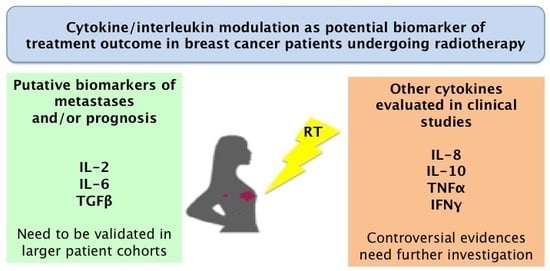
Cytokine Modulation in Breast Cancer Patients Undergoing Radiotherapy: A Revision of the Most Recent Studies
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Interleukins (IL-2, IL-6, IL-8, and IL-10)
2.2. Other Cytokines
2.3. Transforming Growth Factor-β-1 (TGF-β1)
2.4. Interferon Gamma (IFN-γ)
2.5. Chemokines
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
Study Search Strategy and Selection Criteria
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| adj | Adjuvant |
| APBI | Accelerated hypofractionated partial breast irradiation |
| BC | Breast cancer |
| BCS | Breast-conserving surgery |
| CCL | Chemokine ligands |
| CHT | Chemotherapy |
| CRT | Combined chemo/radiotherapy |
| CSF2 | Colony-stimulating factor 2 (granulocyte-macrophage) |
| CTGF | Connective tissue growth factor |
| CTR | Controls |
| CXCL | Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand |
| CYFRA 21-1 | Cytokeratin 21-1 fragment |
| d | Dose/fraction |
| DAMP | Danger-associated molecular pattern |
| EGF | Epidermal grow factor |
| ER | Estrogen |
| FOXP3 | Forkhead box P3, also known as scurfin |
| frs | Fractions |
| GES | Gene-expression signature |
| Gy | Gray |
| HC | Healthy control |
| Her-2 | Human epidermal growth factor receptor-2 |
| HT | Hormonal therapy |
| IBAPBI | Intracavitary brachytherapy accelerated hypofractionated partial breast irradiation |
| IFNA2 | Interferon, alpha 2 |
| IFNβ | Interferon beta |
| IFN-γ | Interferon gamma |
| IL | Interleukin |
| IL-1RA | Interleukin-1 receptor antagonist |
| IL5RA | Interleukin 5 receptor, alpha |
| IL10RB | Interleukin 10 receptor, beta |
| IORT | Intraoperative radiotherapy |
| LH-RH | Luteinizing hormone releasing hormone |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| MCP-1 | Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 |
| MFS | Metastasis-free survival |
| MIC-1/GDF15 | Macrophage inhibitory cytokine 1/growth differentiation factor 15 |
| NA | Not available |
| OPG | Osteoprotegerin |
| OS | Overall survival |
| OSM | Oncostatin M |
| PDGF-AB | Platelet-derived growth factor anti-body |
| PFS | Progression-free survival |
| PR | Progesteron |
| Pts | Patients |
| RA | Retinoic acid |
| RANK | Receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B |
| RIF | Radiation-induced fibrosis |
| RSI | Radiosensitivity index |
| RT | Radiotherapy |
| S | Surgery |
| SBRT | Stereotactic body radiation therapy |
| SCC-Ag | Squamous cell cancer antigen |
| SN | Supernatant |
| TD | Total dose |
| TGF-α | Transforming growth factor alpha |
| TGF-β1(b1) | Transforming growth factor beta-1 |
| TNBCs | Triple-negative breast cancers |
| TNF-α | Tumor necrosis factor-alpha |
| TNFSF13 | Tumor necrosis factor (ligand) superfamily member 13 |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
| WF | Wound fluid |
| y | Years |
References
- Global Cancer Incidence. Available online: https://www.wcrf.org/dietandcancer/cancer-trends/worldwide-cancer-data (accessed on 27 November 2018).
- Nounou, M.I.; ElAmrawy, F.; Ahmed, N.; Abdelraouf, K.; Goda, S.; Syed-Sha-Qhattal, H. Breast Cancer: Conventional Diagnosis and Treatment Modalities and Recent Patents and Technologies. Breast Cancer 2015, 9 (Suppl. 2), 17–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baskar, R.; Lee, K.A.; Yeo, R.; Yeoh, K.W. Cancer and radiation therapy: Current advances and future directions. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2012, 9, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forker, L.J.; Choudhury, A.; Kiltie, A.E. Biomarkers of Tumour Radiosensitivity and Predicting Benefit from Radiotherapy. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 27, 561–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garibaldi, C.; Jereczek-Fossa, B.A.; Marvaso, G.; Dicuonzo, S.; Rojas, D.P.; Cattani, F.; Starzyńska, A.; Ciardo, D.; Surgo, A.; Leonardi, M.C.; et al. Recent advances in radiation oncology. Ecancermedicalscience 2017, 11, 785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Baruch, A. Host microenvironment in breast cancer development: Inflammatory cells, cytokines and chemokines in breast cancer progression: Reciprocal tumor-microenvironment interactions. Breast Cancer Res. 2003, 5, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brix, N.; Tiefenthaller, A.; Anders, H.; Belka, C.; Lauber, K. Abscopal, immunological effects of radiotherapy: Narrowing the gap between clinical and preclinical experiences. Immunol. Rev. 2017, 280, 249–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mole, R.H. Whole body irradiation; radiobiology or medicine? Br. J. Radiol. 1953, 26, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camphausen, K.; Moses, M.A.; Ménard, C.; Sproull, M.; Beecken, W.D.; Folkman, J.; O’Reilly, M.S. Radiation abscopal antitumor effect is mediated through p53. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 1990–1993. [Google Scholar]
- Strigari, L.; Mancuso, M.; Ubertini, V.; Soriani, A.; Giardullo, P.; Benassi, M.; D’Alessio, D.; Leonardi, S.; Soddu, S.; Bossi, G. Abscopal effect of radiation therapy: Interplay between radiation dose and p53 status. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2015, 91, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marconi, R.; Strolin, S.; Bossi, G.; Strigari, L. A meta-analysis of the abscopal effect in preclinical models: Is the biologically effective dose a relevant physical trigger? PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssen, L.M.E.; Ramsay, E.E.; Logsdon, C.D.; Overwijk, W.W. The immune system in cancer metastasis: Friend or foe? J. Immunother. Cancer 2017, 5, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombo, M.; Mirandola, L.; Chiriva-Internati, M.; Basile, A.; Locati, M.; Lesma, E.; Chiaramonte, R.; Platonova, N. Cancer Cells Exploit Notch Signaling to Redefine a Supportive Cytokine Milieu. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorimore, S.A.; Coates, P.J.; Scobie, G.E.; Milne, G.; Wright, E.G. Inflammatory-type responses after exposure to ionizing radiation in vivo: A mechanism for radiation-induced bystander effects? Oncogene 2001, 20, 7085–7095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Formenti, S.C.; Demaria, S. Systemic effects of local radiotherapy. Lancet Oncol. 2009, 10, 718–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wennerberg, E.; Lhuillier, C.; Vanpouille-Box, C.; Pilones, K.A.; García-Martínez, E.; Rudqvist, N.P.; Formenti, S.C.; Demaria, S. Barriers to Radiation-Induced In Situ Tumor Vaccination. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnjatic, S.; Bronte, V.; Brunet, L.R.; Butler, M.O.; Disis, M.L.; Galon, J.; Hakansson, L.G.; Hanks, B.A.; Karanikas, V.; Khleif, S.N.; et al. Identifying baseline immune-related biomarkers to predict clinical outcome of immunotherapy. J. Immunother. Cancer 2017, 5, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Getz, G.S. Thematic review series: The immune system and atherogenesis. Bridging the innate and adaptive immune systems. J. Lipid Res. 2005, 46, 619–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavaillon, J.M. Pro- versus anti-inflammatory cytokines: Myth or reality. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2001, 47, 695–702. [Google Scholar]
- Anestakis, D.; Petanidis, S.; Kalyvas, S.; Nday, C.M.; Tsave, O.; Kioseoglou, E.; Salifoglou, A. Mechanisms and applications of interleukins in cancer immunotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 1691–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mosmann, T.R.; Sad, S. The expanding universe of T-cell subsets: Th1, Th2 and more. Immunol. Today 1996, 17, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallner, F.K.; Hultquist Hopkins, M.; Woodworth, N.; Lindvall Bark, T.; Olofsson, P.; Tilevik, A. Correlation and cluster analysis of immunomodulatory drugs based on cytokine profiles. Pharmacol. Res. 2018, 128, 244–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monastero, R.N.; Pentyala, S. Cytokines as Biomarkers and Their Respective Clinical Cutoff Levels. Int. J. Inflamm. 2017, 2017, 4309485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaue, D.; Micewicz, E.D.; Ratikan, J.A.; Xie, M.W.; Cheng, G.; McBride, W.H. Radiation and inflammation. Semin. Radiat. Oncol. 2015, 25, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santa-Maria, C.A.; Nanda, R. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy in Breast Cancer. J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw. 2018, 16, 1259–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aula, H.; Skyttä, T.; Tuohinen, S.; Luukkaala, T.; Hämäläinen, M.; Virtanen, V.; Raatikainen, P.; Moilanen, E.; Kellokumpu-Lehtinen, P.L. Decreases in TGF-β1 and PDGF levels are associated with echocardiographic changes during adjuvant radiotherapy for breast cancer. Radiat. Oncol. 2018, 13, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfano, C.M.; Peng, J.; Andridge, R.R.; Lindgren, M.E.; Povoski, S.P.; Lipari, A.M.; Agnese, D.M.; Farrar, W.B.; Yee, L.D.; Carson, W.E.; et al. Inflammatory cytokines and Comorbidity development in breast cancer survivors versus noncancer controls: Evidence for accelerated aging? J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 35, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muraro, E.; Furlan, C.; Avanzo, M.; Martorelli, D.; Comaro, E.; Rizzo, A.; Fae, D.A.; Berretta, M.; Militello, L.; Del Conte, A.; et al. Local High-Dose Radiotherapy Induces Systemic Immunomodulating Effects of Potential Therapeutic Relevance in Oligometastatic Breast Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todorović-Raković, N.; Radulovic, M.; Vujasinović, T.; Milovanović, J.; Nikolić-Vukosavljević, D. The prognostic time dependence of intra-tumoural IFNγ mRNA and protein in patients with breast cancer followed for 14 years after surgery and radiotherapy, without subsequent systemic therapy. Eur. Cytokine Netw. 2017, 28, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yang, X. Association between serum cytokines and progression of breast cancer in Chinese population. Medicine (Baltimore) 2017, 96, e8840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Strom, T.; Harrison, L.B.; Giuliano, A.R.; Schell, M.J.; Eschrich, S.A.; Berglund, A.; Fulp, W.; Thapa, R.; Coppola, D.; Kim, S.; et al. Tumour radiosensitivity is associated with immune activation in solid tumours. Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 84, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vidula, N.; Yau, C.; Li, J.; Esserman, L.J.; Rugo, H.S. Receptor activator of nuclear factor kappa B (RANK) expression in primary breast cancer correlates with recurrence-free survival and development of bone metastases in I-SPY1 (CALGB 150007/150012; ACRIN 6657). Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2017, 165, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherer, S.D.; Bauer, J.; Schmaus, A.; Neumaier, C.; Herskind, C.; Veldwijk, M.R.; Wenz, F.; Sleeman, J.P. TGF-β1 Is Present at High Levels in Wound Fluid from Breast Cancer Patients Immediately Post-Surgery, and Is Not Increased by Intraoperative Radiation Therapy (IORT). PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0162221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, M.E.; Meynköhn, A.; Habermann, N.; Wiskemann, J.; Oelmann, J.; Hof, H.; Wessels, S.; Klassen, O.; Debus, J.; Potthoff, K.; et al. Resistance Exercise and Inflammation in Breast Cancer Patients Undergoing Adjuvant Radiation Therapy: Mediation Analysis from a Randomized, Controlled Intervention Trial. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2016, 94, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tudoran, O.; Virtic, O.; Balacescu, L.; Lisencu, C.; Fetica, B.; Gherman, C.; Balacescu, O.; Berindan-Neagoe, I. Baseline blood immunological profiling differentiates between Her2-breast cancer molecular subtypes: Implications for immunomediated mechanisms of treatment response. Onco Targets Ther. 2015, 8, 3415–3423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, N.S.; Floot, B.; van Werkhoven, E.; Schriemer, M.; de Jong-Korlaar, R.; Woerdeman, L.A.; Stewart, F.A.; Scharpfenecker, M. Blood and lymphatic microvessel damage in irradiated human skin: The role of TGF-β, endoglin and macrophages. Radiother. Oncol. 2015, 116, 455–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westbury, C.B.; Haviland, J.; Davies, S.; Gothard, L.; Abdi, B.A.; Sydenham, M.; Bowen, J.; Stratton, R.; Short, S.C.; Yarnold, J.R. Cytokine levels as biomarkers of radiation fibrosis in patients treated with breast radiotherapy. Radiat. Oncol. 2014, 9, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- De Sanctis, V.; Agolli, L.; Visco, V.; Monaco, F.; Muni, R.; Spagnoli, A.; Campanella, B.; Valeriani, M.; Minniti, G.; Osti, M.F.; et al. Cytokines, fatigue, and cutaneous erythema in early stage breast cancer patients receiving adjuvant radiation therapy. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 523568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibayama, O.; Yoshiuchi, K.; Inagaki, M.; Matsuoka, Y.; Yoshikawa, E.; Sugawara, Y.; Akechi, T.; Wada, N.; Imoto, S.; Murakami, K.; et al. Association between adjuvant regional radiotherapy and cognitive function in breast cancer patients treated with conservation therapy. Cancer Med. 2014, 3, 702–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boothe, D.L.; Coplowitz, S.; Greenwood, E.; Barney, C.L.; Christos, P.J.; Parashar, B.; Nori, D.; Chao, K.S.; Wernicke, A.G. Transforming growth factor β-1 (TGF-β1) is a serum biomarker of radiation induced fibrosis in patients treated with intracavitary accelerated partial breast irradiation: Preliminary results of a prospective study. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2013, 87, 1030–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.H.; Zhang, Y.C.; Tan, Y.T.; An, X.; Xue, C.; Deng, Y.F.; Yang, W.; Yuan, X.; Shi, Y.X. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes predict prognosis of breast cancer patients treated with anti-Her-2 therapy. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 5219–5232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciftci, R.; Tas, F.; Yasasever, C.T.; Aksit, E.; Karabulut, S.; Sen, F.; Keskin, S.; Kilic, L.; Yildiz, I.; Bozbey, H.U.; et al. High serum transforming growth factor beta 1 (TGFB1) level predicts better survival in breast cancer. Tumour Biol. 2014, 35, 6941–6948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellevik, T.; Martinez-Zubiaurre, I. Radiotherapy and the tumor stroma: The importance of dose and fractionation. Front. Oncol. 2014, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller, D.; Köhler, G.; Ohlinger, R. Staging procedures in primary breast cancer. Anticancer Res. 2008, 28, 2397–2400. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barajas-Gómez, B.A.; Rosas-Carrasco, O.; Morales-Rosales, S.L.; Pedraza Vázquez, G.; González-Puertos, V.Y.; Juárez-Cedillo, T.; García-Álvarez, J.A.; López-Diazguerrero, N.E.; Damián-Matsumura, P.; Königsberg, M.; et al. Relationship of inflammatory profile of elderly patients serum and senescence-associated secretory phenotype with human breast cancer cells proliferation: Role of IL6/IL8 ratio. Cytokine 2017, 91, 13–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayhan, Z.; Simsek, T.; Ergül, E.; Utkan, N.Z.; Canturk, N.Z.; Cekmen, M. Serum cytokine levels in patients with colorectal cancers according to tumor stages and VEGF gene polymorphism. Hepatogastroenterology 2014, 61, 1889–1894. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chopra, V.; Dinh, T.V.; Hannigan, E.V. Serum levels of interleukins, growth factors and angiogenin in patients with endometrial cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 1997, 123, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koca, Y.S.; Bulbul, M.; Barut, I. The Diagnostic Roles of Cytokines in Hepatobiliary Cancers. Biomed. Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 2979307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, S.A. IL-2: The first effective immunotherapy for human cancer. J. Immunol. 2014, 192, 5451–5458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recchia, F.; Candeloro, G.; Rosselli, M.; Bratta, M.; Pasta, V.; D’Orazi, V.; Fumagalli, L.A.; Rea, S. Adjuvant ovarian suppression, high-dose chemotherapy and immunotherapy for premenopausal patients with high-risk breast cancer. Anticancer Res. 2015, 35, 6847–6854. [Google Scholar]
- Zegers, C.M.L.; Rekers, N.H.; Quaden, D.H.F.; Lieuwes, N.G.; Yaromina, A.; Germeraad, W.T.V.; Wieten, L.; Biessen, E.A.L.; Boon, L.; Neri, D.; et al. Radiotherapy combined with the immunocytokine L19-IL2 provides long-lasting antitumor effects. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 1151–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Z.; Peng, Y.; Cao, L.; Chen, Y.; Li, K.; Fu, B. Correlations between Serum IL-6 Levels and Radiation Pneumonitis in Lung Cancer Patients: A Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2016, 30, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrews, B.; Shariat, S.F.; Kim, J.; Wheeler, T.M.; Slawin, K.M.; Lerner, S.P. Preoperative plasma levels of interleukin-6 and its soluble receptor predict disease recurrence and survival of patients with bladder cancer. J. Urol. 2002, 167, 1475–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanguinete, M.M.M.; Oliveira, P.H.; Martins-Filho, A.; Micheli, D.C.; Tavares-Murta, B.M.; Murta, E.F.C.; Nomelini, R.S. Serum IL-6 and IL-8 Correlate with Prognostic Factors in Ovarian Cancer. Immunol. Investig. 2017, 46, 677–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer, F.; Samson, É.; Douville, P.; Duchesne, T.; Liu, G.; Bairati, I. Serum prognostic markers in head and neck cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 1008–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, D.P.; Li, J.; Tewari, A.K. Inflammation and prostate cancer: The role of interleukin 6 (IL-6). BJU Int. 2014, 113, 986–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siva, S.; MacManus, M.; Kron, T.; Best, N.; Smith, J.; Lobachevsky, P.; Ball, D.; Martin, O. A pattern of early radiation-induced inflammatory cytokine expression is associated with lung toxicity in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.F.; Chen, P.T.; Chen, W.C.; Lu, M.S.; Lin, P.Y.; Lee, K.D. The role of PD-L1 in the radiation response and prognosis for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma related to IL-6 and T-cell immunosuppression. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 7913–7924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, Y.; Ren, Y.; Dai, Z.J.; Wu, C.J.; Ji, Y.H.; Xu, J. IL-6, IL-8 and TNF-a levels correlate with disease stage in breast cancer patients. Adv. Clin. Exp. Med. 2017, 26, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozcuk, H.; Uslu, G.; Samur, M.; Yildiz, M.; Ozben, T.; Ozdogan, M.; Artac, M.; Altunbas, H.; Akan, I.; Savas, B. Tumour necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-6, and fasting serum insulin correlate with clinical outcome in metastatic breast cancer patients treated with chemotherapy. Cytokine 2004, 27, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Chen, L.; Zhang, W.; Liao, Y.; Chen, J.; Shi, Y.; Luo, S. Serum cytokine profile in patients with breast cancer. Cytokine 2017, 89, 173–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Wu, D.; Wu, P.; Wang, Z.; Huang, J. Serum IL-10 predicts worse outcome in cancer patients: A meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0139598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conroy, S.M.; Courneya, K.S.; Brenner, D.R.; Shaw, E.; O’Reilly, R.; Yasui, Y.; Woolcott, C.G.; Friedenreich, C.M. Impact of aerobic exercise on levels of IL-4 and IL-10: Results from two randomized intervention trials. Cancer Med. 2016, 5, 2385–2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dethlefsen, C.; Hojfeldt, G.; Hojman, P. The role of intratumoral and systemic IL-6 in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2013, 138, 657–664. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Xu, F.; Lu, T.; Duan, Z.; Zhang, Z. Interleukin-6 signaling pathway in targeted therapy for cancer. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2012, 38, 904–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Song, N.; Han, S.; Chung, S.; Sung, H.; Lee, J.Y.; Jung, S.; Park, S.K.; Yoo, K.Y.; Han, W.; et al. The associations between immunity-related genes and breast cancer prognosis in Korean women. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, D.E.; O’Keefe, R.A.; Grandis, J.R. Targeting the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 signalling axis in cancer. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 15, 234–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, F.; Anscher, M.S.; Murase, T.; Abbott, B.D.; Iglehart, J.D.; Jirtle, R.L. Elevated plasma transforming growth factor-ß1 levels in breast cancer patients decrease after surgical removal of the tumor. Ann. Surg. 1995, 222, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivanović, V.; Demajo, M.; Krtolica, K.; Krajnović, M.; Konstantinović, M.; Baltić, V.; Prtenjak, G.; Stojiljković, B.; Breberina, M.; Nes, Z.; et al. Elevated plasma TGF-β1 levels correlate with decreased survival of metastatic breast cancer patients. Clin. Chim. Acta 2006, 371, 191–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kajdaniuk, D.; Marek, B.; Kos-Kudla, B.; Buntner, B.; Zwirska-Korczala, K.; Ostrowska, Z.; Nowak, M. Growth hormone and its interactions with chosen parameters of hormonal state in pre-menopausal women after mastectomy for breast cancer on adjuvant chemotherapy. Wiadomosci Lekarskie 2000, 53, 283–288. [Google Scholar]
- Panis, C.; Herrera, A.C.; Victorino, V.J.; Aranome, A.M.F.; Cecchini, R. Screening of circulating tgf-ß levels and its clinicopathological significance in human breast cancer. Anticancer Res. 2013, 33, 737–742. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bryan, J. Interferon was not the miracle cure for cancer hoped for in its early days. Pharm. J. 2008, 280, 637–638. [Google Scholar]
- Gottlöber, P.; Steinert, M.; Bähren, W.; Weber, L.; Gerngross, H.; Peter, R.U. Interferon-gamma in 5 patients with cutaneous radiation syndrome after radiation therapy. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2001, 50, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojic, M.; Takeda, K.; Hayakawa, Y. The dark side of IFN-γ: Its role in promoting cancer immunoevasion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Ref | No. of BC Patients and CTR | Treatment (S, RT, CHT, CRT Combined) | RT TD and d in frs | CHT/HT |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [27] | 73 | Adj RT | 50 Gy and 2 Gy or 42.56 Gy and 2.66 Gy | No |
| [28] | 209 BC + 106 CTR | S, RT, and CHT | Not mentioned | Not mentioned |
| [29] | 21 oligometastatic BC + 14 healthy donors | SBRT | 30 Gy and 10 Gy | Concomitant CHT/HT and trastuzumab |
| [30] | 73 | S + RT | Not mentioned | No |
| [31] | 534 BC (treated) and 452 CTR | RT (66.7%); RT + CHT (33.3%) | 50–74 Gy and 1.8–2.0 Gy | 1 to 6 cycles of platinum-based CHT |
| [32] | 282 | S and post-operative RT | 40–74 Gy and 1.8–2 Gy | No adjuvant systemic therapy (i.e., CHT or HT) |
| [33] | 149 | Post S treatment including additional CHT, HT, or RT was determined by the individual treating physician | In 128 pts (50 Gy and 2 Gy) | 4 cycles of anthracycline based neo-adj CHT with or without taxane (given before or after the anthracycline) followed by S. Trastuzumab to patients with Her-2 amplified disease |
| [34] | 11 (treated) and 12 CTR | IORT | 20 Gy and 20 Gy | No |
| [35] | 103 | Adj RT | 50 Gy and 2 Gy | 55% of patients received HT |
| [36] | 40 | Not mentioned | Not mentioned | Steroids, CHT, or S |
| [37] | 40 (treated) and 8 CTR | CHT yes/no: 30/18 | 50 Gy (45–76) and 2–2.5 Gy | Bisphosphonate treatment |
| [38] | 26 cases and 44 CTR | S and RT | 50 Gy in 25 frs; 41 Gy in 13 frs or 39 Gy in 13 frs, boost 10 Gy in 4 frs | Tamoxifen yes/no: 61/9 Adj; CHT yes/no: 22/48 |
| [39] | 40 (treated) and 10 healthy donors | RT | 50 Gy in 25 frs; 50 Gy in 25 frs + boost of 10 Gy in 4 frs | No |
| [40] | 51 (treated) and 54 CTR | S + adj RT | 50 Gy and 2 Gy | No |
| [41] | 38 | Intracavitary brachytherapy accelerated hypofractionated partial breast irradiation (IBAPBI) | 34.0 Gy in 10 frs and 3.4 Gy twice per day (with a minimum of 6 hours between each treatment, for a total of 5 treatment days) | No |
| Ref | Sample Type | Sampling Timepoints | Cytokines | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| [27] | Blood | Before RT and on the last day of RT | TGF-β1 and PDGF-AB | TGF-β1 and PDGF levels decreased significantly during RT |
| [28] | Blood | From 6 and 18 months after treatment | IL-6, TGF-α, IL-1β | There were no significant baseline differences between survivors and the CTR group in LPS-stimulated TNF-α, IL-6, or IL-1b cytokines, or in the cytokine z score. There were significant differences in the trajectories of stimulated cytokines over time by treatment group with survivors treated with a combination of surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy having the highest increases in stimulated cytokines |
| [29] | Blood and serum | Before and after RT (24 h, 1 and 4 months after RT) | IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, and TNF-α | Compared to controls: increased IL-6; lower IL-8 at baseline increases during SBRT reaching level similar to those of controls; no differences, IL-10, IL-1β, and TNF-α not detectable |
| [30] | Specimen | During resection | Intratumoral IFN-γ mRNA and protein levels | No association with metastasis |
| [31] | Serum | Before and 1 month after treatment | IL-6, IL-8, IL-10, SCC-Ag, and CYFRA 21-1 | Potential markers in the metastasis and BC prognosis |
| [32] | Specimen | During resection | CCL2, CCL3, CCL4, CCL5, CCL8, CCL18, CCL19, CCL21, CXCL9, CXCL10, CXCL11 and CXCL13 | Radiosensitivity and immune activation |
| [33] | Biopsy | Pre-treatment only | RANK/RANK ligand RANK/OPG axis | RANK is increased in Her-2 negative and basal BC, and correlates with worse recurrence, free survival, and risk of bone metastases |
| [34] | Surnatant from S wound fluid | 24 h after IORT | TGF-β1 | Invariant after IORT |
| [35] | Serum | Before, at the end (week 7) and 6 weeks after RT | IL-6, IL-1ra1RA | In the CTR group, IL-6 increased at the end of RT and decreased 6 weeks after RT. IL-6 was invariant in patients performing exercise. IL-1ra was similar in both groups and increased only slightly after RT |
| [36] | Blood | From 8 am to 12 noon at 4-hour intervals before any treatment | IL-10RB, IFNA2, CXCL13, IL-17C, IL-17F, IL-13, CCL26, CSF2, IL-3, OSM, IL-1A, IL-16, IL-5RA, TNFSF13 | All but three genes were downregulated in the blood of triple-negative BC patients. The most downregulated cytokines were IL-17C and IL-17F, IL-17C, better known as IL-21 |
| [37] | Skin biopsy | From 0, 7, to 21 years after RT. | TGF-β1 | Alterations in blood and lymphatic vessel are correlated with changes in TGF-β1 and endoglin levels, and with macrophage infiltration. Bisphosphonate treatment impaired leucocyte influx, but also negatively affected neovessel formation |
| [38] | Serum | From 8.3 up to 12 years (mean 9.9 years) | IL-6 and CTGF | No correlation between IL-6 and age. No correlation between cytokines and RT or fibrosis |
| [39] | Plasma | Baseline, weekly, 3 and 6 months post-treatment | IL-1β, IL-2, IL-6, IL-8, TNF-α, MCP-1, IL-10, VEGF, EGF, INF-β | IL-1b, Il-2, IL-6, and TNFα were increased 4 weeks after RT. |
| [40] | Plasma | 1 year after RT | IL-6 | Elevation of plasma IL-6 levels in patients 1 year post-RT |
| [41] | Serum | Serum was drawn before S before, 1 month after RT, and every subsequent 6 months for 2 years | TGF-β1 | Elevated TGF-β1 levels in patients with moderate to severe radiation-induced fibrosis (RIF) compared with those who experienced none to mild RIF. This elevation was transiently eliminated after surgery and before IBAPBI, but once again it became significant during IBAPBI and persisted at 6 months, 12 months, 18 months, and 24 months |
| Ref | No. of BC Patients and CTR | Treatment (S, RT, CHT, CRT, Combined) | RT TD and d in frs | CHT/HT | Sample Type | Sampling Timepoints | Cytokines | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [42] | 98 | Anti-Her-2 therapy (trastuzumab) | None | No | Biopsy | During resection | FOXP3 | Associated with OS |
| [43] | 96 BC + 30 healthy donors as CTR | Standard treatments after sampling | None | No | Serum | Before any treatment | TGF-β1 | TGF-β1 levels statistically significant and higher in BC patients than in CTR |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Marconi, R.; Serafini, A.; Giovanetti, A.; Bartoleschi, C.; Pardini, M.C.; Bossi, G.; Strigari, L. Cytokine Modulation in Breast Cancer Patients Undergoing Radiotherapy: A Revision of the Most Recent Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20020382
Marconi R, Serafini A, Giovanetti A, Bartoleschi C, Pardini MC, Bossi G, Strigari L. Cytokine Modulation in Breast Cancer Patients Undergoing Radiotherapy: A Revision of the Most Recent Studies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(2):382. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20020382
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarconi, Raffaella, Annalisa Serafini, Anna Giovanetti, Cecilia Bartoleschi, Maria Chiara Pardini, Gianluca Bossi, and Lidia Strigari. 2019. "Cytokine Modulation in Breast Cancer Patients Undergoing Radiotherapy: A Revision of the Most Recent Studies" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 2: 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20020382
APA StyleMarconi, R., Serafini, A., Giovanetti, A., Bartoleschi, C., Pardini, M. C., Bossi, G., & Strigari, L. (2019). Cytokine Modulation in Breast Cancer Patients Undergoing Radiotherapy: A Revision of the Most Recent Studies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(2), 382. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20020382