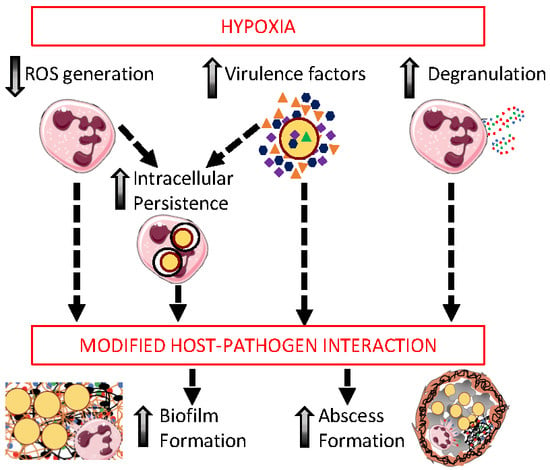
The Impact of Hypoxia on the Host-Pathogen Interaction between Neutrophils and Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
Share and Cite
Hajdamowicz, N.H.; Hull, R.C.; Foster, S.J.; Condliffe, A.M. The Impact of Hypoxia on the Host-Pathogen Interaction between Neutrophils and Staphylococcus aureus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5561. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20225561
Hajdamowicz NH, Hull RC, Foster SJ, Condliffe AM. The Impact of Hypoxia on the Host-Pathogen Interaction between Neutrophils and Staphylococcus aureus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(22):5561. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20225561
Chicago/Turabian StyleHajdamowicz, Natalia H, Rebecca C Hull, Simon J Foster, and Alison M Condliffe. 2019. "The Impact of Hypoxia on the Host-Pathogen Interaction between Neutrophils and Staphylococcus aureus" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 22: 5561. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20225561
APA StyleHajdamowicz, N. H., Hull, R. C., Foster, S. J., & Condliffe, A. M. (2019). The Impact of Hypoxia on the Host-Pathogen Interaction between Neutrophils and Staphylococcus aureus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(22), 5561. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20225561