Chk1 Inhibitor MK-8776 Restores the Sensitivity of Chemotherapeutics in P-glycoprotein Overexpressing Cancer Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. MK-8776 Restored the Sensitivity of Chemotherapeutics in P-gp-Overexpressing Cancer Cells
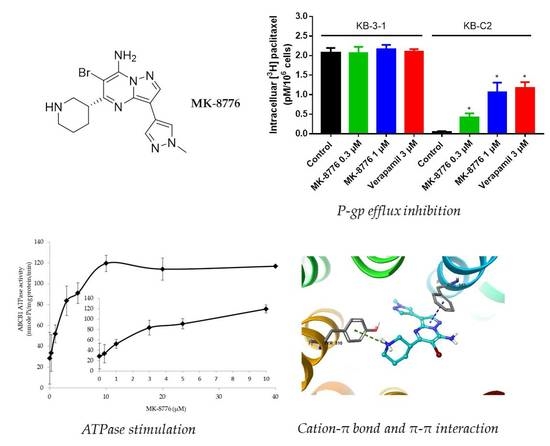
2.2. MK-8776 Increased P-gp Substrate [3H]-Paclitaxel Accumulation and Suppressed its Efflux in KB-C2 Cells
2.3. MK-8776 Did Not Alter the Expression of P-gp in KB-C2 Cells
2.4. MK-8776 Did Not Alter P-gp Subcellular Localization
2.5. MK-8776 Stimulated ATPase Activity
2.6. Induced-Fit Docking (IFD) Simulation Interactions between P-gp and MK-8776
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Cell Lines and Cell Culture
4.3. Cytotoxicity experiments
4.4. Western Blot Analysis
4.5. Immunofluorescence Analysis
4.6. ATPase Assay
4.7. [3H]-Paclitaxel Accumulation and Efflux Assay
4.8. Molecular Modeling of Human ABCB1 Homology Model
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Vasiliou, V.; Vasiliou, K.; Nebert, D.W. Human ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter family. Hum. Genom. 2009, 3, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigam, S.K. What do drug transporters really do? Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 29–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begicevic, R.R.; Falasca, M. ABC Transporters in Cancer Stem Cells: Beyond Chemoresistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fletcher, J.I.; Williams, R.T.; Henderson, M.J.; Norris, M.D.; Haber, M. ABC transporters as mediators of drug resistance and contributors to cancer cell biology. Drug Resist. Updat. 2016, 26, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanke, N.T.; Imler, E.; Marron, M.T.; Seligmann, B.E.; Garland, L.L.; Baker, A.F. Characterization of carfilzomib-resistant non-small cell lung cancer cell lines. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol 2018, 144, 1317–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deshmukh, R.R.; Kim, S.; Elghoul, Y.; Dou, Q.P. P-Glycoprotein Inhibition Sensitizes Human Breast Cancer Cells to Proteasome Inhibitors. J. Cell. Biochem. 2017, 118, 1239–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; Duan, Z.J.; Chang, J.Y.; Zhang, Z.F.; Chu, R.; Li, Y.L.; Dai, K.H.; Mo, G.Q.; Chang, Q.Y. Sinomenine sensitizes multidrug-resistant colon cancer cells (Caco-2) to doxorubicin by downregulation of MDR-1 expression. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, H.S.; Haddad, G.; Thorner, P.S.; DeBoer, G.; Lin, Y.P.; Ondrusek, N.; Yeger, H.; Ling, V. P-glycoprotein expression as a predictor of the outcome of therapy for neuroblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 1991, 325, 1608–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Figueiredo-Pontes, L.L.; Pintao, M.C.; Oliveira, L.C.; Dalmazzo, L.F.; Jacomo, R.H.; Garcia, A.B.; Falcao, R.P.; Rego, E.M. Determination of P-glycoprotein, MDR-related protein 1, breast cancer resistance protein, and lung-resistance protein expression in leukemic stem cells of acute myeloid leukemia. Cytometry B Clin. Cytom. 2008, 74, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leith, C.P.; Kopecky, K.J.; Chen, I.M.; Eijdems, L.; Slovak, M.L.; McConnell, T.S.; Head, D.R.; Weick, J.; Grever, M.R.; Appelbaum, F.R.; et al. Frequency and clinical significance of the expression of the multidrug resistance proteins MDR1/P-glycoprotein, MRP1, and LRP in acute myeloid leukemia: A Southwest Oncology Group Study. Blood 1999, 94, 1086–1099. [Google Scholar]
- Kourti, M.; Vavatsi, N.; Gombakis, N.; Sidi, V.; Tzimagiorgis, G.; Papageorgiou, T.; Koliouskas, D.; Athanassiadou, F. Expression of multidrug resistance 1 (MDR1), multidrug resistance-related protein 1 (MRP1), lung resistance protein (LRP), and breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP) genes and clinical outcome in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Int. J. Hematol. 2007, 86, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, L.J.; Galski, H.; Fojo, A.; Willingham, M.; Lai, S.L.; Gazdar, A.; Pirker, R.; Green, A.; Crist, W.; Brodeur, G.M.; et al. Expression of a multidrug resistance gene in human cancers. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1989, 81, 116–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kathawala, R.J.; Gupta, P.; Ashby, C.J.; Chen, Z.S. The modulation of ABC transporter-mediated multidrug resistance in cancer: A review of the past decade. Drug Resist. Updat. 2015, 18, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Q.; Cai, C.Y.; Gao, H.L.; Ren, L.; Ji, N.; Gupta, P.; Yang, Y.; Shukla, S.; Ambudkar, S.V.; Yang, D.H.; et al. Glesatinib, a c-MET/SMO Dual Inhibitor, Antagonizes P-glycoprotein Mediated Multidrug Resistance in Cancer Cells. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Robey, R.W.; Pluchino, K.M.; Hall, M.D.; Fojo, A.T.; Bates, S.E.; Gottesman, M.M. Revisiting the role of ABC transporters in multidrug-resistant cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 452–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Zhang, H.; Assaraf, Y.G.; Zhao, K.; Xu, X.; Xie, J.; Yang, D.H.; Chen, Z.S. Overcoming ABC transporter-mediated multidrug resistance: Molecular mechanisms and novel therapeutic drug strategies. Drug Resist. Updat. 2016, 27, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.P.; Ohnuma, S.; Ambudkar, S.V. Discovering natural product modulators to overcome multidrug resistance in cancer chemotherapy. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2011, 12, 609–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anreddy, N.; Gupta, P.; Kathawala, R.J.; Patel, A.; Wurpel, J.N.; Chen, Z.S. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors as reversal agents for ABC transporter mediated drug resistance. Molecules 2014, 19, 13848–13877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.F.; Zhang, W.; Zeng, L.; Lei, Z.N.; Cai, C.Y.; Gupta, P.; Yang, D.H.; Cui, Q.; Qin, Z.D.; Chen, Z.S.; et al. Dacomitinib antagonizes multidrug resistance (MDR) in cancer cells by inhibiting the efflux activity of ABCB1 and ABCG2 transporters. Cancer Lett. 2018, 421, 186–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, M.; Pabla, N.; Dong, Z. Checkpoint kinase 1 in DNA damage response cell cycle regulation. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2013, 70, 4009–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smits, V.A.; Gillespie, D.A. DNA damage control: Regulation and functions of checkpoint kinase 1. Febs J. 2015, 282, 3681–3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Z.; Oleinick, N.L.; Zhang, J. ATR/CHK1 inhibitors and cancer therapy. Radiother. Oncol. 2018, 126, 450–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, J.; Tho, L.M.; Xu, N.; Gillespie, D.A. The ATM-Chk2 and ATR-Chk1 pathways in DNA damage signaling and cancer. Adv. Cancer Res. 2010, 108, 73–112. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Webster, J.A.; Tibes, R.; Morris, L.; Blackford, A.L.; Litzow, M.; Patnaik, M.; Rosner, G.L.; Gojo, I.; Kinders, R.; Wang, L.; et al. Randomized phase II trial of cytosine arabinoside with and without the CHK1 inhibitor MK-8776 in relapsed and refractory acute myeloid leukemia. Leuk. Res. 2017, 61, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daud, A.I.; Ashworth, M.T.; Strosberg, J.; Goldman, J.W.; Mendelson, D.; Springett, G.; Venook, A.P.; Loechner, S.; Rosen, L.S.; Shanahan, F.; et al. Phase I dose-escalation trial of checkpoint kinase 1 inhibitor MK-8776 as monotherapy and in combination with gemcitabine in patients with advanced solid tumors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 1060–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.R.; Yang, Z.Z.; Wang, S.J.; Zhang, L.; Luo, J.R.; Feng, Y.; Yu, X.L.; Chen, X.X.; Guo, X.M. The Chk1 inhibitor MK-8776 increases the radiosensitivity of human triple-negative breast cancer by inhibiting autophagy. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2017, 38, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dai, Y.; Chen, S.; Kmieciak, M.; Zhou, L.; Lin, H.; Pei, X.Y.; Grant, S. The novel Chk1 inhibitor MK-8776 sensitizes human leukemia cells to HDAC inhibitors by targeting the intra-S checkpoint and DNA replication and repair. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 878–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bridges, K.A.; Chen, X.; Liu, H.; Rock, C.; Buchholz, T.A.; Shumway, S.D.; Skinner, H.D.; Meyn, R.E. MK-8776, a novel chk1 kinase inhibitor, radiosensitizes p53-defective human tumor cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 71660–71672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zinzi, L.; Capparelli, E.; Cantore, M.; Contino, M.; Leopoldo, M.; Colabufo, N.A. Small and Innovative Molecules as New Strategy to Revert MDR. Front. Oncol 2014, 4, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Q.; Wang, J.Q.; Assaraf, Y.G.; Ren, L.; Gupta, P.; Wei, L.; Ashby, C.J.; Yang, D.H.; Chen, Z.S. Modulating ROS to overcome multidrug resistance in cancer. Drug Resist. Updat 2018, 41, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.J.; Lei, Y.H.; Yao, N.; Wang, C.R.; Hu, N.; Ye, W.C.; Zhang, D.M.; Chen, Z.S. Autophagy and multidrug resistance in cancer. Chin. J. Cancer 2017, 36, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, S.; Spugnini, E.P.; Assaraf, Y.G.; Azzarito, T.; Rauch, C.; Fais, S. Microenvironment acidity as a major determinant of tumor chemoresistance: Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) as a novel therapeutic approach. Drug Resist. Updat. 2015, 23, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baguley, B.C. Multiple drug resistance mechanisms in cancer. Mol. Biotechnol. 2010, 46, 308–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eadie, L.N.; Hughes, T.P.; White, D.L. ABCB1 Overexpression Is a Key Initiator of Resistance to Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitors in CML Cell Lines. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e161470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, M.; Hanfstein, B.; Erben, P.; Wolf, D.; Ernst, T.; Fabarius, A.; Saussele, S.; Purkayastha, D.; Woodman, R.C.; Hofmann, W.K.; et al. MDR1 expression predicts outcome of Ph+ chronic phase CML patients on second-line nilotinib therapy after imatinib failure. Leukemia 2014, 28, 1478–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regulska, K.; Regulski, M.; Karolak, B.; Murias, M.; Stanisz, B. Can cardiovascular drugs support cancer treatment? The rationale for drug repurposing. Drug Discov. Today 2019, 24, 1059–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pushpakom, S.; Iorio, F.; Eyers, P.A.; Escott, K.J.; Hopper, S.; Wells, A.; Doig, A.; Guilliams, T.; Latimer, J.; McNamee, C.; et al. Drug repurposing: Progress, challenges and recommendations. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2019, 18, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beretta, G.L.; Cassinelli, G.; Pennati, M.; Zuco, V.; Gatti, L. Overcoming ABC transporter-mediated multidrug resistance: The dual role of tyrosine kinase inhibitors as multitargeting agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 142, 271–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.J.; Sun, Y.L.; Tiwari, A.K.; Xiao, Z.J.; Sodani, K.; Yang, D.H.; Vispute, S.G.; Jiang, W.Q.; Chen, S.D.; Chen, Z.S. PDE5 inhibitors, sildenafil and vardenafil, reverse multidrug resistance by inhibiting the efflux function of multidrug resistance protein 7 (ATP-binding Cassette C10) transporter. Cancer Sci. 2012, 103, 1531–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Gao, H.L.; Ashar, Y.V.; Karadkhelkar, N.M.; Yoganathan, S.; Chen, Z.S. Ciprofloxacin Enhances the Chemosensitivity of Cancer Cells to ABCB1 Substrates. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruzickova, E.; Janska, R.; Dolezel, P.; Mlejnek, P. Clinically relevant interactions of anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 protein inhibitors with ABC transporters. Pharmazie 2017, 72, 751–758. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mlejnek, P.; Kosztyu, P.; Dolezel, P.; Bates, S.E.; Ruzickova, E. Reversal of ABCB1 mediated efflux by imatinib and nilotinib in cells expressing various transporter levels. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2017, 273, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharom, F.J.; Yu, X.; Chu, J.W.; Doige, C.A. Characterization of the ATPase activity of P-glycoprotein from multidrug-resistant Chinese hamster ovary cells. Biochem. J. 1995, 308(Pt. 2), 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lai, G.M.; Chen, Y.N.; Mickley, L.A.; Fojo, A.T.; Bates, S.E. P-glycoprotein expression and schedule dependence of adriamycin cytotoxicity in human colon carcinoma cell lines. Int. J. Cancer 1991, 49, 696–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, Z.; Tiwari, A.K.; Shukla, S.; Robey, R.W.; Singh, S.; Kim, I.W.; Bates, S.E.; Peng, X.; Abraham, I.; Ambudkar, S.V.; et al. Sildenafil reverses ABCB1- and ABCG2-mediated chemotherapeutic drug resistance. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 3029–3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, N.; Yang, Y.; Lei, Z.N.; Cai, C.Y.; Wang, J.Q.; Gupta, P.; Xian, X.; Yang, D.H.; Kong, D.; Chen, Z.S. Ulixertinib (BVD-523) antagonizes ABCB1- and ABCG2-mediated chemotherapeutic drug resistance. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 158, 274–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, N.; Yang, Y.; Cai, C.Y.; Lei, Z.N.; Wang, J.Q.; Gupta, P.; Shukla, S.; Ambudkar, S.V.; Kong, D.; Chen, Z.S. Selonsertib (GS-4997), an ASK1 inhibitor, antagonizes multidrug resistance in ABCB1- and ABCG2-overexpressing cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2019, 440, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.K.; Zhang, G.N.; Wang, Y.J.; Patel, B.A.; Talele, T.T.; Yang, D.H.; Chen, Z.S. Bafetinib (INNO-406) reverses multidrug resistance by inhibiting the efflux function of ABCB1 and ABCG2 transporters. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, A.; Kowal, J.; Broude, E.; Roninson, I.; Locher, K.P. Structural insight into substrate and inhibitor discrimination by human P-glycoprotein. Science 2019, 363, 753–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]






| Compounds | IC50 ± SD a (μM) (RF b) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KB-3-1 | KB-C2 | HEK293/pcDNA3.1 | HEK293/ABCB1 | |
| Doxorubicin | 0.017 ± 0.011 (1.00) | 1.664 ± 0.064 (97.88) | 0.061 ± 0.020 (1.00) | 0.631 ± 0.150 (10.34) |
| + MK-8776 (0.3 μM) | 0.015 ± 0.003 (0.88) | 0.470 ± 0.041 (27.64) * | 0.067 ± 0.017 (1.10) | 0.181 ± 0.014 (2.97) * |
| + MK-8776 (1 μM) | 0.014 ± 0.004 (0.82) | 0.013 ± 0.004 (0.76) * | 0.058 ± 0.027 (0.95) | 0.056 ± 0.033 (0.92) * |
| + Verapmil (3 μM) | 0.014 ± 0.006 (0.82) | 0.016 ± 0.005 (0.94) * | 0.061 ± 0.008 (1.00) | 0.084 ± 0.009 (1.38) * |
| Paclitaxel | 0.004 ± 0.002 (1.00) | 2.783 ± 0.053 (695.75) | 0.073 ± 0.027 (1.00) | 3.757 ± 0.312 (51.46) |
| + MK-8776 (0.3 μM) | 0.004 ± 0.001 (1.00) | 0.144 ± 0.013 (36.00) * | 0.122 ± 0.050 (1.67) | 0.255 ± 0.084 (3.49) * |
| + MK-8776 (1 μM) | 0.003 ± 0.001 (0.75) | 0.092 ± 0.004 (23.00) * | 0.100 ± 0.020 (1.37) | 0.047 ± 0.004 (0.64) * |
| + Verapamil (3 μM) | 0.003 ± 0.001 (0.75) | 0.017 ± 0.002 (4.25) * | 0.068 ± 0.003 (0.95) | 0.094 ± 0.003 (1.9) * |
| Colchicine | 0.012 ± 0.004 (1.00) | 7.732 ± 0.240 (644.33) | 0.066 ± 0.001 (1.00) | 1.538 ± 0.090 (23.30) |
| + MK-8776 (0.3 μM) | 0.009 ± 0.005 (0.75) | 0.292 ± 0.203 (24.33) * | 0.058 ± 0.007 (0.88) | 0.126 ± 0.106 (1.91) * |
| + MK-8776 (1 μM) | 0.009 ± 0.003 (0.75) | 0.009 ± 0.030 (0.75) * | 0.048 ± 0.009 (0.73) | 0.047 ± 0.021 (0.71) * |
| + Verapamil (3 μM) | 0.008 ± 0.003 (0.66) | 0.006 ± 0.015 (0.5) * | 0.056 ± 0.006 (0.85) | 0.050 ± 0.008 (0.76) * |
| Cisplatin | 2.508 ± 0.432 (1.00) | 3.027 ± 0.343 (1.21) | 2.660 ± 0.430 (1.00) | 3.336 ± 0.900 (1.25) |
| + MK-8776 (0.3 μM) | 2.440 ± 0.264 (0.97) | 2.770 ± 0.167 (1.10) | 2.378 ± 0.136 (0.89) | 2.727 ± 0.592 (1.03) |
| + MK-8776 (1 μM) | 2.431 ± 0.179 (0.97) | 2.652 ± 0.087 (1.05) | 2.474 ± 0.286 (0.93) | 2.611 ± 0.353 (0.98) |
| + Verapamil (3 μM) | 2.309 ± 0.641 (0.92) | 2.098 ± 0.230 (0.84) | 2.388 ± 0.452 (0.90) | 3.115 ± 0.433 (1.17) |
| Compounds | IC50 ± SD a (μM) (RF b) | |
|---|---|---|
| SW620 | SW620/Ad300 | |
| Doxorubicin | 0.031 ± 0.014 (1.00) | 9.950 ± 2.023 (320.97) |
| + MK-8776 (0.3 μM) | 0.028 ± 0.016 (0.90) | 1.362 ± 0.122 (43.94) * |
| + MK-8776 (1 μM) | 0.035 ± 0.012 (1.13) | 0.426 ± 0.184 (13.74) * |
| + Verapmil (3 μM) | 0.038 ± 0.021 (1.23) | 0.096 ± 0.023 (3.10) * |
| Paclitaxel | 0.091 ± 0.015 (1.00) | 21.19 ± 6.25 (232.86) |
| + MK-8776 (0.3 μM) | 0.076 ± 0.038 (0.84) | 1.784 ± 0.125 (19.60) * |
| + MK-8776 (1 μM) | 0.074 ± 0.003 (0.81) | 0.597 ± 0.566 (6.56) * |
| + Verapamil (3 μM) | 0.113 ± 0.006 (1.24) | 0.639 ± 0.023 (7.03) * |
| Cisplatin | 1.481 ± 0.676 (1.00) | 1.514 ± 0.398 (1.02) |
| + MK-8776 (0.3 μM) | 1.329 ± 0.156 (0.90) | 1.423 ± 0.438 (0.94) |
| + MK-8776 (1 μM) | 1.228 ± 0.181(0.83) | 1.266 ± 0.295 (0.84) |
| + Verapamil (3 μM) | 1.164 ± 0.107 (0.79) | 1.851 ± 0.364 (1.25) |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cui, Q.; Cai, C.-Y.; Wang, J.-Q.; Zhang, S.; Gupta, P.; Ji, N.; Yang, Y.; Dong, X.; Yang, D.-H.; Chen, Z.-S. Chk1 Inhibitor MK-8776 Restores the Sensitivity of Chemotherapeutics in P-glycoprotein Overexpressing Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4095. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174095
Cui Q, Cai C-Y, Wang J-Q, Zhang S, Gupta P, Ji N, Yang Y, Dong X, Yang D-H, Chen Z-S. Chk1 Inhibitor MK-8776 Restores the Sensitivity of Chemotherapeutics in P-glycoprotein Overexpressing Cancer Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(17):4095. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174095
Chicago/Turabian StyleCui, Qingbin, Chao-Yun Cai, Jing-Quan Wang, Shuang Zhang, Pranav Gupta, Ning Ji, Yuqi Yang, Xingduo Dong, Dong-Hua Yang, and Zhe-Sheng Chen. 2019. "Chk1 Inhibitor MK-8776 Restores the Sensitivity of Chemotherapeutics in P-glycoprotein Overexpressing Cancer Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 17: 4095. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174095
APA StyleCui, Q., Cai, C.-Y., Wang, J.-Q., Zhang, S., Gupta, P., Ji, N., Yang, Y., Dong, X., Yang, D.-H., & Chen, Z.-S. (2019). Chk1 Inhibitor MK-8776 Restores the Sensitivity of Chemotherapeutics in P-glycoprotein Overexpressing Cancer Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(17), 4095. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174095