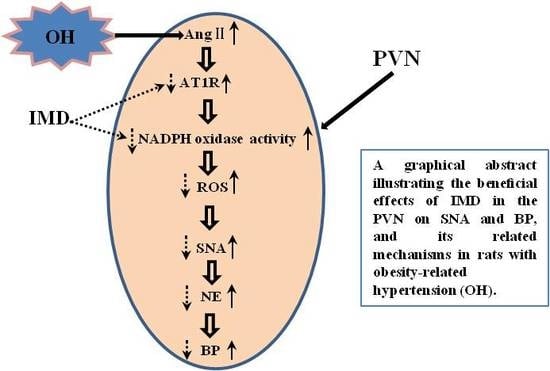
Intermedin in Paraventricular Nucleus Attenuates Ang II-Induced Sympathoexcitation through the Inhibition of NADPH Oxidase-Dependent ROS Generation in Obese Rats with Hypertension
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Metabolic and Anatomical Data
2.2. The Plasma NE Level, SBP and Protein Expressions of AT1R, IMD, CRLR and RAMP1/2/3 in the PVN
2.3. The Effects of Ang II or IMD in the PVN on Basal SNA, and IMD Pretreatment on Ang II-Induced Changes in the RSNA and MAP
2.4. The Effects of the Pretreatment with Saline, Losartan, Tempo, or Apo in the PVN on SNA Response to PVN Microinjection of Ang II
2.5. The Effects of IMD in the PVN on NADPH Oxidase Activity and ROS Level, and IMD Pretreatment on Ang II-induced Changes in the NADPH Activity and ROS Level
2.6. The Efects of ERK Inhibitor on a Ang II-Induced Increase in Basal SNA and ERK Activation, and the Effect of IMD Pretreatment on Ang II-Induced ERK Activation
2.7. The Effects of Chronic IMD Treatment on Sympathetic Nerve Activity, Systolic Blood Pressure, NADPH Activity and ROS Levels in the PVN
2.8. The Effects of Chronic IMD Treatment on Ang II-Induced Sympathoexcitation, ERK Activation and AT1R, NOX2 and NOX4 Protein Expressions in the PVN
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Design
4.1.1. Experiment 1
4.1.2. Experiment 2
4.1.3. Experiment 3
4.1.4. Experiment 4
4.1.5. Experiment 5
4.2. Animals
4.3. SBP Measurements
4.4. General Procedures of the Acute Experiment
4.5. Recording Sympathetic Nerve Activity (SNA)
4.6. PVN Microinjection
4.7. PVN Tissue Microdissection
4.8. In Situ Detection of Superoxide Anions
4.9. Measurement of NADPH Oxidase Activity and ROS Level
4.10. Western Blotting for the Measurement of AT1R, IMD, CRLR, RAMP1/2/3, NOX2 and NOX4 Protein Expression, and Total and Phosphorylated ERK Levels
4.11. The Application of Chronic Infusion of IMD in PVN
4.12. Blood and PVN Samples Preparation
4.13. Measurement of Plasma Glucose, Insulin, Cholesterol and Triglyceride Levels
4.14. Measurement of Plasma NE
4.15. Chemicals
4.16. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lim, K.; Jackson, K.L.; Sata, Y.; Head, G.A. Factors Responsible for Obesity-Related Hypertension. Curr. Hypertens. Rep. 2017, 19, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasic, I.; Lovic, D. Hypertension and cardiometabolic disease. Front. Biosci. 2018, 10, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Lambert, E.A.; Esler, M.D.; Schlaich, M.P.; Dixon, J.; Eikelis, N.; Lambert, G.W. Obesity-Associated Organ Damage and Sympathetic Nervous Activity. Hypertension 2019, 73, 1150–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.; Shen, Y.; Li, P.; Zhao, K.; Chen, X.; Li, Y.; Sheng, Y.; Zhou, B.; Kong, X. Superoxide anions mediate the effects of angiotensin (1–7) analog, alamandine, on blood pressure and sympathetic activity in the paraventricular nucleus. Peptides 2019, 118, 170101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.D.; Liang, Y.F.; Qi, J.; Kang, K.B.; Yu, X.J.; Gao, H.L.; Liu, K.L.; Chen, Y.M.; Shi, X.L.; Xin, G.R.; et al. Carbon Monoxide Attenuates High Salt-Induced Hypertension While Reducing Pro-inflammatory Cytokines and Oxidative Stress in the Paraventricular Nucleus. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, X.J.; Chen, W.S.; Gao, H.L.; Liu, K.L.; Shi, X.L.; Fan, X.Y.; Jia, L.L.; Cui, W.; Zhu, G.Q.; et al. Exercise training attenuates renovascular hypertension partly via RAS- ROS- glutamate pathway in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patel, K.P.; Mayhan, W.G.; Bidasee, K.R.; Zheng, H. Enhanced angiotensin II-mediated central sympathoexcitation in streptozotocin-induced diabetes: Role of superoxide anion. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2011, 300, R311–R320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Sun, B.; He, R. Effect of the changes of NMDA receptor in hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus on cardiac function and sympathetic nervous activity in rats with heart failure. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 493, 1336–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, H.; Kang, Y.M.; Gao, H.L.; Shi, X.L.; Fu, L.Y.; Li, Y.; Jia, X.Y.; Liu, K.L.; Qi, J.; Li, H.B.; et al. Chronic infusion of berberine into the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus attenuates hypertension and sympathoexcitation via the ROS/Erk1/2/iNOS pathway. Phytomedicine 2019, 52, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Coleman, C.G.; Chan, J.; Faraco, G.; Marques-Lopes, J.; Milner, T.A.; Guruju, M.R.; Anrather, J.; Davisson, R.L.; Iadecola, C.; et al. Angiotensin II slow-pressor hypertension enhances NMDA currents and NOX2-dependent superoxide production in hypothalamic paraventricular neurons. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2013, 304, R1096–R1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, Q.B.; Sun, J.; Kang, Y.; Sun, H.J.; Wang, H.S.; Wang, Y.; Zhu, G.Q.; Zhou, Y.B. Superoxide Anions and NO in the Paraventricular Nucleus Modulate the Cardiac Sympathetic Afferent Reflex in Obese Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.; Hay, D.L.; Quirion, R.; Poyner, D.R. The pharmacology of adrenomedullin 2/intermedin. Br. J. Pharm. 2012, 166, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, H.; Kitamura, K.; Kawasaki, M.; Saito, T.; Suzuki, H.; Otsubo, H.; Ohbuchi, T.; Yokoyama, T.; Fujihara, H.; Takei, Y.; et al. Adrenomedullin 2/intermedin-like immunoreactivity in the hypothalamus and brainstem of rats. Auton. Neurosci. 2008, 139, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliver, K.R.; Kane, S.A.; Salvatore, C.A.; Mallee, J.J.; Kinsey, A.M.; Koblan, K.S.; Keyvan-Fouladi, N.; Heavens, R.P.; Wainwright, A.; Jacobson, M.; et al. Cloning, characterization and central nervous system distribution of receptor activity modifying proteins in the rat. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2001, 14, 618–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.B.; Sun, H.J.; Chen, D.; Liu, T.Y.; Han, Y.; Wang, J.J.; Tang, C.S.; Kang, Y.M.; Zhu, G.Q. Intermedin in paraventricular nucleus attenuates sympathetic activity and blood pressure via nitric oxide in hypertensive rats. Hypertension 2014, 63, 330–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, W.W.; Jia, L.X.; Ni, X.Q.; Zhao, L.; Chang, J.R.; Zhang, J.S.; Hou, Y.L.; Zhu, Y.; Guan, Y.F.; Yu, Y.R.; et al. Intermedin1-53 Attenuates Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm by Inhibiting Oxidative Stress. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2016, 36, 2176–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.J.; Su, A.H.; Yang, H.B.; Chen, J.X. Intermedin1-53 protects cardiac function in rats with septic shock via inhibiting oxidative stress and cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2018, 22, 2906–2913. [Google Scholar]
- Qiao, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Su, X.; Qi, Y.; Fan, Y.; Peng, Z. Intermedin inhibits unilateral ureteral obstruction-induced oxidative stress via NADPH oxidase Nox4 and cAMP-dependent mechanisms. Ren. Fail. 2017, 39, 652–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sun, J.; Ren, X.S.; Kang, Y.; Dai, H.B.; Ding, L.; Tong, N.; Zhu, G.Q.; Zhou, Y.B. Intermedin in Paraventricular Nucleus Attenuates Sympathoexcitation and Decreases TLR4-Mediated Sympathetic Activation via Adrenomedullin Receptors in Rats with Obesity-Related Hypertension. Neurosci. Bull. 2019, 35, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Q.; Qin, D.N.; Wang, F.X.; Ren, J.; Li, H.B.; Zhang, M.; Yang, Q.; Miao, Y.W.; Yu, X.J.; Qi, J.; et al. Inhibition of reactive oxygen species in hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus attenuates the renin-angiotensin system and proinflammatory cytokines in hypertension. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2014, 276, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, F.; Zhong, M.K.; Shi, Z.; Gao, X.Y.; Wang, W.; Zhu, G.Q. NAD(P)H oxidase in paraventricular nucleus contributes to the effect of angiotensin II on cardiac sympathetic afferent reflex. Brain Res. 2006, 1082, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buvelot, H.; Jaquet, V.; Krause, K.H. Mammalian NADPH Oxidases. Methods Mol. Biol. (Clifton N.J.) 2019, 1982, 17–36. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, Y.; Liu, R.; Lin, N.; Luo, H.; Tang, J.; Huang, Q.; Sun, H.; Tang, L. NADPH Oxidase Hyperactivity Contributes to Cardiac Dysfunction and Apoptosis in Rats with Severe Experimental Pancreatitis through ROS-Mediated MAPK Signaling Pathway. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 4578175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.R.; Yang, J.W.; Ji, C.S.; Zeng, X.H.; Shi, G.X.; Fisher, M.; Liu, C.Z. Inhibition of NADPH Oxidase-Dependent Oxidative Stress in the Rostral Ventrolateral Medulla Mediates the Antihypertensive Effects of Acupuncture in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Hypertension 2018, 71, 356–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, B.; Beltz, T.G.; Johnson, R.F.; Guo, F.; Hay, M.; Johnson, A.K. PVN adenovirus-siRNA injections silencing either NOX2 or NOX4 attenuate aldosterone/NaCl-induced hypertension in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2012, 302, H733–H741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gasparini, S.; Melo, M.R.; Nascimento, P.A.; Andrade-Franze, G.M.F.; Antunes-Rodrigues, J.; Yosten, G.L.C.; Menani, J.V.; Samson, W.K.; Colombari, E. Interaction of central angiotensin II and aldosterone on sodium intake and blood pressure. Brain Res. 2019, 1720, 146299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhao, M.; Zhao, Z.; Sun, S.; Fraidenburg, D.R.; Tang, H.; Han, Y. Angiotensin-(1-7) in Paraventricular Nucleus Contributes to the Enhanced Cardiac Sympathetic Afferent Reflex and Sympathetic Activity in Chronic Heart Failure Rats. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 42, 2523–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Yang, H.; Song, X.; Wang, J.; Shen, L.; Wang, J. Central blockade of the AT1 receptor attenuates pressor effects via reduction of glutamate release and downregulation of NMDA/AMPA receptors in the rostral ventrolateral medulla of rats with stress-induced hypertension. Hypertens. Res. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.W.; Huang, B.S.; White, R.A.; Chen, A.; Ahmad, M.; Leenen, F.H. Mineralocorticoid and angiotensin II type 1 receptors in the subfornical organ mediate angiotensin II - induced hypothalamic reactive oxygen species and hypertension. Neuroscience 2016, 329, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Tan, L.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Qiu, M.; Li, L.; Zhang, M.; Liang, M.; Li, A. Increased Apoptosis in the Paraventricular Nucleus Mediated by AT1R/Ras/ERK1/2 Signaling Results in Sympathetic Hyperactivity and Renovascular Hypertension in Rats after Kidney Injury. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forrester, S.J.; Booz, G.W.; Sigmund, C.D.; Coffman, T.M.; Kawai, T.; Rizzo, V.; Scalia, R.; Eguchi, S. Angiotensin II Signal Transduction: An Update on Mechanisms of Physiology and Pathophysiology. Physiol Rev. 2018, 98, 1627–1738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Zhou, X.; Yang, H.; Guan, R.; Xin, Y.; Wang, J.; Shen, L.; Zhu, D.; Ma, S.; Wang, J. Upregulation of AT1 Receptor Mediates a Pressor Effect Through ROS-SAPK/JNK Signaling in Glutamatergic Neurons of Rostral Ventrolateral Medulla in Rats With Stress-Induced Hypertension. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hay, D.L.; Garelja, M.L.; Poyner, D.R.; Walker, C.S. Update on the pharmacology of calcitonin/CGRP family of peptides: IUPHAR Review 25. Br. J. Pharm. 2018, 175, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshimoto, T.; Gochou, N.; Fukai, N.; Sugiyama, T.; Shichiri, M.; Hirata, Y. Adrenomedullin inhibits angiotensin II-induced oxidative stress and gene expression in rat endothelial cells. Hypertens. Res. 2005, 28, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Deng, X.; Gong, L.; Chen, X.; Wang, S.; Chen, H.; Chen, X.; Amrit, B.; He, S. The effect of intermedin on angiotensin II and endothelin-1 induced ventricular myocyte hypertrophy in neonatal rat. Clin. Lab. 2013, 59, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogundele, O.M.; Rosa, F.A.; Dharmakumar, R.; Lee, C.C.; Francis, J. Systemic Sympathoexcitation Was Associated with Paraventricular Hypothalamic Phosphorylation of Synaptic CaMKIIalpha and MAPK/ErK. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zucker, I.H.; Gao, L. The regulation of sympathetic nerve activity by angiotensin II involves reactive oxygen species and MAPK. Circ. Res. 2005, 97, 737–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dendorfer, A.; Thornagel, A.; Raasch, W.; Grisk, O.; Tempel, K.; Dominiak, P. Angiotensin II induces catecholamine release by direct ganglionic excitation. Hypertension 2002, 40, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanida, M.; Gotoh, H.; Yamamoto, N.; Wang, M.; Kuda, Y.; Kurata, Y.; Mori, M.; Shibamoto, T. Hypothalamic Nesfatin-1 Stimulates Sympathetic Nerve Activity via Hypothalamic ERK Signaling. Diabetes 2015, 64, 3725–3736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, G.; Xu, S.; Peng, L.; Huang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Gao, X. Angiotensin II upregulates Kv1.5 expression through ROS-dependent transforming growth factor-beta1 and extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 signalings in neonatal rat atrial myocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 454, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gingell, J.J.; Hendrikse, E.R.; Hay, D.L. New Insights into the Regulation of CGRP-Family Receptors. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 40, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









| Parameters | Control | OH |
|---|---|---|
| BW (g) | 531 ± 45 | 653 ± 47 * |
| Plasma glucose (mg/dL) | 139 ± 13 | 151 ± 16 |
| Plasma insulin (ng/mL) | 1.72 ± 0.19 | 3.07 ± 0.32* |
| Plasma cholesterol (mg/dL) | 47.8 ± 5.2 | 63.7 ± 5.8* |
| Plasma triglyceride (mg/dL) | 68.2 ± 6.1 | 95.6 ± 8.7* |
| Sum of WAT mass (g) | 31.9 ± 3.3 | 61.3 ± 5.9* |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kang, Y.; Ding, L.; Dai, H.; Wang, F.; Zhou, H.; Gao, Q.; Xiong, X.; Zhang, F.; Song, T.; Yuan, Y.; et al. Intermedin in Paraventricular Nucleus Attenuates Ang II-Induced Sympathoexcitation through the Inhibition of NADPH Oxidase-Dependent ROS Generation in Obese Rats with Hypertension. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4217. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174217
Kang Y, Ding L, Dai H, Wang F, Zhou H, Gao Q, Xiong X, Zhang F, Song T, Yuan Y, et al. Intermedin in Paraventricular Nucleus Attenuates Ang II-Induced Sympathoexcitation through the Inhibition of NADPH Oxidase-Dependent ROS Generation in Obese Rats with Hypertension. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(17):4217. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174217
Chicago/Turabian StyleKang, Ying, Lei Ding, Hangbing Dai, Fangzheng Wang, Hong Zhou, Qing Gao, Xiaoqing Xiong, Feng Zhang, Tianrun Song, Yan Yuan, and et al. 2019. "Intermedin in Paraventricular Nucleus Attenuates Ang II-Induced Sympathoexcitation through the Inhibition of NADPH Oxidase-Dependent ROS Generation in Obese Rats with Hypertension" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 17: 4217. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174217
APA StyleKang, Y., Ding, L., Dai, H., Wang, F., Zhou, H., Gao, Q., Xiong, X., Zhang, F., Song, T., Yuan, Y., Zhu, G., & Zhou, Y. (2019). Intermedin in Paraventricular Nucleus Attenuates Ang II-Induced Sympathoexcitation through the Inhibition of NADPH Oxidase-Dependent ROS Generation in Obese Rats with Hypertension. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(17), 4217. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20174217