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2005, 14, 2919–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hayakawa, H.; Hayakawa, M.; Kume, A.; Tominaga, S. Soluble ST2 blocks interleukin-33 signaling in allergic airway inflammation. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 26369–26380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunes, T.; Bernardazzi, C.; de Souza, H.S. Interleukin-33 and inflammatory bowel diseases: Lessons from human studies. Mediat. Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 423957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanada, S.; Hakuno, D.; Higgins, L.J.; Schreiter, E.R.; McKenzie, A.N.; Lee, R.T. IL-33 and ST2 comprise a critical biomechanically induced and cardioprotective signaling system. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 1538–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miller, A.M.; Liew, F.Y. The IL-33/ST2 pathway—A new therapeutic target in cardiovascular disease. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 131, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakkar, R.; Lee, R.T. The IL-33/ST2 pathway: Therapeutic target and novel biomarker. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 827–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moussion, C.; Ortega, N.; Girard, J.P. The IL-1-like cytokine IL-33 is constitutively expressed in the nucleus of endothelial cells and epithelial cells in vivo: A novel ‘alarmin’? PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haraldsen, G.; Balogh, J.; Pollheimer, J.; Sponheim, J.; Kuchler, A.M. Interleukin-33–cytokine of dual function or novel alarmin? Trends Immunol. 2009, 30, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carriere, V.; Roussel, L.; Ortega, N.; Lacorre, D.A.; Americh, L.; Aguilar, L.; Bouche, G.; Girard, J.P. IL-33, the IL-1-like cytokine ligand for ST2 receptor, is a chromatin-associated nuclear factor in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 282–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roussel, L.; Erard, M.; Cayrol, C.; Girard, J.P. Molecular mimicry between IL-33 and KSHV for attachment to chromatin through the H2A-H2B acidic pocket. EMBO Rep. 2008, 9, 1006–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Tossberg, J.T.; Spurlock, C.F.; Yao, S.Y.; Aune, T.M.; Sriram, S. Expression of IL-33 and its epigenetic regulation in Multiple Sclerosis. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2014, 1, 307–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.; Mohs, A.; Thomas, M.; Klare, J.; Ross, R.; Schmitz, M.L.; Martin, M.U. The dual function cytokine IL-33 interacts with the transcription factor NF-kappaB to dampen NF-kappaB-stimulated gene transcription. J. Immunol. 2011, 187, 1609–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, W.; Hu, Z. The enigmatic processing and secretion of interleukin-33. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2010, 7, 260–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cayrol, C.; Girard, J.P. The IL-1-like cytokine IL-33 is inactivated after maturation by caspase-1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 9021–9026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cayrol, C.; Girard, J.P. IL-33: An alarmin cytokine with crucial roles in innate immunity, inflammation and allergy. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2014, 31, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bessa, J.; Meyer, C.A.; de Vera Mudry, M.C.; Schlicht, S.; Smith, S.H.; Iglesias, A.; Cote-Sierra, J. Altered subcellular localization of IL-33 leads to non-resolving lethal inflammation. J. Autoimmun. 2014, 55, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talabot-Ayer, D.; Lamacchia, C.; Gabay, C.; Palmer, G. Interleukin-33 is biologically active independently of caspase-1 cleavage. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 19420–19426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.; Nguyen, D.Q.; Falk, W.; Martin, M.U. Caspase 3 inactivates biologically active full length interleukin-33 as a classical cytokine but does not prohibit nuclear translocation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 391, 1512–1516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luthi, A.U.; Cullen, S.P.; McNeela, E.A.; Duriez, P.J.; Afonina, I.S.; Sheridan, C.; Brumatti, G.; Taylor, R.C.; Kersse, K.; Vandenabeele, P.; et al. Suppression of interleukin-33 bioactivity through proteolysis by apoptotic caspases. Immunity 2009, 31, 84–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefrancais, E.; Roga, S.; Gautier, V.; Gonzalez-de-Peredo, A.; Monsarrat, B.; Girard, J.P.; Cayrol, C. IL-33 is processed into mature bioactive forms by neutrophil elastase and cathepsin G. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 1673–1678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lefrancais, E.; Duval, A.; Mirey, E.; Roga, S.; Espinosa, E.; Cayrol, C.; Girard, J.P. Central domain of IL-33 is cleaved by mast cell proteases for potent activation of group-2 innate lymphoid cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 15502–15507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lefrancais, E.; Cayrol, C. Mechanisms of IL-33 processing and secretion: Differences and similarities between IL-1 family members. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2012, 23, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tominaga, S. A putative protein of a growth specific cDNA from BALB/c-3T3 cells is highly similar to the extracellular portion of mouse interleukin 1 receptor. FEBS Lett. 1989, 258, 301–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tominaga, S.; Yokota, T.; Yanagisawa, K.; Tsukamoto, T.; Takagi, T.; Tetsuka, T. Nucleotide sequence of a complementary DNA for human ST2. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1992, 1171, 215–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanagisawa, K.; Takagi, T.; Tsukamoto, T.; Tetsuka, T.; Tominaga, S. Presence of a novel primary response gene ST2L, encoding a product highly similar to the interleukin 1 receptor type 1. FEBS Lett. 1993, 318, 83–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hardman, C.; Ogg, G. Interleukin-33, friend and foe in type-2 immune responses. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2016, 42, 16–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergers, G.; Reikerstorfer, A.; Braselmann, S.; Graninger, P.; Busslinger, M. Alternative promoter usage of the Fos-responsive gene Fit-1 generates mRNA isoforms coding for either secreted or membrane-bound proteins related to the IL-1 receptor. EMBO J. 1994, 13, 1176–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tominaga, S.; Kuroiwa, K.; Tago, K.; Iwahana, H.; Yanagisawa, K.; Komatsu, N. Presence and expression of a novel variant form of ST2 gene product in human leukemic cell line UT-7/GM. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1999, 264, 14–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tago, K.; Noda, T.; Hayakawa, M.; Iwahana, H.; Yanagisawa, K.; Yashiro, T.; Tominaga, S. Tissue distribution and subcellular localization of a variant form of the human ST2 gene product, ST2V. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 285, 1377–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwahana, H.; Hayakawa, M.; Kuroiwa, K.; Tago, K.; Yanagisawa, K.; Noji, S.; Tominaga, S. Molecular cloning of the chicken ST2 gene and a novel variant form of the ST2 gene product, ST2LV. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2004, 1681, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oshikawa, K.; Yanagisawa, K.; Tominaga, S.; Sugiyama, Y. Expression and function of the ST2 gene in a murine model of allergic airway inflammation. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2002, 32, 1520–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwahana, H.; Yanagisawa, K.; Ito-Kosaka, A.; Kuroiwa, K.; Tago, K.; Komatsu, N.; Katashima, R.; Itakura, M.; Tominaga, S. Different promoter usage and multiple transcription initiation sites of the interleukin-1 receptor-related human ST2 gene in UT-7 and TM12 cells. Eur. J. Biochem. 1999, 264, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baba, Y.; Maeda, K.; Yashiro, T.; Inage, E.; Kasakura, K.; Suzuki, R.; Niyonsaba, F.; Hara, M.; Tanabe, A.; Ogawa, H.; et al. GATA2 is a critical transactivator for the human IL1RL1/ST2 promoter in mast cells/basophils: Opposing roles for GATA2 and GATA1 in human IL1RL1/ST2 gene expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 32689–32696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akimoto, M.; Takenaga, K. Role of the IL-33/ST2L axis in colorectal cancer progression. Cell. Immunol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millar, N.L.; O’Donnell, C.; McInnes, I.B.; Brint, E. Wounds that heal and wounds that don’t—The role of the IL-33/ST2 pathway in tissue repair and tumorigenesis. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 61, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funakoshi-Tago, M.; Tago, K.; Hayakawa, M.; Tominaga, S.; Ohshio, T.; Sonoda, Y.; Kasahara, T. TRAF6 is a critical signal transducer in IL-33 signaling pathway. Cell. Signal. 2008, 20, 1679–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milovanovic, M.; Volarevic, V.; Radosavljevic, G.; Jovanovic, I.; Pejnovic, N.; Arsenijevic, N.; Lukic, M.L. IL-33/ST2 axis in inflammation and immunopathology. Immunol. Res. 2012, 52, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Donnell, C.; Mahmoud, A.; Keane, J.; Murphy, C.; White, D.; Carey, S.; O’Riordain, M.; Bennett, M.W.; Brint, E.; Houston, A. An antitumorigenic role for the IL-33 receptor, ST2L, in colon cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 114, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Wei, J.; Mialki, R.K.; Mallampalli, D.F.; Chen, B.B.; Coon, T.; Zou, C.; Mallampalli, R.K.; Zhao, Y. F-box protein FBXL19-mediated ubiquitination and degradation of the receptor for IL-33 limits pulmonary inflammation. Nat. Immunol. 2012, 13, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Tzimas, M.N.; Griswold, D.E.; Young, P.R. Expression of ST2, an interleukin-1 receptor homologue, is induced by proinflammatory stimuli. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1997, 235, 474–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, E.S.; Scott, I.C.; Majithiya, J.B.; Rapley, L.; Kemp, B.P.; England, E.; Rees, D.G.; Overed-Sayer, C.L.; Woods, J.; Bond, N.J.; et al. Oxidation of the alarmin IL-33 regulates ST2-dependent inflammation. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jovanovic, I.; Radosavljevic, G.; Mitrovic, M.; Juranic, V.L.; McKenzie, A.N.; Arsenijevic, N.; Jonjic, S.; Lukic, M.L. ST2 deletion enhances innate and acquired immunity to murine mammary carcinoma. Eur. J. Immunol. 2011, 41, 1902–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jovanovic, I.P.; Pejnovic, N.N.; Radosavljevic, G.D.; Arsenijevic, N.N.; Lukic, M.L. IL-33/ST2 axis in innate and acquired immunity to tumors. Oncoimmunology 2012, 1, 229–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gillibert-Duplantier, J.; Duthey, B.; Sisirak, V.; Salaun, D.; Gargi, T.; Tredan, O.; Finetti, P.; Bertucci, F.; Birnbaum, D.; Bendriss-Vermare, N.; et al. Gene expression profiling identifies sST2 as an effector of ErbB2-driven breast carcinoma cell motility, associated with metastasis. Oncogene 2012, 31, 3516–3524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jovanovic, I.P.; Pejnovic, N.N.; Radosavljevic, G.D.; Pantic, J.M.; Milovanovic, M.Z.; Arsenijevic, N.N.; Lukic, M.L. Interleukin-33/ST2 axis promotes breast cancer growth and metastases by facilitating intratumoral accumulation of immunosuppressive and innate lymphoid cells. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 134, 1669–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, P.; Wan, X.; Cui, B.; Liu, Y.; Qiu, C.; Rong, J.; Zheng, M.; Song, Y.; Chen, L.; He, J.; et al. Interleukin 33 in tumor microenvironment is crucial for the accumulation and function of myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Oncoimmunology 2016, 5, e1063772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milosavljevic, M.Z.; Jovanovic, I.P.; Pejnovic, N.N.; Mitrovic, S.L.; Arsenijevic, N.N.; Simovic Markovic, B.J.; Lukic, M.L. Deletion of IL-33R attenuates VEGF expression and enhances necrosis in mammary carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 18106–18115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, J.Y.; Lim, S.C.; Kim, G.; Yun, H.J.; Ahn, S.G.; Choi, H.S. Interleukin-33/ST2 axis promotes epithelial cell transformation and breast tumorigenesis via upregulation of COT activity. Oncogene 2015, 34, 4928–4938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, D.P.; Zhou, X.Y.; Yao, L.T.; Liu, C.G.; Ma, W.; Jin, F.; Wu, Y.F. Serum soluble ST2 is associated with ER-positive breast cancer. BMC Cancer 2014, 14, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.P.; Ling, D.Y.; Xie, Y.H.; Wu, W.X.; Li, J.R.; Jiang, J.; Zheng, J.L.; Fan, Y.H.; Zhang, Y. The Association of Serum IL-33 and sST2 with Breast Cancer. Dis. Mark. 2015, 2015, 516895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Shen, J.X.; Hu, J.L.; Huang, W.H.; Zhang, G.J. Significance of interleukin-33 and its related cytokines in patients with breast cancers. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jafarzadeh, A.; Minaee, K.; Farsinejad, A.R.; Nemati, M.; Khosravimashizi, A.; Daneshvar, H.; Mohammadi, M.M.; Sheikhi, A.; Ghaderi, A. Evaluation of the circulating levels of IL-12 and IL-33 in patients with breast cancer: Influences of the tumor stages and cytokine gene polymorphisms. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2015, 18, 1189–1198. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yigitbasi, M.R.; Guntas, G.; Atak, T.; Sonmez, C.; Yalman, H.; Uzun, H. The Role of Interleukin-33 as an Inflammatory Marker in Differential Diagnosis of Idiopathic Granulomatous Mastitis and Breast Cancer. J. Investig. Surg 2017, 30, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Cancer Society. Cancer Facts and Figures 2018; American Cancer Society, Ed.; American Cancer Society: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, G.; Qi, H.; Gundersen, M.D.; Yang, H.; Christiansen, I.; Sorbye, S.W.; Goll, R.; Florholmen, J. Dynamics of the IL-33/ST2 network in the progression of human colorectal adenoma to sporadic colorectal cancer. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2015, 64, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Zhu, L.; Lu, X.; Bian, H.; Wu, X.; Yang, W.; Qin, Q. IL-33/ST2 pathway contributes to metastasis of human colorectal cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 453, 486–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maywald, R.L.; Doerner, S.K.; Pastorelli, L.; De Salvo, C.; Benton, S.M.; Dawson, E.P.; Lanza, D.G.; Berger, N.A.; Markowitz, S.D.; Lenz, H.J.; et al. IL-33 activates tumor stroma to promote intestinal polyposis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E2487–E2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mertz, K.D.; Mager, L.F.; Wasmer, M.H.; Thiesler, T.; Koelzer, V.H.; Ruzzante, G.; Joller, S.; Murdoch, J.R.; Brummendorf, T.; Genitsch, V.; et al. The IL-33/ST2 pathway contributes to intestinal tumorigenesis in humans and mice. Oncoimmunology 2016, 5, e1062966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Y.; Davis, C.; Shah, S.; Hughes, D.; Ryan, J.C.; Altomare, D.; Pena, M.M. IL-33 promotes growth and liver metastasis of colorectal cancer in mice by remodeling the tumor microenvironment and inducing angiogenesis. Mol. Carcinog. 2017, 56, 272–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gounaris, E.; Erdman, S.E.; Restaino, C.; Gurish, M.F.; Friend, D.S.; Gounari, F.; Lee, D.M.; Zhang, G.; Glickman, J.N.; Shin, K.; et al. Mast cells are an essential hematopoietic component for polyp development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19977–19982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khazaie, K.; Blatner, N.R.; Khan, M.W.; Gounari, F.; Gounaris, E.; Dennis, K.; Bonertz, A.; Tsai, F.N.; Strouch, M.J.; Cheon, E.; et al. The significant role of mast cells in cancer. Cancer Metast. Rev. 2011, 30, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saadalla, A.M.; Osman, A.; Gurish, M.F.; Dennis, K.L.; Blatner, N.R.; Pezeshki, A.; McNagny, K.M.; Cheroutre, H.; Gounari, F.; Khazaie, K. Mast cells promote small bowel cancer in a tumor stage-specific and cytokine-dependent manner. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 1588–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Akimoto, M.; Maruyama, R.; Takamaru, H.; Ochiya, T.; Takenaga, K. Soluble IL-33 receptor sST2 inhibits colorectal cancer malignant growth by modifying the tumour microenvironment. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fang, M.; Li, Y.; Huang, K.; Qi, S.; Zhang, J.; Zgodzinski, W.; Majewski, M.; Wallner, G.; Gozdz, S.; Macek, P.; et al. IL33 Promotes Colon Cancer Cell Stemness via JNK Activation and Macrophage Recruitment. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 2735–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, Z.; Chen, L.; Souto, F.O.; Canasto-Chibuque, C.; Bongers, G.; Deshpande, M.; Harpaz, N.; Ko, H.M.; Kelley, K.; Furtado, G.C.; et al. Epithelial-derived IL-33 promotes intestinal tumorigenesis in Apc (Min/+) mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eissmann, M.F.; Dijkstra, C.; Wouters, M.A.; Baloyan, D.; Mouradov, D.; Nguyen, P.M.; Davalos-Salas, M.; Putoczki, T.L.; Sieber, O.M.; Mariadason, J.M.; et al. Interleukin 33 Signaling Restrains Sporadic Colon Cancer in an Interferon-gamma-Dependent Manner. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2018, 6, 409–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, K.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Bai, L.; Dong, W.; Gao, K.; Shi, G.; Xia, X.; Wu, L.; Zhang, L. Transgenic expression of IL-33 activates CD8(+) T cells and NK cells and inhibits tumor growth and metastasis in mice. Cancer Lett. 2013, 335, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Wang, X.; Yang, Q.; Zhao, X.; Wen, W.; Li, G.; Lu, J.; Qin, W.; Qi, Y.; Xie, F.; et al. Tumoral expression of IL-33 inhibits tumor growth and modifies the tumor microenvironment through CD8+ T and NK cells. J. Immunol. 2015, 194, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, A.R.; Goldenring, J.R. Injury, repair, inflammation and metaplasia in the stomach. J. Physiol. 2018, 596, 3861–3867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, C.P.; Meyer, A.R.; De Salvo, C.; Choi, E.; Schlegel, C.; Petersen, A.; Engevik, A.C.; Prasad, N.; Levy, S.E.; Peebles, R.S.; et al. A signalling cascade of IL-33 to IL-13 regulates metaplasia in the mouse stomach. Gut 2018, 67, 805–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergis, D.; Kassis, V.; Ranglack, A.; Koeberle, V.; Piiper, A.; Kronenberger, B.; Zeuzem, S.; Waidmann, O.; Radeke, H.H. High Serum Levels of the Interleukin-33 Receptor Soluble ST2 as a Negative Prognostic Factor in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Transl. Oncol. 2013, 6, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brunner, S.M.; Rubner, C.; Kesselring, R.; Martin, M.; Griesshammer, E.; Ruemmele, P.; Stempfl, T.; Teufel, A.; Schlitt, H.J.; Fichtner-Feigl, S. Tumor-infiltrating, interleukin-33-producing effector-memory CD8+ T cells in resected hepatocellular carcinoma prolong patient survival. Hepatology 2015, 61, 1957–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Liu, X.K.; Chu, Z.; Ye, J.C.; Li, K.L.; Zhuang, W.L.; Yang, D.J.; Jiang, Y.F. Detection of interleukin-33 in serum and carcinoma tissue from patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and its clinical implications. J. Int. Med. Res. 2012, 40, 1654–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Z.H.; Li, Y.Y.; Huang, S.Q.; Tan, Z.Q. Genetic variants in IL-33/ST2 pathway with the susceptibility to hepatocellular carcinoma in a Chinese population. Cytokine 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, D.; Rizvi, S.; Razumilava, N.; Bronk, S.F.; Davila, J.I.; Champion, M.D.; Borad, M.J.; Bezerra, J.A.; Chen, X.; Gores, G.J. IL-33 facilitates oncogene-induced cholangiocarcinoma in mice by an interleukin-6-sensitive mechanism. Hepatology 2015, 61, 1627–1642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Razumilava, N.; Gores, G.J.; Walters, S.; Mizuochi, T.; Mourya, R.; Bessho, K.; Wang, Y.H.; Glaser, S.S.; Shivakumar, P.; et al. Biliary repair and carcinogenesis are mediated by IL-33-dependent cholangiocyte proliferation. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 3241–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and National Cancer Institute. United States Cancer Statistics: 1999–2014 Incidence and Mortality Web-Based Report; U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Ed.; Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and National Cancer Institute: Atlanta, GA, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Masamune, A.; Watanabe, T.; Kikuta, K.; Satoh, K.; Kanno, A.; Shimosegawa, T. Nuclear expression of interleukin-33 in pancreatic stellate cells. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2010, 299, G821–G832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmieder, A.; Multhoff, G.; Radons, J. Interleukin-33 acts as a pro-inflammatory cytokine and modulates its receptor gene expression in highly metastatic human pancreatic carcinoma cells. Cytokine 2012, 60, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naumnik, W.; Naumnik, B.; Niewiarowska, K.; Ossolinska, M.; Chyczewska, E. Novel cytokines: IL-27, IL-29, IL-31 and IL-33. Can they be useful in clinical practice at the time diagnosis of lung cancer? Exp. Oncol. 2012, 34, 348–353. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hu, L.A.; Fu, Y.; Zhang, D.N.; Zhang, J. Serum IL-33 as a diagnostic and prognostic marker in non-small cell lung cancer. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2013, 14, 2563–2566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Chen, Z.; Bu, X.; Han, Y.; Shan, S.; Ren, T.; Song, W. IL-33 signaling fuels outgrowth and metastasis of human lung cancer. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 479, 461–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Gao, X.; Wang, J.; Xu, L.; Zheng, Y.; Xu, Y. Interleukin-33 enhanced the migration and invasiveness of human lung cancer cells. Onco Targets Ther. 2018, 11, 843–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, K.; Shan, S.; Yang, Z.; Gu, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.; Ren, T. IL-33 blockade suppresses tumor growth of human lung cancer through direct and indirect pathways in a preclinical model. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 68571–68582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, M.; Bai, Y.; Zhao, S.; Liu, X.; Gao, Y.; Wang, L.; Liu, B.; Ma, D.; Ma, C. Gram-negative bacteria facilitate tumor progression through TLR4/IL-33 pathway in patients with non-small-cell lung cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 13462–13473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.S.; Kim, E.; Heo, J.S.; Bae, D.J.; Lee, J.U.; Lee, T.H.; Lee, H.J.; Chang, H.S.; Park, J.S.; Jang, A.S.; et al. Circulating IL-33 level is associated with the progression of lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2015, 90, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akimoto, M.; Hayashi, J.I.; Nakae, S.; Saito, H.; Takenaga, K. Interleukin-33 enhances programmed oncosis of ST2L-positive low-metastatic cells in the tumour microenvironment of lung cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, M.; Feng, Y.; Yue, C.; Xu, B.; Chen, L.; Jiang, J.; Lu, B.; Zhu, Y. Lower expression level of IL-33 is associated with poor prognosis of pulmonary adenocarcinoma. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saranchova, I.; Han, J.; Zaman, R.; Arora, H.; Huang, H.; Fenninger, F.; Choi, K.B.; Munro, L.; Pfeifer, C.G.; Welch, I.; et al. Type 2 Innate Lymphocytes Actuate Immunity Against Tumours and Limit Cancer Metastasis. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Saranchova, I.; Han, J.; Huang, H.; Fenninger, F.; Choi, K.B.; Munro, L.; Pfeifer, C.; Welch, I.; Wyatt, A.W.; Fazli, L.; et al. Discovery of a Metastatic Immune Escape Mechanism Initiated by the Loss of Expression of the Tumour Biomarker Interleukin-33. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ravichandran, K.; Holditch, S.; Brown, C.N.; Wang, Q.; Ozkok, A.; Weiser-Evans, M.C.; Nemenoff, R.; Miyazaki, M.; Thiessen-Philbrook, H.; Parikh, C.R.; et al. IL-33 deficiency slows cancer growth but does not protect against cisplatin-induced AKI in mice with cancer. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2018, 314, F356–F366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, X.; Barbour, M.; Hou, K.; Gao, C.; Cao, S.; Zheng, J.; Zhao, Y.; Mu, R.; Jiang, H.R. Interleukin-33 predicts poor prognosis and promotes ovarian cancer cell growth and metastasis through regulating ERK and JNK signaling pathways. Mol. Oncol. 2016, 10, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Santulli, P.; Even, M.; Chouzenoux, S.; Millischer, A.E.; Borghese, B.; de Ziegler, D.; Batteux, F.; Chapron, C. Profibrotic interleukin-33 is correlated with uterine leiomyoma tumour burden. Hum. Reprod. 2013, 28, 2126–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Santulli, P.; Borghese, B.; Chouzenoux, S.; Vaiman, D.; Borderie, D.; Streuli, I.; Goffinet, F.; de Ziegler, D.; Weill, B.; Batteux, F.; et al. Serum and peritoneal interleukin-33 levels are elevated in deeply infiltrating endometriosis. Hum. Reprod. 2012, 27, 2001–2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zeng, X.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, Q.Q.; Wang, Y.Y.; Yu, X.Z.; Zhou, B.; Xi, M.R. Clinical Significance of Serum Interleukin-31 and Interleukin-33 Levels in Patients of Endometrial Cancer: A Case Control Study. Dis. Mark. 2016, 2016, 9262919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Li, H.; Liang, F.; Hong, Y.; Jiang, S.; Xiao, L. Examining IL-33 expression in the cervix of HPV-infected patients: A preliminary study comparing IL-33 levels in different stages of disease and analyzing its potential association with IFN-gamma. Med. Oncol. 2014, 31, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.F.; Nieh, S.; Jao, S.W.; Wu, M.Z.; Liu, C.L.; Chang, Y.C.; Lin, Y.S. The paracrine effect of cancer-associated fibroblast-induced interleukin-33 regulates the invasiveness of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J. Pathol. 2013, 231, 180–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gramatzki, D.; Frei, K.; Cathomas, G.; Moch, H.; Weller, M.; Mertz, K.D. Interleukin-33 in human gliomas: Expression and prognostic significance. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 12, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fang, K.M.; Yang, C.S.; Lin, T.C.; Chan, T.C.; Tzeng, S.F. Induced interleukin-33 expression enhances the tumorigenic activity of rat glioma cells. Neuro Oncol. 2014, 16, 552–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tada, H.; Matsuyama, T.; Nishioka, T.; Hagiwara, M.; Kiyoura, Y.; Shimauchi, H.; Matsushita, K. Porphyromonas gingivalis Gingipain-Dependently Enhances IL-33 Production in Human Gingival Epithelial Cells. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, R.; Polic, B.; Welsh, R.M.; Szomolanyi-Tsuda, E. Inflammatory cytokine-mediated evasion of virus-induced tumors from NK cell control. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 961–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa, K.; Yagi-Nakanishi, S.; Nakanishi, Y.; Kondo, S.; Tsuji, A.; Endo, K.; Wakisaka, N.; Murono, S.; Yoshizaki, T. Expression of interleukin-33 is correlated with poor prognosis of patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the tongue. Auris Nasus Larynx 2014, 41, 552–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rossle, M.; Cathomas, G.; Bonapace, L.; Sachs, M.; Dehler, S.; Storz, M.; Huber, G.; Moch, H.; Junt, T.; Mertz, K.D. Interleukin-33 Expression Indicates a Favorable Prognosis in Malignant Salivary Gland Tumors. Int. J. Surg. Pathol. 2016, 24, 394–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, S.N.; Beaugie, C.; O’Sullivan, C.; Leighton, S.; Halliday, G.M. The immune-modulating cytokine and endogenous Alarmin interleukin-33 is upregulated in skin exposed to inflammatory UVB radiation. Am. J. Pathol. 2011, 179, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergot, A.S.; Monnet, N.; Le Tran, S.; Mittal, D.; Al-Kouba, J.; Steptoe, R.J.; Grimbaldeston, M.A.; Frazer, I.H.; Wells, J.W. HPV16 E7 expression in skin induces TSLP secretion, type 2 ILC infiltration and atopic dermatitis-like lesions. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2015, 93, 540–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuda, H.; Komine, M.; Karakawa, M.; Etoh, T.; Tominaga, S.; Ohtsuki, M. Novel splice variants of IL-33: Differential expression in normal and transformed cells. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 2661–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.; Bae, S.; Jhun, H.; Lee, S.; Choi, J.; Kang, T.; Kwak, A.; Hong, K.; Kim, E.; Jo, S.; et al. Identification of Constitutively Active Interleukin 33 (IL-33) Splice Variant. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 20078–20086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Serrels, B.; McGivern, N.; Canel, M.; Byron, A.; Johnson, S.C.; McSorley, H.J.; Quinn, N.; Taggart, D.; Von Kreigsheim, A.; Anderton, S.M.; et al. IL-33 and ST2 mediate FAK-dependent antitumor immune evasion through transcriptional networks. Sci Signal 2017, 10, eaan8355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ding, L.; Ren, J.; Zhang, D.; Li, Y.; Huang, X.; Hu, Q.; Wang, H.; Song, Y.; Ni, Y.; Hou, Y. A novel stromal lncRNA signature reprograms fibroblasts to promote the growth of oral squamous cell carcinoma via LncRNA-CAF/interleukin-33. Carcinogenesis 2018, 39, 397–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mager, L.F.; Riether, C.; Schurch, C.M.; Banz, Y.; Wasmer, M.H.; Stuber, R.; Theocharides, A.P.; Li, X.; Xia, Y.; Saito, H.; et al. IL-33 signaling contributes to the pathogenesis of myeloproliferative neoplasms. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 2579–2591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Levescot, A.; Flamant, S.; Basbous, S.; Jacomet, F.; Feraud, O.; Anne Bourgeois, E.; Bonnet, M.L.; Giraud, C.; Roy, L.; Barra, A.; et al. BCR-ABL-induced deregulation of the IL-33/ST2 pathway in CD34+ progenitors from chronic myeloid leukemia patients. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 2669–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tare, N.; Li, H.; Morschauser, A.; Cote-Sierra, J.; Ju, G.; Renzetti, L.; Lin, T.A. KU812 cells provide a novel in vitro model of the human IL-33/ST2L axis: Functional responses and identification of signaling pathways. Exp. Cell Res. 2010, 316, 2527–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gangemi, S.; Allegra, A.; Profita, M.; Saitta, S.; Gerace, D.; Bonanno, A.; Alonci, A.; Petrungaro, A.; Russo, S.; Musolino, C. Decreased plasma levels of IL-33 could contribute to the altered function of Th2 lymphocytes in patients with polycythemia vera and essential thrombocythemia. Cancer Investig. 2013, 31, 212–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musolino, C.; Allegra, A.; Profita, M.; Alonci, A.; Saitta, S.; Russo, S.; Bonanno, A.; Innao, V.; Gangemi, S. Reduced IL-33 plasma levels in multiple myeloma patients are associated with more advanced stage of disease. Br. J. Haematol. 2013, 160, 709–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musolino, C.; Allegra, A.; Profita, M.; Alonci, A.; Saitta, S.; Bonanno, A.; Gerace, D.; Calabro, L.; Gangemi, S. Reduction in IL-33 plasma levels might be involved in T cell dysregulation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Acta Haematol. 2014, 131, 165–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duault, C.; Betous, D.; Bezombes, C.; Roga, S.; Cayrol, C.; Girard, J.P.; Fournie, J.J.; Poupot, M. IL-33-expanded human Vgamma9Vdelta2 T cells have anti-lymphoma effect in a mouse tumor model. Eur. J. Immunol. 2017, 47, 2137–2141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabelitz, D.; Wesch, D.; Pitters, E.; Zoller, M. Characterization of tumor reactivity of human V gamma 9V delta 2 gamma delta T cells in vitro and in SCID mice in vivo. J. Immunol. 2004, 173, 6767–6776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casetti, R.; Perretta, G.; Taglioni, A.; Mattei, M.; Colizzi, V.; Dieli, F.; D’Offizi, G.; Malkovsky, M.; Poccia, F. Drug-induced expansion and differentiation of V gamma 9V delta 2 T cells in vivo: The role of exogenous IL-2. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 1593–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sicard, H.; Ingoure, S.; Luciani, B.; Serraz, C.; Fournie, J.J.; Bonneville, M.; Tiollier, J.; Romagne, F. In vivo immunomanipulation of V gamma 9V delta 2 T cells with a synthetic phosphoantigen in a preclinical nonhuman primate model. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 5471–5480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zloza, A.; Dharmadhikari, N.D.; Huelsmann, E.J.; Broucek, J.R.; Hughes, T.; Kohlhapp, F.J.; Kaufman, H.L. Low-dose interleukin-2 impairs host anti-tumor immunity and inhibits therapeutic responses in a mouse model of melanoma. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2017, 66, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duault, C.; Franchini, D.M.; Familliades, J.; Cayrol, C.; Roga, S.; Girard, J.P.; Fournie, J.J.; Poupot, M. TCRVgamma9 gammadelta T Cell Response to IL-33: A CD4 T Cell-Dependent Mechanism. J. Immunol. 2016, 196, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Liu, S.B.; Han, P.; Hu, S.; Li, Q.; Wang, Z.F.; Mao-Ying, Q.L.; Chen, H.M.; Jiang, J.W.; et al. Spinal interleukin-33 and its receptor ST2 contribute to bone cancer-induced pain in mice. Neuroscience 2013, 253, 172–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Type of Cancer | Pro- or Anti-Tumorigenic Effect on Tumor | Model Used | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Breast | Pro-tumorigenic | Mouse models | [51,52,54,55,56,57] |
| Patient tissues | [56,57,58,59,60,61] | ||
| Colon | Pro-tumorigenic | Mouse model | [66,67,68,72,73,74] |
| Patient tissue and cell lines | [64,65,72,74] | ||
| Anti-tumorigenic | Mouse model and cell lines | [47,75] | |
| Gastric | Pro-tumorigenic | Mouse model | [78,79] |
| Hepatocellular | Pro-tumorigenic | Patient sera or plasma, resected patient tissues | [80,81,82,83] |
| Hepatobiliary | Pro-tumorigenic | Mouse model of CCA Patient tissues | [84] |
| Pancreatic | Pro-tumorigenic | Cell lines, tissues | [87,88] |
| Lung | Pro-tumorigenic | Patient samples and cell lines | [90,91,92,93,94] |
| Anti-tumorigenic | Patient studies | [95,96,97] | |
| Mouse models | [76,98,99] | ||
| Prostate & kidney | Pro-tumorigenic | Mouse Model | [100] |
| Anti-tumorigenic | Patient tissue | [99] | |
| Ovarian | Pro-tumorigenic | Patient tissues and human ovarian cell lines | [101] |
| Uterine | Pro-tumorigenic | Patient sera | [102,103] |
| Endometrial | Pro-tumorigenic | Patient sera and tissues | [104] |
| Cervical | Pro-tumorigenic | Patient tissue and in vitro studies | [105] |
| Head and Neck | Pro-tumorigenic | Organotypic culture and patient tissues | [106] |
| Brain | Pro-tumorigenic | Patient tissue | [107] |
| Rat model of glioma | [108] | ||
| Mouth | Pro-tumorigenic | Human tissues | [109,111] |
| Mouse model of salivary gland tumor | [110] | ||
| Anti-tumorigenic | Patient tissue immunohistochemistry | [112] | |
| Skin | Pro-tumorigenic | Mouse and human cell lines | [113] |
| Anti-tumorigenic | Mouse models and cell lines | [114] | |
| Squamous cell carcinoma | Pro-tumorigenic | Mouse cell lines and model Cell lines and patient tissues | [117,118] |
| Blood cancers | Pro-tumorigenic | Mouse model and patient biopsies | [119,120] |
| Cell lines | [121] | ||
| Patient plasma and tissues | [122,123,124] | ||
| Lymphoma | Pro-tumorigenic | Mouse model and patient tissue | [125,130] |
| Bone cancer pain | Pro-tumorigenic | Mouse model | [131] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Larsen, K.M.; Minaya, M.K.; Vaish, V.; Peña, M.M.O. The Role of IL-33/ST2 Pathway in Tumorigenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2676. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092676
Larsen KM, Minaya MK, Vaish V, Peña MMO. The Role of IL-33/ST2 Pathway in Tumorigenesis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(9):2676. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092676
Chicago/Turabian StyleLarsen, Kristen M., Maydelis Karla Minaya, Vivek Vaish, and Maria Marjorette O. Peña. 2018. "The Role of IL-33/ST2 Pathway in Tumorigenesis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 9: 2676. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092676
APA StyleLarsen, K. M., Minaya, M. K., Vaish, V., & Peña, M. M. O. (2018). The Role of IL-33/ST2 Pathway in Tumorigenesis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(9), 2676. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092676