MT4-MMP: The GPI-Anchored Membrane-Type Matrix Metalloprotease with Multiple Functions in Diseases
Abstract
:1. Introduction
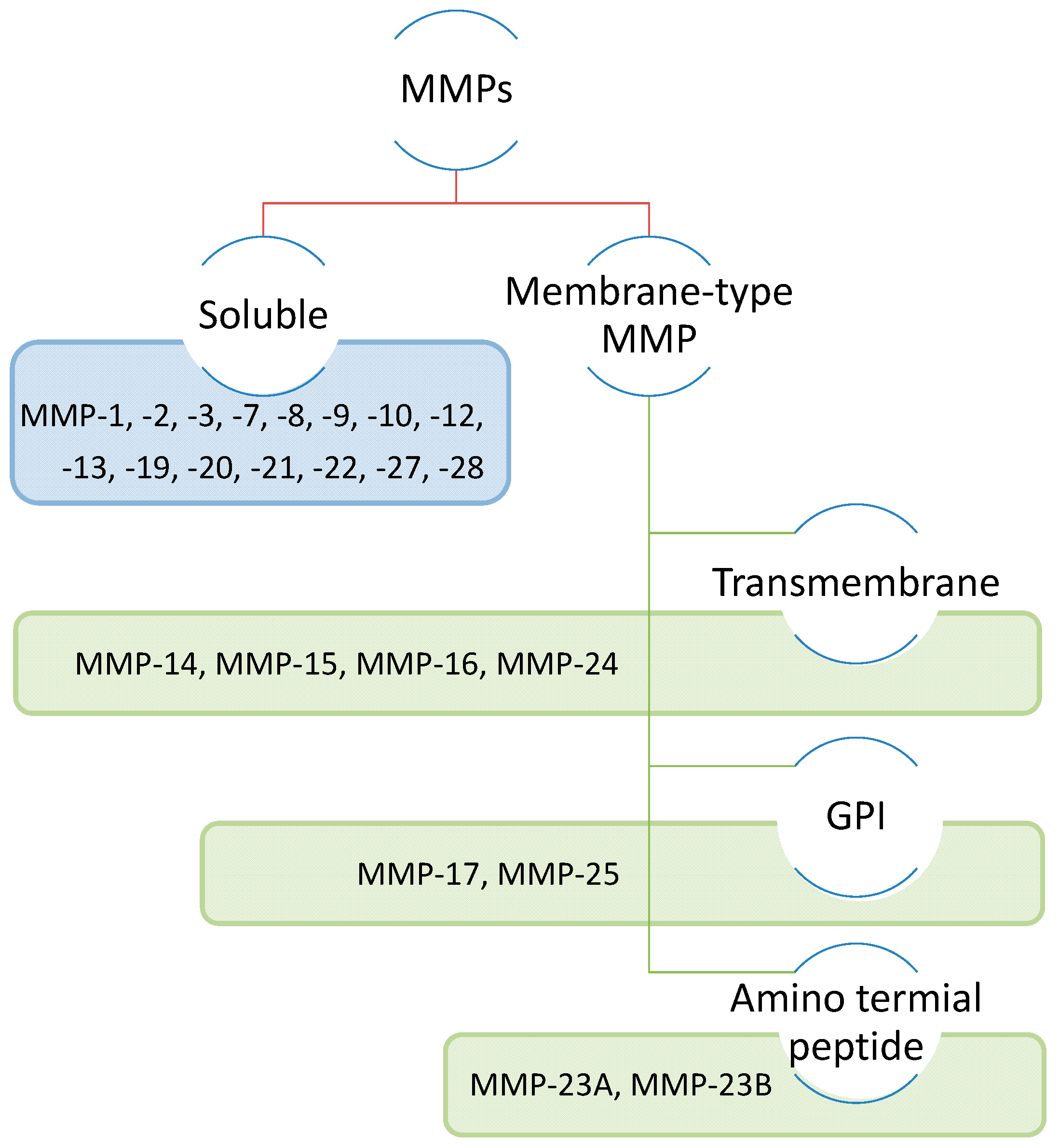
2. Characteristics of the MMP family
3. Biosynthesis and Trafficking
4. Physiological Expression and Functions of MT4-MMP
5. Osteoarthritis
6. Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms and Dissections
7. Cancer
7.1. Gastric Cancer
7.2. Colon Cancer
7.3. Head and Neck Cancer
7.4. Breast Cancer
8. Clinical Inhibitors of MMPs
9. Discussion and Perspectives
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Puente, X.S.; Pendas, A.M.; Llano, E.; Velasco, G.; Lopez-Otin, C. Molecular cloning of a novel membrane-type matrix metalloproteinase from a human breast carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1996, 56, 944–949. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gao, G.; Plaas, A.; Thompson, V.P.; Jin, S.; Zuo, F.; Sandy, J.D. ADAMTS4 (aggrecanase-1) activation on the cell surface involves C-terminal cleavage by glycosylphosphatidyl inositol-anchored membrane type 4-matrix metalloproteinase and binding of the activated proteinase to chondroitin sulfate and heparan sulfate on syndecan-1. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 10042–10051. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.H.; Yang, W.H.; Chang, S.Y.; Tai, S.K.; Tzeng, C.H.; Kao, J.Y.; Wu, K.J.; Yang, M.H. Regulation of membrane-type 4 matrix metalloproteinase by SLUG contributes to hypoxia-mediated metastasis. Neoplasia 2009, 11, 1371–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chabottaux, V.; Ricaud, S.; Host, L.; Blacher, S.; Paye, A.; Thiry, M.; Garofalakis, A.; Pestourie, C.; Gombert, K.; Bruyere, F.; et al. Membrane-type 4 matrix metalloproteinase (MT4-MMP) induces lung metastasis by alteration of primary breast tumour vascular architecture. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2009, 13, 4002–4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Johnson, A.R.; Ye, Q.Z.; Dyer, R.D. Catalytic activities and substrate specificity of the human membrane type 4 matrix metalloproteinase catalytic domain. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 33043–33049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- English, W.R.; Puente, X.S.; Freije, J.M.; Knauper, V.; Amour, A.; Merryweather, A.; Lopez-Otin, C.; Murphy, G. Membrane type 4 matrix metalloproteinase (MMP17) has tumor necrosis factor-alpha convertase activity but does not activate pro-MMP2. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 14046–14055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohail, A.; Sun, Q.; Zhao, H.; Bernardo, M.M.; Cho, J.A.; Fridman, R. MT4-(MMP17) and MT6-MMP (MMP25), A unique set of membrane-anchored matrix metalloproteinases: Properties and expression in cancer. Cancer Metast. Rev. 2008, 27, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Alonso, M.; Garcia-Redondo, A.B.; Guo, D.; Camafeita, E.; Martinez, F.; Alfranca, A.; Mendez-Barbero, N.; Pollan, A.; Sanchez-Camacho, C.; Denhardt, D.T.; et al. Deficiency of MMP17/MT4-MMP proteolytic activity predisposes to aortic aneurysm in mice. Circ. Res. 2015, 117, e13–e26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clemente, C.; Rius, C.; Alonso-Herranz, L.; Martin-Alonso, M.; Pollan, A.; Camafeita, E.; Martinez, F.; Mota, R.A.; Nunez, V.; Rodriguez, C.; et al. MT4-MMP deficiency increases patrolling monocyte recruitment to early lesions and accelerates atherosclerosis. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, G.M.; Giambernardi, T.A.; Grant, A.M.; Klebe, R.J. Overview of expression of matrix metalloproteinases (MMP-17, MMP-18, and MMP-20) in cultured human cells. Matrix Biol. 1999, 18, 145–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimri, L.; Barak, H.; Graeve, L.; Schwartz, B. Restoration of caveolin-1 expression suppresses growth, membrane-type-4 metalloproteinase expression and metastasis-associated activities in colon cancer cells. Mol. Carcinog. 2013, 52, 859–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hieronimus, B.; Pfohl, J.; Busch, C.; Graeve, L. Expression and Characterization of Membrane-Type 4 Matrix Metalloproteinase (MT4-MMP) and its Different Forms in Melanoma. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 42, 198–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chabottaux, V.; Sounni, N.E.; Pennington, C.J.; English, W.R.; van den Brule, F.; Blacher, S.; Gilles, C.; Munaut, C.; Maquoi, E.; Lopez-Otin, C.; et al. Membrane-type 4 matrix metalloproteinase promotes breast cancer growth and metastases. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 5165–5172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzetti, S.; McCulloch, D.R.; Herington, A.C.; van der Spoel, D. Modeling of enzyme-substrate complexes for the metalloproteases MMP-3, ADAM-9 and ADAM-10. J. Comput. Aided Mol. Des. 2003, 17, 551–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Itoh, Y.; Kajita, M.; Kinoh, H.; Mori, H.; Okada, A.; Seiki, M. Membrane type 4 matrix metalloproteinase (MT4-MMP, MMP-17) is a glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored proteinase. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 34260–34266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolkenbrock, H.; Essers, L.; Ulbrich, N.; Will, H. Biochemical characterization of the catalytic domain of membrane-type 4 matrix metalloproteinase. Biol. Chem. 1999, 380, 1103–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sounni, N.E.; Janssen, M.; Foidart, J.M.; Noel, A. Membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase and TIMP-2 in tumor angiogenesis. Matrix Biol. 2003, 22, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Woskowicz, A.M.; Weaver, S.A.; Shitomi, Y.; Ito, N.; Itoh, Y. MT-LOOP-dependent localization of membrane type I matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP) to the cell adhesion complexes promotes cancer cell invasion. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 35126–35137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- English, W.R.; Holtz, B.; Vogt, G.; Knauper, V.; Murphy, G. Characterization of the role of the “MT-loop”: An eight-amino acid insertion specific to progelatinase A (MMP2) activating membrane-type matrix metalloproteinases. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 42018–42026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozanov, D.V.; Hahn-Dantona, E.; Strickland, D.K.; Strongin, A.Y. The low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein LRP is regulated by membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase (MT1-MMP) proteolysis in malignant cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 4260–4268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rikimaru, A.; Komori, K.; Sakamoto, T.; Ichise, H.; Yoshida, N.; Yana, I.; Seiki, M. Establishment of an MT4-MMP-deficient mouse strain representing an efficient tracking system for MT4-MMP/MMP-17 expression in vivo using beta-galactosidase. Genes Cells 2007, 12, 1091–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Host, L.; Paye, A.; Detry, B.; Blacher, S.; Munaut, C.; Foidart, J.M.; Seiki, M.; Sounni, N.E.; Noel, A. The proteolytic activity of MT4-MMP is required for its pro-angiogenic and pro-metastatic promoting effects. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 131, 1537–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Patwari, P.; Gao, G.; Lee, J.H.; Grodzinsky, A.J.; Sandy, J.D. Analysis of ADAMTS4 and MT4-MMP indicates that both are involved in aggrecanolysis in interleukin-1-treated bovine cartilage. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2005, 13, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clements, K.M.; Flannelly, J.K.; Tart, J.; Brockbank, S.M.; Wardale, J.; Freeth, J.; Parker, A.E.; Newham, P. Matrix metalloproteinase 17 is necessary for cartilage aggrecan degradation in an inflammatory environment. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2011, 70, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papke, C.L.; Yamashiro, Y.; Yanagisawa, H. MMP17/MT4-MMP and thoracic aortic aneurysms: OPNing new potential for effective treatment. Circ. Res. 2015, 117, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sternlicht, M.D.; Werb, Z. How matrix metalloproteinases regulate cell behavior. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2001, 17, 463–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, D. Leukolysin/MMP25/MT6-MMP: A novel matrix metalloproteinase specifically expressed in the leukocyte lineage. Cell Res. 1999, 9, 291–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udenfriend, S.; Kodukula, K. How glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored membrane proteins are made. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1995, 64, 563–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truong, A.; Yip, C.; Paye, A.; Blacher, S.; Munaut, C.; Deroanne, C.; Noel, A.; Sounni, N.E. Dynamics of internalization and recycling of the prometastatic membrane type 4 matrix metalloproteinase (MT4-MMP) in breast cancer cells. FEBS J. 2016, 283, 704–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohail, A.; Marco, M.; Zhao, H.; Shi, Q.; Merriman, S.; Mobashery, S.; Fridman, R. Characterization of the dimerization interface of membrane type 4 (MT4)-matrix metalloproteinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 33178–33189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanco, M.J.; Rodriguez-Martin, I.; Learte, A.I.R.; Clemente, C.; Montalvo, M.G.; Seiki, M.; Arroyo, A.G.; Sanchez-Camacho, C. Developmental expression of membrane type 4-matrix metalloproteinase (Mt4-mmp/Mmp17) in the mouse embryo. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leigh, N.R.; Schupp, M.O.; Li, K.; Padmanabhan, V.; Gastonguay, A.; Wang, L.; Chun, C.Z.; Wilkinson, G.A.; Ramchandran, R. Mmp17b is essential for proper neural crest cell migration in vivo. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, I.J.; Zhang, Y.; Meister, M.; Sanes, J.R. Laminar restriction of retinal ganglion cell dendrites and axons: Subtype-specific developmental patterns revealed with transgenic markers. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 1452–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kay, J.N.; de la Huerta, I.; Kim, I.J.; Zhang, Y.; Yamagata, M.; Chu, M.W.; Meister, M.; Sanes, J.R. Retinal ganglion cells with distinct directional preferences differ in molecular identity, structure, and central projections. J. Neurosci. 2011, 31, 7753–7762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srichai, M.B.; Colleta, H.; Gewin, L.; Matrisian, L.; Abel, T.W.; Koshikawa, N.; Seiki, M.; Pozzi, A.; Harris, R.C.; Zent, R. Membrane-type 4 matrix metalloproteinase (MT4-MMP) modulates water homeostasis in mice. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kajita, M.; Kinoh, H.; Ito, N.; Takamura, A.; Itoh, Y.; Okada, A.; Sato, H.; Seiki, M. Human membrane type-4 matrix metalloproteinase (MT4-MMP) is encoded by a novel major transcript: Isolation of complementary DNA clones for human and mouse mt4-mmp transcripts. FEBS Lett. 1999, 457, 353–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gauthier, M.C.; Racine, C.; Ferland, C.; Flamand, N.; Chakir, J.; Tremblay, G.M.; Laviolette, M. Expression of membrane type-4 matrix metalloproteinase (metalloproteinase-17) by human eosinophils. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2003, 35, 1667–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paye, A.; Truong, A.; Yip, C.; Cimino, J.; Blacher, S.; Munaut, C.; Cataldo, D.; Foidart, J.M.; Maquoi, E.; Collignon, J.; et al. EGFR activation and signaling in cancer cells are enhanced by the membrane-bound metalloprotease MT4-MMP. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 6758–6770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Li, B.; Liu, J. miRNA27a regulates arthritis via PPARgamma in vivo and in vitro. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 5454–5462. [Google Scholar]
- Sounni, N.E.; Paye, A.; Host, L.; Noel, A. MT-MMPS as Regulators of Vessel Stability Associated with Angiogenesis. Front. Pharmacol. 2011, 2, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Li, Q.; Jiao, Y.; Qin, L.; Ali, R.; Zhou, J.; Ferruzzi, J.; Kim, R.W.; Geirsson, A.; Dietz, H.C.; et al. Tgfbr2 disruption in postnatal smooth muscle impairs aortic wall homeostasis. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 755–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scatena, M.; Liaw, L.; Giachelli, C.M. Osteopontin: A multifunctional molecule regulating chronic inflammation and vascular disease. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2007, 27, 2302–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isoda, K.; Nishikawa, K.; Kamezawa, Y.; Yoshida, M.; Kusuhara, M.; Moroi, M.; Tada, N.; Ohsuzu, F. Osteopontin plays an important role in the development of medial thickening and neointimal formation. Circ. Res. 2002, 91, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, H.; Steffen, M.C.; Ramos, K.S. Osteopontin regulates alpha-smooth muscle actin and calponin in vascular smooth muscle cells. Cell Biol. Int. 2012, 36, 155–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giachelli, C.; Bae, N.; Lombardi, D.; Majesky, M.; Schwartz, S. Molecular cloning and characterization of 2B7, a rat mRNA which distinguishes smooth muscle cell phenotypes in vitro and is identical to osteopontin (secreted phosphoprotein I, 2aR). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1991, 177, 867–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frischhertz, B.P.; Shamszad, P.; Pedroza, C.; Milewicz, D.M.; Morris, S.A. Thoracic aortic dissection and rupture in conotruncal cardiac defects: A population-based study. Int. J. Cardiol. 2015, 184, 521–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, M.M.; Kiani, I.A.; Ammar, K.A.; Ahmad, M.N.; Khandheria, B.K.; Paterick, T.E.; Jain, R.; Tajik, A.J. Ascending Aortic Aneurysm Is an Inherited Disease: A Contemporary Literature Review Based on Hill’s Criteria of Specificity, Strength of Association, and Biological Coherence. Cardiol. Rev. 2017, 25, 268–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, S.J.; Li, Y.X.; Luo, H.S. Expression and clinical significance of matrix metalloproteinase-17 and -25 in gastric cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2015, 9, 671–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gencer, S.; Cebeci, A.; Irmak-Yazicioglu, M.B. Matrix metalloproteinase gene expressions might be oxidative stress targets in gastric cancer cell lines. Chin. J. Cancer Res. 2013, 25, 322–333. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Somanath, P.R.; Razorenova, O.; Chen, W.S.; Hay, N.; Bornstein, P.; Byzova, T.V. Akt1 regulates pathological angiogenesis, vascular maturation and permeability in vivo. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 1188–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hawighorst, T.; Velasco, P.; Streit, M.; Hong, Y.K.; Kyriakides, T.R.; Brown, L.F.; Bornstein, P.; Detmar, M. Thrombospondin-2 plays a protective role in multistep carcinogenesis: A novel host anti-tumor defense mechanism. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 2631–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fears, C.Y.; Grammer, J.R.; Stewart, J.E., Jr.; Annis, D.S.; Mosher, D.F.; Bornstein, P.; Gladson, C.L. Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein contributes to the antiangiogenic activity of thrombospondin-2 in a murine glioma model. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 9338–9346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salz, T.; Deng, C.; Pampo, C.; Siemann, D.; Qiu, Y.; Brown, K.; Huang, S. Histone Methyltransferase hSETD1A Is a Novel Regulator of Metastasis in Breast Cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. 2015, 13, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yip, C.; Foidart, P.; Somja, J.; Truong, A.; Lienard, M.; Feyereisen, E.; Schroeder, H.; Gofflot, S.; Donneau, A.F.; Collignon, J.; et al. MT4-MMP and EGFR expression levels are key biomarkers for breast cancer patient response to chemotherapy and erlotinib. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 116, 742–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Foidart, P.; Yip, C.; Radermacher, J.; Lienard, M.; Blacher, S.; Montero-Ruiz, L.; Maquoi, E.; Montaudon, E.; Chateau-Joubert, S.; Collignon, J.; et al. Expression of MT4-MMP, EGFR and RB in triple negative breast cancer strongly sensitizes tumors to erlotinib and palbociclib combination therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whittaker, M.; Floyd, C.D.; Brown, P.; Gearing, A.J. Design and therapeutic application of matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors. Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 2735–2776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Stetler-Stevenson, W.G. Overexpression of tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinase 2 up-regulates NF-kappaB activity in melanoma cells. J. Mol. Signal. 2009, 4, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sounni, N.E.; Rozanov, D.V.; Remacle, A.G.; Golubkov, V.S.; Noel, A.; Strongin, A.Y. Timp-2 binding with cellular MT1-MMP stimulates invasion-promoting MEK/ERK signaling in cancer cells. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 126, 1067–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emonard, H.; Duca, L.; Dedieu, S. Editorial: Matricellular Receptors As Potential Targets in Anti-Cancer Therapeutic Strategies. Front. Pharmacol. 2016, 7, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falardeau, P.; Champagne, P.; Poyet, P.; Hariton, C.; Dupont, E. Neovastat, a naturally occurring multifunctional antiangiogenic drug, in phase III clinical trials. Semin. Oncol. 2001, 28, 620–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Chen, S.; Xu, L.; Liu, Y.; Deb, D.K.; Platanias, L.C.; Bergan, R.C. Genistein inhibits p38 map kinase activation, matrix metalloproteinase type 2, and cell invasion in human prostate epithelial cells. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 3470–3478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kousidou, O.C.; Mitropoulou, T.N.; Roussidis, A.E.; Kletsas, D.; Theocharis, A.D.; Karamanos, N.K. Genistein suppresses the invasive potential of human breast cancer cells through transcriptional regulation of metalloproteinases and their tissue inhibitors. Int. J. Oncol. 2005, 26, 1101–1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coussens, L.M.; Fingleton, B.; Matrisian, L.M. Matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors and cancer: Trials and tribulations. Science 2002, 295, 2387–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cathcart, J.; Pulkoski-Gross, A.; Cao, J. Targeting Matrix Metalloproteinases in Cancer: Bringing New Life to Old Ideas. Genes Dis. 2015, 2, 26–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amar, S.; Fields, G.B. Potential clinical implications of recent matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor design strategies. Expert Rev. Proteomics 2015, 12, 445–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.; Paemen, L.; Opdenakker, G.; Froyen, G. Cloning and expression in Escherichia coli of a human gelatinase B-inhibitory single-chain immunoglobulin variable fragment (scFv). FEBS Lett. 1997, 414, 562–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Devy, L.; Huang, L.; Naa, L.; Yanamandra, N.; Pieters, H.; Frans, N.; Chang, E.; Tao, Q.; Vanhove, M.; Lejeune, A.; et al. Selective inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase-14 blocks tumor growth, invasion, and angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 1517–1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naito, S.; Takahashi, T.; Onoda, J.; Yamauchi, A.; Kawai, T.; Kishino, J.; Yamane, S.; Fujii, I.; Fukui, N.; Numata, Y. Development of a neutralizing antibody specific for the active form of matrix metalloproteinase-13. Biochemistry 2012, 51, 8877–8884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessenbrock, K.; Plaks, V.; Werb, Z. Matrix metalloproteinases: Regulators of the tumor microenvironment. Cell 2010, 141, 52–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, S.D.; Joyce, J.A. Proteolytic networks in cancer. Trends Cell Biol. 2011, 21, 228–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Itoh, Y. MT1-MMP: A key regulator of cell migration in tissue. IUBMB Life 2006, 58, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pahwa, S.; Stawikowski, M.J.; Fields, G.B. Monitoring and Inhibiting MT1-MMP during Cancer Initiation and Progression. Cancers 2014, 6, 416–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Delatte, B.; Wang, F.; Ngoc, L.V.; Collignon, E.; Bonvin, E.; Deplus, R.; Calonne, E.; Hassabi, B.; Putmans, P.; Awe, S.; et al. RNA biochemistry. Transcriptome-wide distribution and function of RNA hydroxymethylcytosine. Science 2016, 351, 282–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Substrates | References |
|---|---|
| ECM substrates: | |
| Gelatin | Wang et al., 1999 [5] |
| Fibrin | English et al., 2000 [6] |
| Fibrinogen | English et al., 2000 [6] |
| Other substrates: | |
| proTNF | Wang et al., 1999 [5] |
| English et al., 2000 [6] | |
| COMP | English et al., 2000 [6] |
| α-2-macroglobulin | English et al., 2000 [6] |
| LRP1 | Rozanov et al., 2004 [20] |
| ADAMTS4 | Gao et al., 2004 [2] |
| Patwari et al., 2005 [23] | |
| Clements et al., 2011 [24] | |
| MT4-MMP | Host et al., 2012 [22] |
| Osteopontin | Martin-Alonso et al., 2015 [8] |
| Papke et al., 2015 [25] | |
| Thrombospondin 4 | Martin-Alonso et al., 2015 [8] |
| αM integrin | Clemente et al., 2018 [9] |
| Diseases | Proteolytic Functions | Non-Proteolytic Functions | Unknown |
|---|---|---|---|
| Breast cancer | Angiogenesis 1,2, Metastatic dissemination 1,2 | Cell proliferation 3 | |
| Colon cancer | Metastatic dissemination 4 | ||
| Head and neck cancer | Metastatic dissemination 5, Hypoxia 5 | ||
| Osteoarthritis | Processing of ADAMTS4 p68 isoform 6,7,8 | ||
| Thoracic aortic aneurysms and dissections | Processing of osteopontin 9,10 | ||
| Atherosclerosis | Processing of αMintegrin 11 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yip, C.; Foidart, P.; Noël, A.; Sounni, N.E. MT4-MMP: The GPI-Anchored Membrane-Type Matrix Metalloprotease with Multiple Functions in Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20020354
Yip C, Foidart P, Noël A, Sounni NE. MT4-MMP: The GPI-Anchored Membrane-Type Matrix Metalloprotease with Multiple Functions in Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(2):354. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20020354
Chicago/Turabian StyleYip, Cassandre, Pierre Foidart, Agnès Noël, and Nor Eddine Sounni. 2019. "MT4-MMP: The GPI-Anchored Membrane-Type Matrix Metalloprotease with Multiple Functions in Diseases" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 2: 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20020354
APA StyleYip, C., Foidart, P., Noël, A., & Sounni, N. E. (2019). MT4-MMP: The GPI-Anchored Membrane-Type Matrix Metalloprotease with Multiple Functions in Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(2), 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20020354




