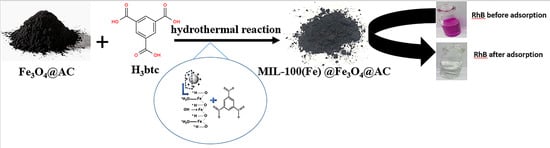
In Situ Synthesis of MIL-100(Fe) at the Surface of Fe3O4@AC as Highly Efficient Dye Adsorbing Nanocomposite
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
Characterization
3. Discussion
3.1. Comparison of Adsorption Capacity
3.2. Effect of pH
3.3. Effect of Adsorbent Dose
3.4. Effect of Contact Time
3.5. Adsorption Kinetics
3.6. Adsorption Isotherms
3.7. Adsorption Thermodynamics
3.8. Recyclability of MIL-100(Fe) @Fe3O4@AC for the RhB Adsorption
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Materials
4.2. Synthesis of Fe3O4@AC Nanocomposite
4.3. Synthesis of MIL-100(Fe) @Fe3O4@AC
4.4. Characterization
4.5. General Approaches for the Adsorption Experiments
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ghorbani, F.; Kamari, S. Core–shell magnetic nanocomposite of Fe3O4@SiO2@NH2 as an efficient and highly recyclable adsorbent of methyl red dye from aqueous environments. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2019, 14, 100333–100349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, L.J.; Ge, F.Y.; Sun, G.H.; Gao, X.J.; Zheng, H.G. Effective adsorption of Congo red by a MOF-based magnetic material. Dalton Trans. 2019, 48, 4650–4656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Wageh, S.; Al-Ghamdi, A.A.; Wang, H.; Yu, J.; Jiang, C. Hierarchical C/NiO-ZnO nanocomposite fibers with enhanced adsorption capacity for Congo red. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 537, 736–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalali, S.; Rahimi, M.R.; Dashtian, K.; Ghaedi, M.; Mosleh, S. One step integration of plasmonic Ag2CrO4/Ag/AgCl into HKUST-1-MOF as novel visible-light driven photocatalyst for highly efficient degradation of mixture dyes pollutants: Its photocatalytic mechanism and modeling. Polyhedron 2019, 166, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molavi, H.; Hakimian, A.; Shojaei, A.; Raeiszadeh, M. Selective dye adsorption by highly water stable metal-organic framework: Long term stability analysis in aqueous media. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 445, 424–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, F.; Sun, Q. Rapid and selective adsorption of cationic dyes by a unique metal-organic framework with decorated pore surface. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 440, 1219–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadi, S.; Manteghi, F.; Tondfekr, R. Removal of Congo red by two new zirconium metal–organic frameworks: Kinetics and isotherm study. Mon. Für Chem. Chem. Mon. 2019, 150, 193–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Liu, J.; Cheng, B.; You, W.; Ho, W.; Tang, H. Hierarchical porous Al2O3@ZnO core-shell microfibres with excellent adsorption affinity for Congo red molecule. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 473, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuzen, M.; Sari, A.; Saleh, T.A. Response surface optimization, kinetic and thermodynamic studies for effective removal of rhodamine B by magnetic AC/CeO2 nanocomposite. J. Env. Manag. 2018, 206, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Ren, X.; Chen, L. Synthesis and characterization of magnetic metal–organic framework for the adsorptive removal of Rhodamine B from aqueous solution. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2016, 34, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira, C.A.; da Silva, F.F.; Jimenez, G.C.; Neto, J.F.; de Souza, D.M.; de Souza, I.A.; Alves, S., Jr. MOF@activated carbon: A new material for adsorption of aldicarb in biological systems. Chem. Commun. (Camb) 2013, 49, 6486–6488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cardoso, N.F.; Lima, E.C.; Royer, B.; Bach, M.V.; Dotto, G.L.; Pinto, L.A.; Calvete, T. Comparison of Spirulina platensis microalgae and commercial activated carbon as adsorbents for the removal of Reactive Red 120 dye from aqueous effluents. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 241, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoodi, N.M.; Oveisi, M.; Taghizadeh, A.; Taghizadeh, M. Novel magnetic amine functionalized carbon nanotube/metal-organic framework nanocomposites: From green ultrasound-assisted synthesis to detailed selective pollutant removal modelling from binary systems. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 368, 746–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadraei, R.; Paganini, M.C.; Calza, P.; Magnacca, G. An Easy Synthesis for Preparing Bio-Based Hybrid Adsorbent Useful for Fast Adsorption of Polar Pollutants. Nanomater. (Basel) 2019, 9, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmoodi, N.M.; Abdi, J.; Taghizadeh, M.; Taghizadeh, A.; Hayati, B.; Shekarchi, A.A.; Vossoughi, M. Activated carbon/metal-organic framework nanocomposite: Preparation and photocatalytic dye degradation mathematical modeling from wastewater by least squares support vector machine. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 233, 660–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadian-Fard-Fini, S.; Salavati-Niasari, M.; Ghanbari, D. Hydrothermal green synthesis of magnetic Fe3O4-carbon dots by lemon and grape fruit extracts and as a photoluminescence sensor for detecting of E. coli bacteria. Spectrochim Acta A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2018, 203, 481–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, X.; Sun, Z.; Meng, H.; Han, Y.; Wu, J.; Xu, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, X. Polyethyleneimine (PEI) incorporated Cu-BTC composites: Extended applications in ultra-high efficient removal of congo red. J. Solid State Chem. 2019, 270, 231–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, H.U.; Lv, X.; Zhang, S.; Wei, W.; ullah, N.; Xie, J. Ternary MIL-100(Fe)@Fe3O4/CA magnetic nanophotocatalysts (MNPCs): Magnetically separable and Fenton-like degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride. Adv. Powder Technol. 2018, 29, 3305–3314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, M.H.; Phan, N.H.; Nguyen, T.D.; Pham, T.T.; Nguyen, V.K.; Vu, T.T.; Nguyen, T.K. Activated carbon/Fe(3)O(4) nanoparticle composite: Fabrication, methyl orange removal and regeneration by hydrogen peroxide. Chemosphere 2011, 85, 1269–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karmakar, S.; Roy, D.; Janiak, C.; De, S. Insights into multi-component adsorption of reactive dyes on MIL-101-Cr metal organic framework: Experimental and modeling approach. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 215, 259–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamedi, A.; Caldera, F.; Trotta, F.; Zarandi, M.B.; Pedrazzo, A.R.; Cecone, C. Metal Organic Frameworks in Medicine. Acta Sci. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 3, 107–109. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoodi, N.M.; Oveisi, M.; Bakhtiari, M.; Hayati, B.; Shekarchi, A.A.; Bagheri, A.; Rahimi, S. Environmentally friendly ultrasound-assisted synthesis of magnetic zeolitic imidazolate framework—Graphene oxide nanocomposites and pollutant removal from water. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 282, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, F.; Qiu, L.G.; Zhu, J. Fe(3)O(4)@MOF core-shell magnetic microspheres as excellent catalysts for the Claisen-Schmidt condensation reaction. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 1596–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yılmaz, E.; Sert, E.; Atalay, F.S. Synthesis, characterization of a metal organic framework: MIL-53 (Fe) and adsorption mechanisms of methyl red onto MIL-53 (Fe). J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2016, 65, 323–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Zhao, H.; Cao, T.; Qian, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, G. Efficient degradation of high concentration azo-dye wastewater by heterogeneous Fenton process with iron-based metal-organic framework. J. Mol. Catal. A Chem. 2015, 400, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, E.; Lo, V.; Minett, A.I.; Harris, A.T.; Church, T.L. Dichotomous adsorption behaviour of dyes on an amino-functionalised metal–organic framework, amino-MIL-101(Al). J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhou, J.; Chen, R.; Shi, R.; Xia, G.; Zhou, S.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, N.; Wang, H.; Guo, Z.; et al. Magnetically guided delivery of DHA and Fe ions for enhanced cancer therapy based on pH-responsive degradation of DHA-loaded Fe3O4@C@MIL-100(Fe) nanoparticles. Biomaterials 2016, 107, 88–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, B.; Long, Y.; Zhang, M.; Ma, J.; Khan, A.; Chowdhury, S.P.; Zhou, X.; Ni, Y. Cellulose-supported magnetic Fe3O4–MOF composites for enhanced dye removal application. Cellulose 2019, 26, 4909–4920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rončević, S.; Nemet, I.; Ferri, T.Z.; Matković-Čalogović, D. Characterization of nZVI nanoparticles functionalized by EDTA and dipicolinic acid: A comparative study of metal ion removal from aqueous solutions. Rsc. Adv. 2019, 9, 31043–31051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wo, R.; Li, Q.-L.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, Y.; Qiao, G.-f.; Lei, K.-y.; Du, P.; Jiang, W. Preparation and Characterization of Functionalized Metal–Organic Frameworks with Core/Shell Magnetic Particles (Fe3O4@SiO2@MOFs) for Removal of Congo Red and Methylene Blue from Water Solution. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2019, 64, 2455–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, P.; Fang, X.; Maimaiti, A.; Yu, G.; Deng, S. Efficient removal of perfluorinated compounds from water using a regenerable magnetic activated carbon. Chemosphere 2019, 224, 187–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, J.; Huang, X.; Wu, Q.P.; Yan, C.H.; Lu, J.F. Efficient peroxymonosulfate activation by Zn/Fe metal-organic framework-derived ZnO/Fe3 O4 @carbon spheres for the degradation of Acid Orange 7. Water Env. Res. 2019, 91, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Han, B.; Hu, X.; Lin, Y.; Wang, X.; Deng, X. Synthesis of Fe3O4 Nanoparticles and their Magnetic Properties. Procedia Eng. 2012, 27, 632–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, N.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, D.; Xu, S. Synthesis and properties of magnetic Fe3O4-activated carbon nanocomposite particles for dye removal. Mater. Lett. 2008, 62, 645–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, M.; Ning, F.; Zhao, J.; Wei, M.; Evans, D.G.; Duan, X. Preparation of Fe3O4@SiO2@layered double hydroxide core-shell microspheres for magnetic separation of proteins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 1071–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Q.; Liu, Y.; Dang, Z. Core-shell structured Fe3O4@GO@MIL-100(Fe) magnetic nanoparticles as heterogeneous photo-Fenton catalyst for 2,4-dichlorophenol degradation under visible light. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 371, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konnova, S.A.; Lvov, Y.M.; Fakhrullin, R.F. Nanoshell Assembly for Magnet-Responsive Oil-Degrading Bacteria. Langmuir 2016, 32, 12552–12558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohan, D.; Sarswat, A.; Singh, V.K.; Alexandre-Franco, M.; Pittman, C.U. Development of magnetic activated carbon from almond shells for trinitrophenol removal from water. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 172, 1111–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamedi, A.; Zarandi, M.B.; Nateghi, M.R. Highly efficient removal of dye pollutants by MIL-101(Fe) metal-organic framework loaded magnetic particles mediated by Poly L-Dopa. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 102882–102894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anyika, C.; Asri, N.A.M.; Majid, Z.A.; Yahya, A.; Jaafar, J. Synthesis and characterization of magnetic activated carbon developed from palm kernel shells. Nanotechnol. Environ. Eng. 2017, 2, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Li, S.; Yang, W.; Gu, F.; Xu, H.; Wang, T.; Sun, D.; Hou, X. Magnetic nanoparticle of metal-organic framework with core-shell structure as an adsorbent for magnetic solid phase extraction of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Talanta 2019, 194, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aslam, S.; Zeng, J.; Subhan, F.; Li, M.; Lyu, F.; Li, Y.; Yan, Z. In situ one-step synthesis of Fe3O4@MIL-100(Fe) core-shells for adsorption of methylene blue from water. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 505, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Tian, J.; Li, Y.; Sun, N.; Mi, S.; Xie, Y.; Chen, Z. Enhanced dyes adsorption from wastewater via Fe3O4 nanoparticles functionalized activated carbon. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 373, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foroutan, R.; Mohammadi, R.; Razeghi, J.; Ramavandi, B. Performance of algal activated carbon/Fe3O4 magnetic composite for cationic dyes removal from aqueous solutions. Algal Res. 2019, 40, 101509–101521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Xu, H.; Zhang, K.; Wei, S.; Deyong, W. High-quality Al@Fe-MOF prepared using Fe-MOF as a micro-reactor to improve adsorption performance for selenite. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 364, 272–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.; Li, Y.; Lv, Z.; Zhou, H.; Yang, X.; Chen, J.; Guo, H. Effective Adsorption and Removal of Phosphate from Aqueous Solutions and Eutrophic Water by Fe-based MOFs of MIL-101. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.Y.; Fu, Y.Q.; Jiang, R.; Jiang, J.H.; Xiao, L.; Zeng, G.M.; Zhao, S.L.; Wang, Y. Adsorption removal of congo red onto magnetic cellulose/Fe3O4/activated carbon composite: Equilibrium, kinetic and thermodynamic studies. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 173, 494–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Wang, J.; Xue, X.; Liu, W.; Kong, Y.; Cheng, R.; Yuan, D. Facile synthesis of Fe3O4@MOF-100(Fe) magnetic microspheres for the adsorption of diclofenac sodium in aqueous solution. Env. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2018, 25, 31705–31717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Chen, D.; Li, N.; Xu, Q.; Li, H.; He, J.; Lu, J. Adsorption and biodegradation of dye in wastewater with Fe3O4@MIL-100 (Fe) core-shell bio-nanocomposites. Chemosphere 2018, 191, 315–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, L.; Lin, H.; Meng, F.; Zhang, F. One-step solvothermal synthesis of Fe3O4@Carbon composites and their application in removing of Cr (VI) and Congo red. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 9646–9652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, T.A.; Al-Absi, A.A. Kinetics, isotherms and thermodynamic evaluation of amine functionalized magnetic carbon for methyl red removal from aqueous solutions. J. Mol. Liq. 2017, 248, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodi, N.M.; Taghizadeh, M.; Taghizadeh, A. Activated carbon/metal-organic framework composite as a bio-based novel green adsorbent: Preparation and mathematical pollutant removal modeling. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 277, 310–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Yuan, X.; Wu, Z.; Zeng, G.; Jiang, L.; Peng, X.; Li, H. Adsorption behavior and mechanism of Mg/Fe layered double hydroxide with Fe3O4-carbon spheres on the removal of Pb(II) and Cu(II). J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 536, 440–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadi, M.; Ghanbari, F. Organic dye degradation through peroxymonosulfate catalyzed by reusable graphite felt/ferriferrous oxide: Mechanism and identification of intermediates. Mater. Res. Bull. 2019, 111, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Kang, X.; Zhang, X.; Cui, X. Gel-like ZnO/Zr-MOF(bpy) nanocomposite for highly efficient adsorption of Rhodamine B dye from aqueous solution. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2019, 134, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, J.; Gu, F.; Chang, J. Fabrication of magnetic lignosulfonate using ultrasonic-assisted in situ synthesis for efficient removal of Cr(VI) and Rhodamine B from wastewater. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 375, 174–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karimi, R.; Yousefi, F.; Ghaedi, M.; Rezaee, Z. Comparison the behavior of ZnO–NP–AC and Na, K doped ZnO–NP–AC for simultaneous removal of Crystal Violet and Quinoline Yellow dyes: Modeling and optimization. Polyhedron 2019, 170, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, F.h.; Ren, Q.h.; Liang, Z.; Chen, D. Synthesis of Graphene Oxide/Metal-Organic Frameworks Composite Materials for Removal of Congo Red from Wastewater. ChemistrySelect 2019, 4, 5755–5762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Xiao, A.; Qiu, H.; Liu, L. Preparation of Magnetic Fe(3)O(4)/MIL-88A Nanocomposite and Its Adsorption Properties for Bromophenol Blue Dye in Aqueous Solution. Nanomater. (Basel) 2019, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Peng, J.; Lv, T.; Sun, C.; He, H. Preparation and performance study of MgFe 2 O 4 /metal–organic framework composite for rapid removal of organic dyes from water. J. Solid State Chem. 2018, 257, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Ma, S.; Yang, H.; Xu, Z.-l. Preparation of Carbonized MOF/MgCl2 Hybrid Products as Dye Adsorbent and Supercapacitor: Morphology Evolution and Mg Salt Effect. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2019, 58, 1601–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Lv, R.; Shi, Z.; Wang, C.; Li, H.; Ge, J.; Ji, Z.; Yang, Y.; Li, B.; Qian, G. A new metal-organic framework with suitable pore size and ttd-type topology revealing highly selective adsorption and separation of organic dyes. J. Solid State Chem. 2019, 277, 159–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyekanmi, A.A.; Ahmad, A.; Hossain, K.; Rafatullah, M. Statistical optimization for adsorption of Rhodamine B dye from aqueous solutions. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 281, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Wu, S.; Cheng, J.; Chen, Y. Indium-based metal-organic framework/graphite oxide composite as an efficient adsorbent in the adsorption of rhodamine B from aqueous solution. J. Alloy. Compd. 2016, 687, 804–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Hou, X.; Liu, S.; Liu, B. One-step synthesis of magnetic and porous Ni@MOF-74(Ni) composite. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2018, 259, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.A.; Kumari, S.; Chowdhury, A.; Hussain, S. Phase Tuned Originated Dual Properties of Cobalt Sulfide Nanostructures as Photocatalyst and Adsorbent for Removal of Dye Pollutants. Acs Appl. Nano Mater. 2018, 1, 3474–3485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Zhou, A.; Yang, W.; Araya, T.; Huang, Y.; Zhao, P.; Johnson, D.; Wang, J.; Ren, Z.J. Complex Formation via Hydrogen bonding between Rhodamine B and Montmorillonite in Aqueous Solution. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Peng, L.; Gan, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Shen, J.; Qian, J.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, W. Facile Preparation of Core-Shell Magnetic Metal-Organic Framework Nanoparticles for the Selective Capture of Phosphopeptides. Acs Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 16338–16347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Initial Conc. (mg/L) | Pseudo-First-Order Model | Pseudo-Second-Order Model | Intraparticle Diffusion Model | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qe | K1 | R2 | qe | K2 | R2 | kid | C | R2 | |
| 50 | 171.19 | 0.1321 | 0.9863 | 217.39 | 9.93 × 10−4 | 0.9987 | 19.815 | 79.908 | 0.8907 |
| 100 | 374.2 | 0.1074 | 0.989 | 454.54 | 2.67 × 10−4 | 0.9978 | 52.048 | 79.093 | 0.9155 |
| 200 | 511.42 | 0.109 | 0.9771 | 666.66 | 2.21 × 10−4 | 0.991 | 69.76 | 142.51 | 0.9036 |
| 300 | 651.05 | 0.1042 | 0.9854 | 833.33 | 1.48 × 10−4 | 0.9993 | 86.894 | 164.82 | 0.9462 |
| 400 | 714.73 | 0.0947 | 0.9502 | 909.09 | 1.19 × 10−4 | 0.995 | 95.971 | 152.67 | 0.9796 |
| T (K) | qexp | Langmuir | Freundlich | Temkin | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qm | b | R2 | KF | n | R2 | KT | A | R2 | ||
| 295 | 726.36 | 769.23 | 0.0884 | 0.9923 | 192.09 | 3.9262 | 0.9153 | 3.974 | 105.66 | 0.969 |
| 305 | 679.42 | 714.28 | 0.0679 | 0.9935 | 153.78 | 3.5486 | 0.898 | 1.903 | 110.12 | 0.9663 |
| 315 | 618.72 | 666.66 | 0.0473 | 0.9951 | 113.39 | 3.1162 | 0.8614 | 0.854 | 116.56 | 0.9486 |
| 325 | 558.72 | 625 | 0.0336 | 0.9911 | 91.09 | 2.9735 | 0.8165 | 0.587 | 111.09 | 0.9099 |
| Adsorbent | qm (mg g−1) | Reference |
|---|---|---|
| Fe3O4/AC | 182.48 | [43] |
| Fe3O4/MIL-100(Fe) | 28.36 | [10] |
| Fabricated magnetic lignosulfonate (MLS) | 22.47 | [56] |
| Zn-MOF | 3.750 | [6] |
| AC/CeO2 | 324.6 | [9] |
| raw orange peel (ROP) | 3.266 | [63] |
| In-MOF@GO-2 | 267 | [64] |
| Ni@MOF-74(Ni) | 177.8 | [65] |
| Cobalt sulphide nanostructures | 1138 | [66] |
| MIL-100(Fe) @Fe3O4@AC | 769.23 | Present study |
| Temp. (K) | Ce (mg L −1) | qe (mg g−1) | ΔG° (kJ mol−1) | ΔH° (kJ mol−1) | ΔS° (J mol−1 K−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 295 | 64.1418 | 543.4328 | −5.2408 | −18.0705 | −43.3417 |
| 305 | 70.3987 | 518.4052 | −5.0626 | ||
| 315 | 80.2147 | 479.1412 | −4.5319 | ||
| 325 | 95.2142 | 419.1432 | −4.0046 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hamedi, A.; Trotta, F.; Borhani Zarandi, M.; Zanetti, M.; Caldera, F.; Anceschi, A.; Nateghi, M.R. In Situ Synthesis of MIL-100(Fe) at the Surface of Fe3O4@AC as Highly Efficient Dye Adsorbing Nanocomposite. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5612. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20225612
Hamedi A, Trotta F, Borhani Zarandi M, Zanetti M, Caldera F, Anceschi A, Nateghi MR. In Situ Synthesis of MIL-100(Fe) at the Surface of Fe3O4@AC as Highly Efficient Dye Adsorbing Nanocomposite. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(22):5612. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20225612
Chicago/Turabian StyleHamedi, Asma, Francesco Trotta, Mahmood Borhani Zarandi, Marco Zanetti, Fabrizio Caldera, Anastasia Anceschi, and Mohammad Reza Nateghi. 2019. "In Situ Synthesis of MIL-100(Fe) at the Surface of Fe3O4@AC as Highly Efficient Dye Adsorbing Nanocomposite" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 22: 5612. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20225612
APA StyleHamedi, A., Trotta, F., Borhani Zarandi, M., Zanetti, M., Caldera, F., Anceschi, A., & Nateghi, M. R. (2019). In Situ Synthesis of MIL-100(Fe) at the Surface of Fe3O4@AC as Highly Efficient Dye Adsorbing Nanocomposite. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(22), 5612. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20225612