Proteomic Analysis of Lipid Rafts from RBL-2H3 Mast Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
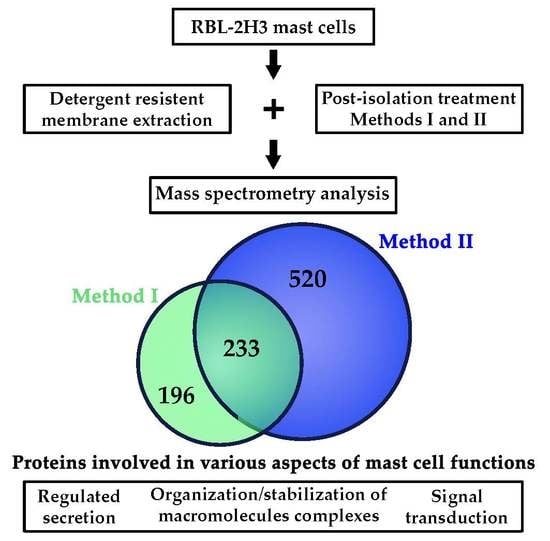
2.1. Obtention of Lipid Rafts from RBL-2H3 Mast Cells
2.2. Identification of Mast Cell Lipid Raft Proteins Using Nano-UPLC-MSE
2.3. Characterization of Mast Cell Lipid Raft Proteins
2.4. Functional Characterization of Mast Cell Lipid Raft Proteome
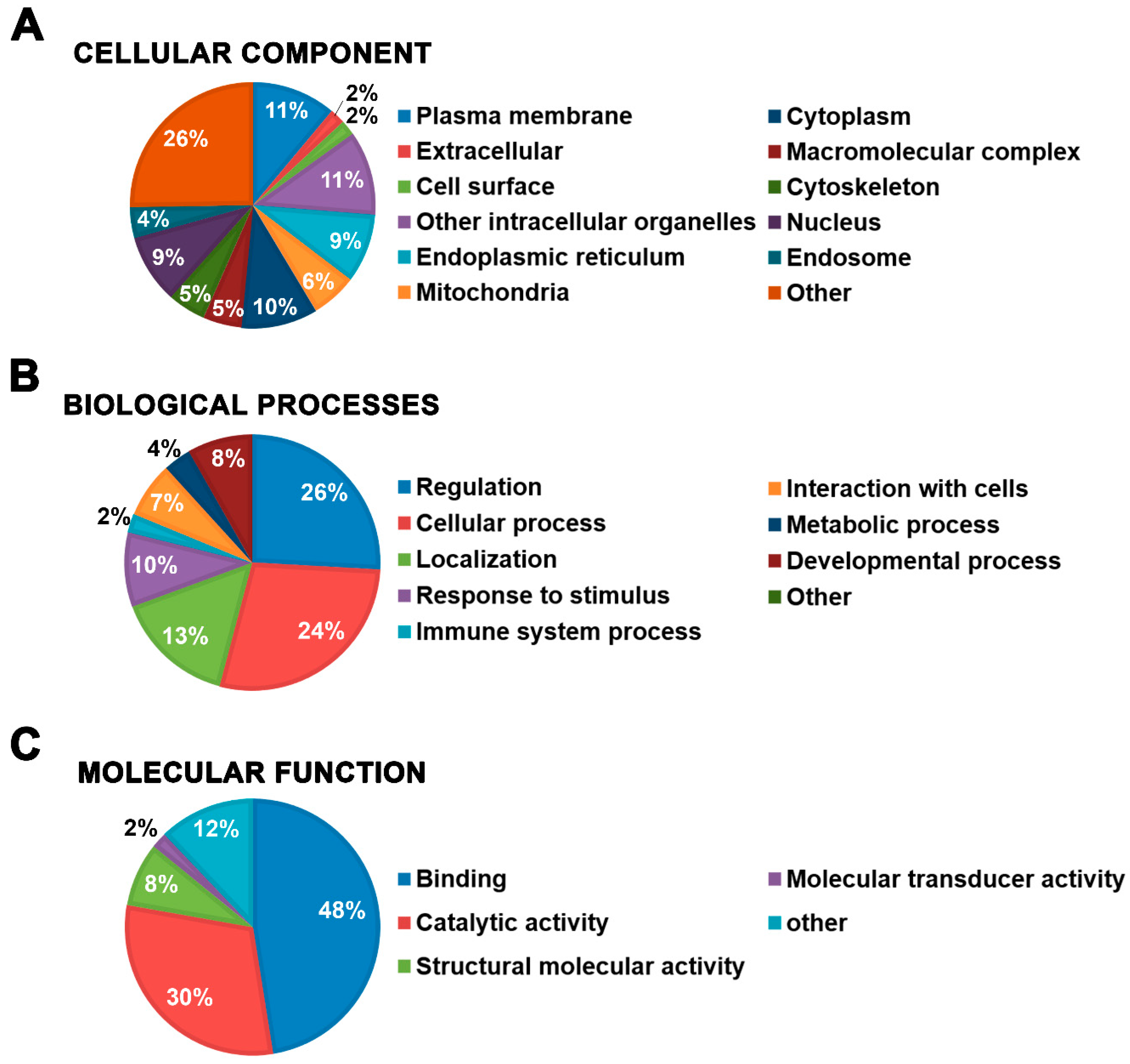
2.5. Distribution among GO Domains of the Mast Cell Lipid Raft Proteins Identified Using Different Post-Isolation Methods
2.6. Functional Enrichment of the Mast Cell Lipid Raft Proteins
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Cell Culture
5.2. Isolation of Lipid Rafts from RBL-2H3 Mast Cells
5.3. Immunoblotting Analysis of Lipid Raft Enriched Fractions
5.4. Extraction and Digestion of Mast Cell Lipid Raft Proteins for Mass Spectrometry
5.5. Nano-Electrospray Ionization Source (ESI) and Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography Mass Spectrometry (UPLC-MSE)
5.6. Data Processing and Protein Identification Analysis
5.7. Bioinformatics Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MC | Mast cell |
| MetI | Method I |
| MetII | Method II |
References
- Pike, L.J. The challenge of lipid rafts. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, S323–S328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Simons, K.; Gerl, M.J. Revitalizing membrane rafts: New tools and insights. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 688–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bieberich, E. Sphingolipids and lipid rafts: Novel concepts and methods of analysis. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2018, 216, 114–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Enoki, T.A.; Heberle, F.A.; Feigenson, G.W. FRET Detects the Size of Nanodomains for Coexisting Liquid-Disordered and Liquid-Ordered Phases. Biophys. J. 2018, 114, 1921–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sezgin, E. Super-resolution optical microscopy for studying membrane structure and dynamics. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2017, 29, 273001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silveira, E.; Souza, A.M.; Mazucato, V.M.; Jamur, M.C.; Oliver, C. Lipid rafts in mast cell biology. J. Lipids 2011, 2011, 752906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Head, B.P.; Patel, H.H.; Insel, P.A. Interaction of membrane/lipid rafts with the cytoskeleton: Impact on signaling and function: Membrane/lipid rafts, mediators of cytoskeletal arrangement and cell signaling. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1838, 532–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingwood, D.; Simons, K. Lipid rafts as a membrane-organizing principle. Science 2010, 327, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sezgin, E.; Levental, I.; Mayor, S.; Eggeling, C. The mystery of membrane organization: Composition, regulation and roles of lipid rafts. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2017, 18, 361–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusumi, A.; Suzuki, K. Toward understanding the dynamics of membrane-raft-based molecular interactions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2005, 1746, 234–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jia, J.Y.; Lamer, S.; Schümann, M.; Schmidt, M.R.; Krause, E.; Haucke, V. Quantitative proteomics analysis of detergent-resistant membranes from chemical synapses: Evidence for cholesterol as spatial organizer of synaptic vesicle cycling. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2006, 5, 2060–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Yan, G.; Gao, M.; Zhang, X. Magnetic capture of polydopamine-encapsulated Hela cells for the analysis of cell surface proteins. J. Proteomics 2018, 172, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, A.D.; Inder, K.L.; Shah, A.K.; Cristino, A.S.; McKie, A.B.; Gabra, H.; Davis, M.J.; Hill, M.M. Integrative Analysis of Subcellular Quantitative Proteomics Studies Reveals Functional Cytoskeleton Membrane-Lipid Raft Interactions in Cancer. J. Proteome Res. 2016, 15, 3451–3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feuk-Lagerstedt, E.; Movitz, C.; Pellmé, S.; Dahlgren, C.; Karlsson, A. Lipid raft proteome of the human neutrophil azurophil granule. Proteomics 2007, 7, 194–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nebl, T.; Pestonjamasp, K.N.; Leszyk, J.D.; Crowley, J.L.; Oh, S.W.; Luna, E.J. Proteomic analysis of a detergent-resistant membrane skeleton from neutrophil plasma membranes. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 43399–43409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Shaw, A.R.; Li, N.; Chen, R.; Mak, A.; Hu, X.; Young, N.; Wishart, D.; Li, L. Liquid chromatography electrospray ionization and matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization tandem mass spectrometry for the analysis of lipid raft proteome of monocytes. Anal. Chim. Acta 2008, 627, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhungana, S.; Merrick, B.A.; Tomer, K.B.; Fessler, M.B. Quantitative proteomics analysis of macrophage rafts reveals compartmentalized activation of the proteasome and of proteasome-mediated ERK activation in response to lipopolysaccharide. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2009, 8, 201–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bini, L.; Pacini, S.; Liberatori, S.; Valensin, S.; Pellegrini, M.; Raggiaschi, R.; Pallini, V.; Baldari, C.T. Extensive temporally regulated reorganization of the lipid raft proteome following T-cell antigen receptor triggering. Biochem. J. 2003, 369, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, S.L.; Chien, C.W.; Han, C.L.; Chen, E.S.; Kao, S.H.; Chen, Y.J.; Liao, F. Temporal proteomics profiling of lipid rafts in CCR6-activated T cells reveals the integration of actin cytoskeleton dynamics. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 283–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Wollscheid, B.; Watts, J.D.; Scheer, B.; Aebersold, R.; DeFranco, A.L. Quantitative proteomic analysis of B cell lipid rafts reveals that ezrin regulates antigen receptor-mediated lipid raft dynamics. Nat. Immunol. 2006, 7, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Man, P.; Novák, P.; Cebecauer, M.; Horváth, O.; Fiserová, A.; Havlícek, V.; Bezouska, K. Mass spectrometric analysis of the glycosphingolipid-enriched microdomains of rat natural killer cells. Proteomics 2005, 5, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foster, L.J.; Chan, Q.W. Lipid raft proteomics: More than just detergent-resistant membranes. Subcell. Biochem. 2007, 43, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Inder, K.L.; Davis, M.; Hill, M.M. Ripples in the pond--using a systems approach to decipher the cellular functions of membrane microdomains. Mol. Biosyst. 2013, 9, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minogue, S.; Waugh, M.G. Lipid rafts, microdomain heterogeneity and inter-organelle contacts: Impacts on membrane preparation for proteomic studies. Biol. Cell 2012, 104, 618–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, A.; Shah, A.D.; Chen, D.; Hill, M.M. RaftProt V2: Understanding membrane microdomain function through lipid raft proteomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D459–D463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, A.; Robinson, H.; Erramouspe, P.J.; Hill, M.M. Advances and challenges in understanding the role of the lipid raft proteome in human health. Expert Rev. Proteomics 2018, 15, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.Z.; Berg, K.B.; Foster, L.J. Mitochondria do not contain lipid rafts, and lipid rafts do not contain mitochondrial proteins. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, 988–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Anand, P.; Singh, B.; Jaggi, A.S.; Singh, N. Mast cells: An expanding pathophysiological role from allergy to other disorders. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 2012, 385, 657–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da Silva, E.Z.; Jamur, M.C.; Oliver, C. Mast cell function: A new vision of an old cell. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2014, 62, 698–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, S.J. The Mast Cell-IgE Paradox: From Homeostasis to Anaphylaxis. Am. J. Pathol. 2016, 186, 212–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahn, T.; Leifheit, E.; Gooch, S.; Sindhu, S.; Weinberg, K. Lipid rafts are required for Kit survival and proliferation signals. Blood 2007, 110, 1739–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holowka, D.; Baird, B. Nanodomains in early and later phases of FcɛRI signalling. Essays Biochem. 2015, 57, 147–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazucato, V.M.; Silveira, E.; Souza, A.M.; Nicoletti, L.M.; Jamur, M.C.; Oliver, C. GD1b-derived gangliosides modulate FcεRI endocytosis in mast cells. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2011, 59, 428–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fridriksson, E.K.; Shipkova, P.A.; Sheets, E.D.; Holowka, D.; Baird, B.; McLafferty, F.W. Quantitative analysis of phospholipids in functionally important membrane domains from RBL-2H3 mast cells using tandem high-resolution mass spectrometry. Biochemistry 1999, 38, 8056–8063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadroddiny, E.; Ai, J.; Carroll, K.; Pham, T.K.; Wright, P.; Pathak, A.; Helm, B. Protein profiling of the secretome of FcεRI activated RBL-2H3.1 cells. Iran. J. Immunol. 2012, 9, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gage, M.C.; Keen, J.N.; Buxton, A.T.; Bedi, M.K.; Findlay, J.B. Proteomic analysis of IgE-mediated secretion by LAD2 mast cells. J. Proteome Res. 2009, 8, 4116–4125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Smith, N.L.; Sil, D.; Holowka, D.A.; McLafferty, F.W.; Baird, B.A. IgE receptor-mediated alteration of membrane-cytoskeleton interactions revealed by mass spectrometric analysis of detergent-resistant membranes. Biochemistry 2009, 48, 6540–6550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dráber, P.; Dráberová, L. Lipid rafts in mast cell signaling. Mol. Immunol. 2002, 38, 1247–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Passante, E.; Frankish, N. The RBL-2H3 cell line: Its provenance and suitability as a model for the mast cell. Inflamm. Res. 2009, 58, 737–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcone, F.H.; Wan, D.; Barwary, N.; Sagi-Eisenberg, R. RBL cells as models for in vitro studies of mast cells and basophils. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 282, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eccleston, E.; Leonard, B.J.; Lowe, J.S.; Welford, H.J. Basophilic leukaemia in the albino rat and a demonstration of the basopoietin. Nat. New Biol. 1973, 244, 73–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barsumian, E.L.; Isersky, C.; Petrino, M.G.; Siraganian, R.P. IgE-induced histamine release from rat basophilic leukemia cell lines: Isolation of releasing and nonreleasing clones. Eur. J. Immunol. 1981, 11, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, J.; Arudchandran, R.; Gonzalez-Espinosa, C.; Manetz, T.S.; Xirasagar, S. A perspective: Regulation of IgE receptor-mediated mast cell responses by a LAT-organized plasma membrane-localized signaling complex. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2001, 124, 137–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janes, P.W.; Ley, S.C.; Magee, A.I. Aggregation of lipid rafts accompanies signaling via the T cell antigen receptor. J. Cell Biol. 1999, 147, 447–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, N.H.; Her, G.R.; Reinhold, V.N.; Brennan, M.J.; Siraganian, R.P.; Ginsburg, V. Monoclonal antibody AA4, which inhibits binding of IgE to high affinity receptors on rat basophilic leukemia cells, binds to novel alpha-galactosyl derivatives of ganglioside GD1b. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 13267–13272. [Google Scholar]
- Sheets, E.D.; Holowka, D.; Baird, B. Critical role for cholesterol in Lyn-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation of FcepsilonRI and their association with detergent-resistant membranes. J. Cell Biol. 1999, 145, 877–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levental, I.; Grzybek, M.; Simons, K. Greasing their way: Lipid modifications determine protein association with membrane rafts. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 6305–6316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorent, J.H.; Levental, I. Structural determinants of protein partitioning into ordered membrane domains and lipid rafts. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2015, 192, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, V.N.; Perlman, D.H.; Costello, C.E.; McComb, M.E. Software tool for researching annotations of proteins: Open-source protein annotation software with data visualization. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 9819–9823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.W.; Sherman, B.T.; Tan, Q.; Collins, J.R.; Alvord, W.G.; Roayaei, J.; Stephens, R.; Baseler, M.W.; Lane, H.C.; Lempicki, R.A. The DAVID Gene Functional Classification Tool: A novel biological module-centric algorithm to functionally analyze large gene lists. Genome Biol. 2007, 8, R183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, K.; Ikonen, E. Functional rafts in cell membranes. Nature 1997, 387, 569–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garner, A.E.; Smith, D.A.; Hooper, N.M. Visualization of detergent solubilization of membranes: Implications for the isolation of rafts. Biophys. J. 2008, 94, 1326–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.A.; Rose, J.K. Sorting of GPI-anchored proteins to glycolipid-enriched membrane subdomains during transport to the apical cell surface. Cell 1992, 68, 533–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.K.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, A.R.; Jang, G.H.; Kim, H.W.; Park, Y.H.; Kim, B.; Park, Y.M.; Beaven, M.A.; Kim, Y.M.; et al. The scaffold protein prohibitin is required for antigen-stimulated signaling in mast cells. Sci. Signal. 2013, 6, ra80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poston, C.N.; Duong, E.; Cao, Y.; Bazemore-Walker, C.R. Proteomic analysis of lipid raft-enriched membranes isolated from internal organelles. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 415, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rabani, V.; Davani, S.; Gambert-Nicot, S.; Meneveau, N.; Montange, D. Comparative lipidomics and proteomics analysis of platelet lipid rafts using different detergents. Platelets 2016, 27, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foster, L.J.; De Hoog, C.L.; Mann, M. Unbiased quantitative proteomics of lipid rafts reveals high specificity for signaling factors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 5813–5818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zech, T.; Ejsing, C.S.; Gaus, K.; de Wet, B.; Shevchenko, A.; Simons, K.; Harder, T. Accumulation of raft lipids in T-cell plasma membrane domains engaged in TCR signalling. EMBO J. 2009, 28, 466–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Souza, S.A.M.; Mazucato, V.M.; de Castro, R.O.; Matioli, F.; Ciancaglini, P.; de Paiva Paulino, T.; Jamur, M.C.; Oliver, C. The alpha-galactosyl derivatives of ganglioside GD(1b) are essential for the organization of lipid rafts in RBL-2H3 mast cells. Exp. Cell Res. 2008, 314, 2515–2528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitomi, T.; Zhang, J.; Nicoletti, L.M.; Grodzki, A.C.; Jamur, M.C.; Oliver, C.; Siraganian, R.P. Phospholipase D1 regulates high-affinity IgE receptor-induced mast cell degranulation. Blood 2004, 104, 4122–4128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, B.S.; Pfeiffer, J.R.; Surviladze, Z.; Gaudet, E.A.; Oliver, J.M. High resolution mapping of mast cell membranes reveals primary and secondary domains of Fc(epsilon)RI and LAT. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 154, 645–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holowka, D.; Sheets, E.D.; Baird, B. Interactions between Fc(epsilon)RI and lipid raft components are regulated by the actin cytoskeleton. J. Cell Sci. 2000, 113, 1009–1019. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Ma, D.W.; Kang, J.X.; Kulka, M. N-3 Polyunsaturated fatty acids inhibit Fc ε receptor I-mediated mast cell activation. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2015, 26, 1580–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, N.; Hamamura, K.; Kotani, N.; Furukawa, K.; Kaneko, K.; Honke, K. Proteomic analysis of ganglioside-associated membrane molecules: Substantial basis for molecular clustering. Proteomics 2012, 12, 3154–3163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, V.L.; Thomas, C.M.; Smart, E.J. Lipid rafts, caveolae and GPI-linked proteins. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2012, 729, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, N.; Nakanishi, M.; Hirashima, N. Flotillin-1 regulates IgE receptor-mediated signaling in rat basophilic leukemia (RBL-2H3) cells. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuermer, C.A.; Lang, D.M.; Kirsch, F.; Wiechers, M.; Deininger, S.O.; Plattner, H. Glycosylphosphatidyl inositol-anchored proteins and fyn kinase assemble in noncaveolar plasma membrane microdomains defined by reggie-1 and -2. Mol. Biol. Cell 2001, 12, 3031–3045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotani, N.; Nakano, T.; Ida, Y.; Ito, R.; Hashizume, M.; Yamaguchi, A.; Seo, M.; Araki, T.; Hojo, Y.; Honke, K.; et al. Analysis of lipid raft molecules in the living brain slices. Neurochem. Int. 2018, 119, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Schey, K.L. Proteomic Analysis of Lipid Raft-Like Detergent-Resistant Membranes of Lens Fiber Cells. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2015, 56, 8349–8360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chowdhury, S.M.; Zhu, X.; Aloor, J.J.; Azzam, K.M.; Gabor, K.A.; Ge, W.; Addo, K.A.; Tomer, K.B.; Parks, J.S.; Fessler, M.B. Proteomic Analysis of ABCA1-Null Macrophages Reveals a Role for Stomatin-Like Protein-2 in Raft Composition and Toll-Like Receptor Signaling. Mol. Cell Proteomics 2015, 14, 1859–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dwyer, D.F.; Barrett, N.A.; Austen, K.F.; Consortium, I.G.P. Expression profiling of constitutive mast cells reveals a unique identity within the immune system. Nat. Immunol. 2016, 17, 878–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gschwandtner, M.; Paulitschke, V.; Mildner, M.; Brunner, P.M.; Hacker, S.; Eisenwort, G.; Sperr, W.R.; Valent, P.; Gerner, C.; Tschachler, E. Proteome analysis identifies L1CAM/CD171 and DPP4/CD26 as novel markers of human skin mast cells. Allergy 2017, 72, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solstad, T.; Bjørgo, E.; Koehler, C.J.; Strozynski, M.; Torgersen, K.M.; Taskén, K.; Thiede, B. Quantitative proteome analysis of detergent-resistant membranes identifies the differential regulation of protein kinase C isoforms in apoptotic T cells. Proteomics 2010, 10, 2758–2768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moltu, K.; Bjorgo, E.; Solstad, T.; Berge, T.; Thiede, B.; Taskén, K. A proteomic approach to screening of dynamic changes in detergent-resistant membranes from activated human primary T cells. J. Proteomics Bioinform. 2013, 6, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resh, M.D. Fatty acylation of proteins: The long and the short of it. Prog. Lipid Res. 2016, 63, 120–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; London, E. Transmembrane protein (perfringolysin o) association with ordered membrane domains (rafts) depends upon the raft-associating properties of protein-bound sterol. Biophys. J. 2013, 105, 2733–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Gassart, A.; Geminard, C.; Fevrier, B.; Raposo, G.; Vidal, M. Lipid raft-associated protein sorting in exosomes. Blood 2003, 102, 4336–4344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Diaz-Rohrer, B.; Levental, K.R.; Levental, I. Rafting through traffic: Membrane domains in cellular logistics. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1838, 3003–3013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salaün, C.; James, D.J.; Chamberlain, L.H. Lipid rafts and the regulation of exocytosis. Traffic 2004, 5, 255–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varshney, P.; Yadav, V.; Saini, N. Lipid rafts in immune signalling: Current progress and future perspective. Immunology 2016, 149, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scorrano, L.; De Matteis, M.A.; Emr, S.; Giordano, F.; Hajnóczky, G.; Kornmann, B.; Lackner, L.L.; Levine, T.P.; Pellegrini, L.; Reinisch, K.; et al. Coming together to define membrane contact sites. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.W.; Lee, J.W.; Choo, H.J.; Lee, C.S.; Jung, S.Y.; Yi, J.S.; Ham, Y.M.; Lee, J.H.; Hong, J.; Kang, M.J.; et al. Mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation system is recruited to detergent-resistant lipid rafts during myogenesis. Proteomics 2010, 10, 2498–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubois, L.; Ronquist, K.K.; Ek, B.; Ronquist, G.; Larsson, A. Proteomic Profiling of Detergent Resistant Membranes (Lipid Rafts) of Prostasomes. Mol. Cell Proteomics 2015, 14, 3015–3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quintana, A.; Schwindling, C.; Wenning, A.S.; Becherer, U.; Rettig, J.; Schwarz, E.C.; Hoth, M. T cell activation requires mitochondrial translocation to the immunological synapse. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 14418–14423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cascianelli, G.; Villani, M.; Tosti, M.; Marini, F.; Bartoccini, E.; Magni, M.V.; Albi, E. Lipid microdomains in cell nucleus. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2008, 19, 5289–5295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Llobregat, J.; Buceta, J.; Reigada, R. Interplay of cytoskeletal activity and lipid phase stability in dynamic protein recruitment and clustering. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelby, S.A.; Veatch, S.L.; Holowka, D.A.; Baird, B.A. Functional nanoscale coupling of Lyn kinase with IgE-FcεRI is restricted by the actin cytoskeleton in early antigen-stimulated signaling. Mol. Biol. Cell 2016, 27, 3645–3658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, R.; Leach, S.; Liu, W.; Ralston, E.; Scheffel, J.; Zhang, W.; Lowell, C.A.; Rivera, J. Molecular editing of cellular responses by the high-affinity receptor for IgE. Science 2014, 343, 1021–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surma, M.A.; Klose, C.; Simons, K. Lipid-dependent protein sorting at the trans-Golgi network. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1821, 1059–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iaea, D.B.; Maxfield, F.R. Membrane order in the plasma membrane and endocytic recycling compartment. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissig, C.; Gruenberg, J. Lipid sorting and multivesicular endosome biogenesis. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a016816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wernersson, S.; Pejler, G. Mast cell secretory granules: Armed for battle. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 478–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blank, U.; Madera-Salcedo, I.K.; Danelli, L.; Claver, J.; Tiwari, N.; Sánchez-Miranda, E.; Vázquez-Victorio, G.; Ramírez-Valadez, K.A.; Macias-Silva, M.; González-Espinosa, C. Vesicular trafficking and signaling for cytokine and chemokine secretion in mast cells. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, N.; Nakanishi, M.; Hirashima, N. Cholesterol depletion inhibits store-operated calcium currents and exocytotic membrane fusion in RBL-2H3 cells. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 11808–11814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Draber, P.; Halova, I.; Polakovicova, I.; Kawakami, T. Signal transduction and chemotaxis in mast cells. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 778, 11–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Psatha, M.; Koffer, A.; Erent, M.; Moss, S.E.; Bolsover, S. Calmodulin spatial dynamics in RBL-2H3 mast cells. Cell Calcium. 2004, 36, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bastan, R.; Peirce, M.J.; Peachell, P.T. Regulation of immunoglobulin E-mediated secretion by protein phosphatases in human basophils and mast cells of skin and lung. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2001, 430, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grochowy, G.; Hermiston, M.L.; Kuhny, M.; Weiss, A.; Huber, M. Requirement for CD45 in fine-tuning mast cell responses mediated by different ligand-receptor systems. Cell Signal. 2009, 21, 1277–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowlkes, V.; Wilson, C.G.; Carver, W.; Goldsmith, E.C. Mechanical loading promotes mast cell degranulation via RGD-integrin dependent pathways. J. Biomech. 2013, 46, 788–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassas, A.; Moura, I.C.; Yamashita, Y.; Scheffel, J.; Guérin-Marchand, C.; Blank, U.; Sims, P.J.; Wiedmer, T.; Monteiro, R.C.; Rivera, J.; et al. Regulation of the tyrosine phosphorylation of Phospholipid Scramblase 1 in mast cells that are stimulated through the high-affinity IgE receptor. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruse, G.; Metcalfe, D.D.; Olivera, A. Functional deregulation of KIT: Link to mast cell proliferative diseases and other neoplasms. Immunol. Allergy Clin. North. Am. 2014, 34, 219–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Xie, Z.; Li, H.; Yue, L.; Pang, Z.; MacNeil, A.J.; Tremblay, M.L.; Tang, J.T.; Lin, T.J. Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) is dispensable for IgE-mediated cutaneous reaction in vivo. Cell Immunol. 2016, 306–307, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halova, I.; Draber, P. Tetraspanins and Transmembrane Adaptor Proteins As Plasma Membrane Organizers-Mast Cell Case. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 4, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dráberová, L.; Shaik, G.M.; Volná, P.; Heneberg, P.; Tůmová, M.; Lebduska, P.; Korb, J.; Dráber, P. Regulation of Ca2+ signaling in mast cells by tyrosine-phosphorylated and unphosphorylated non-T cell activation linker. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 5169–5180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tůmová, M.; Koffer, A.; Simíček, M.; Dráberová, L.; Dráber, P. The transmembrane adaptor protein NTAL signals to mast cell cytoskeleton via the small GTPase Rho. Eur. J. Immunol. 2010, 40, 3235–3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ron, D.; Chen, C.H.; Caldwell, J.; Jamieson, L.; Orr, E.; Mochly-Rosen, D. Cloning of an intracellular receptor for protein kinase C: A homolog of the beta subunit of G proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 839–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ron, D.; Adams, D.R.; Baillie, G.S.; Long, A.; O’Connor, R.; Kiely, P.A. RACK1 to the future–A historical perspective. Cell Commun. Signal. 2013, 11, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballek, O.; Valečka, J.; Dobešová, M.; Broučková, A.; Manning, J.; Řehulka, P.; Stulík, J.; Filipp, D. TCR Triggering Induces the Formation of Lck-RACK1-Actinin-1 Multiprotein Network Affecting Lck Redistribution. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Esterberg, R.; Lachance, V.; Ren, D.; Radde-Gallwitz, K.; Chi, F.; Parent, J.L.; Fritz, A.; Chen, P. Rack1 is required for Vangl2 membrane localization and planar cell polarity signaling while attenuating canonical Wnt activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 2264–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sander, L.E.; Frank, S.P.; Bolat, S.; Blank, U.; Galli, T.; Bigalke, H.; Bischoff, S.C.; Lorentz, A. Vesicle associated membrane protein (VAMP)-7 and VAMP-8, but not VAMP-2 or VAMP-3, are required for activation-induced degranulation of mature human mast cells. Eur. J. Immunol. 2008, 38, 855–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puri, N.; Roche, P.A. Mast cells possess distinct secretory granule subsets whose exocytosis is regulated by different SNARE isoforms. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 2580–2585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guo, Z.; Turner, C.; Castle, D. Relocation of the t-SNARE SNAP-23 from lamellipodia-like cell surface projections regulates compound exocytosis in mast cells. Cell 1998, 94, 537–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brochetta, C.; Suzuki, R.; Vita, F.; Soranzo, M.R.; Claver, J.; Madjene, L.C.; Attout, T.; Vitte, J.; Varin-Blank, N.; Zabucchi, G.; et al. Munc18-2 and syntaxin 3 control distinct essential steps in mast cell degranulation. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, J.D.; Shelby, S.A.; Holowka, D.; Baird, B. Rab11 Regulates the Mast Cell Exocytic Response. Traffic 2016, 17, 1027–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azouz, N.P.; Matsui, T.; Fukuda, M.; Sagi-Eisenberg, R. Decoding the regulation of mast cell exocytosis by networks of Rab GTPases. J. Immunol. 2012, 189, 2169–2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.K.; Mizuno, K.; Wasmeier, C.; Wavre-Shapton, S.T.; Recchi, C.; Catz, S.D.; Futter, C.; Tolmachova, T.; Hume, A.N.; Seabra, M.C. Distinct and opposing roles for Rab27a/Mlph/MyoVa and Rab27b/Munc13-4 in mast cell secretion. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 892–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madera-Salcedo, I.K.; Danelli, L.; Tiwari, N.; Dema, B.; Pacreau, E.; Vibhushan, S.; Birnbaum, J.; Agabriel, C.; Liabeuf, V.; Klingebiel, C.; et al. Tomosyn functions as a PKCδ-regulated fusion clamp in mast cell degranulation. Sci. Signal. 2018, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nika, K.; Acuto, O. Membrane nanodomains in T-cell antigen receptor signalling. Essays Biochem. 2015, 57, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovárová, M.; Tolar, P.; Arudchandran, R.; Dráberová, L.; Rivera, J.; Dráber, P. Structure-function analysis of Lyn kinase association with lipid rafts and initiation of early signaling events after Fcepsilon receptor I aggregation. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 21, 8318–8328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sada, K.; Zhang, J.; Siraganian, R.P. SH2 domain-mediated targeting, but not localization, of Syk in the plasma membrane is critical for FcepsilonRI signaling. Blood 2001, 97, 1352–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, E.G.; da Silva, E.Z.; Zanotto, C.Z.; Oliver, C.; Jamur, M.C. Cross-Linking Mast Cell Specific Gangliosides Stimulates the Release of Newly Formed Lipid Mediators and Newly Synthesized Cytokines. Mediators Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 9160540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacerda Pigosso, L.; Baeza, L.C.; Vieira Tomazett, M.; Batista Rodrigues Faleiro, M.; Brianezi Dignani de Moura, V.M.; Melo Bailão, A.; Borges, C.L.; Alves Parente Rocha, J.; Rocha Fernandes, G.; Gauthier, G.M.; et al. Paracoccidioides brasiliensis presents metabolic reprogramming and secretes a serine proteinase during murine infection. Virulence 2017, 8, 1417–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.Z.; Vissers, J.P.; Silva, J.C.; Golick, D.; Gorenstein, M.V.; Geromanos, S.J. Database searching and accounting of multiplexed precursor and product ion spectra from the data independent analysis of simple and complex peptide mixtures. Proteomics 2009, 9, 1696–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornbeck, P.V.; Kornhauser, J.M.; Tkachev, S.; Zhang, B.; Skrzypek, E.; Murray, B.; Latham, V.; Sullivan, M. PhosphoSitePlus: A comprehensive resource for investigating the structure and function of experimentally determined post-translational modifications in man and mouse. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, D261–D270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanc, M.; David, F.P.A.; van der Goot, F.G. SwissPalm 2: Protein S-Palmitoylation Database. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 2009, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer-Stroh, S.; Koranda, M.; Benetka, W.; Schneider, G.; Sirota, F.L.; Eisenhaber, F. Towards complete sets of farnesylated and geranylgeranylated proteins. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2007, 3, e66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer-Stroh, S.; Gouda, M.; Novatchkova, M.; Schleiffer, A.; Schneider, G.; Sirota, F.L.; Wildpaner, M.; Hayashi, N.; Eisenhaber, F. MYRbase: Analysis of genome-wide glycine myristoylation enlarges the functional spectrum of eukaryotic myristoylated proteins. Genome Biol. 2004, 5, R21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierleoni, A.; Martelli, P.L.; Casadio, R. PredGPI: A GPI-anchor predictor. BMC Bioinformatics 2008, 9, 392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krogh, A.; Larsson, B.; von Heijne, G.; Sonnhammer, E.L. Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden Markov model: Application to complete genomes. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 305, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tulumello, D.V.; Deber, C.M. Efficiency of detergents at maintaining membrane protein structures in their biologically relevant forms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1818, 1351–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]






| Method | Protein Accession | Protein Description | Gene Name | Experimental Evidence | Number of Citations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MetII | P63018 | Heat shock cognate 71 kDa protein | Hspa8 | H (3) M (3) R (3) | 102 |
| MetII | Q9Z1E1 | Flotillin-1 | Flot1 | H (3) M (1) R (3) | 101 |
| MetI; MetII | P15999 | ATP synthase subunit alpha mitochondrial | Atp5fla | H (3) M (3) R (3) | 98 |
| MetI | P10719 | ATP synthase subunit beta mitochondrial | Atp5f1b | H (1) M (1) R (3) | 97 |
| MetI; MetII | Q9Z2L0 | Voltage-dependent anion-selective channel protein 1 | Vdac1 | H (3) M (3) R (3) | 97 |
| MetI; MetII | P67779 | Prohibitin | Phb | H (3) M (1) R (1) | 91 |
| MetI; MetII | P60711 | Actin cytoplasmic 1 | Actb | H (3) M (3) R (3) | 90 |
| MetII | Q9Z2S9 | Flotillin-2 | Flot2 | H (3) M (3) R (3) | 90 |
| MetI; MetII | P81155 | Voltage-dependent anion-selective channel protein 2 | Vdac2 | H (3) M (3) R (1) | 90 |
| MetI; MetII | P06685 | Sodium/potassium-transporting ATPase subunit alpha-1 | Atp1a1 | H (1) M (1) R (1) | 89 |
| MetI; MetII | P04797 | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase | Gapdh | H (1) M (1) R (1) | 88 |
| MetI; MetII | P54311 | Transducin beta-1 | Gnb1 | H (3) M (3) R (3) | 87 |
| MetI | Q07936 | Annexin A2 | Anxa2 | H(1) M (3) R (3) | 86 |
| MetI; MetII | P04897 | Guanine nucleotide-binding protein G(i) subunit alpha-2 | Gnai2 | H (3) M (3) R (3) | 86 |
| MetI; MetII | P06761 | Endoplasmic reticulum chaperone BiP | Hspa5 | H (1) M (1) R (1) | 86 |
| MetI; MetII | P35565 | Calnexin | Canx | H (1) M (1) R (1) | 83 |
| MetI; MetII | G3V6P7 | Myosin heavy chain 9 | Myh9 | H (3) M (3) | 83 |
| MetI | P31000 | Vimentin | Vim | H (3) M (3) R (3) | 81 |
| MetI; MetII | P09527 | Ras-related protein Rab-7a | Rab7a | H (1) M (1) R (1) | 79 |
| MetI; MetII | P26453 | Basigin | Bsg | H (3) M (3) R (3) | 78 |
| MetI; MetII | D4A133 | V-type proton ATPase catalytic subunit A | Atp6v1a | H (3) M (3) | 78 |
| MetI; MetII | P63102 | 14-3-3 protein zeta/delta | Ywhaz | H (1) M (1) R (1) | 77 |
| MetI; MetII | P11442 | Clathrin heavy chain 1 | Cltc | H (3) M (3) R (3) | 77 |
| MetII | F1M779 | Clathrin heavy chain | Cltc | H (3) M (3) R (3) | 77 |
| MetII | Q5XI04 | Erythrocyte band 7 integral membrane protein | Stom | H (1) M (1) | 77 |
| MetI; MetII | P54313 | Transducin beta-2 | Gnb2 | H (3) M (3) R (3) | 76 |
| MetII | B5DEH2 | Erlin-2 | Erlin2 | H (3) M (3) R (3) | 74 |
| MetII | O70377 | Synaptosomal-associated protein 23 (SNAP-23) | Snap23 | H (3) M (3) R (3) | 74 |
| MetI; MetII | P32551 | Cytochrome b-c1 complex subunit 2 mitochondrial | Uqcrc2 | H (3) M (3) R (3) | 72 |
| MetI; MetII | Q5XIH7 | Prohibitin 2 | Phb2 | H (3) M (3) R (3) | 71 |
| GO Term | Unique MetI | Unique MetII | Common |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cellular Component Class | |||
| Cell surface | + | ||
| Cytoplasm | + | ||
| Cytoskeleton | + | + | |
| Endoplasmic reticulum | + | ||
| Endosome | + | ||
| Extracellular | + | ||
| Macromolecular complex | + | ||
| Mitochondria | + | ||
| Nucleus | + | ||
| Other | + | ||
| Other intracellular organelles | + | ||
| Plasma membrane | + | ||
| Ribosomes | + | ||
| Biological Processes Class | |||
| Cellular process | + | ||
| Immune system process | + | + | |
| Interaction with cells/organelles | + | ||
| Localization | + | ||
| Metabolic process | + | ||
| Other | + | ||
| Regulation | + | ||
| Response to stimulus | + | ||
| Molecular Function Class | |||
| Binding | + | ||
| Catalytic activity | + | ||
| Molecular transducer activity | + | ||
| Other | + | ||
| Structural molecular activity | + | ||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Freitas Filho, E.G.; Jaca, L.A.M.; Baeza, L.C.; Soares, C.M.d.A.; Borges, C.L.; Oliver, C.; Jamur, M.C. Proteomic Analysis of Lipid Rafts from RBL-2H3 Mast Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3904. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20163904
Freitas Filho EG, Jaca LAM, Baeza LC, Soares CMdA, Borges CL, Oliver C, Jamur MC. Proteomic Analysis of Lipid Rafts from RBL-2H3 Mast Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(16):3904. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20163904
Chicago/Turabian StyleFreitas Filho, Edismauro Garcia, Luiz Augusto Marin Jaca, Lilian Cristiane Baeza, Célia Maria de Almeida Soares, Clayton Luiz Borges, Constance Oliver, and Maria Célia Jamur. 2019. "Proteomic Analysis of Lipid Rafts from RBL-2H3 Mast Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 16: 3904. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20163904