Mediterranean and MIND Diets Containing Olive Biophenols Reduces the Prevalence of Alzheimer’s Disease
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Search Criteria and Data Collection
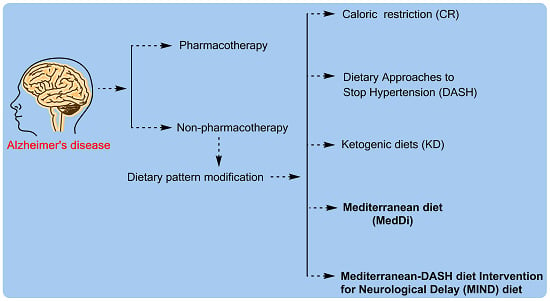
3. Dietary Pattern Attempted in Alzheimer’s Disease Prevention and Treatment
3.1. Calorie Restriction Diet
3.2. Assessment of Calorie Restriction Diet
3.3. Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) Diet
3.4. Assessment of DASH Diet
3.5. Ketogenic Diet (KD)
3.6. Assessment of Ketogenic Diet
4. Promising Dietary Patterns Associated with the Prevention or Attenuation of AD
4.1. Mediterranean Diet
4.2. Assessment of Mediterranean Diet
4.3. MIND Diet
4.4. Assessment of MIND Diet
5. Proposed Mechanism of MedDi and MIND Diets Action against Alzheimer’s Disease
5.1. Olive’s Major and Minor Components
5.2. MedDi against AD Mediated through Olive’s Monounsaturated Fatty Acid
5.3. MedDi Action against AD Mediated through Olive Biophenols
6. Trends of Medical Foods against Alzheimer’s Disease
6.1. Axona
6.2. Souvenaid
6.3. CerefolinNAC
7. Conclusions
8. Future Direction
- The need to stick with a uniform source of olive intake (virgin or extra virgin olive oil or fruit) in the MedDi and MIND diet.
- The measured portion or percentage of olive or olive biophenols are missing in the MedDi and MIND diet. There is a need for a specified and uniform amount of olive inclusion in both diets.
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mattson, M.P.; Arumugam, T.V. Hallmarks of brain aging: Adaptive and pathological modification by metabolic states. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 1176–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.T.; Beiser, A.S.; Breteler, M.M.B.; Fratiglioni, L.; Helmer, C.; Hendrie, H.C.; Honda, H.; Ikram, M.A.; Langa, K.M.; Lobo, A.; et al. The changing prevalence and incidence of dementia over time—Current evidence. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2017, 13, 327–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardy, J.; Selkoe, D.J. The amyloid hypothesis of alzheimer’s disease: Progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science 2002, 297, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raina, P.; Santaguida, P.; Ismaila, A.; Patterson, C.; Cowan, D.; Levine, M.; Booker, L.; Oremus, M. Effectiveness of cholinesterase inhibitors and memantine for treating dementia: Evidence review for a clinical practice guideline. Ann. Intern. Med. 2008, 148, 379–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omar, S.H.; Scott, C.J.; Hamlin, A.S.; Obied, H.K. The protective role of plant biophenols in mechanisms of alzheimer’s disease. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2017, 47, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Scarmeas, N. Dietary patterns in alzheimer’s disease and cognitive aging. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2011, 8, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, E.; Clifton, P.; Goodwill, A.M.; Dennerstein, L.; Campbell, S.; Szoeke, C. Dietary patterns and beta-amyloid deposition in aging australian women. Alzheimers Dement. (N Y) 2018, 4, 535–541. [Google Scholar]
- Solfrizzi, V.; Panza, F.; Frisardi, V.; Seripa, D.; Logroscino, G.; Imbimbo, B.P.; Pilotto, A. Diet and alzheimer’s disease risk factors or prevention: The current evidence. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2011, 11, 677–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnard, N.D.; Bush, A.I.; Ceccarelli, A.; Cooper, J.; de Jager, C.A.; Erickson, K.I.; Fraser, G.; Kesler, S.; Levin, S.M.; Lucey, B.; et al. Dietary and lifestyle guidelines for the prevention of alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2014, 35 (Suppl. 2), S74–S78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, R.F.M.; Pogacnik, L. Food, polyphenols and neuroprotection. Neural Regen Res. 2017, 12, 582–583. [Google Scholar]
- Grant, W.B. Using multicountry ecological and observational studies to determine dietary risk factors for alzheimer’s disease. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2016, 35, 476–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooijmans, C.R.; Van der Zee, C.E.; Dederen, P.J.; Brouwer, K.M.; Reijmer, Y.D.; van Groen, T.; Broersen, L.M.; Lutjohann, D.; Heerschap, A.; Kiliaan, A.J. Dha and cholesterol containing diets influence alzheimer-like pathology, cognition and cerebral vasculature in appswe/ps1de9 mice. Neurobiol. Dis. 2009, 33, 482–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Studzinski, C.M.; Li, F.; Bruce-Keller, A.J.; Fernandez-Kim, S.O.; Zhang, L.; Weidner, A.M.; Markesbery, W.R.; Murphy, M.P.; Keller, J.N. Effects of short-term western diet on cerebral oxidative stress and diabetes related factors in app x ps1 knock-in mice. J. Neurochem. 2009, 108, 860–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardener, S.L.; Rainey-Smith, S.R.; Barnes, M.B.; Sohrabi, H.R.; Weinborn, M.; Lim, Y.Y.; Harrington, K.; Taddei, K.; Gu, Y.; Rembach, A.; et al. Dietary patterns and cognitive decline in an australian study of ageing. Mol. Psychiatry 2015, 20, 860–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shakersain, B.; Santoni, G.; Larsson, S.C.; Faxen-Irving, G.; Fastbom, J.; Fratiglioni, L.; Xu, W. Prudent diet may attenuate the adverse effects of western diet on cognitive decline. Alzheimers Dement. 2016, 12, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tangney, C.C.; Kwasny, M.J.; Li, H.; Wilson, R.S.; Evans, D.A.; Morris, M.C. Adherence to a mediterranean-type dietary pattern and cognitive decline in a community population. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2011, 93, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsson, E.; Karlstrom, B.; Kilander, L.; Byberg, L.; Cederholm, T.; Sjogren, P. Dietary patterns and cognitive dysfunction in a 12-year follow-up study of 70 year old men. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2015, 43, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halagappa, V.K.; Guo, Z.; Pearson, M.; Matsuoka, Y.; Cutler, R.G.; Laferla, F.M.; Mattson, M.P. Intermittent fasting and caloric restriction ameliorate age-related behavioral deficits in the triple-transgenic mouse model of alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2007, 26, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, P.; Shen, Q.; Dong, S.; Xu, Z.; Tsien, J.Z.; Hu, Y. Calorie restriction ameliorates neurodegenerative phenotypes in forebrain-specific presenilin-1 and presenilin-2 double knockout mice. Neurobiol. Aging 2008, 29, 1502–1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahl, D.; Solon-Biet, S.M.; Wang, Q.P.; Wali, J.A.; Pulpitel, T.; Clark, X.; Raubenheimer, D.; Senior, A.M.; Sinclair, D.A.; Cooney, G.J.; et al. Comparing the effects of low-protein and high-carbohydrate diets and caloric restriction on brain aging in mice. Cell Rep. 2018, 25, 2234–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luchsinger, J.A.; Tang, M.X.; Shea, S.; Mayeux, R. Caloric intake and the risk of alzheimer disease. Arch. Neurol. 2002, 59, 1258–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafson, D.; Rothenberg, E.; Blennow, K.; Steen, B.; Skoog, I. An 18-year follow-up of overweight and risk of alzheimer disease. Arch. Intern. Med. 2003, 163, 1524–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, C.K.; Anton, S.D.; Han, H.; York-Crowe, E.; Redman, L.M.; Ravussin, E.; Williamson, D.A. Examination of cognitive function during six months of calorie restriction: Results of a randomized controlled trial. Rejuvenation Res. 2007, 10, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witte, A.V.; Fobker, M.; Gellner, R.; Knecht, S.; Floel, A. Caloric restriction improves memory in elderly humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 1255–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, P.J.; Blumenthal, J.A.; Babyak, M.A.; Craighead, L.; Welsh-Bohmer, K.A.; Browndyke, J.N.; Strauman, T.A.; Sherwood, A. Effects of the dietary approaches to stop hypertension diet, exercise, and caloric restriction on neurocognition in overweight adults with high blood pressure. Hypertension 2010, 55, 1331–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tangney, C.C.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Barnes, L.; Schneider, J.A.; Bennett, D.A.; Morris, M.C. Relation of dash- and mediterranean-like dietary patterns to cognitive decline in older persons. Neurology 2014, 83, 1410–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reger, M.A.; Henderson, S.T.; Hale, C.; Cholerton, B.; Baker, L.D.; Watson, G.S.; Hyde, K.; Chapman, D.; Craft, S. Effects of beta-hydroxybutyrate on cognition in memory-impaired adults. Neurobiol. Aging 2004, 25, 311–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, S.T.; Vogel, J.L.; Barr, L.J.; Garvin, F.; Jones, J.J.; Costantini, L.C. Study of the ketogenic agent ac-1202 in mild to moderate alzheimer’s disease: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, multicenter trial. Nutr. Metab. (Lond.) 2009, 6, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krikorian, R.; Shidler, M.D.; Dangelo, K.; Couch, S.C.; Benoit, S.C.; Clegg, D.J. Dietary ketosis enhances memory in mild cognitive impairment. Neurobiol. Aging 2012, 33, 425.e419–425.e427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hankey, G.J. Nutrition and the risk of stroke. Lancet Neurol. 2012, 11, 66–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivipelto, M.; Helkala, E.L.; Laakso, M.P.; Hanninen, T.; Hallikainen, M.; Alhainen, K.; Iivonen, S.; Mannermaa, A.; Tuomilehto, J.; Nissinen, A.; et al. Apolipoprotein e epsilon4 allele, elevated midlife total cholesterol level, and high midlife systolic blood pressure are independent risk factors for late-life alzheimer disease. Ann. Intern. Med. 2002, 137, 149–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kivipelto, M.; Ngandu, T.; Fratiglioni, L.; Viitanen, M.; Kareholt, I.; Winblad, B.; Helkala, E.L.; Tuomilehto, J.; Soininen, H.; Nissinen, A. Obesity and vascular risk factors at midlife and the risk of dementia and alzheimer disease. Arch. Neurol. 2005, 62, 1556–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azadbakht, L.; Izadi, V.; Ehsani, S.; Esmaillzadeh, A. Effects of the dietary approaches to stop hypertension (dash) eating plan on the metabolic side effects of corticosteroid medications. J. Am. Coll. Nutr. 2016, 35, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sridhar, G.R.; Lakshmi, G.; Nagamani, G. Emerging links between type 2 diabetes and alzheimer’s disease. World J. Diabetes 2015, 6, 744–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schilling, S.; Tzourio, C.; Soumare, A.; Kaffashian, S.; Dartigues, J.F.; Ancelin, M.L.; Samieri, C.; Dufouil, C.; Debette, S. Differential associations of plasma lipids with incident dementia and dementia subtypes in the 3c study: A longitudinal, population-based prospective cohort study. PLoS Med. 2017, 14, e1002265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, S.; Bergeron, N.; Williams, P.T.; Bray, G.A.; Sutherland, B.; Krauss, R.M. Comparison of the dash (dietary approaches to stop hypertension) diet and a higher-fat dash diet on blood pressure and lipids and lipoproteins: A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 103, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branco, A.F.; Ferreira, A.; Simoes, R.F.; Magalhaes-Novais, S.; Zehowski, C.; Cope, E.; Silva, A.M.; Pereira, D.; Sardao, V.A.; Cunha-Oliveira, T. Ketogenic diets: From cancer to mitochondrial diseases and beyond. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 46, 285–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunnane, S.C.; Courchesne-Loyer, A.; Vandenberghe, C.; St-Pierre, V.; Fortier, M.; Hennebelle, M.; Croteau, E.; Bocti, C.; Fulop, T.; Castellano, C.A. Can ketones help rescue brain fuel supply in later life? Implications for cognitive health during aging and the treatment of alzheimer’s disease. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2016, 9, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Auwera, I.; Wera, S.; Van Leuven, F.; Henderson, S.T. A ketogenic diet reduces amyloid beta 40 and 42 in a mouse model of alzheimer’s disease. Nutr. Metab. (Lond.) 2005, 2, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Studzinski, C.M.; MacKay, W.A.; Beckett, T.L.; Henderson, S.T.; Murphy, M.P.; Sullivan, P.G.; Burnham, W.M. Induction of ketosis may improve mitochondrial function and decrease steady-state amyloid-beta precursor protein (app) levels in the aged dog. Brain Res. 2008, 1226, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashiwaya, Y.; Bergman, C.; Lee, J.H.; Wan, R.; King, M.T.; Mughal, M.R.; Okun, E.; Clarke, K.; Mattson, M.P.; Veech, R.L. A ketone ester diet exhibits anxiolytic and cognition-sparing properties, and lessens amyloid and tau pathologies in a mouse model of alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2013, 34, 1530–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, M.K.; Sullivan, D.K.; Mahnken, J.D.; Burns, J.M.; Swerdlow, R.H. Feasibility and efficacy data from a ketogenic diet intervention in alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. (N Y) 2018, 4, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ota, M.; Matsuo, J.; Ishida, I.; Hattori, K.; Teraishi, T.; Tonouchi, H.; Ashida, K.; Takahashi, T.; Kunugi, H. Effect of a ketogenic meal on cognitive function in elderly adults: Potential for cognitive enhancement. Psychopharmacology (Berl.) 2016, 233, 3797–3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangialasche, F.; Kivipelto, M.; Mecocci, P.; Rizzuto, D.; Palmer, K.; Winblad, B.; Fratiglioni, L. High plasma levels of vitamin e forms and reduced alzheimer’s disease risk in advanced age. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2010, 20, 1029–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mangialasche, F.; Solomon, A.; Kareholt, I.; Hooshmand, B.; Cecchetti, R.; Fratiglioni, L.; Soininen, H.; Laatikainen, T.; Mecocci, P.; Kivipelto, M. Serum levels of vitamin e forms and risk of cognitive impairment in a finnish cohort of older adults. Exp. Gerontol. 2013, 48, 1428–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillette-Guyonnet, S.; Secher, M.; Vellas, B. Nutrition and neurodegeneration: Epidemiological evidence and challenges for future research. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 75, 738–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devore, E.E.; Kang, J.H.; Breteler, M.M.; Grodstein, F. Dietary intakes of berries and flavonoids in relation to cognitive decline. Ann. Neurol. 2012, 72, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, M.C. Diet and alzheimer’s disease: What the evidence shows. MedGenMed 2004, 6, 48. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Keys, A. Coronary heart disease in seven countries. Summary. Circulation 1970, 41, I186–I195. [Google Scholar]
- Trichopoulou, A.; Costacou, T.; Bamia, C.; Trichopoulos, D. Adherence to a mediterranean diet and survival in a greek population. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 2599–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocella, C.; Cammisotto, V.; Fianchini, L.; D’Amico, A.; Novo, M.; Castellani, V.; Stefanini, L.; Violi, F.; Carnevale, R. Extra virgin olive oil and cardiovascular diseases: Benefits for human health. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2018, 18, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayr, H.L.; Tierney, A.C.; Kucianski, T.; Thomas, C.J.; Itsiopoulos, C. Australian patients with coronary heart disease achieve high adherence to 6-month mediterranean diet intervention: Preliminary results of the ausmed heart trial. Nutrition 2018, 61, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Becerra-Tomas, N.; Blanco Mejia, S.; Viguiliouk, E.; Khan, T.; Kendall, C.W.C.; Kahleova, H.; Rahelic, D.; Sievenpiper, J.L.; Salas-Salvado, J. Mediterranean diet, cardiovascular disease and mortality in diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis of prospective cohort studies and randomized clinical trials. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez-Gonzalez, M.A.; Salas-Salvado, J.; Estruch, R.; Corella, D.; Fito, M.; Ros, E.; Predimed, I. Benefits of the mediterranean diet: Insights from the predimed study. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2015, 58, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourida, I.; Soni, M.; Thompson-Coon, J.; Purandare, N.; Lang, I.A.; Ukoumunne, O.C.; Llewellyn, D.J. Mediterranean diet, cognitive function, and dementia: A systematic review. Epidemiology 2013, 24, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Psaltopoulou, T.; Sergentanis, T.N.; Panagiotakos, D.B.; Sergentanis, I.N.; Kosti, R.; Scarmeas, N. Mediterranean diet, stroke, cognitive impairment, and depression: A meta-analysis. Ann. Neurol. 2013, 74, 580–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Parsaik, A.K.; Mielke, M.M.; Erwin, P.J.; Knopman, D.S.; Petersen, R.C.; Roberts, R.O. Association of mediterranean diet with mild cognitive impairment and alzheimer’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2014, 39, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasiou, C.A.; Yannakoulia, M.; Kosmidis, M.H.; Dardiotis, E.; Hadjigeorgiou, G.M.; Sakka, P.; Arampatzi, X.; Bougea, A.; Labropoulos, I.; Scarmeas, N. Mediterranean diet and cognitive health: Initial results from the hellenic longitudinal investigation of ageing and diet. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0182048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loughrey, D.G.; Lavecchia, S.; Brennan, S.; Lawlor, B.A.; Kelly, M.E. The impact of the mediterranean diet on the cognitive functioning of healthy older adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Adv. Nutr. 2017, 8, 571–586. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Maguire, B.; Brodaty, H.; O’Leary, F. Dietary patterns and cognitive health in older adults: A systematic review. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2019, 67, 583–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Lorenzo, R.; Pedretti, J.; Grossi, L.; Cuoghi, B.; Varni, C.; Landi, G.; Spattini, L.; Visentini, C.; Ferri, P.; Carubbi, F. The association of mediterranean diet and exercise modifications with anthropometric parameters in a psychiatric community population: A pilot study. Prev. Med. Rep. 2018, 9, 68–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malakou, E.; Linardakis, M.; Armstrong, M.E.G.; Zannidi, D.; Foster, C.; Johnson, L.; Papadaki, A. The combined effect of promoting the mediterranean diet and physical activity on metabolic risk factors in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valls-Pedret, C.; Sala-Vila, A.; Serra-Mir, M.; Corella, D.; de la Torre, R.; Martinez-Gonzalez, M.A.; Martinez-Lapiscina, E.H.; Fito, M.; Perez-Heras, A.; Salas-Salvado, J.; et al. Mediterranean diet and age-related cognitive decline: A randomized clinical trial. JAMA Intern. Med. 2015, 175, 1094–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcason, W. What are the components to the mind diet? J. Acad. Nutr. Diet. 2015, 115, 1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, M.C.; Tangney, C.C.; Wang, Y.; Sacks, F.M.; Bennett, D.A.; Aggarwal, N.T. Mind diet associated with reduced incidence of alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2015, 11, 1007–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morris, M.C.; Tangney, C.C.; Wang, Y.; Sacks, F.M.; Barnes, L.L.; Bennett, D.A.; Aggarwal, N.T. Mind diet slows cognitive decline with aging. Alzheimers Dement. 2015, 11, 1015–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, M.; Jensen, M.K. Association of the mind diet with cognition and risk of alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2016, 27, 303–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calil, S.R.B.; Brucki, S.M.D.; Nitrini, R.; Yassuda, M.S. Adherence to the mediterranean and mind diets is associated with better cognition in healthy seniors but not in mci or ad. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2018, 28, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berendsen, A.M.; Kang, J.H.; Feskens, E.J.M.; de Groot, C.; Grodstein, F.; van de Rest, O. Association of long-term adherence to the mind diet with cognitive function and cognitive decline in american women. J. Nutr. Health Aging 2018, 22, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McEvoy, C.T.; Guyer, H.; Langa, K.M.; Yaffe, K. Neuroprotective diets are associated with better cognitive function: The health and retirement study. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2017, 65, 1857–1862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fito, M.; Cladellas, M.; de la Torre, R.; Marti, J.; Alcantara, M.; Pujadas-Bastardes, M.; Marrugat, J.; Bruguera, J.; Lopez-Sabater, M.C.; Vila, J.; et al. Antioxidant effect of virgin olive oil in patients with stable coronary heart disease: A randomized, crossover, controlled, clinical trial. Atherosclerosis 2005, 181, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quiles, J.L.; Ramírez-Tortosa, M.C.; Yaqoob, P. Olive oil and health; CABI Publishing: Oxford, UK, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Boskou, D. 1—Olive fruit, table olives, and olive oil bioactive constituents. In Olive and Olive Oil Bioactive Constituents; Boskou, D., Ed.; AOCS Press: Urbana, IL, USA, 2015; pp. 1–30. [Google Scholar]
- Obied, H.K.; Prenzler, P.D.; Omar, S.H.; Ismael, R.; Servili, M.; Esposto, S.; Taticchi, A.; Selvaggini, R.; Urbani, S. Chapter six—Pharmacology of olive biophenols. In Advances in Molecular Toxicology; Fishbein, J.C., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; Volume 6, pp. 195–242. [Google Scholar]
- Omar, S.H.; Kerr, P.G.; Scott, C.J.; Hamlin, A.S.; Obied, H.K. Olive (olea europaea l.) biophenols: A nutriceutical against oxidative stress in sh-sy5y cells. Molecules 2017, 22, 1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Servili, M.; Selvaggini, R.; Esposto, S.; Taticchi, A.; Montedoro, G.; Morozzi, G. Health and sensory properties of virgin olive oil hydrophilic phenols: Agronomic and technological aspects of production that affect their occurrence in the oil. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1054, 113–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Incani, A.; Serra, G.; Atzeri, A.; Melis, M.P.; Serreli, G.; Bandino, G.; Sedda, P.; Campus, M.; Tuberoso, C.I.; Deiana, M. Extra virgin olive oil phenolic extracts counteract the pro-oxidant effect of dietary oxidized lipids in human intestinal cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 90, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Council of the European Union. Regulation (eu) no 528/2012 of the european parliament and of the council of 22 may 2012 concerning the making available on the market and use of biocidal products. Off. J. Eur. Union 2018, 167, 1–123. [Google Scholar]
- Alagna, F.; Mariotti, R.; Panara, F.; Caporali, S.; Urbani, S.; Veneziani, G.; Esposto, S.; Taticchi, A.; Rosati, A.; Rao, R.; et al. Olive phenolic compounds: Metabolic and transcriptional profiling during fruit development. BMC Plant Biol. 2012, 12, 162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paiva-Martins, F.; Gordon, M.H. Interactions of ferric ions with olive oil phenolic compounds. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 2704–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bendini, A.; Cerretani, L.; Carrasco-Pancorbo, A.; Gomez-Caravaca, A.M.; Segura-Carretero, A.; Fernandez-Gutierrez, A.; Lercker, G. Phenolic molecules in virgin olive oils: A survey of their sensory properties, health effects, antioxidant activity and analytical methods. An overview of the last decade. Molecules 2007, 12, 1679–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snowden, S.G.; Ebshiana, A.A.; Hye, A.; An, Y.; Pletnikova, O.; O’Brien, R.; Troncoso, J.; Legido-Quigley, C.; Thambisetty, M. Association between fatty acid metabolism in the brain and alzheimer disease neuropathology and cognitive performance: A nontargeted metabolomic study. PLoS Med. 2017, 14, e1002266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, J.M.; Shelness, G.S.; Rudel, L.L. Monounsaturated fatty acids and atherosclerosis: Opposing views from epidemiology and experimental animal models. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2007, 9, 494–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lorgeril, M.; Salen, P. The mediterranean diet: Rationale and evidence for its benefit. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2008, 10, 518–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estruch, R.; Ros, E.; Salas-Salvado, J.; Covas, M.I.; Corella, D.; Aros, F.; Gomez-Gracia, E.; Ruiz-Gutierrez, V.; Fiol, M.; Lapetra, J.; et al. Primary prevention of cardiovascular disease with a mediterranean diet supplemented with extra-virgin olive oil or nuts. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, e34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardener, H.; Rundek, T.; Wright, C.B.; Gu, Y.; Scarmeas, N.; Homma, S.; Russo, C.; Elkind, M.S.; Sacco, R.L.; Di Tullio, M.R. A mediterranean-style diet and left ventricular mass (from the northern manhattan study). Am. J. Cardiol. 2015, 115, 510–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panza, F.; Solfrizzi, V.; Colacicco, A.M.; D’Introno, A.; Capurso, C.; Torres, F.; Del Parigi, A.; Capurso, S.; Capurso, A. Mediterranean diet and cognitive decline. Public Health Nutr. 2004, 7, 959–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solfrizzi, V.; Colacicco, A.M.; D’Introno, A.; Capurso, C.; Torres, F.; Rizzo, C.; Capurso, A.; Panza, F. Dietary intake of unsaturated fatty acids and age-related cognitive decline: A 8.5-year follow-up of the italian longitudinal study on aging. Neurobiol. Aging 2006, 27, 1694–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazza, E.; Fava, A.; Ferro, Y.; Rotundo, S.; Romeo, S.; Bosco, D.; Pujia, A.; Montalcini, T. Effect of the replacement of dietary vegetable oils with a low dose of extravirgin olive oil in the mediterranean diet on cognitive functions in the elderly. J. Transl. Med. 2018, 16, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sastre, M.; Klockgether, T.; Heneka, M.T. Contribution of inflammatory processes to alzheimer’s disease: Molecular mechanisms. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 2006, 24, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L’Homme, L.; Esser, N.; Riva, L.; Scheen, A.; Paquot, N.; Piette, J.; Legrand-Poels, S. Unsaturated fatty acids prevent activation of nlrp3 inflammasome in human monocytes/macrophages. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 2998–3008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urpi-Sarda, M.; Casas, R.; Chiva-Blanch, G.; Romero-Mamani, E.S.; Valderas-Martinez, P.; Arranz, S.; Andres-Lacueva, C.; Llorach, R.; Medina-Remon, A.; Lamuela-Raventos, R.M.; et al. Virgin olive oil and nuts as key foods of the mediterranean diet effects on inflammatory biomakers related to atherosclerosis. Pharmacol. Res. 2012, 65, 577–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdomo, L.; Beneit, N.; Otero, Y.F.; Escribano, O.; Diaz-Castroverde, S.; Gomez-Hernandez, A.; Benito, M. Protective role of oleic acid against cardiovascular insulin resistance and in the early and late cellular atherosclerotic process. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2015, 14, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Vliet, P. Cholesterol and late-life cognitive decline. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2012, 30 (Suppl. 2), S147–S162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anstey, K.J.; Ashby-Mitchell, K.; Peters, R. Updating the evidence on the association between serum cholesterol and risk of late-life dementia: Review and meta-analysis. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2017, 56, 215–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnoni, G.V.; Natali, F.; Geelen, M.J.H.; Siculella, L. Chapter 152—Oleic acid as an inhibitor of fatty acid and cholesterol synthesis. In Olives and Olive Oil in Health and Disease Prevention; Preedy, V.R., Watson, R.R., Eds.; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 2010; pp. 1365–1373. [Google Scholar]
- Amtul, Z.; Westaway, D.; Cechetto, D.F.; Rozmahel, R.F. Oleic acid ameliorates amyloidosis in cellular and mouse models of alzheimer’s disease. Brain Pathol. 2011, 21, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Miranda, J.; Perez-Jimenez, F.; Ros, E.; De Caterina, R.; Badimon, L.; Covas, M.I.; Escrich, E.; Ordovas, J.M.; Soriguer, F.; Abia, R.; et al. Olive oil and health: Summary of the ii international conference on olive oil and health consensus report, jaen and cordoba (spain) 2008. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2010, 20, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omar, S.H.; Scott, C.J.; Hamlin, A.S.; Obied, H.K. Biophenols: Enzymes (beta-secretase, cholinesterases, histone deacetylase and tyrosinase) inhibitors from olive (olea europaea l.). Fitoterapia 2018, 128, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omar, S.H.; Scott, C.J.; Hamlin, A.S.; Obied, H.K. Olive biophenols reduces alzheimer’s pathology in sh-sy5y cells and appswe mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 20, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitsavos, C.; Panagiotakos, D.B.; Tzima, N.; Chrysohoou, C.; Economou, M.; Zampelas, A.; Stefanadis, C. Adherence to the mediterranean diet is associated with total antioxidant capacity in healthy adults: The attica study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 82, 694–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salas-Salvado, J.; Garcia-Arellano, A.; Estruch, R.; Marquez-Sandoval, F.; Corella, D.; Fiol, M.; Gomez-Gracia, E.; Vinoles, E.; Aros, F.; Herrera, C.; et al. Components of the mediterranean-type food pattern and serum inflammatory markers among patients at high risk for cardiovascular disease. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2008, 62, 651–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carluccio, M.A.; Siculella, L.; Ancora, M.A.; Massaro, M.; Scoditti, E.; Storelli, C.; Visioli, F.; Distante, A.; De Caterina, R. Olive oil and red wine antioxidant polyphenols inhibit endothelial activation: Antiatherogenic properties of mediterranean diet phytochemicals. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2003, 23, 622–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Bock, M.; Derraik, J.G.; Brennan, C.M.; Biggs, J.B.; Morgan, P.E.; Hodgkinson, S.C.; Hofman, P.L.; Cutfield, W.S. Olive (olea europaea l.) leaf polyphenols improve insulin sensitivity in middle-aged overweight men: A randomized, placebo-controlled, crossover trial. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez-Villegas, A.; Galbete, C.; Martinez-Gonzalez, M.A.; Martinez, J.A.; Razquin, C.; Salas-Salvado, J.; Estruch, R.; Buil-Cosiales, P.; Marti, A. The effect of the mediterranean diet on plasma brain-derived neurotrophic factor (bdnf) levels: The predimed-navarra randomized trial. Nutr. Neurosci. 2011, 14, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lockyer, S.; Rowland, I.; Spencer, J.P.E.; Yaqoob, P.; Stonehouse, W. Impact of phenolic-rich olive leaf extract on blood pressure, plasma lipids and inflammatory markers: A randomised controlled trial. Eur. J. Nutr. 2017, 56, 1421–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lockyer, S.; Corona, G.; Yaqoob, P.; Spencer, J.P.; Rowland, I. Secoiridoids delivered as olive leaf extract induce acute improvements in human vascular function and reduction of an inflammatory cytokine: A randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, cross-over trial. Br. J. Nutr. 2015, 114, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin-Pelaez, S.; Mosele, J.I.; Pizarro, N.; Farras, M.; de la Torre, R.; Subirana, I.; Perez-Cano, F.J.; Castaner, O.; Sola, R.; Fernandez-Castillejo, S.; et al. Effect of virgin olive oil and thyme phenolic compounds on blood lipid profile: Implications of human gut microbiota. Eur. J. Nutr. 2017, 56, 119–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossi, C.; Rigacci, S.; Ambrosini, S.; Ed Dami, T.; Luccarini, I.; Traini, C.; Failli, P.; Berti, A.; Casamenti, F.; Stefani, M. The polyphenol oleuropein aglycone protects tgcrnd8 mice against ass plaque pathology. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e71702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Sperry, J.B.; Crowe, A.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Smith, A.B., 3rd; Lee, V.M. Inhibition of tau fibrillization by oleocanthal via reaction with the amino groups of tau. J. Neurochem. 2009, 110, 1339–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, K.; Xu, J.; Zou, X.; Li, Y.; Chen, C.; Zheng, A.; Li, H.; Li, H.; Szeto, I.M.; Shi, Y.; et al. Hydroxytyrosol prevents diet-induced metabolic syndrome and attenuates mitochondrial abnormalities in obese mice. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 67, 396–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valls, R.M.; Farras, M.; Suarez, M.; Fernandez-Castillejo, S.; Fito, M.; Konstantinidou, V.; Fuentes, F.; Lopez-Miranda, J.; Giralt, M.; Covas, M.I.; et al. Effects of functional olive oil enriched with its own phenolic compounds on endothelial function in hypertensive patients. A randomised controlled trial. Food Chem. 2015, 167, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadopoulou, A.; Petrotos, K.; Stagos, D.; Gerasopoulos, K.; Maimaris, A.; Makris, H.; Kafantaris, I.; Makri, S.; Kerasioti, E.; Halabalaki, M.; et al. Enhancement of antioxidant mechanisms and reduction of oxidative stress in chickens after the administration of drinking water enriched with polyphenolic powder from olive mill waste waters. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalski, K.; Mulak, A. Brain-gut-microbiota axis in alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2019, 25, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cattaneo, A.; Cattane, N.; Galluzzi, S.; Provasi, S.; Lopizzo, N.; Festari, C.; Ferrari, C.; Guerra, U.P.; Paghera, B.; Muscio, C.; et al. Association of brain amyloidosis with pro-inflammatory gut bacterial taxa and peripheral inflammation markers in cognitively impaired elderly. Neurobiol. Aging 2017, 49, 60–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Legarrea, P.; Fuller, N.R.; Zulet, M.A.; Martinez, J.A.; Caterson, I.D. The influence of mediterranean, carbohydrate and high protein diets on gut microbiota composition in the treatment of obesity and associated inflammatory state. Asia Pac. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 23, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Queipo-Ortuno, M.I.; Boto-Ordonez, M.; Murri, M.; Gomez-Zumaquero, J.M.; Clemente-Postigo, M.; Estruch, R.; Cardona Diaz, F.; Andres-Lacueva, C.; Tinahones, F.J. Influence of red wine polyphenols and ethanol on the gut microbiota ecology and biochemical biomarkers. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 95, 1323–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thaipisuttikul, P.; Galvin, J.E. Use of medical foods and nutritional approaches in the treatment of alzheimer’s disease. Clin. Pract. (Lond.) 2012, 9, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, R.C. Medical foods for alzheimer’s disease. Drugs Aging 2011, 28, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Bemis, M.; Desilets, A.R. Role of medium chain triglycerides (axona(r)) in the treatment of mild to moderate alzheimer’s disease. Am. J. Alzheimers Dis. Other Dement. 2014, 29, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheltens, P.; Kamphuis, P.J.; Verhey, F.R.; Olde Rikkert, M.G.; Wurtman, R.J.; Wilkinson, D.; Twisk, J.W.; Kurz, A. Efficacy of a medical food in mild alzheimer’s disease: A randomized, controlled trial. Alzheimers Dement. 2010, 6, 1–10.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankle, W.R.; Hara, J.; Barrentine, L.W.; Curole, M.V. Cerefolinnac therapy of hyperhomocysteinemia delays cortical and white matter atrophy in alzheimer’s disease and cerebrovascular disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2016, 54, 1073–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheltens, P.; Twisk, J.W.; Blesa, R.; Scarpini, E.; von Arnim, C.A.; Bongers, A.; Harrison, J.; Swinkels, S.H.; Stam, C.J.; de Waal, H.; et al. Efficacy of souvenaid in mild alzheimer’s disease: Results from a randomized, controlled trial. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2012, 31, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, S.H. Oleuropein in olive and its pharmacological effects. Sci. Pharm. 2010, 78, 133–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omar, S.H. Chapter 4—Biophenols: Impacts and prospects in anti-alzheimer drug discovery. In Discovery and Development of Neuroprotective Agents from Natural Products; Brahmachari, G., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 103–148. [Google Scholar]
- Abuznait, A.H.; Qosa, H.; Busnena, B.A.; El Sayed, K.A.; Kaddoumi, A. Olive-oil-derived oleocanthal enhances beta-amyloid clearance as a potential neuroprotective mechanism against alzheimer’s disease: In vitro and in vivo studies. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2013, 4, 973–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qosa, H.; Batarseh, Y.S.; Mohyeldin, M.M.; El Sayed, K.A.; Keller, J.N.; Kaddoumi, A. Oleocanthal enhances amyloid-beta clearance from the brains of tgswdi mice and in vitro across a human blood-brain barrier model. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2015, 6, 1849–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA Panel on Dietetic Products, Nutrition and Allergies (NDA). Scientific opinion on the substantiation of health claims related to polyphenols in olive and protection of ldl particles from oxidative damage (id 1333, 1638, 1639, 1696, 2865), maintenance of normal blood hdl cholesterol concentrations (id 1639), maintenance of normal blood pressure (id 3781), “anti-inflammatory properties” (id 1882), “contributes to the upper respiratory tract health” (id 3468), “can help to maintain a normal function of gastrointestinal tract” (3779), and “contributes to body defences against external agents” (id 3467) pursuant to article 13(1) of regulation (ec) no 1924/2006. EFSA J. 2011, 9, 2033. [Google Scholar]
- van den Berg, E.; Kloppenborg, R.P.; Kessels, R.P.; Kappelle, L.J.; Biessels, G.J. Type 2 diabetes mellitus, hypertension, dyslipidemia and obesity: A systematic comparison of their impact on cognition. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2009, 1792, 470–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yates, K.F.; Sweat, V.; Yau, P.L.; Turchiano, M.M.; Convit, A. Impact of metabolic syndrome on cognition and brain: A selected review of the literature. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2012, 32, 2060–2067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tosti, V.; Bertozzi, B.; Fontana, L. Health benefits of the mediterranean diet: Metabolic and molecular mechanisms. J. Gerontol A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2018, 73, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Dietary Model | Study Type | Outcomes | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Calorie restricted | Caloric restriction (25%) alone or with physical exercise (6 months) | Daily energy deficit was not significantly associated with change in cognitive test performance | [23] |
| Calorie restricted | Caloric restriction (30% reduction) diet with limitation of 1200 kcal/day for 3 months | Significant increase in verbal memory scores (mean increase 20%; p < 0.001) | [24] |
| Calorie restricted (DASH Diet) | Caloric restriction with physical exercise (4 months) | Participants on the DASH diet combined with a behavioural weight management programme exhibited greater improvements in executive function memory-learning (p = 0.008) and psychomotor speed (p = 0.023) compared with the usual diet control | [25] |
| DASH Diet | DASH diet was administered in older people | DASH score was associated with a slower rate of global cognitive decline by 0.007 standardized units (standard error of estimate = 0.003, p = 0.03) | [26] |
| Ketogenic Diet | Medium chain triglycerides (MCT) in AD patients | Facilitated performance on the (ADAS-cog) Subscale and associated with rise in ketone bodies | [27] |
| Ketogenic Diet | Oral administration of ketogenic compound AC-1202 (10–20 g) in AD patients | Significant improvement in the ADAS-cog | [28] |
| Ketogenic Diet | Administration of carbohydrate (5–10%) per day in older adults with MCI | Significant improvement in verbal memory performance | [29] |
| Activity | Study | Action | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Antioxidant | In vitro | Verbascoside, oleuropein, and caffeic acid scavenges superoxide radical and protected H₂O₂-induced SH-SY5Y cells | [5,75] |
| Cardioprotective | Randomised controlled trial | OLE reduces blood pressure and plasma TC, LDL-C and TAG | [106] |
| Randomised controlled trial | OLE improve vascular function and reduce inflammatory cytokine (IL-8) | [107] | |
| Randomised controlled trial | Virgin olive oil phenolic compounds cause increase in bifidobacteria population together with increase in biophenols microbial metabolites | [108] | |
| Neuroprotective | In vivo | Oleuropein aglycone reduces Aβ42 deposition, plaque deposit, and improves the cognitive performance | [109] |
| In vitro | Oleocanthal inhibited aggregation of tau protein | [110] | |
| In vitro and in vivo | Oleuropein and hydroxytyrosol reduces Aβ42 aggregation in SH-SY5Y cells and plaques formation in mice | [100] | |
| Metabolic syndrome | In vivo | Hydroxytyrosol decrease fasting glucose level in obese mice | [111] |
| Randomised controlled trial | Olive oil phenolic compounds improve endothelial function in hypertensive patients | [112] | |
| Randomised controlled trial | OLE improve insulin sensitivity and pancreatic β-cell secretory capacity | [104] | |
| Enzyme modification | In vitro | Olive mill waste phenolic compounds increase GSH levels in erythrocytes | [113] |
| In vitro | Olive biophenols inhibited AChE, BChE, BACE-1 and HDAC | [99] |
| Brand Name | Ingredients | Mechanism of Action | Significance | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Axona | Caprylic triglyceride | Caprylic acid to ketone bodies metabolism provided an alternative energy source for neurons with compromised glucose utilization | Cause significant increase in serum ketone bodies 2 h after administration. A significant difference was found between Axona and placebo groups in mean change from baseline in ADAS-cog score on days 45 and 90 of administration (Axona group improving and controls worsening) | [28] |
| Souvenaid | Omega-3 fatty acids (eicosapentaenoic acid, Docosahexaenoic acid), vitamins B6, B12, C, and E, choline, folic acid, selenium, uridine monophosphate, phospholipids | Effects on deficits in neuronal membrane composition and function as well as improvement of synapse formation | A significant improvement was found in delayed verbal recall and unchanged clinical outcomes after daily administration for 12 weeks. | [121] |
| A significant improvement in memory domain function was found and assessed with a neuropsychological test battery | [123] | |||
| CrerefolinNAC | L-methylfolate, methylcobalamin, N-acetyl-cysteine | Effects on metabolic imbalances and neurovascular oxidative stress in hyper-homocysteinemia | A significant decrease in hippocampal and cortical atrophy rates were found in participants with both AD and hyperhomocysteinemia | [122] |
© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Omar, S.H. Mediterranean and MIND Diets Containing Olive Biophenols Reduces the Prevalence of Alzheimer’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2797. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20112797
Omar SH. Mediterranean and MIND Diets Containing Olive Biophenols Reduces the Prevalence of Alzheimer’s Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(11):2797. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20112797
Chicago/Turabian StyleOmar, Syed Haris. 2019. "Mediterranean and MIND Diets Containing Olive Biophenols Reduces the Prevalence of Alzheimer’s Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 11: 2797. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20112797
APA StyleOmar, S. H. (2019). Mediterranean and MIND Diets Containing Olive Biophenols Reduces the Prevalence of Alzheimer’s Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(11), 2797. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20112797