Asymmetric (ADMA) and Symmetric (SDMA) Dimethylarginines in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Clinical Approach
Abstract
:1. Introduction
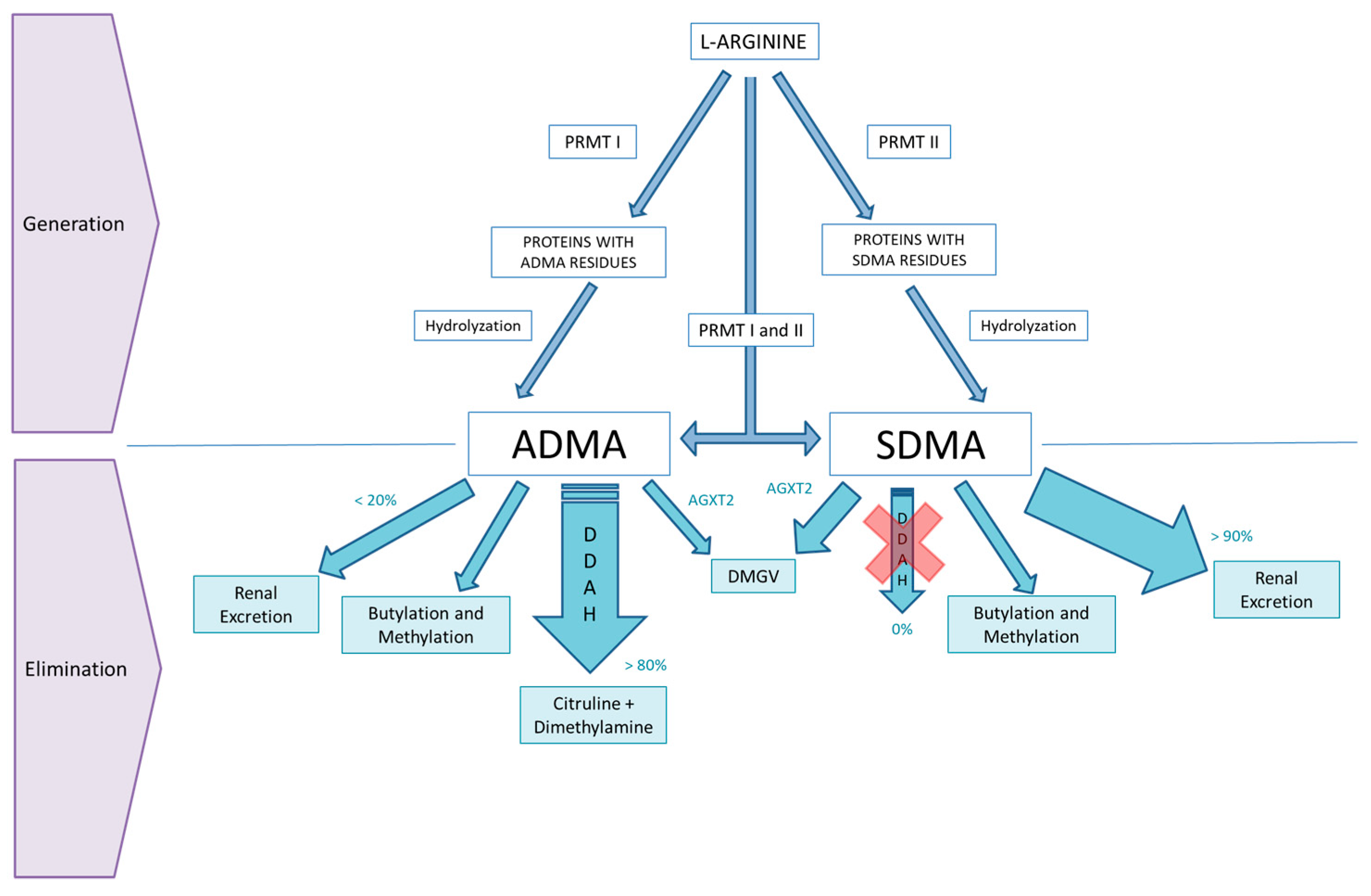
2. ADMA and SDMA Metabolism
3. SDMA, Mortality and Cardiovascular Disease
4. SDMA and Chronic Kidney Disease
5. ADMA, Mortality and Cardiovascular Disease
6. ADMA and Chronic Kidney Disease
7. ADMA and Dialysis
8. ADMA and Hypertension
9. ADMA and Ageing
10. ADMA, Endothelial Dysfunction and Inflammation
11. ADMA and Drugs: A Modifiable Risk Factor?
12. Conclusions
13. Take-Home Messages
- ADMA and SDMA are not only uremic toxins but also independent risk markers for all-cause mortality and cardiovascular disease.
- Both ADMA and SDMA are increased in patients with end-stage renal disease, but SDMA is a much more sensitive marker to changes in renal function than ADMA, as it is removed almost exclusively by the kidneys.
- SDMA is good marker of renal function, which has been shown to be better than CKD-EPI and MDRD-derived eGFR for the assessment of kidney function in certain population groups.
- ADMA is also associated with ageing, hypertension, progression of kidney failure, and renal fibrosis.
- ADMA could be a potentially modifiable risk factor as certain drugs could decrease ADMA levels. However, it is not yet clear whether this reduction will be of clinical relevance.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kakimoto, Y.; Akazawa, S. Isolation and identification of N-G, N-G-and N-G, N’G-dimethyl-arginine, N-epsilon-mono-, di-, and trimethyllysine, and glucosylgalactosyl-and galactosyl-delta-hydroxylysine from human urine. J. Boil. Chem. 1970, 245, 5751–5758. [Google Scholar]
- Leone, A.; Moncada, S.; Vallance, P.; Calver, A.; Collier, J. Accumulation of an endogenous inhibitor of nitric oxide synthesis in chronic renal failure. Lancet 1992, 339, 572–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoccali, C.; Bode-Böger, S.M.; Mallamaci, F.; Benedetto, F.A.; Tripepi, G.; Malatino, L.S.; Cataliotti, A.; Bellanuova, I.; Fermo, I.; Frölich, J.C.; et al. Plasma concentration of asymmetrical dimethylarginine and mortality in patients with end-stage renal disease: A prospective study. Lancet 2001, 358, 2113–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kielstein, J.T.; Salpeter, S.R.; Bode-Boeger, S.M.; Cooke, J.P.; Fliser, D. Symmetric dimethylarginine (SDMA) as endogenous marker of renal function—A meta-analysis. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2006, 21, 2446–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanholder, R.; De Smet, R.; Glorieux, G.; Argilés, A.; Baurmeister, U.; Brunet, P.; Clark, W.; Cohen, G.; De Deyn, P.P.; Deppisch, R.; et al. Review on uremic toxins: Classification, concentration, and interindividual variability. Kidney Int. 2003, 63, 1934–1943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schlesinger, S.; Sonntag, S.R.; Lieb, W.; Maas, R. Asymmetric and Symmetric Dimethylarginine as Risk Markers for Total Mortality and Cardiovascular Outcomes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Prospective Studies. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, 0165811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiper, J.M. The DDAH-ADMA-NOS pathway. Ther. Drug. Monit. 2005, 27, 744–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodionov, R.N.; Murry, D.J.; Vaulman, S.F.; Stevens, J.W.; Lentz, S.R. Human alanine-glyoxylate aminotransferase 2 lowers asymmetric dimethylarginine and protects from inhibition of nitric oxide production. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 5385–5391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caglar, K.; Yilmaz, M.; Sonmez, A.; Cakir, E.; Kaya, A.; Acikel, C.; Eyileten, T.; Yenicesu, M.; Oguz, Y.; Bilgi, C.; et al. ADMA, proteinuria, and insulin resistance in Non-Diabetic stage I chronic kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2006, 70, 781–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kielstein, J.T.; Böger, R.H.; Bode-Böger, S.M.; Frölich, J.C.; Haller, H.; Ritz, E.; Fliser, D. Marked increase of asymmetric dimethylarginine in patients with incipient primary chronic renal disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2002, 13, 170–176. [Google Scholar]
- Morales, Y.; Cáceres, T.; May, K.; Hevel, J.M. Biochemistry and regulation of the protein arginine methyltransferases (PRMTs). Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2016, 590, 138–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leiper, J.; Nandi, M.; Torondel, B.; Murray-Rust, J.; Malaki, M.; O’Hara, B.; Rossiter, S.; Anthony, S.; Madhani, M.; Selwood, D.; et al. Disruption of methylarginine metabolism impairs vascular homeostasis. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 198–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caplin, B.; Wang, Z.; Slaviero, A.; Tomlinson, J.; Dowsett, L.; Delahaye, M.; Salama, A.; Wheeler, D.C.; Leiper, J. Alanine-Glyoxylate Aminotransferase-2 Metabolizes Endogenous Methylarginines, Regulates NO, and Controls Blood Pressure. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Boil. 2012, 32, 2892–2900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ogawa, T.; Kimoto, M.; Sasaoka, K. Occurrence of a new enzyme catalyzing the direct conversion of NG, NG-dimethyl-L-arginine to L-Citrulline in rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1987, 148, 671–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ronden, R.A.; Houben, A.J.H.M.; Teerlink, T.; Bakker, J.A.; Bierau, J.; Stehouwer, C.D.A.; De Leeuw, P.W.; Kroon, A.A. Reduced renal plasma clearance does not explain increased plasma asymmetric dimethylarginine in hypertensive subjects with mild to moderate renal insufficiency. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2012, 303, F149–F156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tutarel, O.; Denecke, A.; Martens-Lobenhoffer, J.; Schieffer, B.; Westhoff-Bleck, M.; Bode-Böger, S.; Kielstein, J. Symmetrical Dimethylarginine Outperforms CKD-EPI and MDRD-Derived eGFR for the Assessment of Renal Function in Patients with Adult Congenital Heart Disease. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2011, 34, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kielstein, J.T.; Veldink, H.; Martens-Lobenhoffer, J.; Haller, H.; Burg, M.; Lorenzen, J.M.; Lichtinghagen, R.; Bode-Böger, S.M.; Kliem, V. SDMA is an early marker of change in GFR after living-related kidney donation. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2011, 26, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepers, E.; Speer, T.; Bode-Böger, S.M.; Fliser, D.; Kielstein, J.T. Dimethylarginines ADMA and SDMA: The Real Water-Soluble Small Toxins? Semin. Nephrol. 2014, 34, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijveldt, R. The liver is an important organ in the metabolism of asymmetrical dimethylarginine (ADMA). Clin. Nutr. 2003, 22, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siroen, M.P.; Van Der Sijp, J.R.M.; Teerlink, T.; Van Schaik, C.; Nijveldt, R.J.; Van Leeuwen, P.A.M. The human liver clears both asymmetric and symmetric dimethylarginine. Hepatology 2005, 41, 559–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schepers, E.; Barreto, D.V.; Liabeuf, S.; Glorieux, G.; Eloot, S.; Barreto, F.C.; Massy, Z.; Vanholder, R.; On behalf of the European Uremic Toxin Work Group (EUTox). Symmetric Dimethylarginine as a Proinflammatory Agent in Chronic Kidney Disease. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 6, 2374–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Speer, T.; Rohrer, L.; Blyszczuk, P.; Shroff, R.; Kuschnerus, K.; Kränkel, N.; Kania, G.; Zewinger, S.; Akhmedov, A.; Shi, Y.; et al. Abnormal High-Density Lipoprotein Induces Endothelial Dysfunction via Activation of Toll-like Receptor-2. Immunity 2013, 38, 754–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tutarel, O.; Röntgen, P.; Bode-Böger, S.M.; Martens-Lobenhoffer, J.; Westhoff-Bleck, M.; Diller, G.-P.; Bauersachs, J.; Kielstein, J.T. Symmetrical dimethylarginine is superior to NT-proBNP for detecting systemic ventricular dysfunction in adults after atrial repair for transposition of the great arteries. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 168, 4415–4416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bode-Böger, S.M.; Scalera, F.; Kielstein, J.T.; Martens-Lobenhoffer, J.; Breithardt, G.; Fobker, M.; Reinecke, H. Symmetrical Dimethylarginine: A New Combined Parameter for Renal Function and Extent of Coronary Artery Disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 1128–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meinitzer, A.; Seelhorst, U.; Wellnitz, B.; Halwachs-Baumann, G.; Boehm, B.O.; Winkelmann, B.R.; März, W. Asymmetrical dimethylarginine independently predicts total and cardiovascular mortality in individuals with angiographic coronary artery disease (the Ludwigshafen Risk and Cardiovascular Health study). Clin. Chem. 2007, 53, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegerink, B.; Maas, R.; Vossen, C.Y.; Schwedhelm, E.; Koenig, W.; Böger, R.; Rothenbacher, D.; Brenner, H.; Breitling, L.P. Asymmetric and symmetric dimethylarginine and risk of secondary cardiovascular disease events and mortality in patients with stable coronary heart disease: The KAROLA follow-up study. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2013, 102, 193–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulze, F.; Carter, A.M.; Schwedhelm, E.; Ajjan, R.; Maas, R.; Von Holten, R.-A.; Atzler, D.; Grant, P.J.; Böger, R.H. Symmetric dimethylarginine predicts all-cause mortality following ischemic stroke. Atheroscler. 2010, 208, 518–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, M.; Fleck, C.; Wolf, G.; Stein, G. Asymmetrical (ADMA) and symmetrical dimethylarginine (SDMA) as potential risk factors for cardiovascular and renal outcome in chronic kidney disease–Possible candidates for paradoxical epidemiology? Amino Acids 2006, 30, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lüneburg, N.; Von Holten, R.; Topper, R.F.; Schwedhelm, E.; Maas, R.; Böger, R.H. Symmetric dimethylarginine is a marker of detrimental outcome in the acute phase after ischaemic stroke: Role of renal function. Clin. Sci. 2012, 122, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavalca, V.; Veglia, F.; Squellerio, I.; De Metrio, M.; Rubino, M.; Porro, B.; Moltrasio, M.; Tremoli, E.; Marenzi, G. Circulating Levels of Dimethylarginines, Chronic Kidney Disease and Long-Term Clinical Outcome in Non-ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, 48499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.-L.; Wang, S.; Li, N.-S.; Zhang, X.-H.; Deng, H.-W.; Li, Y.-J. The inhibitory effect of simvastatin on the ADMA-induced inflammatory reaction is mediated by MAPK pathways in endothelial cells. Biochem. Cell Boil. 2007, 85, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strobel, J.; Mieth, M.; Endreß, B.; Auge, D.; König, J.; Fromm, M.F.; Maas, R. Interaction of the cardiovascular risk marker asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) with the human cationic amino acid transporter 1 (CAT1). J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2012, 53, 392–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schepers, E.; Glorieux, G.; Dhondt, A.; Leybaert, L.; Vanholder, R. Role of symmetric dimethylarginine in vascular damage by increasing ROS via store-operated calcium influx in monocytes. Nephrol Dial. Transpl. 2009, 24, 1429–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goonasekera, C.D.; Rees, D.D.; Woolard, P.; Frend, A.; Shah, V.; Dillon, M.J. Nitric oxide synthase inhibitors and hypertension in children and adolescents. J. Hypertens. 1997, 15, 901–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, H.-C.; Hsu, C.-N.; Huang, C.-F.; Lo, M.-H.; Chien, S.-J.; Tain, Y.-L. Urinary arginine methylation index associated with ambulatory blood pressure abnormalities in children with chronic kidney disease. J. Am. Soc. Hypertens. 2012, 6, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emrich, I.E.; Zawada, A.M.; Martens-Lobenhoffer, J.; Fliser, D.; Wagenpfeil, S.; Heine, G.H.; Bode-Böger, S.M. Symmetric dimethylarginine (SDMA) outperforms asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) and other methylarginines as predictor of renal and cardiovascular outcome in non-dialysis chronic kidney disease. Clin. Res. Cardiol. 2018, 107, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderstam, B.; Katzarski, K.; Bergstrom, J. Serum levels of NG, NG-dimethyl-L-arginine, a potential endogenous nitric oxide inhibitor in dialysis patients. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1997, 8, 1437–1442. [Google Scholar]
- Valkonen, V.-P.; Päivä, H.; Salonen, J.T.; A Lakka, T.; Lehtimäki, T.; Laakso, J.; Laaksonen, R. Risk of acute coronary events and serum concentration of asymmetrical dimethylarginine. Lancet 2001, 358, 2127–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, J.M.; Terrin, N.; Wang, X.; Greene, T.; Beck, G.J.; Kusek, J.W.; Collins, A.J.; Sarnak, M.J.; Menon, V. Asymmetric Dimethylarginine and Mortality in Stages 3 to 4 Chronic Kidney Disease. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2009, 4, 1115–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacAllister, R.J.; Rambausek, M.H.; Vallance, P.; Williams, D.; Hoffmann, K.-H.; Ritz, E. Concentration of dimethyl-L-arginine in the plasma of patients with end-stage renal failure. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 1996, 11, 2449–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kielstein, J.T.; Zoccali, C. Asymmetric Dimethylarginine: A Cardiovascular Risk Factor and a Uremic Toxin Coming of Age? Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2005, 46, 186–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kielstein, J.T.; Impraim, B.; Simmel, S.; Bode-Böger, S.M.; Tsikas, D.; Frölich, J.C.; Hoeper, M.M.; Haller, H.; Fliser, D. Cardiovascular Effects of Systemic Nitric Oxide Synthase Inhibition With Asymmetrical Dimethylarginine in Humans. Circulation 2004, 109, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eiselt, J.; Rajdl, D.; Racek, J.; Vostry, M.; Rulcova, K.; Wirth, J. Asymmetric Dimethylarginine and Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease-a One-Year Follow-Up Study. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2014, 39, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihout, F.; Shweke, N.; Bigé, N.; Jouanneau, C.; Dussaule, J.C.; Ronco, P.; Chatziantoniou, C.; Boffa, J.J. Asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) induces chronic kidney disease through a mechanism involving collagen and TGF-beta1 synthesis. J. Pathol. 2011, 223, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kielstein, J.T.; Zoccali, C. Asymmetric dimethylarginine: A novel marker of risk and a potential target for therapy in chronic kidney disease. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2008, 17, 609–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalera, F.; Kielstein, J.T.; Martens-Lobenhoffer, J.; Postel, S.C.; Täger, M.; Bode-Böger, S.M. Erythropoietin Increases Asymmetric Dimethylarginine in Endothelial Cells: Role of Dimethylarginine Dimethylaminohydrolase. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2005, 16, 892–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, X.Q.; Vaziri, N.D. Erythropoietin Depresses Nitric Oxide Synthase Expression by Human Endothelial Cells. Hypertension 1999, 33, 894–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoro, M.; Nakayama, Y.; Yamagishi, S.-I.; Ando, R.; Sugiyama, M.; Ito, S.; Yano, J.; Taguchi, K.; Kaida, Y.; Saigusa, D.; et al. Asymmetric Dimethylarginine Contributes to the Impaired Response to Erythropoietin in CKD-Anemia. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 2670–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, R.J.; Domico, J.; Samsell, L.S.; Yokota, S.; Tracy, T.S.; Sorkin, M.I.; Engels, K.; Baylis, C. Indices of Activity of the Nitric Oxide System in Hemodialysis Patients. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 1999, 34, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kielstein, J.T.; Böger, R.H.; Bode-Böger, S.M.; Schäffer, J.; Barbey, M.; Koch, K.M.; Frölich, J.C. Asymmetric dimethylarginine plasma concentrations differ in patients with end-stage renal disease: Relationship to treatment method and atherosclerotic disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1999, 10, 594–600. [Google Scholar]
- Kielstein, J.; Böger, R.; Bode-Böger, S.; Martens-Lobenhoffer, J.; Lonnemann, G.; Frölich, J.; Haller, H.; Fliser, D. Low dialysance of asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA)-in vivo and in vitro evidence of significant protein binding. Clin. Nephrol. 2004, 62, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schröder, M.; Riedel, E.; Beck, W.; Deppisch, R.M.; Pommer, W. Increased reduction of dimethylarginines and lowered interdialytic blood pressure by the use of biocompatible membranes. Kidney Int. 2001, 59, S19–S24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kalousová, M.; Kielstein, J.T.; Hodková, M.; Zima, T.; Dusilová-Sulková, S.; Martens-Lobenhoffer, J.; Bode-Boger, S.M. No Benefit of Hemodiafiltration over Hemodialysis in Lowering Elevated Levels of Asymmetric Dimethylarginine in ESRD Patients. Blood Purif. 2006, 24, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beerenhout, C.H.; Luik, A.J.; Jeuken-Mertens, S.G.J.; Bekers, O.; Menheere, P.; Hover, L.; Klaassen, L.; Van Der Sande, F.M.; Cheriex, E.C.; Meert, N.; et al. Pre-dilution on-line haemofiltration vs low-flux haemodialysis: A randomized prospective study. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2005, 20, 1155–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dominiczak, A.F.; Bohr, D.F. Nitric Oxide and Its Putative Role in Hypertension. Hypertension 1995, 25, 1202–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnal, J.-F.; Michel, J.-B.; Harrison, D.G. Nitric oxide in the pathogenesis of hypertension. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 1995, 4, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achan, V.; Broadhead, M.; Malaki, M.; Whitley, G.; Leiper, J.; MacAllister, R.; Vallance, P. Asymmetric Dimethylarginine Causes Hypertension and Cardiac Dysfunction in Humans and Is Actively Metabolized by Dimethylarginine Dimethylaminohydrolase. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Boil. 2003, 23, 1455–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- MacAllister, R.; Vallance, P. Nitric oxide in essential and renal hypertension. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1994, 5, 1057–1065. [Google Scholar]
- Bech, J.N.; Nielsen, C.B.; Pedersen, E.B. Effects of systemic NO synthesis inhibition on RPF, GFR, UNa, and vasoactive hormones in healthy humans. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 1996, 270, F845–F851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruilope, L.M.; Lahera, V.; Rodicio, J.L.; Romero, J.C. Participation of nitric oxide in the regulation of renal function: Possible role in the genesis of arterial hypertension. J. Hypertens. 1994, 12, 625–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kielstein, J.; Simmel, S.; Bode-Böger, S.; Roth, H.; Schmidt-Gayk, H.; Haller, H.; Fliser, D. Subpressor Dose Asymmetric Dimethylarginine Modulates Renal Function in Humans through Nitric Oxide Synthase Inhibition. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2004, 27, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuguma, K.; Ueda, S.; Yamagishi, S.-I.; Matsumoto, Y.; Kaneyuki, U.; Shibata, R.; Fujimura, T.; Matsuoka, H.; Kimoto, M.; Kato, S.; et al. Molecular Mechanism for Elevation of Asymmetric Dimethylarginine and Its Role for Hypertension in Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 2176–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Miyazaki, H.; Matsuoka, H.; Cooke, J.P.; Usui, M.; Ueda, S.; Okuda, S.; Imaizumi, T. Endogenous nitric oxide synthase inhibitor: A novel marker of atherosclerosis. J. Cardiol. 1999, 33, 1141–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perticone, F.; Sciacqua, A.; Maio, R.; Perticone, M.; Maas, R.; Böger, R.H.; Tripepi, G.; Sesti, G.; Zoccali, C. Asymmetric Dimethylarginine, L-Arginine, and Endothelial Dysfunction in Essential Hypertension. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2005, 46, 518–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Surdacki, A.; Nowicki, M.; Sandmann, J.; Tsikas, D.; Boeger, R.H.; Bode-Boeger, S.M.; Kruszelnicka-Kwiatkowska, O.; Kokot, F.; Dubiel, J.S.; Froelich, J.C. Reduced Urinary Excretion of Nitric Oxide Metabolites and Increased Plasma Levels of Asymmetric Dimethylarginine in Men with Essential Hypertension. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 1999, 33, 652–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, N.; Osanai, T.; Kamada, T.; Katoh, T.; Takahashi, K.; Okumura, K. Study on the relationship between plasma nitrite and nitrate level and salt sensitivity in human hypertension: Modulation of nitric oxide synthesis by salt intake. Circulation 2000, 101, 856–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoccali, C. Asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA): A cardiovascular and renal risk factor on the move. J. Hypertens. 2006, 24, 611–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuoka, H.; Itoh, S.; Kimoto, M.; Kohno, K.; Tamai, O.; Wada, Y.; Yasukawa, H.; Iwami, G.; Okuda, S.; Imaizumi, T. Asymmetrical Dimethylarginine, an Endogenous Nitric Oxide Synthase Inhibitor, in Experimental Hypertension. Hypertension 1997, 29, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mattson, D.L.; Higgins, D.J. Influence of Dietary Sodium Intake on Renal Medullary Nitric Oxide Synthase. Hypertension 1996, 27, 688–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osanai, T.; Saitoh, M.; Sasaki, S.; Tomita, H.; Matsunaga, T.; Okumura, K. Effect of Shear Stress on Asymmetric Dimethylarginine Release From Vascular Endothelial Cells. Hypertension 2003, 42, 985–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ueda, S.; Yamagishi, S.-I.; Kaida, Y.; Okuda, S. Asymmetric dimethylarginine may be a missing link between cardiovascular disease and chronic kidney disease (Review Article). Nephrology 2007, 12, 582–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kielstein, J.T.; Bode-Boger, S.M.; Frolich, J.C.; Ritz, E.; Haller, H.; Fliser, D. Asymmetric Dimethylarginine, Blood Pressure, and Renal Perfusion in Elderly Subjects. Circulation 2003, 107, 1891–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sverdlov, A.L.; Ngo, D.T.; Chan, W.P.A.; Chirkov, Y.Y.; Horowitz, J.D. Aging of the Nitric Oxide System: Are We as Old as Our NO? J. Am. Hear. Assoc. 2014, 3, e000973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scalera, F.; Borlak, J.; Beckmann, B.; Martens-Lobenhoffer, J.; Thum, T.; Tager, M.; Bode-Boger, S.M. Endogenous Nitric Oxide Synthesis Inhibitor Asymmetric Dimethyl l-Arginine Accelerates Endothelial Cell Senescence. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Boil. 2004, 24, 1816–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tripepi, G.; Raso, F.M.; Sijbrands, E.; Seck, M.S.; Maas, R.; Boger, R.; Witteman, J.; Rapisarda, F.A.; Malatino, L.; Mallamaci, F.; et al. Inflammation and Asymmetric Dimethylarginine for Predicting Death and Cardiovascular Events in ESRD Patients. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 6, 1714–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zoccali, C.; Mallamaci, F.; Tripepi, G. Inflammation and Atherosclerosis in End-Stage Renal Disease. Blood Purif. 2003, 21, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stenvinkel, P.; Ketteler, M.; Johnson, R.J.; Lindholm, B.; Pecoits-Filho, R.; Riella, M.; Heimbürger, O.; Cederholm, T.; Girndt, M. IL-10, IL-6, and TNF-α: Central factors in the altered cytokine network of uremia—The good, the bad, and the ugly. Kidney Int. 2005, 67, 1216–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krzyzanowska, K.; Mittermayer, F.; Wolzt, M.; Schernthaner, G. Asymmetric Dimethylarginine Predicts Cardiovascular Events in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 1834–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zoccali, C.; Maas, R.; Cutrupi, S.; Pizzini, P.; Finocchiaro, P.; Cambareri, F.; Panuccio, V.; Martorano, C.; Schulze, F.; Enia, G.; et al. Asymmetric dimethyl-arginine (ADMA) response to inflammation in acute infections. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2007, 22, 801–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghebremariam, Y.T.; LePendu, P.; Lee, J.C.; Erlanson, D.A.; Slaviero, A.; Shah, N.H.; Leiper, J.; Cooke, J.P. Unexpected effect of proton pump inhibitors: Elevation of the cardiovascular risk factor asymmetric dimethylarginine. Circulation 2013, 128, 845–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva-Damaso, E.; Oliva-Damaso, N.; Rodriguez-Esparragon, F.; Payan, J.; Marañes, A.; Parodis, Y.; Baamonde-Laborda, L.E.; Diaz, N.V.; Rodriguez-Perez, J.C. Asymmetric Dimethylarginine (ADMA) Levels Are Lower in Hemodialysis Patients Treated With Paricalcitol. Kidney Int. Rep. 2017, 2, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinhart, G.A. Vitamin D analogs: Novel therapeutic agents for cardiovascular disease? Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs 2004, 5, 947–951. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu-Wong, J.R.; Nakane, M.; Traylor, L.; Ruan, X.; Kroeger, P.E.; Tian, J. Cardiovascular disease in chronic kidney failure: Is there a role for vitamin D analogs? Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs 2005, 6, 245–254. [Google Scholar]
- Zoccali, C.; Curatola, G.; Panuccio, V.; Tripepi, R.; Pizzini, P.; Versace, M.; Bolignano, D.; Cutrupi, S.; Politi, R.; Tripepi, G.; et al. Paricalcitol and Endothelial Function in Chronic Kidney Disease Trial. Hypertension 2014, 64, 1005–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Torino, C.; Pizzini, P.; Cutrupi, S.; Tripepi, R.; Tripepi, G.; Mallamaci, F.; Zoccali, C. Vitamin D and methylarginines in chronic kidney disease (CKD). PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatematsu, S.; Wakino, S.; Kanda, T.; Homma, K.; Yoshioka, K.; Hasegawa, K.; Sugano, N.; Kimoto, M.; Saruta, T.; Hayashi, K. Role of Nitric Oxide–Producing and–Degrading Pathways in Coronary Endothelial Dysfunction in Chronic Kidney Disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 18, 741–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, S.; Santha, T.; Leone, A.; Wilcox, C. Effects of amlodipine and valsartan on oxidative stress and plasma methylarginines in end-stage renal disease patients on hemodialysis. Kidney Int. 2006, 70, 2109–2115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stühlinger, M.C.; Abbasi, F.; Chu, J.W.; Lamendola, C.; McLaughlin, T.L.; Cooke, J.P.; Reaven, G.M.; Tsao, P.S. Relationship Between Insulin Resistance and an Endogenous Nitric Oxide Synthase Inhibitor. JAMA 2002, 287, 1420–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cross, J.M.; Donald, A.E.; Kharbanda, R.; Deanfield, J.E.; Woolfson, R.G.; MacAllister, R.J. Acute administration of L-arginine does not improve arterial endothelial function in chronic renal failure. Kidney Int. 2001, 60, 2318–2323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hand, M.F.; Haynes, W.G.; Webb, D.J. Hemodialysis and L-arginine, but not D-arginine, correct renal failure-associated endothelial dysfunction. Kidney Int. 1998, 53, 1068–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulman, S.P.; Becker, L.C.; Kass, D.A.; Champion, H.C.; Terrin, M.L.; Forman, S.; Ernst, K.V.; Kelemen, M.D.; Townsend, S.N.; Capriotti, A.; et al. L-arginine therapy in acute myocardial infarction: The Vascular Interaction With Age in Myocardial Infarction (VINTAGE MI) randomized clinical trial. JAMA 2006, 295, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, A.M.; Harada, R.; Nair, N.; Balasubramanian, N.; Cooke, J.P. L-Arginine Supplementation in Peripheral Arterial Disease: No Benefit and Possible Harm. Circulation 2007, 116, 188–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, A.; Egashira, K.; Narishige, T.; Muramatsu, K.; Takeshita, A. Renin-Angiotensin System is Involved in the Mechanism of Increased Serum Asymmetric Dimethylarginine in Essential Hypertension. Jpn. Circ. J. 2001, 65, 775–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delles, C.; Schneider, M.P.; John, S.; Gekle, M.; Schmieder, R.E. Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibition and angiotensin II AT1-receptor blockade reduce the levels of asymmetrical N(G), N(G)-dimethylarginine in human essential hypertension. Am. J. Hypertens. 2002, 15, 590–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Napoli, C.; Sica, V.; De Nigris, F.; Pignalosa, O.; Condorelli, M.; Ignarro, L.; Liguori, A. Sulfhydryl angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition induces sustained reduction of systemic oxidative stress and improves the nitric oxide pathway in patients with essential hypertension. Am. Hear. J. 2004, 148, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fliser, D.; Wagner, K.-K.; Loos, A.; Tsikas, D.; Haller, H. Chronic Angiotensin II Receptor Blockade Reduces (Intra) Renal Vascular Resistance in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2005, 16, 1135–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asagami, T.; Abbasi, F.; Stuelinger, M.; Lamendola, C.; McLaughlin, T.; Cooke, J.; Reaven, G.; Tsao, P. Metformin treatment lowers asymmetric dimethylarginine concentrations in patients with type 2 diabetes. Metabolism 2002, 51, 843–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakino, S.; Hayashi, K.; Tatematsu, S.; Hasegawa, K.; Takamatsu, I.; Kanda, T.; Homma, K.; Yoshioka, K.; Sugano, N.; Saruta, T. Pioglitazone Lowers Systemic Asymmetric Dimethylarginine by Inducing Dimethylarginine Dimethylaminohydrolase in Rats. Hypertens. Res. 2005, 28, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wascher, T.C.; Schmoelzer, I.; Wiegratz, A.; Stuehlinger, M.; Kotzka, J.; Enderle, M.; Mueller-Wieland, D.; Mueller-Wieland, D. Reduction of postchallenge hyperglycaemia prevents acute endothelial dysfunction in subjects with impaired glucose tolerance. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2005, 35, 551–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Post, M.S.; Verhoeven, M.O.; Van Der Mooren, M.J.; Kenemans, P.; Stehouwer, C.D.A.; Teerlink, T. Effect of Hormone Replacement Therapy on Plasma Levels of the Cardiovascular Risk Factor Asymmetric Dimethylarginine: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled 12-Week Study in Healthy Early Postmenopausal Women. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 4221–4226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Teerlink, T.; Neele, S.J.M.; De Jong, S.; Netelenbos, J.C.; Stehouwer, C.D.A. Oestrogen replacement therapy lowers plasma levels of asymmetrical dimethylarginine in healthy postmenopausal women. Clin. Sci. 2003, 105, 67–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Holden, D.P.; Cartwright, J.E.; Nussey, S.S.; Whitley, G.S.J. Estrogen Stimulates Dimethylarginine Dimethylaminohydrolase Activity and the Metabolism of Asymmetric Dimethylarginine. Circulation 2003, 108, 1575–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sydow, K.; Munzel, T. ADMA and oxidative stress. Atheroscler. Suppl. 2003, 4, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holven, K.B.; Haugstad, T.S.; Holm, T.; Aukrust, P.; Ose, L.; Nenseter, M.S. Folic acid treatment reduces elevated plasma levels of asymmetric dimethylarginine in hyperhomocysteinaemic subjects. Br. J. Nutr. 2003, 89, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saran, R.; Novak, J.E.; Desai, A.; Abdulhayoglu, E.; Warren, J.S.; Bustami, R.; Handelman, G.J.; Barbato, D.; Weitzel, W.; D’Alecy, L.G.; et al. Impact of vitamin E on plasma asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) in chronic kidney disease (CKD): A pilot study. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2003, 18, 2415–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillis, K.; Stevens, K.K.; Bell, E.; Patel, R.K.; Jardine, A.G.; Morris, S.T.W.; Schneider, M.P.; Delles, C.; Mark, P.B. Ascorbic acid lowers central blood pressure and asymmetric dimethylarginine in chronic kidney disease. Clin. Kidney J. 2018, 11, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Eid, H.M.; Eritsland, J.; Larsen, J.; Arnesen, H.; Seljeflot, I. Increased levels of asymmetric dimethylarginine in populations at risk for atherosclerotic disease. Effects of pravastatin. Atherosclerosis 2003, 166, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Päivä, H.; Laakso, J.; Lehtimäki, T.; Isomustajärvi, M.; Ruokonen, I.; Laaksonen, R. Effect of High-Dose Statin Treatment on Plasma Concentrations of Endogenous Nitric Oxide Synthase Inhibitors. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2003, 41, 219–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.-M.; Ding, Y.-A.; Leu, H.-B.; Yin, W.-H.; Sheu, W.H.-H.; Chu, K.-M. Effect of rosuvastatin on plasma levels of asymmetric dimethylarginine in patients with hypercholesterolemia. Am. J. Cardiol. 2004, 94, 157–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, S.P.; Gibson, M.F.; Rimmer, D.M.; Gibson, T.M.; Sharp, B.R.; Lefer, D.J. Direct vascular and cardioprotective effects of rosuvastatin, a new HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2002, 40, 1172–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laufs, U.; La Fata, V.; Plutzky, J.; Liao, J.K. Upregulation of Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase by HMG CoA Reductase Inhibitors. Circulation 1998, 97, 1129–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shishehbor, M.H.; Brennan, M.-L.; Aviles, R.J.; Fu, X.; Penn, M.S.; Sprecher, D.L.; Hazen, S.L. Statins Promote Potent Systemic Antioxidant Effects Through Specific Inflammatory Pathways. Circulation 2003, 108, 426–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maas, R.; Mieth, M.; Titze, S.I.; Hübner, S.; Fromm, M.F.; Kielstein, J.T.; Schneider, M.P.; Eckardt, K.-U.; Meiselbach, H.; Schneider, M.; et al. Drugs linked to plasma homoarginine in chronic kidney disease patients—A cross-sectional analysis of the German Chronic Kidney Disease cohort. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2018, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, T.; Chouinard, M.; Cox, A.L.; Sipes, P.; Marcelo, M.; Ficorilli, J.; Li, S.; Gao, H.; Ryan, T.P.; Michael, M.D.; et al. Farnesoid X Receptor Agonist Reduces Serum Asymmetric Dimethylarginine Levels through Hepatic Dimethylarginine Dimethylaminohydrolase-1 Gene Regulation. J. Boil. Chem. 2006, 281, 39831–39838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ferrigno, A.; Di Pasqua, L.G.; Berardo, C.; Siciliano, V.; Rizzo, V.; Adorini, L.; Richelmi, P.; Vairetti, M. The farnesoid X receptor agonist obeticholic acid upregulates biliary excretion of asymmetric dimethylarginine via MATE-1 during hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0191430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tain, Y.L.; Hsu, C.N. Toxic Dimethylarginines: Asymmetric Dimethylarginine (ADMA) and Symmetric Dimethylarginine (SDMA). Toxins 2017, 9, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Oliva-Damaso, E.; Oliva-Damaso, N.; Rodriguez-Esparragon, F.; Payan, J.; Baamonde-Laborda, E.; Gonzalez-Cabrera, F.; Santana-Estupiñan, R.; Rodriguez-Perez, J.C. Asymmetric (ADMA) and Symmetric (SDMA) Dimethylarginines in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Clinical Approach. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3668. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20153668
Oliva-Damaso E, Oliva-Damaso N, Rodriguez-Esparragon F, Payan J, Baamonde-Laborda E, Gonzalez-Cabrera F, Santana-Estupiñan R, Rodriguez-Perez JC. Asymmetric (ADMA) and Symmetric (SDMA) Dimethylarginines in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Clinical Approach. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(15):3668. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20153668
Chicago/Turabian StyleOliva-Damaso, Elena, Nestor Oliva-Damaso, Francisco Rodriguez-Esparragon, Juan Payan, Eduardo Baamonde-Laborda, Fayna Gonzalez-Cabrera, Raquel Santana-Estupiñan, and Jose Carlos Rodriguez-Perez. 2019. "Asymmetric (ADMA) and Symmetric (SDMA) Dimethylarginines in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Clinical Approach" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 15: 3668. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20153668
APA StyleOliva-Damaso, E., Oliva-Damaso, N., Rodriguez-Esparragon, F., Payan, J., Baamonde-Laborda, E., Gonzalez-Cabrera, F., Santana-Estupiñan, R., & Rodriguez-Perez, J. C. (2019). Asymmetric (ADMA) and Symmetric (SDMA) Dimethylarginines in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Clinical Approach. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(15), 3668. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20153668





