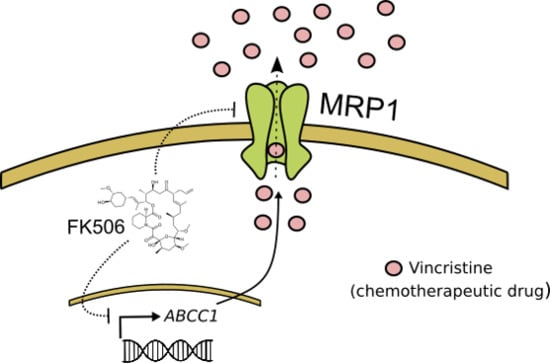
FK506 Attenuates the MRP1-Mediated Chemoresistant Phenotype in Glioblastoma Stem-Like Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
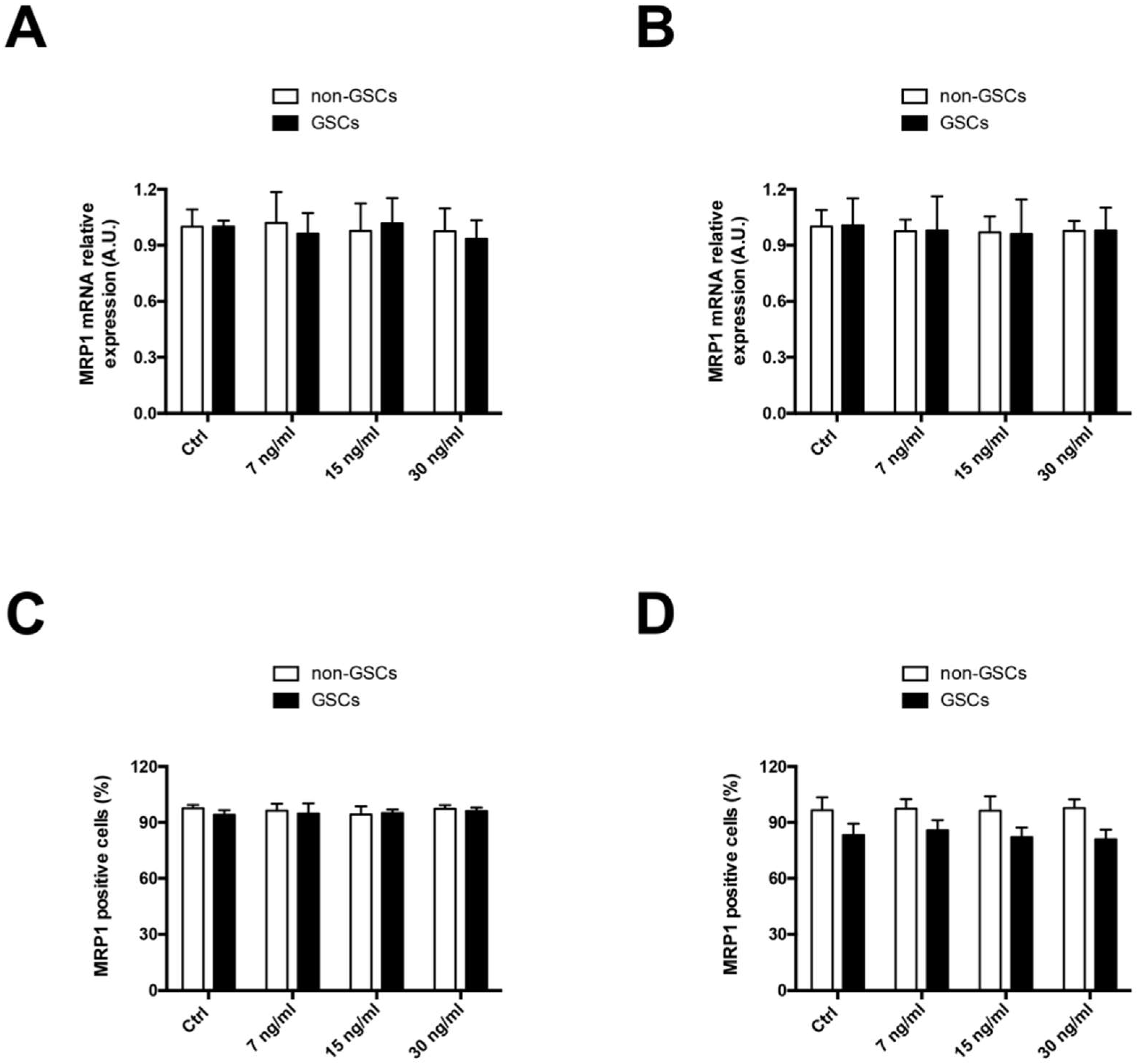
2.1. FK506 Decrease MRP1 Activity in Glioblastoma Stem-Like Cells
2.2. FK506 Promotes Apoptosis and MRP1-Dependent Chemo-Sensitization to Vincristine in GSCs
2.3. FK506 Promotes MRP1-Dependent Chemo-Sensitization In Vivo to Vincristine in GSC-Derived Tumors
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Culture
4.2. RT-qPCR
4.3. Immunocytofluorescence
4.4. Flow Cytometry
4.5. CFDA-Retention Assay
4.6. MTT Assay
4.7. Trypan Blue Staining Assay
4.8. Western Blot
4.9. Annexin-V/Propidium Iodide Assay
4.10. Generation of GSC-Derivative Subcutaneous Tumors
4.11. Immunohystochemistry
4.12. Graphs and Statistics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cloughesy, T.F.; Cavenee, W.K.; Mischel, P.S. Glioblastoma: From molecular pathology to targeted treatment. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2014, 9, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanif, F.; Muzaffar, K.; Perveen, K.; Malhi, S.M.; Simjee, S.U. Glioblastoma Multiforme: A Review of its Epidemiology and Pathogenesis through Clinical Presentation and Treatment. Asian. Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2017, 18, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Torres, A.; Vargas, Y.; Uribe, D.; Jaramillo, C.; Gleisner, A.; Salazar-Onfray, F.; López, M.N.; Melo, R.; Oyarzún, C.; San Martín, R.; et al. Adenosine A3 receptor elicits chemoresistance mediated by multiple resistance-associated protein-1 in human glioblastoma stem-like cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 67373–67386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Minniti, G.; Muni, R.; Lanzetta, G.; Marchetti, P.; Enrici, R.M. Chemotherapy for glioblastoma: Current treatment and future perspectives for cytotoxic and targeted agents. Anticancer Res. 2009, 29, 5171–5184. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Arévalo, Á.S.T.; Erices, J.I.; Uribe, D.A.; Howden, J.; Niechi, I.; Muñoz, S.; Martín, R.S.; Monrás, C.A.Q. Current Therapeutic Alternatives and New Perspectives in Glioblastoma Multiforme. Curr. Med. Chem. 2017, 24, 2781–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, M.E. Glioblastoma: Overview of Disease and Treatment. Clin. J. Oncol. Nurs. 2016, 20 (Suppl. 5), S2–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz, R.J.; Ali, S.; Qadir, M.G.; De La Fuente, M.I.; Ivan, M.E.; Komotar, R.J. The role of bevacizumab in the treatment of glioblastoma. J. Neurooncol. 2017, 133, 455–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wenger, K.J.; Wagner, M.; You, S.J.; Franz, K.; Harter, P.N.; Burger, M.C.; Voss, M.; Ronellenfitsch, M.W.; Fokas, E.; Steinbach, J.P.; Bähr, O. Bevacizumab as a last-line treatment for glioblastoma following failure of radiotherapy, temozolomide and lomustine. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 1141–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Ali, S.; Clarke, J.; Cha, S. Bevacizumab in Recurrent Glioma: Patterns of Treatment Failure and Implications. Brain. Tumor. Res. Treat. 2017, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, U.Y.; Huang, Y.C.; Yang, T.C.; Yang, S.T.; Liu, S.C.; Chang, T.M.; Kau, Y.C.; Liu, S.J. Concurrent Chemotherapy of Malignant Glioma in Rats by Using Multidrug-Loaded Biodegradable Nanofibrous Membranes. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 30630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tivnan, A.; Zakaria, Z.; O′Leary, C.; Kögel, D.; Pokorny, J.L.; Sarkaria, J.N.; Prehn, J.H. Inhibition of multidrug resistance protein 1 (MRP1) improves chemotherapy drug response in primary and recurrent glioblastoma multiforme. Front Neurosci. 2015, 16, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quezada, C.; Peigñan, L.; Segura, R.; Riquelme, F.; Melo, R.; Rojas, Z.D.; Ayach, F.; San Martín, R.; Cárcamo, J.G. Study of resistance to chemotherapy mediated by ABC transporters in biopsies of glioblastoma multiforme. Rev. Med. Chil. 2011, 139, 415–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkens, S. Structure and mechanism of ABC transporters. F1000Prime. Rep. 2015, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robey, R.W.; Pluchino, K.M.; Hall, M.D.; Fojo, A.T.; Bates, S.E.; Gottesman, M.M. Revisiting the role of ABC transporters in multidrug-resistant cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2018, 1, 452–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uribe, D.; Torres, Á.; Rocha, J.D.; Niechi, I.; Oyarzún, C.; Sobrevia, L.; San Martín, R.; Quezada, C. Multidrug resistance in glioblastoma stem-like cells: Role of the hypoxic microenvironment and adenosine signaling. Mol. Aspects Med. 2017, 55, 140–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auffinger, B.; Spencer, D.; Pytel, P.; Ahmed, A.U.; Lesniak, M.S. The role of glioma stem cells in chemotherapy resistance and glioblastoma multiforme recurrence. Expert. Rev. Neurother. 2015, 15, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yi, Y.; Hsieh, I.Y.; Huang, X.; Li, J.; Zhao, W. Glioblastoma Stem-Like Cells: Characteristics, Microenvironment, and Therapy. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Cheng, L.; Guryanova, O.A.; Wu, Q.; Bao, S. Cancer stem cells in glioblastoma--molecular signaling and therapeutic targeting. Protein Cell. 2010, 1, 638–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrido, W.; Muñoz, M.; San Martín, R.; Quezada, C. FK506 confers chemosensitivity to anticancer drugs in glioblastoma multiforme cells by decreasing the expression of the multiple resistance-associated protein-1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 411, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langemann, D.; Trochimiuk, M.; Appl, B.; Hundsdoerfer, P.; Reinshagen, K.; Eschenburg, G. Sensitization of neuroblastoma for vincristine-induced apoptosis by Smac mimetic LCL161 is attended by G2 cell cycle arrest but is independent of NFκB, RIP1 and TNF-α. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 87763–87772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, R.; Torres, Á.; Ojeda, K.; Uribe, D.; Rocha, D.; Erices, J.; Niechi, I.; Ehrenfeld, P.; San Martín, R.; Quezada, C. The Adenosine A₃ Receptor Regulates Differentiation of Glioblastoma Stem-Like Cells to Endothelial Cells under Hypoxia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scholzen, T.; Gerdes, J. The Ki-67 protein: From the known and the unknown. J. Cell. Physiol. 2000, 182, 311–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawahara, T.; Kashiwagi, E.; Ide, H.; Li, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Miyamoto, Y.; Netto, G.J.; Ishiguro, H.; Miyamoto, H. Cyclosporine A and tacrolimus inhibit bladder cancer growth through down-regulation of NFATc1. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 1582–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Naito, M.; Oh-hara, T.; Yamazaki, A.; Danki, T.; Tsuruo, T. Reversal of multidrug resistance by an immunosuppressive agent FK-506. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 1992, 29, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokogawa, K.; Takahashi, M.; Tamai, I.; Konishi, H.; Nomura, M.; Moritani, S.; Miyamoto, K.; Tsuji, A. P-glycoprotein-dependent disposition kinetics of tacrolimus: Studies in mdr1a knockout mice. Pharm. Res. 1999, 16, 1213–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pawarode, A.; Shukla, S.; Minderman, H.; Fricke, S.M.; Pinder, E.M.; O’Loughlin, K.L.; Ambudkar, S.V.; Baer, M.R. Differential effects of the immunosuppressive agents cyclosporin A, tacrolimus and sirolimus on drug transport by multidrug resistance proteins. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2007, 60, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hemenway, C.S.; Heitman, J. Immunosuppressant target protein FKBP12 is required for P-glycoprotein function in yeast. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 18527–18534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geisler, M.; Girin, M.; Brandt, S.; Vincenzetti, V.; Plaza, S.; Paris, N.; Kobae, Y.; Maeshima, M.; Billion, K.; Kolukisaoglu, U.H.; et al. Arabidopsis immunophilin-like TWD1 functionally interacts with vacuolar ABC transporters. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2004, 15, 3393–3405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, D.W.; Yang, X. Activation of procaspases by FK506 binding protein-mediated oligomerization. Sci. Signal. 2003, 28, pl1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydin, B.; Patil, M.; Bekele, N.; Wolff, J.E. Vincristine in high-grade glioma. Anticancer Res. 2010, 30, 2303–2310. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Park, K.J.; Yu, M.O.; Park, D.H.; Park, J.Y.; Chung, Y.G.; Kang, S.H. Role of vincristine in the inhibition of angiogenesis in glioblastoma. Neurol. Res. 2016, 38, 871–879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arceci, R.J.; Stieglitz, K.; Bierer, B.E. Immunosuppressants FK506 and rapamycin function as reversal agents of the multidrug resistance phenotype. Blood 1992, 80, 1528–1536. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nieth, C.; Lage, H. Induction of the ABC-transporters Mdr1/P-gp (Abcb1), mrpl (Abcc1), and bcrp (Abcg2) during establishment of multidrug resistance following exposure to mitoxantrone. J. Chemother. 2005, 17, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.W.; Cho, H.Y.; Na, G.; Yoo, M.R.; Seo, S.K.; Hur, D.Y.; Han, J.; Lee, C.K.; Choi, I. CD40 stimulation induces vincristine resistance via AKT activation and MRP1 expression in a human multiple myeloma cell line. Immunol. Lett. 2012, 144, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, W.J.; Lan, F.; He, Q.; Lee, A.; Tang, C.Z.; Dong, L.; Lan, B.; Ma, X.; Wu, J.C.; Shen, L. Inducible expression of stem cell associated intermediate filament nestin reveals an important role in glioblastoma carcinogenesis. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 128, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakimoto, H.; Mohapatra, G.; Kanai, R.; Curry, W.T., Jr.; Yip, S.; Nitta, M.; Patel, A.P.; Barnard, Z.R.; Stemmer-Rachamimov, A.O.; Louis, D.N.; et al. Maintenance of primary tumor phenotype and genotype in glioblastoma stem cells. Neuro Oncol. 2012, 14, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stylli, S.S.; Luwor, R.B.; Ware, T.M.; Tan, F.; Kaye, A.H. Mouse models of glioma. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2015, 22, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyle, F.M.; Eller, S.L.; Grossman, S.A. Penetration of intra-arterially administered vincristine in experimental brain tumor. Neuro Oncol. 2004, 6, 300–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Torres, Á.; Arriagada, V.; Erices, J.I.; Toro, M.D.l.Á.; Rocha, J.D.; Niechi, I.; Carrasco, C.; Oyarzún, C.; Quezada, C. FK506 Attenuates the MRP1-Mediated Chemoresistant Phenotype in Glioblastoma Stem-Like Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2697. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092697
Torres Á, Arriagada V, Erices JI, Toro MDlÁ, Rocha JD, Niechi I, Carrasco C, Oyarzún C, Quezada C. FK506 Attenuates the MRP1-Mediated Chemoresistant Phenotype in Glioblastoma Stem-Like Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(9):2697. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092697
Chicago/Turabian StyleTorres, Ángelo, Valentina Arriagada, José Ignacio Erices, María De los Ángeles Toro, José Dellis Rocha, Ignacio Niechi, Cristian Carrasco, Carlos Oyarzún, and Claudia Quezada. 2018. "FK506 Attenuates the MRP1-Mediated Chemoresistant Phenotype in Glioblastoma Stem-Like Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 9: 2697. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092697
APA StyleTorres, Á., Arriagada, V., Erices, J. I., Toro, M. D. l. Á., Rocha, J. D., Niechi, I., Carrasco, C., Oyarzún, C., & Quezada, C. (2018). FK506 Attenuates the MRP1-Mediated Chemoresistant Phenotype in Glioblastoma Stem-Like Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(9), 2697. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092697