ASD Phenotype—Genotype Associations in Concordant and Discordant Monozygotic and Dizygotic Twins Stratified by Severity of Autistic Traits
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
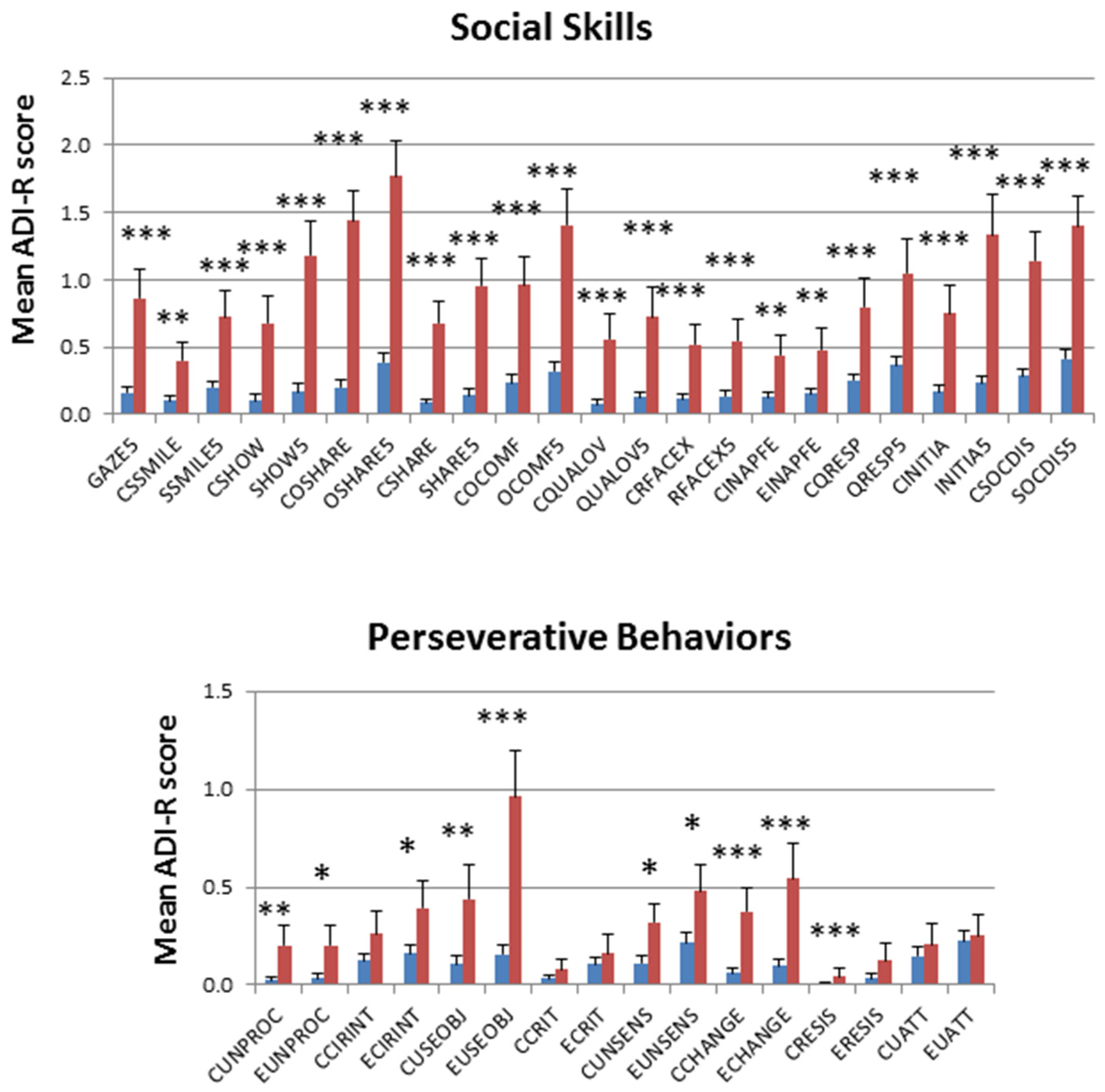
2.1. Deep Phenotypic Analyses of MZ and DZ Twins: Influence of Zygosity and Diagnostic Concordance
2.2. Genotype–Phenotype Relationships Revealed by Quantitative Trait Association Analyses
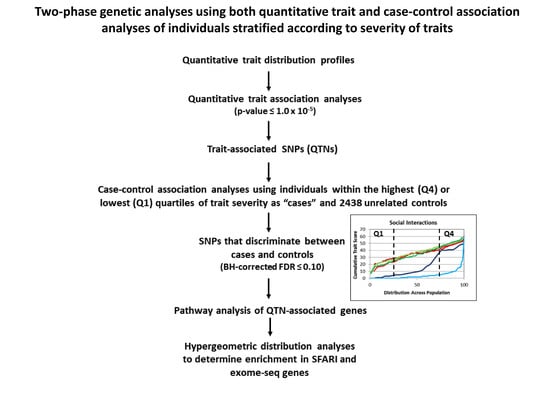
2.3. Case-Control Association Analyses Based on Individuals Stratified by Trait Severity for Each Subgroup of Twins
2.4. Enrichment of Known Autism Risk Genes from Case-Control Association Analyses
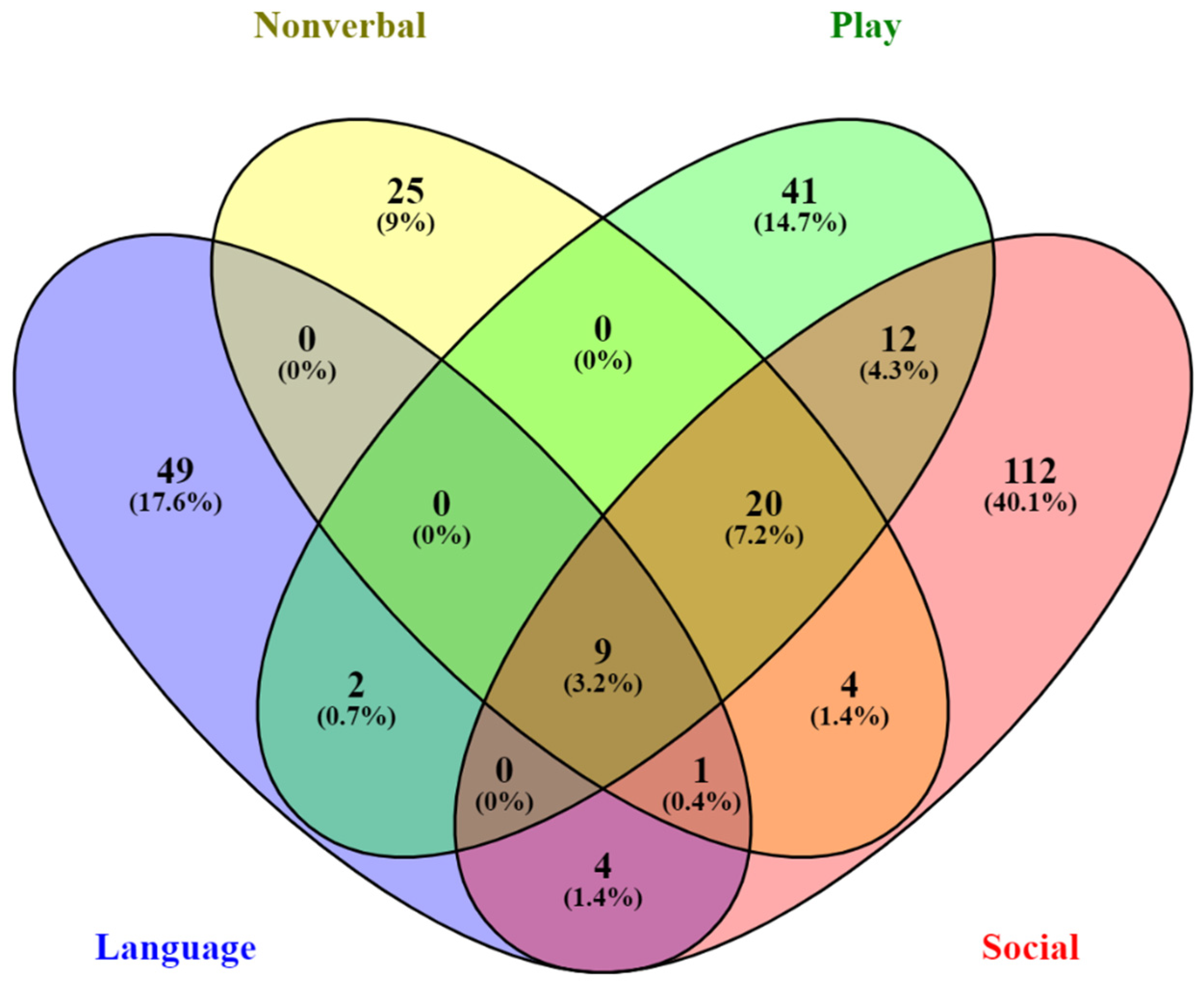
2.5. Functional Analysis of Genes Associated with QTNs from Quantitative Trait and Case-Control Association Analyses
2.6. Case-Control Association Analysis Using dNA.DZ Twins as Controls for dA.DZ Co-Twins
3. Discussion
3.1. Severity of Autistic Traits Are Strongly Influenced by Genetics
3.2. Quantitative Trait Association Analyses Reveal SNPs that Associate with a Specific ASD Trait
3.3. Trait-Associated QTNs Can Discriminate between Cases and Controls
3.4. Genetic Differences between Discordant DZ Twins Strongly Associate with Autism Risk Genes
3.5. Advantages and Limitations of Study Design
4. Summary
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. ASD Subphenotype Analysis and Generation of Trait Severity Distribution Profiles
5.2. Source of Genetic Data
5.3. Quantitative Trait Loci (QTL) Association Analyses
5.4. Case-Control Association Analyses
5.5. SNP Annotation and Functional Analyses of Associated Genes
5.6. Hypergeometric Distribution Analyses for Gene Enrichment
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5); American Psychiatric Publishing: Washington, DC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Masi, A.; DeMayo, M.M.; Glozier, N.; Guastella, A.J. An overview of autism spectrum disorder, heterogeneity and treatment options. Neurosci. Bull. 2017, 33, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, A.; Le Couteur, A.; Gottesman, I.; Bolton, P. Autism as a strongly genetic disorder: Evidence from a british twin study. Psychol. Med. 1995, 25, 63–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronald, A.; Hoekstra, R.A. Autism spectrum disorders and autistic traits: A decade of new twin studies. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part B Neuropsychiatr. Genet. 2011, 156, 255–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trouton, A.; Spinath, F.M.; Plomin, R. Twins Early Development Study (TEDS): A multivariate, longitudinal genetic investigation of language, cognition and behavior problems in childhood. Twin Res. 2002, 5, 444–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mevel, K.; Fransson, P.; Bölte, S. Multimodal brain imaging in autism spectrum disorder and the promise of twin research. Autism 2015, 19, 527–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frans, E.M.; Sandin, S.; Reichenberg, A.; Långström, N.; Lichtenstein, P.; McGrath, J.J.; Hultman, C.M. Autism risk across generations: A population-based study of advancing grandpaternal and paternal age. JAMA Psychiatry 2013, 70, 516–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bölte, S.; Willfors, C.; Berggren, S.; Norberg, J.; Poltrago, L.; Mevel, K.; Coco, C.; Fransson, P.; Borg, J.; Sitnikov, R.; et al. The roots of autism and ADHD twin study in Sweden (RATSS). Twin Res. Hum. Genet. 2014, 17, 164–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallmayer, J.; Cleveland, S.; Torres, A.; Phillips, J.; Cohen, B.; Torigoe, T.; Miller, J.; Fedele, A.; Collins, J.; Smith, K.; et al. Genetic heritability and shared environmental factors among twin pairs with autism. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2011, 68, 1095–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaugler, T.; Klei, L.; Sanders, S.J.; Bodea, C.A.; Goldberg, A.P.; Lee, A.B.; Mahajan, M.; Manaa, D.; Pawitan, Y.; Reichert, J.; et al. Most genetic risk for autism resides with common variation. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 881–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tick, B.; Bolton, P.; Happé, F.; Rutter, M.; Rijsdijk, F. Heritability of autism spectrum disorders: A meta-analysis of twin studies. J. Child Psychol. Psychiatry Allied Discip. 2016, 57, 585–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colvert, E.; Tick, B.; McEwen, F.; Stewart, C.; Curran, S.R.; Woodhouse, E.; Gillan, N.; Hallett, V.; Lietz, S.; Garnett, T.; et al. Heritability of autism spectrum disorder in a UK population-based twin sample. JAMA Psychiatry 2015, 72, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, M.J.; Gustafsson, P.; Larsson, H.; Gillberg, C.; Lundström, S.; Lichstenstein, P. Examining the association between autistic traits and atypical sensory reactivity: A twin study. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2018, 57, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, G.J.; Shakeshaft, N.G.; Plomin, R. Face identity recognition and the social difficulties component of the autism-like phenotype: Evidence for phenotypic and genetic links. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2018, 48, 2758–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isaksson, J.; Van’t Westeinde, A.; Cauvet, É.; Kuja-Halkola, R.; Lundin, K.; Neufeld, J.; Willfors, C.; Bolte, S. Social cognition in autism and other neurodevelopmental disorders: A co-twin control study. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2019, 49, 2838–2848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lord, C.; Rutter, M.; Couteur, A.L. Autism diagnostic interview-revised: A revised version of a diagnostic interview for caregivers of individuals with possible pervasive developmental disorders. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 1994, 24, 659–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, V.W.; Steinberg, M.E. Novel clustering of items from the autism diagnostic interview-revised to define phenotypes within autism spectrum disorders. Autism Res. 2009, 2, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, V.W.; Sarachana, T.; Kim, K.S.; Nguyen, A.; Kulkarni, S.; Steinberg, M.E.; Luu, T.; Lai, Y.; Lee, N.H. Gene expression profiling differentiates autism case-controls and phenotypic variants of autism spectrum disorders: Evidence for Circadian rhythm dysfunction in severe autism. Autism Res. 2009, 2, 78–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, V.W.; Addington, A.; Hyman, A. Novel autism subtype-dependent genetic variants are revealed by quantitative trait and subphenotype association analyses of published GWAS data. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebizadeh, Z.; Arking, D.E.; Hu, V.W. A novel stratification method in linkage studies to address inter and intra family heterogeneity in autism. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veatch, O.J.; Pendergast, J.S.; Allen, M.J.; Leu, R.M.; Johnson, C.H.; Elsea, S.H.; Malow, B.A. Genetic variation in melatonin pathway enzymes in children with autism spectrum disorder and comorbid sleep onset delay. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2014, 45, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talebizadeh, Z.; Shah, A.; DiTacchio, L. The potential role of a retrotransposed gene and a long noncoding RNA in regulating an X-linked chromatin gene (KDM5C): Novel epigenetic mechanism in autism. Autism Res. 2019, 12, 1007–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iossifov, I.; O’Roak, B.J.; Sanders, S.J.; Ronemus, M.; Krumm, N.; Levy, D.; Stessman, H.A.; Witherspoon, K.T.; Vives, L.; Patterson, K.E.; et al. The contribution of de novo coding mutations to autism spectrum disorder. Nature 2014, 515, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ronald, A.; Happé, F.; Price, T.S.; Baron-Cohen, S.; Plomin, R. Phenotypic and genetic overlap between autistic traits at the extremes of the general population. J. Am. Acad. Child Adolesc. Psychiatry 2006, 45, 1206–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, E.B.; Koenen, K.C.; McCormick, M.C.; Munir, K.; Hallett, V.; Happé, F.; Plomin, R.; Ronald, A. Evidence that autistic traits show the same etiology in the general population and at the quantitative extremes (5%, 2.5%, and 1%). Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2011, 68, 1113–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazier, T.W.; Thompson, L.; Youngstrom, E.A.; Law, P.; Hardan, A.Y.; Eng, C.; Morris, N. A twin study of heritable and shared environmental contributions to autism. J. Autism Dev. Disord. 2014, 44, 2013–2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veatch, O.J.; Sutcliffe, J.S.; Warren, Z.E.; Keenan, B.T.; Potter, M.H.; Malow, B.A. Shorter sleep duration is associated with social impairment and comorbidities in ASD. Autism Res. 2017, 10, 1221–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKenna, B.; Koomar, T.; Vervier, K.; Kremsreiter, J.; Michaelson, J.J. Whole-genome sequencing in a family with twin boys with autism and intellectual disability suggests multimodal polygenic risk. Cold Spring Harbor Mol. Case Stud. 2018, 4, a003285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egawa, J.; Watanabe, Y.; Sugimoto, A.; Nunokawa, A.; Shibuya, M.; Igeta, H.; Inoue, E.; Hoya, S.; Orime, N.; Hayashi, T.; et al. Whole-exome sequencing in a family with a monozygotic twin pair concordant for autism spectrum disorder and a follow-up study. Psychiatry Res. 2015, 229, 599–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamouli, S.; Anderlid, B.-M.; Willfors, C.; Thiruvahindrapuram, B.; Wei, J.; Berggren, S.; Nordgren, A.; Scherer, S.W.; Lichtenstein, P.; Tammimies, K.; et al. Copy number variation analysis of 100 twin pairs enriched for neurodevelopmental disorders. Twin Res. Hum. Genet. 2018, 21, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, V.W. Cluster Analyses of Females with Autism According to ADI-R Severity Scores. Unpublished.
- Robinson, E.B.; Koenen, K.C.; McCormick, M.C.; Munir, K.; Hallett, V.; Happé, F.; Plomin, R.; Ronald, A. A multivariate twin study of autistic traits in 12-year-olds: Testing the fractionable autism triad hypothesis. Behav. Genet. 2012, 42, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhang, H.; Ma, D.; Bucan, M.; Glessner, J.T.; Abrahams, B.S.; Salyakina, D.; Imielinski, M.; Bradfield, J.P.; Sleiman, P.M.A.; et al. Common genetic variants on 5p14.1 associate with autism spectrum disorders. Nature 2009, 459, 528–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purcell, S.; Neale, B.; Todd-Brown, K.; Thomas, L.; Ferreira, M.A.R.; Bender, D.; Maller, J.; Sklar, P.; De Bakker, P.I.W.; Daly, M.J.; et al. PLINK: A tool set for whole-genome association and population-based linkage analyses. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2007, 81, 559–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveros, J.C.; Venny. An Interactive Tool for Comparing Lists with Venn’s Diagrams. 2007. Available online: http://bioinfogp.cnb.csic.es/tools/venny/index.html (accessed on 17 June 2019).
- Spitzer, M.; Wildenhain, J.; Rappsilber, J.; Tyers, M. BoxPlotR: A web tool for generation of box plots. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 121–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riva, A.; Kohane, I.S. SNPper: Retrieval and analysis of human SNPs. Bioinformatics 2002, 18, 1681–1685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayem Ullah, A.Z.; Oscanoa, J.; Wang, J.; Nagano, A.; Lemoine, N.R.; Chelala, C. SNPnexus: Assessing the functional relevance of genetic variation to facilitate the promise of precision medicine. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, W109–W113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, S.N.; Kollu, R.; Banerjee-Basu, S. AutDB: A gene reference resource for autism research. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, D832–D836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Spoken Language | Nonverbal Commun. | Play Skills | Social Skills | Pers. Behav. | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ADAM12 | KLHL29 | ABHD6 | MGAT4C | ADAMTS8 | KALRN | ABCC4 | DCAF16 | LHPP | RCOR1 | APOLD1 |
| ALOX12P1 | L3MBTL4 | ADAMTS8 | MICA | ADPRHL1 | KIRREL3 | ABCD3 | DCDC5 | LMO1 | REV1 | BNIP3L |
| ANGPT1 | LHFPL3 | AGMO | MTCP1 | AGMO | L3MBTL4 | ACBD5 | DGKH | LPPR4 | RNASE8 | C2orf88 |
| BMP5 | LHX4 | AK097143 | NCALD | AMPD3 | LARGE | ADAMTS8 | DLG2 | LPPR5 | RNF144B | CDH13 |
| BMPR2 | LRRFIP1 | ANKRD44 | NCAPG | ANKRD44 | LCORL | ADARB1 | DMRT2 | LRIG3 | RPTOR | CORO2A |
| C12orf42 | LYPD6B | ANKS1B | NOP58 | BEND4 | LECT1 | AGMO | DNAH9 | LRRC4C | RUNX1 | FAM136B |
| C3orf55 | MGAT4C | BCAS3 | NUP210P1 | BMPR2 | MARK3 | AKAP6 | DPF3 | MAGI3 | SGCZ | FHAD1 |
| CCDC152 | MGAT5 | BMPR2 | PAX3 | C1orf143 | MGAT4C | ALPK1 | ELK3 | MARK3 | SHISA6 | GABRR2 |
| CCDC85A | NCALD | CADM1 | PCDHGA1 | CA10 | MTCP1 | AMPD2 | ELOVL6 | MCPH1 | SLC16A9 | GPC6 |
| CCND3 | NOP58 | CCDC85A | PIEZO2 | CCDC102B | MYH11 | ANKRD32 | EPHB1 | MECOM | SLC44A1 | GRAMD1C |
| CD101 | NOS1AP | CCND3 | PLCXD3 | CCDC60 | NCALD | ANKRD44 | EPS15 | MGAT4C | SLCO2B1 | GRIP1 |
| CDK5R1 | NPAS3 | CDH20 | RARB | CCDC8 | NCAPG | AOC1 | EYS | MMP9 | SPATA13 | IL31RA |
| CHRM1 | NRXN1 | CEP95 | RNF24 | CCDC85A | NOP58 | ARHGAP26 | FAM210B | MTCP1 | SPOP | KCNAB1 |
| CHRNA7 | NTM | CHL1 | RYR2 | CCND3 | NRG2 | ARL15 | FAM89A | MYH11 | SRD5A1 | MAML2 |
| CNTN1 | OVCH2 | CMKLR1 | SKAP2 | CHN2 | PAG1 | ASAP1 | FAT4 | MYO18B | SRGAP3 | MRPS6 |
| CNTN4 | PAX3 | COL20A1 | SLC22A23 | CHRM3 | PARK2 | ASXL3 | FBXL7 | NAALAD2 | ST6GALNAC3 | MTBP |
| CPM | PDE4B | CSMD1 | SLC27A6 | CLMP | PAX3 | BC093087 | FCER2 | NCALD | STAC | MXRA5 |
| CREM | PIEZO2 | DCAF16 | SPATA13 | CMKLR1 | PAX7 | BMPR2 | FHIT | NCAPG | STK11 | OR2H2 |
| CSMD1 | PPIE | DLG2 | STAC | CMTM7 | PCDHGA1 | BPIFB1 | FRRS1L | NDRG2 | STX8 | PLCB1 |
| DCTN5 | SLC1A7 | EPHB1 | STK32B | COBLL1 | PLCXD3 | C10orf11 | GCNT1 | NOP58 | SUPT3H | PLD6 |
| DGKH | SLC30A8 | EYS | THEG5 | CPE | PSD3 | C6orf106 | GNE | OPA3 | THEG5 | PRICKLE1 |
| DSCAM | SMEK1 | FAT4 | TMEM38A | CSMD1 | RARB | C9orf171 | GRID1 | P4HA2 | THSD4 | PTPRD |
| DSCAML1 | STX8 | FLVCR1 | TRIOBP | CTNND2 | RPTOR | CA10 | GRID2 | PARK2 | TMEM108 | RAPGEF5 |
| E2F7 | SYT6 | GCNT1 | WBSCR17 | DCAF16 | SH3PXD2B | CASP6 | GRM7 | PAX3 | TMEM135 | RNLS |
| EP400 | TCHP | IL1R2 | WNK2 | DFFA | SLC16A9 | CASP8 | HBS1L | PCDHGA1 | TMEM245 | SLC22A18 |
| FAM49B | TLN2 | ITIH5 | ZNF207 | DISC1 | SLCO4A1 | CCDC102B | HDAC11 | PCSK5 | TNS3 | SORBS2 |
| FMN1 | TMEM192 | KCNIP4 | DLG2 | SOX5 | CCDC85A | HIST1H1D | PDE8A | TRDN | ST8SIA5 | |
| GOSR1 | TNS3 | L3MBTL4 | DNAJC10 | SPOP | CCND3 | HIST1H2BF | PDGFC | TTC27 | SYNPO2L | |
| GPR139 | TOP2B | LARGE | DPF3 | STAC | CCSER1 | HIST1H4E | PFKP | USP37 | UNC13C | |
| ID3 | UNC5D | LCORL | E2F7 | STEAP1B | CDH8 | HIST1H4G | PIEZO2 | WDSUB1 | ||
| JAZF1 | WWC2 | LDB2 | EPHB1 | STK38 | CDK17 | IGSF21 | PITPNA | WNK2 | ||
| KIAA0947 | YY1 | LIM2 | EYS | TECRL | CDK2 | IKBKAP | PKD1L1 | XYLT1 | ||
| KIAA1549 | LRRC4C | FAT4 | THEG5 | CEP95 | ITGB3 | PLCXD3 | ZFP64 | |||
| FIP1L1 | TMEM144 | CMIP | KCND2 | PLXDC1 | ZNF142 | |||||
| FZD4 | TMEM161B | CMKLR1 | KCNIP4 | PREP | ZNF630 | |||||
| GALNTL6 | TNFSF12 | CMYA5 | KIAA0319 | PRKCDBP | ZNF804B | |||||
| GCNT1 | TP53 | CNTN1 | KIAA1377 | PSD3 | ||||||
| GPR56 | TRDN | COLEC12 | KIF13A | PTPRE | ||||||
| GREM1 | VAV3 | CR2 | KLF12 | PTPRK | ||||||
| HBS1L | WNK2 | CSMD1 | L3MBTL4 | RABGAP1L | ||||||
| ID3 | ZCCHC14 | CTNNAL1 | LARGE | RARB | ||||||
| ITSN1 | ZNF385D | CTTNBP2 | LCORL | RBFOX1 | ||||||
| Hypergeometric Distribution Analyses of Enrichment of SFARI Genes Among ASD Trait-Associated Genes | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Trait | Number of Trait-Associated Genes | # Genes Represented within SFARI Gene | p-Value * for Enrichment |
| Language deficits | 65 | 11 | 4.20 × 10−4 |
| Nonverbal communication | 59 | 5 | 2.01 × 10−1 |
| Play skills | 84 | 9 | 3.30 × 10−2 |
| Social skills | 162 | 19 | 9.48 × 10−4 |
| Perseverative behaviors | 29 | 5 | 1.68 × 10−2 |
| Case Groups (Combined Q1 and Q4) vs. Unaffected Controls | Number of Case-Associated Genes | # Genes Represented within SFARI Gene | Q-Value * for Enrichment |
|---|---|---|---|
| dA.MZ | 13 | 0 | 1 |
| dA.DZ | 8 | 0 | 1 |
| dNA.MZ | 53 | 9 | 1.69 × 10−3 |
| dNA.DZ | 19 | 4 | 1.59 × 10−2 |
| cMZ | 29 | 2 | 4.58 × 10−1 |
| cDZ | 23 | 4 | 3.10 × 10−2 |
| Functions Annotation | p-Value * | Genes |
|---|---|---|
| cell-cell adhesion of neurons | 9.52 × 10−6 | CDK5R1, CNTN4, NRXN1 |
| guidance of axons | 9.66 × 10−6 | CDK5R1, CNTN1, CNTN4, LHX4, NRXN1, UNC5D |
| fasciculation of axons | 8.24 × 10−5 | CDK5R1, CNTN1, CNTN4 |
| abnormal morphology of brain | 1.86 × 10−4 | CDK5R1, CHRM1, CHRNA7, CNTN1, ID3, LHX4, NPAS3, TOP2B |
| GABA-mediated receptor currents | 6.98 × 10−4 | CHRNA7, NRXN1 |
| abnormal morphology of granule cells | 9.17 × 10−4 | CDK5R1, CNTN1 |
| abnormal morphology of nervous system | 1.48 × 10−3 | CDK5R1, CHRM1, CHRNA7, CNTN1, CNTN4, ID3, LHX4, NPAS3, TOP2B |
| stratification of cerebral cortex | 1.75 × 10−3 | CDK5R1, TOP2B |
| formation of brain | 2.52 × 10−3 | BMP5, CDK5R1, CNTN1, CREM, DSCAML1, NPAS3, TOP2B |
| memory | 2.58 × 10−3 | CDK5R1, CHRM1, CHRNA7, CREM, NPAS3 |
| abnormal morphology of molecular layer of cerebellum | 2.63 × 10−3 | CDK5R1, CNTN1 |
| formation of enteric ganglion | 2.82 × 10−3 | PAX3 |
| morphology of motor cortex | 2.82 × 10−3 | CDK5R1 |
| origination of axons | 2.82 × 10−3 | CDK5R1 |
| reorganization of molecular layer | 2.82 × 10−3 | CDK5R1 |
| sprouting of mossy fiber cells | 2.82 × 10−3 | CDK5R1 |
| Functions Annotation | p-Value * | Genes |
|---|---|---|
| organization of mossy fibers | 2.60 × 10−3 | CHL1 |
| formation of enteric ganglion | 2.60 × 10−3 | PAX3 |
| targeting of retinal ganglion cells | 2.60 × 10−3 | EPHB1 |
| cell-cell adhesion of astrocytes | 2.60 × 10−3 | CADM1 |
| maintenance of neural crest | 5.18 × 10−3 | PAX3 |
| survival of neural crest | 5.18 × 10−3 | PAX3 |
| innervation of forelimb | 7.77 × 10−3 | BMPR2 |
| differentiation of satellite cells | 1.03 × 10−2 | PAX3 |
| morphogenesis of optic nerve | 1.29 × 10−2 | EPHB1 |
| migration of pyramidal neurons | 1.29 × 10−2 | CHL1 |
| abnormal pruning of axons | 1.29 × 10−2 | EPHB1 |
| excitatory postsynaptic potential of neurons | 1.39 × 10−2 | DLG2, RARB |
| formation of pyramidal neurons | 1.55 × 10−2 | CHL1 |
| synaptic depression of collateral synapses | 1.80 × 10−2 | EPHB1 |
| synaptic transmission of collateral synapses | 1.80 × 10−2 | EPHB1 |
| abnormal morphology of axons | 2.29 × 10−2 | CHL1, EPHB1 |
| development of retinal pigment epithelium | 2.31 × 10−2 | RARB |
| abnormal morphology of optic tract | 2.31 × 10−2 | EPHB1 |
| abnormal morphology of hypoglossal nerve | 2.82 × 10−2 | RARB |
| abnormal morphology of olfactory receptor neurons | 3.32 × 10−2 | CHL1 |
| abnormal morphology of mossy fibers | 4.07 × 10−2 | CHL1 |
| projection of axons | 4.57 × 10−2 | CHL1 |
| synaptic transmission of nervous tissue | 4.74 × 10−2 | ANKS1B, EPHB1 |
| abnormal morphology of neural arch | 4.82 × 10−2 | RARB |
| Functions Annotation | p-Value * | Genes |
|---|---|---|
| formation of dendritic spines | 6.97 × 10−4 | ITSN1, KALRN |
| short-term depression of calyx-type synapse | 7.29 × 10−4 | ITSN1 |
| neurotransmission of synapse | 8.88 × 10−4 | CHRM3, PRKN |
| formation of tip of neurite-like extensions | 1.46 × 10−3 | KALRN |
| elongation of dendritic spine neck | 1.46 × 10−3 | ITSN1 |
| long-term potentiation of Purkinje cells | 1.46 × 10−3 | CHRM3 |
| arrest in axonal transport of mitochondria | 1.46 × 10−3 | PRKN |
| quantity of catecholaminergic neurons | 1.46 × 10−3 | PRKN |
| length of neurons | 2.18 × 10−3 | ITSN1, KALRN |
| excitation of striatal neurons | 2.18 × 10−3 | PRKN |
| differentiation of satellite cells | 2.91 × 10−3 | PAX7 |
| replenishment of synaptic vesicles | 2.91 × 10−3 | ITSN1 |
| abnormal morphology of locus ceruleus | 2.91 × 10−3 | PRKN |
| afterhyperpolarization of pyramidal neurons | 4.36 × 10−3 | CHRM3 |
| morphology of corticcal neurons | 4.36 × 10−3 | KALRN |
| sensorimotor integration | 5.09 × 10−3 | PRKN |
| abnormal morphology of substantia nigra | 5.81 × 10−3 | PRKN |
| neurotransmission | 6.89 × 10−3 | CHRM3,,KALRN, PRKN |
| morphogenesis of dendritic spines | 7.26 × 10−3 | KALRN |
| retraction of dendrites | 7.99 × 10−3 | KALRN |
| maturation of dendritic spines | 8.71 × 10−3 | KALRN |
| length of axons | 9.43 × 10−3 | KALRN |
| abnormal morphology of cerebral cortex | 9.91 × 10−3 | KALRN,,PRKN |
| length of dendritic spines | 1.38 × 10−2 | ITSN1 |
| coordination | 1.43 × 10−2 | KALRN, PRKN |
| Functions Annotation | p-Value * | Genes |
|---|---|---|
| abnormal morphology of thoracic vertebra | 1.19 × 10−3 | DMRT2, FAT4, NDRG2 |
| action potential of neurons | 4.63 × 10−3 | DLG2, GRID2, KCND2, PARK7, RARB |
| abnormal morphology of Purkinje cells | 4.78 × 10−3 | CNTN1, GRID2, PITPNA |
| innervation of climbing fiber | 7.24 × 10−3 | GRID2 |
| formation of enteric ganglion | 7.24 × 10−3 | PAX3 |
| development of climbing fiber | 7.24 × 10−3 | GRID2 |
| differentiation of branchial motor neurons | 7.24 × 10−3 | RUNX1 |
| targeting of retinal ganglion cells | 7.24 × 10−3 | EPHB1 |
| differentiation of visceral motor neurons | 7.24 × 10−3 | RUNX1 |
| abnormal morphology of Golgi interneurons | 7.24 × 10−3 | CNTN1 |
| proliferation of neuroglia | 7.26 × 10−3 | CCND3, CDK2, CNTN1, MMP9, RUNX1 |
| abnormal morphology of white matter | 7.39 × 10−3 | PITPNA, SRGAP3 |
| function of blood-brain barrier | 9.99 × 10−3 | ABCC4, MMP9 |
| abnormal morphology of lumbar vertebra | 1.09 × 10−2 | DMRT2, FAT4 |
| function of brain | 1.12 × 10−2 | ABCC4, KCNIP4, MMP9 |
| morphology of brain | 1.18 × 10−2 | CASP6, CNTN1, EPHB1, GRID1, GRID2, MCPH1, MECOM, PARK7, PITPNA, SRGAP3 |
| axonogenesis | 1.31 × 10−2 | CASP6, EPHB1, GRID2, LRRC4C, PTPRE, STK11 |
| arrest in cell cycle progression of oligodendrocyte precursor cells | 1.44 × 10−2 | CDK2 |
| abnormal morphology of superior ganglion of glossopharyngeal nerve | 1.44 × 10−2 | MECOM |
| delay in initiation of pruning of axons | 1.44 × 10−2 | CASP6 |
| maintenance of neural crest | 1.44 × 10−2 | PAX3 |
| blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier function | 1.44 × 10−2 | ABCC4 |
| Diseases or Functions Annotation | p-value * | Genes |
|---|---|---|
| paired-pulse facilitation of parallel fiber-Purkinje cell synapses | 1.27 × 10−3 | UNC13C |
| early infantile epileptic encephalopathy type 12 | 1.27 × 10−3 | PLCB1 |
| loss of hippocampal neurons | 6.36 × 10−3 | PLCB1 |
| epilepsy | 1.27 × 10−2 | GABRR2, PLCB1, PRICKLE1 |
| afterhyperpolarization of neurons | 2.27 × 10−2 | KCNAB1 |
| progressive myoclonic epilepsy | 2.64 × 10−2 | PRICKLE1 |
| status epilepticus | 4.13 × 10−2 | GABRR2 |
| density of synapse | 4.61 × 10−2 | GRIP1 |
| sedation | 4.61 × 10−2 | GABRR2 |
| Functions Annotation | p-value * | Genes |
|---|---|---|
| abnormal morphology of pyramidal neurons | 5.59 × 10−5 | CHL1, CHRNA7, KALRN |
| GABA-mediated receptor currents | 4.19 × 10−4 | CHRNA7, NRXN1 |
| abnormal morphology of cerebral cortex | 1.12 × 10−3 | CHL1, CHRNA7, KALRN, NPAS3 |
| organization of mossy fibers | 2.19 × 10−3 | CHL1 |
| cell-cell adhesion of astrocytes | 2.19 × 10−3 | CADM1 |
| developmental process of synapse | 2.35 × 10−3 | CADM1, CHRNA7, KALRN, NRXN1 |
| formation of tip of neurite-like extensions | 4.37 × 10−3 | KALRN |
| hyperexcitation of hippocampal neurons; short-term potentiation of hippocampus; nicotine-mediated receptor current | 4.37 × 10−3 | CHRNA7 |
| abnormal morphology of enlarged fourth cerebral ventricle | 6.54 × 10−3 | NPAS3 |
| miniature excitatory postsynaptic currents | 7.15 × 10−3 | KALRN, NRXN1 |
| abnormal morphology of lateral cerebral ventricle | 7.64 × 10−3 | CHL1, NPAS3 |
| differentiation of satellite cells | 8.71 × 10−3 | PAX7 |
| abnormal morphology of cingulate gyrus | 8.71 × 10−3 | NPAS3 |
| abnormal morphology of GABAergic neurons | 8.71 × 10−3 | CHRNA7 |
| migration of pyramidal neurons | 1.09 × 10−2 | CHL1 |
| pervasive developmental disorder | 1.13 × 10−2 | BCAS3, PREP, SLC1A7 |
| excitatory postsynaptic current | 1.26 × 10−2 | KALRN, NRXN1 |
| morphology of cortical neurons | 1.30 × 10−2 | KALRN |
| formation of pyramidal neurons | 1.30 × 10−2 | CHL1 |
| maturatin of neurons | 1.46 × 10−2 | KALRN, NRXN1 |
| branching of axons | 1.49 × 10−2 | KALRN, STK11 |
| prepulse inhibition | 1.56 × 10−2 | KALRN, NRXN1 |
| abnormal morphology of enlarged third cerebral ventricle | 1.74 × 10−2 | NPAS3 |
| paired-pulse inhibition | 1.74 × 10−2 | NRXN1 |
| coordination | 1.79 × 10−2 | CHRNA7, KALRN, NPAS3 |
| abnormal morphology of cerebral aqueduct | 1.95 × 10−2 | NPAS3 |
| morphogenesis of dendritic spines | 2.16 × 10−2 | KALRN |
| retraction of dendrites | 2.38 × 10−2 | KALRN |
| activation of dopaminergic neurons | 2.59 × 10−2 | CHRNA7 |
| maturation of dendritic spines | 2.59 × 10−2 | KALRN |
| abnormal morphology of olfactory receptor neurons | 2.81 × 10−2 | CHL1 |
| length of axons | 2.81 × 10−2 | KALRN |
| spatial memory | 2.88 × 10−2 | CHRNA7, KALRN, NPAS3 |
| sleep disorders | 3.06 × 10−2 | CHRNA7, PDE4B |
| neurotransmission | 3.20 × 10−2 | ANKS1B, CHRNA7, KALRN, NRXN1 |
| development of neurons | 3.44 × 10−2 | CADM1, CHL1, CHRNA7, KALRN, NRXN1, STK11 |
| Diseases or Functions Annotation | p-Value * | Genes |
|---|---|---|
| adhesion of cerebellar granule cell | 8.65 × 10−4 | ADGRG1 |
| migration of CA1 neuron | 8.65 × 10−4 | DISC1 |
| abnormal morphology of lumbar dorsal root ganglion | 8.62 × 10−3 | GABBR1 |
| abnormal morphology of somatic nervous system | 1.03 × 10−2 | GABBR1 |
| pervasive developmental disorder | 1.44 × 10−2 | CORO2A, GABBR1 |
| abnormal morphology of sciatic nerve | 1.46 × 10−2 | GABBR1 |
| positioning of neurons | 1.55 × 10−2 | DISC1 |
| development of olfactory cilia | 1.80 × 10−2 | DISC1 |
| progressive myoclonic epilepsy | 1.80 × 10−2 | PRICKLE1 |
| maturation of synapse | 1.89 × 10−2 | DISC1 |
| migration of neuronal progenitor cells | 1.97 × 10−2 | ADGGRG1 |
| fragile X syndrome | 2.48 × 10−2 | GABBR1 |
| elongation of axons | 2.73 × 10−2 | DISC1 |
| migration of neurons | 2.81 × 10−2 | ADGRG1, DISC1 |
| abnormal morphology of myelin sheath | 2.99 × 10−2 | GABBR1 |
| differentiation of oligodendroccyte precursor cells | 3.24 × 10−2 | DISC1 |
| absense seizure | 3.24 × 10−2 | GABBR1 |
| passive avoidance learning | 3.49 × 10−2 | GABBR1 |
| inhibitory postsynaptic current | 4.41 × 10−2 | GABBR1 |
| electrophysiology of nervous system | 4.74 × 10−2 | GABBR1 |
| Diseases or Functions Annotation | p-Value * | Genes |
|---|---|---|
| morphology of brain | 1.51 × 10−3 | DSCAM, LHX4, PRKN, TOP2B |
| abnormal morphology of abducens nerve | 1.73 × 10−3 | LHX4 |
| arrest in axonal transport of mitochondria | 1.73 × 10−3 | PRKN |
| quantity of catecholaminergic neurons | 1.73 × 10−3 | PRKN |
| delay in specification of corticotroph cells | 1.73 × 10−3 | LHX4 |
| excitation of striatal neurons | 2.59 × 10−3 | PRKN |
| startle response | 2.60 × 10−3 | PLCB1, PRKN |
| development of granule cell layer | 3.46 × 10−3 | CREM |
| function of central pattern generator | 3.46 × 10−3 | DSCAM, LHX4, PRKN, TOP2B |
| development of cortical subplate | 3.46 × 10−3 | TOP2B |
| abnormal morphology of locus ceruleus | 3.46 × 10−3 | PRKN |
| morphogenesis of dendrites | 3.67 × 10−3 | DSCAM, FMN1 |
| loss of hippocampal neurons | 4.32 × 10−3 | PLCB1, PRKN |
| development of central nervous system | 5.75 × 10−3 | CREM, PLCB1, PRKN, TOP2B |
| abnormal morphology of amacrine cells | 6.04 × 10−3 | DSCAM |
| sensorimotor integration | 6.04 × 10−3 | PRKN |
| abnormal morphology of substantia nigra | 6.90 × 10−3 | PRKN |
| abnormal morphology of neurons | 7.53 × 10−3 | DSCAM, LHX4, PRKN |
| abnormal morphology of nervous system | 8.50 × 10−3 | DSCAM, LHX4, PRKN, TOP2B |
| abnormal morphology of hypoglossal nerve | 9.48 × 10−3 | LHX4 |
| thickness of cerebral cortex | 1.03 × 10−2 | DSCAM |
| quantity of gonadotropes | 1.12 × 10−2 | LHX4 |
| innervation of motor neurons | 1.20 × 10−2 | TOP2B |
| abnormal morphology of brain | 1.22 × 10−2 | LHX4, PRKN, TOP2B |
| loss of neurons | 1.27 × 10−2 | PLCB1, PRKN |
| curvature of vertebral column | 1.80 × 10−2 | TOP2B |
| formation of brain | 1.83 × 10−2 | CREM, PLCB1, TOP2B |
| stratification of cerebral cortex | 1.89 × 10−2 | TOP2B |
| innervation of muscle | 1.89 × 10−2 | TOP2B |
| abnormal morphology of adenohypophysis | 1.97 × 10−2 | LHX4 |
| quantity of nerve ending | 2.14 × 10−2 | PRKN |
| guidance of motor axons | 2.23 × 10−2 | LHX4 |
| loss of dopaminergic neurons | 2.23 × 10−2 | PRKN |
| abnormal morphology of spinal nerve | 2.48 × 10−2 | LHX4 |
| fasciculation of axons | 2.56 × 10−2 | DSCAM |
| abnormal morphology of motor neurons | 2.82 × 10−2 | LHX4 |
| neuritogenesis | 3.00 × 10−2 | DSCAM, FMN1, TOP2B |
| abnormal morphology of subventricular zone | 3.07 × 10−2 | TOP2B |
| memory | 3.36 × 10−2 | CREM, PLCB1 |
| morphology of dendritic spines | 3.57 × 10−2 | DSCAM |
| quantity of dendritic spines | 3.99 × 10−2 | DSCAM |
| development of spinal cord | 4.49 × 10−2 | TOP2B |
| abnormal morphology of olfactory bulb | 4.57 × 10−2 | TOP2B |
| cell viability of cortical neurons | 4.74 × 10−2 | PRKN |
| electrophysiology of nervous system | 4.74 × 10−2 | PRKN |
| Case-control Association Analysis of dA.DZ vs. dNA.DZ | Overlap with SFARI | Overlap with Exome-seq # | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (146 genes associated with SNPs with p ≤ 0.05 and OR ≥ 3) | * Q = 1.84 × 10−7 | * Q = 4.64 × 10−8 | |||||
| ABCA13 | DCC | KCTD16 | PCSK6 | RPH3AL | ABCA13 | ABCA13 | OR1J2 |
| ACVRL1 | DKK3 | KIAA0232 | PDCD4 | SCOC | CACNA1A | ALDH3B2 | PCM1 |
| ALDH3B2 | DMD | KIAA1407 | PDE3A | SEC16B | CACNA2D3 | ALMS1 | PCSK6 |
| ALMS1 | DNAH5 | KLHDC7A | PDE9A | SETBP1 | CNTN4 | ARHGAP28 | PDCD4 |
| ANO4 | DST | KLHL1 | PDGFD | SFMBT2 | CSMD1 | ATP8B4 | PDE9A |
| ARHGAP28 | ESRRB | KSR2 | PDXK | SLC12A2 | CTNND2 | C20orf96 | PDGFD |
| ATP8B4 | EXOSC1 | LDLRAD3 | PDZD2 | SLC22A23 | DMD | CACNA1A | PDZD2 |
| ATXN3 | FAM216A | LIN52 | PEX13 | SLC25A21 | DST | CACNA2D3 | PKNOX2 |
| BBIP1 | FAM89A | LPHN3 | PGAM1P5 | SLC39A11 | ESRRB | CDK14 | PLCG2 |
| C20orf96 | FAT4 | LRP11 | PIP5K1B | SLC5A12 | FER | CSMD1 | PRKAG2 |
| CACNA1A | FER | LRP1B | PIP5K1C | SLIT3 | FHIT | CSMD3 | PRKCE |
| CACNA2D3 | FERMT1 | MAL2 | PKNOX2 | SMC6 | GABRB1 | CTNND2 | PRPF4B |
| CACNG2 | FHIT | MARCH1 | PLCG2 | SNTG2 | GRIP1 | DCC | PSD3 |
| CARD6 | FLIP1L | MAST4 | POU2F3 | SNX9 | MCPH1 | DMD | RBMS3 |
| CCDC102B | FREM1 | MCPH1 | PPARGC1A | SORCS2 | NELL1 | DNAH5 | RHBDF2 |
| CCDC111 | GABRB1 | MIPEP | PRKAG2 | SYT9 | NTNG1 | DST | RNF213 |
| CCDC176 | GALC | MPP7 | PRKCE | TBCE | NXPH1 | ESRRB | ROBO1 |
| CCDC3 | GAS7 | MYO15B | PRKG1 | TMEM182 | PSD3 | FAT4 | RPH3AL |
| CD36 | GNN | MYOM3 | PRPF4B | TMTC2 | RBMS3 | FERMT1 | SCOC |
| CDK14 | GPR124 | NCOR2 | PSD3 | TRIP11 | ROBO1 | GALC | SEC16B |
| CDKAL1 | GPR125 | NELL1 | QRTRTD1 | TTC7A | SETBP1 | HEG1 | SETBP1 |
| CLYBL | GRIP1 | NMNAT2 | RABGAP1L | TUBGCP5 | SLC39A11 | KIAA0232 | SLC22A23 |
| CMSS1 | HAL | NRDE2 | RASGEF1B | VIT | SLIT3 | KIAA1407 | SLC39A11 |
| CNOT10 | HEG1 | NTNG1 | RBMS3 | XRCC4 | SNTG2 | LRP11 | SMC6 |
| CNTN4 | HSPA12A | NXPH1 | RCN1 | YIPF5 | TUBGCP5 | LRP1B | TMTC2 |
| CSMD1 | HVCN1 | OAS2 | RGS17 | ZDDGGC16 | MCPH1 | TRIP11 | |
| CSMD3 | IFT81 | OR1J2 | RHBDF2 | MYOM3 | TTC7A | ||
| CTNND2 | IRS1 | OR8U8 | RNF180 | NCOR2 | TUBGCP5 | ||
| CWC27 | KCNIP4 | PALLD | RNF213 | NELL1 | YIPF5 | ||
| CYMP | KCNN3 | PCM1 | ROBO1 | NTNG1 | |||
| Function Annotation | p-Value * | Genes |
|---|---|---|
| development of neurons | 5.50 × 10−6 | ADGRL3, CACNA1A, CACNG2, CNTN4, CTNND2, DCC, DMD, FER, GAS7, KLHL1, NTNG1, PALLD, PCM1, PIP5K1B, PIP5K1C, PRKCE, PRKG1, ROBO1, SLC12A2, SLIT3, TBCE |
| neuritogenesis | 3.57 × 10−5 | CACNA1A, CNTN4, CTNND2, DCC, FER, GAS7, KLHL1, NTNG1, PALLD, PIP5K1B, PIP5K1C, PRKCE, PRKG1, ROBO1, SLIT3, TBCE |
| axonogenesis | 2.58 × 10−4 | CACNA1A, CNTN4, DCC, NTNG1, PIP5K1C, PRKG1, ROBO1, TBCE |
| migration of neurons | 6.40 × 10−4 | ADGRL3, DCC, PCM1, PEX13, PIP5K1C, PRKG1, ROBO1, SLC12A2 |
| development of sensory projections | 7.83 × 10−4 | ROBO1, SLIT3 |
| pathfinding of neurons | 2.02 × 10−3 | DCC, ROBO1 |
| morphology of nervous system | 2.62 × 10−3 | ADGRA2, BBIP1, CACNA1A, CNTN4, DCC, KLHL1, MCPH1, NCOR2, PALLD, PCSK6, PEX13, PPARGC1A, ROBO1, SLC12A2, XRCC4 |
| guidance of axons | 4.61 × 10−3 | CNTN4, DCC, PRKG1, ROBO1, SLIT3 |
| abnormal morphology of forebrain | 4.80 × 10−3 | ADGRA2, BBIP1, DCC, NCOR2, PPARGC1A, ROBO1 |
| formation of dendrites | 4.83 × 10−3 | CACNA1A, GAS7, KLHL1, PRKG1, ROBO1 |
| developmental process of synapse | 5.28 × 10−3 | ADGRL3, CACNA1A, CACNG2, DCC, DMD, SLC12A2 |
| quantity of oxytocin neurons | 6.19 × 10−3 | DCC |
| synaptic transmission of stellate cells | 6.19 × 10−3 | CACNG2 |
| guidance of corticocortical axons | 1.23 × 10−2 | ROBO1 |
| quantity of vasopressin neurons | 1.23 × 10−2 | DCC |
| activation of Purkinje cells | 1.23 × 10−2 | CACNA1A |
| afterhyperpolarization of dopaminergic neurons | 1.23 × 10−2 | KCNN3 |
| size of hippocampal commissure | 1.23 × 10−2 | ROBO1 |
| startle response | 1.74 × 10−2 | CACNA2D3, CSMD1, PPARGC1A |
| inhibition of presympathetic neurons | 1.85 × 10−2 | SLC12A2 |
| fragmentation of myelin sheath | 1.85 × 10−2 | GALC |
| maturation of cerebellum | 1.85 × 10−2 | CACNA1A |
| turnover of synaptic vesicles | 1.85 × 10−2 | CACNA1A |
| density of synapse | 2.20 × 10−2 | CTNND2, GRIP1 |
| morphogenesis of neurites | 2.43 × 10−2 | CACNA1A, CNTN4, CTNND2, FER, GAS7, PALLD, PRKG1, ROBO1 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, V.W.; Devlin, C.A.; Debski, J.J. ASD Phenotype—Genotype Associations in Concordant and Discordant Monozygotic and Dizygotic Twins Stratified by Severity of Autistic Traits. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3804. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20153804
Hu VW, Devlin CA, Debski JJ. ASD Phenotype—Genotype Associations in Concordant and Discordant Monozygotic and Dizygotic Twins Stratified by Severity of Autistic Traits. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(15):3804. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20153804
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Valerie W., Christine A. Devlin, and Jessica J. Debski. 2019. "ASD Phenotype—Genotype Associations in Concordant and Discordant Monozygotic and Dizygotic Twins Stratified by Severity of Autistic Traits" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 15: 3804. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20153804
APA StyleHu, V. W., Devlin, C. A., & Debski, J. J. (2019). ASD Phenotype—Genotype Associations in Concordant and Discordant Monozygotic and Dizygotic Twins Stratified by Severity of Autistic Traits. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(15), 3804. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20153804