Novel Diamide-Based Benzenesulfonamides as Selective Carbonic Anhydrase IX Inhibitors Endowed with Antitumor Activity: Synthesis, Biological Evaluation and In Silico Insights
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
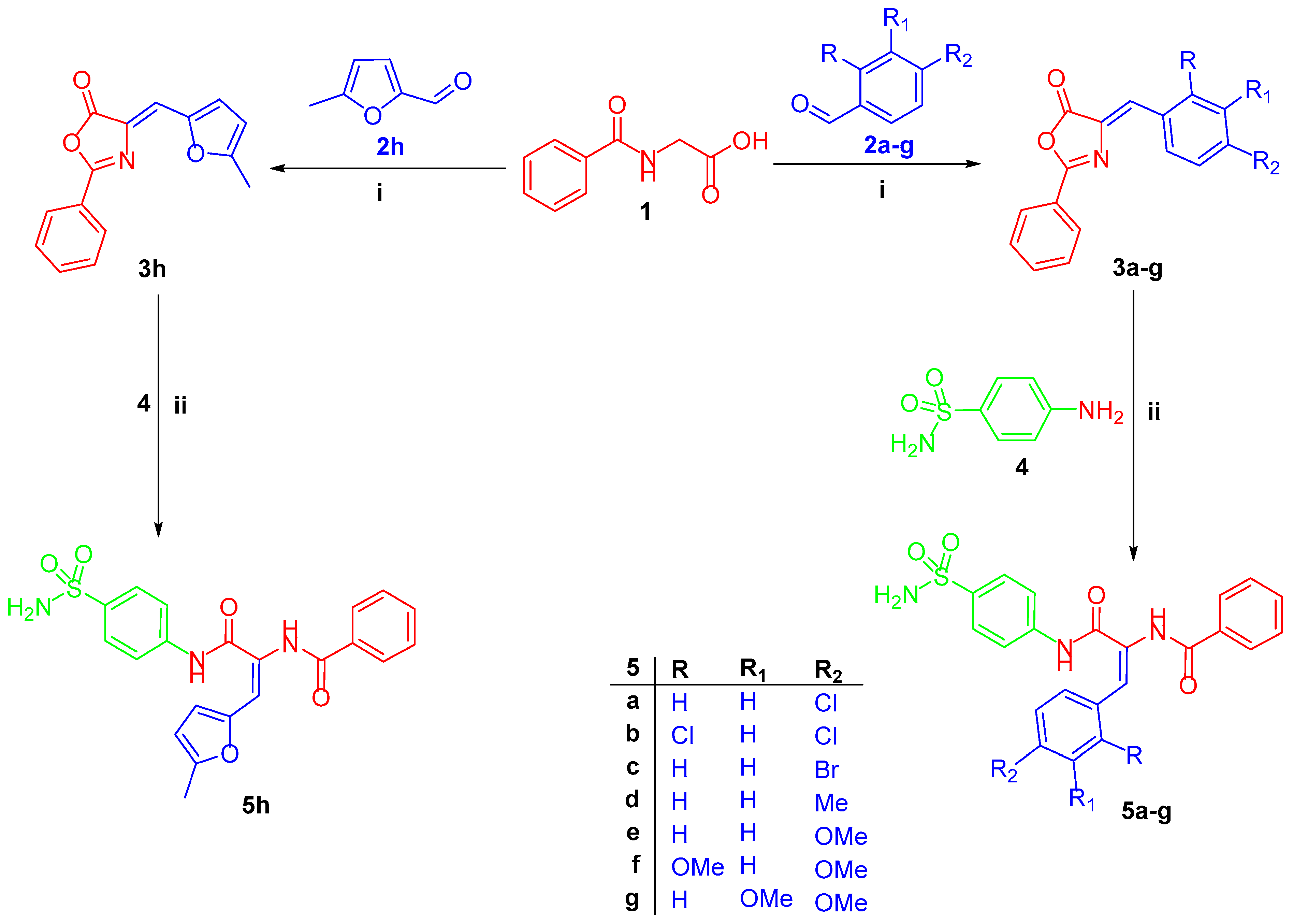
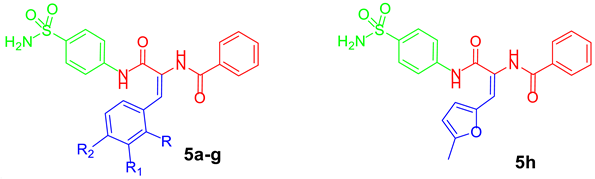
2.1. Chemistry
2.2. Biological Evaluation
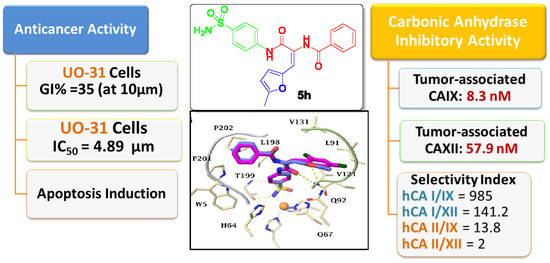
2.2.1. Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibition
2.2.2. Antitumor Activity
Antitumor Activity towards 60 Cancer Cell Lines (NCI, USA)
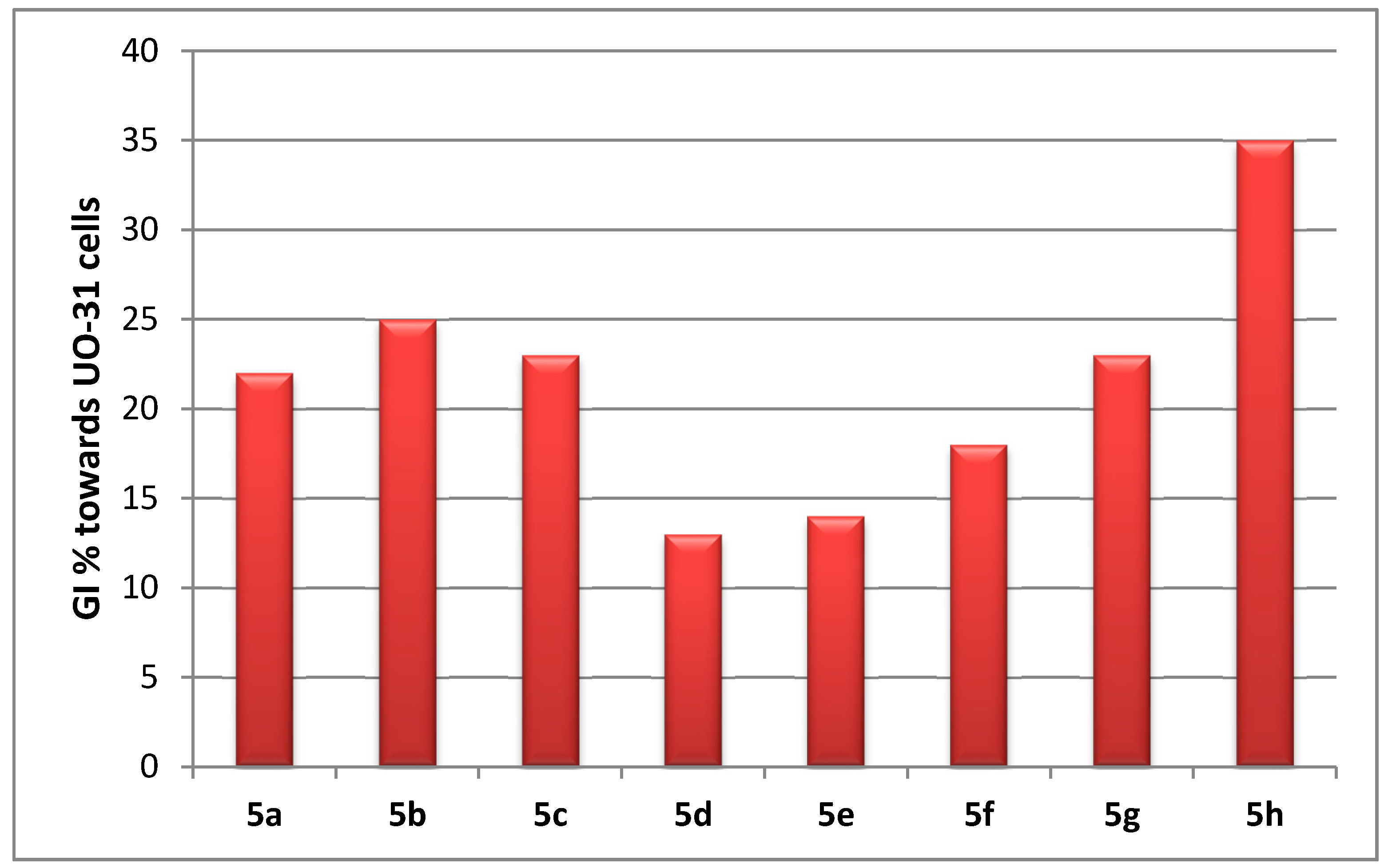
Anti-Proliferative Activity towards Renal Cancer UO-31 Cell Line
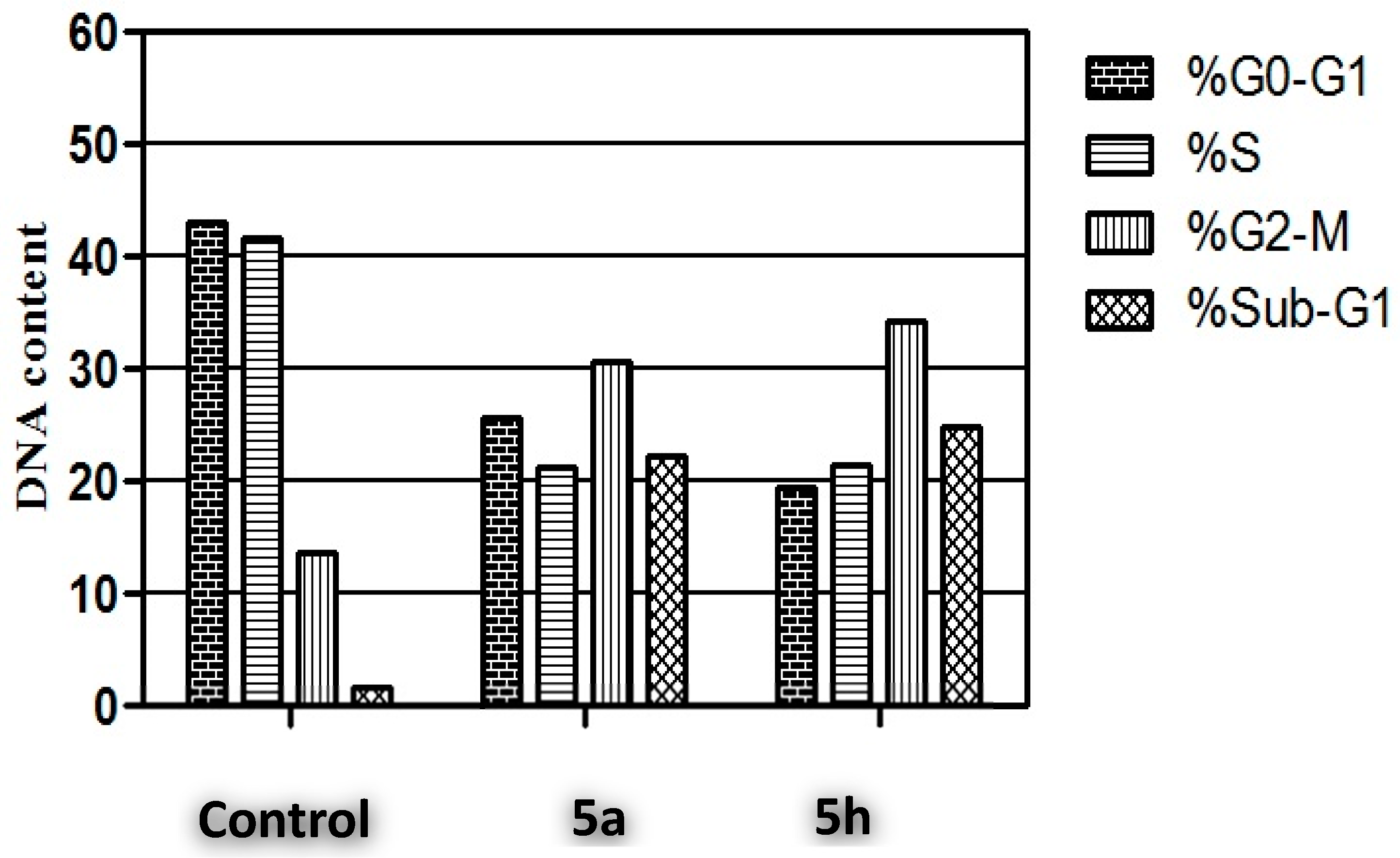
Cell Cycle Analysis
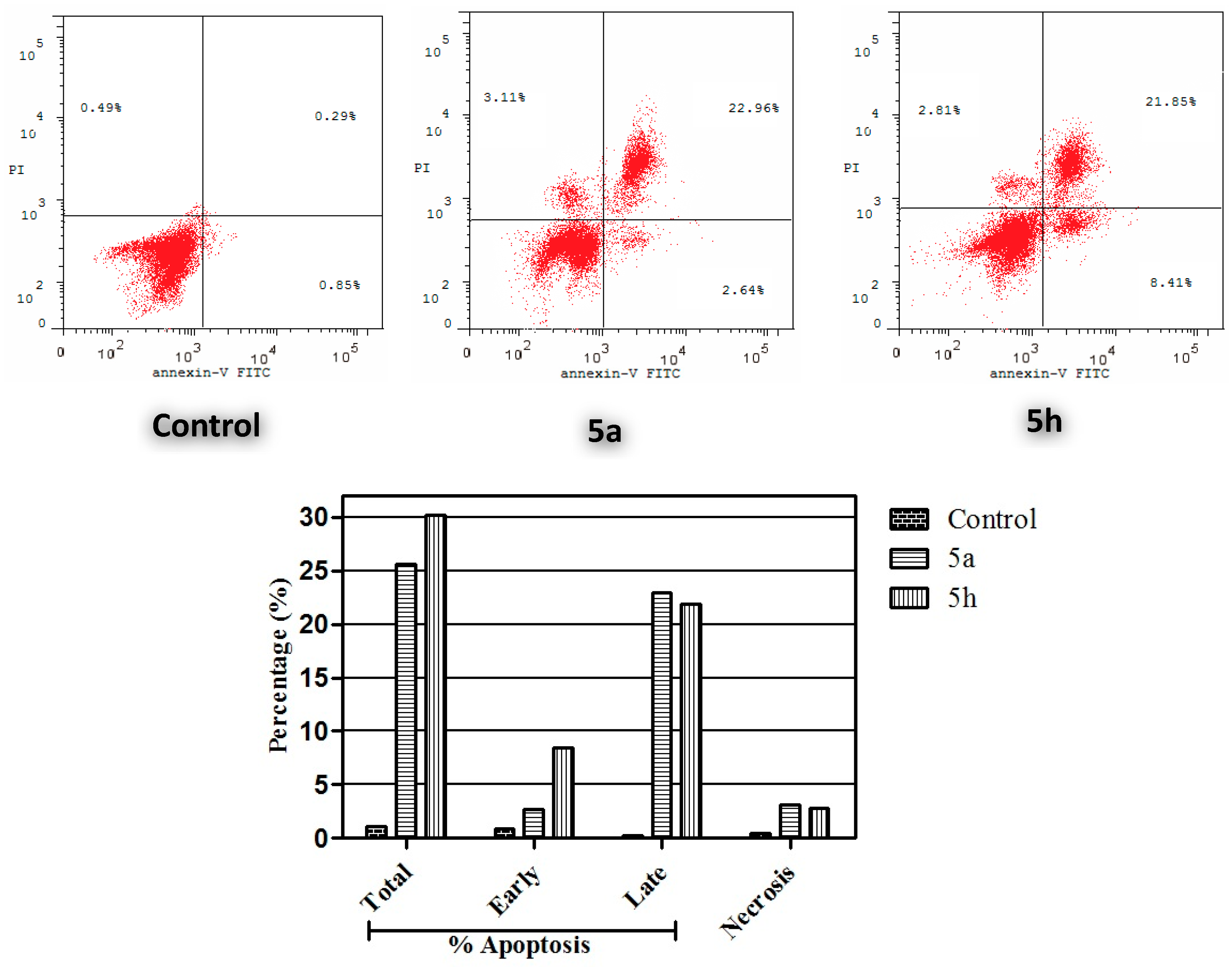
Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Assay
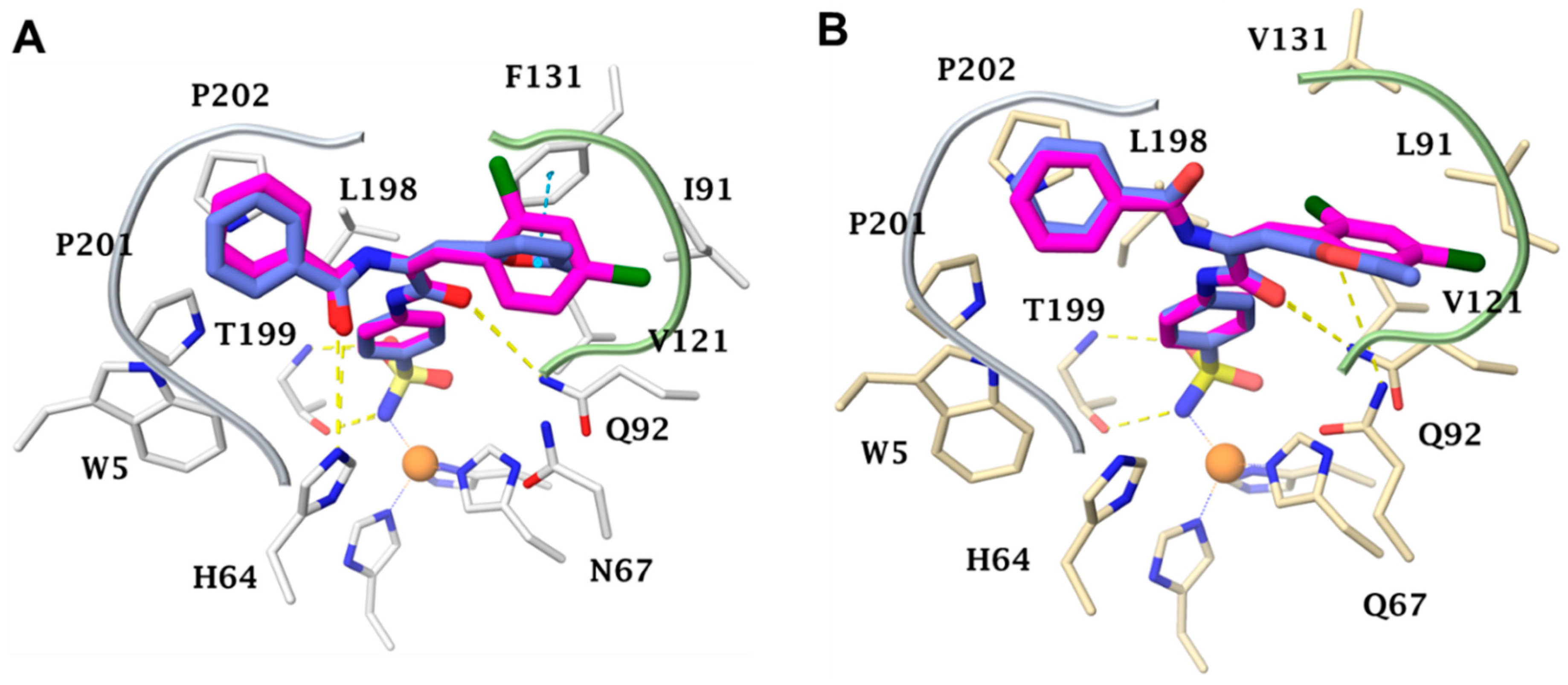
2.3. Molecular Modelling Study
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemistry
3.1.1. General
3.1.2. General Procedure for Preparation of Target Diamide-Based Benzenesulfonamides 5a–h
N-(1-(4-Chlorophenyl)-3-oxo-3-((4-sulfamoylphenyl)amino)prop-1-en-2-yl)benzamide (5a)
N-(1-(2,4-Dichlorophenyl)-3-oxo-3-((4-sulfamoylphenyl)amino)prop-1-en-2-yl)benzamide (5b)
N-(1-(4-Bromophenyl)-3-oxo-3-((4-sulfamoylphenyl)amino)prop-1-en-2-yl)benzamide (5c)
N-(3-Oxo-3-((4-sulfamoylphenyl)amino)-1-(p-tolyl)prop-1-en-2-yl)benzamide (5d)
N-(1-(4-Methoxyphenyl)-3-oxo-3-((4-sulfamoylphenyl)amino)prop-1-en-2-yl)benzamide (5e)
N-(1-(2,4-Dimethoxyphenyl)-3-oxo-3-((4-sulfamoylphenyl)amino)prop-1-en-2-yl)benzamide (5f)
N-(1-(3,4-Dimethoxyphenyl)-3-oxo-3-((4-sulfamoylphenyl)amino)prop-1-en-2-yl)benzamide (5g)
N-(1-(5-Methylfuran-2-yl)-3-oxo-3-((4-sulfamoylphenyl)amino)prop-1-en-2-yl)benzamide (5h)
3.2. Biological Evaluation
3.2.1. CA Inhibitory Assay
3.2.2. Anticancer Activity towards 60 Cancer Cell Lines (NCI, Bethesda, MD, USA)
3.2.3. Antiproliferative Activity towards Renal Cancer UO-31 Cell Line
3.2.4. Cell Cycle Analysis
3.2.5. Annexin V-FITC Apoptosis Assay
3.2.6. Molecular Docking Simulations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alterio, V.; Di Fiore, A.; D’Ambrosio, K.; Supuran, C.T.; De Simone, G. Multiple Binding Modes of Inhibitors to Carbonic Anhydrases: How to Design Specific Drugs Targeting 15 Different Isoforms? Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 4421–4468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozensoy Guler, O.; Capasso, C.; Supuran, C.T. A magnificent enzyme superfamily: Carbonic anhydrases, their purification and characterization. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2016, 31, 689–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vullo, D.; Durante, M.; Di Leva, F.S.; Cosconati, S.; Masini, E.; Scozzafava, A.; Novellino, E.; Supuran, C.T.; Carta, F. Monothiocarbamates Strongly Inhibit Carbonic Anhydrases in Vitro and Possess Intraocular Pressure Lowering Activity in an Animal Model of Glaucoma. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 5857–5867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Supuran, C.T. Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibition and the Management of Hypoxic Tumors. Metabolites 2017, 7, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gieling, R.G.; Babur, M.; Mamnani, L.; Burrows, N.; Telfer, B.A.; Carta, F.; Winum, J.-Y.; Scozzafava, A.; Supuran, C.T.; Williams, K.J. Antimetastatic Effect of Sulfamate Carbonic Anhydrase IX Inhibitors in Breast Carcinoma Xenografts. J. Med. Chem. 2012, 55, 5591–5600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacchiano, F.; Carta, F.; McDonald, P.C.; Lou, Y.; Vullo, D.; Scozzafava, A.; Dedhar, S.; Supuran, C.T. Ureido-Substituted Benzenesulfonamides Potently Inhibit Carbonic Anhydrase IX and Show Antimetastatic Activity in a Model of Breast Cancer Metastasis. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 54, 1896–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo-Ashour, M.F.; Eldehna, W.M.; Nocentini, A.; Ibrahim, H.S.; Bua, S.; Abdel-Aziz, H.A.; Abou-Seri, S.M.; Supuran, C.T. Novel synthesized SLC-0111 thiazole and thiadiazole analogues: Determination of their carbonic anhydrase inhibitory activity and molecular modeling studies. Bioorg. Chem. 2019, 87, 794–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldehna, W.M.; Abo-Ashour, M.F.; Berrino, E.; Vullo, D.; Ghabbour, H.A.; Al-Rashood, S.T.; Hassan, G.S.; Alkahtani, H.M.; Almehizia, A.A.; Alharbi, A.; et al. SLC-0111 enaminone analogs, 3/4-(3-aryl-3-oxopropenyl) aminobenzenesulfonamides, as novel selective subnanomolar inhibitors of the tumor-associated carbonic anhydrase isoform IX. Bioorganic Chem. 2019, 83, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, H.S.; Allam, H.A.; Mahmoud, W.R.; Bonardi, A.; Nocentini, A.; Gratteri, P.; Ibrahim, E.S.; Abdel-Aziz, H.A.; Supuran, C.T. Dual-tail arylsulfone-based benzenesulfonamides differently match the hydrophobic and hydrophilic halves of human carbonic anhydrases active sites: Selective inhibitors for the tumor-associated hCA IX isoform. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 152, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldehna, W.M.; Fares, M.; Ceruso, M.; Ghabbour, H.A.; Abou-Seri, S.M.; Abdel-Aziz, H.A.; El Ella, D.A.A.; Supuran, C.T. Amido/ureidosubstituted benzenesulfonamides-isatin conjugates as low nanomolar/subnanomolar inhibitors of the tumor-associated carbonic anhydrase isoform XII. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 110, 259–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldehna, W.M.; Abo-Ashour, M.F.; Nocentini, A.; El-Haggar, R.S.; Bua, S.; Bonardi, A.; Al-Rashood, S.T.; Hassan, G.S.; Gratteri, P.; Abdel-Aziz, H.A.; et al. Enhancement of the tail hydrophobic interactions within the carbonic anhydrase IX active site via structural extension: Design and synthesis of novel N-substituted isatins-SLC-0111 hybrids as carbonic anhydrase inhibitors and antitumor agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 162, 147–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eldehna, W.M.; Nocentini, A.; Al-Rashood, S.T.; Hassan, G.S.; Alkahtani, H.M.; Almehizia, A.A.; Reda, A.M.; Abdel-Aziz, H.A.; Supuran, C.T. Tumor-associated carbonic anhydrase isoform IX and XII inhibitory properties of certain isatin-bearing sulfonamides endowed with in vitro anticancer activity towards colon cancer, Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2018, 81, 425–432. [Google Scholar]
- Eldehna, W.M.; Abo-Ashour, M.F.; Nocentini, A.; Gratteri, P.; Eissa, I.H.; Fares, M.; Ismael, O.E.; Ghabbour, H.A.; Elaasser, M.M.; Abdel-Aziz, H.A.; et al. Novel 4/3-((4-oxo-5-(2-oxoindolin-3-ylidene)thiazolidin-2-ylidene)amino) benzenesulfonamides: Synthesis, carbonic anhydrase inhibitory activity, anticancer activity and molecular modelling studies. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 139, 250–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jun, E.E. Ueber die Condensation der Hippursäure mit Phtalsäureanhydrid und mit Benzaldehyd. Justus Liebigs Ann. Chem. 1893, 275, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acheson, R.M.; Booth, D.A.; Brettle, R.; Harris, A.M. 694. The synthesis of some acylglycines and related oxazolones. J. Chem. Soc. 1960, 3457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cleary, T.; Rawalpally, T.; Kennedy, N.; Chavez, F. Catalyzing the Erlenmeyer Plöchl reaction: Organic bases versus sodium acetate. Tetrahedron Lett. 2010, 51, 1533–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalifah, R.G. The carbon dioxide hydration activity of carbonic anhydrase. I. Stop-flow kinetic studies on the native human isoenzymes B and C. J. Boil. Chem. 1971, 246, 2561–2573. [Google Scholar]
- Skehan, P.; Scudiero, D.; Vistica, D.; Bokesch, H.; Kenney, S.; Storeng, R.; Monks, A.; McMahon, J.; Warren, J.T.; Boyd, M.R. New Colorimetric Cytotoxicity Assay for Anticancer-Drug Screening. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1990, 82, 1107–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldehna, W.M.; El Kerdawy, A.M.; Al-Ansary, G.H.; Al-Rashood, S.T.; Ali, M.M.; Mahmoud, A.E. Type IIA-Type IIB protein tyrosine kinase inhibitors hybridization as an efficient approach for potent multikinase inhibitor development: Design, synthesis, anti-proliferative activity, multikinase inhibitory activity and molecular modeling of novel indolinone-based ureides and amides. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 163, 37–53. [Google Scholar]
- Eldehna, W.M.; Fares, M.; Ibrahim, H.S.; Alsherbiny, M.A.; Aly, M.H.; Ghabbour, H.A.; Abdel-Aziz, H.A.; Eynde, J.J.V.; Mayence, A. Synthesis and Cytotoxic Activity of Biphenylurea Derivatives Containing Indolin-2-one Moieties. Molecules 2016, 21, 762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T. Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: Application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J. Immunol. Methods 1983, 65, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocentini, A.; Ferraroni, M.; Carta, F.; Ceruso, M.; Gratteri, P.; Lanzi, C.; Masini, E.; Supuran, C.T. Benzenesulfonamides Incorporating Flexible Triazole Moieties Are Highly Effective Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors: Synthesis and Kinetic, Crystallographic, Computational, and Intraocular Pressure Lowering Investigations. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 10692–10704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitans, J.; Kazaks, A.; Balode, A.; Ivanova, J.; Zalubovskis, R.; Supuran, C.T.; Tars, K. Efficient Expression and Crystallization System of Cancer-Associated Carbonic Anhydrase Isoform IX. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 9004–9009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parveen, M.; Ali, A.; Ahmed, S.; Malla, A.M.; Alam, M.; Pereira Silva, P.S.; Silva, M.R.; Lee, D.U. Synthesis, bioassay, crystal structure and ab initio studies of Erlenmeyer azlactones, Spectrochim. Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2013, 104, 538–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, P.A.; Devine, K.; Paradisi, F. A simple and efficient method for the synthesis of Erlenmeyer azlactones. Tetrahedron 2009, 65, 2935–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alafeefy, A.M.; Ahmad, R.; Abdulla, M.; Eldehna, W.M.; Al-Tamimi, A.M.S.; Abdel-Aziz, H.A.; Al-Obaid, O.; Carta, F.; Al-Kahtani, A.A.; Supuran, C.T. Development of certain new 2-substituted-quinazolin-4-yl-aminobenzenesulfonamide as potential antitumor agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 109, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fares, M.; Eladwy, R.A.; Nocentini, A.; El Hadi, S.R.A.; Ghabbour, H.A.; Abdel-Megeed, A.; Eldehna, W.M.; Abdel-Aziz, H.A.; Supuran, C.T. Synthesis of bulky-tailed sulfonamides incorporating pyrido [2, 3-d][1,2,4] triazolo [4, 3-a] pyrimidin-1 (5H)-yl) moieties and evaluation of their carbonic anhydrases I, II, IV and IX inhibitory effects. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2017, 25, 2210–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abo-Ashour, M.F.; Eldehna, W.M.; Nocentini, A.; Ibrahim, H.S.; Bua, S.; Abou-Seri, S.M.; Supuran, C.T. Novel hydrazido benzenesulfonamides-isatin conjugates: Synthesis, carbonic anhydrase inhibitory activity and molecular modeling studies. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 157, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melis, C.; Meleddu, R.; Angeli, A.; Distinto, S.; Bianco, G.; Capasso, C.; Cottiglia, F.; Angius, R.; Supuran, C.T.; Maccioni, E. Isatin: A privileged scaffold for the design of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2017, 32, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monks, A.; Scudiero, D.; Skehan, P.; Shoemaker, R.; Paull, K.; Vistica, D.; Hose, C.; Langley, J.; Cronise, P.; Vaigro-Wolff, A.; et al. Feasibility of a High-Flux Anticancer Drug Screen Using a Diverse Panel of Cultured Human Tumor Cell Lines. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1991, 83, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beverly, A.T. Cancer Drug Discovery and Development. In Anticancer Drug Development Guide: Preclinical Screening, Clinical Trials and Approval, 2nd ed.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, USA, 2014; pp. 41–62, (Chapter 1). [Google Scholar]
- Boyd, M.R.; Paull, K.D. Some practical considerations and applications of the National Cancer Institute in vitro anticancer drug discovery screen. Drug Dev. Res. 1995, 34, 91–109. [Google Scholar]
- Eldehna, W.M.; Hassan, G.S.; Al-Rashood, S.T.; Al-Warhi, T.; Altyar, A.E.; Alkahtani, H.M.; Almehizia, A.A.; Abdel-Aziz, H.A. Synthesis and in vitro anticancer activity of certain novel 1-(2-methyl-6-arylpyridin-3-yl)-3-phenylureas as apoptosis-inducing agents. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2019, 34, 322–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abo-Ashour, M.F.; Eldehna, W.M.; George, R.F.; Abdel-Aziz, M.M.; Elaasser, M.M.; Gawad, N.M.A.; Gupta, A.; Bhakta, S.; Abou-Seri, S.M. Novel indole-thiazolidinone conjugates: Design, synthesis and whole-cell phenotypic evaluation as a novel class of antimicrobial agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 160, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almahli, H.; Hadchity, E.; Jaballah, M.Y.; Daher, R.; Ghabbour, H.A.; Kabil, M.M.; Al-Shakliah, N.S.; Eldehna, W.M. Development of novel synthesized phthalazinone-based PARP-1 inhibitors with apoptosis inducing mechanism in lung cancer. Bioorg. Chem. 2018, 77, 443–456. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, R.S.; Abou-Seri, S.M.; Eldehna, W.M.; Ismail, N.S.; Elgazwi, S.M.; Ghabbour, H.A.; Ahmed, M.S.; Halaweish, F.T.; El Ella, D.A.A. Novel series of 6-(2-substitutedacetamido)-4-anilinoquinazolines as EGFR-ERK signal transduction inhibitors in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 155, 782–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabt, A.; Abdelhafez, O.M.; El-Haggar, R.S.; Madkour, H.M.F.; Eldehna, W.M.; El-Khrisy, E.E.-D.A.M.; Abdel-Rahman, M.A.; Rashed, L.A. Novel coumarin-6-sulfonamides as apoptotic anti-proliferative agents: Synthesis, in vitro biological evaluation, and QSAR studies. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2018, 33, 1095–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eldehna, W.M.; El-Naggar, D.H.; Hamed, A.R.; Ibrahim, H.S.; Ghabbour, H.A.; Abdel-Aziz, H.A.; Ghabbour, H.A. Abdel-Aziz One-pot three-component synthesis of novel spirooxindoles with potential cytotoxic activity against triple-negative breast cancer MDAMB-231 cells. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2018, 33, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldehna, W.M.; Almahli, H.; Al-Ansary, G.H.; Ghabbour, H.A.; Aly, M.H.; Ismael, O.E.; Al-Dhfyan, A.; Abdel-Aziz, H.A. Synthesis and in vitro anti-proliferative activity of some novel isatins conjugated with quinazoline/phthalazine hydrazines against triple-negative breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells as apoptosis-inducing agents. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2017, 32, 600–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldehna, W.M.; Abo-Ashour, M.F.; Ibrahim, H.S.; Al-Ansary, G.H.; Ghabbour, H.A.; Elaasser, M.M.; Ahmed, H.Y.A.; Safwat, N.A. Novel [(3-indolylmethylene)hydrazono]indolin-2-ones as apoptotic anti-proliferative agents: Design, synthesis and in vitro biological evaluation. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2018, 33, 686–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrödinger Suite Release 2018-2: (a) Maestrov.11.6; (b) Epik, v.4.4; (c) Impact, v.7.9; (d) Prime, v.5.2; (e) Macromodel v.12.0. (f) Glide, v.7.9; Schrödinger, L.L.C.: New York, NY, USA, 2018.
- Nocentini, A.; Carta, F.; Tanc, M.; Selleri, S.; Supuran, C.T.; Bazzicalupi, C.; Gratteri, P. Deciphering the Mechanism of Human Carbonic Anhydrases Inhibition with Sulfocoumarins: Computational and Experimental Studies. Chemistry 2018, 24, 7840–7844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocentini, A.; Gratteri, P.; Supuran, C.T. Phosphorus versus Sulfur: Discovery of Benzenephosphonamidates as Versatile Sulfonamide-Mimic Chemotypes Acting as Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors. Chemistry 2019, 25, 1188–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocentini, A.; Bonardi, A.; Gratteri, P.; Cerra, B.; Gioiello, A.; Supuran, C.T. Steroids interfere with human carbonic anhydrase activity by using alternative binding mechanisms. J. Enzym. Inhib. Med. Chem. 2018, 33, 1453–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Comp. | R | R1 | R2 | KI (nM)* | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| hCA I | hCA II | hCA IX | hCA XII | ||||
| 5a | H | H | Cl | 3955.7 | 68.3 | 8.8 | 16.1 |
| 5b | Cl | H | Cl | 5977.6 | 223.9 | 18.3 | 10.5 |
| 5c | H | H | Br | 2397.8 | 251.9 | 33.5 | 55.4 |
| 5d | H | H | CH3 | 796.1 | 94.4 | 62.1 | 60.2 |
| 5e | H | H | OCH3 | 1006.4 | 127.7 | 78.0 | 42.8 |
| 5f | OCH3 | H | OCH3 | 5132.7 | 294.2 | 73.7 | 134.5 |
| 5g | H | OCH3 | OCH3 | 2207.7 | 448.0 | 123.3 | 9.8 |
| 5h | - | - | - | 8175.4 | 114.8 | 8.3 | 57.9 |
| AAZ | - | - | - | 250.0 | 12.0 | 25.0 | 5.7 |
 | |||||||
| Cmpd | I/IX | II/IX | I/XII | II/XII |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5a | 449.5 | 7.8 | 245.7 | 4.2 |
| 5b | 326.6 | 12.2 | 569.2 | 21.3 |
| 5c | 71.6 | 7.5 | 43.3 | 4.5 |
| 5d | 12.8 | 1.5 | 13.2 | 1.7 |
| 5e | 12.9 | 1.4 | 23.5 | 3 |
| 5f | 69.9 | 4 | 38.2 | 2.2 |
| 5g | 17.9 | 3.6 | 225.3 | 45.7 |
| 5h | 985 | 13.8 | 141.2 | 2 |
| AAZ | 10.0 | 0.5 | 43.9 | 2.2 |
| Compound | IC50 (μM) a |
|---|---|
| UO-31 | |
| 5a | 6.53 ± 0.38 |
| 5b | 16.68 ± 0.92 |
| 5h | 4.89 ± 0.22 |
| Staurosporine | 7.25 ± 0.43 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abdelrahman, M.A.; Eldehna, W.M.; Nocentini, A.; Bua, S.; Al-Rashood, S.T.; Hassan, G.S.; Bonardi, A.; Almehizia, A.A.; Alkahtani, H.M.; Alharbi, A.; et al. Novel Diamide-Based Benzenesulfonamides as Selective Carbonic Anhydrase IX Inhibitors Endowed with Antitumor Activity: Synthesis, Biological Evaluation and In Silico Insights. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2484. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102484
Abdelrahman MA, Eldehna WM, Nocentini A, Bua S, Al-Rashood ST, Hassan GS, Bonardi A, Almehizia AA, Alkahtani HM, Alharbi A, et al. Novel Diamide-Based Benzenesulfonamides as Selective Carbonic Anhydrase IX Inhibitors Endowed with Antitumor Activity: Synthesis, Biological Evaluation and In Silico Insights. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(10):2484. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102484
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbdelrahman, Mohamed A., Wagdy M. Eldehna, Alessio Nocentini, Silvia Bua, Sara T. Al-Rashood, Ghada S. Hassan, Alessandro Bonardi, Abdulrahman A. Almehizia, Hamad M. Alkahtani, Amal Alharbi, and et al. 2019. "Novel Diamide-Based Benzenesulfonamides as Selective Carbonic Anhydrase IX Inhibitors Endowed with Antitumor Activity: Synthesis, Biological Evaluation and In Silico Insights" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 10: 2484. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102484
APA StyleAbdelrahman, M. A., Eldehna, W. M., Nocentini, A., Bua, S., Al-Rashood, S. T., Hassan, G. S., Bonardi, A., Almehizia, A. A., Alkahtani, H. M., Alharbi, A., Gratteri, P., & Supuran, C. T. (2019). Novel Diamide-Based Benzenesulfonamides as Selective Carbonic Anhydrase IX Inhibitors Endowed with Antitumor Activity: Synthesis, Biological Evaluation and In Silico Insights. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(10), 2484. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102484