Beyond TCR Signaling: Emerging Functions of Lck in Cancer and Immunotherapy
Abstract
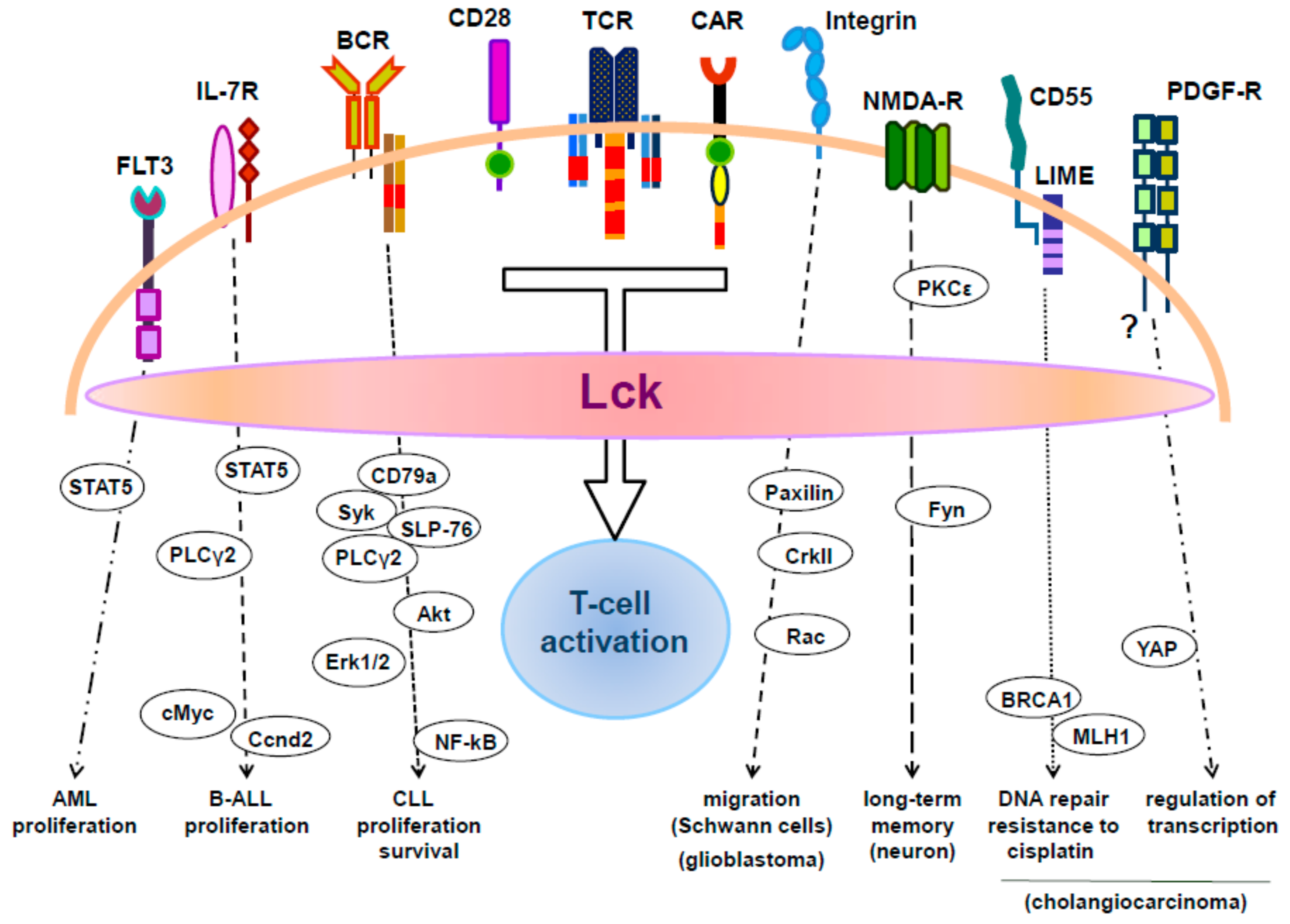
1. Introduction
2. Regulation of Lck Activation
3. The Role of Lck in T-Cell Activation
4. Lck Function in CAR T Cells
5. Expression and Function of Lck in Leukemic Cells
5.1. Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)
5.2. Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (ALL) of the B-Cell Compartment
5.3. Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML)
5.4. Chronic Myeloid Leukemia (CML)
6. The Role of Lck in Tumors of Non-Hematopoietic Origin
7. Lck in the Nervous System
8. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALL | acute lymphoid leukemia |
| AML | acute myeloid leukemia |
| CAR | chimeric antigen receptor |
| CML | chronic myeloid leukemia |
| SFK | src family kinase |
| WT | wild-type |
References
- Marth, J.D.; Peet, R.; Krebs, E.G.; Perlmutter, R.M. A lymphocyte-specific protein-tyrosine kinase gene is rearranged and overexpressed in the murine t cell lymphoma lstra. Cell 1985, 43, 393–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voronova, A.F.; Sefton, B.M. Expression of a new tyrosine protein kinase is stimulated by retrovirus promoter insertion. Nature 1986, 319, 682–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventimiglia, L.N.; Alonso, M.A. The role of membrane rafts in lck transport, regulation and signalling in t-cells. Biochem. J. 2013, 454, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Courtney, A.H.; Amacher, J.F.; Kadlecek, T.A.; Mollenauer, M.N.; Au-Yeung, B.B.; Kuriyan, J.; Weiss, A. A phosphosite within the sh2 domain of lck regulates its activation by cd45. Mol. Cell 2017, 67, 498–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodfellow, H.S.; Frushicheva, M.P.; Ji, Q.; Cheng, D.A.; Kadlecek, T.A.; Cantor, A.J.; Kuriyan, J.; Chakraborty, A.K.; Salomon, A.; Weiss, A. The catalytic activity of the kinase zap-70 mediates basal signaling and negative feedback of the t cell receptor pathway. Sci. Signal. 2015, 8, ra49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkler, D.G.; Park, I.; Kim, T.; Payne, N.S.; Walsh, C.T.; Strominger, J.L.; Shin, J. Phosphorylation of ser-42 and ser-59 in the n-terminal region of the tyrosine kinase p56lck. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 5176–5180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, D.; Barr, V.A.; Akpan, I.; Mittelstadt, P.R.; Singha, L.I.; Samelson, L.E.; Ashwell, J.D. Recruitment of calcineurin to the tcr positively regulates t cell activation. Nat. Immunol. 2017, 18, 196–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watts, J.D.; Sanghera, J.S.; Pelech, S.L.; Aebersold, R. Phosphorylation of serine 59 of p56lck in activated t cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1993, 268, 23275–23282. [Google Scholar]
- Stefanova, I.; Hemmer, B.; Vergelli, M.; Martin, R.; Biddison, W.E.; Germain, R.N. Tcr ligand discrimination is enforced by competing erk positive and shp-1 negative feedback pathways. Nat. Immunol. 2003, 4, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poltorak, M.; Arndt, B.; Kowtharapu, B.S.; Reddycherla, A.V.; Witte, V.; Lindquist, J.A.; Schraven, B.; Simeoni, L. Tcr activation kinetics and feedback regulation in primary human t cells. Cell Commun. Signal. 2013, 11, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laham, L.E.; Mukhopadhyay, N.; Roberts, T.M. The activation loop in lck regulates oncogenic potential by inhibiting basal kinase activity and restricting substrate specificity. Oncogene 2000, 19, 3961–3970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amrein, K.E.; Sefton, B.M. Mutation of a site of tyrosine phosphorylation in the lymphocyte-specific tyrosine protein kinase, p56lck, reveals its oncogenic potential in fibroblasts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1988, 85, 4247–4251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stirnweiss, A.; Hartig, R.; Gieseler, S.; Lindquist, J.A.; Reichardt, P.; Philipsen, L.; Simeoni, L.; Poltorak, M.; Merten, C.; Zuschratter, W.; et al. T cell activation results in conformational changes in the src family kinase lck to induce its activation. Sci. Signal. 2013, 6, ra13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philipsen, L.; Reddycherla, A.V.; Hartig, R.; Gumz, J.; Kastle, M.; Kritikos, A.; Poltorak, M.P.; Prokazov, Y.; Turbin, E.; Weber, A.; et al. De novo phosphorylation and conformational opening of the tyrosine kinase lck act in concert to initiate t cell receptor signaling. Sci. Signal. 2017, 10, eaaf4736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liaunardy-Jopeace, A.; Murton, B.L.; Mahesh, M.; Chin, J.W.; James, J.R. Encoding optical control in lck kinase to quantitatively investigate its activity in live cells. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2017, 24, 1155–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simeoni, L. Lck activation: Puzzling the pieces together. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 102761–102762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papatriantafyllou, M. Signal transduction: Lck regulation is hidden in details. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 222–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nika, K.; Soldani, C.; Salek, M.; Paster, W.; Gray, A.; Etzensperger, R.; Fugger, L.; Polzella, P.; Cerundolo, V.; Dushek, O.; et al. Constitutively active lck kinase in t cells drives antigen receptor signal transduction. Immunity 2010, 32, 766–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swamy, M.; Beck-Garcia, K.; Beck-Garcia, E.; Hartl, F.A.; Morath, A.; Yousefi, O.S.; Dopfer, E.P.; Molnar, E.; Schulze, A.K.; Blanco, R.; et al. A cholesterol-based allostery model of t cell receptor phosphorylation. Immunity 2016, 44, 1091–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, J.M.; Brodsky, M.H.; Irving, B.A.; Levin, S.D.; Perlmutter, R.M.; Littman, D.R. Interaction of the unique n-terminal region of tyrosine kinase p56lck with cytoplasmic domains of cd4 and cd8 is mediated by cysteine motifs. Cell 1990, 60, 755–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.J.; Dinner, A.R.; Qi, S.; Irvine, D.J.; Huppa, J.B.; Davis, M.M.; Chakraborty, A.K. Cd4 enhances t cell sensitivity to antigen by coordinating lck accumulation at the immunological synapse. Nat. Immunol. 2004, 5, 791–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, P.W.; Sun, Z.Y.; Blacklow, S.C.; Wagner, G.; Eck, M.J. A zinc clasp structure tethers lck to t cell coreceptors cd4 and cd8. Science 2003, 301, 1725–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Laethem, F.; Sarafova, S.D.; Park, J.H.; Tai, X.; Pobezinsky, L.; Guinter, T.I.; Adoro, S.; Adams, A.; Sharrow, S.O.; Feigenbaum, L.; et al. Deletion of cd4 and cd8 coreceptors permits generation of alphabetat cells that recognize antigens independently of the mhc. Immunity 2007, 27, 735–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roh, K.H.; Lillemeier, B.F.; Wang, F.; Davis, M.M. The coreceptor cd4 is expressed in distinct nanoclusters and does not colocalize with t-cell receptor and active protein tyrosine kinase p56lck. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E1604–E1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irvine, D.J.; Purbhoo, M.A.; Krogsgaard, M.; Davis, M.M. Direct observation of ligand recognition by t cells. Nature 2002, 419, 845–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casas, J.; Brzostek, J.; Zarnitsyna, V.I.; Hong, J.S.; Wei, Q.; Hoerter, J.A.; Fu, G.; Ampudia, J.; Zamoyska, R.; Zhu, C.; et al. Ligand-engaged tcr is triggered by lck not associated with cd8 coreceptor. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Guo, X.; Shi, X.; Li, C.; Wu, W.; Yan, C.; Wang, H.; Li, H.; Xu, C. Ionic cd3-lck interaction regulates the initiation of t-cell receptor signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E5891–E5899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courtney, A.H.; Lo, W.L.; Weiss, A. Tcr signaling: Mechanisms of initiation and propagation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2018, 43, 108–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith-Garvin, J.E.; Koretzky, G.A.; Jordan, M.S. T cell activation. Annu Rev. Immunol. 2009, 27, 591–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brownlie, R.J.; Zamoyska, R. T cell receptor signalling networks: Branched, diversified and bounded. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, W.L.; Shah, N.H.; Ahsan, N.; Horkova, V.; Stepanek, O.; Salomon, A.R.; Kuriyan, J.; Weiss, A. Lck promotes zap70-dependent lat phosphorylation by bridging zap70 to lat. Nat. Immunol. 2018, 19, 733–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabouridis, P.S.; Isenberg, D.A.; Jury, E.C. A negatively charged domain of lat mediates its interaction with the active form of lck. Mol. Membr. Biol. 2011, 28, 487–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arbulo-Echevarria, M.M.; Narbona-Sanchez, I.; Fernandez-Ponce, C.M.; Vico-Barranco, I.; Rueda-Ygueravide, M.D.; Dustin, M.L.; Miazek, A.; Duran-Ruiz, M.C.; Garcia-Cozar, F.; Aguado, E. A stretch of negatively charged amino acids of linker for activation of t-cell adaptor has a dual role in t-cell antigen receptor intracellular signaling. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esensten, J.H.; Helou, Y.A.; Chopra, G.; Weiss, A.; Bluestone, J.A. Cd28 costimulation: From mechanism to therapy. Immunity 2016, 44, 973–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobbins, J.; Gagnon, E.; Godec, J.; Pyrdol, J.; Vignali, D.A.; Sharpe, A.H.; Wucherpfennig, K.W. Binding of the cytoplasmic domain of cd28 to the plasma membrane inhibits lck recruitment and signaling. Sci. Signal. 2016, 9, ra75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, K.F.; Yokosuka, T.; Canonigo-Balancio, A.J.; Isakov, N.; Saito, T.; Altman, A. A motif in the v3 domain of the kinase pkc-theta determines its localization in the immunological synapse and functions in t cells via association with cd28. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 1105–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hui, E.; Cheung, J.; Zhu, J.; Su, X.; Taylor, M.J.; Wallweber, H.A.; Sasmal, D.K.; Huang, J.; Kim, J.M.; Mellman, I.; et al. T cell costimulatory receptor cd28 is a primary target for pd-1-mediated inhibition. Science 2017, 355, 1428–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akimzhanov, A.M.; Boehning, D. Rapid and transient palmitoylation of the tyrosine kinase lck mediates fas signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 11876–11880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ness, J.K.; Snyder, K.M.; Tapinos, N. Lck tyrosine kinase mediates beta1-integrin signalling to regulate schwann cell migration and myelination. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuras, Z.; Kucher, V.; Gordon, S.M.; Neumeier, L.; Chimote, A.A.; Filipovich, A.H.; Conforti, L. Modulation of kv1.3 channels by protein kinase a i in t lymphocytes is mediated by the disc large 1-tyrosine kinase lck complex. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2012, 302, C1504–C1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benmebarek, M.R.; Karches, C.H.; Cadilha, B.L.; Lesch, S.; Endres, S.; Kobold, S. Killing mechanisms of chimeric antigen receptor (car) t cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hickey, J.W.; Kosmides, A.K.; Schneck, J.P. Engineering platforms for t cell modulation. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2018, 341, 277–362. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shah, N.N.; Maatman, T.; Hari, P.; Johnson, B. Multi targeted car-t cell therapies for b-cell malignancies. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahmasebi, S.; Elahi, R.; Esmaeilzadeh, A. Solid tumors challenges and new insights of car t cell engineering. Stem Cell Rev. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kofler, D.M.; Chmielewski, M.; Rappl, G.; Hombach, A.; Riet, T.; Schmidt, A.; Hombach, A.A.; Wendtner, C.M.; Abken, H. Cd28 costimulation impairs the efficacy of a redirected t-cell antitumor attack in the presence of regulatory t cells which can be overcome by preventing lck activation. Mol. Ther. 2011, 19, 760–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suryadevara, C.M.; Desai, R.; Farber, S.H.; Choi, B.D.; Swartz, A.M.; Shen, S.H.; Gedeon, P.C.; Snyder, D.J.; Herndon, J.E., 2nd; Healy, P.; et al. Preventing lck activation in car t cells confers treg resistance but requires 4-1bb signaling for them to persist and treat solid tumors in nonlymphodepleted hosts. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 358–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golumba-Nagy, V.; Kuehle, J.; Hombach, A.A.; Abken, H. Cd28-zeta car t cells resist tgf-beta repression through il-2 signaling, which can be mimicked by an engineered il-7 autocrine loop. Mol. Ther. 2018, 26, 2218–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davenport, A.J.; Cross, R.S.; Watson, K.A.; Liao, Y.; Shi, W.; Prince, H.M.; Beavis, P.A.; Trapani, J.A.; Kershaw, M.H.; Ritchie, D.S.; et al. Chimeric antigen receptor t cells form nonclassical and potent immune synapses driving rapid cytotoxicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E2068–E2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salter, A.I.; Ivey, R.G.; Kennedy, J.J.; Voillet, V.; Rajan, A.; Alderman, E.J.; Voytovich, U.J.; Lin, C.; Sommermeyer, D.; Liu, L.; et al. Phosphoproteomic analysis of chimeric antigen receptor signaling reveals kinetic and quantitative differences that affect cell function. Sci. Signal. 2018, 11, eaat6753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadue, P.; Morton, N.; Stein, P.L. The src family tyrosine kinase fyn regulates natural killer t cell development. J. Exp. Med. 1999, 190, 1189–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olszowy, M.W.; Leuchtmann, P.L.; Veillette, A.; Shaw, A.S. Comparison of p56lck and p59fyn protein expression in thymocyte subsets, peripheral t cells, nk cells, and lymphoid cell lines. J. Immunol. 1995, 155, 4236–4240. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Einspahr, K.J.; Abraham, R.T.; Dick, C.J.; Leibson, P.J. Protein tyrosine phosphorylation and p56lck modification in il-2 or phorbol ester-activated human natural killer cells. J. Immunol. 1990, 145, 1490–1497. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Majolini, M.B.; D’Elios, M.M.; Galieni, P.; Boncristiano, M.; Lauria, F.; Del Prete, G.; Telford, J.L.; Baldari, C.T. Expression of the t-cell-specific tyrosine kinase lck in normal b-1 cells and in chronic lymphocytic leukemia b cells. Blood 1998, 91, 3390–3396. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Paterson, J.C.; Tedoldi, S.; Craxton, A.; Jones, M.; Hansmann, M.L.; Collins, G.; Roberton, H.; Natkunam, Y.; Pileri, S.; Campo, E.; et al. The differential expression of lck and baff-receptor and their role in apoptosis in human lymphomas. Haematologica 2006, 91, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, Q.; Henriquez, J.E.; Crawford, R.B.; Kaminski, N.E. Lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase (lck) is involved in the aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated impairment of immunoglobulin secretion in human primary b cells. Toxicol. Sci. 2018, 165, 322–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulivieri, C.; Valensin, S.; Majolini, M.B.; Matthews, R.J.; Baldari, C.T. Normal b-1 cell development but defective bcr signaling in lck-/- mice. Eur. J. Immunol. 2003, 33, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dal Porto, J.M.; Burke, K.; Cambier, J.C. Regulation of bcr signal transduction in b-1 cells requires the expression of the src family kinase lck. Immunity 2004, 21, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Knethen, A.; Abts, H.; Kube, D.; Diehl, V.; Tesch, H. Expression of p56lck in b-cell neoplasias. Leuk Lymphoma 1997, 26, 551–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abts, H.; Jucker, M.; Diehl, V.; Tesch, H. Human chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells regularly express mrnas of the protooncogenes lck and c-fgr. Leuk Res. 1991, 15, 987–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rouer, E.; Dreyfus, F.; Melle, J.; Benarous, R. Pattern of expression of five alternative transcripts of the lck gene in different hematopoietic malignancies: Correlation of the level of lck messenger rna i b with the immature phenotype of the malignancy. Cell Growth Differ. 1994, 5, 659–666. [Google Scholar]
- Rai, K.R.; Jain, P. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (cll)-then and now. Am. J. Hematol. 2016, 91, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casola, S.; Perucho, L.; Tripodo, C.; Sindaco, P.; Ponzoni, M.; Facchetti, F. The b-cell receptor in control of tumor b-cell fitness: Biology and clinical relevance. Immunol. Rev. 2019, 288, 198–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamatopoulos, K.; Agathangelidis, A.; Rosenquist, R.; Ghia, P. Antigen receptor stereotypy in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 2017, 31, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallat, L.D.; Park, Y.; Li, C.; Gribben, J.G. Temporal genetic program following b-cell receptor cross-linking: Altered balance between proliferation and death in healthy and malignant b cells. Blood 2007, 109, 3989–3997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Buchner, M.; Fuchs, S.; Prinz, G.; Pfeifer, D.; Bartholome, K.; Burger, M.; Chevalier, N.; Vallat, L.; Timmer, J.; Gribben, J.G.; et al. Spleen tyrosine kinase is overexpressed and represents a potential therapeutic target in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 5424–5432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Contri, A.; Brunati, A.M.; Trentin, L.; Cabrelle, A.; Miorin, M.; Cesaro, L.; Pinna, L.A.; Zambello, R.; Semenzato, G.; Donella-Deana, A. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia b cells contain anomalous lyn tyrosine kinase, a putative contribution to defective apoptosis. J. Clin. Invest. 2005, 115, 369–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herman, S.E.; Gordon, A.L.; Hertlein, E.; Ramanunni, A.; Zhang, X.; Jaglowski, S.; Flynn, J.; Jones, J.; Blum, K.A.; Buggy, J.J.; et al. Bruton tyrosine kinase represents a promising therapeutic target for treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia and is effectively targeted by pci-32765. Blood 2011, 117, 6287–6296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carreras, J.; Villamor, N.; Colomo, L.; Moreno, C.; Ramon y Cajal, S.; Crespo, M.; Tort, F.; Bosch, F.; Lopez-Guillermo, A.; Colomer, D.; et al. Immunohistochemical analysis of zap-70 expression in b-cell lymphoid neoplasms. J. Pathol. 2005, 205, 507–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolz, J.C.; Tschumper, R.C.; Pittner, B.T.; Darce, J.R.; Kay, N.E.; Jelinek, D.F. Zap-70 is expressed by a subset of normal human b-lymphocytes displaying an activated phenotype. Leukemia 2005, 19, 1018–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crespo, M.; Villamor, N.; Gine, E.; Muntanola, A.; Colomer, D.; Marafioti, T.; Jones, M.; Camos, M.; Campo, E.; Montserrat, E.; et al. Zap-70 expression in normal pro/pre b cells, mature b cells, and in b-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Clin. Cancer Res. 2006, 12, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scielzo, C.; Camporeale, A.; Geuna, M.; Alessio, M.; Poggi, A.; Zocchi, M.R.; Chilosi, M.; Caligaris-Cappio, F.; Ghia, P. Zap-70 is expressed by normal and malignant human b-cell subsets of different maturational stage. Leukemia 2006, 20, 689–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bekeredjian-Ding, I.; Doster, A.; Schiller, M.; Heyder, P.; Lorenz, H.M.; Schraven, B.; Bommhardt, U.; Heeg, K. Tlr9-activating DNA up-regulates zap70 via sustained pkb induction in igm+ b cells. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 8267–8277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marklin, M.; Heitmann, J.S.; Fuchs, A.R.; Truckenmuller, F.M.; Gutknecht, M.; Bugl, S.; Saur, S.J.; Lazarus, J.; Kohlhofer, U.; Quintanilla-Martinez, L.; et al. Nfat2 is a critical regulator of the anergic phenotype in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rassenti, L.Z.; Huynh, L.; Toy, T.L.; Chen, L.; Keating, M.J.; Gribben, J.G.; Neuberg, D.S.; Flinn, I.W.; Rai, K.R.; Byrd, J.C.; et al. Zap-70 compared with immunoglobulin heavy-chain gene mutation status as a predictor of disease progression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2004, 351, 893–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calpe, E.; Codony, C.; Baptista, M.J.; Abrisqueta, P.; Carpio, C.; Purroy, N.; Bosch, F.; Crespo, M. Zap-70 enhances migration of malignant b lymphocytes toward ccl21 by inducing ccr7 expression via igm-erk1/2 activation. Blood 2011, 118, 4401–4410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Widhopf, G.; Huynh, L.; Rassenti, L.; Rai, K.R.; Weiss, A.; Kipps, T.J. Expression of zap-70 is associated with increased b-cell receptor signaling in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2002, 100, 4609–4614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Apgar, J.; Huynh, L.; Dicker, F.; Giago-McGahan, T.; Rassenti, L.; Weiss, A.; Kipps, T.J. Zap-70 directly enhances igm signaling in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2005, 105, 2036–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laufer, J.M.; Lyck, R.; Legler, D.F. Zap70 expression enhances chemokine-driven chronic lymphocytic leukemia cell migration and arrest by valency regulation of integrins. FASEB J. 2018, 32, 4824–4835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobessi, S.; Laurenti, L.; Longo, P.G.; Sica, S.; Leone, G.; Efremov, D.G. Zap-70 enhances b-cell-receptor signaling despite absent or inefficient tyrosine kinase activation in chronic lymphocytic leukemia and lymphoma b cells. Blood 2007, 109, 2032–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Huynh, L.; Apgar, J.; Tang, L.; Rassenti, L.; Weiss, A.; Kipps, T.J. Zap-70 enhances igm signaling independent of its kinase activity in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2008, 111, 2685–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Till, K.J.; Allen, J.C.; Talab, F.; Lin, K.; Allsup, D.; Cawkwell, L.; Bentley, A.; Ringshausen, I.; Duckworth, A.D.; Pettitt, A.R.; et al. Lck is a relevant target in chronic lymphocytic leukaemia cells whose expression variance is unrelated to disease outcome. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talab, F.; Allen, J.C.; Thompson, V.; Lin, K.; Slupsky, J.R. Lck is an important mediator of b-cell receptor signaling in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells. Mol. Cancer Res. 2013, 11, 541–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harr, M.W.; Caimi, P.F.; McColl, K.S.; Zhong, F.; Patel, S.N.; Barr, P.M.; Distelhorst, C.W. Inhibition of lck enhances glucocorticoid sensitivity and apoptosis in lymphoid cell lines and in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Cell Death Differ. 2010, 17, 1381–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, J.C.; Talab, F.; Slupsky, J.R. Targeting b-cell receptor signaling in leukemia and lymphoma: How and why? Int. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2016, 5, 37–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theofani, E.; Alexis, S.; Costeas, P.; Andriopoulos, C.; Feleskoura, G.; Zikos, P.; Aktypi, A.; Spyridonidis, A.; Nika, K. Ectopic lck expression in cll demarcates intratumoral subpopulations with aberrant b-cell receptor signaling. Blood Adv. 2018, 2, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dezorella, N.; Katz, B.Z.; Shapiro, M.; Polliack, A.; Perry, C.; Herishanu, Y. Slp76 integrates into the b-cell receptor signaling cascade in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells and is associated with an aggressive disease course. Haematologica 2016, 101, 1553–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terwilliger, T.; Abdul-Hay, M. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia: A comprehensive review and 2017 update. Blood Cancer J. 2017, 7, e577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cazzaniga, V.; Bugarin, C.; Bardini, M.; Giordan, M.; te Kronnie, G.; Basso, G.; Biondi, A.; Fazio, G.; Cazzaniga, G. Lck over-expression drives stat5 oncogenic signaling in pax5 translocated bcp-all patients. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 1569–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Accordi, B.; Espina, V.; Giordan, M.; VanMeter, A.; Milani, G.; Galla, L.; Ruzzene, M.; Sciro, M.; Trentin, L.; De Maria, R.; et al. Functional protein network activation mapping reveals new potential molecular drug targets for poor prognosis pediatric bcp-all. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duque-Afonso, J.; Lin, C.H.; Han, K.; Wei, M.C.; Feng, J.; Kurzer, J.H.; Schneidawind, C.; Wong, S.H.; Bassik, M.C.; Cleary, M.L. E2a-pbx1 remodels oncogenic signaling networks in b-cell precursor acute lymphoid leukemia. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 6937–6949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shallis, R.M.; Wang, R.; Davidoff, A.; Ma, X.; Zeidan, A.M. Epidemiology of acute myeloid leukemia: Recent progress and enduring challenges. Blood Rev. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohl, S.R.; Bullinger, L.; Rucker, F.G. New targeted agents in acute myeloid leukemia: New hope on the rise. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Cui, Y.; Shen, J.; Dobson, H.; Sun, G. Evidence for activated lck protein tyrosine kinase as the driver of proliferation in acute myeloid leukemia cell, ctv-1. Leuk Res. 2019, 78, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Kong, D.; Qin, F.; Sun, J.; Dong, Y. Identification of potential therapeutic target genes, key mirnas and mechanisms in acute myeloid leukemia based on bioinformatics analysis. Med. Oncol. 2015, 32, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marhall, A.; Kazi, J.U.; Ronnstrand, L. The src family kinase lck cooperates with oncogenic flt3/itd in cellular transformation. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chougule, R.A.; Kazi, J.U.; Ronnstrand, L. Fyn expression potentiates flt3-itd induced stat5 signaling in acute myeloid leukemia. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 9964–9974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kivioja, J.L.; Thanasopoulou, A.; Kumar, A.; Kontro, M.; Yadav, B.; Majumder, M.M.; Javarappa, K.K.; Eldfors, S.; Schwaller, J.; Porkka, K.; et al. Dasatinib and navitoclax act synergistically to target nup98-nsd1(+)/flt3-itd(+) acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2018, 33, 1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aladag, E.; Haznedaroglu, I.C. Current perspectives for the treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 2019, 49, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Cortes, J.; Rea, D.; Lipton, J.H. Treatment-free remission with first- and second-generation tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Am. J. Hematol. 2019, 94, 346–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Chen, B. The role of dasatinib in the management of chronic myeloid leukemia. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2015, 9, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosti, G.; Castagnetti, F.; Gugliotta, G.; Baccarani, M. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors in chronic myeloid leukaemia: Which, when, for whom? Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 14, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hochhaus, A.; Kantarjian, H. The development of dasatinib as a treatment for chronic myeloid leukemia (cml): From initial studies to application in newly diagnosed patients. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 139, 1971–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ptasznik, A.; Nakata, Y.; Kalota, A.; Emerson, S.G.; Gewirtz, A.M. Short interfering rna (sirna) targeting the lyn kinase induces apoptosis in primary, and drug-resistant, bcr-abl1(+) leukemia cells. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 1187–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolff, N.C.; Veach, D.R.; Tong, W.P.; Bornmann, W.G.; Clarkson, B.; Ilaria, R.L., Jr. Pd166326, a novel tyrosine kinase inhibitor, has greater antileukemic activity than imatinib mesylate in a murine model of chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood 2005, 105, 3995–4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Ferri, C.; Bianchini, M.; Bengio, R.; Larripa, I. Expression of lyn and pten genes in chronic myeloid leukemia and their importance in therapeutic strategy. Blood Cells Mol. Dis. 2014, 52, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donato, N.J.; Wu, J.Y.; Stapley, J.; Gallick, G.; Lin, H.; Arlinghaus, R.; Talpaz, M. Bcr-abl independence and lyn kinase overexpression in chronic myelogenous leukemia cells selected for resistance to sti571. Blood 2003, 101, 690–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ban, K.; Gao, Y.; Amin, H.M.; Howard, A.; Miller, C.; Lin, Q.; Leng, X.; Munsell, M.; Bar-Eli, M.; Arlinghaus, R.B.; et al. Bcr-abl1 mediates up-regulation of fyn in chronic myelogenous leukemia. Blood 2008, 111, 2904–2908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Meng, F.; Lu, H.; Kong, L.; Bornmann, W.; Peng, Z.; Talpaz, M.; Donato, N.J. Lyn regulates bcr-abl and gab2 tyrosine phosphorylation and c-cbl protein stability in imatinib-resistant chronic myelogenous leukemia cells. Blood 2008, 111, 3821–3829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, M.M.; Howard, A.; Irwin, M.E.; Gao, Y.; Lu, X.; Multani, A.; Chandra, J. Expression and activity of fyn mediate proliferation and blastic features of chronic myelogenous leukemia. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irwin, M.E.; Johnson, B.P.; Manshouri, R.; Amin, H.M.; Chandra, J. A nox2/egr-1/fyn pathway delineates new targets for tki-resistant malignancies. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 23631–23646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Pelletier, S.; Buchdunger, E.; Warmuth, M.; Fabbro, D.; Hallek, M.; Van Etten, R.A.; Li, S. Requirement of src kinases lyn, hck and fgr for bcr-abl1-induced b-lymphoblastic leukemia but not chronic myeloid leukemia. Nat. Genet. 2004, 36, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doki, N.; Kitaura, J.; Uchida, T.; Inoue, D.; Kagiyama, Y.; Togami, K.; Isobe, M.; Ito, S.; Maehara, A.; Izawa, K.; et al. Fyn is not essential for bcr-abl-induced leukemogenesis in mouse bone marrow transplantation models. Int. J. Hematol. 2012, 95, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santpere, G.; Alcaraz-Sanabria, A.; Corrales-Sanchez, V.; Pandiella, A.; Gyorffy, B.; Ocana, A. Transcriptome evolution from breast epithelial cells to basal-like tumors. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, T.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Song, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Li, Z.; Tian, J. Identification of personalized chemoresistance genes in subtypes of basal-like breast cancer based on functional differences using pathway analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, G.; Rangaswami, H.; Jain, S.; Kundu, G.C. Hypoxia regulates cross-talk between syk and lck leading to breast cancer progression and angiogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 11322–11331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koster, A.; Landgraf, S.; Leipold, A.; Sachse, R.; Gebhart, E.; Tulusan, A.H.; Ronay, G.; Schmidt, C.; Dingermann, T. Expression of oncogenes in human breast cancer specimens. Anticancer Res. 1991, 11, 193–201. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, C.N.; Lee, M.S.; Wei, W.; Manyam, G.; Jiang, Z.Q.; Lu, Y.; Morris, J.; Broom, B.; Menter, D.; Vilar-Sanchez, E.; et al. Proteomic features of colorectal cancer identify tumor subtypes independent of oncogenic mutations and independently predict relapse-free survival. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2017, 24, 4051–4058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janikowska, G.; Janikowski, T.; Pyka-Pajak, A.; Mazurek, U.; Janikowski, M.; Gonciarz, M.; Lorenc, Z. Potential biomarkers for the early diagnosis of colorectal adenocarcinoma-transcriptomic analysis of four clinical stages. Cancer Biomark. 2018, 22, 89–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veillette, A.; Foss, F.M.; Sausville, E.A.; Bolen, J.B.; Rosen, N. Expression of the lck tyrosine kinase gene in human colon carcinoma and other non-lymphoid human tumor cell lines. Oncogene Res. 1987, 1, 357–374. [Google Scholar]
- Krystal, G.W.; DeBerry, C.S.; Linnekin, D.; Litz, J. Lck associates with and is activated by kit in a small cell lung cancer cell line: Inhibition of scf-mediated growth by the src family kinase inhibitor pp1. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 4660–4666. [Google Scholar]
- Mahabeleshwar, G.H.; Kundu, G.C. Tyrosine kinase p56lck regulates cell motility and nuclear factor kappab-mediated secretion of urokinase type plasminogen activator through tyrosine phosphorylation of ikappabalpha following hypoxia/reoxygenation. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 52598–52612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindauer, M.; Hochhaus, A. Dasatinib. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2014, 201, 27–65. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sugihara, T.; Werneburg, N.W.; Hernandez, M.C.; Yang, L.; Kabashima, A.; Hirsova, P.; Yohanathan, L.; Sosa, C.; Truty, M.J.; Vasmatzis, G.; et al. Yap tyrosine phosphorylation and nuclear localization in cholangiocarcinoma cells are regulated by lck and independent of lats activity. Mol. Cancer Res. 2018, 16, 1556–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, T.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Liang, Y.; Shi, H.; Sun, B.; Yin, D.; Sun, J.; Song, R.; et al. Yap is a critical oncogene in human cholangiocarcinoma. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 17206–17220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saygin, C.; Wiechert, A.; Rao, V.S.; Alluri, R.; Connor, E.; Thiagarajan, P.S.; Hale, J.S.; Li, Y.; Chumakova, A.; Jarrar, A.; et al. Cd55 regulates self-renewal and cisplatin resistance in endometrioid tumors. J. Exp. Med. 2017, 214, 2715–2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brdickova, N.; Brdicka, T.; Angelisova, P.; Horvath, O.; Spicka, J.; Hilgert, I.; Paces, J.; Simeoni, L.; Kliche, S.; Merten, C.; et al. Lime: A new membrane raft-associated adaptor protein involved in cd4 and cd8 coreceptor signaling. J. Exp. Med. 2003, 198, 1453–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, R.K.; Yoon, C.H.; Hyun, K.H.; Lee, H.; An, S.; Park, M.J.; Kim, M.J.; Lee, S.J. Role of lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase (lck) in the expansion of glioma-initiating cells by fractionated radiation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 402, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Zhang, W.; Yang, X.; Wheeler, C.G.; Langford, C.P.; Wu, L.; Filippova, N.; Friedman, G.K.; Ding, Q.; Fathallah-Shaykh, H.M.; et al. The role of src family kinases in growth and migration of glioma stem cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 45, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zepecki, J.P.; Snyder, K.M.; Moreno, M.M.; Fajardo, E.; Fiser, A.; Ness, J.; Sarkar, A.; Toms, S.A.; Tapinos, N. Regulation of human glioma cell migration, tumor growth, and stemness gene expression using a lck targeted inhibitor. Oncogene 2019, 38, 1734–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Colome, A.M.; Lee-Rivera, I.; Benavides-Hidalgo, R.; Lopez, E. Paxillin: A crossroad in pathological cell migration. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 10, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birge, R.B.; Kalodimos, C.; Inagaki, F.; Tanaka, S. Crk and crkl adaptor proteins: Networks for physiological and pathological signaling. Cell Commun. Signal. 2009, 7, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rupniewska, E.; Roy, R.; Mauri, F.A.; Liu, X.; Kaliszczak, M.; Bellezza, G.; Cagini, L.; Barbareschi, M.; Ferrero, S.; Tommasi, A.M.; et al. Targeting autophagy sensitises lung cancer cells to src family kinase inhibitors. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 27346–27362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theus, M.H.; Wei, L.; Francis, K.; Yu, S.P. Critical roles of src family tyrosine kinases in excitatory neuronal differentiation of cultured embryonic stem cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2006, 312, 3096–3107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohnishi, H.; Murata, Y.; Okazawa, H.; Matozaki, T. Src family kinases: Modulators of neurotransmitter receptor function and behavior. Trends Neurosci. 2011, 34, 629–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omri, B.; Crisanti, P.; Marty, M.C.; Alliot, F.; Fagard, R.; Molina, T.; Pessac, B. The lck tyrosine kinase is expressed in brain neurons. J. Neurochem. 1996, 67, 1360–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Tan, H.; Allee, G.; Benes, C.; Barnier, J.V.; Vincent, J.D.; Fagard, R. Expression of a novel form of the p56lck protooncogene in rat cerebellar granular neurons. J. Neurochem. 1996, 67, 2306–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omri, B.; Blancher, C.; Neron, B.; Marty, M.C.; Rutin, J.; Molina, T.J.; Pessac, B.; Crisanti, P. Retinal dysplasia in mice lacking p56lck. Oncogene 1998, 16, 2351–2356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Tan, J.; Town, T.; Mullan, M. Cd45 inhibits cd40l-induced microglial activation via negative regulation of the src/p44/42 mapk pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 37224–37231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.J.; Monje, F.J.; Li, L.; Hoger, H.; Pollak, D.D.; Lubec, G. Alzheimer’s disease risk factor lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase regulates long-term synaptic strengthening, spatial learning and memory. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, 743–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, O.N.; Rajanikant, K.; Min, J.; Smith, J.; Baek, S.H.; Serfozo, K.; Hejabian, S.; Lee, K.Y.; Kassab, M.; Majid, A. Lymphocyte cell kinase activation mediates neuroprotection during ischemic preconditioning. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 7278–7286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Yamagata, H.D.; Taguchi, K.; Akatsu, H.; Kamino, K.; Yamamoto, T.; Kosaka, K.; Takeda, M.; Kondo, I.; Miki, T. Lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase is a novel risk gene for alzheimer disease. J. Neurol. Sci. 2005, 238, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Um, J.W.; Nygaard, H.B.; Heiss, J.K.; Kostylev, M.A.; Stagi, M.; Vortmeyer, A.; Wisniewski, T.; Gunther, E.C.; Strittmatter, S.M. Alzheimer amyloid-beta oligomer bound to postsynaptic prion protein activates fyn to impair neurons. Nat. Neurosci. 2012, 15, 1227–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Um, J.W.; Strittmatter, S.M. Amyloid-beta induced signaling by cellular prion protein and fyn kinase in alzheimer disease. Prion 2013, 7, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, G.; Thangavel, R.; Sharma, V.M.; Litersky, J.M.; Bhaskar, K.; Fang, S.M.; Do, L.H.; Andreadis, A.; Van Hoesen, G.; Ksiezak-Reding, H. Phosphorylation of tau by fyn: Implications for alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 2304–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, G.; Newman, S.T.; Gard, D.L.; Band, H.; Panchamoorthy, G. Tau interacts with src-family non-receptor tyrosine kinases. J. Cell Sci. 1998, 111 (Pt. 21), 3167–3177. [Google Scholar]
- Nygaard, H.B. Targeting fyn kinase in alzheimer’s disease. Biol. Psychiatry 2018, 83, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bommhardt, U.; Schraven, B.; Simeoni, L. Beyond TCR Signaling: Emerging Functions of Lck in Cancer and Immunotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3500. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20143500
Bommhardt U, Schraven B, Simeoni L. Beyond TCR Signaling: Emerging Functions of Lck in Cancer and Immunotherapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(14):3500. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20143500
Chicago/Turabian StyleBommhardt, Ursula, Burkhart Schraven, and Luca Simeoni. 2019. "Beyond TCR Signaling: Emerging Functions of Lck in Cancer and Immunotherapy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 14: 3500. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20143500
APA StyleBommhardt, U., Schraven, B., & Simeoni, L. (2019). Beyond TCR Signaling: Emerging Functions of Lck in Cancer and Immunotherapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(14), 3500. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20143500




