Material Characterization of Magnetorheological Elastomers with Corroded Carbonyl Iron Particles: Morphological Images and Field-dependent Viscoelastic Properties
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussions
2.1. Morphological Results and Discussions
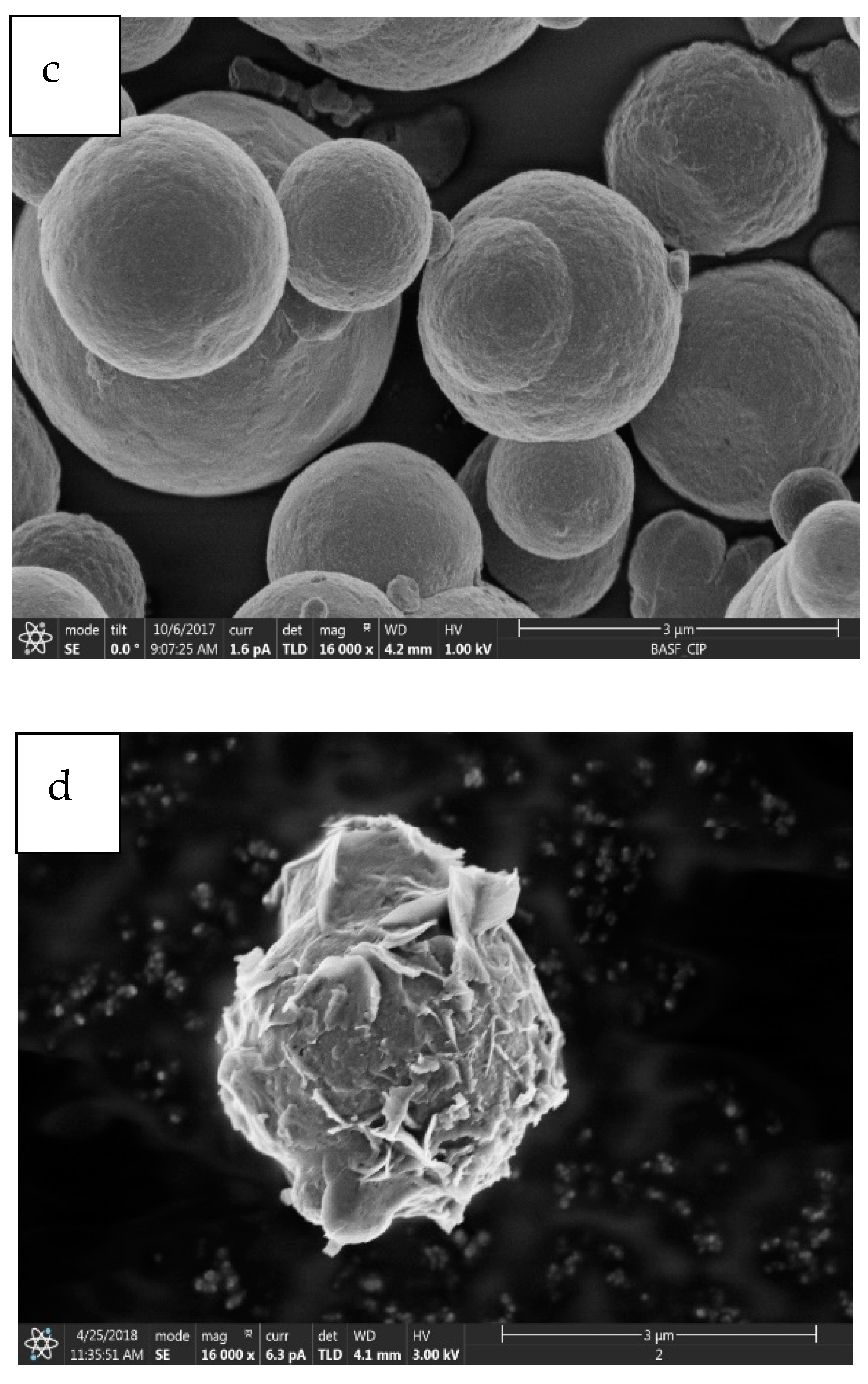
2.1.1. Morphological Properties
2.1.2. Phase Characterization
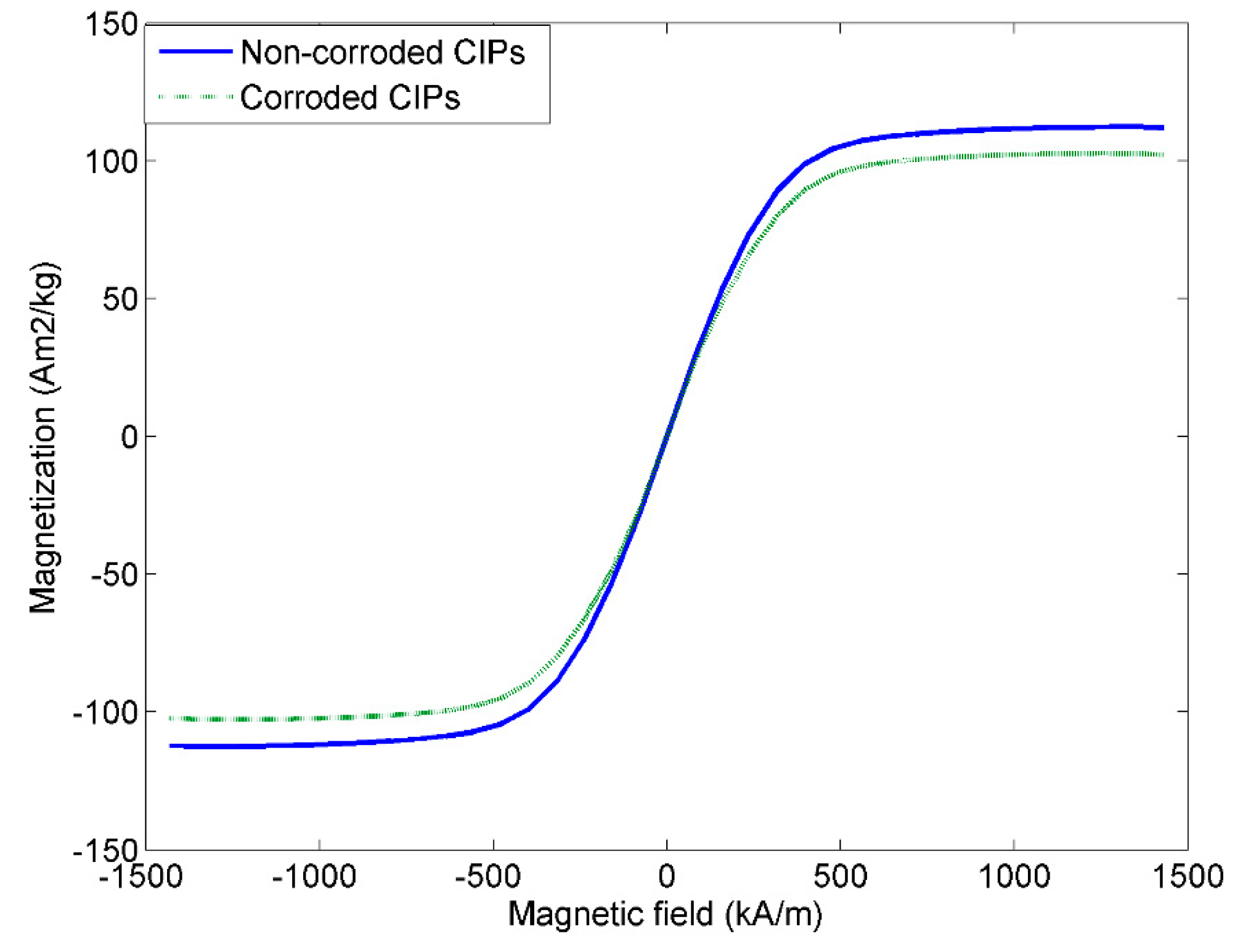
2.1.3. Vibrating Sample Magnetometer
2.2. Rheological Results and Discussions
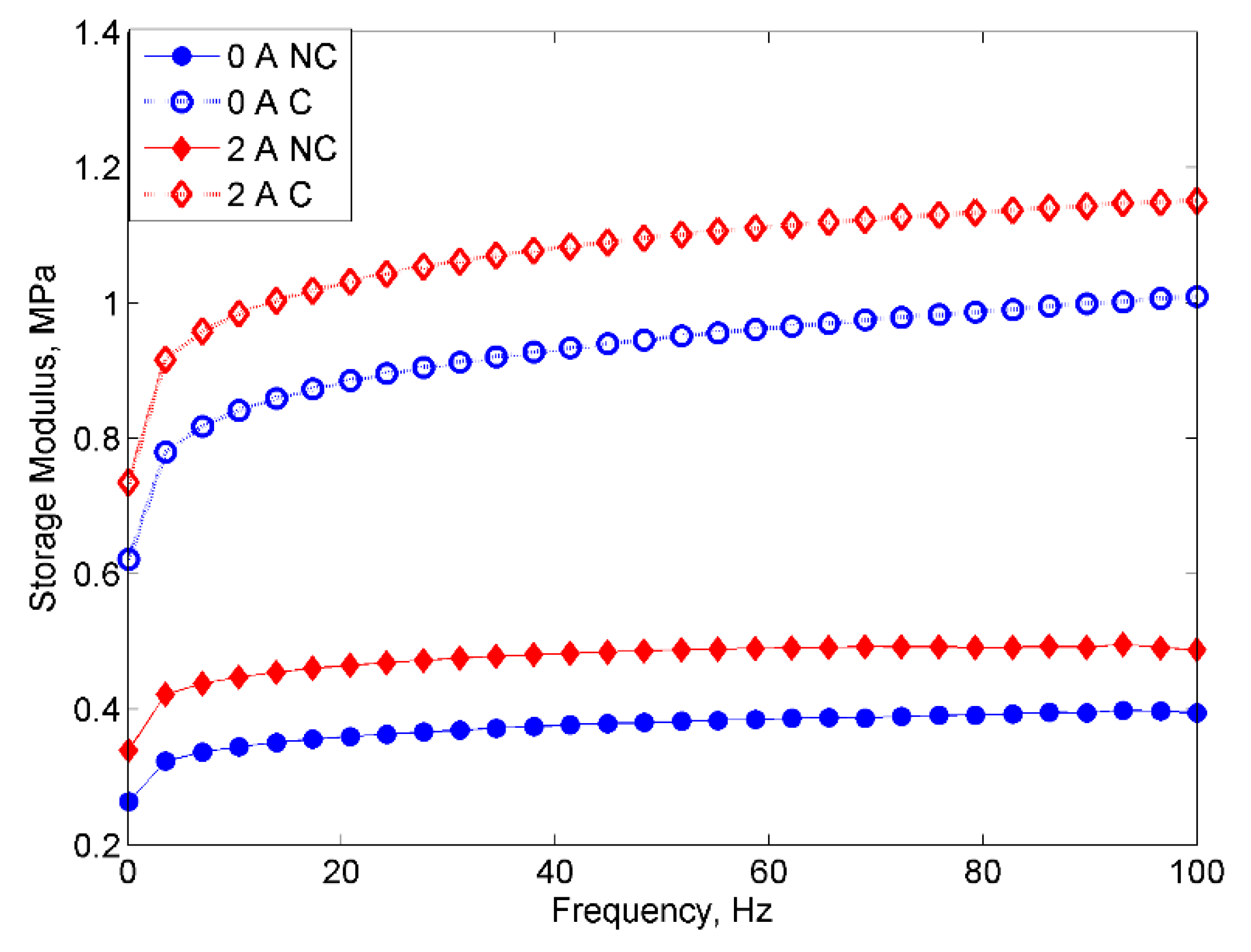
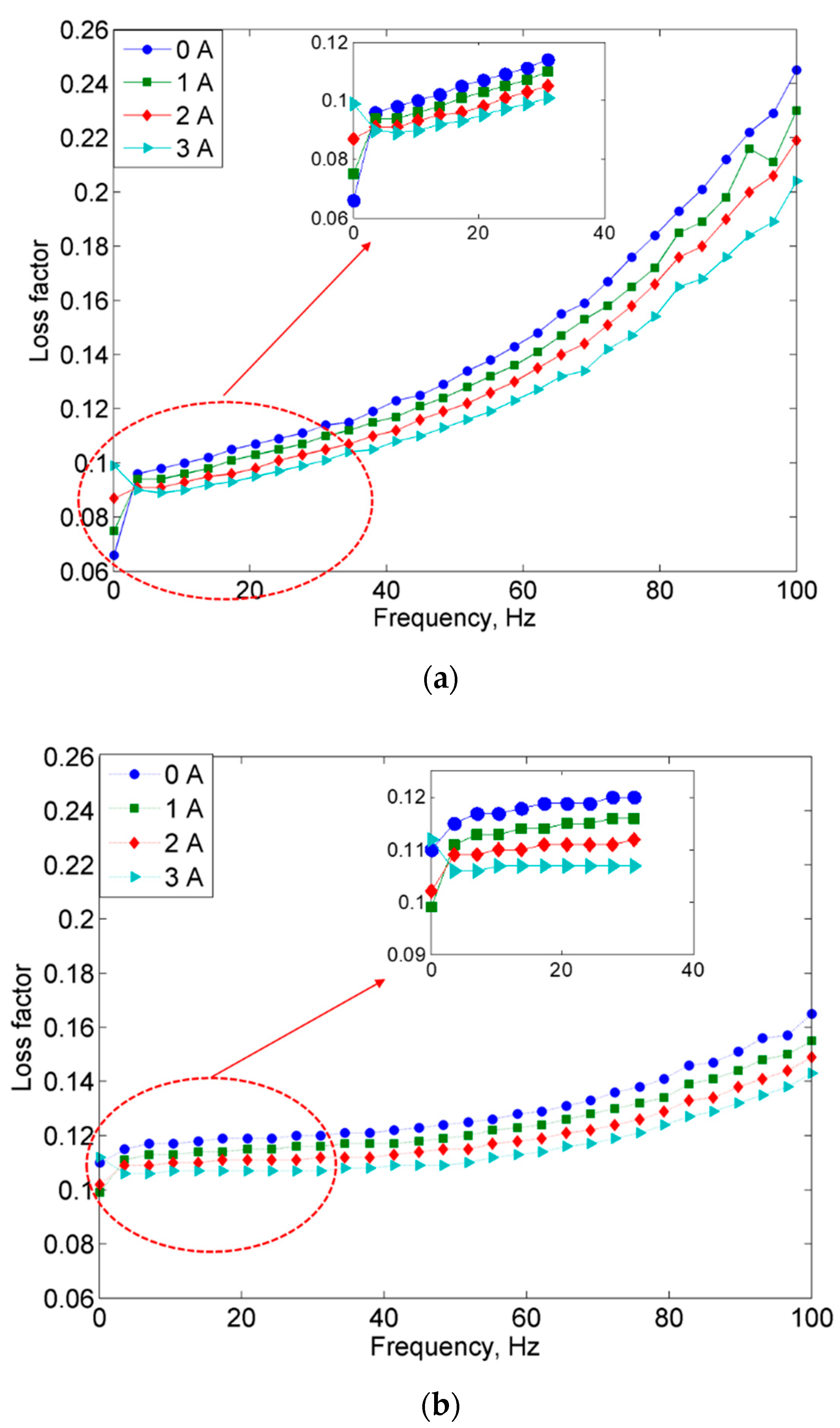
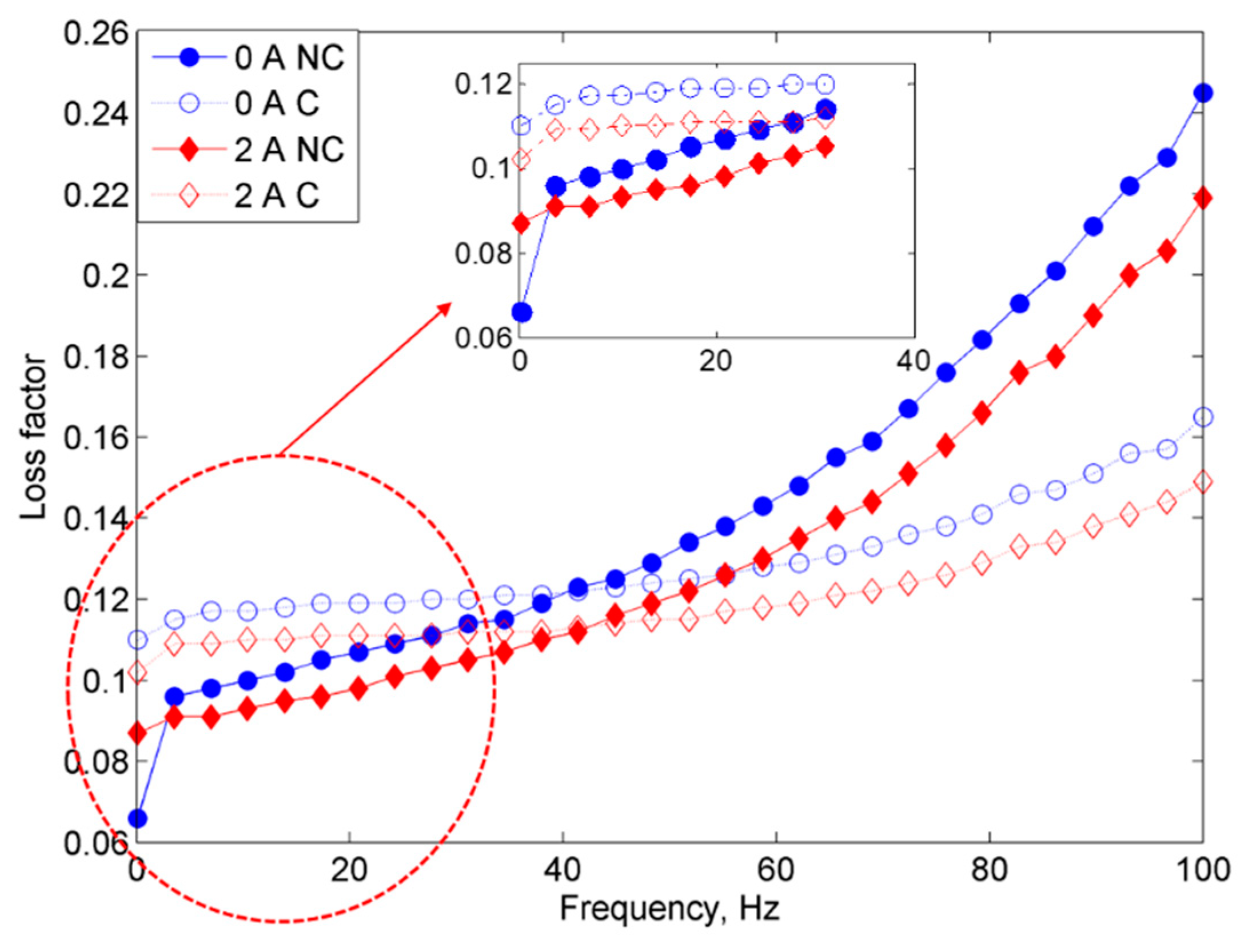
2.2.1. Frequency Sweep Test
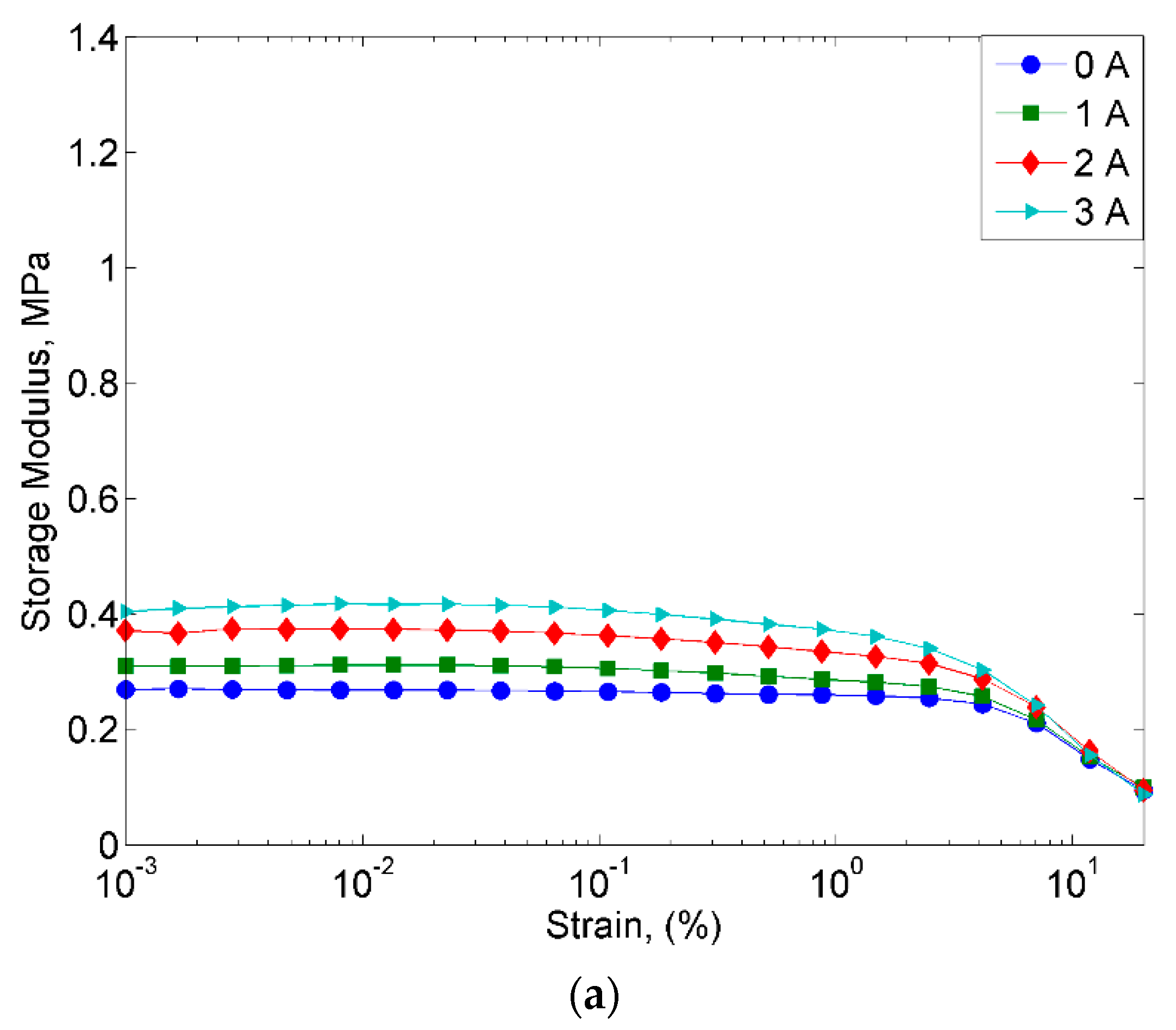
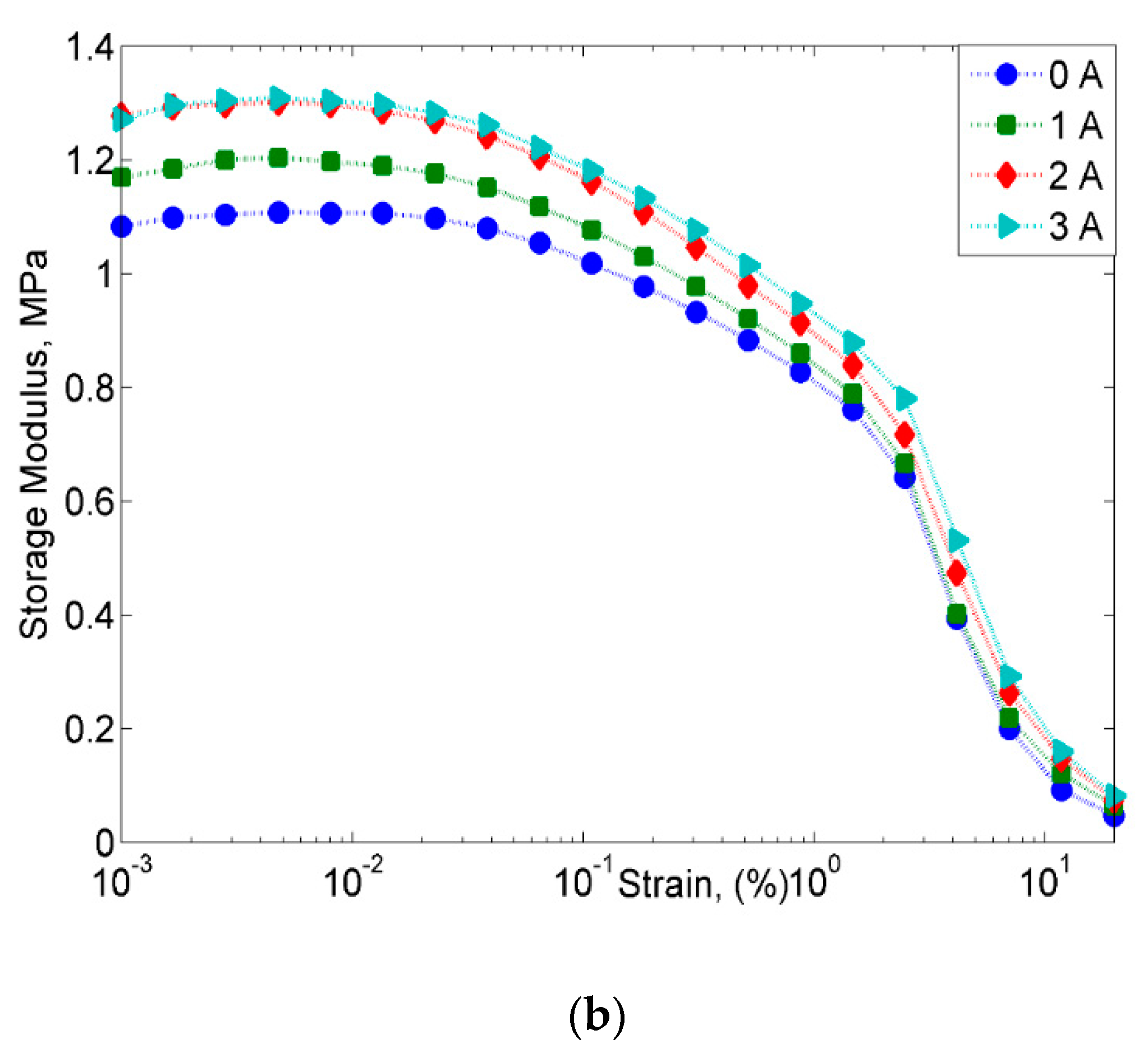
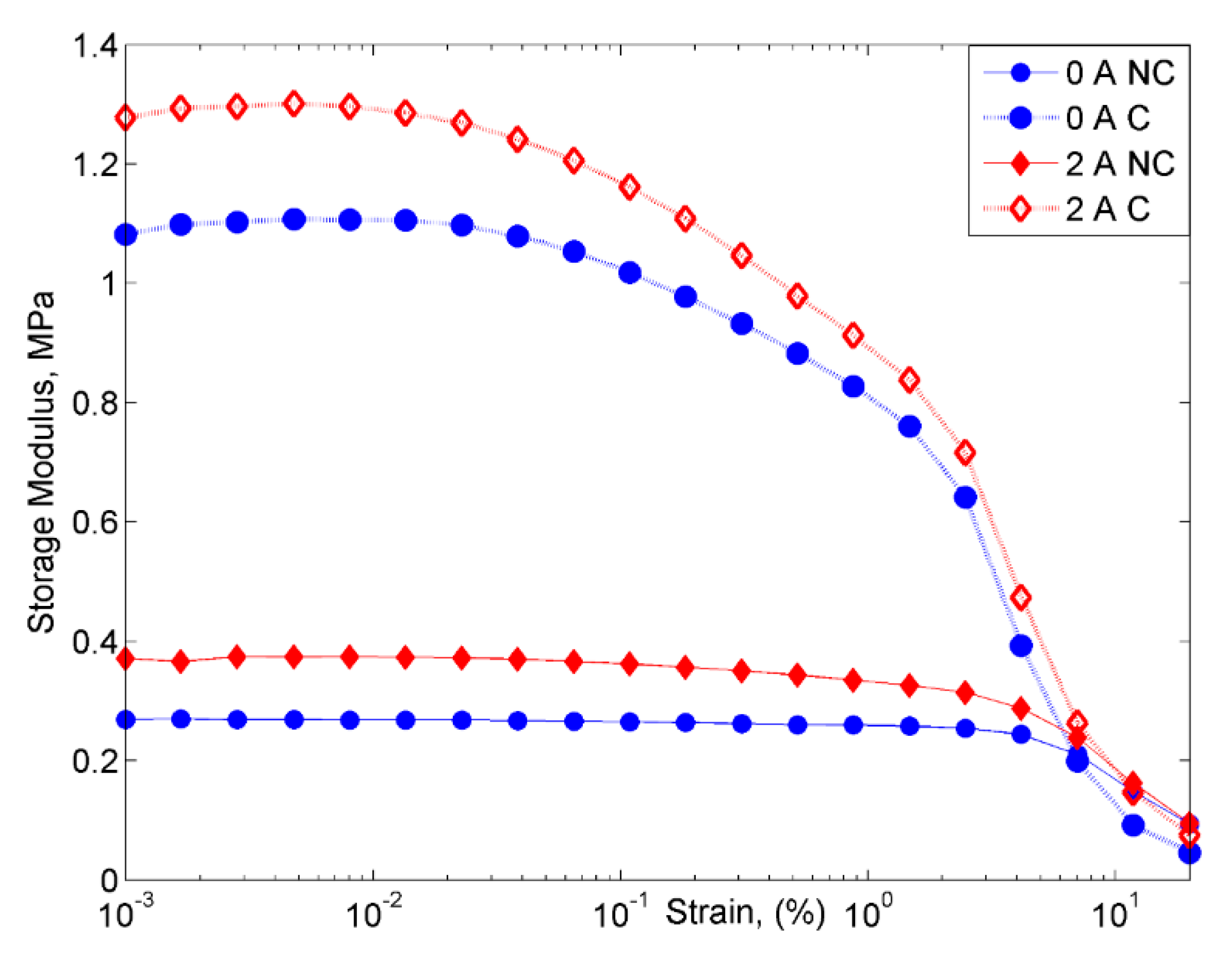
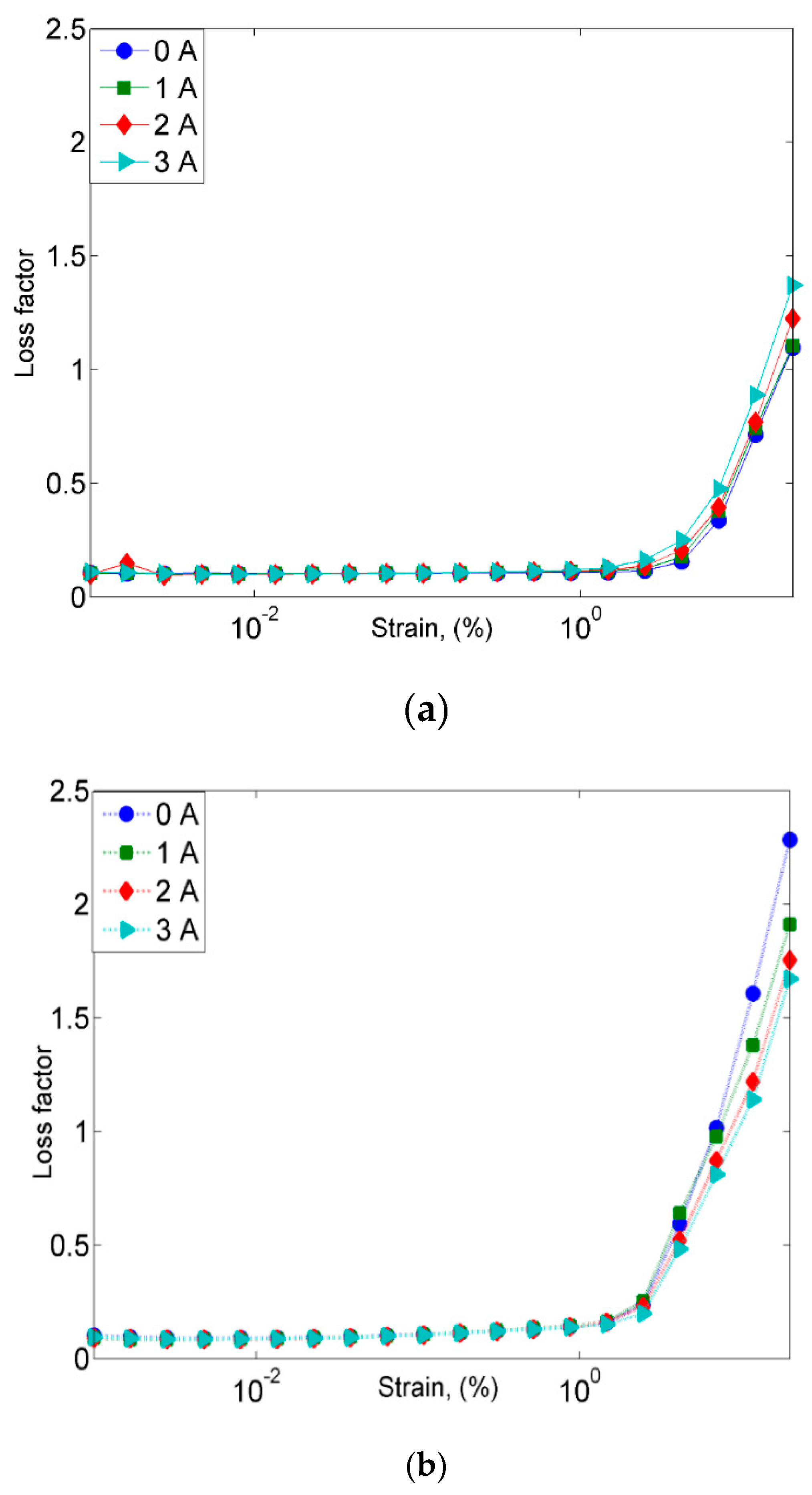
2.2.2. Strain Sweep Test
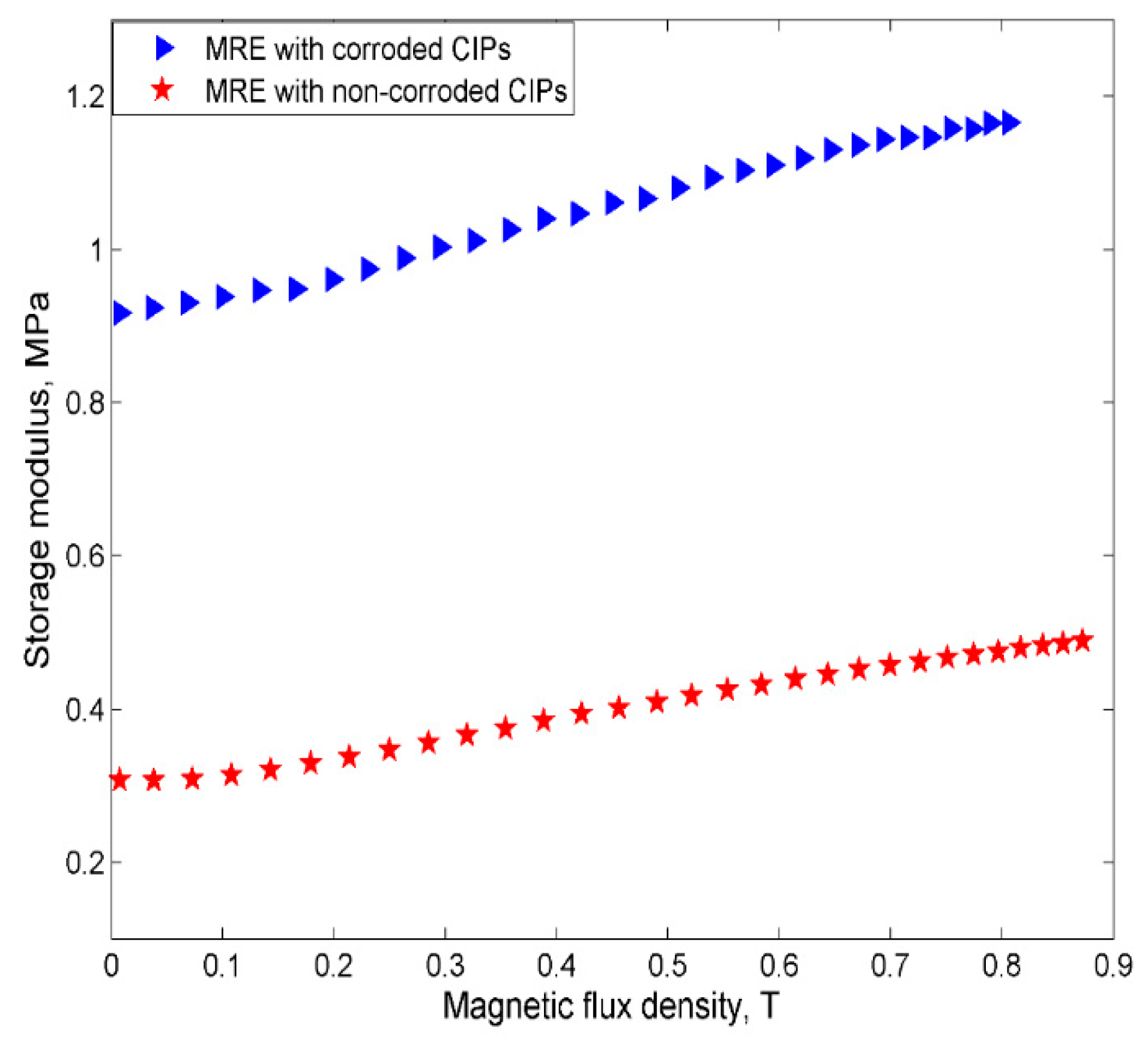
2.2.3. Current Sweep Test
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Samples Preparation
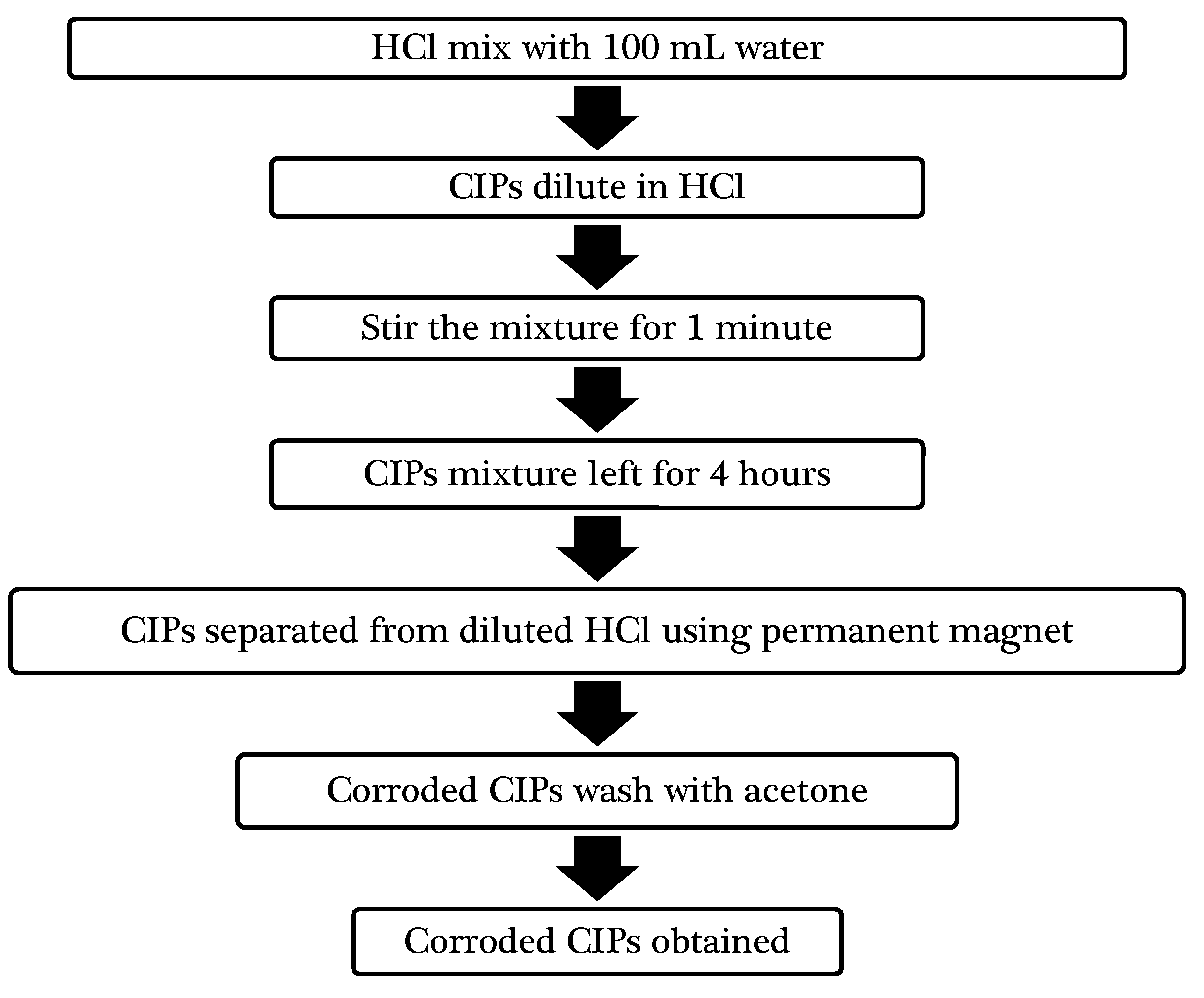
3.1.1. Corroded CIPs
3.1.2. MRE Fabrication
3.1.3. MRE Characterization
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- It has been observed that the increment of almost 23 wt% of oxygen in the corroded CIPs exhibited a higher oxidized condition in the CIPs. From the physiochemical analyses, the corroded CIPs modified the bonding strength between the CIPs as a result of new outer layers formed from the wetting process during the immersion process.
- (2)
- The outer layers of corroded CIPs significantly altered the magnetic behavior of the CIPs by slightly reducing the magnetic saturation of the corroded CIPs by almost 10%.
- (3)
- However, despite the deterioration of the magnetic properties, the rheological properties such as storage modulus of the MRE with corroded CIPs exhibited an increasing trend in both off- and on-state conditions.
- (4)
- The result also revealed the “bridge”, which occurred during the corrosion process, to have enhanced bonding between CIPs by strengthening the connection between the magnetic particles.
- (5)
- On the other hand, the damping properties MRE with non-corroded CIPs displayed a declining trend with the increasing magnetic fields in the frequency sweep, which contradicted with the results obtained from the strain sweep analysis.
- (6)
- Since the MR effect of the corroded CIPs decreased by up to 114% as compared to the non-corroded CIPs, the findings from this study assert that the MRE reactivity can be affected by the chemical reactions of corrosion and the change in the field-dependent rheological properties is quite “unpredictable”.
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aziz, S.A.A.; Mazlan, S.A.; Ismail, N.I.N.; Ubaidillah; Choi, S.B.; Nordin, N.A.; Mohamad, N. A comparative assessment of different dispersing aids in enhancing magnetorheological elastomer properties. Smart Mater. Struct. 2018, 27, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, L.; Gong, X.; Fan, Y.; Xuan, S. Preparation and mechanical properties of the magnetorheological elastomer based on natural rubber/rosin glycerin hybrid matrix. Smart Mater. Struct. 2013, 22, 115029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sorokin, V.V.; Ecker, E.; Stepanov, G.V.; Shamonin, M.; Monkman, G.J.; Kramarenko, E.Y.; Khokhlov, A.R. Experimental study of the magnetic field enhanced Payne effect in magnetorheological elastomers. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 8765–8776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hapipi, N.; Aziz, S.A.A.; Mazlan, S.A.; Ubaidillah; Choi, S.B.; Mohamad, N.; Khairi, M.H.A.; Fatah, A.Y.A. The field-dependent rheological properties of plate-like carbonyl iron particle-based magnetorheological elastomers. Results Phys. 2019, 12, 2146–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad Khairi, M.H.; Mazlan, S.A.; Ubaidillah; Ku Ahmad, K.Z.; Choi, S.-B.; Abdul Aziz, S.A.; Yunus, N.A. The field-dependent complex modulus of magnetorheological elastomers consisting of sucrose acetate isobutyrate ester. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2017, 28, 1993–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, G.; Harrison, P. Large-strain behavior of Magneto-Rheological Elastomers tested under uniaxial compression and tension, and pure shear deformations. Polym. Test. 2015, 42, 122–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elie, L.D.; Ginder, J.M.; Stewart, W.M.; Nichols, M.E. Variable stiffness bushing using magnetorheological elastomers. Eur. Pat. Appl. 96307979.3, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Wahab, N.A.A.; Mazlan, S.A.; Ubaidillah; Kamaruddin, S.; Ismail, N.I.N.; Choi, S.B.; Sharif, A.H.R. Fabrication and investigation on field-dependent properties of natural rubber based magneto-rheological elastomer isolator. Smart Mater. Struct. 2016, 25, 107002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, J. Finite element design and analysis of adaptive base isolator utilizing laminated multiple magnetorheological elastomer layers. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2015, 26, 1861–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorsteinsson, F.; Gudmundsson, I.; Lecomte, C. Prosthetic and Orthotic Devices Having Magnetorheological Elastomer Spring with Controllable Stiffness. U.S. Patent 10010434, 28 July 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Shabdin, M.K.; Rahman, M.A.A.; Mazlan, S.A.; Ubaidillah; Hapipi, N.M.; Adiputra, D.; Aziz, S.A.A.; Bahiuddin, I.; Choi, S.B. Material characterizations of gr-based magnetorheological elastomer for possible sensor applications: Rheological and resistivity properties. Materials (Basel) 2019, 12, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, T.F.; Li, W.H.; Deng, Y.M. Sensing capabilities of graphite based MR elastomers. Smart Mater. Struct. 2011, 20, 025022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, F.; Lan, X.; Zhou, Y. Effects of aging on the structural, mechanical, and thermal properties of the silicone rubber current transformer insulation bushing for a 500 kV substation. Springerplus 2016, 5, 790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Shou, J.-Q.; Zhang, Z.-Y.; Zhao, G.-Z.; Liu, Y.-Q. Effect of curing temperature on properties of semi-efficient vulcanized natural rubber. J. Elastomers Plast. 2016, 48, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashi, S.; Varley, R.; De Souza, M.; Al-Assafi, S.; Di Pietro, A.; de Lavigne, C.; Fox, B. Mechanical, Thermal, and Morphological Behavior of Silicone Rubber during Accelerated Aging. Polym. Plast. Technol. Eng. 2018, 57, 1687–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, D.; Lin, Y.; Ma, H.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Deng, K. Experimental studies on CO2 corrosion of rubber materials for packer under compressive stress in gas wells. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2017, 80, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarlin, E.; Hoikkanen, M.; Frisk, L.; Vuorinen, J.; Vippola, M.; Lepistö, T. Ageing of corrosion resistant steel/rubber/composite hybrid structures. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2014, 49, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozawa, K.; Kakubo, T.; Shimizu, K.; Amino, N.; Mase, K.; Izumi, Y.; Muro, T.; Komatsu, T. High-resolution photoelectron spectroscopy study of degradation of rubber-to-brass adhesion by thermal aging. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 268, 117–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Song, Y.W.; Zhang, H.; Yang, H.X.; Song, Z.L. A comparative study on the corrosion behavior of NdFeB magnets in different electrolyte solutions. Mater. Corros. 2008, 59, 794–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, D.S.; Bogart, M.B.; Brossia, C.S.; Cragnolino, G.A. Corrosion of Iron Under Alternating Wet and Dry Conditions. Corrosion 2000, 56, 470–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.-M.; Kim, S.; Park, Y.-D.; Kang, J.-W.; Choi, S.-B. Field-dependent characteristics of magnetorheological fluids containing corroded iron particles. Smart Mater. Struct. 2015, 24, 115016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plachy, T.; Kutalkova, E.; Sedlacik, M.; Vesel, A.; Masar, M.; Kuritka, I. Impact of corrosion process of carbonyl iron particles on magnetorheological behavior of their suspensions. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 66, 362–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cvek, M.; Mrlik, M.; Sevcik, J.; Sedlacik, M. Tailoring Performance, Damping, and Surface Properties of Magnetorheological Elastomers via Particle-Grafting Technology. Polymers (Basel) 2018, 10, 1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngolemasango, E.F.; Bennett, M.; Clarke, J. Kinetics of the effect of ageing on tensile properties of a natural rubber compound. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2006, 102, 3732–3740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Xuan, S.; Guo, C.; Gong, X. Dimorphic magnetorheological fluid with improved rheological properties. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2011, 323, 3246–3250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shilan, S.T.; Mazlan, S.A.; Ido, Y.; Hajalilou, A.; Jeyadevan, B.; Choi, S.-B.; Yunus, N.A. A comparison of field-dependent rheological properties between spherical and plate-like carbonyl iron particles-based magneto-rheological fluids. Smart Mater. Struct. 2016, 25, 095025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, F.F.; Kim, J.H.; Choi, H.J. Synthesis of core–shell structured PS/Fe3O4 microbeads and their magnetorheology. Polymer (Guildf) 2009, 50, 2290–2293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdul Aziz, S.A.; Mazlan, S.A.; Nik Ismail, N.I.; Choi, S.-B.; Ubaidillah; Yunus, N.A.B. An enhancement of mechanical and rheological properties of magnetorheological elastomer with multiwall carbon nanotubes. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2017, 28, 3127–3138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunkara, S.R.; Root, T.W.; Ulicny, J.C.; Klingenberg, D.J. Iron oxidation and its impact on MR behavior. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2009, 149, 012081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostafa, A.; Abouel-Kasem, A.; Bayoumi, M.R.; El-Sebaie, M.G. Rubber-Filler Interactions and Its Effect in Rheological and Mechanical Properties of Filled Compounds. J. Test. Eval. 2010, 38, 101942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oréfice, R.L.; Hench, L.L.; Brennan, A.B. Effect of particle morphology on the mechanical and thermo-mechanical behavior of polymer composites. J. Brazilian Soc. Mech. Sci. 2001, 23, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, L.; Xu, X.; Zhang, J.; Shao, J.; Zhao, Y. Performance of oxidation-reduction potential-based hydrolysis and acidification process for high-strength antibiotic wastewater treatment. Desalin. Water Treat. 2016, 57, 7287–7292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmanian, N.; Naji, A.; Ghadiri, M. Effects of process parameters on granules properties produced in a high shear granulator. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2011, 89, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakhimbayev, S.M.; Tolypina, N.M.; Khakhaleva, E.N. Influence of reactive fillers on concrete corrosion resistance. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2018, 327, 032046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kolman, D.G.; Butt, D.I. Behavior of A Novel SiC/AL2O3/Al Composite Exposed to Chloride Environements. In Passivity and Localized Corrosion: An International Symposium in Honor of Professor Norio Sato; Seo, M., MacDougall, B., Takahashi, H., Kelly, R.G., Eds.; The Electrochemical Society Inc.: Pennington, NJ, USA, 1999; pp. 463–472. ISBN 1-56677-250-8. [Google Scholar]
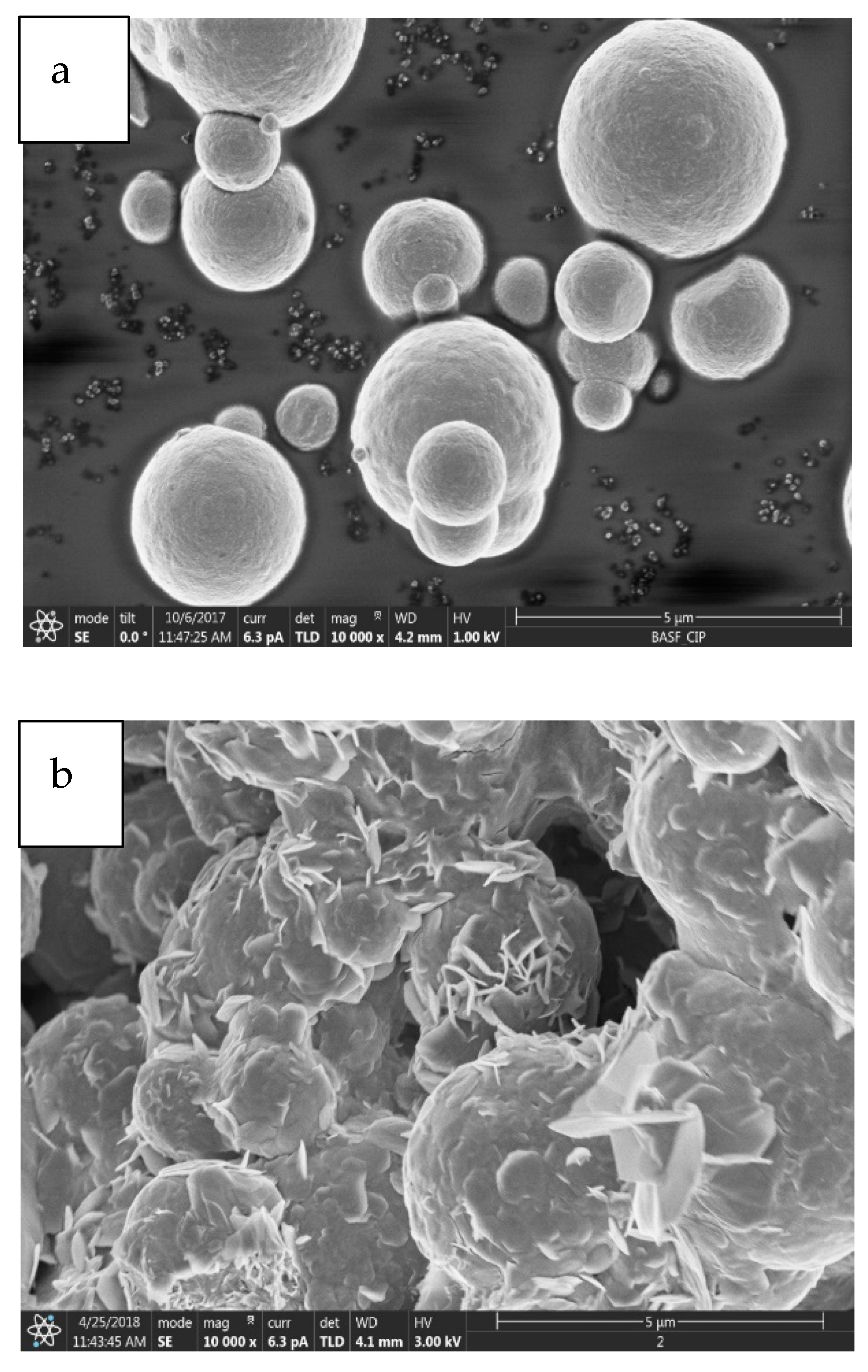

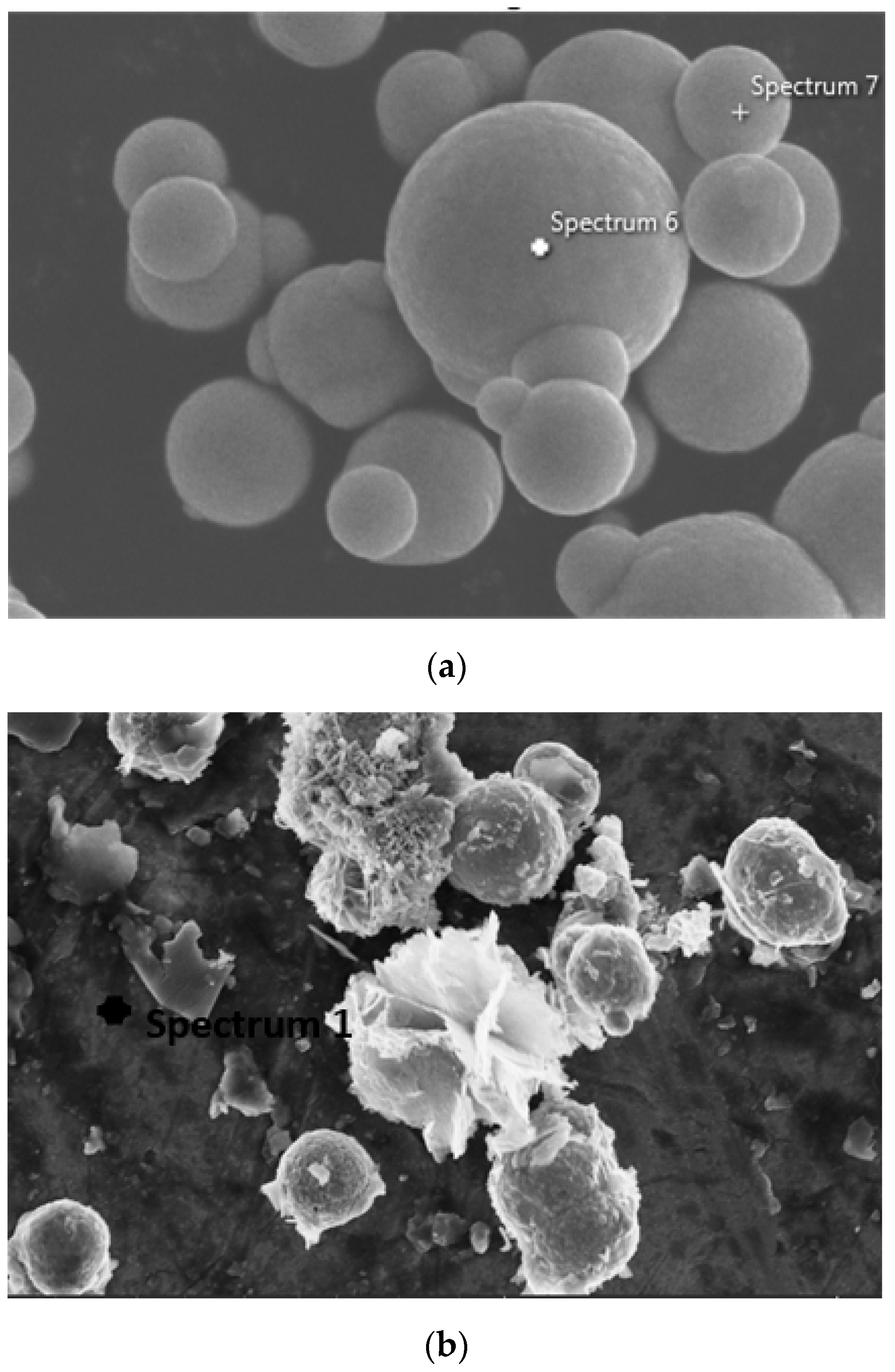



| Sample | Element | Weight % |
|---|---|---|
| Non-corroded CIPs | Fe | 99.79 |
| O | 0.21 | |
| Corroded CIPs | Fe | 77.06 |
| O | 22.94 |
| Samples | Ms (Am2/kg) | Mr (Am2/kg) | Hc (kA/m) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MRE with non-corroded CIPs | 112.3 | 1.30 | 0.70 |
| MRE with corroded CIPs | 102.2 | 1.28 | 0.68 |
| Samples | Initial Storage Modulus | Maximum Storage Modulus | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Current (A) | Current (A) | |||||||
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| MRE with non-corroded particles | 0.26 | 0.29 | 0.34 | 0.39 | 0.38 | 0.43 | 0.49 | 0.55 |
| MRE with corroded CIPs | 0.62 | 0.68 | 0.74 | 0.79 | 1.01 | 1.05 | 1.16 | 1.22 |
| Samples | Initial Storage Modulus (MPa) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Current (A) | ||||
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | |
| MRE with non-corroded particles | 0.26 | 0.31 | 0.37 | 0.40 |
| MRE with corroded CIPs | 1.08 | 1.17 | 1.28 | 1.27 |
| Samples | Initial Modulus, G’ (MPa) | Absolute MR Effect, Δ G’ | MR Effect (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| MRE with non-corroded CIPs | 0.3070 | 0.1817 | 58.19 |
| MRE with corroded CIPs | 0.9168 | 0.2489 | 27.15 |
| Properties | Values/Limits |
|---|---|
| Form | Liquid |
| pH | <1, at 20 °C |
| Relative density | ca. 1.19 g/cm3, at 20 °C |
| Water solubility | Soluble, at 20 °C |
| Corrosion | May corrosive to metals |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aziz, S.A.B.A.; Mazlan, S.A.; Nordin, N.A.; Abd Rahman, N.A.N.; Ubaidillah, U.; Choi, S.-B.; Mohamad, N. Material Characterization of Magnetorheological Elastomers with Corroded Carbonyl Iron Particles: Morphological Images and Field-dependent Viscoelastic Properties. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3311. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20133311
Aziz SABA, Mazlan SA, Nordin NA, Abd Rahman NAN, Ubaidillah U, Choi S-B, Mohamad N. Material Characterization of Magnetorheological Elastomers with Corroded Carbonyl Iron Particles: Morphological Images and Field-dependent Viscoelastic Properties. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(13):3311. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20133311
Chicago/Turabian StyleAziz, Siti Aishah Binti Abdul, Saiful Amri Mazlan, Nur Azmah Nordin, Nor Azlin Nazira Abd Rahman, U Ubaidillah, Seung-Bok Choi, and Norzilawati Mohamad. 2019. "Material Characterization of Magnetorheological Elastomers with Corroded Carbonyl Iron Particles: Morphological Images and Field-dependent Viscoelastic Properties" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 13: 3311. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20133311
APA StyleAziz, S. A. B. A., Mazlan, S. A., Nordin, N. A., Abd Rahman, N. A. N., Ubaidillah, U., Choi, S.-B., & Mohamad, N. (2019). Material Characterization of Magnetorheological Elastomers with Corroded Carbonyl Iron Particles: Morphological Images and Field-dependent Viscoelastic Properties. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(13), 3311. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20133311








