Expanding the Genetic Code for Site-Directed Spin-Labeling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
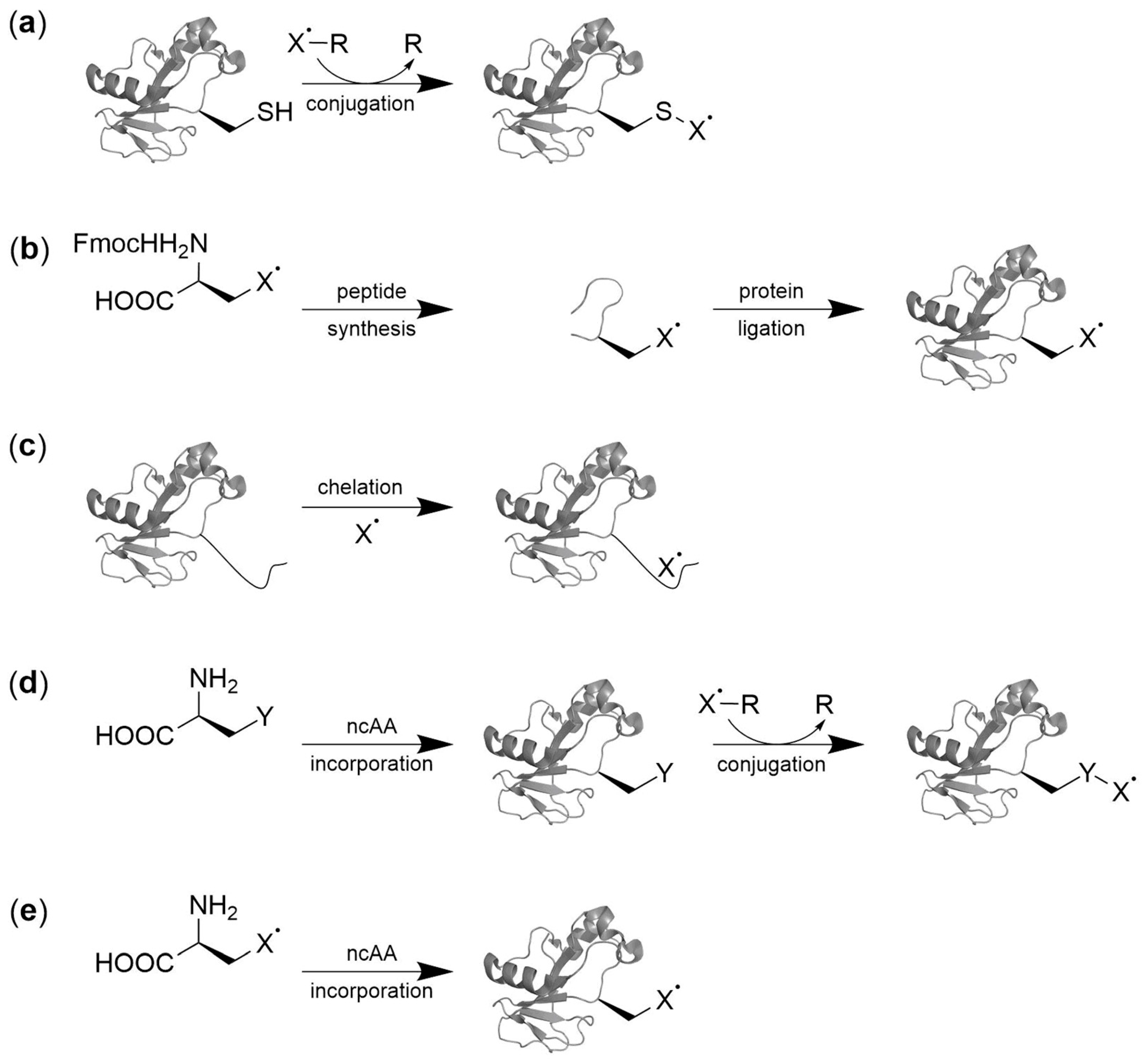
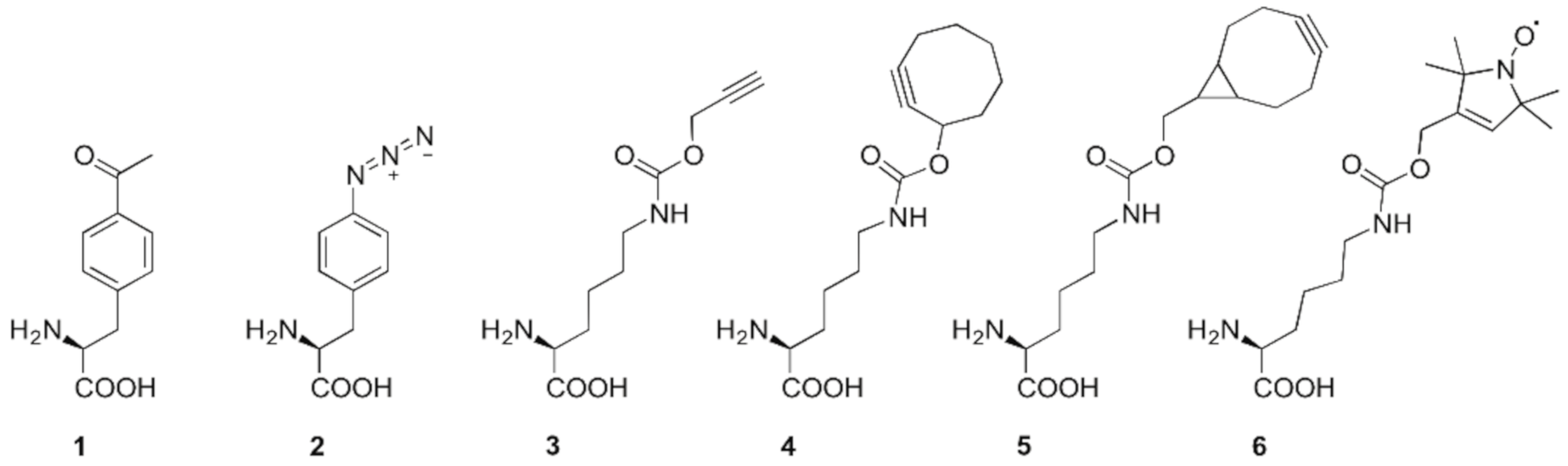
2. Spin Labeling by Bioorthogonal Conjugation with Noncanonical Amino Acids
2.1. Condensation Reactions with Ketone Amino Acids
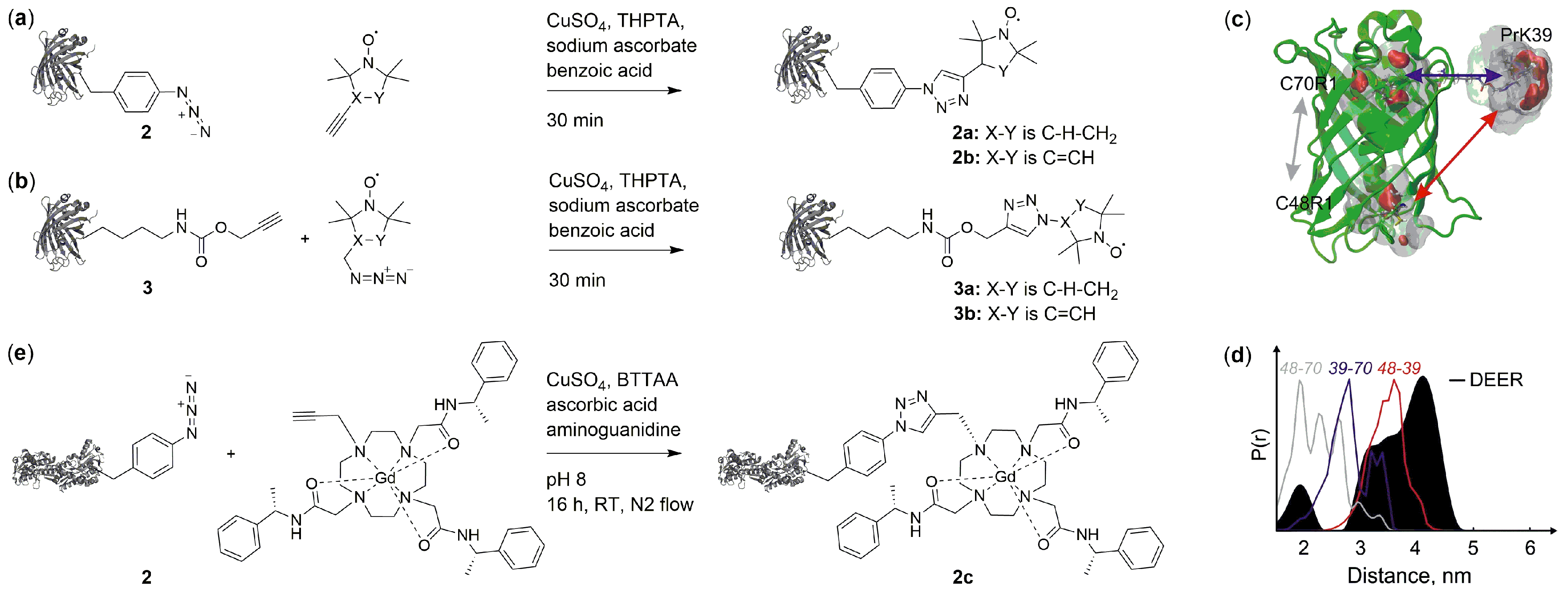
2.2. Copper(I)-Catalzyed Azide-Alkyne Cycloadditions (CuAAC)
2.3. Copper-Free Azide-Alkyne Cycloadditions
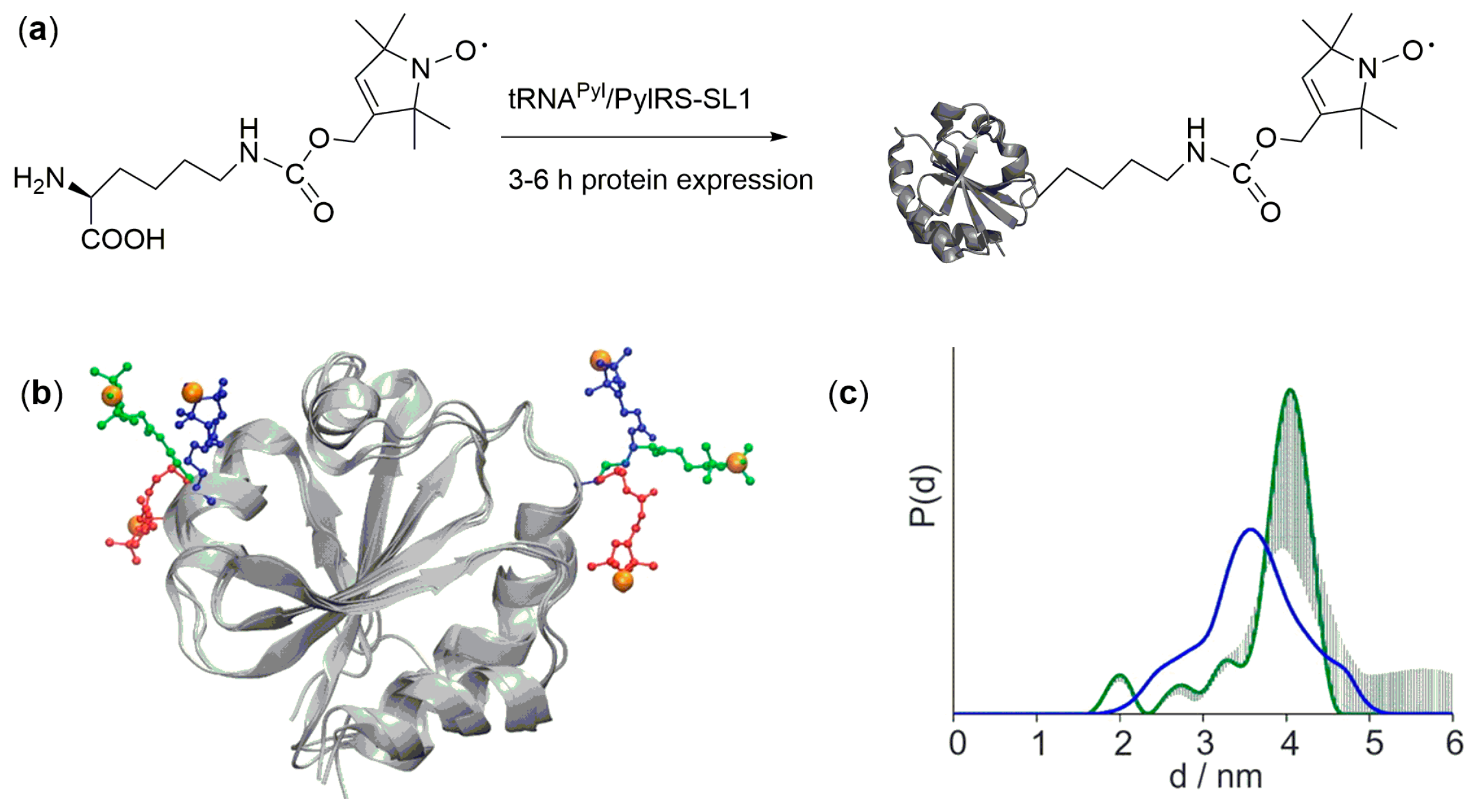
3. Direct Encoding of Spin Labeled Noncanonical Amino Acids
4. Future Directions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| aaRS | Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase |
| BTTAA | 2-[4-((bis[(1-tert-butyl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methyl]- amino)methyl)-1H-1,2,3-triazol-1-yl]acetic acid |
| CuAAC | Copper(I)-catalzyed azide-alkyne cycloaddition |
| cw | Continuous wave |
| DEER | Double electron-electron resonance |
| DODA | 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid |
| DOTA | 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetra-acetic acid |
| DTPA | Diethylene triamine pentaacetic acid |
| EPR | Electron paramagnetic resonance |
| Gd(III) | Gadolinium |
| MTSL | Methanethiosulfonate spin label |
| ncAA | Noncanonical amino acids |
| SDSL | Site-directed spin labeling |
| SPAAC | Strain-promoted azide-alkyne click reaction |
| SPIEDAC | Strain-promoted-inverse-electron-demand Diels–Alder cycloadditions |
| T4L | T4-lysozyme |
| THPTA | Tris- [(1-hydroxy-propyl-1H-1,2,3-triazol-4-yl)methyl]amine |
References
- Altenbach, C.; Flitsch, S.L.; Khorana, H.G.; Hubbell, W.L. Structural studies on transmembrane proteins. 2. Spin labeling of bacteriorhodopsin mutants at unique cysteines. J. Biochem. 1989, 28, 7806–7812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbell, W.L.; Lopez, C.J.; Altenbach, C.; Yang, Z. Technological advances in site-directed spin labeling of proteins. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2013, 23, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Becker, C.F.W.; Lausecker, K.; Balog, M.; Kalai, T.; Hideg, K.; Steinhoff, H.J.; Engelhard, M. Incorporation of spin-labelled amino acids into proteins. Magn. Reson. Chem. 2005, 43, S34–S39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldauf, C.; Schulze, K.; Lueders, P.; Bordignon, E.; Tampe, R. In-situ spin labeling of his-tagged proteins: Distance measurements under in-cell conditions. Chemistry 2013, 19, 13714–13719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunningham, T.F.; Putterman, M.R.; Desai, A.; Horne, W.S.; Saxena, S. The double-histidine Cu2+-binding motif: A highly rigid, site-specific spin probe for electron spin resonance distance measurements. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2015, 54, 6330–6334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ching, H.V.; Mascali, F.C.; Bertrand, H.C.; Bruch, E.M.; Demay-Drouhard, P.; Rasia, R.M.; Policar, C.; Tabares, L.C.; Un, S. The Use of Mn(II) Bound to His-tags as Genetically Encodable Spin-Label for Nanometric Distance Determination in Proteins. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2016, 7, 1072–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barthelmes, D.; Gränz, M.; Barthelmes, K.; Allen, K.N.; Imperiali, B.; Prisner, T.; Schwalbe, H. Encoded loop-lanthanide-binding tags for long-range distance measurements in proteins by NMR and EPR spectroscopy. J. Biomol. NMR 2015, 63, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Roser, P.; Schmidt, M.J.; Drescher, M.; Summerer, D. Site-directed spin labeling of proteins for distance measurements in vitro and in cells. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2016, 14, 5468–5476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klare, J.P.; Steinhoff, H.J. Spin labeling EPR. Photosynth. Res. 2009, 102, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, J.W. Expanding and reprogramming the genetic code. Nature 2017, 550, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffith, O.H.; Waggoner, A. Nitroxide free radicals: Spin labels for probing biomolecular structure. Acc. Chem. Res. 1969, 2, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azarkh, M.; Okle, O.; Eyring, P.; Dietrich, D.R.; Drescher, M. Evaluation of spin labels for in-cell EPR by analysis of nitroxide reduction in cell extract of Xenopus laevis oocytes. J. Magn. Reson. 2011, 212, 450–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krstić, I.; Hänsel, R.; Romainczyk, O.; Engels, J.W.; Dötsch, V.; Prisner, T.F. Long-range distance measurements on nucleic acids in cells by pulsed EPR spectroscopy. Angew. Chem. 2011, 123, 5176–5180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couet, W.; Brasch, R.; Sosnovsky, G.; Tozer, T. Factors affecting nitroxide reduction in ascorbate solution and tissue homogenates. J. Magn. Reson. 1985, 3, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belkin, S.; Mehlhorn, R.J.; Hideg, K.; Hankovsky, O.; Packer, L. Reduction and destruction rates of nitroxide spin probes. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1987, 256, 232–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haugland, M.M.; Lovett, J.E.; Anderson, E.A. Advances in the synthesis of nitroxide radicals for use in biomolecule spin labelling. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2018, 47, 668–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paletta, J.T.; Pink, M.; Foley, B.; Rajca, S.; Rajca, A. Synthesis and reduction kinetics of sterically shielded pyrrolidine nitroxides. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 5322–5325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karthikeyan, G.; Bonucci, A.; Casano, G.; Gerbaud, G.; Abel, S.; Thomé, V.; Kodjabachian, L.; Magalon, A.; Guigliarelli, B.; Belle, V. A Bioresistant Nitroxide Spin Label for In-Cell EPR Spectroscopy: In Vitro and In Oocytes Protein Structural Dynamics Studies. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 1366–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumas, A.; Lercher, L.; Spicer, C.D.; Davis, B.G. Designing logical codon reassignment—Expanding the chemistry in biology. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 50–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martorana, A.; Bellapadrona, G.; Feintuch, A.; Di Gregorio, E.; Aime, S.; Goldfarb, D. Probing protein conformation in cells by EPR distance measurements using Gd3+ spin labeling. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 13458–13465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, M.; Gross, A.; Jeschke, G.; Godt, A.; Drescher, M. Gd(III)-PyMTA label is suitable for in-cell EPR. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 15366–15378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theillet, F.-X.; Binolfi, A.; Bekei, B.; Martorana, A.; Rose, H.M.; Stuiver, M.; Verzini, S.; Lorenz, D.; van Rossum, M.; Goldfarb, D. Structural disorder of monomeric α-synuclein persists in mammalian cells. Nature 2016, 530, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, J.; Liu, W.; Schultz, P.G. A genetically encoded bidentate, metal-binding amino acid. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2007, 46, 9239–9242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.S.; Spraggon, G.; Schultz, P.G.; Wang, F. Genetic Incorporation of a Metal-Ion Chelating Amino Acid into Proteins as a Biophysical Probe. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 2481–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, K.; Chin, J.W. Cellular incorporation of unnatural amino acids and bioorthogonal labeling of proteins. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 4764–4806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, B.; Sikora, A.; Bordignon, E.; Jeschke, G.; Cafiso, D.S.; Prisner, T.F. Distance Measurement on an Endogenous Membrane Transporter in E. coli Cells and Native Membranes Using EPR Spectroscopy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2015, 54, 6196–6199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, B.; Sikora, A.; Cafiso, D.S. Ligand Induced Conformational Changes of a Membrane Transporter in E. coli Cells Observed with DEER/PELDOR. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 1844–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Brock, A.; Schultz, P.G. Addition of the keto functional group to the genetic code of Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, J.W.; Cropp, T.A.; Anderson, J.C.; Mukherji, M.; Zhang, Z.; Schultz, P.G. An Expanded Eukaryotic Genetic Code. Science 2003, 301, 964–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Brock, A.; Chen, S.; Chen, S.; Schultz, P.G. Genetic incorporation of unnatural amino acids into proteins in mammalian cells. Nat. Methods 2007, 4, 239–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleissner, M.R.; Brustad, E.M.; Kálai, T.; Altenbach, C.; Cascio, D.; Peters, F.B.; Hideg, K.; Peuker, S.; Schultz, P.G.; Hubbell, W.L. Site-directed spin labeling of a genetically encoded unnatural amino acid. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 21637–21642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garbuio, L.; Bordignon, E.; Brooks, E.K.; Hubbell, W.L.; Jeschke, G.; Yulikov, M. Orthogonal spin labeling and Gd(III)-nitroxide distance measurements on bacteriophage T4-lysozyme. J. Phys. Chem. B 2013, 117, 3145–3153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostovtsev, V.V.; Green, L.G.; Fokin, V.V.; Sharpless, K.B. A stepwise Huisgen cycloaddition process: Copper(I)-catalyzed regioselective “ligation” of azides and terminal alkynes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 2708–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, P.; Wunnicke, D.; Steinhoff, H.J.; Seela, F. Site-directed spin-labeling of DNA by the azide-alkyne ‘Click’ reaction: Nanometer distance measurements on 7-deaza-2′-deoxyadenosine and 2′-deoxyuridine nitroxide conjugates spatially separated or linked to a ‘dA-dT’ base pair. Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 14385–14396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kálai, T.; Hubbell, W.L.; Hideg, K. Click reactions with nitroxides. Synthesis 2009, 2009, 1336–1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, D.C.; McKay, C.S.; Legault, M.C.; Danielson, D.C.; Blake, J.A.; Pegoraro, A.F.; Stolow, A.; Mester, Z.; Pezacki, J.P. Cellular consequences of copper complexes used to catalyze bioorthogonal click reactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 17993–18001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiick, K.L.; Saxon, E.; Tirrell, D.A.; Bertozzi, C.R. Incorporation of azides into recombinant proteins for chemoselective modification by the Staudinger ligation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, J.W.; Santoro, S.W.; Martin, A.B.; King, D.S.; Wang, L.; Schultz, P.G. Addition of p-azido-L-phenylalanine to the genetic code of Escherichia coli. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 9026–9027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.P.; Lusic, H.; Neumann, H.; Kapadnis, P.B.; Deiters, A.; Chin, J.W. Genetic encoding and labeling of aliphatic azides and alkynes in recombinant proteins via a pyrrolysyl-tRNA synthetase/tRNACUA pair and click chemistry. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 8720–8721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, D.D.; Young, T.S.; Jahnz, M.; Ahmad, I.; Spraggon, G.; Schultz, P.G. An evolved aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase with atypical polysubstrate specificity. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 1894–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelkader, E.H.; Feintuch, A.; Yao, X.; Adams, L.A.; Aurelio, L.; Graham, B.; Goldfarb, D.; Otting, G. Protein conformation by EPR spectroscopy using gadolinium tags clicked to genetically encoded p-azido-L-phenylalanine. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 15898–15901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelkader, E.H.; Lee, M.D.; Feintuch, A.; Cohen, M.R.; Swarbrick, J.D.; Otting, G.; Graham, B.; Goldfarb, D. A new Gd3+ spin label for Gd3+–Gd3+ distance measurements in proteins produces narrow distance distributions. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2015, 6, 5016–5021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, D.B.; Xu, J.; Shen, Z.; Takimoto, J.K.; Schultz, M.D.; Schmitz, R.J.; Xiang, Z.; Ecker, J.R.; Briggs, S.P.; Wang, L. RF1 knockout allows ribosomal incorporation of unnatural amino acids at multiple sites. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2011, 7, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, D.B.F.; Wang, C.; Xu, J.F.; Schultz, M.D.; Schmitz, R.J.; Ecker, J.R.; Wang, L. Release Factor One Is Nonessential in Escherichia coli. ACS Chem. Biol. 2012, 7, 1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukai, T.; Hayashi, A.; Iraha, F.; Sato, A.; Ohtake, K.; Yokoyama, S.; Sakamoto, K. Codon reassignment in the Escherichia coli genetic code. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, 8188–8195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lajoie, M.J.; Rovner, A.J.; Goodman, D.B.; Aerni, H.R.; Haimovich, A.D.; Kuznetsov, G.; Mercer, J.A.; Wang, H.H.; Carr, P.A.; Mosberg, J.A.; et al. Genomically Recoded Organisms Expand Biological Functions. Science 2013, 342, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kucher, S.; Korneev, S.; Tyagi, S.; Apfelbaum, R.; Grohmann, D.; Lemke, E.A.; Klare, J.P.; Steinhoff, H.J.; Klose, D. Orthogonal spin labeling using click chemistry for in vitro and in vivo applications. J. Magn. Reson. 2017, 275, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arpino, J.A.; Rizkallah, P.J.; Jones, D.D. Crystal structure of enhanced green fluorescent protein to 1.35 Å resolution reveals alternative conformations for Glu222. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e47132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubbell, W.L.; Hideg, K.; Kálai, T.; Fleissner, M.R.; Jek, J. Synthesis of new spin labels for Cu-free click conjugation. Tetrahedron Lett. 2011, 52, 2747–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Plass, T.; Milles, S.; Koehler, C.; Schultz, C.; Lemke, E.A. Genetically encoded copper-free click chemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 3878–3881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, K.; Davis, L.; Wallace, S.; Mahesh, M.; Cox, D.J.; Blackman, M.L.; Fox, J.M.; Chin, J.W. Genetic Encoding of Bicyclononynes and trans-Cyclooctenes for Site-Specific Protein Labeling in Vitro and in Live Mammalian Cells via Rapid Fluorogenic Diels-Alder Reactions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 10317–10320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrmann, A.; Milles, S.; Plass, T.; Dommerholt, J.; Verkade, J.M.M.; Wießler, M.; Schultz, C.; van Hest, J.C.M.; van Delft, F.L.; Lemke, E.A. Genetic Encoding of a Bicyclo[6.1.0]nonyne-Charged Amino Acid Enables Fast Cellular Protein Imaging by Metal-Free Ligation. ChemBioChem 2012, 13, 2094–2099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattani, J.; Subramaniam, V.; Drescher, M. Room-temperature in-cell EPR spectroscopy: α-Synuclein disease variants remain intrinsically disordered in the cell. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017, 19, 18147–18151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, M.J.; Borbas, J.; Drescher, M.; Summerer, D. A genetically encoded spin label for electron paramagnetic resonance distance measurements. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 1238–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, M.J.; Fedoseev, A.; Bücker, D.; Borbas, J.; Peter, C.; Drescher, M.; Summerer, D. EPR Distance Measurements in Native Proteins with Genetically Encoded Spin Labels. ACS Chem. Biol. 2015, 10, 2764–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, M.J.; Fedoseev, A.; Summerer, D.; Drescher, M. Genetically Encoded Spin Labels for In Vitro and In-Cell EPR Studies of Native Proteins. Methods Enzymol. 2015, 563, 483–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Braun, T.; Drescher, M.; Summerer, D. Expanding the Genetic Code for Site-Directed Spin-Labeling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 373. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20020373
Braun T, Drescher M, Summerer D. Expanding the Genetic Code for Site-Directed Spin-Labeling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(2):373. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20020373
Chicago/Turabian StyleBraun, Theresa, Malte Drescher, and Daniel Summerer. 2019. "Expanding the Genetic Code for Site-Directed Spin-Labeling" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 2: 373. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20020373
APA StyleBraun, T., Drescher, M., & Summerer, D. (2019). Expanding the Genetic Code for Site-Directed Spin-Labeling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(2), 373. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20020373





