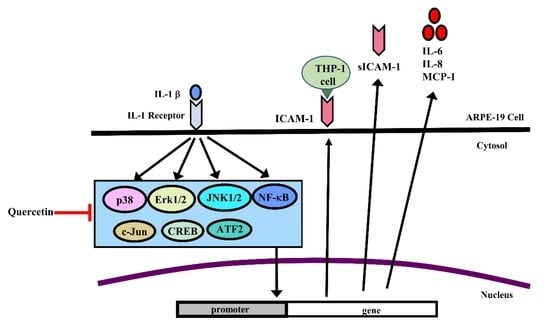
Quercetin Inhibits the Production of IL-1β-Induced Inflammatory Cytokines and Chemokines in ARPE-19 Cells via the MAPK and NF-κB Signaling Pathways
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. IL-1β Induces the Expression of ICAM-1, sICAM-1, IL-6, IL-8 and MCP-1 in ARPE-19 Cells
2.2. Quercetin Inhibits the Expression of ICAM-1, sICAM-1, IL-6, IL-8 and MCP-1 in IL-1β-Stimulated ARPE-19 Cells
2.3. Quercetin Suppresses Inflammatory Signaling Pathways in ARPE-19 Cells
2.4. MAPK Inhibitors Decrease the IL-1β-Induced Expression of sICAM-1, IL-6, IL-8 and MCP-1 in ARPE-19 Cells
2.5. Quercetin Decreases Nuclear Factor (NF)-κB Activation in IL-1β-Stimulated ARPE-19 Cells
2.6. Quercetin Attenuates THP-1 Cell Adherence to IL-1β-Stimulated ARPE-19 Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. Cell Viability Assay
4.4. ELISA
4.5. Preparation of Cell Extracts and Western Blot Analysis
4.6. Total RNA Extraction and RT-qPCR
4.7. Immunofluorescence Staining
4.8. Monocyte Adhesion Assay
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AMD | age-related macular degeneration |
| ATF | activating transcription factor |
| ARPE-19 cells | human retinal pigment epithelial cells |
| CREB | cAMP response element-binding protein |
| DMSO | dimethyl sulfoxide |
| EDTA | ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid |
| ELISA | enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| ERK | extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| FBS | fetal bovine serum |
| GAPDH | glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| IκB | inhibitor of NF-κB |
| ICAM-1 | intercellular adhesion molecule-1 |
| IKK | inhibitor of nuclear factor κ-B kinase |
| IL-1β | interleukin-1β |
| IL-6 | interleukin-6 |
| IL-8 | interleukin-8 |
| JNK | c-Jun N-terminal kinase |
| MAPK | mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| MCP-1 | monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 |
| MMP | matrix metalloproteinase |
| MTT | 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide |
| NF-κB | nuclear factor κB |
| PBS | phosphate-buffered saline |
| SDS | sodium dodecyl sulfate |
| TNF-α | tumor necrosis factor-α |
References
- Toops, K.A.; Tan, L.X.; Lakkaraju, A. A detailed three-step protocol for live imaging of intracellular traffic in polarized primary porcine RPE monolayers. Exp. Eye Res. 2014, 124, 74–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jong, P.T. Age-related macular degeneration. N. Engl. J. Med. 2006, 355, 1474–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holtkamp, G.M.; Van Rossem, M.; de Vos, A.F.; Willekens, B.; Peek, R.; Kijlstra, A. Polarized secretion of IL-6 and IL-8 by human retinal pigment epithelial cells. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1998, 112, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kutty, R.K.; Nagineni, C.N.; Samuel, W.; Vijayasarathy, C.; Hooks, J.J.; Redmond, T.M. Inflammatory cytokines regulate microRNA-155 expression in human retinal pigment epithelial cells by activating JAK/STAT pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 402, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, W.L.; Su, X.; Li, X.; Cheung, C.M.; Klein, R.; Cheng, C.Y.; Wong, T.Y. Global prevalence of age-related macular degeneration and disease burden projection for 2020 and 2040: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Glob. Health 2014, 2, e106–e116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, P.; Liew, G.; Gopinath, B.; Wong, T.Y. Age-related macular degeneration. Lancet 2018, 392, 1147–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, J.Z. Age-related macular degeneration (AMD): Pathogenesis and therapy. Pharmacol. Rep. 2006, 58, 353–363. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, K.; Zhang, L.; Weinreb, R.N. Ophthalmic drug discovery: Novel targets and mechanisms for retinal diseases and glaucoma. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2012, 11, 541–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knickelbein, J.E.; Chan, C.C.; Sen, H.N.; Ferris, F.L.; Nussenblatt, R.B. Inflammatory Mechanisms of Age-related Macular Degeneration. Int. Ophthalmol. Clin. 2015, 55, 63–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechner, J.; Chen, M.; Hogg, R.E.; Toth, L.; Silvestri, G.; Chakravarthy, U.; Xu, H. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells from neovascular age-related macular degeneration patients produce higher levels of chemokines CCL2 (MCP-1) and CXCL8 (IL-8). J. Neuroinflamm. 2017, 14, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motohashi, R.; Noma, H.; Yasuda, K.; Kotake, O.; Goto, H.; Shimura, M. Dynamics of Inflammatory Factors in Aqueous Humor during Ranibizumab or Aflibercept Treatment for Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Ophthalmic Res. 2017, 58, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mimura, T.; Funatsu, H.; Noma, H.; Shimura, M.; Kamei, Y.; Yoshida, M.; Kondo, A.; Watanabe, E.; Mizota, A. Aqueous Humor Levels of Cytokines in Patients with Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Ophthalmologica 2018, 241, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, T.; Takeuchi, M.; Karasawa, Y.; Enoki, T.; Ito, M. Intraocular inflammatory cytokines in patients with neovascular age-related macular degeneration before and after initiation of intravitreal injection of anti-VEGF inhibitor. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.Q.; Yang, F.Y.; Wang, M.S.; Shi, B.K.; Chen, D.X.; Chen, D.; Zhou, Q.; He, Q.B.; Ma, L.X.; Cheng, W.L.; et al. Quercetin protects against chronic prostatitis in rat model through NF-kappaB and MAPK signaling pathways. Prostate 2018, 78, 790–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hytti, M.; Piippo, N.; Salminen, A.; Honkakoski, P.; Kaarniranta, K.; Kauppinen, A. Quercetin alleviates 4-hydroxynonenal-induced cytotoxicity and inflammation in ARPE-19 cells. Exp. Eye Res. 2015, 132, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.S.; Chae, M.K.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, E.J. Anti-inflammatory effect of quercetin in a whole orbital tissue culture of Graves’ orbitopathy. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2012, 96, 1117–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, M.; Palumbo, R.; Mupo, A.; Tosto, M.; Iacomino, G.; Scognamiglio, A.; Tedesco, I.; Galano, G.; Russo, G.L. Flavonoid quercetin sensitizes a CD95-resistant cell line to apoptosis by activating protein kinase Calpha. Oncogene 2003, 22, 3330–3342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Liu, M.; Tuo, J.; Shen, D.; Chan, C.C. The effects of quercetin in cultured human RPE cells under oxidative stress and in Ccl2/Cx3cr1 double deficient mice. Exp. Eye Res. 2010, 91, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Hu, J.; Sui, J.; Jiang, L.; Cong, Y.; Ren, G. Quercetin is able to alleviate TGF-beta-induced fibrosis in renal tubular epithelial cells by suppressing miR-21. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 16, 2442–2448. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Premoli, M.; Aria, F.; Bonini, S.A.; Maccarinelli, G.; Gianoncelli, A.; Memo, M.; Mastinu, A. Cannabimimetic plants: Are they new cannabinoidergic modulators? Planta 2019, 249, 1681–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eid, H.M.; Haddad, P.S. The Antidiabetic Potential of Quercetin: Underlying Mechanisms. Curr. Med. Chem. 2017, 24, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nam, J.S.; Sharma, A.R.; Nguyen, L.T.; Chakraborty, C.; Sharma, G.; Lee, S.S. Application of Bioactive Quercetin in Oncotherapy: From Nutrition to Nanomedicine. Molecules 2016, 21, 108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jana, N.; Bretislav, G.; Pavel, S.; Pavla, U. Potential of the Flavonoid Quercetin to Prevent and Treat Cancer—Current Status of Research. Klin. Onkol. 2018, 31, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Suganthy, N.; Devi, K.P.; Nabavi, S.F.; Braidy, N.; Nabavi, S.M. Bioactive effects of quercetin in the central nervous system: Focusing on the mechanisms of actions. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 84, 892–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miltonprabu, S.; Tomczyk, M.; Skalicka-Wozniak, K.; Rastrelli, L.; Daglia, M.; Nabavi, S.F.; Alavian, S.M.; Nabavi, S.M. Hepatoprotective effect of quercetin: From chemistry to medicine. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 108, 365–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basu, A.; Das, A.S.; Majumder, M.; Mukhopadhyay, R. Antiatherogenic Roles of Dietary Flavonoids Chrysin, Quercetin, and Luteolin. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2016, 68, 89–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gormaz, J.G.; Quintremil, S.; Rodrigo, R. Cardiovascular Disease: A Target for the Pharmacological Effects of Quercetin. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2015, 15, 1735–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKay, T.B.; Karamichos, D. Quercetin and the ocular surface: What we know and where we are going. Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood) 2017, 242, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, S.; Mao, L.; Gong, Y.; Sun, T.; Gu, Q. Role of quercetin in protecting ARPE19 cells against H2O2induced injury via nuclear factor erythroid 2 like 2 pathway activation and endoplasmic reticulum stress inhibition. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 3461–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.; Yun, S.; Lee, H.; Yang, J. Quercetin Mitigates Inflammatory Responses Induced by Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Mouse Retinal Photoreceptor Cells through Suppression of Nuclear Factor Kappa B. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.; Gupta, S.K.; Nag, T.C.; Srivastava, S.; Saxena, R.; Jha, K.A.; Srinivasan, B.P. Retinal neuroprotective effects of quercetin in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Exp. Eye Res. 2014, 125, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min, Y.D.; Choi, C.H.; Bark, H.; Son, H.Y.; Park, H.H.; Lee, S.; Park, J.W.; Park, E.K.; Shin, H.I.; Kim, S.H. Quercetin inhibits expression of inflammatory cytokines through attenuation of NF-kappaB and p38 MAPK in HMC-1 human mast cell line. Inflamm. Res. 2007, 56, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Li, X.; Yue, Y.; Li, J.; He, T.; He, Y. The inhibitory effect of quercetin on IL-6 production by LPS-stimulated neutrophils. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2005, 2, 455–460. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nanua, S.; Zick, S.M.; Andrade, J.E.; Sajjan, U.S.; Burgess, J.R.; Lukacs, N.W.; Hershenson, M.B. Quercetin blocks airway epithelial cell chemokine expression. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2006, 35, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, P.; Shi, Q.; Xu, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, W.; Wang, H. Quercetin suppresses NF-kappaB and MCP-1 expression in a high glucose-induced human mesangial cell proliferation model. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2012, 30, 119–125. [Google Scholar]
- Bian, Y.; Liu, P.; Zhong, J.; Hu, Y.; Zhuang, S.; Fan, K.; Liu, Z. Quercetin Attenuates Adhesion Molecule Expression in Intestinal Microvascular Endothelial Cells by Modulating Multiple Pathways. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2018, 63, 3297–3304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, B.; Yang, T.; Song, X.; Hu, X.; Fan, H.; Lu, X.; Chen, L.; Cheng, D.; Wang, T.; Liu, D.; et al. Quercetin inhibits IL-1 beta-induced ICAM-1 expression in pulmonary epithelial cell line A549 through the MAPK pathways. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2009, 36, 1825–1832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhang, W.J.; Frei, B. Quercetin inhibits LPS-induced adhesion molecule expression and oxidant production in human aortic endothelial cells by p38-mediated Nrf2 activation and antioxidant enzyme induction. Redox Biol. 2016, 9, 104–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, Z.M.; Elner, S.G.; Yoshida, A.; Kunkel, S.L.; Su, J.; Elner, V.M. Activation of p38, ERK1/2 and NIK pathways is required for IL-1beta and TNF-alpha-induced chemokine expression in human retinal pigment epithelial cells. Exp. Eye Res. 2001, 73, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hytti, M.; Piippo, N.; Korhonen, E.; Honkakoski, P.; Kaarniranta, K.; Kauppinen, A. Fisetin and luteolin protect human retinal pigment epithelial cells from oxidative stress-induced cell death and regulate inflammation. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.T.; Liu, S.W.; Chi, P.L.; Lin, C.C.; Hsiao, L.D.; Yang, C.M. TNF-alpha mediates PKCdelta/JNK1/2/c-Jun-dependent monocyte adhesion via ICAM-1 induction in human retinal pigment epithelial cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117911. [Google Scholar]
- Ozal, S.A.; Turkekul, K.; Gurlu, V.; Guclu, H.; Erdogan, S. Esculetin Protects Human Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells from Lipopolysaccharide-induced Inflammation and Cell Death. Curr. Eye Res. 2018, 43, 1169–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oeckinghaus, A.; Hayden, M.S.; Ghosh, S. Crosstalk in NF-κB signaling pathways. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Lin, J.M.; Li, X.S.; Li, J. Quercetin ameliorates LPS-induced inflammation in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells by inhibition of the TLR2-NF-kappaB pathway. Genet. Mol. Res. 2016, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indra, M.R.; Karyono, S.; Ratnawati, R.; Malik, S.G. Quercetin suppresses inflammation by reducing ERK1/2 phosphorylation and NF kappa B activation in Leptin-induced Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells (HUVECs). BMC Res. Notes 2013, 6, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granado-Serrano, A.B.; Martin, M.A.; Bravo, L.; Goya, L.; Ramos, S. Quercetin attenuates TNF-induced inflammation in hepatic cells by inhibiting the NF-kappaB pathway. Nutr. Cancer 2012, 64, 588–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Meng, X.; Yuan, Y.; Shen, F.; Li, C.; Yang, J. Quercetin exerts cardiovascular protective effects in LPS-induced dysfunction in vivo by regulating inflammatory cytokine expression, NF-kappaB phosphorylation, and caspase activity. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 446, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Gong, X.; Yang, Y.; Huang, L.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, P.; Wan, R.; Zhang, B. Hepatoprotective effect of quercetin against LPS/d-GalN induced acute liver injury in mice by inhibiting the IKK/NF-kappaB and MAPK signal pathways. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 52, 281–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.L.; Huang, W.C.; Cheng, S.C.; Liou, C.J. Fisetin inhibits the generation of inflammatory mediators in interleukin-1beta-induced human lung epithelial cells by suppressing the NF-kappaB and ERK1/2 pathways. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 60, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambati, J.; Atkinson, J.P.; Gelfand, B.D. Immunology of age-related macular degeneration. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 438–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugeswari, P.; Shukla, D.; Kim, R.; Namperumalsamy, P.; Stitt, A.W.; Muthukkaruppan, V. Angiogenic potential of vitreous from Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy and Eales’ Disease patients. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ehlers, J.P.; Fekrat, S. Retinal vein occlusion: Beyond the acute event. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2011, 56, 281–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitcup, S.M.; Nussenblatt, R.B.; Lightman, S.L.; Hollander, D.A. Inflammation in retinal disease. Int. J. Inflam. 2013, 2013, 724648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Bai, Y.; Xie, W.; Shi, X.; Li, F.; Yang, F.; Sun, Y.; Huang, L.; Li, X. Interleukin-1beta Level Is Increased in Vitreous of Patients with Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration (nAMD) and Polypoidal Choroidal Vasculopathy (PCV). PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125150. [Google Scholar]
- Kuppner, M.C.; McKillop-Smith, S.; Forrester, J.V. TGF-beta and IL-1 beta act in synergy to enhance IL-6 and IL-8 mRNA levels and IL-6 production by human retinal pigment epithelial cells. Immunology 1995, 84, 265–271. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lechner, J.; Chen, M.; Hogg, R.E.; Toth, L.; Silvestri, G.; Chakravarthy, U.; Xu, H. Alterations in Circulating Immune Cells in Neovascular Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elner, V.M.; Scales, W.; Elner, S.G.; Danforth, J.; Kunkel, S.L.; Strieter, R.M. Interleukin-6 (IL-6) gene expression and secretion by cytokine-stimulated human retinal pigment epithelial cells. Exp. Eye Res. 1992, 54, 361–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benson, M.T.; Shepherd, L.; Rees, R.C.; Rennie, I.G. Production of interleukin-6 by human retinal pigment epithelium in vitro and its regulation by other cytokines. Curr. Eye Res. 1992, 11, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elner, V.M.; Strieter, R.M.; Elner, S.G.; Baggiolini, M.; Lindley, I.; Kunkel, S.L. Neutrophil chemotactic factor (IL-8) gene expression by cytokine-treated retinal pigment epithelial cells. Am. J. Pathol. 1990, 136, 745–750. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.T.; Chen, P.L.; Chang, Y.H.; Chien, M.W.; Chen, Y.H.; Lu, D.W. Glucosamine sulfate inhibits leukocyte adhesion in response to cytokine stimulation of retinal pigment epithelial cells in vitro. Exp. Eye Res. 2006, 83, 1052–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elner, S.G.; Strieter, R.M.; Elner, V.M.; Rollins, B.J.; Del Monte, M.A.; Kunkel, S.L. Monocyte chemotactic protein gene expression by cytokine-treated human retinal pigment epithelial cells. Lab. Invest. 1991, 64, 819–825. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Froio, R.M.; Sciuto, T.E.; Dvorak, A.M.; Alon, R.; Luscinskas, F.W. ICAM-1 regulates neutrophil adhesion and transcellular migration of TNF-alpha-activated vascular endothelium under flow. Blood 2005, 106, 584–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitcup, S.M.; Chan, C.C.; Li, Q.; Nussenblatt, R.B. Expression of cell adhesion molecules in posterior uveitis. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1992, 110, 662–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.T.; Liang, J.B.; Chou, C.L.; Chien, M.W.; Shyu, R.C.; Chou, P.I.; Lu, D.W. Glucosamine sulfate inhibits TNF-alpha and IFN-gamma-induced production of ICAM-1 in human retinal pigment epithelial cells in vitro. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2006, 47, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Rothlein, R.; Mainolfi, E.A.; Czajkowski, M.; Marlin, S.D. A form of circulating ICAM-1 in human serum. J. Immunol. 1991, 147, 3788–3793. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Witkowska, A.M.; Borawska, M.H. Soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (sICAM-1): An overview. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2004, 15, 91–98. [Google Scholar]
- Whiteman, S.C.; Bianco, A.; Knight, R.A.; Spiteri, M.A. Human rhinovirus selectively modulates membranous and soluble forms of its intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) receptor to promote epithelial cell infectivity. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 11954–11961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakatsuki, T.; Kimura, K.; Kimura, F.; Shinomiya, N.; Ohtsubo, M.; Ishizawa, M.; Yamamoto, M. A distinct mRNA encoding a soluble form of ICAM-1 molecule expressed in human tissues. Cell Adhes. Commun. 1995, 3, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, M.; Wielkoszynski, T.; Marek, B.; Kos-Kudla, B.; Swietochowska, E.; Sieminska, L.; Kajdaniuk, D.; Glogowska-Szelag, J.; Nowak, K. Blood serum levels of vascular cell adhesion molecule (sVCAM-1), intercellular adhesion molecule (sICAM-1) and endothelial leucocyte adhesion molecule-1 (ELAM-1) in diabetic retinopathy. Clin. Exp. Med. 2008, 8, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bellis, A.; Di Martino, S.; Fiordelisi, F.; Muccitelli, V.I.; Sinisi, A.A.; Abbate, G.F.; Gargano, D.; Bellastella, A.; Bizzarro, A. Soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (sICAM-1) concentrations in Graves’ disease patients followed up for development of ophthalmopathy. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1998, 83, 1222–1225. [Google Scholar]
- Zaman, A.G.; Edelsten, C.; Stanford, M.R.; Graham, E.M.; Ellis, B.A.; Direskeneli, H.; D’Cruz, D.P.; Hughes, G.R.; Dumonde, D.C.; Wallace, G.R. Soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (sICAM-1) as a marker of disease relapse in idiopathic uveoretinitis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1994, 95, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozderya, A.; Aydin, K.; Temizkan, S.; Dogru Abbasoglu, S.; Vural, P.; Altuntas, Y. High circulating levels of sICAM-1 and sVCAM-1 in the patients with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis. Endocr. Res. 2017, 42, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fathollahi, A.; Massoud, A.; Amirzargar, A.A.; Aghili, B.; Nasli Esfahani, E.; Rezaei, N. sICAM-1, sVCAM-1 and sE-Selectin Levels in Type 1 Diabetes. Fetal Pediatr. Pathol. 2018, 37, 69–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Pablo, R.; Monserrat, J.; Reyes, E.; Diaz, D.; Rodriguez-Zapata, M.; de la Hera, A.; Prieto, A.; Alvarez-Mon, M. Circulating sICAM-1 and sE-Selectin as biomarker of infection and prognosis in patients with systemic inflammatory response syndrome. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2013, 24, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klimiuk, P.A.; Fiedorczyk, M.; Sierakowski, S.; Chwiecko, J. Soluble cell adhesion molecules (sICAM-1, sVCAM-1, and sE-selectin) in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2007, 36, 345–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, P.; Demel, U.; Tilz, G.P.; Krejs, G.J. Time course of plasma soluble intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (sICAM-1) is related to severity of acute pancreatitis. Hepatogastroenterology 1999, 46, 2565–2571. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Planck, S.R.; Dang, T.T.; Graves, D.; Tara, D.; Ansel, J.C.; Rosenbaum, J.T. Retinal pigment epithelial cells secrete interleukin-6 in response to interleukin-1. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1992, 33, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sprague, A.H.; Khalil, R.A. Inflammatory cytokines in vascular dysfunction and vascular disease. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2009, 78, 539–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, T.; Narazaki, M.; Kishimoto, T. IL-6 in inflammation, immunity, and disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a016295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmane, S.L.; Kremlev, S.; Amini, S.; Sawaya, B.E. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1): An overview. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2009, 29, 313–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, M.; Hasanreisoglu, M.; Feldman, A.; Axer-Siegel, R.; Sonis, P.; Maharshak, I.; Monselise, Y.; Gurevich, M.; Weinberger, D. Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in the aqueous humour of patients with age-related macular degeneration. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2012, 40, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, E.B. Inflammation in dry age-related macular degeneration. Ophthalmologica 2007, 221, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Z.J.; Li, P.; Wang, L. Magnetic nanoparticles conjugated with “RPE cell -MCP-1 antibody -VEGF antibody” compounds for the targeted therapy of age-related macular degeneration: A hypothesis. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2017, 10, 812–814. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Izumi-Nagai, K.; Nagai, N.; Ozawa, Y.; Mihara, M.; Ohsugi, Y.; Kurihara, T.; Koto, T.; Satofuka, S.; Inoue, M.; Tsubota, K.; et al. Interleukin-6 receptor-mediated activation of signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 (STAT3) promotes choroidal neovascularization. Am. J. Pathol. 2007, 170, 2149–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Z.; Wu, X.; Song, M.; Li, P.; Wang, L. Oxidative damage induces MCP-1 secretion and macrophage aggregation in age-related macular degeneration (AMD). Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2016, 254, 2469–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.S.; Lee, H.J.; Choi, S.H.; Chang, E.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, E.J. Quercetin inhibits IL-1beta-induced inflammation, hyaluronan production and adipogenesis in orbital fibroblasts from Graves’ orbitopathy. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e26261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abengozar-Vela, A.; Calonge, M.; Stern, M.E.; Gonzalez-Garcia, M.J.; Enriquez-De-Salamanca, A. Quercetin and Resveratrol Decrease the Inflammatory and Oxidative Responses in Human Ocular Surface Epithelial Cells. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2015, 56, 2709–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, S.C.; Wu, Y.H.; Huang, W.C.; Pang, J.S.; Huang, T.H.; Cheng, C.Y. Anti-inflammatory property of quercetin through downregulation of ICAM-1 and MMP-9 in TNF-alpha-activated retinal pigment epithelial cells. Cytokine 2019, 116, 48–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Hollborn, M.; Grosche, A.; Reichenbach, A.; Wiedemann, P.; Bringmann, A.; Kohen, L. Effects of the vegetable polyphenols epigallocatechin-3-gallate, luteolin, apigenin, myricetin, quercetin, and cyanidin in primary cultures of human retinal pigment epithelial cells. Mol. Vis. 2014, 20, 242–258. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Kim, H.J.; Sparrow, J.R. Quercetin and cyanidin-3-glucoside protect against photooxidation and photodegradation of A2E in retinal pigment epithelial cells. Exp. Eye Res. 2017, 160, 45–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neil, J.D.; Ammit, A.J.; Clark, A.R. MAPK p38 regulates inflammatory gene expression via tristetraprolin: Doing good by stealth. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2018, 94, 6–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krupkova, O.; Sadowska, A.; Kameda, T.; Hitzl, W.; Hausmann, O.N.; Klasen, J.; Wuertz-Kozak, K. p38 MAPK Facilitates Crosstalk Between Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and IL-6 Release in the Intervertebral Disc. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.F.; Wang, Y.L.; Gao, C.; Gu, Y.T.; Huang, J.; Wang, J.H.; Wang, J.H.; Zhang, Z. Salvianolic acid A attenuates kidney injury and inflammation by inhibiting NF-kappaB and p38 MAPK signaling pathways in 5/6 nephrectomized rats. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2018, 39, 1855–1864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, P.A.; Braune, A.; Holzlwimmer, G.; Quintanilla-Fend, L.; Haller, D. Quercetin inhibits TNF-induced NF-kappaB transcription factor recruitment to proinflammatory gene promoters in murine intestinal epithelial cells. J. Nutr. 2007, 137, 1208–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerszten, R.E.; Garcia-Zepeda, E.A.; Lim, Y.C.; Yoshida, M.; Ding, H.A.; Gimbrone, M.A., Jr.; Luster, A.D.; Luscinskas, F.W.; Rosenzweig, A. MCP-1 and IL-8 trigger firm adhesion of monocytes to vascular endothelium under flow conditions. Nature 1999, 398, 718–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiraoka, M.; Nitta, N.; Nagai, M.; Shimokado, K.; Yoshida, M. MCP-1-induced enhancement of THP-1 adhesion to vascular endothelium was modulated by HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor through RhoA GTPase-, but not ERK1/2-dependent pathway. Life Sci. 2004, 75, 1333–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.R.; Hsieh, S.L.; Ho, F.M.; Lin, W.W. Decoy receptor 3 increases monocyte adhesion to endothelial cells via NF-kappa B-dependent up-regulation of intercellular adhesion molecule-1, VCAM-1, and IL-8 expression. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 1647–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liou, C.J.; Lai, Y.R.; Chen, Y.L.; Chang, Y.H.; Li, Z.Y.; Huang, W.C. Matrine Attenuates COX-2 and ICAM-1 Expressions in Human Lung Epithelial Cells and Prevents Acute Lung Injury in LPS-Induced Mice. Mediators Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 3630485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| Gene | Primers | (5′-3′ Sequence) | GenBank Accession Number | Product Size (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-6 | Forward Reverse | TCGGTCCAGTTGCCTTCTC GAGGTGAGTGGCTGTCTGT | NM_000600 | 121 |
| IL-8 | Forward Reverse | GCAGAGGGTTGTGGAGAAGT TGGCATCTTCACTGATTCTTGG | NM_000584 | 90 |
| MCP-1 | Forward Reverse | GAATCACCAGCAGCAAGTGT GAGTGTTCAAGTCTTCGGAGTT | NM_002982 | 149 |
| ICAM-1 | Forward Reverse | ACCATCTACAGCTTTCCGGC CTGAGACCTCTGGCTTCGTC | NM_000201.2 | 55 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cheng, S.-C.; Huang, W.-C.; S. Pang, J.-H.; Wu, Y.-H.; Cheng, C.-Y. Quercetin Inhibits the Production of IL-1β-Induced Inflammatory Cytokines and Chemokines in ARPE-19 Cells via the MAPK and NF-κB Signaling Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2957. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20122957
Cheng S-C, Huang W-C, S. Pang J-H, Wu Y-H, Cheng C-Y. Quercetin Inhibits the Production of IL-1β-Induced Inflammatory Cytokines and Chemokines in ARPE-19 Cells via the MAPK and NF-κB Signaling Pathways. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(12):2957. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20122957
Chicago/Turabian StyleCheng, Shu-Chen, Wen-Chung Huang, Jong-Hwei S. Pang, Yi-Hong Wu, and Ching-Yi Cheng. 2019. "Quercetin Inhibits the Production of IL-1β-Induced Inflammatory Cytokines and Chemokines in ARPE-19 Cells via the MAPK and NF-κB Signaling Pathways" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 12: 2957. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20122957
APA StyleCheng, S.-C., Huang, W.-C., S. Pang, J.-H., Wu, Y.-H., & Cheng, C.-Y. (2019). Quercetin Inhibits the Production of IL-1β-Induced Inflammatory Cytokines and Chemokines in ARPE-19 Cells via the MAPK and NF-κB Signaling Pathways. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(12), 2957. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20122957