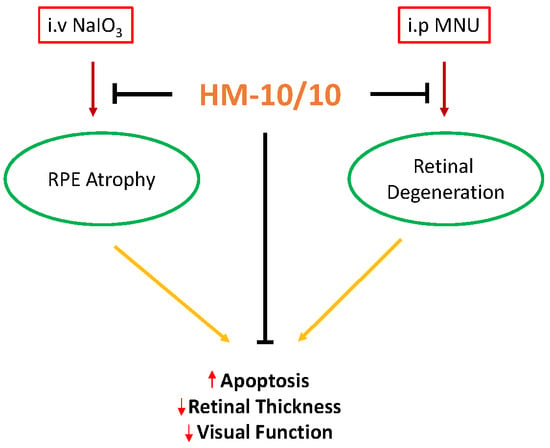
A Novel HDL-Mimetic Peptide HM-10/10 Protects RPE and Photoreceptors in Murine Models of Retinal Degeneration
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. HM-10/10 Peptide Significantly Inhibited Cell Death from tBH Treatment of hfRPE Cells
2.2. HM-10/10 Peptide Significantly Reduced Apoptotic Cell Death from NaIO3 Treatment of hfRPE Cells
2.3. HM-10/10 Peptide Protected hfRPE Cells from Oxidative Stress by Inhibiting Activation of Caspase-3/7
2.4. Optimizing NaIO3 Doses In Vivo
2.5. In Vivo Assessment of Retinal Structure Using Optical Coherence Tomography
2.6. HM-10/10 Caused Protection of Photoreceptor Degeneration and Improvement of Visual Function in MNU Mouse Model of Retinal Degeneration
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Mice
4.2. HM-10/10 Peptide
4.3. hfRPE Cell Culture Experiments
4.4. Western Blot Analysis
4.5. Immunohistochemistry (IHC) Staining
4.6. TUNEL Assay
4.7. Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography (SD-OCT) and Fundus Images
4.8. Electroretinography
4.9. Animal Models
4.9.1. NaIO3 Model
4.9.2. MNU Model
4.10. Statistical Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AMD | Age-related macular degeneration |
| BW | Body weight |
| ERG | Electroretinography |
| HDL | High density lipoprotein |
| RPE | Retinal pigment epithelium |
| MNU | N-methyl-N-nitrosourea |
| NaIO3 | Sodium iodate |
| PR | Photoreceptor |
| SD-OCT | Spectral domain optical coherence tomography |
| tBH+ | tert-Butyl hydroperoxide |
| TUNEL | Terminal deoxyuridine triphosphate nick-end labeling |
References
- Pennington, K.L.; DeAngelis, M.M. Epidemiology of age-related macular degeneration (AMD): Associations with cardiovascular disease phenotypes and lipid factors. Eye Vis. 2016, 3, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navab, M.; Reddy, S.T.; Van Lenten, B.J.; Anantharamaiah, G.M.; Fogelman, A.M. The role of dysfunctional HDL in atherosclerosis. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, S145–S149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Su, F.; Kozak, K.R.; Imaizumi, S.; Gao, F.; Amneus, M.W.; Grijalva, V.; Ng, C.; Wagner, A.; Hough, G.; Farias-Eisner, G.; et al. Apolipoprotein A-I (apoA-I) and apoA-I mimetic peptides inhibit tumor development in a mouse model of ovarian cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 19997–20002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Su, F.; Grijalva, V.; Navab, K.; Ganapathy, E.; Meriwether, D.; Imaizumi, S.; Navab, M.; Fogelman, A.M.; Reddy, S.T.; Farias-Eisner, R. HDL mimetics inhibit tumor development in both induced and spontaneous mouse models of colon cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2012, 11, 1311–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; Vasquez, S.X.; Su, F.; Roberts, S.; Shah, N.; Grijalva, V.; Imaizumi, S.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Ganapathy, E.; Meriwether, D.; et al. L-5F, an apolipoprotein A-I mimetic, inhibits tumor angiogenesis by suppressing VEGF/basic FGF signaling pathways. Integr. Biol. 2011, 3, 479–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganapathy, E.; Su, F.; Meriwether, D.; Devarajan, A.; Grijalva, V.; Gao, F.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Anantharamaiah, G.M.; Navab, M.; Fogelman, A.M.; et al. D-4F, an apoA-I mimetic peptide, inhibits proliferation and tumorigenicity of epithelial ovarian cancer cells by upregulating the antioxidant enzyme MnSOD. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 130, 1071–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, F.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Navab, M.; Grijalva, V.; Su, F.; Fogelman, A.M.; Reddy, S.T.; Farias-Eisner, R. Apolipoprotein A-I mimetic peptides inhibit expression and activity of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α in human ovarian cancer cell lines and a mouse ovarian cancer model. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2012, 342, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sreekumar, P.G.; Ishikawa, K.; Spee, C.; Mehta, H.H.; Wan, J.; Yen, K.; Cohen, P.; Kannan, R.; Hinton, D.R. The mitochondrial-derived peptide humanin protects RPE cells from oxidative stress, senescence, and mitochondrial dysfunction. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2016, 57, 1238–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kannan, R.; Zhang, N.; Sreekumar, P.G.; Spee, C.K.; Rodriguez, A.; Barron, E.; Hinton, D.R. Stimulation of apical and basolateral VEGF-A and VEGF-C secretion by oxidative stress in polarized retinal pigment epithelial cells. Mol. Vis. 2006, 12, 1649–1659. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhou, P.; Kannan, R.; Spee, C.; Sreekumar, P.G.; Dou, G.; Hinton, D.R. Protection of retina by αB-crystallin in sodium iodate induced retinal degeneration. PLoS ONE 2014, 5, e98275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kannan, R.; Hinton, D.R. Sodium ioate induced retinal degeneratin: New insights from an old model. Neural Regen. Res. 2014, 9, 2044–2045. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Navab, M.; Ruchala, P.; Waring, A.J.; Lehrer, R.I.; Hama, S.; Hough, G.; Palgunachari, M.N.; Anantharamaiah, G.M.; Fogelman, A.M. A novel method for oral delivery of apolipoprotein mimetic peptides synthesized from all L-amino acids. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, 1538–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Navab, M.; Anantharamaiah, G.M.; Reddy, S.T.; Van Lenten, B.J.; Datta, G.; Garber, D.; Fogelman, A.M. Potential clinical utility of high-density lipoprotein-mimetic peptides. Curr. Opin Lipidol. 2006, 17, 440–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, C.R.; Garber, D.W.; Anantharamaiah, G.M. Anti-inflammatory and cholesterol-reducing properties of apolipoprotein mimetics: A review. J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 2007–2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navab, M.; Anantharamaiah, G.M.; Reddy, S.T.; Van Lenten, B.J.; Wagner, A.C.; Hama, S.; Hough, G.; Bachini, E.; Garber, D.W.; Mishra, V.K.; et al. An oral apoJ peptide renders HDL antiinflammatory in mice and monkeys and dramatically reduces atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-null mice. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2005, 25, 1932–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloedon, L.T.; Dunbar, R.; Duffy, D.; Pinell-Salles, P.; Norris, R.; DeGroot, B.J.; Movva, R.; Navab, M.; Fogelman, A.M.; Rader, D.J. Safety, pharmacokinetics, and pharmacodynamics of oral apoA-I mimetic peptide D-4F in high-risk cardiovascular patients. J. Lipid Res. 2008, 49, 1344–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dunbar, R.L.; Movva, R.; Bloedon, L.T.; Duffy, D.; Norris, R.B.; Navab, M.; Fogelman, A.M.; Rader, D.J. Oral apolipoprotein A-I mimetic D-4F lowers HDL-inflammatory index in high-risk patients: A first-in-human multiple dose, randomized controlled trial. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2017, 10, 455–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, C.E.; Weissbach, N.; Kjems, L.; Ayalasomayajula, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chang, I.; Navab, M.; Hama, S.; Hough, G.; Reddy, S.T.; et al. Treatment of patients with cardiovascular disease with L-4F, an apoA-I mimetic, did not improve select biomarkers of HDL function. J. Lipid Res. 2011, 52, 361–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navab, M.; Reddy, S.T.; Anantharamaiah, G.M.; Imaizumi, S.; Hough, G.; Hama, S.; Fogelman, A.M. Intestine may be a major site of action for the apoA-I mimetic peptide 4F whether administered subcutaneously or orally. J. Lipid Res. 2011, 52, 1200–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Navab, M.; Reddy, S.T.; Anantharamaiah, G.M.; Hough, G.; Buga, G.M.; Danciger, J.; Fogelman, A.M. D-4F-mediated reduction in metabolites of arachidonic and linoleic acids in the small intestine is associated with decreased inflammation in low-density lipoprotein receptor-null mice. J. Lipid Res. 2012, 53, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chattopadhyay, A.; Navab, M.; Hough, G.; Gao, F.; Meriwether, D.; Grijalva, V.; Springstead, J.R.; Palgnachari, M.N.; Namiri-Kalantari, R.; Su, F.; et al. A novel approach to oral apoA-I mimetic therapy. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 995–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Navab, M.; Hough, G.; Buga, G.M.; Su, F.; Wagner, A.C.; Meriwether, D.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Gao, F.; Grijalva, V.; Danciger, J.S.; et al. Transgenic 6F tomatoes act on the small intestine to prevent systemic inflammation and dyslipidemia caused by Western diet and intestinally derived lysophosphatidic acid. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 3403–3418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Navab, M.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Hough, G.; Meriwether, D.; Fogelman, S.I.; Wagner, A.C.; Grijalva, V.; Su, F.; Anantharamaiah, G.M.; Hwang, L.H.; et al. Source and role of intestinally derived lysophosphatidic acid in dyslipidemia and atherosclerosis. J. Lipid Res. 2015, 56, 871–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chattopadhyay, A.; Grijalva, V.; Hough, G.; Su, F.; Mukherjee, P.; Farias-Eisner, R.; Anantharamaiah, G.M.; Faull, K.F.; Hwang, L.H.; Navab, M.; et al. Efficacy of tomato concentrates in mouse models of dyslipidemia and cancer. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2015, 3, e00154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, A.; Navab, M.; Hough, G.; Grijalva, V.; Mukherjee, P.; Fogelman, H.R.; Hwang, L.H.; Faull, K.F.; Lusis, A.J.; Reddy, S.T.; et al. Tg6F ameliorates the increase in oxidized phospholipids in the jejunum of mice fed unsaturated LysoPC or WD. J. Lipid Res. 2016, 57, 832–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mukherjee, P.; Hough, G.; Chattopadhyay, A.; Navab, M.; Fogelman, H.R.; Meriwether, D.; Williams, K.; Bensinger, S.; Moller, T.; Faull, K.F.; et al. Transgenic tomatoes expressing the 6F peptide and ezetimibe prevent diet-induced increases of IFN-β and cholesterol 25-hydroxylase in jejunum. J. Lipid Res. 2017, 58, 1636–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, A.; Yang, X.; Mukherjee, P.; Sulaiman, D.; Fogelman, H.R.; Grijalva, V.; Dubinett, S.; Wasler, T.C.; Paul, M.K.; Salehi-Rad, R.; et al. Treating the intestine with oral apoA-I mimetic Tg6F reduces tumor burden in mouse models of metastatic lung cancer. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 9032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiuchi, K.; Yoshizawa, K.; Shikata, N.; Moriguchi, K.; Tsubura, A. Morphologic characteristics of retinal degeneration induced by sodium iodate in mice. Curr. Eye Res. 2002, 25, 373–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enzmann, V.; Row, B.W.; Yamauchi, Y.; Kheirandish, L.; Gozal, D.; Kaplan, H.J.; McCall, M.A. Behavioral and anatomical abnormalities in a sodium iodate-induced model of retinal pigment epithelium degeneration. Exp. Eye Res. 2006, 82, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, L.M.; Zulliger, R.; Wolf-Schnurrbusch, U.E.; Katagiri, Y.; Kaplan, H.J.; Wolf, S.; Enzmann, V. Decreased visual function after patchy loss of retinal pigment epithelium induced by low-dose sodium iodate. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2009, 50, 4004–4010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machalińska, A.; Lejkowska, R.; Duchnik, M.; Kawa, M.; Rogińska, D.; Wiszniewska, B.; Machaliński, B. Dose-dependent retinal changes following sodium iodate administration: Application of spectral-domain optical coherence tomography for monitoring of retinal injury and endogenous regeneration. Curr. Eye Res. 2014, 39, 1033–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachdeva, M.M.; Cano, M.; Handa, J.T. Nrf2 signaling is impaired in the aging RPE given an oxidative insult. Exp. Eye Res. 2014, 119, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Lu, Y.; Rodrigues, G.A. Resveratrol protects RPE cells from sodium iodate by modulating PPARα and PPARδ. Exp. Eye Res. 2014, 118, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.G.; Li, Q.; Liu, Z.X.; Wang, J.J.; Wang, X.X.; Qin, M.; Wen, Q.S. Curcumin attenuates insulin resistance in hepatocytes by inducing Nrf2 nuclear translocation. Hepatogastroenterology 2011, 58, 2106–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.L.; Nam, S.M.; Chang, B.J.; Nahm, S.S.; Lee, J.H. Ultrastructural Changes and Expression of PCNA and RPE65 in Sodium Iodate-Induced Acute Retinal Pigment Epithelium Degeneration Model. Neurochem. Res. 2018, 43, 1010–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanus, J.; Anderson, C.; Sarraf, D.; Ma, J.; Wang, S. Retinal pigment epithelial cell necroptosis in response to sodium iodate. Cell Death Discov. 2016, 2, 16054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jarrett, S.G.; Lin, H.; Godley, B.F.; Boulton, M.E. Mitochondrial DNA damage and its potential role in retinal degeneration. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2008, 27, 596–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreekumar, P.G.; Ding, Y.; Ryan, S.J.; Kannan, R.; Hinton, D.R. Regulation of thioredoxin by ceramide in retinal pigment epithelial cells. Exp. Eye Res. 2009, 88, 410–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sreekumar, P.G.; Spee, C.; Ryan, S.J.; Cole, S.P.; Kannan, R.; Hinton, D.R. Mechanism of RPE cell death in α-crystallin deficient mice: A novel and critical role for MRP1-mediated GSH efflux. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e33420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marí, M.; Morales, A.; Colell, A.; García-Ruiz, C.; Kaplowitz, N.; Fernández-Checa, J.C. Mitochondrial glutathione: Features, regulation and role in disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1830, 3317–3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dou, G.; Sreekumar, P.G.; Spee, C.; He, S.; Ryan, S.J.; Kannan, R.; Hinton, D.R. Deficiency of αB crystallin augments ER stress-induced apoptosis by enhancing mitochondrial dysfunction. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2012, 53, 1111–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsunaga, D.; Sreekumar, P.G.; Ishikawa, K.; Terasaki, H.; Barron, E.; Cohen, P.; Kannan, R.; Hinton, D.R. Humanin Protects RPE Cells from Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Induced Apoptosis by Upregulation of Mitochondrial Glutathione. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambati, J.; Fowler, B.J. Mechanisms of age-related macular degeneration. Neuron 2012, 75, 26–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarallo, V.; Hirano, Y.; Gelfand, B.D.; Dridi, S.; Kerur, N.; Kim, Y.; Cho, W.G.; Kaneko, H.; Fowler, B.J.; Bogdanovich, S. DICER1 loss and Alu RNA induce age-related macular degeneration via the NLRP3 inflammasome and MyD88. Cell 2012, 149, 847–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Pan, T.; Shen, H.; Xi, H.; Yuan, S.; Liu, Q. The rescue effect of mesenchymal stem cell on sodium iodate-induced retinal pigment epithelial cell death through deactivation of NF-κB-mediated NLRP3 inflammasome. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 103, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsubura, A.; Yoshizawa, K.; Kuwata, M.; Uehara, N. Animal models for retinitis pigmentosa induced by MNU; disease progression, mechanisms and therapeutic trials. Histol. Histopathol. 2010, 25, 933–944. [Google Scholar]
- Zulliger, R.; Lecaudé, S.; Eigeldinger-Berthou, S.; Wolf-Schnurrbusch, U.E.; Enzmann, V. Caspase-3-independent photoreceptor degeneration by N-methyl-N-nitrosourea (MNU) induces morphological and functional changes in the mouse retina. Graefes. Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2011, 249, 859–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshizawa, K.; Nambu, H.; Yang, J.; Oishi, Y.; Senzaki, H.; Shikata, N.; Miki, H.; Tsubura, A. Mechanisms of photoreceptor cell apoptosis induced by N-methyl-N-nitrosourea in Sprague-Dawley rats. Lab. Invest. 1999, 79, 1359–1367. [Google Scholar]
- Reisenhofer, M.; Balmer, J.; Zulliger, L.R.; Enzmann, V. Multiple programmed cell death pathways are involved in N-methyl-N-nitrosourea-induced photoreceptor degeneration. Graefes. Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2015, 253, 721–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyttinen, J.M.T.; Błasiak, J.; Niittykoski, M.; Kinnunen, K.; Kauppinen, A.; Salminen, A.; Kaarniranta, K. DNA damage response and autophagy in the degeneration of retinal pigment epithelial cells-Implications for age-related macular degeneration (AMD). Ageing Res. Rev. 2017, 36, 64–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karunadharma, P.P.; Nordgaard, C.L.; Olsen, T.W.; Ferrington, D.A. Mitochondrial DNA damage as a potential mechanism for age-related macular degeneration. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2010, 51, 5470–5479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terluk, M.R.; Kapphahn, R.J.; Soukup, L.M.; Gong, H.; Gallardo, C.; Montezuma, S.R.; Ferrington, D.A. Investigating mitochondria as a target for treating age-related macular degeneration. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 7304–7311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonoda, S.; Spee, C.; Barron, E.; Ryan, S.J.; Kannan, R.; Hinton, D.R. A protocol for the culture and differentiation of highly polarized human retinal pigment epithelial cells. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 662–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, W.; Sreekuma, P.G.; Valluripalli, V.; Shi, P.; Wang, J.; Lin, Y.A.; Cui, H.; Kannan, R.; Hinton, D.R.; MacKay, J.A. Protein polymer nanoparticles engineered as chaperones protect against apoptosis in human retinal pigment epithelial cells. J. Control. Release 2014, 19, 4–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.; Chen, T.; Fang, W.; Peng, G.; Wang, L.; Qin, L.; Liu, B.; Fei Huang, Y. The temporal topography of the N-Methyl-N-nitrosourea induced photoreceptor degeneration in mouse retina. Sci. Rep. 2015, 21, 18612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Deng, X.G.; Sun, Q.N.; Zhong, Z.Q. Ganoderma spore lipid inhibits N-methyl-N-nitrosourea-induced retinal photoreceptor apoptosis in vivo. Exp. Eye Res. 2010, 90, 397–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Su, F.; Spee, C.; Araujo, E.; Barron, E.; Wang, M.; Ghione, C.; Hinton, D.R.; Nusinowitz, S.; Kannan, R.; Reddy, S.T.; et al. A Novel HDL-Mimetic Peptide HM-10/10 Protects RPE and Photoreceptors in Murine Models of Retinal Degeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4807. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20194807
Su F, Spee C, Araujo E, Barron E, Wang M, Ghione C, Hinton DR, Nusinowitz S, Kannan R, Reddy ST, et al. A Novel HDL-Mimetic Peptide HM-10/10 Protects RPE and Photoreceptors in Murine Models of Retinal Degeneration. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(19):4807. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20194807
Chicago/Turabian StyleSu, Feng, Christine Spee, Eduardo Araujo, Eric Barron, Mo Wang, Caleb Ghione, David R. Hinton, Steven Nusinowitz, Ram Kannan, Srinivasa T. Reddy, and et al. 2019. "A Novel HDL-Mimetic Peptide HM-10/10 Protects RPE and Photoreceptors in Murine Models of Retinal Degeneration" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 19: 4807. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20194807