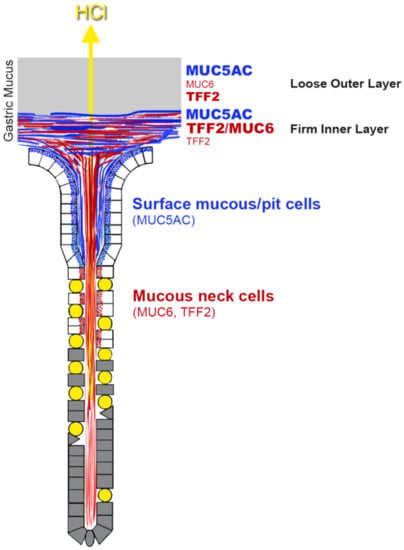
Different Forms of TFF2, A Lectin of the Human Gastric Mucus Barrier: In Vitro Binding Studies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characterization of Human Gastric Extracts by SEC and Western Blot Analysis
2.2. Stepwise Extraction of TFF2 from Human Gastric Mucosa
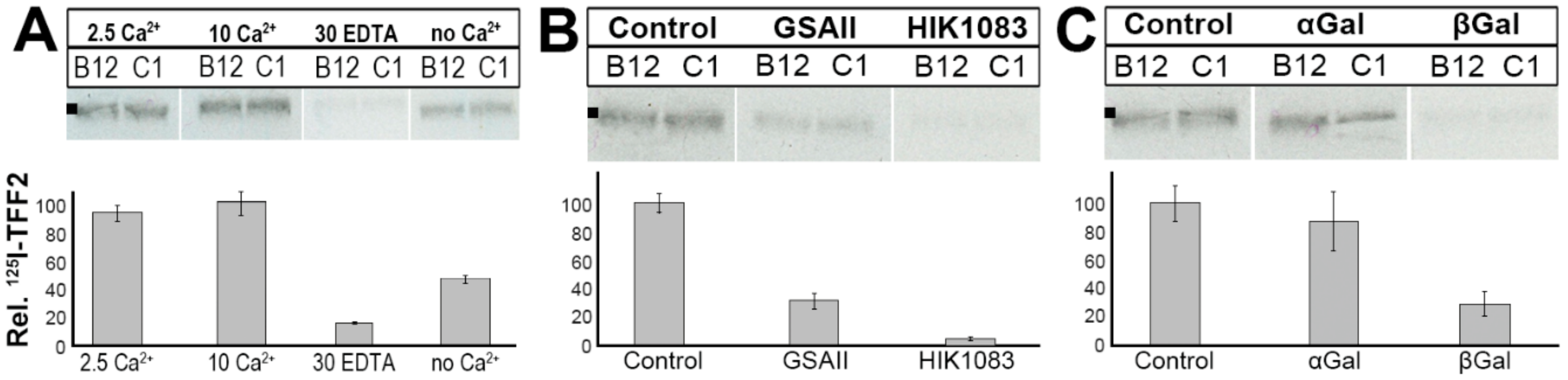
2.3. Binding of 125I-TFF2 to Human Gastric Mucin In Vitro (Overlay Assay)
2.4. Binding of 125I-TFF2 to Porcine Gastric Mucin in Solution
3. Discussion
3.1. TFF2 Occurs in Mucin-Bound and Low-Molecular-Mass Forms in the Human Gastric Mucosa: Differences to Porcine TFF2
3.2. Soluble and Insoluble Forms of TFF2 in the Human Gastric Mucus
3.3. TFF2 Binds to Mucin MUC6 In Vitro
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Human Tissue
4.2. Extraction of Proteins
4.3. Protein Purification by SEC
4.4. SDS-PAGE, Agarose Gel Electrophoresis, and Western Blot Analysis
4.5. Digestion with Peptide-N-glycosidase F (PNGase F)
4.6. TFF2 Binding Studies
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AgGE | Agarose gel electrophoresis |
| PAS | Periodic acid-Schiff |
| SDS-PAGE | Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
| SEC | Size exclusion chromatography |
| TFF | Trefoil factor family |
References
- Tomasetto, C.; Rio, M.C.; Gautier, C.; Wolf, C.; Hareuveni, M.; Chambon, P.; Lathe, R. hSP, the domain-duplicated homolog of pS2 protein, is co-expressed with pS2 in stomach but not in breast carcinoma. EMBO J. 1990, 9, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thim, L. Trefoil peptides: From structure to function. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 1997, 53, 888–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, F.E.; Semple, J.I.; Newton, J.L.; Westley, B.R. The human two domain trefoil protein, TFF2, is glycosylated in vivo in the stomach. Gut 2000, 46, 454–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hoffmann, W. TFF peptides. In Handbook of Biologically Active Peptides, 2nd ed.; Kastin, A., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 1338–1345. [Google Scholar]
- Hanby, A.M.; Poulsom, R.; Singh, S.; Elia, G.; Jeffery, R.E.; Wright, N.A. Spasmolytic polypeptide is a major antral peptide: Distribution of the trefoil peptides human spasmolytic polypeptide and pS2 in the stomach. Gastroenterology 1993, 105, 1110–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanby, A.M.; Poulsom, R.; Elia, G.; Singh, S.; Longcroft, J.M.; Wright, N.A. The expression of the trefoil peptides pS2 and human spasmolytic polypeptide (hSP) in ‘gastric metaplasia’ of the proximal duodenum: Implications for the nature of ‘gastric metaplasia’. J. Pathol. 1993, 169, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ota, H.; Hayama, M.; Momose, M.; El-Zimaity, H.M.; Matsuda, K.; Sano, K.; Maruta, F.; Okumura, N.; Katsuyama, T. Co-localization of TFF2 with gland mucous cell mucin in gastric mucous cells and in extracellular mucous gel adherent to normal and damaged gastric mucosa. Histochem. Cell Biol. 2006, 126, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouznetsova, I.; Kalinski, T.; Meyer, F.; Hoffmann, W. Self-renewal of the human gastric epithelium: New insights from expression profiling using laser microdissection. Mol. Biosyst. 2011, 7, 1105–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, W. Current Status on Stem Cells and Cancers of the Gastric Epithelium. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 19153–19169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahnen, D.J.; Poulsom, R.; Stamp, G.W.; Elia, G.; Pike, C.; Jeffery, R.; Longcroft, J.; Rio, M.C.; Chambon, P.; Wright, N.A. The ulceration-associated cell lineage (UACL) reiterates the Brunner’s gland differentiation programme but acquires the proliferative organization of the gastric gland. J. Pathol. 1994, 173, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, K.; Savoy, L.A.; Thim, L.; Christensen, M.; Jorgensen, K.H. Revised amino acid sequence of pancreatic spasmolytic polypeptide exhibits greater similarity with an inducible pS2 peptide found in a human breast cancer cell line. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1989, 998, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanisch, F.G.; Ragge, H.; Kalinski, T.; Meyer, F.; Kalbacher, H.; Hoffmann, W. Human gastric TFF2 peptide contains an N-linked fucosylated N,N’-diacetyllactosediamine (LacdiNAc) oligosaccharide. Glycobiology 2013, 23, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rossez, Y.; Gosset, P.; Boneca, I.G.; Magalhaes, A.; Ecobichon, C.; Reis, C.A.; Cieniewski-Bernard, C.; Curt, M.J.C.; Leonard, R.; Maes, E.; et al. The LacdiNAc-specific adhesin LabA mediates adhesion of Helicobacter pylori to human gastric mucosa. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 210, 1286–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semple, J.I.; Newton, J.L.; Westley, B.R.; May, F.E. Dramatic diurnal variation in the concentration of the human trefoil peptide TFF2 in gastric juice. Gut 2001, 48, 648–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouznetsova, I.; Laubinger, W.; Kalbacher, H.; Kalinski, T.; Meyer, F.; Roessner, A.; Hoffmann, W. Biosynthesis of gastrokine-2 in the human gastric mucosa: Restricted spatial expression along the antral gland axis and differential interaction with TFF1, TFF2 and mucins. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2007, 20, 899–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stürmer, R.; Müller, S.; Hanisch, F.G.; Hoffmann, W. Porcine gastric TFF2 is a mucus constituent and differs from pancreatic TFF2. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2014, 33, 895–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, W. TFF2, a MUC6-binding lectin stabilizing the gastric mucus barrier and more. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 47, 806–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thim, L.; Madsen, F.; Poulsen, S.S. Effect of trefoil factors on the viscoelastic properties of mucus gels. Eur. J. Clin. Invest. 2002, 32, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjellev, S.; Nexo, E.; Thim, L.; Poulsen, S.S. Systemically administered trefoil factors are secreted into the gastric lumen and increase the viscosity of gastric contents. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2006, 149, 92–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanisch, F.G.; Bonar, D.; Schloerer, N.; Schroten, H. Human trefoil factor 2 is a lectin that binds α-GlcNAc-capped mucin glycans with antibiotic activity against Helicobacter pylori. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 27363–27375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishihara, K.; Kurihara, M.; Goso, Y.; Urata, T.; Ota, H.; Katsuyama, T.; Hotta, K. Peripheral α-linked N-acetylglucosamine on the carbohydrate moiety of mucin derived from mammalian gastric gland mucous cells: Epitope recognized by a newly characterized monoclonal antibody. Biochem. J. 1996, 318, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ihida, K.; Suganuma, T.; Tsuyama, S.; Murata, F. Glycoconjugate histochemistry of the rat fundic gland using Griffonia simplicifolia agglutinin-II during the development. Am. J. Anat. 1988, 182, 250–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oinuma, T.; Ide, S.; Kawano, J.; Suganuma, T. Purification and immunohistochemistry of Griffonia simplicifolia agglutinin-II-binding mucus glycoprotein in rat stomach. Glycobiology 1994, 4, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordman, H.; Davies, J.R.; Carlstedt, I. Mucus glycoproteins from pig gastric mucosa: Different mucins are produced by the surface epithelium and the glands. Biochem. J. 1998, 331, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Wang, P.; Hoshino, H.; Ito, Y.; Kobayashi, M.; Nakayama, J.; Seeberger, P.H.; Fukuda, M. α1,4GlcNAc-capped mucin-type O-glycan inhibits cholesterol α-glucosyltransferase from Helicobacter pylori and suppresses H. pylori growth. Glycobiology 2008, 18, 549–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, J. Dual roles of gastric gland mucin-specific O-glycans in prevention of gastric cancer. Acta Histochem. Cytochem. 2014, 47, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chwieralski, C.E.; Schnurra, I.; Thim, L.; Hoffmann, W. Epidermal growth factor and trefoil factor family 2 synergistically trigger chemotaxis on BEAS-2B cells via different signaling cascades. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2004, 31, 528–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, W. Trefoil factor family (TFF) peptides: Regulators of mucosal regeneration and repair, and more. Peptides 2004, 25, 727–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenbroucke, K.; Hans, W.; Van Huysse, J.; Neirynck, S.; Demetter, P.; Remaut, E.; Rottiers, P.; Steidler, L. Active delivery of trefoil factors by genetically modified Lactococcus lactis prevents and heals acute colitis in mice. Gastroenterology 2004, 127, 502–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baus-Loncar, M.; Kayademir, T.; Takaishi, S.; Wang, T. Trefoil factor family 2 deficiency and immune response. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2005, 62, 2947–2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurt-Jones, E.A.; Cao, L.; Sandor, F.; Rogers, A.B.; Whary, M.T.; Nambiar, P.R.; Cerny, A.; Bowen, G.; Yan, J.; Takaishi, S.; et al. Trefoil family factor 2 is expressed in murine gastric and immune cells and controls both gastrointestinal inflammation and systemic immune responses. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fox, J.G.; Rogers, A.B.; Whary, M.T.; Ge, Z.; Ohtani, M.; Jones, E.K.; Wang, T.C. Accelerated progression of gastritis to dysplasia in the pyloric antrum of TFF2 -/- C57BL6 x Sv129 Helicobacter pylori-infected mice. Am. J. Pathol. 2007, 171, 1520–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baus-Lončar, M.; Schmid, J.; Lalani el, N.; Rosewell, I.; Goodlad, R.A.; Stamp, G.W.; Blin, N.; Kayademir, T. Trefoil factor 2 (TFF2) deficiency in murine digestive tract influences the immune system. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2005, 16, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thim, L.; Mørtz, E. Isolation and characterization of putative trefoil peptide receptors. Regul. Pept. 2000, 90, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, W. Trefoil factor family (TFF) peptides and chemokine receptors: A promising relationship. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 6505–6510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braga Emidio, N.; Hoffmann, W.; Brierley, S.M.; Muttenthaler, M. Trefoil factor family: Unresolved questions and clinical perspectives. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2019, 44, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitner, V.M.; Walker, G.F.; Bernkop-Schnurch, A. Thiolated polymers: Evidence for the formation of disulphide bonds with mucus glycoproteins. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2003, 56, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marczynski, M.; Kasdorf, B.T.; Altaner, B.; Wenzler, A.; Gerland, U.; Lieleg, O. Transient binding promotes molecule penetration into mucin hydrogels by enhancing molecular partitioning. Biomat. Sci. 2018, 6, 3373–3387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stürmer, R.; Harder, S.; Schlüter, H.; Hoffmann, W. Commercial porcine gastric mucin preparations, also used as artificial saliva, are a rich source for the lectin TFF2: In vitro binding studies. ChemBioChem 2018, 19, 2598–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, H.F. Molecular and cellular aspects of thiol-disulfide exchange. In Advances in Enzymology and Related Areas of Molecular Biology; Meister, A., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1990; Volume 63, pp. 69–172. [Google Scholar]
- Poole, L.B. The basics of thiols and cysteines in redox biology and chemistry. Free Radical Biol. Med. 2015, 80, 148–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otto, W.R.; Rao, J.; Cox, H.M.; Kotzian, E.; Lee, C.Y.; Goodlad, R.A.; Lane, A.; Gorman, M.; Freemont, P.A.; Hansen, H.F.; et al. Effects of pancreatic spasmolytic polypeptide (PSP) on epithelial cell function. Eur. J. Biochem. 1996, 235, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johansson, M.E.; Sjovall, H.; Hansson, G.C. The gastrointestinal mucus system in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubota, S.; Yamauchi, K.; Sugano, M.; Kawasaki, K.; Sugiyama, A.; Matsuzawa, K.; Akamatsu, T.; Ohmoto, Y.; Ota, H. Pathophysiological investigation of the gastric surface mucous gel layer of patients with Helicobacter pylori infection by using immunoassays for trefoil factor family 2 and gastric gland mucous cell-type mucin in gastric juice. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2011, 56, 3498–3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanisch, F.G.; Chai, W.; Rosankiewicz, J.R.; Lawson, A.M.; Stoll, M.S.; Feizi, T. Core-typing of O-linked glycans from human gastric mucins. Lack of evidence for the occurrence of the core sequence Gal1-6GalNAc. Eur. J. Biochem. 1993, 217, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillipson, M.; Atuma, C.; Henriksnas, J.; Holm, L. The importance of mucus layers and bicarbonate transport in preservation of gastric juxtamucosal pH. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2002, 282, G211–G219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ota, H.; Katsuyama, T. Alternating laminated array of two types of mucin in the human gastric surface mucous layer. Histochem. J. 1992, 24, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossez, Y.; Maes, E.; Lefebvre Darroman, T.; Gosset, P.; Ecobichon, C.; Curt, M.J.C.; Boneca, I.G.; Michalski, J.C.; Robbe-Masselot, C. Almost all human gastric mucin O-glycans harbor blood group A, B or H antigens and are potential binding sites for Helicobacter pylori. Glycobiology 2012, 22, 1193–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albert, T.K.; Laubinger, W.; Müller, S.; Hanisch, F.G.; Kalinski, T.; Meyer, F.; Hoffmann, W. Human intestinal TFF3 forms disulfide-linked heteromers with the mucus-associated FCGBP protein and is released by hydrogen sulfide. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 3108–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagla, W.; Wiede, A.; Kölle, S.; Hoffmann, W. Differential expression of the TFF-peptides xP1 and xP4 in the gastrointestinal tract of Xenopus laevis. Cell Tissue Res. 1998, 291, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouznetsova, I.; Peitz, U.; Vieth, M.; Meyer, F.; Vestergaard, E.M.; Malfertheiner, P.; Roessner, A.; Lippert, H.; Hoffmann, W. A gradient of TFF3 (trefoil factor family 3) peptide synthesis within the normal human gastric mucosa. Cell. Tissue Res 2004, 316, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiede, A.; Jagla, W.; Welte, T.; Köhnlein, T.; Busk, H.; Hoffmann, W. Localization of TFF3, a new mucus-associated peptide of the human respiratory tract. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 1999, 159, 1330–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Thim, L.; Norris, K.; Norris, F.; Nielsen, P.F.; Bjorn, S.E.; Christensen, M.; Petersen, J. Purification and characterization of the trefoil peptide human spasmolytic polypeptide (hSP) produced in yeast. FEBS Lett. 1993, 318, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, K.H.; Thim, L.; Jacobsen, H.E. Pancreatic Spasmolytic Polypeptide (PSP): I. Preparation and initial chemical characterization of a new polypeptide from porcine pancreas. Regul. Peptides 1982, 3, 207–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Heuer, F.; Stürmer, R.; Heuer, J.; Kalinski, T.; Lemke, A.; Meyer, F.; Hoffmann, W. Different Forms of TFF2, A Lectin of the Human Gastric Mucus Barrier: In Vitro Binding Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5871. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20235871
Heuer F, Stürmer R, Heuer J, Kalinski T, Lemke A, Meyer F, Hoffmann W. Different Forms of TFF2, A Lectin of the Human Gastric Mucus Barrier: In Vitro Binding Studies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(23):5871. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20235871
Chicago/Turabian StyleHeuer, Franziska, René Stürmer, Jörn Heuer, Thomas Kalinski, Antje Lemke, Frank Meyer, and Werner Hoffmann. 2019. "Different Forms of TFF2, A Lectin of the Human Gastric Mucus Barrier: In Vitro Binding Studies" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 23: 5871. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20235871
APA StyleHeuer, F., Stürmer, R., Heuer, J., Kalinski, T., Lemke, A., Meyer, F., & Hoffmann, W. (2019). Different Forms of TFF2, A Lectin of the Human Gastric Mucus Barrier: In Vitro Binding Studies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(23), 5871. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20235871