Syndecan-4 Inhibits the Development of Pulmonary Fibrosis by Attenuating TGF-β Signaling
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Time Course of Syndecan-4 Expression in Lung Tissues
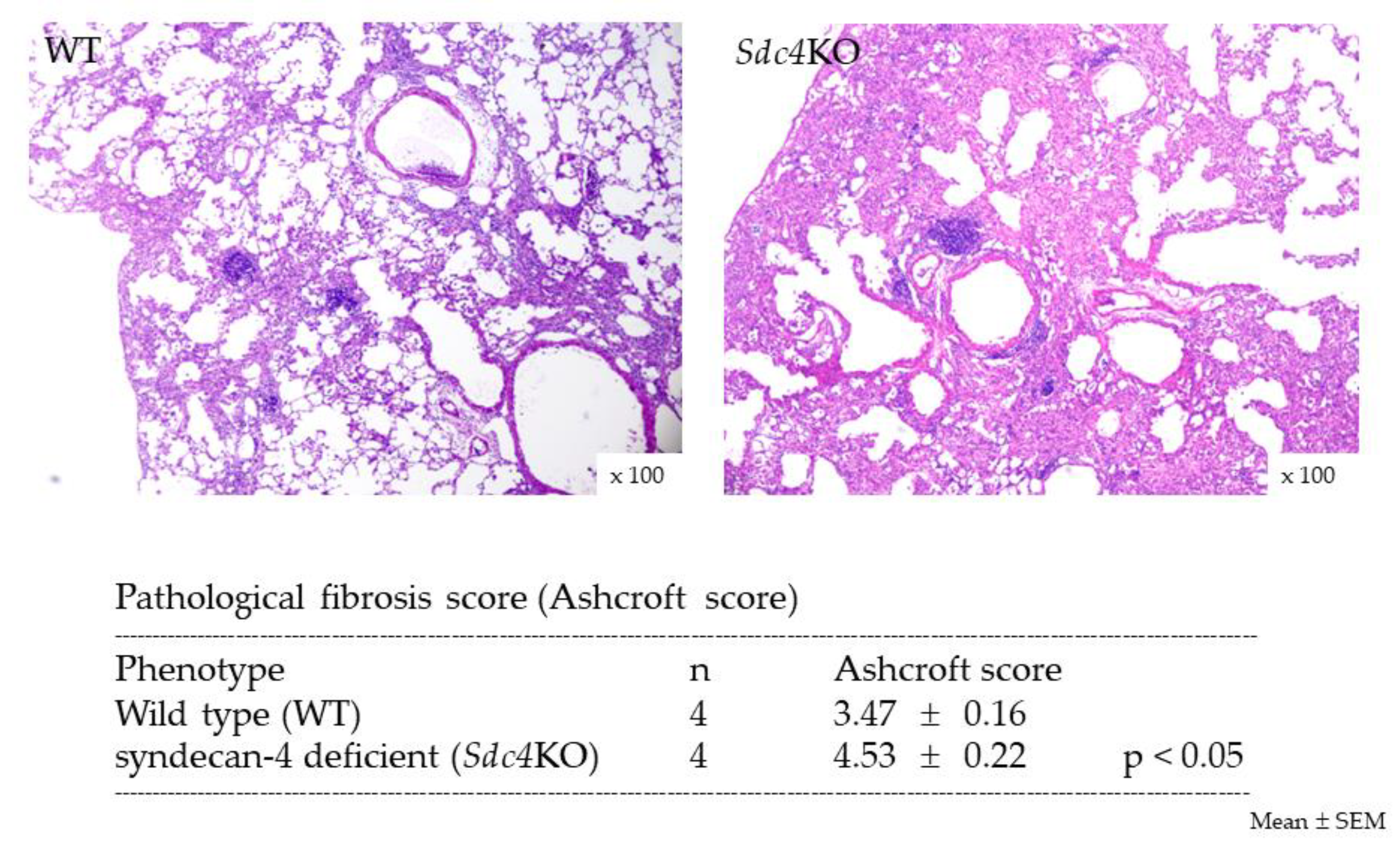
2.2. Pulmonary Fibrosis in Syndecan-4 Deficient Mice
2.3. Bronchoalveolar Lavage Findings in Syndecan-4 Deficient Mice
2.4. TGF-β Expression in Syndecan-4 Deficient Mice
2.5. Effect of Syndecan-4 on TGF-β-induced Upregulation of Collagen and α-SMA in Lung Fibroblasts
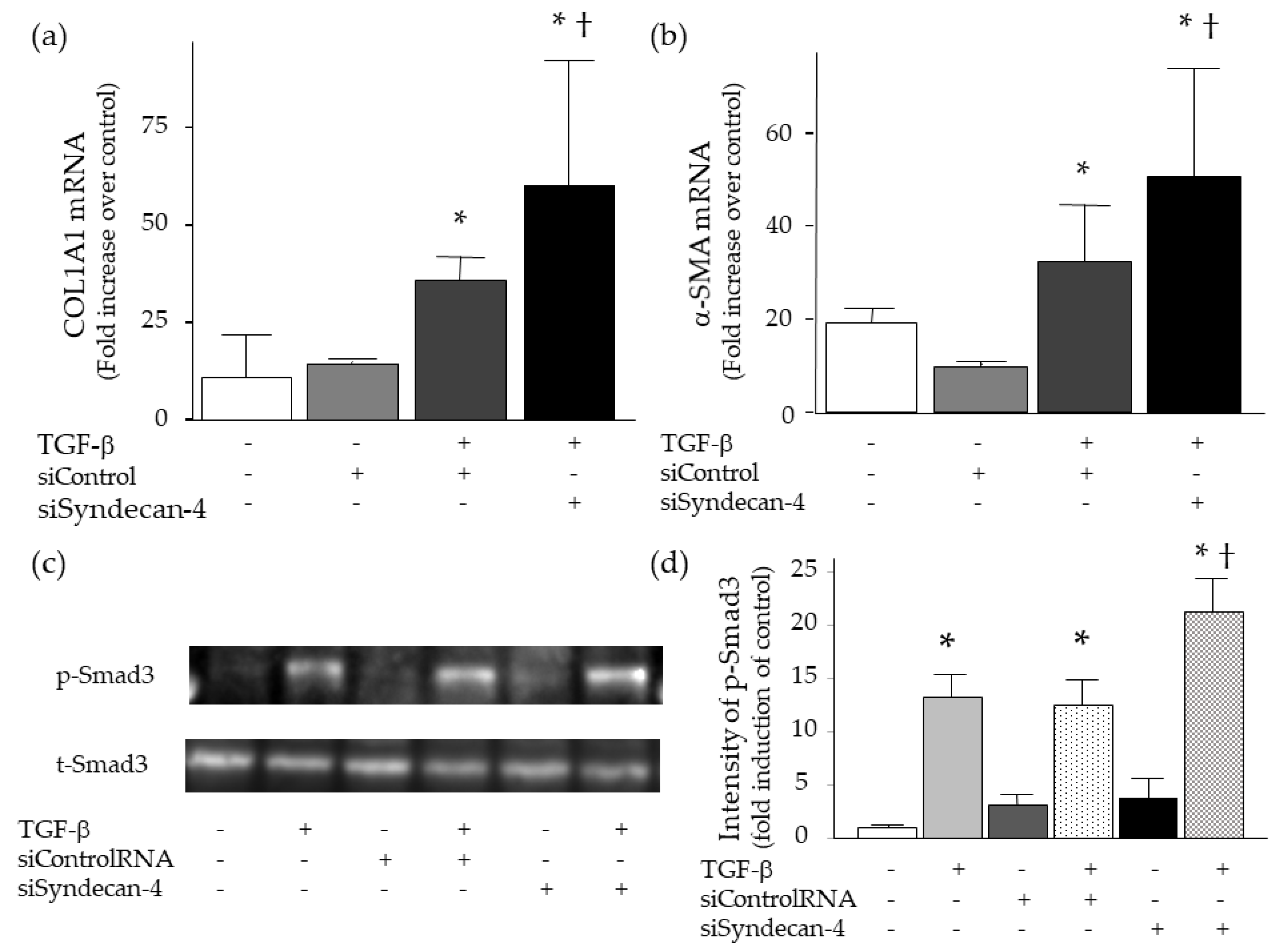
2.6. Effect of Syndecan-4 Knock-Down on TGF-β-Induced Upregulation of Collagen and α-SMA in Lung Fibroblasts
2.7. Binding of TGF-β to Syndecan-4
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Animal Protocols
4.3. Time Course of Syndecan-4 Expression
4.4. Isolation of RNA
4.5. Measurement of mRNA
4.6. Measurement of Collagen Content
4.7. Pathological Evaluation of Lung Sections
4.8. Measurement of TGF-β
4.9. Measurement of Phosphorylated SMAD3
4.10. Cell Culture
4.11. Knock-Down of Syndecan-4
4.12. Western Blot Analysis
4.13. In Vitro Binding Assay
4.14. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Natsuizaka, M.; Chiba, H.; Kuronuma, K.; Otsuka, M.; Kudo, K.; Mori, M.; Bando, M.; Sugiyama, Y.; Takahashi, H. Epidemiologic survey of Japanese patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and investigation of ethnic differences. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 190, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomos, I.P.; Tzouvelekis, A.; Aidinis, V.; Manali, E.D.; Bouros, E.; Bouros, D.; Papiris, S.A. Extracellular matrix remodeling in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. It is the ‘bed’ that counts and not ‘the sleepers’. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2017, 11, 299–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frey, H.; Schroeder, N.; Manon-Jensen, T.; Iozzo, R.V.; Schaefer, L. Biological interplay between proteoglycans and their innate immune receptors in inflammation. Febs. J. 2013, 280, 2165–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, S.; Wight, T.N.; Frevert, C.W. Proteoglycans: key regulators of pulmonary inflammation and the innate immune response to lung infection. Anat. Rec. (Hoboken) 2010, 293, 968–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iozzo, R.V.; Schaefer, L. Proteoglycan form and function: A comprehensive nomenclature of proteoglycans. Matrix Biol. 2015, 42, 11–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanino, Y.; Chang, M.Y.; Wang, X.; Gill, S.E.; Skerrett, S.; McGuire, J.K.; Sato, S.; Nikaido, T.; Kojima, T.; Munakata, M.; et al. Syndecan-4 regulates early neutrophil migration and pulmonary inflammation in response to lipopolysaccharide. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2012, 47, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, J.R.; Schuksz, M.; Esko, J.D. Heparan sulphate proteoglycans fine-tune mammalian physiology. Nature 2007, 446, 1030–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, I.; Chang, M.Y.; Wight, T.N.; Frevert, C.W. Proteoglycans as Immunomodulators of the Innate Immune Response to Lung Infection. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2018, 66, 241–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parish, C.R. The role of heparan sulphate in inflammation. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 6, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agere, S.A.; Kim, E.Y.; Akhtar, N.; Ahmed, S. Syndecans in chronic inflammatory and autoimmune diseases: pathological insights and therapeutic opportunities. J. Cell. Physiol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gotte, M. Syndecans in inflammation. FASEB J. 2003, 17, 575–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikaido, T.; Tanino, Y.; Sato, Y.; Togawa, R.; Wang, X.; Shibata, Y. Syndecans in pulmonary diseases. In Advances in Medicine and Biology; Berhardt, L.V., Ed.; Nova Science Publishers, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2019; Volume 138, pp. 171–193. [Google Scholar]
- Brule, S.; Charnaux, N.; Sutton, A.; Ledoux, D.; Chaigneau, T.; Saffar, L.; Gattegno, L. The shedding of syndecan-4 and syndecan-1 from HeLa cells and human primary macrophages is accelerated by SDF-1/CXCL12 and mediated by the matrix metalloproteinase-9. Glycobiology 2006, 16, 488–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipphardt, M.; Song, J.W.; Ratliff, B.B.; Dihazi, H.; Muller, G.A.; Goligorsky, M.S. Endothelial dysfunction is a superinducer of syndecan-4: fibrogenic role of its ectodomain. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2018, 314, H484–H496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pruessmeyer, J.; Martin, C.; Hess, F.M.; Schwarz, N.; Schmidt, S.; Kogel, T.; Hoettecke, N.; Schmidt, B.; Sechi, A.; Uhlig, S.; et al. A disintegrin and metalloproteinase 17 (ADAM17) mediates inflammation-induced shedding of syndecan-1 and -4 by lung epithelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 555–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramnath, R.; Foster, R.R.; Qiu, Y.; Cope, G.; Butler, M.J.; Salmon, A.H.; Mathieson, P.W.; Coward, R.J.; Welsh, G.I.; Satchell, S.C. Matrix metalloproteinase 9-mediated shedding of syndecan 4 in response to tumor necrosis factor alpha: a contributor to endothelial cell glycocalyx dysfunction. FASEB J. 2014, 28, 4686–4699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikaido, T.; Tanino, Y.; Wang, X.; Sato, S.; Misa, K.; Fukuhara, N.; Sato, Y.; Fukuhara, A.; Uematsu, M.; Suzuki, Y.; et al. Serum Syndecan-4 as a Possible Biomarker in Patients With Acute Pneumonia. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 212, 1500–1508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishiguro, K.; Kadomatsu, K.; Kojima, T.; Muramatsu, H.; Iwase, M.; Yoshikai, Y.; Yanada, M.; Yamamoto, K.; Matsushita, T.; Nishimura, M.; et al. Syndecan-4 deficiency leads to high mortality of lipopolysaccharide-injected mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 47483–47488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kon, S.; Ikesue, M.; Kimura, C.; Aoki, M.; Nakayama, Y.; Saito, Y.; Kurotaki, D.; Diao, H.; Matsui, Y.; Segawa, T.; et al. Syndecan-4 protects against osteopontin-mediated acute hepatic injury by masking functional domains of osteopontin. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishiguro, K.; Kadomatsu, K.; Kojima, T.; Muramatsu, H.; Matsuo, S.; Kusugami, K.; Saito, H.; Muramatsu, T. Syndecan-4 deficiency increases susceptibility to kappa-carrageenan-induced renal damage. Lab. Invest. 2001, 81, 509–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Li, G.; Xie, J.; Chen, J.; Li, R.; Wu, H.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Q.; Gu, R.; Xu, B. Syndecan-4 deficiency accelerates the transition from compensated hypertrophy to heart failure following pressure overload. Cardiovasc. Pathol. 2017, 28, 74–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Zhang, J.; Lin, H.; Li, Z.; Sun, X.; Xin, D.; Yang, M.; Sun, L.; Li, L.; Wang, H.; et al. Syndecan-4 negatively regulates antiviral signalling by mediating RIG-I deubiquitination via CYLD. Nat Commun 2016, 7, 11848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, Y.; Tanino, Y.; Wang, X.; Nikaido, T.; Sato, S.; Misa, K.; Togawa, R.; Frevert, C.W.; Munakata, M. Baseline serum syndecan-4 predicts prognosis after the onset of acute exacerbation of idiopathic interstitial pneumonia. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0176789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, D.; Liang, J.; Campanella, G.S.; Guo, R.; Yu, S.; Xie, T.; Liu, N.; Jung, Y.; Homer, R.; Meltzer, E.B.; et al. Inhibition of pulmonary fibrosis in mice by CXCL10 requires glycosaminoglycan binding and syndecan-4. J. Clin. Invest. 2010, 120, 2049–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoso, A.; Kikuchi, T.; Tode, N.; Hirano, T.; Komatsu, R.; Damayanti, T.; Motohashi, H.; Yamamoto, M.; Kojima, T.; Uede, T.; et al. Syndecan 4 Mediates Nrf2-dependent Expansion of Bronchiolar Progenitors That Protect Against Lung Inflammation. Mol. Ther. 2016, 24, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Shi-Wen, X.; van Beek, J.; Kennedy, L.; McLeod, M.; Renzoni, E.A.; Bou-Gharios, G.; Wilcox-Adelman, S.; Goetinck, P.F.; Eastwood, M.; et al. Matrix contraction by dermal fibroblasts requires transforming growth factor-beta/activin-linked kinase 5, heparan sulfate-containing proteoglycans, and MEK/ERK: insights into pathological scarring in chronic fibrotic disease. Am. J. Pathol. 2005, 167, 1699–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevikbas, F.; Schaefer, L.; Uhlig, P.; Robenek, H.; Theilmeier, G.; Echtermeyer, F.; Bruckner, P. Unilateral nephrectomy leads to up-regulation of syndecan-2- and TGF-beta-mediated glomerulosclerosis in syndecan-4 deficient male mice. Matrix Biol. 2008, 27, 42–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarpellini, A.; Huang, L.; Burhan, I.; Schroeder, N.; Funck, M.; Johnson, T.S.; Verderio, E.A. Syndecan-4 knockout leads to reduced extracellular transglutaminase-2 and protects against tubulointerstitial fibrosis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014, 25, 1013–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Wang, J.; Li, R.; Dai, Q.; Yong, Y.; Zong, B.; Xu, Y.; Li, E.; Ferro, A.; Xu, B. Syndecan-4 over-expression preserves cardiac function in a rat model of myocardial infarction. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2012, 53, 250–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herum, K.M.; Lunde, I.G.; Skrbic, B.; Florholmen, G.; Behmen, D.; Sjaastad, I.; Carlson, C.R.; Gomez, M.F.; Christensen, G. Syndecan-4 signaling via NFAT regulates extracellular matrix production and cardiac myofibroblast differentiation in response to mechanical stress. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2013, 54, 73–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kliment, C.R.; Englert, J.M.; Gochuico, B.R.; Yu, G.; Kaminski, N.; Rosas, I.; Oury, T.D. Oxidative stress alters syndecan-1 distribution in lungs with pulmonary fibrosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 3537–3545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Klass, C.; Woods, A. Syndecan-2 regulates transforming growth factor-beta signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 15715–15718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, X.D.; Mlakar, L.R.; Yamaguchi, Y.; Su, Y.; Larregina, A.T.; Pilewski, J.M.; Feghali-Bostwick, C.A. Syndecan-2 is a novel target of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-3 and is over-expressed in fibrosis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e43049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mytilinaiou, M.; Bano, A.; Nikitovic, D.; Berdiaki, A.; Voudouri, K.; Kalogeraki, A.; Karamanos, N.K.; Tzanakakis, G.N. Syndecan-2 is a key regulator of transforming growth factor beta 2/Smad2-mediated adhesion in fibrosarcoma cells. IUBMB Life 2013, 65, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, S.; Majid, M.; Baker, A.B. Syndecan-4 enhances PDGF-BB activity in diabetic wound healing. Acta Biomater 2016, 42, 56–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toba-Ichihashi, Y.; Yamaoka, T.; Ohmori, T.; Ohba, M. Up-regulation of Syndecan-4 contributes to TGF-beta1-induced epithelial to mesenchymal transition in lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells. Biochem. Biophys. Rep. 2016, 5, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yue, X.; Li, X.; Nguyen, H.T.; Chin, D.R.; Sullivan, D.E.; Lasky, J.A. Transforming growth factor-beta1 induces heparan sulfate 6-O-endosulfatase 1 expression in vitro and in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 20397–20407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, X.; Lu, J.; Auduong, L.; Sides, M.D.; Lasky, J.A. Overexpression of Sulf2 in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Glycobiology 2013, 23, 709–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Luo, F.; Chen, C.; Chen, X.; Wu, M. Killing two birds with one stone: dual blockade of integrin and FGF signaling through targeting syndecan-4 in postoperative capsular opacification. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Auduong, L.; White, E.S.; Yue, X. Up-regulation of heparan sulfate 6-O-sulfation in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2014, 50, 106–114. [Google Scholar]
- Haeger, S.M.; Yang, Y.; Schmidt, E.P. Heparan Sulfate in the Developing, Healthy, and Injured Lung. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2016, 55, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanino, Y.; Makita, H.; Miyamoto, K.; Betsuyaku, T.; Ohtsuka, Y.; Nishihira, J.; Nishimura, M. Role of macrophage migration inhibitory factor in bleomycin-induced lung injury and fibrosis in mice. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2002, 283, L156–L162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, W.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Choi, S.I.; Kim, B.K.; Lee, E.J.; In, K.H.; Lee, M.G. Toll-like receptor expression in pulmonary sensory neurons in the bleomycin-induced fibrosis model. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashcroft, T.; Simpson, J.M.; Timbrell, V. Simple method of estimating severity of pulmonary fibrosis on a numerical scale. J. Clin. Pathol. 1988, 41, 467–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tanino, Y.; Wang, X.; Nikaido, T.; Misa, K.; Sato, Y.; Togawa, R.; Kawamata, T.; Kikuchi, M.; Frevert, C.W.; Tanino, M.; et al. Syndecan-4 Inhibits the Development of Pulmonary Fibrosis by Attenuating TGF-β Signaling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4989. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20204989
Tanino Y, Wang X, Nikaido T, Misa K, Sato Y, Togawa R, Kawamata T, Kikuchi M, Frevert CW, Tanino M, et al. Syndecan-4 Inhibits the Development of Pulmonary Fibrosis by Attenuating TGF-β Signaling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(20):4989. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20204989
Chicago/Turabian StyleTanino, Yoshinori, Xintao Wang, Takefumi Nikaido, Kenichi Misa, Yuki Sato, Ryuichi Togawa, Takaya Kawamata, Masami Kikuchi, Charles W. Frevert, Mishie Tanino, and et al. 2019. "Syndecan-4 Inhibits the Development of Pulmonary Fibrosis by Attenuating TGF-β Signaling" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 20: 4989. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20204989
APA StyleTanino, Y., Wang, X., Nikaido, T., Misa, K., Sato, Y., Togawa, R., Kawamata, T., Kikuchi, M., Frevert, C. W., Tanino, M., Kojima, T., & Shibata, Y. (2019). Syndecan-4 Inhibits the Development of Pulmonary Fibrosis by Attenuating TGF-β Signaling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(20), 4989. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20204989




