The Association and Significance of p53 in Gynecologic Cancers: The Potential of Targeted Therapy
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Significance of p53 in Gynecologic Cancers
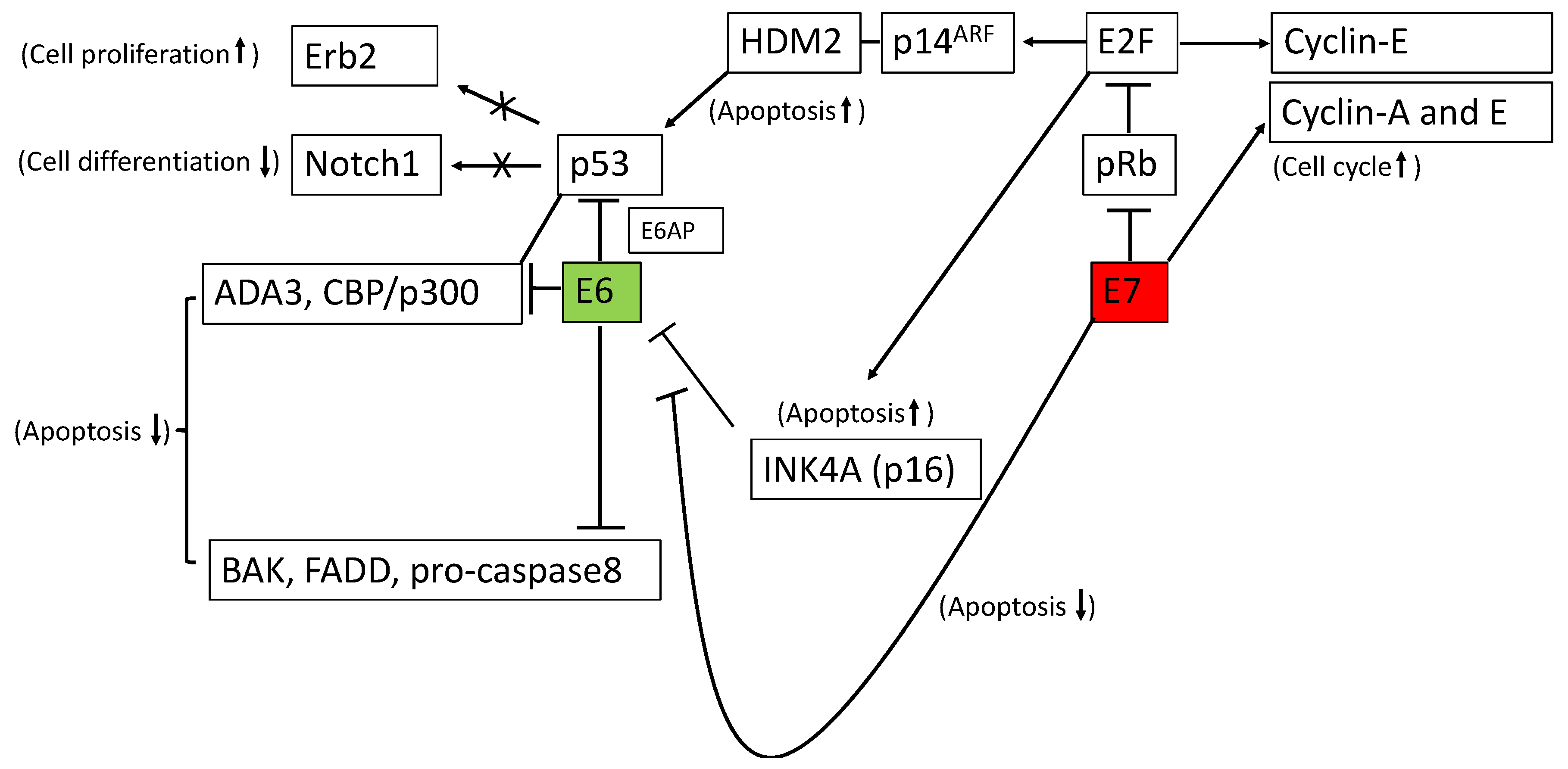
2.1. Significance of p53 in Cervical Cancer
2.2. Significance of p53 in Endometrial Cancer
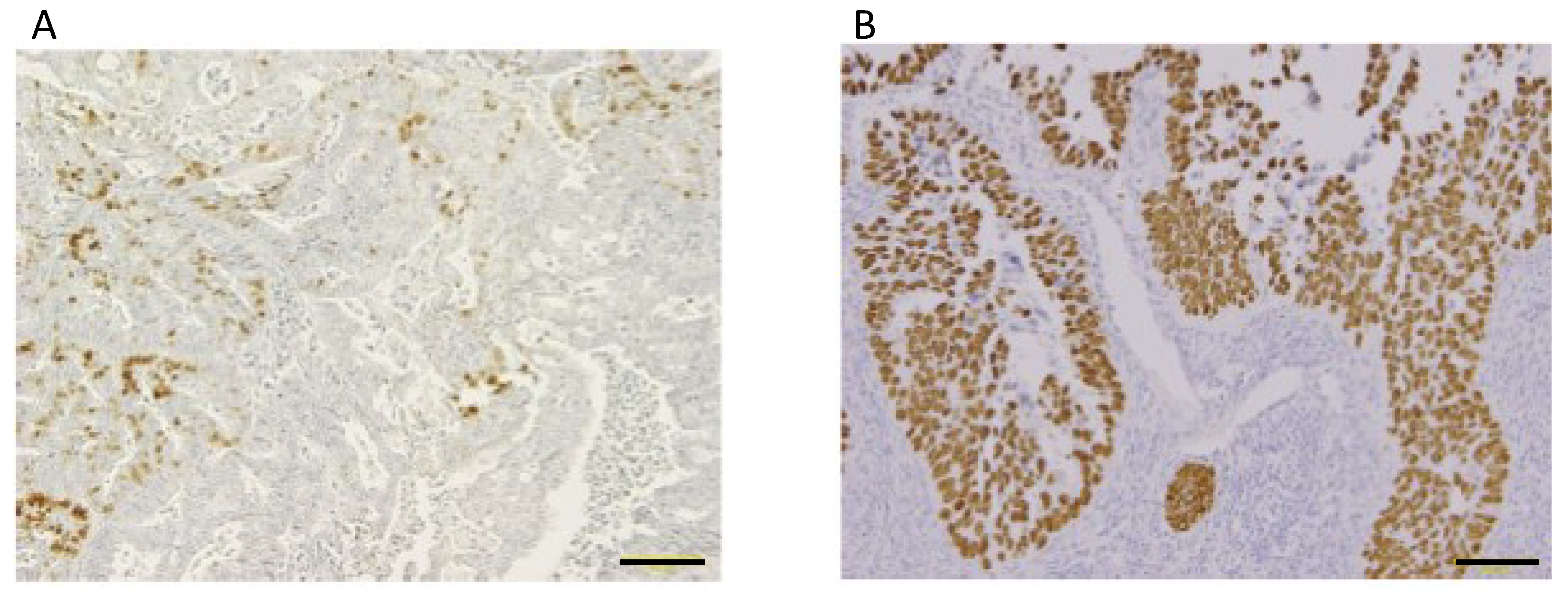
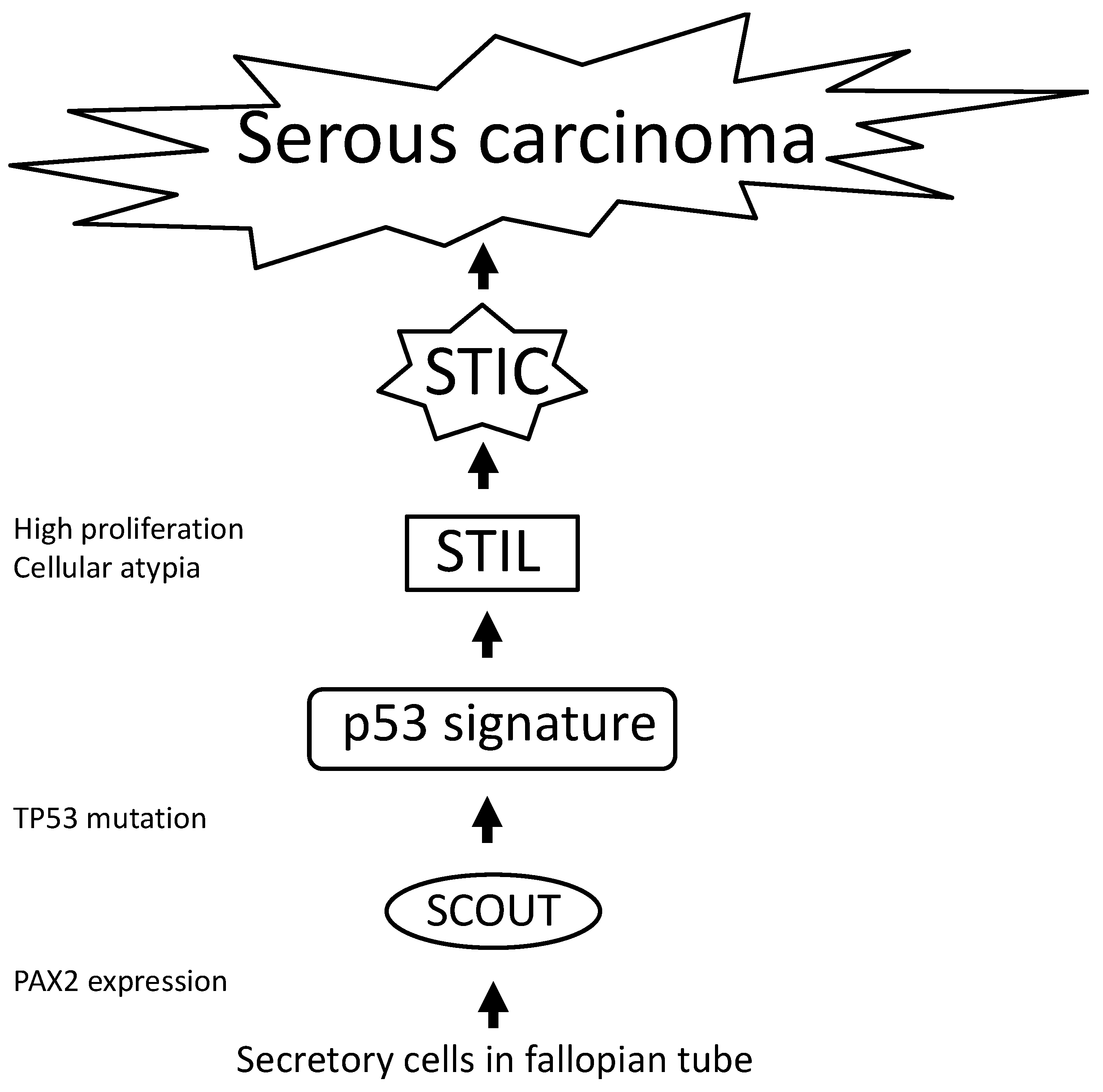
2.3. Significance of p53 in Ovarian Cancer
3. Clinical Application Using p53
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BRCA1/2 | Breast cancer type 1/2 susceptibility protein |
| FADD | Fas-associated protein with death domain |
| HDM2 | Human Double Minute2 |
| H2AX | H2A histone family member X |
| KRAS | v-Ki-ras2 Kirsten rat sarcoma viral oncogene homolog |
| MDM2 | Mouse double minute 2 homolog |
| PAX2 | Paired box gene 2 |
| PERP | p53 apoptosis effector related to PMP-22 |
| PMP | Peripheral myelin protein |
| PTEN | Phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted from chromosome 10 |
| PUMA | p53 upregulated modulator of apoptosis |
| RB | Retinoblastoma protein |
References
- Linzer, D.I.; Levine, A.J. Characterization of a 54K Dalton cellular SV40 tumor antigen present in SV40-transformed cells and uninfected embryonal carcinoma cells. Cell 1979, 17, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, D.P. p53, guardian of the genome. Nature 1992, 358, 15–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, M.C.; Xu, X.K.; Zhao, Y.; Mahanand, C.; Zhu, T.; Deng, H.; Nevo, E.; Du, J.Z.; Chen, X.Q. Functional Diversity of p53 in Human and Wild Animals. Front. Endocrinol. 2019, 10, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EI-Deiry, W.S.; Tokino, T.; Velculescu, V.E.; Levy, D.B.; Parsons, R.; Trent, J.M.; Lin, D.; Mercer, W.E.; Kinzler, K.W.; Vogelstein, B. WAF1, a potential mediator of p53 tumorsuppression. Cell 1993, 75, 817–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Hannon, G.J.; Zhang, H.; Casso, D.; Kobayashi, R.; Beach, D. p21 is a universal inhibitor of cyclin kinases. Nature 1993, 366, 701–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Attardi, L.D.; Reczek, E.E.; Cosmas, C.; Demicco, E.G.; McCurrach, M.E.; Lowe, S.W.; Jacks, T. PERP, an apoptosis-associated target of p53, is a novel member of the PMP-22/gas3 family. Genome Dev. 2000, 14, 704–718. [Google Scholar]
- Petitjean, A.; Mathe, E.; Kato, S.; Ishioka, C.; Tavtigian, S.V.; Hainaut, P.; Olivier, M. Impact of mutant p53 functional properties onTP53mutation patterns and tumor phenotype: Lessons from recent developments in the IARC TP53 database. Hum. Mutat. 2007, 28, 622–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivier, M.; Hollstein, M.; Hainaut, P. TP53 mutations in human cancers: Origins, consequences, and clinical use. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, M.F.; Morano, W.F.; Lee, J.; Gleeson, E.; Babcock, B.D.; Michl, J.; Sarafraz-Yazdi, E.; Pincus, M.R.; Bowne, W.B. Emerging Role of MDM2 as Target for Anti-Cancer Therapy: A Review. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2016, 46, 627–634. [Google Scholar]
- Burgess, A.; Chia, K.M.; Haupt, S.; Thomas, D.; Haupt, Y.; Lim, E. Clinical Overview of MDM2/X-Targeted Therapies. Front. Oncol. 2016, 6, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffner, M.; Werness, B.A.; Huibregtse, J.M.; Levine, A.J.; Howley, P.M. The E6 oncoprotein encoded by human papillomavirus types 16 and 18 promotes the degradation of p53. Cell 1990, 63, 1129–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boussios, S.; Moschetta, M.; Zarkavelis, G.; Papadaki, A.; Kefas, A.; Tatsi, K. Ovarian sex-cord stromal tumours and small cell tumours: Pathological, genetic and management aspects. Crit. Rev. Oncol. 2017, 120, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hussain, S.P.; Harris, C.C. Molecular epidemiology of human cancer: Contribution ofmutation spectra studies of tumor suppressor genes. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 4023–4037. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Beroud, C.; Soussi, T. The UMD-p53 database: New mutations and analysis tools. Hum. Mutat. 2003, 21, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaginuma, Y.; Westphal, H. Analysis of the p53 gene in human uterine carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res. 1991, 5, 6506–6509. [Google Scholar]
- Leroy, B.; Girard, L.; Hollestelle, A.; Minna, J.D.; Gazdar, A.F.; Soussi, T. Analysis of TP53 Mutation Status in Human Cancer Cell Lines: A Reassessment. Hum. Mutat. 2014, 35, 756–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zur Hausen, H. Papillomaviruses and cancer: From basic studies to clinical application. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Huang, X.; Zhang, Y. Involvement of Human Papillomaviruses in Cervical Cancer. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zerfass, K.; Schulze, A.; Spitkovsky, D.; Friedman, V.; Henglein, B.; Jansen-Dürr, P. Sequential activation of cyclin E and cyclin A gene expression by human papillomavirus type 16 E7 through sequences necessary for transformation. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 6389–6399. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Jones, D.L.; Alani, R.M.; Münger, K. The human papillomavirus E7 oncoprotein can uncouple cellular differentiation and proliferation in human keratinocytes by abrogating p21Cip1-mediated inhibition of cdk2. Genes Dev. 1997, 11, 2101–2111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harry, J.B.; Funk, J.O.; Waga, S.; Espling, E.; Stillman, B.; Galloway, D.A. Inhibition of CDK activity and PCNA-dependent DNA replication by p21 is blocked by interaction with the HPV-16 E7 oncoprotein. Genes Dev. 1997, 11, 2090–2100. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Zerfass-Thome, K.; Zwerschke, W.; Mannhardt, B.; Tindle, R.; Botz, J.W.; Jansen-Dürr, P. Inactivation of the cdk inhibitor p27KIP1 by the human papillomavirus type 16 E7 oncoprotein. Oncogene 1996, 13, 2323–2330. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bates, S.; Phillips, A.C.; Clark, P.A.; Stott, F.; Peters, G.; Ludwig, R.L.; Vousden, K.H. p14ARF links the tumour suppressors RB and p53. Nature 1998, 395, 124–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, J.D.; Taylor, L.J.; Roussel, M.F.; Sherr, C.J.; Bar-Sagi, D. Nucleolar Arf sequesters Mdm2 and activates p53. Nat. Cell Biol. 1995, 1, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiyono, T.; Narisawa-Saito, M.; Narisawa-Saito, M. Basic mechanisms of high-risk human papillomavirus-induced carcinogenesis: Roles of E6 and E7 proteins. Cancer Sci. 2007, 98, 1505–1511. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, A.; Zhao, Y.; Meng, G.; Zeng, M.; Srinivasan, S.; Delmolino, L.M.; Gao, Q.; Dimri, G.; Weber, G.F.; Wazer, D.E.; et al. Human Papillomavirus Oncoprotein E6 Inactivates the Transcriptional Coactivator Human ADA3. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002, 22, 5801–5812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thomas, M.; Banks, L. Human papillomavirus (HPV) E6 interactions with Bak are conserved amongst E6 proteins from high and low risk HPV types. J. Gen. Virol. 1999, 80, 1513–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippova, M.; Parkhurst, L.; Duerksen-Hughes, P.J. The Human Papillomavirus 16 E6 Protein Binds to Fas-associated Death Domain and Protects Cells from Fas-triggered Apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 25729–25744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Garnett, T.O.; Filippova, M.; Duerksen-Hughes, P.J. Accelerated degradation of FADD and procaspase 8 in cells expressing human papilloma virus 16 E6 impairs TRAIL-mediated apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2006, 13, 1915–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Filippova, M.; Johnson, M.M.; Bautista, M.; Filippov, V.; Fodor, N.; Tungteakkhun, S.S.; Williams, K.; Duerksen-Hughes, P.J. The Large and Small Isoforms of Human Papillomavirus Type 16 E6 Bind to and Differentially Affect Procaspase 8 Stability and Activity. J. Virol. 2007, 81, 4116–4129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tungteakkhun, S.S.; Filippova, M.; Neidigh, J.W.; Fodor, N.; Duerksen-Hughes, P.J. The Interaction between Human Papillomavirus Type 16 and FADD Is Mediated by a Novel E6 Binding Domain. J. Virol. 2008, 82, 9600–9614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nicolas, M.; Wolfer, A.; Raj, K.; Kummer, J.A.; Mill, P.; Van Noort, M.; Hui, C.C.; Clevers, H.; Dotto, G.P.; Radtke, F. Notch1 functions as a tumor suppressor in mouse skin. Nat. Genet. 2003, 33, 416–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rangarajan, A.; Talora, C.; Okuyama, R.; Nicolas, M.; Mammucari, C.; Oh, H.; Aster, J.C.; Krishna, S.; Metzger, D.; Chambon, P.; et al. Notch signaling is a direct determinant of keratinocyte growth arrest and entry into differentiation. EMBO J. 2001, 20, 3427–3436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Talora, C.; Sgroi, D.C.; Crum, C.P.; Dotto, G.P. Specific down-modulation of Notch1 signaling in cervical cancer cells is required for sustained HPV-E6/E7 expression and late steps of malignant transformation. Genome Res. 2002, 16, 2252–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yugawa, T.; Handa, K.; Narisawa-Saito, M.; Ohno, S.I.; Fujita, M.; Kiyono, T. Regulation of Notch1 Gene Expression by p53 in Epithelial Cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2007, 27, 3732–3742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Narisawa-Saito, M.; Handa, K.; Yugawa, T.; Ohno, S.; Fujita, M.; Kiyono, T. HPV16 E6-mediated stabilization of ErbB2 in neoplastic transformation of human cervical keratinocytes. Oncogene 2007, 26, 2988–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, M.; Banks, L. Inhibition of Bak-induced apoptosis by HPV-18 E6. Oncogene 1998, 17, 2943–2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kyo, S.; Nakamura, M.; Kiyono, T.; Maida, Y.; Kanaya, T.; Tanaka, M.; Yatabe, N.; Inoue, M. Successful Immortalization of Endometrial Glandular Cells with Normal Structural and Functional Characteristics. Am. J. Pathol. 2003, 163, 2259–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, J.; Li, X.J.; Zhu, W.; Liu, X.P. Detection and pathological value of papillomavirus DNA and p16INK4A and p53 protein expression in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. Oncol. Lett. 2014, 7, 738–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grace, V.M.B.; Shalini, J.V.; Lekha, T.T.S.; Devaraj, S.N.; Devaraj, H. Co-overexpression of p53 and bcl-2 proteins in HPV-induced squamous cell carcinoma of the uterine cervix. Gynecol. Oncol. 2003, 91, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stănculescu, R.; Ceauşu, M.; Ceauşu, Z.; Bausic, V. Immunofluorescence expression of Ki-67, p53 and cyclin inhibitors (p16ink4a, p21 and p27) in low-grade cervical lesions versus high-grade cervical lesions. Research study on cell cultures. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2013, 54, 725–734. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Son, S.M.; Noh, K.I.; Lee, H.C.; Park, Y.J.; Jeong, E.H.; Kim, H.S.; Song, H.G. Evaluation of p16INk4a, pRb, p53 and Ki-67 expression in cervical squamous neoplasia. J. Biomed. Res. 2012, 13, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Shin, J.G.; Ko, G.H.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, H.W. Studies on the Expression of the p16 (INK4A), p53, and Ki-67 Labeling Index in Inflammatory and Neoplastic Diseases of the Uterine Cervix. Korean J. Pathol. 2004, 38, 238–243. [Google Scholar]
- Mitildzans, A.; Arechvo, A.; Rezeberga, D.; Isajevs, S. Expression of p63, p53 and Ki-67 in Patients with Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia. Turk. J. Pathol. 2017, 33, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tagle, D.K.J.; Sotelo, D.H.; Illades-Aguiar, B.; Leyva-Vazquez, M.A.; Alfaro, E.F.; Coronel, Y.C.; Hernández, O.D.M.; Romero, L.D.C.A. Expression of E6, p53 and p21 proteins and physical state of HPV16 in cervical cytologies with and without low grade lesions. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Med. 2014, 7, 186–193. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carrilho, C.; Gouveia, P.; Cantel, M.; Alberto, M.; Buane, L.; David, L. Characterization of Human Papillomavirus Infection, P53 and Ki-67 Expression in Cervix Cancer of Mozambican Women. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2003, 199, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitrakakis, C.; Kymionis, G.; Diakomanolis, E.; Papaspyrou, I.; Rodolakis, A.; Arzimanoglou, I.; Leandros, E.; Michalas, S. The Possible Role of p53 and bcl-2 Expression in Cervical Carcinomas and Their Premalignant Lesions. Gynecol. Oncol. 2000, 77, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, D.C.; Gonçalves, A.K.; Cobucci, R.N.; Mendonça, R.C.; Lima, P.H.; Cavalcanti, G.; Júnior, G.C. Immunohistochemical expression of p16, Ki-67 and p53 in cervical lesions—A systematic review. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2017, 213, 723–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bokhman, J.V. Two pathogenetic types of endometrial carcinoma. Gynecol. Oncol. 1983, 15, 10–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cristofano, A.; Ellenson, L.H. Endometrial carcinoma. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2007, 2, 57–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, D.J.; O’Mara, T.A.; Glubb, D.M.; Painter, J.N.; Cheng, T.; Folkerd, E.; Doody, D.; Dennis, J.; Webb, P.M.; Gorman, M.; et al. CYP19A1 fine-mapping and Mendelian randomization: Estradiol is causal for endometrial cancer. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2016, 23, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tashiro, H.; Blazes, M.S.; Wu, R.; Cho, K.R.; Bose, S.; Wang, S.I.; Li, J.; Parsons, R.; Ellenson, L.H. Mutations in PTEN are frequent in endometrial carcinoma but rare in other common gynecological malignancies. Cancer Res. 1997, 57, 3935–3940. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Enomoto, T.; Fujita, M.; Inoue, M.; Rice, J.M.; Nakajima, R.; Tanizawa, O.; Nomura, T. Alterations of the p53 tumor suppressor gene and its association with activation of the c-K-ras-2 protooncogene in premalignant and malignant lesions of the human uterine endometrium. Cancer Res. 1993, 53, 1883–1888. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.H.; Wang, J.; Lee, K.Y.; Franco, H.L.; Broaddus, R.R.; Lydon, J.P.; Jeong, J.W.; Demayo, F.J. The synergistic effect of conditional Pten loss and oncogenic K-ras mutation on endometrial cancer development occurs via decreased progesterone receptor action. J. Oncol. 2010, 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, W.; Xiang, L.; Fadare, O.; Kong, B. A Proposed Model for Endometrial Serous Carcinogenesis. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2011, 35, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samarnthai, N.; Hall, K.; Yeh, I.T. Molecular Profiling of Endometrial Malignancies. Obstet. Gynecol. Int. 2010, 2010, 162363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandoth, C.; Schultz, N.; Cherniack, A.D.; Akbani, R.; Liu, Y.; Shen, H.; Robertson, A.G.; Pashtan, I.; Shen, R.; Benz, C.C.; et al. Integrated genomic characterization of endometrial carcinoma. Nature 2013, 497, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Schultheis, A.M.; Martelotto, L.G.; De Filippo, M.R.; Piscuglio, S.; Ng, C.K.Y.; Hussein, Y.R.; Reis-Filho, J.S.; Soslow, R.A.; Weigelt, B.; Piscuoglio, S. TP53 Mutational Spectrum in Endometrioid and Serous Endometrial Cancers. Int. J. Gynecol. Pathol. 2016, 35, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kohler, M.F.; Berchuck, A.; Davidoff, A.M.; Humphrey, P.A.; Dodge, R.K.; Iglehart, J.D.; Soper, J.T.; Clarke-Pearson, D.L.; Bast, R.C., Jr.; Marks, J.R. Overexpression and mutation of p53 in endometrial carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1992, 52, 1622–1627. [Google Scholar]
- Inoue, M.; Okayama, A.; Fujita, M.; Enomoto, T.; Sakata, M.; Tanizawa, O.; Ueshima, H. Clinicopathological characteristics of p53 overexpression in endometrial cancers. Int. J. Cancer 1994, 58, 14–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherman, M.E.; Bur, M.E.; Kurman, R.J. p53 in endometrial cancer and its putative precursors: Evidence for diverse pathways of tumorigenesis. Hum. Pathol. 1995, 26, 1268–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohler, M.F.; Carney, P.; Dodge, R.; Soper, J.T.; Clarke-Pearson, D.L.; Marks, J.R.; Berchuck, A. p53 overexpression in advanced-stage endometrial adenocarcinoma. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 1996, 175, 1246–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soong, R.; Knowles, S.; Williams, K.; Hammond, I.; Wysocki, S.; Iacopetta, B. Overexpression of p53 protein is an independent prognostic indicator in human endometrial carcinoma. Br. J. Cancer 1996, 74, 562–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Strang, P.; Nordstöm, B.; Nilsson, S.; Bergström, R.; Tribukait, B. Mutant p53 protein as a predictor of survival in endometrial carcinoma. Eur. J. Cancer 1996, 32, 598–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bancher-Todesca, D.; Gitsch, G.; Williams, K.E.; Kohlberger, P.; Neunteufel, W.; Obermair, A.; Heinze, G.; Breitenecker, G.; Hacker, N.F. p53 Protein Overexpression: A Strong Prognostic Factor in Uterine Papillary Serous Carcinoma. Gynecol. Oncol. 1998, 71, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kounelis, S.; Kapranos, N.; Kouri, E.; Coppola, D.; Papadaki, H.; Jones, M.W. Immunohistochemical Profile of Endometrial Adenocarcinoma: A Study of 61 Cases and Review of the Literature. Mod. Pathol. 2000, 13, 379–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coronado, P.J.; Vidart, J.A.; Lopez-Asenjo, J.A.; Fasero, M.; Furio-Bacete, V.; Magrina, J.; Escudero, M. P53 overexpression predicts endometrial carcinoma recurrence better than HER-2/neu overexpression. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 2001, 98, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, H. Immunohistochemical expression of cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases, tumor-suppressor gene products, Ki-67, and sex steroid receptors in endometrial carcinoma: Positive staining for cyclin A as a poor prognostic indicator. Hum. Pathol. 2003, 34, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzuki, C.; Matsumoto, T.; Sonoue, H.; Arakawa, A.; Furugen, Y.; Kinoshita, K. Prognostic significance of the infiltrative pattern invasion in endometrioid adenocarcinoma of the endometrium. Pathol. Int. 2003, 53, 495–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, Y.T.; Kang, S.; Kang, D.H.; Yoo, K.Y.; Park, I.A.; Bang, Y.J.; Kim, J.W.; Park, N.H.; Kang, S.B.; Lee, H.P.; et al. Cyclooxygenase-2 and p53 expressions in endometrial cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. Prev. Biomark. 2004, 13, 1538–1542. [Google Scholar]
- Dupont, J.; Wang, X.; Marshall, D.S.; Leitão, M.; Hedvat, C.V.; Hummer, A.; Thaler, H.; O’Reilly, R.J.; Soslow, R.A. Wilms Tumor Gene (WT1) and p53 expression in endometrial carcinomas: A study of 130 cases using a tissue microarray. Gynecol. Oncol. 2004, 94, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pansare, V.; Munkarah, A.R.; Schimp, V.; Haitham Arabi, M.; Saed, G.M.; Morris, R.T.; Ali-Fehmi, R. Increased expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha in type I and type II endometrial carcinomas. Mod. Pathol. 2007, 20, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urabe, R.; Hachisuga, T.; Kurita, T.; Kagami, S.; Kawagoe, T.; Matsuura, Y.; Shimajiri, S. Prognostic significance of overexpression of p53 in uterine endometrioid adenocarcinomas with an analysis of nuclear grade. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2014, 40, 812–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edmondson, R.; Crosbie, E.; Nickkho-Amiry, M.; Kaufmann, A.; Stelloo, E.; Nijman, H.; Leary, A.; Auguste, A.; Mileshkin, L.; Pollock, P.; et al. Markers of the p53 pathway further refine molecular profiling in high-risk endometrial cancer: A Trans PORTEC initiative. Gynecol. Oncol. 2017, 146, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obata, T.; Nakamura, M.; Mizumoto, Y.; Iizuka, T.; Ono, M.; Terakawa, J.; Daikoku, T.; Fujiwara, H. Dual expression of immunoreactive estrogen receptor β and p53 is a potential predictor of regional lymph node metastasis and postoperative recurrence in endometrial endometrioid carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0188641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, R.L.; Royds, J.A.; Burton, J.L.; Heatley, M.K.; Wells, M. Direct sequencing of the p53 gene shows absence of mutations in endometrioid endometrial adenocarcinomas expressing p53 protein. Histopathology 1998, 33, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touqan, N.; Diggle, C.P.; Verghese, E.T.; Perry, S.; Horgan, K.; Merchant, W.; Anwar, R.; Markham, A.F.; Carr, I.M.; Achuthan, R. An observational study on the expression levels of MDM2 and MDMX proteins, and associated effects on P53 in a series of human liposarcomas. BMC Clin. Pathol. 2013, 13, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treeck, O.; Häring, J.; Skrzypczak, M.; Stegerer, A.; Lattrich, C.; Weber, F.; Görse, R.; Ortmann, O. Estrogen receptor β transcript variants associate with oncogene expression in endometrial cancer. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2012, 29, 1127–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujimoto, J.; Hirose, R.; Sakaguchi, H.; Tamaya, T. Clinical Significance of Expression of Estrogen Receptor α and β mRNAs in Ovarian Cancers. Oncology 2000, 58, 334–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.G.; Strom, A.; Lindberg, K.; Gustafsson, J.A. Estrogen receptor beta decreases survival of p53-defective cancer cells after DNA damage by impairing G2/M checkpoint signaling. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2011, 127, 417–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartman, J.; Edvardsson, K.; Lindberg, K.; Zhao, C.; Williams, C.; Ström, A.; Gustafsson, J.A. Tumor Repressive Functions of Estrogen Receptor in SW480 Colon Cancer Cells. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 6100–6106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurman, R.J.; Shih, I.M. The dualistic model of ovarian carcinogenesis: Revisited, revised, and expanded. Am. J. Pathol. 2016, 186, 733–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, A.J.; Dwight, T.; Gill, A.J.; Dickson, K.A.; Zhu, Y.; Clarkson, A.; Gard, G.B.; Maidens, J.; Valmadre, S.; Clifton-Bligh, R.; et al. Assessing mutant p53 in primary high-grade serous ovarian cancer using immunohistochemistry and massively parallel sequencing. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, A.A.; Etemadmoghadam, D.; Temple, J.; Lynch, A.G.; Riad, M.; Sharma, R.; Stewart, C.; Fereday, S.; Caldas, C.; DeFazio, A.; et al. Driver mutations in TP53 are ubiquitous in high grade serous carcinoma of the ovary. J. Pathol. 2010, 221, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medeiros, F.; Muto, M.G.; Lee, Y.; Elvin, J.A.; Callahan, M.J.; Feltmate, C.; Garber, J.E.; Cramer, D.W.; Crum, C.P. The tubal fimbria is a preferred site for early adenocarcinoma in women with familial ovarian cancer syndrome. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2006, 30, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miki, Y.; Swensen, J.; Shattuck-Eidens, D.; Futreal, P.; Harshman, K.; Tavtigian, S.; Liu, Q.; Cochran, C.; Bennett, L.; Ding, W.; et al. A strong candidate for the breast and ovarian cancer susceptibility gene BRCA1. Science 1994, 266, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldgar, D.E.; Neuhausen, S.L.; Steele, L.; Fields, P.; Ward, J.H.; Tran, T.; Ngyuen, K.; Stratton, M.R.; Easton, D.F. A 45-year follow-up of kindred 107 and the search for BRCA2. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. Monogr. 1995, 17, 15–19. [Google Scholar]
- Ford, D.; Easton, D.; Stratton, M.; Narod, S.; Goldgar, D.; Devilee, P.; Bishop, D.; Weber, B.; Lenoir, G.; Chang-Claude, J.; et al. Genetic Heterogeneity and Penetrance Analysis of the BRCA1 and BRCA2 Genes in Breast Cancer Families. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1998, 62, 676–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kauff, N.D.; Satagopan, J.M.; Robson, M.E.; Scheuer, L.; Hensley, M.; Hudis, C.A.; Ellis, N.A.; Boyd, J.; Borgen, P.I.; Barakat, R.R.; et al. Risk-Reducing Salpingo-oophorectomy in Women with aBRCA1orBRCA2Mutation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 1609–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, M.S.; Meyer, L.A.; Deavers, M.T.; Daniels, M.S.; Keeler, E.R.; Mok, S.C.; Gershenson, D.M.; Lu, K.H. Microscopic and early-stage ovarian cancers in BRCA1/2 mutation carriers: Building a model for early BRCA-associated tumorigenesis. Cancer Prev. Res. 2011, 4, 463–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kindelberger, D.W.; Lee, Y.; Miron, A.; Hirsch, M.S.; Feltmate, C.; Medeiros, F.; Callahan, M.J.; Garner, E.O.; Gordon, R.W.; Birch, C.; et al. Intraepithelial Carcinoma of the Fimbria and Pelvic Serous Carcinoma: Evidence for a Causal Relationship. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2007, 31, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, Y.; Miron, A.; Drapkin, R.; Nucci, M.R.; Medeiros, F.; Saleemuddin, A.; Garber, J.; Birch, C.; Mou, H.; Gordon, R.W.; et al. A candidate precursor to serous carcinoma that originates in the distal fallopian tube. J. Pathol. 2007, 211, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, E.; Kurman, R.J.; Vang, R.; Sehdev, A.S.; Han, G.; Soslow, R.; Wang, T.L.; Shih, I.M. TP53 mutations in serous tubal intraepithelial carcinoma and concurrent pelvic high-grade serous carcinoma--evidence supporting the clonal relationship of the two lesions. J. Pathol. 2012, 226, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visvanathan, K.; Vang, R.; Shaw, P.; Gross, A.; Soslow, R.; Parkash, V.; Shih, I.M.; Kurman, R.J. Diagnosis of serous tubal intraepithelial carcinoma based on morphologic and immunohistochemical features: A reproducibility study. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2011, 35, 1766–1775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, E.Y.; Mehra, K.; Mehrad, M.; Ning, G.; Miron, A.; Mutter, G.L.; Monte, N.; Quade, B.J.; McKeon, F.D.; Yassin, Y.; et al. Secretory cell outgrowth, PAX2 and serous carcinogenesis in the Fallopian tube. J. Pathol. 2010, 222, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Ning, Y.; Abu Shahin, N.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yuan, B.; Cragun, J.M.; Chambers, S.K.; Hatch, K.; et al. Secretory cell expansion with aging: Risk for pelvic serous carcinogenesis. Gynecol. Oncol. 2013, 131, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soong, T.R.; Howitt, B.E.; Horowitz, N.; Nucci, M.R.; Crum, C.P. The fallopian tube, “precursor escape” and narrowing the knowledge gap to the origins of high-grade serous carcinoma. Gynecol. Oncol. 2019, 152, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pothuri, B.; Leitao, M.M.; Levine, D.A.; Viale, A.; Olshen, A.B.; Arroyo, C.; Bogomolniy, F.; Olvera, N.; Lin, O.; Soslow, R.A.; et al. Genetic Analysis of the Early Natural History of Epithelial Ovarian Carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boussios, S.; Karathanasi, A.; Cooke, D.; Neille, C.; Sadauskaite, A.; Moschetta, M.; Zakynthinakis-Kyriakou, N.; Pavlidis, N. PARP Inhibitors in Ovarian Cancer: The Route to “Ithaca”. Diagnostics 2019, 9, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boussios, S.; Karihtala, P.; Moschetta, M.; Karathanasi, A.; Sadauskaite, A.; Rassy, E.; Pavlidis, N. Combined Strategies with Poly (ADP-Ribose) Polymerase (PARP) Inhibitors for the Treatment of Ovarian Cancer: A Literature Review. Diagnostics 2019, 9, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, J.; Nguyen, D.; Lawrence, D.; Kemp, B.; Carrasco, C.; Ferson, D.; Hong, W.; Komaki, R.; Lee, J.; Nesbitt, J.; et al. Retrovirus–mediated wild–type P53 gene transfer to tumors of patients with lung cancer. Nat. Med. 1996, 2, 985–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, T.; Tanaka, N.; Kanazawa, S.; Ohtani, S.; Saijo, Y.; Nukiwa, T.; Yoshimura, K.; Sato, T.; Eto, Y.; Chada, S.; et al. Multicenter Phase I Study of Repeated Intratumoral Delivery of Adenoviralp53in Patients with Advanced Non–Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 1689–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabrilovich, D.I. INGN 201 (Advexin): Adenoviral p53 gene therapy for cancer. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2006, 6, 823–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drugs, R.D. INGN 201: Ad-p53, Ad5CMV-p53, adenoviral p53, p53 gene therapy-introgen, RPR/INGN 201. Drugs R D 2007, 8, 176–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Kling, J. China offers alternative gateway for experimental drugs. Nat. Biotechnol. 2006, 24, 117–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.W.; Li, L.; Li, D.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Li, W.; Xu, X.; Zhang, M.J.; Chandler, L.A.; Lin, H.; et al. The First Approved Gene Therapy Product for Cancer Ad-p53 (Gendicine): 12 Years in the Clinic. Hum. Gene Ther. 2018, 29, 160–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, Y.; Tazawa, H.; Hashimoto, Y.; Kojima, T.; Kuroda, S.; Yano, S.; Yoshida, R.; Uno, F.; Mizuguchi, H.; Ohtsuru, A.; et al. A novel apoptotic mechanism of genetically engineered adenovirus-mediated tumour-specific p53 overexpression through E1A-dependent p21 and MDM2 suppression. Eur. J. Cancer 2012, 48, 2282–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kyo, S.; Takakura, M.; Inoue, M. Telomerase activity in cancer as a diagnostic and therapeutic target. Histol. Histopathol. 2000, 15, 813–824. [Google Scholar]
- Takakura, M.; Kyo, S.; Kanaya, T.; Hirano, H.; Takeda, J.; Yutsudo, M.; Inoue, M. Cloning of human telomerase catalytic subunit (hTERT) gene promoter and identification of proximal core promoter sequences essential for transcriptional activation in immortalized and cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1999, 59, 551–557. [Google Scholar]
- Hasei, J.; Sasaki, T.; Tazawa, H.; Osaki, S.; Yamakawa, Y.; Kunisada, T.; Yoshida, A.; Hashimoto, Y.; Onishi, T.; Uno, F.; et al. Dual Programmed Cell Death Pathways Induced by p53 Transactivation Overcome Resistance to Oncolytic Adenovirus in Human Osteosarcoma Cells. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 314–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tisato, V.; Voltan, R.; Gonelli, A.; Secchiero, P.; Zauli, G. MDM2/X inhibitors under clinical evaluation: Perspectives for the management of hematological malignancies and pediatric cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2017, 10, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Library of Medicine. Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/home (accessed on 27 November 2017).
- Vassilev, L.T.; Vu, B.T.; Graves, B.; Carvajal, D.; Podlaski, F.; Filipovic, Z.; Kong, N.; Kammlott, U.; Lukacs, C.; Klein, C.; et al. In Vivo Activation of the p53 Pathway by Small-Molecule Antagonists of MDM2. Science 2004, 303, 844–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Su, X.; Chen, W.J.; Xiao, S.W.; Li, X.F.; Xu, G.; Pan, J.J.; Zhang, S.W. Effect and Safety of Recombinant Adenovirus-p53 Transfer Combined with Radiotherapy on Long-Term Survival of Locally Advanced Cervical Cancer. Hum. Gene Ther. 2016, 27, 1008–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kajitani, K.; Honda, K.I.; Terada, H.; Yasui, T.; Sumi, T.; Koyama, M.; Ishiko, O. Human Papillomavirus E6 Knockdown Restores Adenovirus Mediated-estrogen Response Element Linked p53 Gene Transfer in HeLa Cells. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2015, 16, 8239–8245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, N.N.; Yong, Z.L.; Yusof, R.; Watson, R.J. HPV 16E7 and 48E7 proteins use different mechanisms to target p130 to overcome cell cycle block. Virol. J. 2016, 13, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Gersbach, E.; Zhang, X.; Xu, X.; Dong, R.; Lee, P.; Liu, J.; Kong, B.; Shao, C.; Wei, J.J. miR-106a represses the Rb tumor suppressor p130 to regulate cellular proliferation and differentiation in high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma. Mol. Cancer Res. 2013, 11, 1314–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldmana, R.; Gatalicaa, Z.; Reddya, S.K.; Tewarib, K.S. Paving the road to personalized medicine in cervical cancer: Theranostic biomarker evaluation in a 592-specimen library. Gynecol. Oncol. 2015, 137, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Authors | Histology | n | Positive Rate (%) | Prognostic Factor | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kohler et al. | End | 75 | 13 | N/A | [59] |
| Non-End | 32 | 38 | |||
| Total | 107 | 21 | |||
| Inoue et al. | End | 126 | 11 | Yes | [60] |
| Non-End | 13 | 67 | |||
| Total | 139 | 17 | |||
| Sherman et al. | End | 45 | 20 | N/A | [61] |
| Non-End | 46 | 83 | |||
| Total | 91 | 52 | |||
| Kohler et al. | End | 115 | 30 | Yes | [62] |
| Non-End | 64 | 44 | |||
| Total | 179 | 36 | |||
| Soong et al. | End | 94 | 19 | Yes | [63] |
| Non-End | 28 | 54 | |||
| Total | 122 | 27 | |||
| Strang et al. | All | 183 | 45 | Yes | [64] |
| Bamcher-Todesca et al. | Non-End | 23 | 48 | Yes | [65] |
| Kouneils et al. | End | 40 | 35 | N/A | [66] |
| Non-End | 21 | 76 | |||
| Total | 61 | 49 | |||
| Coronado et al. | End | 87 | 10 | Yes | [67] |
| Non-End | 27 | 30 | |||
| Total | 114 | 18 | |||
| Shih et al. | All | 82 | 45 | Yes | [68] |
| Suzki et al. | End | 112 | 44 | Yes | [69] |
| Jeon et al. | End | 147 | 20 | N.S | [70] |
| Non-End | 5 | 40 | |||
| Total | 152 | 20 | |||
| Dupont et al. | End | 99 | 14 | N/A | [71] |
| Non-End | 31 | 41 | |||
| Total | 120 | 21 | |||
| Pansare et al. | End | 108 | 17 | Yes | [72] |
| Non-End | 41 | 82 | |||
| Total | 149 | 35 | |||
| Urabe et al. | End | 332 | 17 | Yes | [73] |
| Edmondson et al. | End | 86 | 28 | Yes | [74] |
| Non-End | 28 | 86 | |||
| Total | 114 | 43 | |||
| Obata et al. | End | 154 | 34 | Yes | [75] |
| End; Endometrioid |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nakamura, M.; Obata, T.; Daikoku, T.; Fujiwara, H. The Association and Significance of p53 in Gynecologic Cancers: The Potential of Targeted Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5482. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20215482
Nakamura M, Obata T, Daikoku T, Fujiwara H. The Association and Significance of p53 in Gynecologic Cancers: The Potential of Targeted Therapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(21):5482. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20215482
Chicago/Turabian StyleNakamura, Mitsuhiro, Takeshi Obata, Takiko Daikoku, and Hiroshi Fujiwara. 2019. "The Association and Significance of p53 in Gynecologic Cancers: The Potential of Targeted Therapy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 21: 5482. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20215482
APA StyleNakamura, M., Obata, T., Daikoku, T., & Fujiwara, H. (2019). The Association and Significance of p53 in Gynecologic Cancers: The Potential of Targeted Therapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(21), 5482. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20215482





