Glucagon Control on Food Intake and Energy Balance
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. Background
1.2. Glucagon Peptides
1.3. Glucagon Receptor
1.4. Objectives
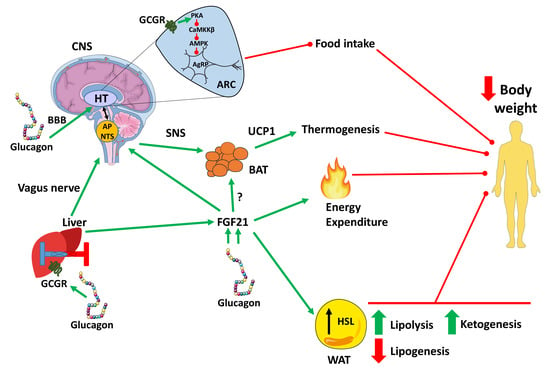
2. The Effect of Glucagon on Satiety and Appetite Suppression
3. Glucagon on Body Weight, Energy Expenditure and Thermogenesis
3.1. Glucagon on Body Weight
3.2. Glucagon on Energy Expenditure
3.3. Glucagon on Thermogenesis
4. The Effect of Glucagon on Lipid Metabolism
5. Novel Approaches against Obesity and Diabetes Targeting the Glucagon Receptor
Dual and Triple Agonists Approach Targeting GCGR
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kimball CP, M.J. Aqueous extracts of pancreas. III. Some precipitaton reactions to insulin. J. Biol. Chem. 1923, 58, 337–346. [Google Scholar]
- Quesada, I.; Tuduri, E.; Ripoll, C.; Nadal, A. Physiology of the pancreatic alpha-cell and glucagon secretion: Role in glucose homeostasis and diabetes. J. Endocrinol. 2008, 199, 5–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habegger, K.M.; Heppner, K.M.; Geary, N.; Bartness, T.J.; DiMarchi, R.; Tschop, M.H. The metabolic actions of glucagon revisited. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2010, 6, 689–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, V.K.; Hynes, M.A.; Jin, C.; Towle, A.C.; Lauder, J.M.; Lund, P.K. Cellular localization of proglucagon/glucagon-like peptide I messenger RNAs in rat brain. J. Neurosci. Res. 1986, 16, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drucker, D.J.; Asa, S. Glucagon gene expression in vertebrate brain. J. Biol. Chem. 1988, 263, 13475–13478. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ohneda, A.; Ohneda, M. Effect of glicentin-related peptides upon the secretion of insulin and glucagon in the canine pancreas. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 1988, 155, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whiting, L.; Stewart, K.W.; Hay, D.L.; Harris, P.W.; Choong, Y.S.; Phillips, A.R.; Brimble, M.A.; Cooper, G.J. Glicentin-related pancreatic polypeptide inhibits glucose-stimulated insulin secretion from the isolated pancreas of adult male rats. Physiol. Rep. 2015, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Zhou, F.; Li, X.; Chang, B.; Li, D.; Wang, Y.; Tong, Q.; Xu, Y.; Fukuda, M.; Zhao, J.J.; et al. Central GLP-2 enhances hepatic insulin sensitivity via activating PI3K signaling in POMC neurons. Cell Metab. 2013, 18, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, P.T.; Naslund, E.; Gryback, P.; Jacobsson, H.; Hartmann, B.; Holst, J.J.; Hellstrom, P.M. Peripheral administration of GLP-2 to humans has no effect on gastric emptying or satiety. Regul. Pept. 2003, 116, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, W.E.; Siegel, E.G.; Creutzfeldt, W. Glucagon-like peptide-1 but not glucagon-like peptide-2 stimulates insulin release from isolated rat pancreatic islets. Diabetologia 1985, 28, 704–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sandoval, D.A.; D’Alessio, D.A. Physiology of proglucagon peptides: Role of glucagon and GLP-1 in health and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2015, 95, 513–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holst, J.J.; Bersani, M.; Johnsen, A.H.; Kofod, H.; Hartmann, B.; Orskov, C. Proglucagon processing in porcine and human pancreas. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 18827–18833. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Larsen, P.J.; Tang-Christensen, M.; Holst, J.J.; Orskov, C. Distribution of glucagon-like peptide-1 and other preproglucagon-derived peptides in the rat hypothalamus and brainstem. Neuroscience 1997, 77, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segre, G.V.; Goldring, S.R. Receptors for secretin, calcitonin, parathyroid hormone (PTH)/PTH-related peptide, vasoactive intestinal peptide, glucagonlike peptide 1, growth hormone-releasing hormone, and glucagon belong to a newly discovered G-protein-linked receptor family. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 1993, 4, 309–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svoboda, M.; Tastenoy, M.; Vertongen, P.; Robberecht, P. Relative quantitative analysis of glucagon receptor mRNA in rat tissues. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 1994, 105, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieffer, T.J.; Heller, R.S.; Unson, C.G.; Weir, G.C.; Habener, J.F. Distribution of glucagon receptors on hormone-specific endocrine cells of rat pancreatic islets. Endocrinology 1996, 137, 5119–5125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Muller, T.D.; Finan, B.; Clemmensen, C.; DiMarchi, R.D.; Tschop, M.H. The New Biology and Pharmacology of Glucagon. Physiol. Rev. 2017, 97, 721–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulman, J.L.; Carleton, J.L.; Whitney, G.; Whitehorn, J.C. Effect of glucagon on food intake and body weight in man. J. Appl. Physiol. 1957, 11, 419–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penick, S.B.; Hinkle, L.E., Jr. Depression of food intake induced in healthy subjects by glucagon. N. Engl. J. Med. 1961, 264, 893–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinones, M.; Al-Massadi, O.; Gallego, R.; Ferno, J.; Dieguez, C.; Lopez, M.; Nogueiras, R. Hypothalamic CaMKKbeta mediates glucagon anorectic effect and its diet-induced resistance. Mol. Metab. 2015, 4, 961–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geary, N.; Asarian, L. Estradiol increases glucagon’s satiating potency in ovariectomized rats. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2001, 281, R1290–R1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geary, N.; Le Sauter, J.; Noh, U. Glucagon acts in the liver to control spontaneous meal size in rats. Am. J. Physiol. 1993, 264, R116–R122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Sauter, J.; Noh, U.; Geary, N. Hepatic portal infusion of glucagon antibodies increases spontaneous meal size in rats. Am. J. Physiol. 1991, 261, R162–R165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raben, A.; Andersen, H.B.; Christensen, N.J.; Madsen, J.; Holst, J.J.; Astrup, A. Evidence for an abnormal postprandial response to a high-fat meal in women predisposed to obesity. Am. J. Physiol. 1994, 267, E549–E559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsson, G.; Uvnas-Wallensten, K. Effect of teasing and sham feeding on plasma glucagon concentration in dogs. Acta Physiol. Scand. 1977, 100, 298–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weatherford, S.C.; Ritter, S. Lesion of vagal afferent terminals impairs glucagon-induced suppression of food intake. Physiol. Behav. 1988, 43, 645–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inokuchi, A.; Oomura, Y.; Nishimura, H. Effect of intracerebroventricularly infused glucagon on feeding behavior. Physiol. Behav. 1984, 33, 397–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, W.A.; Kastin, A.J. Peptides and the blood-brain barrier: Lipophilicity as a predictor of permeability. Brain Res. Bull. 1985, 15, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoosein, N.M.; Gurd, R.S. Identification of glucagon receptors in rat brain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1984, 81, 4368–4372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, E.K.; Mackey, M.A.; Snover, D.C.; Schneider, P.D.; Rucker, R.D., Jr.; Allen, C.E.; Buchwald, H. Suppression of weight gain by glucagon in obese Zucker rats. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 1984, 40, 320–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloom, S.R.; Polak, J.M. Glucagonoma syndrome. Am. J. Med. 1987, 82, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Castro, J.M.; Paullin, S.K.; DeLugas, G.M. Insulin and glucagon as determinants of body weight set point and microregulation in rats. J. Comp. Physiol. Psychol. 1978, 92, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelling, R.W.; Du, X.Q.; Dichmann, D.S.; Romer, J.; Huang, H.; Cui, L.; Obici, S.; Tang, B.; Holst, J.J.; Fledelius, C.; et al. Lower blood glucose, hyperglucagonemia, and pancreatic alpha cell hyperplasia in glucagon receptor knockout mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 1438–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conarello, S.L.; Jiang, G.; Mu, J.; Li, Z.; Woods, J.; Zycband, E.; Ronan, J.; Liu, F.; Roy, R.S.; Zhu, L.; et al. Glucagon receptor knockout mice are resistant to diet-induced obesity and streptozotocin-mediated beta cell loss and hyperglycaemia. Diabetologia 2007, 50, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryce, G.F.; Johnson, P.R.; Sullivan, A.C.; Stern, J.S. Insulin and glucagon: Plasma levels and pancreatic release in the genetically obese Zucker rat. Horm. Metab. Res. 1977, 9, 366–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, I.W.; Salter, J.M.; Best, C.H. Calorigenic action of glucagon. Nature 1957, 180, 1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, K.S. Hyperglucagonemia increases resting metabolic rate in man during insulin deficiency. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1987, 64, 896–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JM, S. Metabolic Effects of Glucagon in the Wistar Rat. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1960, 8, 535–539. [Google Scholar]
- Habegger, K.M.; Stemmer, K.; Cheng, C.; Müller, T.D.; Heppner, K.M.; Ottaway, N.; Holland, J.; Hembree, J.L.; Smiley, D.; Gelfanov, V.; et al. Fibroblast growth factor 21 mediates specific glucagon actions. Diabetes 2013, 62, 1453–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.; Nason, S.; Holleman, C.; Pepin, M.; Wilson, L.; Berryhill, T.F.; Wende, A.R.; Steele, C.; Young, M.E.; Barnes, S.; et al. Glucagon Receptor Signaling Regulates Energy Metabolism via Hepatic Farnesoid X Receptor and Fibroblast Growth Factor 21. Diabetes 2018, 67, 1773–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, K.; Kuroshima, A. Modified metabolic responsiveness to glucagon in cold-acclimated and heat-acclimated rats. Life Sci. 1982, 30, 785–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billington, C.J.; Briggs, J.E.; Link, J.G.; Levine, A.S. Glucagon in physiological concentrations stimulates brown fat thermogenesis in vivo. Am. J. Physiol. 1991, 261, R501–R507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seitz, H.J.; Krone, W.; Wilke, H.; Tarnowski, W. Rapid rise in plasma glucagon induced by acute cold exposure in man and rat. Pflug. Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 1981, 389, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinoshita, K.; Ozaki, N.; Takagi, Y.; Murata, Y.; Oshida, Y.; Hayashi, Y. Glucagon is essential for adaptive thermogenesis in brown adipose tissue. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 3484–3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beaudry, J.L.; Kaur, K.D.; Varin, E.M.; Baggio, L.L.; Cao, X.; Mulvihill, E.E.; Stern, J.H.; Campbell, J.E.; Scherer, P.E.; Drucker, D.J.; et al. The brown adipose tissue glucagon receptor is functional but not essential for control of energy homeostasis in mice. Mol. Metab. 2019, 22, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem, V.; Izzi-Engbeaya, C.; Coello, C.; Thomas, D.B.; Chambers, E.S.; Comninos, A.N.; Buckley, A.; Win, Z.; Al-Nahhas, A.; Rabiner, E.A.; et al. Glucagon increases energy expenditure independently of brown adipose tissue activation in humans. DiabetesObes. Metab. 2016, 18, 72–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atrens, D.M.; Menendez, J.A. Glucagon and the paraventricular hypothalamus: Modulation of energy balance. Brain Res. 1993, 630, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billington, C.J.; Bartness, T.J.; Briggs, J.; Levine, A.S.; Morley, J.E. Glucagon stimulation of brown adipose tissue growth and thermogenesis. Am. J. Physiol. 1987, 252, R160–R165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dicker, A.; Zhao, J.; Cannon, B.; Nedergaard, J. Apparent thermogenic effect of injected glucagon is not due to a direct effect on brown fat cells. Am. J. Physiol. 1998, 275, R1674–R1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caren, R.; Corbo, L. Glucagon and cholesterol metabolism. Metab. Clin. Exp. 1960, 9, 938–945. [Google Scholar]
- Paloyan, E.; Harper, P.V., Jr. Glucagon as a regulating factor of plasma lipids. Metab. Clin. Exp. 1961, 10, 315–323. [Google Scholar]
- Guettet, C.; Rostaqui, N.; Navarro, N.; Lecuyer, B.; Mathe, D. Effect of chronic glucagon administration on the metabolism of triacylglycerol-rich lipoproteins in rats fed a high sucrose diet. J. Nutr. 1991, 121, 24–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caren, R.; Corbo, L. Transfer of plasma lipid to platelets by action of glucagon. Metab. Clin. Exp. 1970, 19, 598–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penhos, J.C.; Wu, C.H.; Daunas, J.; Reitman, M.; Levine, R. Effect of glucagon on the metabolism of lipids and on urea formation by the perfused rat liver. Diabetes 1966, 15, 740–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eaton, R.P. Hypolipemic action of glucagon in experimental endogenous lipemia in the rat. J. Lipid Res. 1973, 14, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guettet, C.; Mathe, D.; Riottot, M.; Lutton, C. Effects of chronic glucagon administration on cholesterol and bile acid metabolism. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta 1988, 963, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guettet, C.; Mathe, D.; Navarro, N.; Lecuyer, B. Effects of chronic glucagon administration on rat lipoprotein composition. Biochim. Et Biophys. Acta 1989, 1005, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guettet, C.; Rostaqui, N.; Mathe, D.; Lecuyer, B.; Navarro, N.; Jacotot, B. Effect of chronic glucagon administration on lipoprotein composition in normally fed, fasted and cholesterol-fed rats. Lipids 1991, 26, 451–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perea, A.; Clemente, F.; Martinell, J.; Villanueva-Penacarrillo, M.L.; Valverde, I. Physiological effect of glucagon in human isolated adipocytes. Horm. Metab. Res. 1995, 27, 372–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, M.L.; Byrne, M.J.; Silver, J. Growth-hormone release by glucagon. Lancet 1969, 1, 289–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldhausl, W.; Haydl, H.; Nowotny, P. ACTH and cortisol responses to glucagon stimulation. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1976, 43, 675–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarcione, E.J.; Back, N.; Sokal, J.E.; Mehlman, B.; Knoblock, E. Elevation of plasma epinephrine levels produced by glucagon in vivo. Endocrinology 1963, 72, 523–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longuet, C.; Sinclair, E.M.; Maida, A.; Baggio, L.L.; Maziarz, M.; Charron, M.J.; Drucker, D.J. The glucagon receptor is required for the adaptive metabolic response to fasting. Cell Metab. 2008, 8, 359–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pegorier, J.P.; Garcia-Garcia, M.V.; Prip-Buus, C.; Duee, P.H.; Kohl, C.; Girard, J. Induction of ketogenesis and fatty acid oxidation by glucagon and cyclic AMP in cultured hepatocytes from rabbit fetuses. Evidence for a decreased sensitivity of carnitine palmitoyltransferase I to malonyl-CoA inhibition after glucagon or cyclic AMP treatment. Biochem. J. 1989, 264, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vons, C.; Pegorier, J.P.; Girard, J.; Kohl, C.; Ivanov, M.A.; Franco, D. Regulation of fatty-acid metabolism by pancreatic hormones in cultured human hepatocytes. Hepatology 1991, 13, 1126–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunning, B.E.; Gerich, J.E. The role of alpha-cell dysregulation in fasting and postprandial hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes and therapeutic implications. Endocr. Rev. 2007, 28, 253–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ontko, J.A.; Zilversmit, D.B. Correlation between concentrations of circulating free fatty acids and ketone bodies. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1966, 121, 319–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Harken, D.R.; Dixon, C.W.; Heimberg, M. Hepatic lipid metabolism in experimental diabetes. V. The effect of concentration of oleate on metabolism of triglycerides and on ketogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 1969, 244, 2278–2285. [Google Scholar]
- Gerich, J.E.; Lorenzi, M.; Bier, D.M.; Schneider, V.; Tsalikian, E.; Karam, J.H.; Forsham, P.H. Prevention of human diabetic ketoacidosis by somatostatin. Evidence for an essential role of glucagon. N. Engl. J. Med. 1975, 292, 985–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schade, D.S.; Eaton, R.P. Modulation of fatty acid metabolism by glucagon in man. IV. Effects of a physiologic hormone infusion in normal man. Diabetes 1976, 25, 978–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parrilla, R.; Goodman, M.N.; Toews, C.J. Effect of glucagon: Insulin ratios on hepatic metabolism. Diabetes 1974, 23, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genuth, S.M. Constant intravenous insulin infusion in diabetic ketoacidosis. JAMA 1973, 223, 1348–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wellman, P.J.; Maher, T.J. Synergistic interactions between fenfluramine and phentermine. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 1999, 23, 723–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gault, V.A.; Kerr, B.D.; Harriott, P.; Flatt, P.R. Administration of an acylated GLP-1 and GIP preparation provides added beneficial glucose-lowering and insulinotropic actions over single incretins in mice with Type 2 diabetes and obesity. Clin. Sci. (Lond.) 2011, 121, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschop, M.H.; Finan, B.; Clemmensen, C.; Gelfanov, V.; Perez-Tilve, D.; Muller, T.D.; DiMarchi, R.D. Unimolecular Polypharmacy for Treatment of Diabetes and Obesity. Cell Metab. 2016, 24, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muller, T.D.; Clemmensen, C.; Finan, B.; DiMarchi, R.D.; Tschop, M.H. Anti-Obesity Therapy: From Rainbow Pills to Polyagonists. Pharmacol. Rev. 2018, 70, 712–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinones, M.; Ferno, J.; Dieguez, C.; Nogueiras, R.; Al-Massadi, O. Exciting advances in GPCR-based drugs discovery for treating metabolic disease and future perspectives. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2019, 14, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Day, J.W.; Ottaway, N.; Patterson, J.T.; Gelfanov, V.; Smiley, D.; Gidda, J.; Findeisen, H.; Bruemmer, D.; Drucker, D.J.; Chaudhary, N.; et al. A new glucagon and GLP-1 co-agonist eliminates obesity in rodents. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2009, 5, 749–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemmensen, C.; Chabenne, J.; Finan, B.; Sullivan, L.; Fischer, K.; Küchler, D.; Sehrer, L.; Ograjsek, T.; Hofmann, S.M.; Schriever, S.C.; et al. GLP-1/glucagon coagonism restores leptin responsiveness in obese mice chronically maintained on an obesogenic diet. Diabetes 2014, 63, 1422–1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pocai, A.; Carrington, P.E.; Adams, J.R.; Wright, M.; Eiermann, G.; Zhu, L.; Du, X.; Petrov, A.; Lassman, M.E.; Jiang, G.; et al. Glucagon-like peptide 1/glucagon receptor dual agonism reverses obesity in mice. Diabetes 2009, 58, 2258–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evers, A.; Haack, T.; Lorenz, M.; Bossart, M.; Elvert, R.; Henkel, B.; Stengelin, S.; Kurz, M.; Glien, M.; Dudda, A.; et al. Design of Novel Exendin-Based Dual Glucagon-like Peptide 1 (GLP-1)/Glucagon Receptor Agonists. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 4293–4303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, S.J.; Konkar, A.; Hornigold, D.C.; Trevaskis, J.L.; Jackson, R.; Fritsch Fredin, M.; Jansson-Löfmark, R.; Naylor, J.; Rossi, A.; Bednarek, M.; et al. Robust anti-obesity and metabolic effects of a dual GLP-1/glucagon receptor peptide agonist in rodents and non-human primates. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2016, 18, 1176–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambery, P.; Parker, V.E.; Stumvoll, M.; Posch, M.G.; Heise, T.; Plum-Moerschel, L.; Tsai, L.F.; Robertson, D.; Jain, M.; Petrone, M.; et al. MEDI0382, a GLP-1 and glucagon receptor dual agonist, in obese or overweight patients with type 2 diabetes: A randomised, controlled, double-blind, ascending dose and phase 2a study. Lancet 2018, 391, 2607–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tillner, J.; Posch, M.G.; Wagner, F.; Teichert, L.; Hijazi, Y.; Einig, C.; Keil, S.; Haack, T.; Wagner, M.; Bossart, M.; et al. A novel dual glucagon-like peptide and glucagon receptor agonist SAR425899: Results of randomized, placebo-controlled first-in-human and first-in-patient trials. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2019, 21, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, V.K.; Kerr, B.D.; Flatt, P.R.; Gault, V.A. A novel GIP-oxyntomodulin hybrid peptide acting through GIP, glucagon and GLP-1 receptors exhibits weight reducing and anti-diabetic properties. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013, 85, 1655–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gault, V.A.; Bhat, V.K.; Irwin, N.; Flatt, P.R. A novel glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1)/glucagon hybrid peptide with triple-acting agonist activity at glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide, GLP-1, and glucagon receptors and therapeutic potential in high fat-fed mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 35581–35591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, V.K.; Kerr, B.D.; Vasu, S.; Flatt, P.R.; Gault, V.A. A DPP-IV-resistant triple-acting agonist of GIP, GLP-1 and glucagon receptors with potent glucose-lowering and insulinotropic actions in high-fat-fed mice. Diabetologia 2013, 56, 1417–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finan, B.; Yang, B.; Ottaway, N.; Smiley, D.L.; Ma, T.; Clemmensen, C.; Chabenne, J.; Zhang, L.; Habegger, K.M.; Fischer, K.; et al. A rationally designed monomeric peptide triagonist corrects obesity and diabetes in rodents. Nat. Med. 2015, 21, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jall, S.; Sachs, S.; Clemmensen, C.; Finan, B.; Neff, F.; DiMarchi, R.D.; Tschop, M.H.; Muller, T.D.; Hofmann, S.M. Monomeric GLP-1/GIP/glucagon triagonism corrects obesity, hepatosteatosis, and dyslipidemia in female mice. Mol. Metab. 2017, 6, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Al-Massadi, O.; Fernø, J.; Diéguez, C.; Nogueiras, R.; Quiñones, M. Glucagon Control on Food Intake and Energy Balance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3905. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20163905
Al-Massadi O, Fernø J, Diéguez C, Nogueiras R, Quiñones M. Glucagon Control on Food Intake and Energy Balance. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(16):3905. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20163905
Chicago/Turabian StyleAl-Massadi, Omar, Johan Fernø, Carlos Diéguez, Ruben Nogueiras, and Mar Quiñones. 2019. "Glucagon Control on Food Intake and Energy Balance" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 16: 3905. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20163905
APA StyleAl-Massadi, O., Fernø, J., Diéguez, C., Nogueiras, R., & Quiñones, M. (2019). Glucagon Control on Food Intake and Energy Balance. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(16), 3905. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20163905