Functional Variation of Two Novel Cellulases, Pv-eng-5 and Pv-eng-8, and the Heat Shock 90 Gene, Pv-hsp-90, in Pratylenchus vulnus and Their Expression in Response to Different Temperature Stress
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characterization of Pv-eng-5 and Pv-eng-8 Endoglucanases
2.2. Gene Structure
2.3. Pv-eng-8 Expression Profile
2.4. Tissue Localization of Pv-eng-8 mRNA in P. vulnus
2.5. Effects of Pv-eng-5 and Pv-eng-8 Silencing on P. vulnus Reproduction
2.6. Effect of Temperature on Reproduction and Motility of P. vulnus
2.7. Cloning and Sequencing of the Partial Pv-hsp-90 Gene in P. vulnus
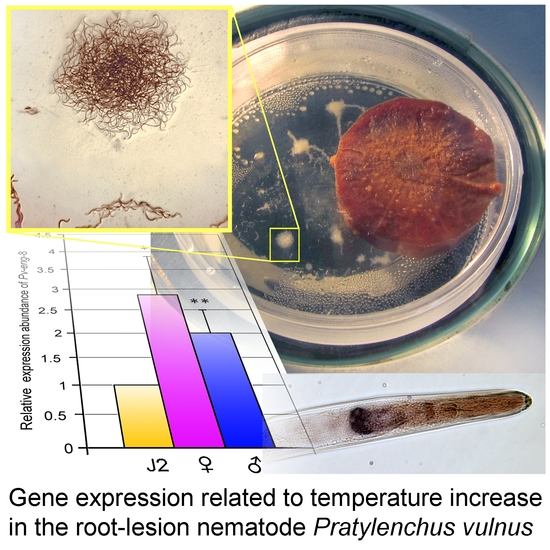
2.8. Expression Profiles of Pv-hsp-90, Pv-eng-1, and Pv-eng-8 under Non Stressed and Stressed Temperature Conditions
2.9. Analysis of Cellular Response to Temperature Stress
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Nematode Collection and Nematode Extraction
4.2. DNA and RNA Extraction
4.3. DNA Amplification and Cloning of Pv-eng-8, Pv-eng-5, and Pv-hsp-90
4.4. Rapid Amplification of cDNA ends (RACE)
4.5. Phylogenetic Analysis
4.6. Localization of Pv-eng-8 Transcript
4.7. Expression Level of Pv-eng-8
4.8. Pv-eng-8 and Pv-eng-5 Knock-Down by Using ds-RNA
4.9. Effect of Pv-eng-5 and Pv-eng-8 RNAi on Reproduction of the Nematodes
4.10. Effect of Temperature on Reproduction of P. vulnus
4.11. In Vitro Cellular Response to Different Temperatures
4.12. In Vivo Cellular Response to Different Temperatures
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Filipjev, I.N. On the classification of the Tylenchinae. Proc. Helminthol. Soc. Wash. 1936, 3, 80–82. [Google Scholar]
- Castillo, P.; Vovlas, N. Pratylenchus (Nematoda: Pratylenchidae): Diagnosis, Biology, Pathogenecity and Management; E. J. Brill: Leiden, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, J.T.; Haegeman, A.; Danchin, E.G.J.; Gaur, H.S.; Helder, J.; Jones, M.G.K.; Kikuchi, T.; Manzanilla-López, R.; Palomares-Rius, J.E.; Wesemael, W.M.L.; et al. Top 10 plant-parasitic nematodes in molecular plant pathology. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2013, 14, 946–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, M.G.K.; Fosu-Nyarko, J. Molecular biology of root lesion nematodes (Pratylenchus spp.) and their interaction with host plants. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2014, 164, 163–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zunke, U. Observation on the invasion and endoparasitic behaviour of the root lesion nematodes Pratylenchus penetrans. J. Nematol. 1990, 22, 309–322. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stoffelen, R.; Tam, V.T.T.; Swennen, R.L.; De Waele, D. Effect of time and inoculum density on the reproduction of Pratylenchus coffeae and Radopholus similis populations on carrot disks. Nematology 1999, 1, 243–250. [Google Scholar]
- De Meutter, J.; Tytgat, T.; Van der Schueren, E.; Smant, G.; Schots, A.; Coomans, A.; Van Montagu, M.; Gheysen, G. Cloning of two endoglucanase genes from Heterodera schachtii. In Mededelingen Faculteit Land Bouwwetenschappen Universiteit Gent; Rijksuniversiteit te Gent, Fakulteit van de Landbouwkundige en Toegepaste Biologische Wetenschappe: Ghent, Belgium, 1998; pp. 619–623. [Google Scholar]
- Fanelli, E.; Troccoli, A.; Picardi, E.; Pousis, C.; De Luca, F. Molecular characterization and functional analysis of four β-1,4-endoglucanases from the root-lesion nematode Pratylenchus vulnus. Plant Pathol. 2014, 63, 1436–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, B.; Allen, R.; Davis, E.L.; Baum, T.J.; Hussey, R.S. Developmental expression and biochemical properties and biochemical properties of a β-1,4-endoglucanase family in the soybean cyst nematodes, Heterodera glycines. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2004, 5, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goellner, M.; Smant, G.; De Boer, J.M.; Baum, T.J.; Davis, E.L. Isolation of beta-1,4-endoglucanase genes from Globodera tabacum and their expression during parasitism. J. Nematol. 2000, 32, 154–165. [Google Scholar]
- Kikuchi, T.; Cotton, J.A.; Dalzell, J.J.; Hasegawa, K.; Kanzaki, N.; McVeigh, P.; Takanashi, T.; Tsai, I.J.; Assefa, S.A.; Cock, P.J.A.; et al. Genomic insights into the original of parasitism in the emerging plant pathogen Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyndt, T.; Haegeman, A.; Gheysen, G. Evolution of GHF5 endoglucanase gene structure in plant parasitic nematodes: No evidence for an early domain shuffling event. BMC Evol. Biol. 2008, 8, 305–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosso, M.N.; Favery, B.; Piotte, C.; Arthaud, L.; de Boer, J.M.; Hussey, R.S.; Bakker, J.; Baum, T.J.; Abad, P. Isolation of a cDNA encoding a β-1,4-endoglucanase in the root-knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita and expression analysis during plant parasitism. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 1999, 12, 585–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uehara, T.; Kushida, A.; Momota, Y. PCR-based cloning of two β-1,4-endoglucanasesfrom the root-lesion nematode Pratylenchus penetrans. Nematology 2011, 3, 335–341. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.; Smant, G.; Davis, E. Functional screening yields a new β-1,4-endoglucanase gene from Heterodera glycines that may be the product of recent gene duplication. Mol. Plant-Microbe Interact. 2011, 14, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wubben, M.J.; Ganji, S.; Callahan, F.E. Identification and molecular characterization of a β-1,4-endoglucanase gene (Rr-eng-1) from Rotylenchulus reniformis. J. Nematol. 2010, 42, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vieira, P.; Maier, T.; Eves-van den Akker, S.; Verma, R.; Wantoch, S.; Eisenback, J.D.; Kamo, K. The Pratylenchus penetrans transcriptome as a source for the development of alternative control strategies: Mining of putative genes involved in parasitism and evaluation of in planta RNAi. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0144674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, P.; Maier, T.; Eves-van den Akker, S.; Howe, D.K.; Zasada, I.; Baum, T.; Eisenback, J.D.; Kamo, K. Identification of candidate effector genes of Pratylenchus penetrans. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abad, P.; Gouzy, J.; Aury, J.M.; Castagnone-Sereno, P.; Danchin, E.G.J.; Deleury, E.; Perfus- Barbeoch, L.; Anthouard, V.; Artiguenave, F.; Blok, V.C.; et al. Genome sequence of the metazoan plant-parasitic nematode Meloidogyne incognita. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 909–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ledger, T.N.; Jaubert, S.; Bosselut, N.; Abad, P.; Rosso, M.N. Characterization of a new β-1,4-endglucanase gene from the root-knot nematode Meloidogyne incognita and evolutionary scheme for phytonematode family 5 glycosyl hydrolases. Gene 2006, 382, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo, P.; Trapero-Casas, J.L.; Jiménez-Diaz, R.M. Effect of time, temperature, and inoculum density on reproduction of Pratylenchus thornei in carrot disk cultures. J. Nematol. 1995, 27, 120–124. [Google Scholar]
- Doucet, M.; Lax, P.; Di Rienzo, J.A.; Pinochet, J.; Baujard, P. Temperature-induced morphometrical variability in an isolate of Pratylenchus vulnus Allen & Jensen, 1951 (Nematoda: Tylenchida). Nematology 2011, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Kaczmarek, A.; MacKenzie, K.; Kettle, H.; Blok, V.C. Influence of soil temperature on Globodera rostochiensis and Globodera pallida. Phytopathol. Medit. 2014, 53, 396–405. [Google Scholar]
- Phillips, W.S.; Kieran, S.R.; Zasada, I.A. Relationship between temperature and development in Globodera ellingtonae. J. Nematol. 2015, 47, 283–289. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Thompson, J.P.; Clewett, T.G.; O’Reilly, M.M. Temperature response of root-lesion nematode (Pratylenchus thornei) reproduction on wheat cultivars has implications for resistance screening and wheat production. Ann. Appl. Biol. 2015, 167, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Towson, A.J.; Lear, B. Effect of temperature on reproduction and motility of Pratylenchus vulnus. J. Nematol. 1982, 14, 602–603. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Evangelista, C.C.S.; Vieira Guidelli, G.; Borges, G.; Araujo, T.F.; Campos Pereira, T. Multiple genes contribute to anhydrobiosis (tolerance to extreme desiccation) in the nematode Panagrolaimus superbus. Genet. Mol. Biol. 2017, 40, 790–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swanepoel, J.V.S.; Loots, G.C. The influence of temperature on anhydrobiosis of Pratylenchus zeae. Phytophylactica 1988, 20, 31–33. [Google Scholar]
- Vovlas, N.; Castillo, P.; Troccoli, A. Plant-parasitic nematodes of olive. In Olive Diseases and Disorders; Schena, L., Agosteo, G.E., Cacciola, S.O., Eds.; T.C. 37/661, Trivandrum-695 023; Transworld Research Network: Kerala, India, 2011; pp. 329–356. [Google Scholar]
- Inserra, R.; Zepp, A.; Vovlas, N. I Pratylenchus dell’Italia meridionale. Nematol. Medit. 1979, 7, 137–162. [Google Scholar]
- Generale, I.D. Decreti ministeriali relativi alle norme tecniche per la produzione di materiali di moltiplicazione di alcunespecie da frutto. 2007. Available online: http://www.gazzettaufficiale.it/eli/gu/2007/06/20/141/so/142/sg/pdf (accessed on 20 June 2007).
- Henrissat, B. A classification of glycosyl hydrolases based on amino acid sequence similarities. Biochem. J. 1991, 280, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blummenthal, T.; Steward, K. RNA processing and gene structure. In C. elegans II.; Riddle, D.L., Blummenthal, T., Meyer, B.J., Priess, J.R., Eds.; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: New York, NY, USA, 1997; pp. 117–145. [Google Scholar]
- Rybarczyk-Mydlowska, K.; Maboreke, H.R.; van Megen, H.; van den Elsen, S.; Mooyman, P.; Smant, G.; Bakker, J.; Helder, J. Rather than by direct acquisition via lateral gene transfer, GHF5 cellulases were passed on from early Pratylenchidae to root-knot and cyst nematodes. BMC Evol. Biol. 2012, 12, 221–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danchin, E.G.; Rosso, M.N.; Vieira, P.; de Almeida-Engler, J.; Coutinho, P.M.; Henrissat, B.; Abad, P. Multiple lateral gene transfers and duplications have promoted plant parasitism ability in nematodes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 17651–17656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danchin, E.G.; Perfus-Barbeoch, L.; Rancurel, C.; Thorpe, P.; Da Rocha, M.; Bajew, S.; Neilson, R.; Sokolova, E.; Da Silva, C.; Guy, J.; et al. The transcriptomes of Xiphinema index and Longidorus elongatus suggest independent acquisition of some plant parasitism genes by horizontal gene transfer in early-branching nematodes. Genes 2017, 8, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haegeman, A.; Jones, J.T.; Danchin, E.G.J. Horizontal gene transfer in nematodes: A catalyst for plant parasitism? Mol. Plant Microbe Interac. 2011, 24, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lilley, C.J.; Maqbool, A.; Wu, D.; Yusup, H.B.; Jones, L.M.; Birch, P.R.; Banfield, M.J.; Urwin, P.E.; Eves-van den Akker, S. Effector gene birth in plant parasitic nematodes: Neofunctionalization of a housekeeping glutathione synthetase gene. PLoS Genet. 2018, 14, e1007310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masonbrink, R.; Maier, T.R.; Muppirala, U.; Seetharam, A.S.; Lord, E.; Juvale, P.S.; Schmutz, J.; Johnson, N.T.; Korkin, D.; Mitchum, M.G.; et al. The genome of the soybean cyst nematode (Heterodera glycines) reveals complex patterns of duplications involved in the evolution of parasitism genes. bioRxiv 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paganini, J.; Campan-Fournier, A.; Da Rocha, M.; Gouret, P.; Pontarotti, P.; Wajnberg, E.; Abad, P.; Danchin, E.G.J. Contribution of lateral gene transfer to the genome composition and parasitic ability of root-knot nematodes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.L.; Kuo, T.H.; Tsay, T.T.; Tsay, I.J.; Chen, P.J. Glycoside Hydrolase (GH) 45 and 5 candidate cellulases in Aphelenchoidesbesseyi isolated from bird’s-nest fern. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, W.E.; Schuster, L.N.; Bartelmes, G.; Dieterich, C.; Sommer, R.J. Horizontal gene transfer of microbial cellulases into nematode genomes is associated with functional assimilation and gene turnover. BMC Evol. Biol. 2011, 11, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Várnai, A.; Siika-aho, M.; Viikari, L. Carbohydrate-binding modules (CBMs) revisited: Reduced amount of water counterbalances the need for CBMs. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2013, 6, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fosu-Nyarko, J.; Jones, M.G.K. Advances in understanding the molecular mechanisms of root lesion nematode host interactions. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2016, 54, 253–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danchin, E.G.; Guzeeva, E.A.; Mantelin, S.; Berepiki, A.; Jones, J.T. Horizontal gene transfer from bacteriahas enabled the plant-parasitic nematode Globodera pallida to feed on host-derived sucrose. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1571–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holterman, M.; Karegar, A.; Mooijman, P.; van Megen, H.; van den Elsen, E.; Vervoort, M.T.; Quist, C.W.; Karssen, G.; Decraemer, W.; Opperman, C.H. Disparate gain and loss of parasitic abilities among nematode lineages. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, Y.; Smant, G.; Stokkermans, J.; Qin, L.; Helder, J.; Baum, T.; Schots, A.; Davis, E. Genomic organization of four β-1,4-endoglucanase genes in plant-parasitic cyst nematodes and its evolutionary implications. Gene 1998, 220, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eves-van den Akker, S.; Laetsch, D.R.; Thorpe, P.; Lilley, C.J.; Danchin, E.G.J.; Da Rocha, M.; Rancurel, C.M.; Holroyd, N.E.; Cotton, J.A.; Szitenberg, A.; et al. The genome of the yellow potato cyst nematode, Globodera rostochiensis, reveals insights into the basis of parasitism and virulence. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farrer, T.; Roller, A.B.; Kent, W.J.; Zahler, A.M. Analysis of the role of Caenorhabditis elegans GC-AG introns in regulated splicing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2002, 30, 3360–3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Babenko, V.N.; Rogozin, I.B.; Mekhedov, S.L.; Koonin, E.V. Prevalence of intron gain over intron loss in the evolution of paralogous gene families. Nuc. Acids Res. 2004, 32, 3724–3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondrashov, F.A.; Rogozin, I.B.; Wolf, Y.I.; Koonin, E.V. Selection in the evolution of gene duplications. Genome Biol. 2002, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogozin, I.B.; Carmel, L.; Csuros, M.; Koonin, E.V. Origin and evolution of spliceosomal introns. Biol. Direct 2012, 7, 11–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodelsperger, C.; Streit, A.; Sommer, R.J. Structure, Function and Evolution of the Nematode Genome; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, L.N.; Sommer, R.J. Expressional and functional variation of horizontally acquired cellulases in the nematode Pristionchus pacificus. Gene 2012, 506, 274–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. Evolution of gene duplication: An update. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2003, 18, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haegeman, A.; Kyndt, T.; Gheysen, G. The role of pseudo-endoglucanases in the evolution of nematode cell wall-modifying proteins. J. Mol. Evol. 2010, 70, 441–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haegeman, A.; Mantelin, S.; Jones, J.T.; Gheysen, G. Functional roles of effectors of plant-parasitic nematodes. Gene 2012, 492, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.; Peng, D.; Long, H.; He, W.; Qiao, F.; Wang, G.; Huang, W. Characterisation and functional importance of B-1,4-engoglucanases from the potato rot nematode, Ditylenchus destructor. Nematology 2014, 16, 505–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haegeman, A.; Jacob, J.; Vanholme, B.; Kyndt, T.; Gheysen, G. A family of GHF5 endo-1,4-beta-glucanases in the migratory plant parasitic nematode Radopholus similis. Plant Pathol. 2008, 57, 581–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crook-McMahon, H.M.; Oláhová, M.; Button, E.L.; Winter, J.J.; Veal, E.A. Genome-wide screening identifies new genes required for stress-induced phase 2 detoxification gene expression in animals. BMC Biol. 2014, 12, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espada, M.; Silva, A.C.; Eves van den Akker, S.; Cock, P.J.A.; Mota, M.; Jones, J.T. Identification and characterization of parasitism genes from the pinewood nematode Bursaphelenchus xylophilus reveals a multilayered detoxification strategy. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2016, 17, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lourenço-Tessutti, I.T.; SouzaJunior, J.D.; Martins-de-Sa, D.; Viana, A.A.; Carneiro, R.M.; Togawa, R.C.; de Almeida-Engler, J.; Batista, J.A.; Silva, M.C.; Fragoso, R.R.; et al. Knock-down of heat-shock protein 90 and isocitrate lyase gene expression reduced root-knot nematode reproduction. Phytopathology 2015, 105, 628–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Rosa, B.A.; Jasmer, D.P.; Mitreva, M. Pan-Nematoda transcriptomic elucidation of essential intestinal functions and therapeutic targets with broad potential. EBioMedicine 2015, 2, 1079–1089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somashekar, N.; Prasad, J.S.; Ganguly, A.K. Impact of climate change on soil nematodes—Implications for sustainable agriculture. Indian J. Nematol. 2010, 40, 125–134. [Google Scholar]
- Freckman, D.W.; Caswell, E.P. The ecology of nematodes in the agroecosystems. Ann. Rev. Phytopathol. 1985, 23, 275–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Luca, F.; Di Vito, M.; Fanelli, E.; Reyes, A.; Greco, N.; De Giorgi, C. Characterization of the heat shock protein 90 gene in the plant parasitic nematode Meloidogyne artiellia and its expression as related to different developmental stages and temperature. Gene 2009, 440, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Vito, M.; Catalano, F.; Zaccheo, G.; Sadikiz, M.; Kharrat, M. Response of lines of faba bean to six populations of root lesion nematodes (Pratylenchus spp.) from the Mediterranean region. Nematol. Medit. 2002, 30, 107–109. [Google Scholar]
- Skantar, A.M.; Carta, L.K. Molecular characterization and phylogenetic evaluation of nucleotide and protein sequences from the heat shock protein 90 gene of selected nematodes. J. Nematol. 2004, 36, 466–480. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. A simple method to control over-alignment in the MAFFT multiple sequence alignment program. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 1933–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Tamura, K. MEGA7: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 7.0 for Bigger Datasets. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1870–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Boer, J.M.; Yan, Y.; Smant, G.; Davis, E.L.; Baum, T.J. In situ hybridization to messanger RNA in Heterodera glycines. J. Nematol. 1998, 30, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]









| Primer | Sequence 5′–3′ |
|---|---|
| ENG1 | TA(T/C)GTIAT(T/C/A)GTIGA(T/C)TGGCA |
| ENG2 | GTICC(A/G)TA(T/C)TCIGTIAC(A/G)AA |
| U831 | AAYAARACMAAGCCNTYTGGAC |
| L1110 | TCRCARTTVTCCATGATRAAVAC |
| Pv-5DB_for2 | AGTCGAGCGGCGATGGCAC |
| Pv-5DB_for3 | GGCACTGTCGACACTTCGG |
| Pv-eng-8_REV3 | CTTGGTGCGAAGATCGGCC |
| Pv-eng-8-RACE5′1 | CTGCGCAATTGCCGCATTC |
| Pv-eng-8-RACE 5′2 | CGCTTGGATTGCTCAAATAGC |
| Pv-eng-8_FOR1 | GAACAATCTTCGAAGGACT |
| Pv-eng-8_REV1 | ACCCCCTCCCATTGTCTAGCC |
| Pv-eng-8_FOR2 | GGCTAGACAATGGGAGGGGGT |
| Pv-eng-8_REV0 | GGTCGAATTTATGAGTTAGCGG |
| T7eng5dsfor1 | TAATACGACTCACTATAGGGCATCACTAGCTCGTGGAAT |
| eng5dsrev | CAGTATGATGTTCAGGAGCA |
| eng5dsfor1 | CATCACTAGCTCGTGGAAT |
| T7eng5dsrev | TAATACGACTCACTATAGGGCAGTATGATGTTCAGGAGCA |
| T7eng8_FOR2 | TAATACGACTCACTATAGGGGGCTAGACAATGGGAGGGGT |
| T7eng8_REV0 | TAATACGACTCACTATAGGG GGTCGAATTTATGAGTTAGCGG |
| GFPFOR | CACATGAAGCAGCACGACT |
| GFPREV | GATATAGACGTTGTGGCTGT |
| Pv-hsp-FOR | GGACGCGTAATCCGGATGA |
| Pv-hsp-REV | ACGGAGCGCGTTGGGGAAC |
| LRTfor2 | TCTGCGTCCGCATCGATTAC |
| LRTREV | TGGCTAATCAGCATGCAGTG |
| UPM | CTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGCAAGCAGTGGTATCAACGCAGAGT |
| UPS | CTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGC |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fanelli, E.; Troccoli, A.; De Luca, F. Functional Variation of Two Novel Cellulases, Pv-eng-5 and Pv-eng-8, and the Heat Shock 90 Gene, Pv-hsp-90, in Pratylenchus vulnus and Their Expression in Response to Different Temperature Stress. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20010107
Fanelli E, Troccoli A, De Luca F. Functional Variation of Two Novel Cellulases, Pv-eng-5 and Pv-eng-8, and the Heat Shock 90 Gene, Pv-hsp-90, in Pratylenchus vulnus and Their Expression in Response to Different Temperature Stress. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(1):107. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20010107
Chicago/Turabian StyleFanelli, Elena, Alberto Troccoli, and Francesca De Luca. 2019. "Functional Variation of Two Novel Cellulases, Pv-eng-5 and Pv-eng-8, and the Heat Shock 90 Gene, Pv-hsp-90, in Pratylenchus vulnus and Their Expression in Response to Different Temperature Stress" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 1: 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20010107
APA StyleFanelli, E., Troccoli, A., & De Luca, F. (2019). Functional Variation of Two Novel Cellulases, Pv-eng-5 and Pv-eng-8, and the Heat Shock 90 Gene, Pv-hsp-90, in Pratylenchus vulnus and Their Expression in Response to Different Temperature Stress. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(1), 107. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20010107