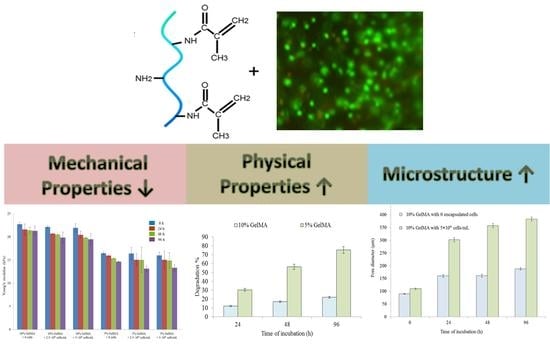
Effects of Encapsulated Cells on the Physical–Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Gelatin Methacrylate Hydrogels
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
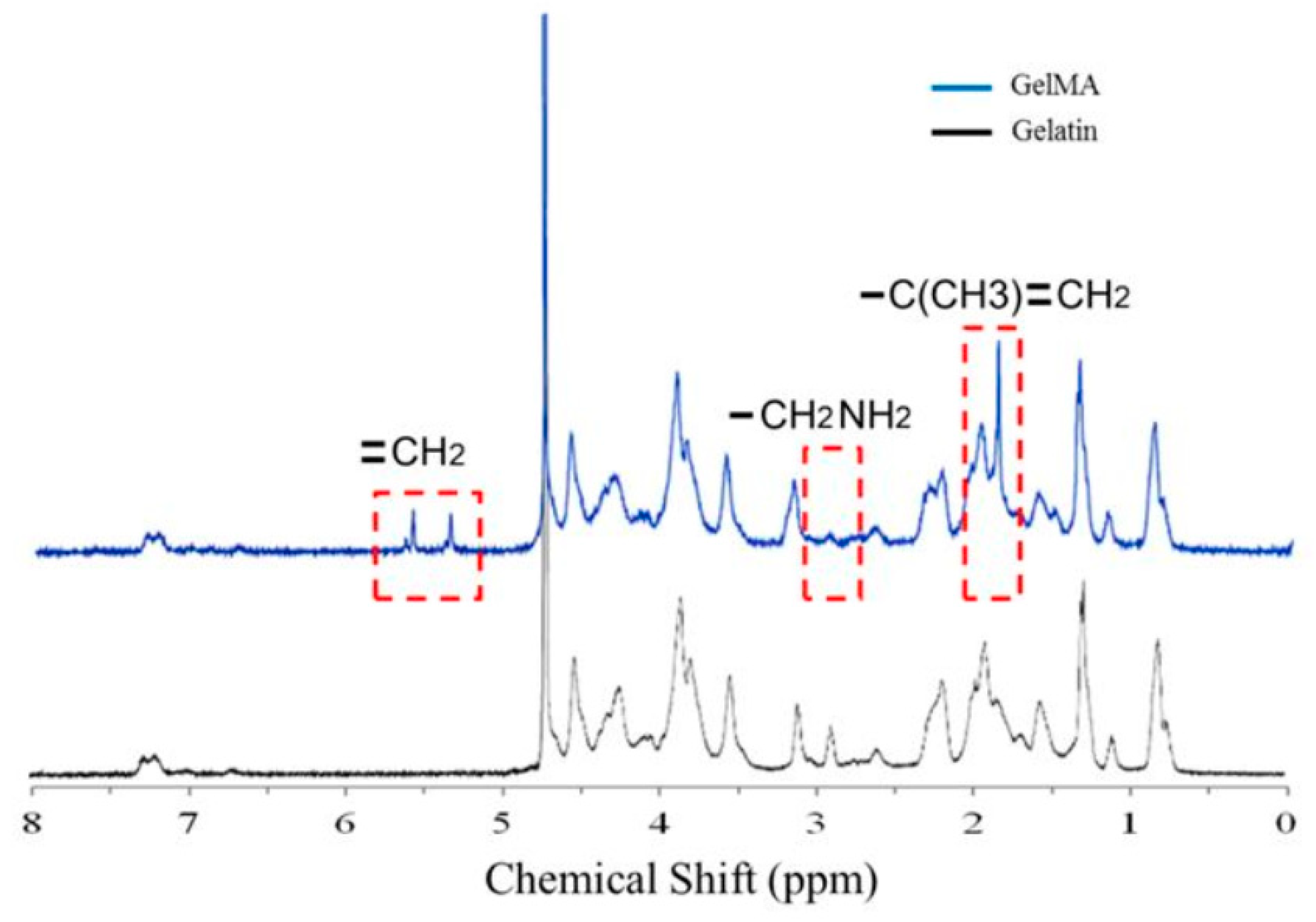
2.1. Characterization of GelMA Functionalization
2.2. Mechanical Properties
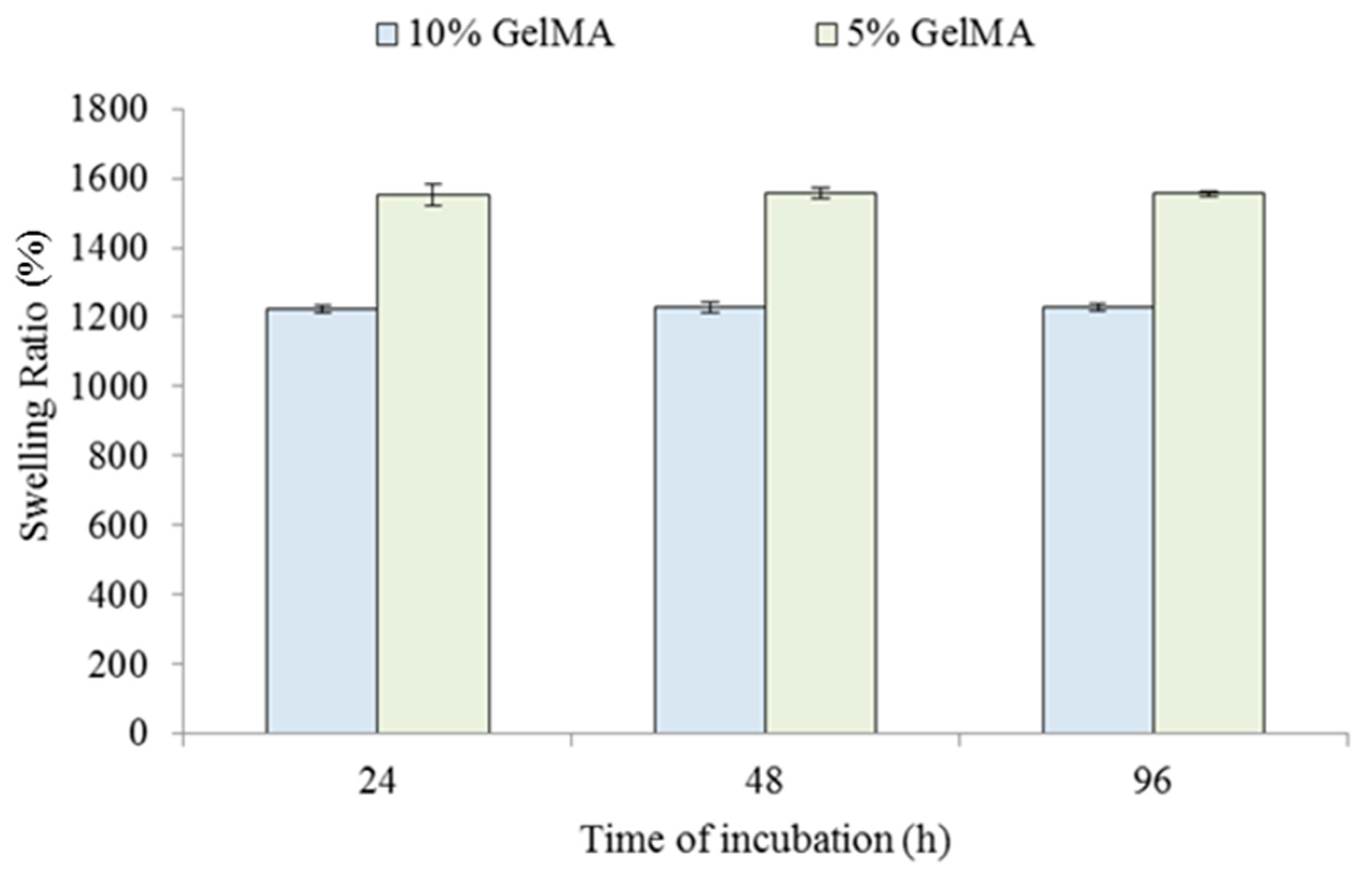
2.3. Physical Properties
2.4. Microstructure
2.5. Cell Viability
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Methods
3.2.1. Mechanical Property Measurement
3.2.2. Physical Property Measurement
3.2.3. Pore Size Measurement
3.2.4. Cell Viability Assessment
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle’s Medium |
| DPBS | Dulbecco’s phosphate-buffered saline |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| GelMA | Gelatin methacrylate |
| UV | Ultraviolet |
References
- Zhang, Z.; Jin, Y.; Yin, J.; Xu, C.; Xiong, R.; Christensen, K.; Ringeisen, B.R.; Chrisey, D.B.; Huang, Y. Evaluation of bioink printability for bioprinting applications. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2018, 5, 041304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drury, J.L.; Mooney, D.J. Hydrogels for tissue engineering: Scaffold design variables and applications. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 4337–4351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Xu, C. Predictive Modeling of Droplet Formation Processes in Inkjet-Based Bioprinting. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2018, 140, 101007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamoorthy, S.; Zhang, Z.; Xu, C. Biofabrication of 3D cellular structures based on GelMA-alginate interpenetrating network hydrogel. J. Biomater. Appl. 2019, 33, 1005–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nichol, J.W.; Koshy, S.T.; Bae, H.; Hwang, C.M.; Yamanlar, S.; Khademhosseini, A. Cell-laden microengineered gelatin methacrylate hydrogels. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 5536–5544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyvis, T.; De Smedt, S.; Demeester, J.; Hennink, W. Influence of the degradation mechanism of hydrogels on their elastic and swelling properties during degradation. Macromolecules 2000, 33, 4717–4725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicodemus, G.D.; Bryant, S.J. Cell encapsulation in biodegradable hydrogels for tissue engineering applications. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2008, 14, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.Y.; Mooney, D.J. Hydrogels for tissue engineering. Chem. Rev. 2001, 101, 1869–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, C.M.; Sant, S.; Masaeli, M.; Kachouie, N.N.; Zamanian, B.; Lee, S.-H.; Khademhosseini, A. Fabrication of three-dimensional porous cell-laden hydrogel for tissue engineering. Biofabrication 2010, 2, 035003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiele, J.; Ma, Y.; Bruekers, S.M.; Ma, S.; Huck, W.T. 25th anniversary article: Designer hydrogels for cell cultures: A materials selection guide. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 125–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeltinger, J.; Sherwood, J.K.; Graham, D.A.; Müeller, R.; Griffith, L.G. Effect of pore size and void fraction on cellular adhesion, proliferation, and matrix deposition. Tissue Eng. 2001, 7, 557–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Lang, Q.; Yildirimer, L.; Lin, Z.Y.; Cui, W.; Annabi, N.; Ng, K.W.; Dokmeci, M.R.; Ghaemmaghami, A.M.; Khademhosseini, A. Photocrosslinkable gelatin hydrogel for epidermal tissue engineering. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2016, 5, 108–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikkhah, M.; Eshak, N.; Zorlutuna, P.; Annabi, N.; Castello, M.; Kim, K.; Dolatshahi-Pirouz, A.; Edalat, F.; Bae, H.; Yang, Y. Directed endothelial cell morphogenesis in micropatterned gelatin methacrylate hydrogels. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 9009–9018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutter, M.; Siepmann, J.; Hennink, W.E.; Jiskoot, W. Recombinant gelatin hydrogels for the sustained release of proteins. J. Control. Release 2007, 119, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Den Bulcke, A.I.; Bogdanov, B.; De Rooze, N.; Schacht, E.H.; Cornelissen, M.; Berghmans, H. Structural and Rheological Properties of Methacrylamide Modified Gelatin Hydrogels. Biomacromolecules 2000, 1, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.C.; Lin, R.Z.; Qi, H.; Yang, Y.; Bae, H.; Melero-Martin, J.M.; Khademhosseini, A. Functional human vascular network generated in photocrosslinkable gelatin methacrylate hydrogels. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 2027–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuurman, W.; Levett, P.A.; Pot, M.W.; van Weeren, P.R.; Dhert, W.J.; Hutmacher, D.W.; Melchels, F.P.; Klein, T.J.; Malda, J. Gelatin-methacrylamide hydrogels as potential biomaterials for fabrication of tissue-engineered cartilage constructs. Macromol. Biosci. 2013, 13, 551–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klotz, B.J.; Gawlitta, D.; Rosenberg, A.J.; Malda, J.; Melchels, F.P. Gelatin-methacryloyl hydrogels: Towards biofabrication-based tissue repair. Trends Biotechnol. 2016, 34, 394–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colosi, C.; Shin, S.R.; Manoharan, V.; Massa, S.; Costantini, M.; Barbetta, A.; Dokmeci, M.R.; Dentini, M.; Khademhosseini, A. Microfluidic Bioprinting of Heterogeneous 3D Tissue Constructs Using Low-Viscosity Bioink. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, K.; Trujillo-de Santiago, G.; Alvarez, M.M.; Tamayol, A.; Annabi, N.; Khademhosseini, A. Synthesis, properties, and biomedical applications of gelatin methacryloyl (GelMA) hydrogels. Biomaterials 2015, 73, 254–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoch, E.; Schuh, C.; Hirth, T.; Tovar, G.E.; Borchers, K. Stiff gelatin hydrogels can be photo-chemically synthesized from low viscous gelatin solutions using molecularly functionalized gelatin with a high degree of methacrylation. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2012, 23, 2607–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, K.; Li, X.; Schrobback, K.; Sheikhi, A.; Annabi, N.; Leijten, J.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.S.; Hutmacher, D.W.; Klein, T.J.; et al. Structural analysis of photocrosslinkable methacryloyl-modified protein derivatives. Biomaterials 2017, 139, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Chen, S.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Kawazoe, N.; Chen, G. 3D culture of chondrocytes in gelatin hydrogels with different stiffness. Polymers 2016, 8, 269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pepelanova, I.; Kruppa, K.; Scheper, T.; Lavrentieva, A. Gelatin-Methacryloyl (GelMA) hydrogels with defined degree of functionalization as a versatile toolkit for 3D cell culture and extrusion bioprinting. Bioengineering 2018, 5, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.; Friis, E.A.; Gehrke, S.H.; Detamore, M.S. Mechanical testing of hydrogels in cartilage tissue engineering: Beyond the compressive modulus. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2013, 19, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Chai, W.; Huang, Y.; Markwald, R.R. Scaffold-free inkjet printing of three-dimensional zigzag cellular tubes. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2012, 109, 3152–3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Christensen, K.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, Y.; Fu, J.; Markwald, R.R. Predictive compensation-enabled horizontal inkjet printing of alginate tubular constructs. Manuf. Lett. 2013, 1, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Christensen, K.; Huang, Y.; Fu, J.; Markwald, R.R. Freeform vertical and horizontal fabrication of alginate-based vascular-like tubular constructs using inkjetting. J. Manuf. Sci. Eng. 2014, 136, 061020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, A.; Memic, A.; Annabi, N.; Hossain, M.; Paul, A.; Dokmeci, M.R.; Dehghani, F.; Khademhosseini, A. Electrospun scaffolds for tissue engineering of vascular grafts. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 11–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takai, E.; Costa, K.D.; Shaheen, A.; Hung, C.T.; Guo, X.E. Osteoblast elastic modulus measured by atomic force microscopy is substrate dependent. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2005, 33, 963–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mauck, R.; Wang, C.-B.; Oswald, E.; Ateshian, G.; Hung, C. The role of cell seeding density and nutrient supply for articular cartilage tissue engineering with deformational loading. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2003, 11, 879–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cha, C.; Liechty, W.B.; Khademhosseini, A.; Peppas, N.A. Designing biomaterials to direct stem cell fate. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 9353–9358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hjortnaes, J.; Camci-Unal, G.; Hutcheson, J.D.; Jung, S.M.; Schoen, F.J.; Kluin, J.; Aikawa, E.; Khademhosseini, A. Directing valvular interstitial cell myofibroblast-like differentiation in a hybrid hydrogel platform. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2015, 4, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, C.; Zhuang, X.; He, P.; Xiao, C.; He, C.; Sun, J.; Chen, X.; Jing, X. Synthesis of biodegradable thermo-and pH-responsive hydrogels for controlled drug release. Polymer 2009, 50, 4308–4316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, J.; Yan, M.; Wang, Y.; Fu, J.; Suo, H. 3D Bioprinting of Low-Concentration Cell-Laden Gelatin Methacrylate (GelMA) Bioinks with a Two-Step Cross-linking Strategy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 6849–6857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peak, C.W.; Wilker, J.J.; Schmidt, G. A review on tough and sticky hydrogels. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2013, 291, 2031–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| GelMA Concentration (w/v) | Cell Density (× 106 cells/mL) | Maximum Strain (%) at 0 h | Tensile Strength (MPa) at 0 h | Maximum Strain (%) at 96 h | Tensile Strength (MPa) at 96 h |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5% | 0 | 23 | 0.028 | 11 | 0.001 |
| 2.5 | 22 | 0.027 | 9 | 0.0007 | |
| 5 | 19 | 0.026 | 7 | 0.0006 | |
| 10% | 0 | 57 | 0.033 | 33 | 0.028 |
| 2.5 | 55 | 0.032 | 29 | 0.026 | |
| 5 | 51 | 0.030 | 23 | 0.015 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Krishnamoorthy, S.; Noorani, B.; Xu, C. Effects of Encapsulated Cells on the Physical–Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Gelatin Methacrylate Hydrogels. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5061. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20205061
Krishnamoorthy S, Noorani B, Xu C. Effects of Encapsulated Cells on the Physical–Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Gelatin Methacrylate Hydrogels. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(20):5061. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20205061
Chicago/Turabian StyleKrishnamoorthy, Srikumar, Behnam Noorani, and Changxue Xu. 2019. "Effects of Encapsulated Cells on the Physical–Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Gelatin Methacrylate Hydrogels" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 20: 5061. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20205061
APA StyleKrishnamoorthy, S., Noorani, B., & Xu, C. (2019). Effects of Encapsulated Cells on the Physical–Mechanical Properties and Microstructure of Gelatin Methacrylate Hydrogels. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(20), 5061. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20205061