Role of Semaphorins in Immunopathologies and Rheumatic Diseases
Abstract
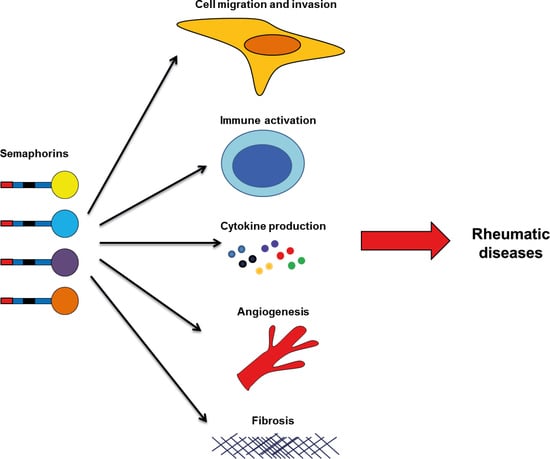
:1. Introduction
2. Rheumatoid Arthritis
3. Systemic Sclerosis
4. Osteoarthritis
5. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
6. Spondyloarthritis
7. Concluding Remarks and Future Perspectives
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gourley, M.; Miller, F.W. Mechanisms of disease: Environmental factors in the pathogenesis of rheumatic disease. Nat. Clin. Pract. Rheumatol. 2007, 3, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldblatt, F.; O’Neill, S.G. Clinical aspects of autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Lancet (Lond. Engl.) 2013, 382, 797–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vos, T.; Flaxman, A.D.; Naghavi, M.; Lozano, R.; Michaud, C.; Ezzati, M.; Shibuya, K.; Salomon, J.A.; Abdalla, S.; Aboyans, V.; et al. Years lived with disability (YLDs) for 1160 sequelae of 289 diseases and injuries 1990–2010: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 2012, 380, 2163–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takamatsu, H.; Kumanogoh, A. Diverse roles for semaphorin S plexin signaling in the immune system. Trends Immunol. 2012, 33, 127–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumanogoh, A.; Kikutani, H. Immunological functions of the neuropilins and plexins as receptors for semaphorins. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 802–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizui, M.; Kumanogoh, A.; Kikutani, H. Immune semaphorins: Novel features of neural guidance molecules. J. Clin. Immunol. 2009, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Worzfeld, T.; Offermanns, S. Semaphorins and plexins as therapeutic targets. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2014, 13, 603–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, K.; Kumanogoh, A.; Kikutani, H. Semaphorins and their receptors in immune cell interactions. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishide, M.; Kumanogoh, A. The role of semaphorins in immune responses and autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2018, 14, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Verhaagen, J.; Harvey, A.R. Receptor complexes for each of the Class 3 Semaphorins. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2012, 6, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Zhu, L. Semaphorins and their receptors: From axonal guidance to atherosclerosis. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamagnone, L. Emerging Role of Semaphorins as Major Regulatory Signals and Potential Therapeutic Targets in Cancer. Cancer Cell 2012, 22, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Neufeld, G.; Kessler, O. The semaphorins: Versatile regulators of tumour progression and tumour angiogenesis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2008, 8, 632–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, C.; Giraudo, E. The role of semaphorins and their receptors in vascular development and cancer. Exp. Cell Res. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roth, L.; Koncina, E.; Satkauskas, S.; Crémel, G.; Aunis, D.; Bagnard, D. The many faces of semaphorins: From development to pathology. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2009, 66, 649–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaur, P.; Bielenberg, D.R.; Samuel, S.; Bose, D.; Zhou, Y.; Gray, M.J.; Dallas, N.A.; Fan, F.; Xia, L.; Lu, J.; et al. Role of class 3 semaphorins and their receptors in tumor growth and angiogenesis. Clin. Cancer Res. 2009, 15, 6763–6770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, D.; Kumanogoh, A. The role of Sema4A in angiogenesis, immune responses, carcinogenesis, and retinal systems. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2016, 10, 692–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Law, J.W.S.; Lee, A.Y.W. The Role of Semaphorins and Their Receptors in Gliomas. J. Signal Transduct. 2012, 2012, 902854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, R.; Kumar, D.; Tomar, D.; Chakraborty, G.; Kumar, S.; Kundu, G.C. The potential of class 3 semaphorins as both targets and therapeutics in cancer. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2015, 19, 427–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muratori, C.; Tamagnone, L. Semaphorin Signals Tweaking the Tumor Microenvironment, 1st ed.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.D.; Ivashkiv, L.B. Roles of semaphorins in the immune and hematopoietic system. Rheumatol. Int. 2009, 29, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.; Kumanogoh, A. Semaphorins in bone development, homeostasis, and disease. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goshima, Y.; Sasaki, Y.; Yamashita, N.; Nakamura, F. Class 3 semaphorins as a therapeutic target. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2012, 16, 933–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McInnes, I.B.; Schett, G. Pathogenetic insights from the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet 2017, 389, 2328–2337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McInnes, I.B.; Schett, G. The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 2205–2219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koch, A.E. Chemokines and their receptors in rheumatoid arthritis: Future targets? Arthritis Rheum. 2005, 52, 710–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tak, P.P.; Bresnihan, B. The pathogenesis and prevention of joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis: Advances from synovial biopsy and tissue analysis. Arthritis Rheum. 2000, 43, 2619–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McInnes, I.B.; Schett, G. Cytokines in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2007, 7, 429–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInnes, I.B.; Buckley, C.D.; Isaacs, J.D. Cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis—Shaping the immunological landscape. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2015, 12, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolen, J.S.; Aletaha, D. Rheumatoid arthritis therapy reappraisal: Strategies, opportunities and challenges. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2015, 11, 276–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, L.E.; Weidler, C.; Falk, W.; Angele, P.; Schaumburger, J.; Schölmerich, J.; Straub, R.H. Increased Prevalence of Semaphorin 3C, a Repellent of Sympathetic Nerve Fibers, in the Synovial Tissue of Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2004, 50, 1156–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catalano, A. The neuroimmune semaphorin-3A reduces inflammation and progression of experimental autoimmune arthritis. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 6373–6383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takagawa, S.; Nakamura, F.; Kumagai, K.; Nagashima, Y.; Goshima, Y.; Saito, T. Decreased semaphorin3A expression correlates with disease activity and histological features of rheumatoid arthritis. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2013, 14, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, Y.; Yin, Z.; Li, J.; Li, K.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y. Adenovirus-mediated delivery of Sema3A alleviates rheumatoid arthritis in a serum-transfer induced mouse model. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 66270–66280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, M.W.; Malvar Fernández, B.; Newsom, S.P.; van Buul, J.D.; Radstake, T.R.D.J.; Baeten, D.L.; Tak, P.P.; Reedquist, K.A.; García, S. Class 3 semaphorins modulate the invasive capacity of rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Rheumatology 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Song, G.; Zheng, Y.; Tan, W.; Pan, J.; Zhao, Y.; Chang, X. Expression of Semaphorin 4A and its potential role in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015, 17, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, Y.; Ogata, A.; Kang, S.; Ebina, K.; Shi, K.; Nojima, S.; Kimura, T.; Ito, D.; Morimoto, K.; Nishide, M.; et al. Semaphorin 4D contributes to rheumatoid arthritis by inducing inflammatory cytokine production: Pathogenic and therapeutic implications. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 1481–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Wu, X.; Chen, M.; Wang, W.; Xv, W.; Ye, L.; Wu, D.; Xue, J.; Sun, W.; Luo, J.; et al. Elevated semaphorin5A in systemic lupus erythematosus is in association with disease activity and lupus nephritis. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2017, 188, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Wang, H. Semaphorin 7A as a potential immune regulator and promising therapeutic target in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrielli, A.; Avvedimento, E.V.; Krieg, T. Scleroderma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2009, 360, 1989–2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattanaik, D.; Brown, M.; Postlethwaite, B.C.; Postlethwaite, A.E. Pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis. Front. Immunol. 2015, 6, 272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Rhijn-Brouwer, F.C.; Gremmels, H.; Fledderus, J.O.; Radstake, T.R.; Verhaar, M.C.; van Laar, J.M. Cellular Therapies in Systemic Sclerosis: Recent Progress. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2016, 18, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denton, C.P.; Khanna, D. Systemic sclerosis. Lancet 2017, 390, 1685–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruni, C.; Praino, E.; Allanore, Y.; Distler, O.; Gabrielli, A.; Iannone, F.; Matucci-Cerinic, M. Use of biologics and other novel therapies for the treatment of systemic sclerosis. Expert Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2017, 13, 469–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Wu, W.; Sun, X.; Yang, J.; Xu, J.; Fu, W.; Li, M. New insights into CD4+ T cell abnormalities in systemic sclerosis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2016, 28, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, Y.S.; Kong, J.; Cheema, G.S.; Keen, C.L.; Wick, G.; Gershwin, M.E. The Immunobiology of Systemic Sclerosis. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 38, 132–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brembilla, N.C.; Chizzolini, C. T cell abnormalities in systemic sclerosis with a focus on Th17 cells. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2012, 23, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lafyatis, R. Innate immunity and inflammation in systemic sclerosis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2010, 21, 617–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Bon, L.; Cossu, M.; Radstake, T.R. An update on an immune system that goes awry in systemic sclerosis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2011, 23, 505–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabquer, B.J.; Koch, A.E. Angiogenesis and Vasculopathy in Systemic Sclerosis: Evolving Concepts. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2012, 14, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, S.; Wei, J.; Tourtellotte, W.G.; Hinchcliff, M.; Gottardi, C.G.; Varga, J. Fibrosis in systemic sclerosis: Common and unique pathobiology. Fibrogenes Tissue Repair 2012, 5, S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chizzolini, C.; Brembilla, N.C.; Montanari, E.; Truchetet, M.E. Fibrosis and immune dysregulation in systemic sclerosis. Autoimmun. Rev. 2011, 10, 276–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rimar, D.; Nov, Y.; Rosner, I.; Slobodin, G.; Rozenbaum, M.; Halasz, K.; Haj, T.; Jiries, N.; Kaly, L.; Boulman, N.; et al. Semaphorin 3A: An immunoregulator in systemic sclerosis. Rheumatol. Int. 2015, 35, 1625–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romano, E.; Chora, I.; Manetti, M.; Mazzotta, C.; Rosa, I.; Bellando-Randone, S.; Blagojevic, J.; Soares, R.; Avouac, J.; Allanore, Y.; et al. Decreased expression of neuropilin-1 as a novel key factor contributing to peripheral microvasculopathy and defective angiogenesis in systemic sclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 1541–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazzotta, C.; Romano, E.; Bruni, C.; Manetti, M.; Lepri, G.; Bellando-Randone, S.; Blagojevic, J.; Ibba-Manneschi, L.; Matucci-Cerinic, M.; Guiducci, S. Plexin-D1/Semaphorin 3E pathway may contribute to dysregulation of vascular tone control and defective angiogenesis in systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besliu, A.; Banica, L.; Predeteanu, D.; Vlad, V.; Ionescu, R.; Pistol, G.; Opris, D.; Berghea, F.; Stefanescu, M.; Matache, C. Peripheral blood lymphocytes analysis detects CD100/SEMA4D alteration in systemic sclerosis patients. Autoimmunity 2011, 44, 427–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, H.Y.; Gao, W.; Chong, F.R.; Liu, H.Y.; Zhang, J. Semaphorin 4A enhances lung fibrosis through activation of Akt via PlexinD1 receptor. J. Biosci. 2015, 40, 855–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, Y.; Reilkoff, R.; Peng, X.; Russell, T.; Chen, Q.; Mathai, S.K.; Homer, R.; Gulati, M.; Siner, J.; Elias, J.; et al. Role of semaphorin 7a signaling in transforming growth factor beta1-induced lung fibrosis and scleroderma-related interstitial lung disease. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 2484–2494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Minicis, S.; Rychlicki, C.; Agostinelli, L.; Saccomanno, S.; Trozzi, L.; Candelaresi, C.; Bataller, R.; Millán, C.; Brenner, D.A.; Vivarelli, M.; et al. Semaphorin 7A Contributes to TGF-β—Mediated Liver Fibrogenesis. Am. J. Pathol. 2013, 183, 820–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.; Lee, C.G.; Homer, R.J.; Elias, J.A. Semaphorin 7A plays a critical role in TGF-β 1–induced pulmonary fibrosis. J. Exp. Med. 2007, 204, 1083–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loeser, R.F.; Goldring, S.R.; Scanzello, C.R.; Goldring, M.B. Osteoarthritis: A disease of the joint as an organ. Arthritis Rheum. 2012, 64, 1697–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reynard, L.N.; Loughlin, J. Maturitas Genetics and epigenetics of osteoarthritis. Maturitas 2012, 71, 200–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gómez, R.; Villalvilla, A.; Largo, R.; Gualillo, O.; Herrero-beaumont, G. TLR4 signalling in osteoarthritis—Finding targets for candidate DMOADs. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldring, S.R.; Goldring, M.B. Changes in the osteochondral unit. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016, 12, 632–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raman, S.; FitzGerald, U.; Murphy, J.M. Interplay of Inflammatory Mediators with Epigenetics and Cartilage Modifications in Osteoarthritis. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2018, 6, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okubo, M.; Kimura, T.; Fujita, Y.; Mochizuki, S.; Niki, Y.; Enomoto, H.; Suda, Y.; Toyama, Y.; Okada, Y. Semaphorin 3A is expressed in human osteoarthritic cartilage and antagonizes vascular endothelial growth factor 165-promoted chondrocyte migration: An implication for chondrocyte cloning. Arthritis Rheum. 2011, 63, 3000–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, J.; Wei, X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Lu, J.; Lu, Y.; Cui, M.; Zhang, X.; Li, F. Inflammatory milieu cultivated Sema3A signaling promotes chondrocyte apoptosis in knee osteoarthritis. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 2891–2899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sumi, C.; Hirose, N.; Yanoshita, M.; Takano, M.; Nishiyama, S.; Okamoto, Y.; Asakawa, Y.; Tanimoto, K. Semaphorin 3A inhibits inflammation in chondrocytes under excessive mechanical stress. Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 5703651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, M.; Nakashima, T.; Taniguchi, M.; Kodama, T.; Kumanogoh, A.; Takayanagi, H. Osteoprotection by semaphorin 3A. Nature 2012, 485, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsokos, G.C. Systemic lupus erythematosus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 2110–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadasz, Z.; Toubi, E. Semaphorin 3A-a marker for disease activity and a potential putative disease-modifying treatment in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 2012, 21, 1266–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vadasz, Z.; Ben-Izhak, O.; Bejar, J.; Sabo, E.; Kessel, A.; Storch, S.; Toubi, E. The involvement of immune semaphorins and neuropilin-1 in lupus nephritis. Lupus 2011, 20, 1466–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vadasz, Z.; Peri, R.; Eiza, N.; Slobodin, G.; Balbir-Gurman, A.; Toubi, E. The Expansion of CD25 high IL-10 high FoxP3 high B Regulatory Cells Is in Association with SLE Disease Activity. J. Immunol. Res. 2015, 2015, 254245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bejar, J.; Kessler, O.; Sabag, A.D.; Sabo, E.; Itzhak, O.B.; Neufeld, G.; Vadasz, Z. Semaphorin3A: A Potential Therapeutic Tool for Lupus Nephritis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moz, S.; Aita, A.; Basso, D.; Ramonda, R.; Plebani, M.; Punzi, L. Spondyloarthritis: Matrix metalloproteinasesas biomarkers of pathogenesis and response to tumor necrosis factor (TNFα) inhibitors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sieper, J.; Poddubnyy, D. Axial spondyloarthritis. Lancet (Lond. Engl.) 2017, 390, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambarus, C.; Yeremenko, N.; Tak, P.P.; Baeten, D. Pathogenesis of spondyloarthritis: Autoimmune or autoinflammatory? Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2012, 24, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruithof, E.; Baeten, D.; De Rycke, L.; Vandooren, B.; Foell, D.; Roth, J.; Cañete, J.D.; Boots, A.M.; Veys, E.M.; De Keyser, F. Synovial histopathology of psoriatic arthritis, both oligo- and polyarticular, resembles spondyloarthropathy more than it does rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2005, 7, R569–R580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baeten, D.; Demetter, P.; Cuvelier, C.; Van den Bosch, F.; Kruithof, E.; Van Damme, N.; Verbruggen, G.; Mielants, H.; Veys, E.M.; De Keyser, F. Comparative study of the synovial histology in rheumatoid arthritis, spondyloarthropathy, and osteoarthritis: Influence of disease duration and activity. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2000, 59, 945–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrotta, F.M.; Ceccarelli, F.; Barbati, C.; Colasanti, T.; Montepaone, M.; Alessandri, C.; Valesini, G.; Lubrano, E. Assessment of semaphorin 3A and its role in bone remodelling in a group of ankylosing spondylitis patients. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2017, 35, 313–316. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, H.T.; Lin, Y.F.; Chou, C.T.; Tsai, C.Y. Semaphorin 3A in Ankylosing Spondylitis. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moots, R.J.; Naisbett-Groet, B. The efficacy of biologic agents in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and an inadequate response to tumour necrosis factor inhibitors: A systematic review. Rheumatol. (Oxf.) 2012, 51, 2252–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonard, J.E.; Fisher, T.L.; Winter, L.A.; Cornelius, C.A.; Reilly, C.; Smith, E.S.; Zauderer, M. Nonclinical Safety Evaluation of VX15/2503, a Humanized IgG4 Anti-SEMA4D Antibody. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2015, 14, 964–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Patnaik, A.; Weiss, G.J.; Leonard, J.E.; Rasco, D.W.; Sachdev, J.C.; Fisher, T.L.; Winter, L.A.; Reilly, C.; Parker, R.B.; Mutz, D.; et al. Safety, Pharmacokinetics, and Pharmacodynamics of a Humanized Anti-Semaphorin 4D Antibody, in a First-In-Human Study of Patients with Advanced Solid Tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 827–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaGanke, C.; Samkoff, L.; Edwards, K.; Henson, L.J.; Repovic, P.; Lynch, S.; Stone, L.; Mattson, D.; Galluzzi, A.; Fisher, T.L.; et al. Safety/tolerability of the anti-semaphorin 4D antibody VX15/2503 in a randomized phase 1 trial. Neurol. Neuroimmunol. NeuroInflamm. 2017, 4, e367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


© 2019 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Garcia, S. Role of Semaphorins in Immunopathologies and Rheumatic Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20020374
Garcia S. Role of Semaphorins in Immunopathologies and Rheumatic Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(2):374. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20020374
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcia, Samuel. 2019. "Role of Semaphorins in Immunopathologies and Rheumatic Diseases" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 2: 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20020374
APA StyleGarcia, S. (2019). Role of Semaphorins in Immunopathologies and Rheumatic Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(2), 374. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20020374