“Biological Adhesion” is a Significantly Regulated Molecular Process during Long-Term Primary In Vitro Culture of Oviductal Epithelial Cells (Oecs): A Transcriptomic and Proteomic Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
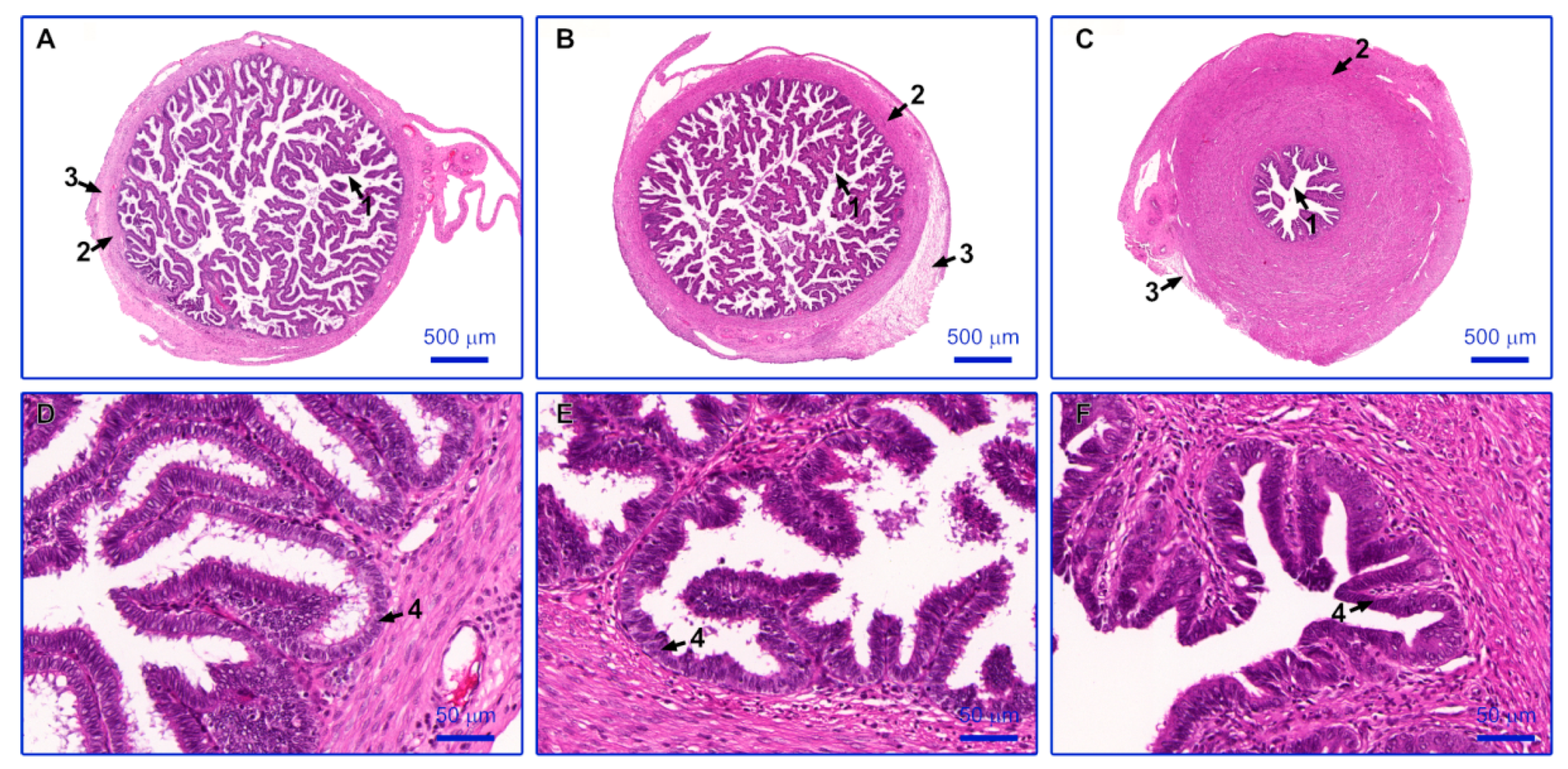
2.1. Histological Evaluation
2.2. Oviductal Epithelial Cell (OEC) Culture
2.3. Microarray Expression Analysis
2.4. nanoLC-MALDI-TOF/TOF MS/MS Analysis
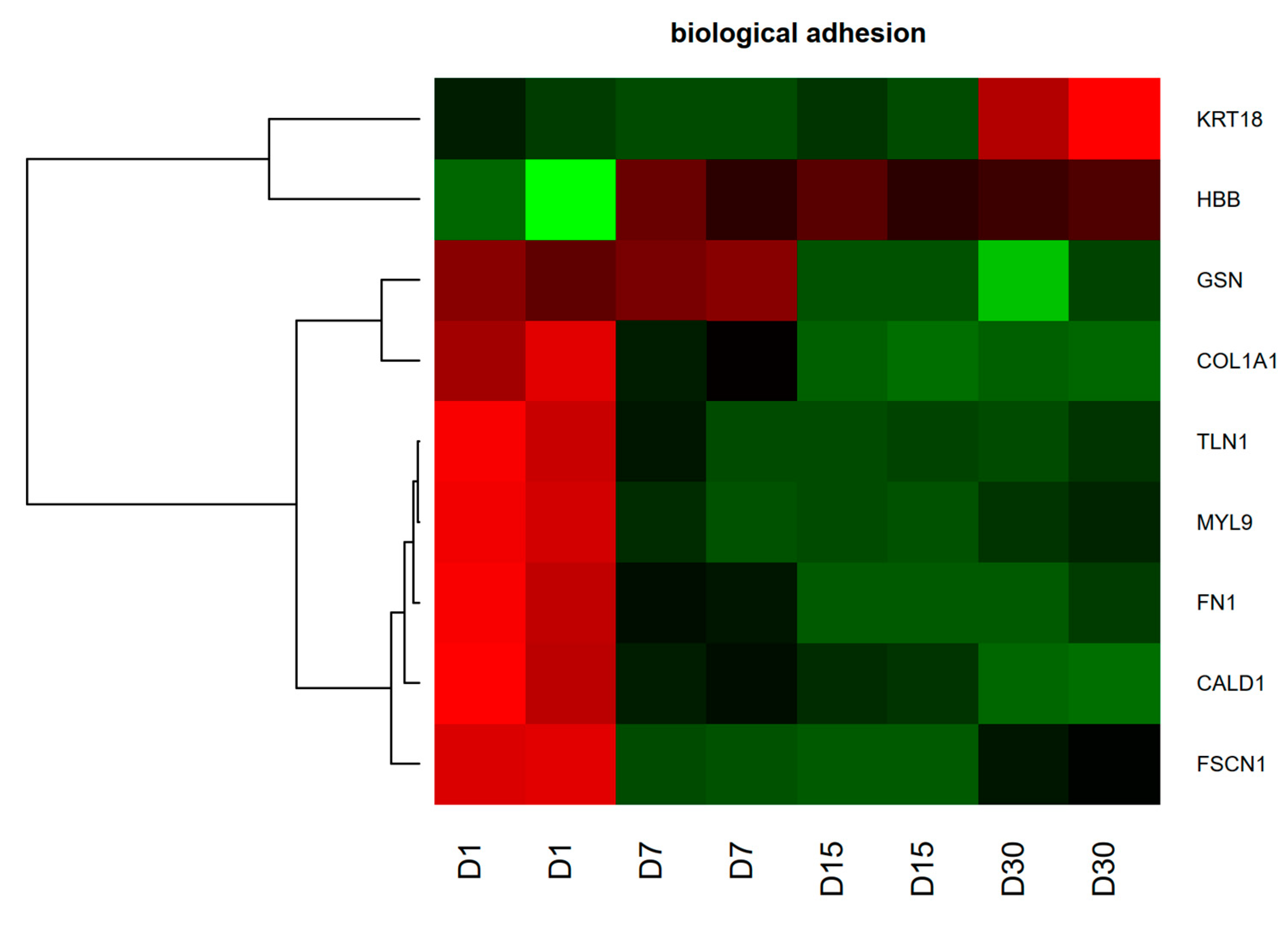
2.5. Genes and Proteins of Interest
2.6. RT-qPCR Analysis of Genes of Interest
2.7. Western Blot Analysis of Proteins of Interest
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Tissue Collection
4.2. Histological Evaluation
4.3. Primary Long-Term Culture of OECs
4.4. RNA Isolation from Oviductal Epithelial Cells (OECs)
4.5. Microarray Expression Analysis and Statistics
4.6. Protein Digestion
4.7. nanoLC-MALDI-TOF/TOF MS/MS Analysis
4.8. Selection of Genes of Interest
4.9. RT-qPCR Validation
4.10. Sodium Dodecyl Sulphate-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE) and Western Blot Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abe, H. The mammalian oviductal epithelium: Regional variations in cytological and functional aspects of the oviductal secretory cells. Histol. Histopathol. 1996, 11, 743–768. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Buhi, W.C.; Alvarez, I.M.; Kouba, A.J. Secreted proteins of the oviduct. Cells Tissues Organs 2000, 166, 165–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyons, R.A.; Saridogan, E.; Djahanbakhch, O. The reproductive significance of human Fallopian tube cilia. Hum. Reprod. Update 2006, 12, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cal, S.; Freije, J.M.P.; López, J.M.; Takada, Y.; López-Otín, C. ADAM 23/MDC3, a Human disintegrin That promotes cell adhesion via interaction with the αvβ3 Integrin through an RGD-independent Mechanism. Mol. Biol. Cell 2000, 11, 1457–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsanou, E.; Peschos, D.; Batistatou, A.; Charalabopoulos, A.; Charalabopoulos, K. The E-cadherin adhesion molecule and colorectal cancer. A global literature approach. Anticancer Res. 2008, 28, 3815–3826. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Tully, O.; Ngo, B.; Zitin, M.; Mullin, J.M. Epithelial tight junctional changes in colorectal cancer tissues. Sci. World J. 2011, 11, 826–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kempisty, B.; Ziółkowska, A.; Ciesiółka, S.; Piotrowska, H.; Antosik, P.; Bukowska, D.; Nowicki, M.; Brussow, K.P.; Zabel, M. Study on connexin gene and protein expression and cellular distribution in relation to real-time proliferation of porcine granulosa cells. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2014, 28, 625–635. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kölle, S.; Dubielzig, S.; Reese, S.; Wehrend, A.; König, P.; Kummer, W. Ciliary transport, gamete interaction, and effects of the early embryo in the oviduct: Ex vivo analyses using a new digital videomicroscopic system in the cow. Biol. Reprod. 2009, 81, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coy, P.; García-Vázquez, F.A.; Visconti, P.E.; Avilés, M. Roles of the oviduct in mammalian fertilization. Reproduction 2012, 144, 649–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maillo, V.; Sánchez-Calabuig, M.J.; Lopera-Vasquez, R.; Hamdi, M.; Gutierrez-Adan, A.; Lonergan, P.; Rizos, D. Oviductal response to gametes and early embryos in mammals. Reproduction 2016, 152, R127–R141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tokuhiro, K.; Ikawa, M.; Benham, A.M.; Okabe, M. Protein disulfide isomerase homolog PDILT is required for quality control of sperm membrane protein ADAM3 and male fertility [corrected]. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 3850–3855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caballero, J.N.; Gervasi, M.G.; Veiga, M.F.; Dalvit, G.C.; Perez-Martínez, S.; Cetica, P.D.; Vazquez-Levin, M.H. Epithelial cadherin is present in bovine oviduct epithelial cells and gametes, and is involved in fertilization-related events. Theriogenology 2014, 81, 1189–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonella-Diaza, A.M.; Andrade, S.C.d.S.; Sponchiado, M.; Pugliesi, G.; Mesquita, F.S.; Van Hoeck, V.; de Francisco, R.S.; Gasparin, G.R.; Coutinho, L.L.; Binelli, M. Size of the ovulatory follicle dictates spatial differences in the oviductal transcriptome in cattle. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0145321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, J.A.; Freeman, D.A.; Vanderwall, D.K.; Woods, G.L. Prostaglandin E2 secretion by oviductal transport-stage equine embryos. Biol. Reprod. 1991, 45, 540–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smits, K.; De Coninck, D.I.M.; Van Nieuwerburgh, F.; Govaere, J.; Van Poucke, M.; Peelman, L.; Deforce, D.; Van Soom, A. The equine embryo influences immune-related gene expression in the oviduct. Biol. Reprod. 2016, 94, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hugentobler, S.A.; Diskin, M.G.; Leese, H.J.; Humpherson, P.G.; Watson, T.; Sreenan, J.M.; Morris, D.G. Amino acids in oviduct and uterine fluid and blood plasma during the estrous cycle in the bovine. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2007, 74, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugentobler, S.A.; Morris, D.G.; Sreenan, J.M.; Diskin, M.G. Ion concentrations in oviduct and uterine fluid and blood serum during the estrous cycle in the bovine. Theriogenology 2007, 68, 538–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hugentobler, S.A.; Humpherson, P.G.; Leese, H.J.; Sreenan, J.M.; Morris, D.G. Energy substrates in bovine oviduct and uterine fluid and blood plasma during the oestrous cycle. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2008, 75, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Oh, H.J.; Kim, M.J.; Kim, G.A.; Choi, Y.B.; Jo, Y.K.; Nugraha, S.M.E.; Lee, C.B. Oocyte maturation-related gene expression in the canine oviduct, cumulus cells, and oocytes and effect of co-culture with oviduct cells on in vitro maturation of oocytes. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 2017, 34, 929–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Oh, H.J.; Kim, M.J.; Setyawan, E.; Maha, N.; Lee, B.C. Interaction of the EGFR signaling pathway with porcine cumulus oocyte complexes and oviduct cells in a coculture system. J. Cell Physiol. 2018, 234, 4030–4043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kervancioglu, M.E.; Saridogan, E.; Atasü, T.; Camlibel, T.; Demircan, A.; Sarikamis, B.; Djahanbakhch, O. Human Fallopian tube epithelial cell co-culture increases fertilization rates in male factor infertility but not in tubal or unexplained infertility. Hum. Reprod. 1997, 12, 1253–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauersachs, S.; Rehfeld, S.; Ulbrich, S.E.; Mallok, S.; Prelle, K.; Wenigerkind, H.; Einspanier, R.; Blum, H.; Wolf, E. Monitoring gene expression changes in bovine oviduct epithelial cells during the oestrous cycle. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2004, 32, 449–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerny, K.L.; Garrett, E.; Walton, A.J.; Anderson, L.H.; Bridges, P.J. A transcriptomal analysis of bovine oviductal epithelial cells collected during the follicular phase versus the luteal phase of the estrous cycle. Reprod. Biol. Endocrinol. 2015, 13, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maillo, V.; de Frutos, C.; O’Gaora, P.; Forde, N.; Burns, G.W.; Spencer, T.E.; Gutierez, A.A.; Lonergan, P.; Rizos, D. Spatial differences in gene expression in the bovine oviduct. Reproduction 2016, 152, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gandolfi, F. Functions of proteins secreted by oviduct epithelial cells. Microsc. Res. Tech. 1995, 32, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, D.J. Regulation of sperm function by oviduct fluid and the epithelium: Insight into the role of glycans. Reprod. Domest. Anim. 2015, 50 (Suppl. 2), 31–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeve, L.; Ledger, W.L.; Pacey, A.A. Does the Arg-Gly-Asp (RGD) adhesion sequence play a role in mediating sperm interaction with the human endosalpinx? Hum. Reprod. 2003, 18, 1461–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.W.R.; Liao, S.B.; Chiu, P.C.N.; Tam, W.W.; Ho, J.C.; Ng, E.H.Y.; Ho, P.C.; Yeung, W.S.B.; Tang, F.; Sum, O.W. Expression of adrenomedullin in human oviduct, its regulation by the hormonal cycle and contact with spermatozoa, and its effect on ciliary beat frequency of the oviductal epithelium. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, E18–E25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazeli, A.; Affara, N.A.; Hubank, M.; Holt, W.V. Sperm-induced modification of the oviductal gene expression profile after natural insemination in mice. Biol. Reprod. 2004, 71, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Úbeda, R.; García-Vázquez, F.A.; Romar, R.; Gadea, J.; Muñoz, M.; Hunter, R.H.F.; Coy, P. Oviductal transcriptome is modified after insemination during spontaneous ovulation in the sow. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0130128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiou, A.S.; Snijders, A.P.L.; Sostaric, E.; Aflatoonian, R.; Vazquez, J.L.; Vazquez, J.M.; Roca, J.; Martinez, E.A.; Wright, P.C.; Fazeli, A. Modulation of the oviductal environment by gametes. J. Proteome Res. 2007, 6, 4656–4666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dadashpour Davachi, N.; Zare Shahneh, A.; Kohram, H.; Zhandi, M.; Shamsi, H.; Hajiyavand, A.M.; Saadat, M. Differential influence of ampullary and isthmic derived epithelial cells on zona pellucida hardening and in vitro fertilization in ovine. Reprod. Biol. 2016, 16, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nishimura, R.; Kato, K.; Fujiwara, S.; Ohashi, K.; Mizuno, K. Solo and keratin filaments regulate epithelial tubule morphology. Cell Struct. Funct. 2018, 43, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roxas, J.L.; Vedantam, G.; Viswanathan, V.K. Epithelial maturity influences EPEC-induced desmosomal alterations. Gut Microb. 2018, 10, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlegel, N.; Meir, M.; Heupel, W.-M.; Holthöfer, B.; Leube, R.E.; Waschke, J. Desmoglein 2-mediated adhesion is required for intestinal epithelial barrier integrity. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2010, 298, G774–G783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jansen, R.P. Endocrine response in the fallopian tube. Endocr. Rev. 1984, 5, 525–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Lee, J.E.; Heynen-Genel, S.; Suyama, E.; Ono, K.; Lee, K.; Ideker, T.; Blanc, P.A.; Gleeson, G.K. Functional genomic screen for modulators of ciliogenesis and cilium length. Nature 2010, 464, 1048–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ulbrich, S.E.; Zitta, K.; Hiendleder, S.; Wolf, E. In vitro systems for intercepting early embryo-maternal cross-talk in the bovine oviduct. Theriogenology 2010, 73, 802–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almiñana, C.; Tsikis, G.; Labas, V.; Uzbekov, R.; da Silveira, J.C.; Bauersachs, S.; Mermillod, P. Deciphering the oviductal extracellular vesicles content across the estrous cycle: Implications for the gametes-oviduct interactions and the environment of the potential embryo. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalali, B.M.; Likszo, P.; Andronowska, A.; Skarzynski, D.J. Alterations in the distribution of actin and its binding proteins in the porcine endometrium during early pregnancy: Possible role in epithelial remodeling and embryo adhesion. Theriogenology 2018, 116, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, M.A. Integrins and extracellular matrix in mechanotransduction. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 2, a005066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, S.; Svineng, G.; Wennerberg, K.; Armulik, A.; Lohikangas, L. Fibronectin-integrin interactions. Front. Biosci. 1997, 2, d126–d146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bronson, R.A.; Fusi, F.M. Integrins and human reproduction. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 1996, 2, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Armant, D.R. Integrin-mediated adhesion and signaling during blastocyst implantation. Cells Tissues Organs 2002, 172, 190–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sreenivas, D.; Kaladhar, D.S.; Samy, A.P.; Kumar, R.S. Understanding mechanism of in vitro maturation, fertilization and culture of sheep embryoes through in silico analysis. Bioinformation 2012, 8, 1030–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goossens, K.; Van Soom, A.; Van Zeveren, A.; Favoreel, H.; Peelman, L.J. Quantification of fibronectin 1 (FN1) splice variants, including two novel ones, and analysis of integrins as candidate FN1 receptors in bovine preimplantation embryos. BMC Dev. Biol. 2009, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.-F.; Yao, Y.-Q.; Kwok, K.-L.; Xu, J.-S.; Yeung, W.S.B. Early developing embryos affect the gene expression patterns in the mouse oviduct. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 292, 564–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.-S.; Cheng, W.T.K.; Wu, H.-K.; Choo, K.-B. Identification of genes expressed in the epithelium of porcine oviduct containing early embryos at various stages of development. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2000, 56, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almiñana, C.; Heath, P.R.; Wilkinson, S.; Sanchez-Osorio, J.; Cuello, C.; Parrilla, I.; Gil, M.A.; Vazquez, J.L.; Vazquez, J.M.; Roca, J.; et al. Early developing pig embryos mediate their own environment in the maternal tract. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.-F.; Yeung, W.S.B. Gamete/embryo—Oviduct interactions: Implications on in vitro culture. Hum. Fertil. 2006, 9, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szóstek-Mioduchowska, A.Z.; Lukasik, K.; Skarzynski, D.J.; Okuda, K. Effect of transforming growth factor -β1 on α-smooth muscle actin and collagen expression in equine endometrial fibroblasts. Theriogenology 2019, 124, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arai, K.Y.; Nishiyama, T. Developmental changes in extracellular matrix messenger RNAs in the mouse placenta during the second half of pregnancy: Possible factors involved in the regulation of placental extracellular matrix expression. Biol. Reprod. 2007, 77, 923–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitasaka, H.; Kawai, T.; Hoque, S.A.M.; Umehara, T.; Fujita, Y.; Shimada, M. Inductions of granulosa cell luteinization and cumulus expansion are dependent on the fibronectin-integrin pathway during ovulation process in mice. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0192458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, D.; Thomas, C.J.; Taylor, V.J.; Burke, R.D. Integrins on eggs: focal adhesion kinase is activated at fertilization, forms a complex with integrins, and is necessary for cortex formation and cell cycle initiation. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2013, 24, 3472–3481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaczynski, P.; Baryla, M.; Goryszewska, E.; Bauersachs, S.; Waclawik, A. Prostaglandin F2α promotes embryo implantation and development in the pig. Reproduction 2018, 156, 405–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Critchley, D.R.; Gingras, A.R. Talin at a glance. J. Cell Sci. 2008, 121, 1345–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kawashima, I.; Liu, Z.; Mullany, L.K.; Mihara, T.; Richards, J.S.; Shimada, M. EGF-like factors induce expansion of the cumulus cell-oocyte complexes by activating calpain-mediated cell movement. Endocrinology 2012, 153, 3949–3959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Nadai, C.; Fenichel, P.; Donzeau, M.; Epel, D.; Ciapa, B. Characterisation and role of integrins during gametic interaction and egg activation. Zygote 1996, 4, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Priddle, H.; Hemmings, L.; Monkley, S.; Woods, A.; Patel, B.; Sutton, D.; Dunn, G.A.; Zicha, D.; Critchley, D.R. Disruption of the talin gene compromises focal adhesion assembly in undifferentiated but not differentiated embryonic stem cells. J. Cell Biol. 1998, 142, 1121–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Yu, L.; Qu, T.; Hu, Y.; Yuan, D.; Zhang, S.; Xu, Q.; Zhao, Y.-B.; Zhang, J.-H.; Yue, L.-M. The changes of cytoskeletal proteins induced by the fast effect of estrogen in mouse blastocysts and its roles in implantation. Reprod. Sci. 2017, 24, 1639–1646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semich, R.; Robenek, H. Organization of the cytoskeleton and the focal contacts of bovine aortic endothelial cells cultured on type I and III collagen. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1990, 38, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacáková, L.; Mares, V.; Lisá, V.; Svorcík, V. Molecular mechanisms of improved adhesion and growth of an endothelial cell line cultured on polystyrene implanted with fluorine ions. Biomaterials 2000, 21, 1173–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, X.; Yu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, B.; Sun, J.; Shen, H.; Kong, C. The role of fascin in migration and invasion of urothelial carcinoma of the bladder. Urol. Int. 2013, 91, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, T.-Y.; Mei, L.-L.; Qiu, Y.-T.; Shi, Z.-Z. Identification of candidate target genes of genomic aberrations in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 12, 2956–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adams, J.C. Fascin-1 as a biomarker and prospective therapeutic target in colorectal cancer. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2015, 15, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Huang, B.; Wu, Z.; Sun, X.; Zeng, Y.; Wang, Y. Expression of Fascin-1 protein in breast cancer and its clinicopathologic correlation. Zhonghua Bing Li Xue Za Zhi 2014, 43, 451–454. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, C.J.R.; Crook, M.; Loi, S. Fascin expression in endocervical neoplasia: Correlation with tumour morphology and growth pattern. J. Clin. Pathol. 2012, 65, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, I.; Han, C.; Jin, S.; Lee, B.; Choi, H.; Kwon, J.T.; Kim, D.; Kim, J.; Lifirsu, E.; Park, J.W.; et al. Myosin regulatory light chains are required to maintain the stability of myosin II and cellular integrity. Biochem. J. 2011, 434, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cuomo, M.E.; Knebel, A.; Platt, G.; Morrice, N.; Cohen, P.; Mittnacht, S. Regulation of microfilament organization by kaposi sarcoma-associated herpes virus-cyclin·CDK6 phosphorylation of caldesmon. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 35844–35858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, A.; Galanello, R. Beta-thalassemia. Genet. Med. 2010, 12, 61–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chermuła, B.; Brązert, M.; Jeseta, M.; Ożegowska, K.; Sujka-Kordowska, P.; Konwerska, A.; Bryja, A.; Kranc, W.; Jankowski, M.; Nawrocki, M.J.; et al. The unique mechanisms of cellular proliferation, migration and apoptosis are regulated through oocyte maturational development—A complete transcriptomic and histochemical study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 20, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aldarmahi, A. Establishment and characterization of female reproductive tract epithelial cell culture. J. Microsc. Ultrastruct. 2017, 5, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kidson, A.; Schoevers, E.; Langendijk, P.; Verheijden, J.; Colenbrander, B.; Bevers, M. The effect of oviductal epithelial cell co-culture during in vitro maturation on sow oocyte morphology, fertilization and embryo development. Theriogenology 2003, 59, 1889–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranc, W.; Jankowski, M.; Budna, J.; Celichowski, P.; Khozmi, R.; Bryja, A.; Borys, S.; Dyszkiewicz-Konwinska, M.; Jeseta, M.; Magas, M.; et al. Amino acids metabolism and degradation is regulated during porcine oviductal epithelial cells (OECs) primary culture in vitro—A signaling pathways activation approach. Med. J. Cell. Biol. 2018, 6, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranc, W.; Brązert, M.; Ożegowska, K.; Budna-Tukan, J.; Celichowski, P.; Jankowski, M.; Bryja, A.; Nawrocki, M.J.; Popis, M.; Jeseta, M.; et al. Response to abiotic and organic substances stimulation belongs to ontologic groups significantly up-regulated in porcine immature oocytes. Med. J. Cell. Biol. 2018, 6, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matysiak, J.; Hajduk, J.; Mayer, F.; Hebeler, R.; Kokot, Z.J. Hyphenated LC–MALDI–ToF/ToF and LC–ESI–QToF approach in proteomic characterization of honeybee venom. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 121, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryja, A.; Dyszkiewicz-Konwińska, M.; Jankowski, M.; Celichowski, P.; Stefańska, K.; Chamier-Gliszczyńska, A.; Popis, M.; Mehr, K.; Bukowska, D.; Antosik, P.; et al. Ion homeostasis and transport are regulated by genes differentially expressed in porcine buccal pouch mucosal cells during long-term culture in vitro-a microarray approach. Bryja Al Med. J. Cell. Biol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.W.; Sherman, B.T.; Tan, Q.; Collins, J.R.; Alvord, W.G.; Roayaei, J.; Stephens, R.; Baseler, W.M.; Clifford, H.L.; Lempicki, R.A. The DAVID Gene functional classification tool: A novel biological module-centric algorithm to functionally analyze large gene lists. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, R183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Name | Forward Primer (5’–3’) | Reverse Primer (5’–3’) |
|---|---|---|
| FN1 | TGAGCCTGAAGAGACCTGCT | CAGCTCCAATGCAGGTACAG |
| KRT18 | GGGCTCAGATCTTTGCAAGT | GTCTCATACTTGACTCTGAAGTCATC |
| GSN | AGAAACAGATCTGGAGAATCGAA | CGCCCTGCCAGTTGTAGAT |
| COL1A1 | GGTCTCCCAGGTCCTAAGG | GCTAGGACCAGTTTCACCCT |
| TLN1 | AGGCCAGAAAGAGTGTGACA | CCGTTCTTGGCATTTTGGGA |
| FSCN1 | CGCAGGTCAACATCTACAGC | CTCGAGAGTGTAGCCTGTGG |
| MYL9 | GGCCTTCAACATGATCGACC | GCTTCTCCCCAAACATGGTG |
| CALD1 | CACAAGCTCAAACACACCGA | TCAGCTCCTCCAGTTCCAAG |
| HBB | GTGACGGCCTGAAACATCTC | CTGGCCCACAAGTACCACTA |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Budna-Tukan, J.; Światły-Błaszkiewicz, A.; Celichowski, P.; Kałużna, S.; Konwerska, A.; Sujka-Kordowska, P.; Jankowski, M.; Kulus, M.; Jeseta, M.; Piotrowska-Kempisty, H.; et al. “Biological Adhesion” is a Significantly Regulated Molecular Process during Long-Term Primary In Vitro Culture of Oviductal Epithelial Cells (Oecs): A Transcriptomic and Proteomic Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3387. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20143387
Budna-Tukan J, Światły-Błaszkiewicz A, Celichowski P, Kałużna S, Konwerska A, Sujka-Kordowska P, Jankowski M, Kulus M, Jeseta M, Piotrowska-Kempisty H, et al. “Biological Adhesion” is a Significantly Regulated Molecular Process during Long-Term Primary In Vitro Culture of Oviductal Epithelial Cells (Oecs): A Transcriptomic and Proteomic Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(14):3387. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20143387
Chicago/Turabian StyleBudna-Tukan, Joanna, Agata Światły-Błaszkiewicz, Piotr Celichowski, Sandra Kałużna, Aneta Konwerska, Patrycja Sujka-Kordowska, Maurycy Jankowski, Magdalena Kulus, Michal Jeseta, Hanna Piotrowska-Kempisty, and et al. 2019. "“Biological Adhesion” is a Significantly Regulated Molecular Process during Long-Term Primary In Vitro Culture of Oviductal Epithelial Cells (Oecs): A Transcriptomic and Proteomic Study" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 14: 3387. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20143387
APA StyleBudna-Tukan, J., Światły-Błaszkiewicz, A., Celichowski, P., Kałużna, S., Konwerska, A., Sujka-Kordowska, P., Jankowski, M., Kulus, M., Jeseta, M., Piotrowska-Kempisty, H., Józkowiak, M., Antosik, P., Bukowska, D., Skowroński, M. T., Matysiak, J., Nowicki, M., & Kempisty, B. (2019). “Biological Adhesion” is a Significantly Regulated Molecular Process during Long-Term Primary In Vitro Culture of Oviductal Epithelial Cells (Oecs): A Transcriptomic and Proteomic Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(14), 3387. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20143387









