Gene–Environment Interactions on Body Fat Distribution
Abstract
:1. Introduction
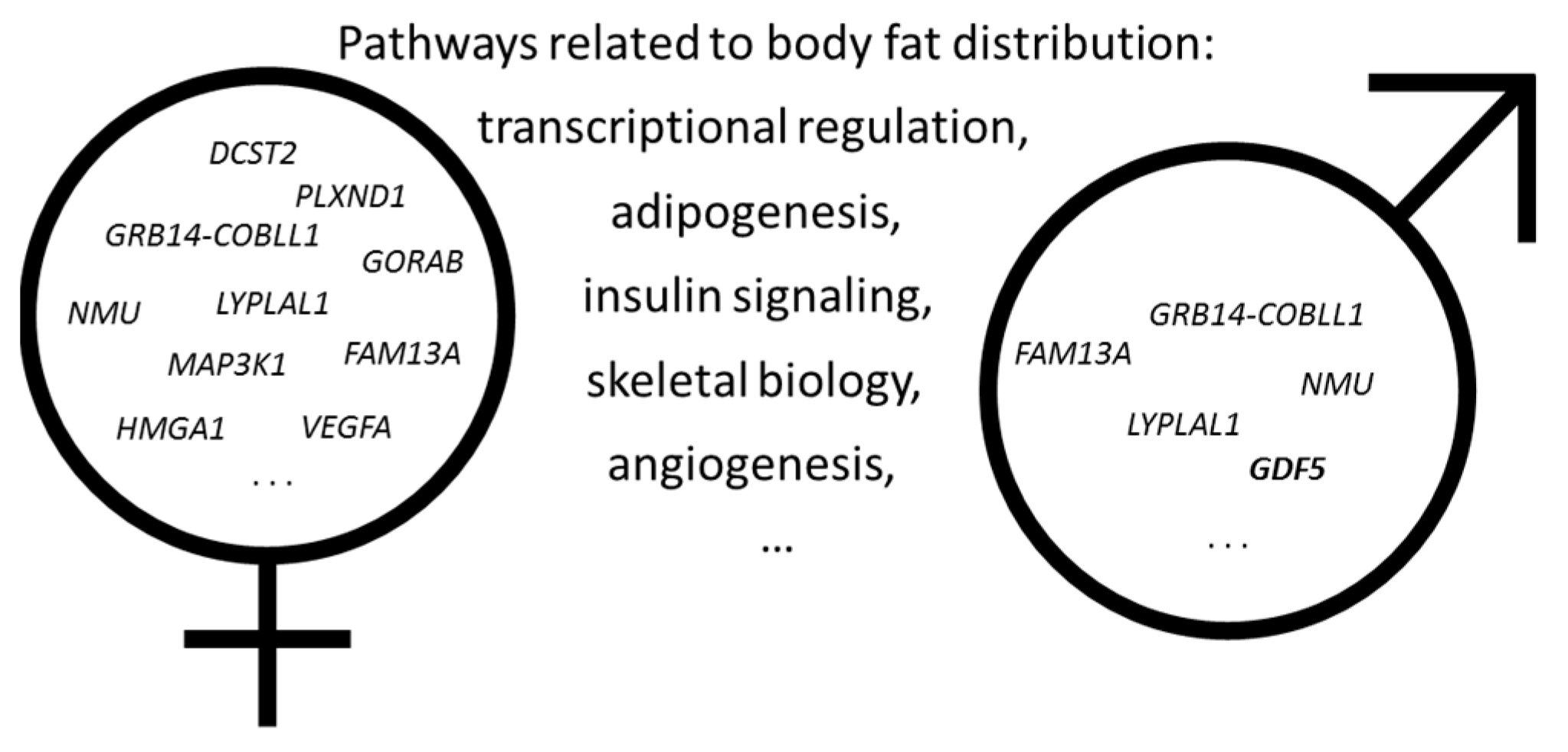
2. Genetics of Obesity and Body Fat Distribution
3. Gene–Environment Interaction on Obesity and Body Fat Distribution in Observational Studies
4. Genotype and Changes in Weight and Body Fat Distribution in Response to Diet/Lifestyle Interventions
5. Insight into the Role of the Gut Microbiota and Metabolites in Obesity and Body Fat Distribution
6. Summary and Future Direction
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ogden, C.L.; Carroll, M.D.; Fryar, C.D.; Flegal, K.M. Prevalence of Obesity Among Adults and Youth: United States, 2011-2014. Nchs Data Brief. 2015, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Zwicker, L.; Brownell, K.D.; Swinburn, B.; Ashe, M.; Cawley, J.H.; Roberto, C.A.; Huang, T.T.-K.; Costa, S.A.; Hawkes, C. Patchy progress on obesity prevention: Emerging examples, entrenched barriers, and new thinking. Lancet 2015, 385, 2400–2409. [Google Scholar]
- Afshin, A.; Forouzanfar, M.H.; Reitsma, M.B.; Sur, P.; Estep, K.; Lee, A.; Marczak, L.; Mokdad, A.H.; Moradi-Lakeh, M.; Naghavi, M.; et al. Health Effects of Overweight and Obesity in 195 Countries over 25 Years. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fryar, C.D.; Kruszon-Moran, D.; Gu Q, O.C. Mean Body Weight, Height, Waist Circumference, and Body Mass Index Among Adults: United States, 1999–2000 Through 2015–2016; Technical Report for Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Hyattsville, MD, USA, December 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, T.; Lyon, C.J.; Bergin, S.; Caligiuri, M.A.; Hsueh, W.A. Obesity, inflammation, and cancer. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2016, 11, 421–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campbell, J.M.; Lane, M.; Owens, J.A.; Bakos, H.W. Paternal obesity negatively affects male fertility and assisted reproduction outcomes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Reprod. Biomed. Online 2015, 31, 593–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carey, V.J.; Walters, E.E.; Colditz, G.A.; Solomon, C.G.; Willet, W.C.; Rosner, B.A.; Speizer, F.E.; Manson, J.E. Body fat distribution and risk of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus in women: The Nurses’ Health Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1997, 145, 614–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Rimm, E.B.; Stampfer, M.J.; Willett, W.C.; Hu, F.B. Comparison of abdominal adiposity and overall obesity in predicting risk of type 2 diabetes among men. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 81, 555–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Canoy, D. Distribution of body fat and risk of coronary heart disease in men and women. Curr. Opin. Cardiol. 2008, 23, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pischon, T.; CJ, G.; GS, H.; Rifai, N.; FB, H.; EB, R.; Pischon, T.; Girman, C.J.; Hotamisligil, G.S.; Rifai, N.; et al. Plasma adiponectin levels and risk of myocardial infarction in men. Jama J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2004, 291, 1730–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neeland, I.J.; Ross, R.; Despres, J.-P.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Yamashita, S.; Shai, I.; Seidell, J.; Magni, P.; Santos, R.D.; Arsenault, B.; et al. Visceral and ectopic fat, atherosclerosis, and cardiometabolic disease: A position statement. Lancet. Diabetes Endocrinol. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S2213858719300841 (accessed on 10 July 2019). [CrossRef]
- Abraham, T.M.; Pedley, A.; Massaro, J.M.; Hoffmann, U.; Fox, C.S. Association Between Visceral and Subcutaneous Adipose Depots and Incident Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors. Circulation 2015, 132, 1639–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hickson, D.A.; Taylor, H.A.; May, W.D.; Liu, J.; Fox, C.S.; Carr, J.J.; Hairston, K.G. Impact of Abdominal Visceral and Subcutaneous Adipose Tissue on Cardiometabolic Risk Factors: The Jackson Heart Study. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 5419–5426. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Neeland, I.J.; Poirier, P.; Després, J.P. Cardiovascular and Metabolic Heterogeneity of Obesity. Circulation 2018, 137, 1391–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jean-Pierre, D. Body Fat Distribution and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease. Circulation 2012, 126, 1301–1313. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Shungin, D.; Winkler, T.W.; Croteau-Chonka, D.C.; Ferreira, T.; Locke, A.E.; Mägi, R.; Strawbridge, R.J.; Pers, T.H.; Fischer, K.; Justice, A.E. New genetic loci link adipose and insulin biology to body fat distribution. Nature 2015, 518, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snijder, M.B.; Dekker, J.M.; Visser, M.; Bouter, L.M.; Stehouwer, C.D.A.; Kostense, P.J.; Yudkin, J.S.; Heine, R.J.; Nijpels, G.; Seidell, J.C. Associations of hip and thigh circumferences independent of waist circumference with the incidence of type 2 diabetes: The Hoorn Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2003, 77, 1192–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yusuf, S.; Hawken, S.; Ounpuu, S.; Bautista, L.; Franzosi, M.G.; Commerford, P.; Lang, C.C.; Rumboldt, Z.; Onen, C.L.; Lisheng, L.; et al. Obesity and the risk of myocardial infarction in 27,000 participants from 52 countries: A case-control study. Lancet 2005, 366, 1640–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, C.; Craig, C.L.; Katzmarzyk, P.T. Influence of central and extremity circumferences on all-cause mortality in men and women. Obes. (Silver Spring) 2008, 16, 2690–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozaki, K.; Ohnishi, Y.; Iida, A.; Sekine, A.; Yamada, R.; Tsunoda, T.; Sato, H.; Sato, H.; Hori, M.; Nakamura, Y. Functional SNPs in the lymphotoxin-α gene that are associated with susceptibility to myocardial infarction. Nat. Genet. 2002, 32, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.; Cho, Y.A. Gene-environment interaction and obesity. Nutr. Rev. 2008, 66, 684–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L. Personalized nutrition and obesity. Ann. Med. 2014, 46, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chagnon, Y.C.; Perusse, L.; Bouchard, C. Familial aggregation of obesity, candidate genes and quantitative trait loci. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 1997, 8, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérusse, L.; Rice, T.K.; Bouchard, C. Evidence of a genetic component to obesity from genetic epidemiology. Handb. Obes. Epidemiol. Etiol. Physiopathol. 2013, 91–104. [Google Scholar]
- Bouchard, C.; Després, J.-P.; Mauriège, P. Genetic and nongenetic determinants of regional fat distribution. Endocr. Rev. 1993, 14, 72–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bray, M.S.; Loos, R.J.F.; McCaffery, J.M.; Ling, C.; Franks, P.W.; Weinstock, G.M.; Snyder, M.P.; Vassy, J.L.; Agurs-Collins, T.; Group, C.W. NIH working group report—using genomic information to guide weight management: From universal to precision treatment. Obesity 2016, 24, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stunkard, A.J.; Foch, T.T.; Hrubec, Z. A twin study of human obesity. JAMA 1986, 256, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elks, C.E.; den Hoed, M.; Zhao, J.H.; Sharp, S.J.; Wareham, N.J.; Loos, R.J.F.; Ong, K.K. Variability in the heritability of body mass index: A systematic review and meta-regression. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 2012, 3, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dongen, J.; Willemsen, G.; Chen, W.-M.; de Geus, E.J.C.; Boomsma, D.I. Heritability of metabolic syndrome traits in a large population-based sample. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 2914–2923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herrera, B.M.; Lindgren, C.M. The genetics of obesity. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2010, 10, 498–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulit, S.L.; Karaderi, T.; Lindgren, C.M. Sexual dimorphisms in genetic loci linked to body fat distribution. Biosci. Rep. 2017, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindgren, C.M.; Heid, I.M.; Randall, J.C.; Lamina, C.; Steinthorsdottir, V.; Qi, L.; Speliotes, E.K.; Thorleifsson, G.; Willer, C.J.; Herrera, B.M.; et al. Genome-wide association scan meta-analysis identifies three Loci influencing adiposity and fat distribution. PloS Genet. 2009, 5, e1000508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, C.S.; Liu, Y.; White, C.C.; Feitosa, M.; Smith, A.V.; Heard-Costa, N.; Lohman, K.; Johnson, A.D.; Foster, M.C.; Greenawalt, D.M. Genome-wide association for abdominal subcutaneous and visceral adipose reveals a novel locus for visceral fat in women. PloS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yengo, L.; Sidorenko, J.; Kemper, K.E.; Zheng, Z.; Wood, A.R.; Weedon, M.N.; Frayling, T.M.; Hirschhorn, J.; Yang, J.; Visscher, P.M. Meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies for height and body mass index in approximately 700000 individuals of European ancestry. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2018, 27, 3641–3649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Locke, A.; Kahali, B.; Berndt, S.; Justice, A.; Pers, T. Genetic studies of body mass index yield new insights for obesity biology. Nature 2015, 518, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pulit, S.L.; Stoneman, C.; Morris, A.P.; Wood, A.R.; Glastonbury, C.A.; Tyrrell, J.; Yengo, L.; Ferreira, T.; Marouli, E.; Ji, Y.; et al. Meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies for body fat distribution in 694 649 individuals of European ancestry. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2019, 28, 166–174. [Google Scholar]
- Rask-Andersen, M.; Karlsson, T.; Ek, W.E.; Johansson, Å. Genome-wide association study of body fat distribution identifies adiposity loci and sex-specific genetic effects. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turcot, V.; Lu, Y.; Highland, H.M.; Schurmann, C.; Justice, A.E.; Fine, R.S.; Bradfield, J.P.; Esko, T.; Giri, A.; Graff, M.; et al. Protein-altering variants associated with body mass index implicate pathways that control energy intake and expenditure in obesity. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justice, A.E.; Karaderi, T.; Highland, H.M.; Young, K.L.; Graff, M.; Lu, Y.; Turcot, V.; Auer, P.L.; Fine, R.S.; Guo, X.; et al. Protein-coding variants implicate novel genes related to lipid homeostasis contributing to body-fat distribution. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 452–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fox, C.S.; White, C.C.; Lohman, K.; Heard-Costa, N.; Cohen, P.; Zhang, Y.; Johnson, A.D.; Emilsson, V.; Liu, C.-T.; Chen, Y.-D.I.; et al. Genome-wide association of pericardial fat identifies a unique locus for ectopic fat. PloS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.; Yiorkas, A.M.; Frau, F.; Mook-Kanamori, D.; Staiger, H.; Thomas, E.L.; Atabaki-Pasdar, N.; Campbell, A.; Tyrrell, J.; Jones, S.E.; et al. Genome-Wide and Abdominal MRI Data Provide Evidence That a Genetically Determined Favorable Adiposity Phenotype Is Characterized by Lower Ectopic Liver Fat and Lower Risk of Type 2 Diabetes, Heart Disease, and Hypertension. Diabetes 2019, 68, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Langefeld, C.D.; Ziegler, J.T.; Taylor, K.D.; Norris, J.M.; Chen, Y.-D.I.; Hellwege, J.N.; Guo, X.; Allison, M.A.; Speliotes, E.K.; et al. Genome-Wide Study of Subcutaneous and Visceral Adipose Tissue Reveals Novel Sex-Specific Adiposity Loci in Mexican Americans. Obes. (Silver Spring) 2018, 26, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, M.C.; Yang, Q.; Hwang, S.-J.; Hoffmann, U.; Fox, C.S. Heritability and genome-wide association analysis of renal sinus fat accumulation in the Framingham Heart Study. Bmc Med. Genet. 2011, 12, 148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norris, J.M.; Langefeld, C.D.; Talbert, M.E.; Wing, M.R.; Haritunians, T.; Fingerlin, T.E.; Hanley, A.J.G.; Ziegler, J.T.; Taylor, K.D.; Haffner, S.M.; et al. Genome-wide association study and follow-up analysis of adiposity traits in Hispanic Americans: The IRAS Family Study. Obes. (Silver Spring) 2009, 17, 1932–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loos, R.J. The genetics of adiposity. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 2018, 50, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ried, J.S.; Jeff, J.M.; Chu, A.Y.; Bragg-Gresham, J.L.; Van Dongen, J.; Huffman, J.E.; Ahluwalia, T.S.; Cadby, G.; Eklund, N.; Eriksson, J.; et al. A principal component meta-analysis on multiple anthropometric traits identifies novel loci for body shape. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaput, J.-P.; Doucet, E.; Tremblay, A. Obesity: A disease or a biological adaptation? An update. Obes. Rev. 2012, 13, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L. Gene-diet interaction and weight loss. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2014, 25, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tropf, F.C.; Lee, S.H.; Verweij, R.M.; Stulp, G.; van der Most, P.J.; de Vlaming, R.; Bakshi, A.; Briley, D.A.; Rahal, C.; Hellpap, R.; et al. Hidden heritability due to heterogeneity across seven populations. Nat. Hum. Behav. 2017, 1, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rokholm, B.; Silventoinen, K.; Tynelius, P.; Gamborg, M.; Sorensen, T.I.A.; Rasmussen, F. Increasing genetic variance of body mass index during the Swedish obesity epidemic. PloS ONE 2011, 6, e27135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rokholm, B.; Silventoinen, K.; Angquist, L.; Skytthe, A.; Kyvik, K.O.; Sorensen, T.I.A. Increased genetic variance of BMI with a higher prevalence of obesity. PloS ONE 2011, 6, e20816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaprio, J. Twins and the mystery of missing heritability: The contribution of gene-environment interactions. J. Intern. Med. 2012, 272, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manolio, T.A.; Collins, F.S.; Cox, N.J.; Goldstein, D.B.; Hindorff, L.A.; Hunter, D.J.; McCarthy, M.I.; Ramos, E.M.; Cardon, L.R.; Chakravarti, A.; et al. Finding the missing heritability of complex diseases. Nature 2009, 461, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Perusse, L.; Bouchard, C. Gene-diet interactions in obesity. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 72, 1285S–1290S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.; Wang, T.; Heianza, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Sun, D.; Kang, J.H.; Pasquale, L.R.; Rimm, E.B.; Manson, J.E.; Hu, F.B.; et al. Habitual consumption of long-chain n-3 PUFAs and fish attenuates genetically associated long-term weight gain. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2019, 109, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Q.; Downer, M.K.; Kilpelainen, T.O.; Taal, H.R.; Barton, S.J.; Ntalla, I.; Standl, M.; Boraska, V.; Huikari, V.; Kiefte-de Jong, J.C.; et al. Dietary Intake, FTO Genetic Variants, and Adiposity: A Combined Analysis of Over 16,000 Children and Adolescents. Diabetes 2015, 64, 2467–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, C.M.; Kesse-Guyot, E.; McManus, R.; Hercberg, S.; Lairon, D.; Planells, R.; Roche, H.M. High dietary saturated fat intake accentuates obesity risk associated with the fat mass and obesity-associated gene in adults. J. Nutr. 2012, 142, 824–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corella, D.; Arnett, D.K.; Tucker, K.L.; Kabagambe, E.K.; Tsai, M.; Parnell, L.D.; Lai, C.-Q.; Lee, Y.-C.; Warodomwichit, D.; Hopkins, P.N.; et al. A high intake of saturated fatty acids strengthens the association between the fat mass and obesity-associated gene and BMI. J. Nutr. 2011, 141, 2219–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilella, M.; Nunes de Oliveira Costa, G.; Lima Barreto, M.; Alexandrina Figueredo, C.; Maria Alcantara-Neves, N.; Cunha Rodrigues, L.; Maria Alvim de Matos, S.; Leovigildo Fiaccone, R.; Oliveira, P.; Rocha, A.; et al. Effect of dietary consumption as a modifier on the association between FTO gene variants and excess body weight in children from an admixed population in Brazil: The Social Changes, Asthma and Allergy in Latin America (SCAALA) cohort study. Br. J. Nutr. 2017, 117, 1503–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedel, C.; von Kries, R.; Fenske, N.; Strauch, K.; Ness, A.R.; Beyerlein, A. Interactions of genetic and environmental risk factors with respect to body fat mass in children: Results from the ALSPAC study. Obes. (Silver Spring) 2013, 21, 1238–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenfield, J.R.; Samaras, K.; Campbell, L.V.; Jenkins, A.B.; Kelly, P.J.; Spector, T.D. Moderate Alcohol Consumption, Dietary Fat Composition, and Abdominal Obesity in Women: Evidence for Gene-Environment Interaction. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 88, 5381–5386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qi, Q.; Chu, A.Y.; Kang, J.H.; Huang, J.; Rose, L.M.; Jensen, M.K.; Liang, L.; Curhan, G.C.; Pasquale, L.R.; Wiggs, J.L.; et al. Fried food consumption, genetic risk, and body mass index: Gene-diet interaction analysis in three US cohort studies. BMJ 2014, 348, g1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, M.; Ellervik, C.; Huang, T.; Jensen, M.K.; Curhan, G.C.; Pasquale, L.R.; Kang, J.H.; Wiggs, J.L.; Hunter, D.J.; Willett, W.C.; et al. Diet quality and genetic association with body mass index: Results from 3 observational studies. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2018, 108, 1291–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razquin, C.; Martinez, J.A.; Martinez-Gonzalez, M.A.; Salas-Salvado, J.; Estruch, R.; Marti, A. A 3-year Mediterranean-style dietary intervention may modulate the association between adiponectin gene variants and body weight change. Eur. J. Nutr. 2010, 49, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nettleton, J.A.; Follis, J.L.; Ngwa, J.S.; Smith, C.E.; Ahmad, S.; Tanaka, T.; Wojczynski, M.K.; Voortman, T.; Lemaitre, R.N.; Kristiansson, K.; et al. Gene x dietary pattern interactions in obesity: Analysis of up to 68 317 adults of European ancestry. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015, 24, 4728–4738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Heianza, Y.; Sun, D.; Huang, T.; Ma, W.; Rimm, E.B.; Manson, J.E.; Hu, F.B.; Willett, W.C.; Qi, L. Improving adherence to healthy dietary patterns, genetic risk, and long term weight gain: Gene-diet interaction analysis in two prospective cohort studies. BMJ 2018, 360, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, A.I.; Wauthier, F.; Donnelly, P. Multiple novel gene-by-environment interactions modify the effect of FTO variants on body mass index. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, Q.; Li, Y.; Chomistek, A.K.; Kang, J.H.; Curhan, G.C.; Pasquale, L.R.; Willett, W.C.; Rimm, E.B.; Hu, F.B.; Qi, L. Television watching, leisure time physical activity, and the genetic predisposition in relation to body mass index in women and men. Circulation 2012, 126, 1821–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyrrell, J.; Wood, A.R.; Ames, R.M.; Yaghootkar, H.; Beaumont, R.N.; Jones, S.E.; Tuke, M.A.; Ruth, K.S.; Freathy, R.M.; Davey Smith, G.; et al. Gene–obesogenic environment interactions in the UK Biobank study. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2017, 46, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Rukh, G.; Varga, T.V.; Ali, A.; Kurbasic, A.; Shungin, D.; Ericson, U.; Koivula, R.W.; Chu, A.Y.; Rose, L.M.; et al. Gene x physical activity interactions in obesity: Combined analysis of 111,421 individuals of European ancestry. PloS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilpelainen, T.O.; Qi, L.; Brage, S.; Sharp, S.J.; Sonestedt, E.; Demerath, E.; Ahmad, T.; Mora, S.; Kaakinen, M.; Sandholt, C.H.; et al. Physical activity attenuates the influence of FTO variants on obesity risk: A meta-analysis of 218,166 adults and 19,268 children. PloS Med. 2011, 8, e1001116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Q.; Chu, A.Y.; Kang, J.H.; Jensen, M.K.; Curhan, G.C.; Pasquale, L.R.; Ridker, P.M.; Hunter, D.J.; Willett, W.C.; Rimm, E.B.; et al. Sugar-sweetened beverages and genetic risk of obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 1387–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunkwall, L.; Chen, Y.; Hindy, G.; Rukh, G.; Ericson, U.; Barroso, I.; Johansson, I.; Franks, P.W.; Orho-Melander, M.; Renstrom, F. Sugar-sweetened beverage consumption and genetic predisposition to obesity in 2 Swedish cohorts. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 104, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olsen, N.J.; Angquist, L.; Larsen, S.C.; Linneberg, A.; Skaaby, T.; Husemoen, L.L.N.; Toft, U.; Tjonneland, A.; Halkjaer, J.; Hansen, T.; et al. Interactions between genetic variants associated with adiposity traits and soft drinks in relation to longitudinal changes in body weight and waist circumference. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 104, 816–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Hennein, R.; Liu, C.; Long, M.T.; Hoffmann, U.; Jacques, P.F.; Lichtenstein, A.H.; Hu, F.B.; Levy, D. Improved Diet Quality Associates With Reduction in Liver Fat—Particularly in Individuals With High Genetic Risk Scores for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, S.; Mejia-Guevara, I.; Estrada, K.; Liu, S.Y.; Glymour, M.M. Association of a Genetic Risk Score With Body Mass Index Across Different Birth Cohorts. JAMA 2016, 316, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Celis-Morales, C.; Lyall, D.M.; Guo, Y.; Steell, L.; Llanas, D.; Ward, J.; Mackay, D.F.; Biello, S.M.; Bailey, M.E.; Pell, J.P.; et al. Sleep characteristics modify the association of genetic predisposition with obesity and anthropometric measurements in 119,679 UK Biobank participants. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2017, 105, 980–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjornland, T.; Langaas, M.; Grill, V.; Mostad, I.L. Assessing gene-environment interaction effects of FTO, MC4R and lifestyle factors on obesity using an extreme phenotype sampling design: Results from the HUNT study. PloS ONE 2017, 12, e0175071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, B.C.; Kanters, S.; Bandayrel, K.; Wu, P.; Naji, F.; Siemieniuk, R.A.; Ball, G.D.C.; Busse, J.W.; Thorlund, K.; Guyatt, G.; et al. Comparison of weight loss among named diet programs in overweight and obese adults: A meta-analysis. JAMA 2014, 312, 923–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacks, F.M.; Bray, G.A.; Carey, V.J.; Smith, S.R.; Ryan, D.H.; Anton, S.D.; McManus, K.; Champagne, C.M.; Bishop, L.M.; Laranjo, N.; et al. Comparison of weight-loss diets with different compositions of fat, protein, and carbohydrates. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 859–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Qi, Q.; Zhang, C.; Smith, S.R.; Hu, F.B.; Sacks, F.M.; Bray, G.A.; Qi, L. FTO genotype and 2-year change in body composition and fat distribution in response to weight-loss diets: The POUNDS LOST Trial. Diabetes 2012, 61, 3005–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heianza, Y.; Sun, D.; Ma, W.; Zheng, Y.; Champagne, C.M.; Bray, G.A.; Sacks, F.M.; Qi, L. Gut-microbiome-related LCT genotype and 2-year changes in body composition and fat distribution: The POUNDS Lost Trial. Int. J. Obes. (Lond) 2018, 42, 1565–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heianza, Y.; Ma, W.; Huang, T.; Wang, T.; Zheng, Y.; Smith, S.R.; Bray, G.A.; Sacks, F.M.; Qi, L. Macronutrient Intake-Associated FGF21 Genotype Modifies Effects of Weight-Loss Diets on 2-Year Changes of Central Adiposity and Body Composition: The POUNDS Lost Trial. Diabetes Care 2016, 39, 1909–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goni, L.; Sun, D.; Heianza, Y.; Wang, T.; Huang, T.; Martinez, J.A.; Shang, X.; Bray, G.A.; Smith, S.R.; Sacks, F.M.; et al. A circadian rhythm-related MTNR1B genetic variant modulates the effect of weight-loss diets on changes in adiposity and body composition: The POUNDS Lost trial. Eur. J. Nutr. 2019, 58, 1381–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattei, J.; Qi, Q.; Hu, F.B.; Sacks, F.M.; Qi, L. TCF7L2 genetic variants modulate the effect of dietary fat intake on changes in body composition during a weight-loss intervention. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 96, 1129–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, X.; Qi, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Huang, T.; Lathrop, M.; Zelenika, D.; Bray, G.A.; Sacks, F.M.; Liang, L.; Qi, L. Neuropeptide Y genotype, central obesity, and abdominal fat distribution: The POUNDS LOST trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 102, 514–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.; Wang, T.; Heianza, Y.; Sun, D.; Ivey, K.; Durst, R.; Schwarzfuchs, D.; Stampfer, M.J.; Bray, G.A.; Sacks, F.M.; et al. HNF1A variant, energy-reduced diets and insulin resistance improvement during weight loss: The POUNDS Lost trial and DIRECT. Diabetes. Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 1445–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, J.; Koch, L.; Emmerling, C.; Vierkotten, J.; Peters, T.; Bruning, J.C.; Ruther, U. Inactivation of the Fto gene protects from obesity. Nature 2009, 458, 894–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Church, C.; Moir, L.; McMurray, F.; Girard, C.; Banks, G.T.; Teboul, L.; Wells, S.; Bruning, J.C.; Nolan, P.M.; Ashcroft, F.M.; et al. Overexpression of Fto leads to increased food intake and results in obesity. Nat. Genet. 2010, 42, 1086–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terra, X.; Auguet, T.; Porras, J.A.; Quintero, Y.; Aguilar, C.; Luna, A.M.; Hernandez, M.; Sabench, F.; del Castillo, D.; Richart, C. Anti-inflammatory profile of FTO gene expression in adipose tissues from morbidly obese women. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2010, 26, 1041–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livingstone, K.M.; Celis-Morales, C.; Papandonatos, G.D.; Erar, B.; Florez, J.C.; Jablonski, K.A.; Razquin, C.; Marti, A.; Heianza, Y.; Huang, T.; et al. FTO genotype and weight loss: Systematic review and meta-analysis of 9563 individual participant data from eight randomised controlled trials. BMJ 2016, 354, i4707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, F.H.; Tremaroli, V.; Nookaew, I.; Bergstrom, G.; Behre, C.J.; Fagerberg, B.; Nielsen, J.; Backhed, F. Gut metagenome in European women with normal, impaired and diabetic glucose control. Nature 2013, 498, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, N.; Wong, F.S.; Wen, L. The role of gut microbiota in the development of type 1, type 2 diabetes mellitus and obesity. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2015, 16, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cani, P.D. Gut microbiota and obesity: Lessons from the microbiome. Brief. Funct. Genom. 2013, 12, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geurts, L.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Delzenne, N.M.; Knauf, C.; Cani, P.D. Gut microbiota controls adipose tissue expansion, gut barrier and glucose metabolism: Novel insights into molecular targets and interventions using prebiotics. Benef. Microbes 2014, 5, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Ley, R.E.; Mahowald, M.A.; Magrini, V.; Mardis, E.R.; Gordon, J.I. An obesity-associated gut microbiome with increased capacity for energy harvest. Nature 2006, 444, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turnbaugh, P.J.; Hamady, M.; Yatsunenko, T.; Cantarel, B.L.; Duncan, A.; Ley, R.E.; Sogin, M.L.; Jones, W.J.; Roe, B.A.; Affourtit, J.P.; et al. A core gut microbiome in obese and lean twins. Nature 2009, 457, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, R.E.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Klein, S.; Gordon, J.I. Microbial ecology: Human gut microbes associated with obesity. Nature 2006, 444, 1022–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Chatelier, E.; Nielsen, T.; Qin, J.; Prifti, E.; Hildebrand, F.; Falony, G.; Almeida, M.; Arumugam, M.; Batto, J.-M.; Kennedy, S.; et al. Richness of human gut microbiome correlates with metabolic markers. Nature 2013, 500, 541–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartstra, A.V.; Bouter, K.E.C.; Backhed, F.; Nieuwdorp, M. Insights into the role of the microbiome in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okeke, F.; Roland, B.C.; Mullin, G.E. The role of the gut microbiome in the pathogenesis and treatment of obesity. Glob. Adv. Heal. Med. 2014, 3, 44–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, G.K.; Mullin, G.E. The Gut Microbiome and Obesity. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 18, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Den Besten, G.; van Eunen, K.; Groen, A.K.; Venema, K.; Reijngoud, D.-J.; Bakker, B.M. The role of short-chain fatty acids in the interplay between diet, gut microbiota, and host energy metabolism. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 2325–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhernakova, A.; Kurilshikov, A.; Bonder, M.J.; Tigchelaar, E.F.; Schirmer, M.; Vatanen, T.; Mujagic, Z.; Vila, A.V.; Falony, G.; Vieira-Silva, S.; et al. Population-based metagenomics analysis reveals markers for gut microbiome composition and diversity. Science 2016, 352, 565–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sonnenburg, J.L.; Backhed, F. Diet-microbiota interactions as moderators of human metabolism. Nature 2016, 535, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cotillard, A.; Kennedy, S.P.; Kong, L.C.; Prifti, E.; Pons, N.; Le Chatelier, E.; Almeida, M.; Quinquis, B.; Levenez, F.; Galleron, N.; et al. Dietary intervention impact on gut microbial gene richness. Nature 2013, 500, 585–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Kurilshikov, A.; Radjabzadeh, D.; Turpin, W.; Croitoru, K.; Bonder, M.J.; Jackson, M.A.; Medina-Gomez, C.; Frost, F.; Homuth, G.; et al. Meta-analysis of human genome-microbiome association studies: The MiBioGen consortium initiative. Microbiome 2018, 6, 101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonder, M.J.; Kurilshikov, A.; Tigchelaar, E.F.; Mujagic, Z.; Imhann, F.; Vila, A.V.; Deelen, P.; Vatanen, T.; Schirmer, M.; Smeekens, S.P.; et al. The effect of host genetics on the gut microbiome. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 1407–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turpin, W.; Espin-Garcia, O.; Xu, W.; Silverberg, M.S.; Kevans, D.; Smith, M.I.; Guttman, D.S.; Griffiths, A.; Panaccione, R.; Otley, A.; et al. Association of host genome with intestinal microbial composition in a large healthy cohort. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 1413–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Thingholm, L.B.; Skiecevičie, J.; Rausch, P.; Kummen, M.; Hov, J.R.; Degenhardt, F.; Heinsen, F.A.; Rühlemann, M.C.; Szymczak, S.; et al. Genome-wide association analysis identifies variation in Vitamin D receptor and other host factors influencing the gut microbiota. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 1396–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zierer, J.; Jackson, M.A.; Kastenmuller, G.; Mangino, M.; Long, T.; Telenti, A.; Mohney, R.P.; Small, K.S.; Bell, J.T.; Steves, C.J.; et al. The fecal metabolome as a functional readout of the gut microbiome. Nat. Genet. 2018, 50, 790–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Sun, H.; Wang, X. Emerging role and recent applications of metabolomics biomarkers in obesity disease research. Rsc Adv. 2017, 7, 14966–14973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rietman, A.; Stanley, T.L.; Clish, C.; Mootha, V.; Mensink, M.; Grinspoon, S.K.; Makimura, H. Associations between plasma branched-chain amino acids, β-aminoisobutyric acid and body composition. J. Nutr. Sci. 2016, 5, e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, F.-P.J.; Montoliu, I.; Collino, S.; Scherer, M.; Guy, P.; Tavazzi, I.; Thorimbert, A.; Moco, S.; Rothney, M.P.; Ergun, D.L.; et al. Topographical body fat distribution links to amino acid and lipid metabolism in healthy obese women. PloS ONE 2013, 8, e73445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanzu, F.A.; Vinaixa, M.; Papageorgiou, A.; Parrizas, M.; Correig, X.; Delgado, S.; Carmona, F.; Samino, S.; Vidal, J.; Gomis, R. Obesity rather than regional fat depots marks the metabolomic pattern of adipose tissue: An untargeted metabolomic approach. Obes. (Silver Spring) 2014, 22, 698–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogl, L.H.; Kaye, S.M.; Rämö, J.T.; Kangas, A.J.; Soininen, P.; Hakkarainen, A.; Lundbom, J.; Lundbom, N.; Ortega-Alonso, A.; Rissanen, A. Abdominal obesity and circulating metabolites: A twin study approach. Metabolism 2016, 65, 111–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goossens, G.H. The metabolic phenotype in obesity: Fat mass, body fat distribution, and adipose tissue function. Obes. Facts 2017, 10, 207–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Ceglarek, U.; Huang, T.; Li, L.; Rood, J.; Ryan, D.H.; Bray, G.A.; Sacks, F.M.; Schwarzfuchs, D.; Thiery, J.; et al. Weight-loss diets and 2-y changes in circulating amino acids in 2 randomized intervention trials. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2016, 103, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.H.; Crosslin, D.R.; Haynes, C.S.; Nelson, S.; Turer, C.B.; Stevens, R.D.; Muehlbauer, M.J.; Wenner, B.R.; Bain, J.R.; Laferrere, B.; et al. Branched-chain amino acid levels are associated with improvement in insulin resistance with weight loss. Diabetologia 2012, 55, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltais-Payette, I.; Boulet, M.-M.; Prehn, C.; Adamski, J.; Tchernof, A. Circulating glutamate concentration as a biomarker of visceral obesity and associated metabolic alterations. Nutr. Metab. (Lond) 2018, 15, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Sadanala, K.C.; Kim, E.-K. A Metabolomic Approach to Understanding the Metabolic Link between Obesity and Diabetes. Mol. Cells 2015, 38, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.J.; Larson, M.G.; Vasan, R.S.; Cheng, S.; Rhee, E.P.; McCabe, E.; Lewis, G.D.; Fox, C.S.; Jacques, P.F.; Fernandez, C.; et al. Metabolite profiles and the risk of developing diabetes. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 448–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heianza, Y.; Sun, D.; Smith, S.R.; Bray, G.A.; Sacks, F.M.; Qi, L. Changes in Gut Microbiota-Related Metabolites and Long-term Successful Weight Loss in Response to Weight-Loss Diets: The POUNDS Lost Trial. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 413–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, C.S.; Chambers, E.S.; Morrison, D.J.; Frost, G. The role of short chain fatty acids in appetite regulation and energy homeostasis. Int. J. Obes. 2015, 39, 1331–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- LI, X.; SHIMIZU, Y.; KIMURA, I. Gut microbial metabolite short-chain fatty acids and obesity. Biosci. MicrobiotaFood Heal. 2017, 36, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chu, H.; Duan, Y.; Yang, L.; Schnabl, B. Small metabolites, possible big changes: A microbiota-centered view of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Gut 2018, 68, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chambers, E.S.; Viardot, A.; Psichas, A.; Morrison, D.J.; Murphy, K.G.; Zac-Varghese, S.E.K.; MacDougall, K.; Preston, T.; Tedford, C.; Finlayson, G.S.; et al. Effects of targeted delivery of propionate to the human colon on appetite regulation, body weight maintenance and adiposity in overweight adults. Gut 2015, 64, 1744–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goffredo, M.; Mass, K.; Parks, E.J.; Wagner, D.A.; McClure, E.A.; Graf, J.; Savoye, M.; Pierpont, B.; Cline, G.; Santoro, N. Role of Gut Microbiota and Short Chain Fatty Acids in Modulating Energy Harvest and Fat Partitioning in Youth. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 101, 4367–4376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kettunen, J.; Demirkan, A.; Würtz, P.; Draisma, H.H.M.; Haller, T.; Rawal, R.; Vaarhorst, A.; Kangas, A.J.; Lyytikäinen, L.-P.; Pirinen, M.; et al. Genome-wide study for circulating metabolites identifies 62 loci and reveals novel systemic effects of LPA. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 11122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, T.; Hicks, M.; Yu, H.-C.; Biggs, W.H.; Kirkness, E.F.; Menni, C.; Zierer, J.; Small, K.S.; Mangino, M.; Messier, H. Whole-genome sequencing identifies common-to-rare variants associated with human blood metabolites. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Qi, Q.; Liang, J.; Bray, G.A.; Hu, F.B.; Sacks, F.M.; Qi, L. Genetic determinant for amino acid metabolites and changes in body weight and insulin resistance in response to weight-loss diets: The preventing overweight using novel dietary strategies (POUNDS LOST) trial. Circulation 2013, 127, 1283–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauderman, W.J.; Zhang, P.; Morrison, J.L.; Lewinger, J.P. Finding novel genes by testing G x E interactions in a genome-wide association study. Genet. Epidemiol. 2013, 37, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boonstra, P.S.; Mukherjee, B.; Gruber, S.B.; Ahn, J.; Schmit, S.L.; Chatterjee, N. Tests for Gene-Environment Interactions and Joint Effects With Exposure Misclassification. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 183, 237–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Robinson, M.R.; English, G.; Moser, G.; Lloyd-jones, L.R.; Triplett, A.; Zhu, Z.; Nolte, I.M.; Van Vliet-ostaptchouk, J.V.; Snieder, H. Genotype-covariate interaction effects and the heritability of adult body mass index. Nat. Publ. Gr. 2017, 49, 1174–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abadi, A.; Alyass, A.; Robiou du Pont, S.; Bolker, B.; Singh, P.; Mohan, V.; Diaz, R.; Engert, J.C.; Yusuf, S.; Gerstein, H.C.; et al. Penetrance of Polygenic Obesity Susceptibility Loci across the Body Mass Index Distribution. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2017, 101, 925–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nagpal, S.; Gibson, G.; Marigorta, U.M. Pervasive Modulation of Obesity Risk by the Environment and Genomic Background. Genes (Basel) 2018, 9, 411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Study | Genetic Factor | Environment Factor | Major Finding |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zhang et al. [81] | Obesity-related FTO variant rs1558902 | Dietary protein | Dietary protein significantly modified the FTO genotype in relation to weight loss and improvement in body composition and abdominal fat distribution |
| Heianza et al. [82] | Gut microbiota related LCT variant rs4988235 | Dietary protein | In response to a high-protein diet, the G allele of LCT variant rs4988235 was associated with a greater reduction of whole-body fat %, trunk fat %, SAT, VAT, and TAT. |
| Heianza et al. [83] | Macronutrient intake related FGF21 variant rs838147 | Dietary carbohydrate/fat | Dietary carbohydrate/fat intake significant interaction with the FGF21 genotype on 2-year changes in WC, percentage of total fat mass, and percentage of trunk fat |
| Goni et al. [84] | Circadian rhythm-related MTNR1B genetic variant rs10830963 | Dietary fat | Carriers of the G allele of the MTNR1B genotype and low-/high-fat diet on changes in weight, BMI, waist circumference (WC) and total body fat |
| Mattei et al. [85] | TCF7L2 gene variant rs12255372 | Dietary fat | Significant interactions were observed for rs12255372 T allele and fat intake for changes in BMI, total fat mass, and trunk fat mass; TT carriers have more reductions in body composition when consuming a low-fat diet. |
| Lin et al. [86] | NPY variant rs16147 | Dietary fat | The rs16147 T allele appeared to associate with a more adverse change in the abdominal fat deposition in the high-fat diet group than in the low-fat diet group. |
| Huang et al. [87] | HNF1A gene variant rs7957197 | Dietary fat | Individuals with T allele of HNF1A rs7957197 have a greater decrease in body weight, WC when consuming a high-fat diet. |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Qi, L. Gene–Environment Interactions on Body Fat Distribution. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3690. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20153690
Li X, Qi L. Gene–Environment Interactions on Body Fat Distribution. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(15):3690. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20153690
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xiang, and Lu Qi. 2019. "Gene–Environment Interactions on Body Fat Distribution" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 15: 3690. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20153690
APA StyleLi, X., & Qi, L. (2019). Gene–Environment Interactions on Body Fat Distribution. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(15), 3690. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20153690






